-
 KAA Recognizes 4 Distinguished Alumni of the Year
The KAIST Alumni Association (KAA) recognized four distinguished alumni of the year during a ceremony on February 25 in Seoul. The four Distinguished Alumni Awardees are Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the KAIST Department of Chemistry, Hyunshil Ahn, head of the AI Economy Institute and an editorial writer at The Korea Economic Daily, CEO Hwan-ho Sung of PSTech, and President Hark Kyu Park of Samsung Electronics.
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang who received his MS from the Department of Chemistry in 1985 has been a pioneer in the novel field of ‘carbon-hydrogen bond activation reactions’. He has significantly contributed to raising Korea’s international reputation in natural sciences and received the Kyungam Academic Award in 2013, the 14th Korea Science Award in 2015, the 1st Science and Technology Prize of Korea Toray in 2018, and the Best Scientist/Engineer Award Korea in 2019. Furthermore, he was named as a Highly Cited Researcher who ranked in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index for seven consecutive years from 2015 to 2021, demonstrating his leadership as a global scholar.
Hyunshil Ahn, a graduate of the School of Business and Technology Management with an MS in 1985 and a PhD in 1987, was appointed as the first head of the AI Economy Institute when The Korea Economic Daily was the first Korean media outlet to establish an AI economy lab. He has contributed to creating new roles for the press and media in the 4th industrial revolution, and added to the popularization of AI technology through regulation reform and consulting on industrial policies.
PSTech CEO Hwan-ho Sung is a graduate of the School of Electrical Engineering where he received an MS in 1988 and a PhD in EMBA in 2008. He has run the electronics company PSTech for over 20 years and successfully localized the production of power equipment, which previously depended on foreign technology. His development of the world’s first power equipment that can be applied to new industries including semiconductors and displays was recognized through this award.
Samsung Electronics President Hark Kyu Park graduated from the School of Business and Technology Management with an MS in 1986. He not only enhanced Korea’s national competitiveness by expanding the semiconductor industry, but also established contract-based semiconductor departments at Korean universities including KAIST, Sungkyunkwan University, Yonsei University, and Postech, and semiconductor track courses at KAIST, Sogang University, Seoul National University, and Postech to nurture professional talents. He also led the national semiconductor coexistence system by leading private sector-government-academia collaborations to strengthen competence in semiconductors, and continues to make unconditional investments in strong small businesses.
KAA President Chilhee Chung said, “Thanks to our alumni contributing at the highest levels of our society, the name of our alma mater shines brighter. As role models for our younger alumni, I hope greater honours will follow our awardees in the future.”
2022.03.03 View 8931
KAA Recognizes 4 Distinguished Alumni of the Year
The KAIST Alumni Association (KAA) recognized four distinguished alumni of the year during a ceremony on February 25 in Seoul. The four Distinguished Alumni Awardees are Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the KAIST Department of Chemistry, Hyunshil Ahn, head of the AI Economy Institute and an editorial writer at The Korea Economic Daily, CEO Hwan-ho Sung of PSTech, and President Hark Kyu Park of Samsung Electronics.
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang who received his MS from the Department of Chemistry in 1985 has been a pioneer in the novel field of ‘carbon-hydrogen bond activation reactions’. He has significantly contributed to raising Korea’s international reputation in natural sciences and received the Kyungam Academic Award in 2013, the 14th Korea Science Award in 2015, the 1st Science and Technology Prize of Korea Toray in 2018, and the Best Scientist/Engineer Award Korea in 2019. Furthermore, he was named as a Highly Cited Researcher who ranked in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index for seven consecutive years from 2015 to 2021, demonstrating his leadership as a global scholar.
Hyunshil Ahn, a graduate of the School of Business and Technology Management with an MS in 1985 and a PhD in 1987, was appointed as the first head of the AI Economy Institute when The Korea Economic Daily was the first Korean media outlet to establish an AI economy lab. He has contributed to creating new roles for the press and media in the 4th industrial revolution, and added to the popularization of AI technology through regulation reform and consulting on industrial policies.
PSTech CEO Hwan-ho Sung is a graduate of the School of Electrical Engineering where he received an MS in 1988 and a PhD in EMBA in 2008. He has run the electronics company PSTech for over 20 years and successfully localized the production of power equipment, which previously depended on foreign technology. His development of the world’s first power equipment that can be applied to new industries including semiconductors and displays was recognized through this award.
Samsung Electronics President Hark Kyu Park graduated from the School of Business and Technology Management with an MS in 1986. He not only enhanced Korea’s national competitiveness by expanding the semiconductor industry, but also established contract-based semiconductor departments at Korean universities including KAIST, Sungkyunkwan University, Yonsei University, and Postech, and semiconductor track courses at KAIST, Sogang University, Seoul National University, and Postech to nurture professional talents. He also led the national semiconductor coexistence system by leading private sector-government-academia collaborations to strengthen competence in semiconductors, and continues to make unconditional investments in strong small businesses.
KAA President Chilhee Chung said, “Thanks to our alumni contributing at the highest levels of our society, the name of our alma mater shines brighter. As role models for our younger alumni, I hope greater honours will follow our awardees in the future.”
2022.03.03 View 8931 -
 SM CEP Soo-Man Lee to Teach at the KAIST School of Computing
The Founder and Chief Executive Producer of SM Entertainment Soo-Man Lee was appointed as a distinguished visiting professor in the KAIST School of Computing. His three-year term starts on March 1.
KAIST and the SM Entertainment signed an MOU on joint research on the metaverse last year and Lee’s appointment is the extension of their mutual collaborations in fields where technologies converge and will encourage innovative advancements in engineering technology and the entertainment industry.
Lee, who completed a graduate program in computer science at California State University Northridge will give special leadership lectures for both undergraduate and graduate students, and will participate in metaverse-related research as a consultant.
In particular, Professor Lee will participate in joint research with the tentatively named Metaverse Institute affiliated with the KAIST Institute for Artificial Intelligence. The institute will help SM Entertainment stay ahead of the global metaverse market by using the avatars of celebrities, and lend itself to raising the already strong brand power of the K-pop leader.
Professor Lee said, “I am grateful that KAIST, the very cradle of Korea’s science and technology, has given me the opportunity to meet its students as a visiting professor. We will lead the metaverse world, in which Korea is emerging as a market leader, with the excellent contents and technology unique to our country, and work together to lead the future global entertainment market.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “The ability to expand our limitless creativity in the metaverse is indispensable for us as we adapt to this new era. We hope that the vision and creative insights of Executive Producer Lee, which have allowed him to look ahead into the future of the entertainment contents market, will have a positive and fresh impact on the members of KAIST.”
The global influence and reputation of Executive Producer Lee has been well established through his various awards. He was the first Korean to be listed on Variety500 for five consecutive years from 2017 to 2021. He was also the first Korean awardee of the Asia Game Changer Awards in 2016, the first cultural figure to receive the YoungSan Diplomacy Award in 2017, the only Korean to be listed on the 2020 Billboard Impact List, and he has also received the K-pop Contribution Award at the 10th Gaon Chart Music Awards. He recently introduced Play2Create (P2C), a new interactive and creative culture in which re-creation can be enjoyed like a game using IP, and is leading the establishment of the P2C ecosystem.
2022.03.03 View 6789
SM CEP Soo-Man Lee to Teach at the KAIST School of Computing
The Founder and Chief Executive Producer of SM Entertainment Soo-Man Lee was appointed as a distinguished visiting professor in the KAIST School of Computing. His three-year term starts on March 1.
KAIST and the SM Entertainment signed an MOU on joint research on the metaverse last year and Lee’s appointment is the extension of their mutual collaborations in fields where technologies converge and will encourage innovative advancements in engineering technology and the entertainment industry.
Lee, who completed a graduate program in computer science at California State University Northridge will give special leadership lectures for both undergraduate and graduate students, and will participate in metaverse-related research as a consultant.
In particular, Professor Lee will participate in joint research with the tentatively named Metaverse Institute affiliated with the KAIST Institute for Artificial Intelligence. The institute will help SM Entertainment stay ahead of the global metaverse market by using the avatars of celebrities, and lend itself to raising the already strong brand power of the K-pop leader.
Professor Lee said, “I am grateful that KAIST, the very cradle of Korea’s science and technology, has given me the opportunity to meet its students as a visiting professor. We will lead the metaverse world, in which Korea is emerging as a market leader, with the excellent contents and technology unique to our country, and work together to lead the future global entertainment market.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “The ability to expand our limitless creativity in the metaverse is indispensable for us as we adapt to this new era. We hope that the vision and creative insights of Executive Producer Lee, which have allowed him to look ahead into the future of the entertainment contents market, will have a positive and fresh impact on the members of KAIST.”
The global influence and reputation of Executive Producer Lee has been well established through his various awards. He was the first Korean to be listed on Variety500 for five consecutive years from 2017 to 2021. He was also the first Korean awardee of the Asia Game Changer Awards in 2016, the first cultural figure to receive the YoungSan Diplomacy Award in 2017, the only Korean to be listed on the 2020 Billboard Impact List, and he has also received the K-pop Contribution Award at the 10th Gaon Chart Music Awards. He recently introduced Play2Create (P2C), a new interactive and creative culture in which re-creation can be enjoyed like a game using IP, and is leading the establishment of the P2C ecosystem.
2022.03.03 View 6789 -
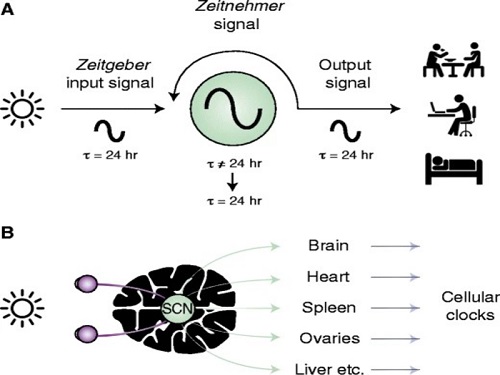 Scientist Discover How Circadian Rhythm Can Be Both Strong and Flexible
Study reveals that master and slave oscillators function via different molecular mechanisms
From tiny fruit flies to human beings, all animals on Earth maintain their daily rhythms based on their internal circadian clock. The circadian clock enables organisms to undergo rhythmic changes in behavior and physiology based on a 24-hour circadian cycle. For example, our own biological clock tells our brain to release melatonin, a sleep-inducing hormone, at night time.
The discovery of the molecular mechanism of the circadian clock was bestowed the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2017. From what we know, no one centralized clock is responsible for our circadian cycles. Instead, it operates in a hierarchical network where there are “master pacemaker” and “slave oscillator”.
The master pacemaker receives various input signals from the environment such as light. The master then drives the slave oscillator that regulates various outputs such as sleep, feeding, and metabolism. Despite the different roles of the pacemaker neurons, they are known to share common molecular mechanisms that are well conserved in all lifeforms. For example, interlocked systems of multiple transcriptional-translational feedback loops (TTFLs) composed of core clock proteins have been deeply studied in fruit flies.
However, there is still much that we need to learn about our own biological clock. The hierarchically-organized nature of master and slave clock neurons leads to a prevailing belief that they share an identical molecular clockwork. At the same time, the different roles they serve in regulating bodily rhythms also raise the question of whether they might function under different molecular clockworks.
Research team led by Professor Kim Jae Kyoung from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, a chief investigator at the Biomedical Mathematics Group at the Institute for Basic Science, used a combination of mathematical and experimental approaches using fruit flies to answer this question. The team found that the master clock and the slave clock operate via different molecular mechanisms.
In both master and slave neurons of fruit flies, a circadian rhythm-related protein called PER is produced and degraded at different rates depending on the time of the day. Previously, the team found that the master clock neuron (sLNvs) and the slave clock neuron (DN1ps) have different profiles of PER in wild-type and Clk-Δ mutant Drosophila. This hinted that there might be a potential difference in molecular clockworks between the master and slave clock neurons.
However, due to the complexity of the molecular clockwork, it was challenging to identify the source of such differences. Thus, the team developed a mathematical model describing the molecular clockworks of the master and slave clocks. Then, all possible molecular differences between the master and slave clock neurons were systematically investigated by using computer simulations. The model predicted that PER is more efficiently produced and then rapidly degraded in the master clock compared to the slave clock neurons. This prediction was then confirmed by the follow-up experiments using animal.
Then, why do the master clock neurons have such different molecular properties from the slave clock neurons? To answer this question, the research team again used the combination of mathematical model simulation and experiments. It was found that the faster rate of synthesis of PER in the master clock neurons allows them to generate synchronized rhythms with a high level of amplitude. Generation of such a strong rhythm with high amplitude is critical to delivering clear signals to slave clock neurons.
However, such strong rhythms would typically be unfavorable when it comes to adapting to environmental changes. These include natural causes such as different daylight hours across summer and winter seasons, up to more extreme artificial cases such as jet lag that occurs after international travel. Thanks to the distinct property of the master clock neurons, it is able to undergo phase dispersion when the standard light-dark cycle is disrupted, drastically reducing the level of PER. The master clock neurons can then easily adapt to the new diurnal cycle. Our master pacemaker’s plasticity explains how we can quickly adjust to the new time zones after international flights after just a brief period of jet lag.
It is hoped that the findings of this study can have future clinical implications when it comes to treating various disorders that affect our circadian rhythm. Professor Kim notes, “When the circadian clock loses its robustness and flexibility, the circadian rhythms sleep disorders can occur. As this study identifies the molecular mechanism that generates robustness and flexibility of the circadian clock, it can facilitate the identification of the cause of and treatment strategy for the circadian rhythm sleep disorders.” This work was supported by the Human Frontier Science Program.
-PublicationEui Min Jeong, Miri Kwon, Eunjoo Cho, Sang Hyuk Lee, Hyun Kim, Eun Young Kim, and Jae Kyoung Kim, “Systematic modeling-driven experiments identify distinct molecularclockworks underlying hierarchically organized pacemaker neurons,” February 22, 2022, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyoung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.02.23 View 11600
Scientist Discover How Circadian Rhythm Can Be Both Strong and Flexible
Study reveals that master and slave oscillators function via different molecular mechanisms
From tiny fruit flies to human beings, all animals on Earth maintain their daily rhythms based on their internal circadian clock. The circadian clock enables organisms to undergo rhythmic changes in behavior and physiology based on a 24-hour circadian cycle. For example, our own biological clock tells our brain to release melatonin, a sleep-inducing hormone, at night time.
The discovery of the molecular mechanism of the circadian clock was bestowed the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2017. From what we know, no one centralized clock is responsible for our circadian cycles. Instead, it operates in a hierarchical network where there are “master pacemaker” and “slave oscillator”.
The master pacemaker receives various input signals from the environment such as light. The master then drives the slave oscillator that regulates various outputs such as sleep, feeding, and metabolism. Despite the different roles of the pacemaker neurons, they are known to share common molecular mechanisms that are well conserved in all lifeforms. For example, interlocked systems of multiple transcriptional-translational feedback loops (TTFLs) composed of core clock proteins have been deeply studied in fruit flies.
However, there is still much that we need to learn about our own biological clock. The hierarchically-organized nature of master and slave clock neurons leads to a prevailing belief that they share an identical molecular clockwork. At the same time, the different roles they serve in regulating bodily rhythms also raise the question of whether they might function under different molecular clockworks.
Research team led by Professor Kim Jae Kyoung from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, a chief investigator at the Biomedical Mathematics Group at the Institute for Basic Science, used a combination of mathematical and experimental approaches using fruit flies to answer this question. The team found that the master clock and the slave clock operate via different molecular mechanisms.
In both master and slave neurons of fruit flies, a circadian rhythm-related protein called PER is produced and degraded at different rates depending on the time of the day. Previously, the team found that the master clock neuron (sLNvs) and the slave clock neuron (DN1ps) have different profiles of PER in wild-type and Clk-Δ mutant Drosophila. This hinted that there might be a potential difference in molecular clockworks between the master and slave clock neurons.
However, due to the complexity of the molecular clockwork, it was challenging to identify the source of such differences. Thus, the team developed a mathematical model describing the molecular clockworks of the master and slave clocks. Then, all possible molecular differences between the master and slave clock neurons were systematically investigated by using computer simulations. The model predicted that PER is more efficiently produced and then rapidly degraded in the master clock compared to the slave clock neurons. This prediction was then confirmed by the follow-up experiments using animal.
Then, why do the master clock neurons have such different molecular properties from the slave clock neurons? To answer this question, the research team again used the combination of mathematical model simulation and experiments. It was found that the faster rate of synthesis of PER in the master clock neurons allows them to generate synchronized rhythms with a high level of amplitude. Generation of such a strong rhythm with high amplitude is critical to delivering clear signals to slave clock neurons.
However, such strong rhythms would typically be unfavorable when it comes to adapting to environmental changes. These include natural causes such as different daylight hours across summer and winter seasons, up to more extreme artificial cases such as jet lag that occurs after international travel. Thanks to the distinct property of the master clock neurons, it is able to undergo phase dispersion when the standard light-dark cycle is disrupted, drastically reducing the level of PER. The master clock neurons can then easily adapt to the new diurnal cycle. Our master pacemaker’s plasticity explains how we can quickly adjust to the new time zones after international flights after just a brief period of jet lag.
It is hoped that the findings of this study can have future clinical implications when it comes to treating various disorders that affect our circadian rhythm. Professor Kim notes, “When the circadian clock loses its robustness and flexibility, the circadian rhythms sleep disorders can occur. As this study identifies the molecular mechanism that generates robustness and flexibility of the circadian clock, it can facilitate the identification of the cause of and treatment strategy for the circadian rhythm sleep disorders.” This work was supported by the Human Frontier Science Program.
-PublicationEui Min Jeong, Miri Kwon, Eunjoo Cho, Sang Hyuk Lee, Hyun Kim, Eun Young Kim, and Jae Kyoung Kim, “Systematic modeling-driven experiments identify distinct molecularclockworks underlying hierarchically organized pacemaker neurons,” February 22, 2022, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyoung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.02.23 View 11600 -
 A Mathematical Model Shows High Viral Transmissions Reduce the Progression Rates for Severe Covid-19
The model suggests a clue as to when a pandemic will turn into an endemic
A mathematical model demonstrated that high transmission rates among highly vaccinated populations of COVID-19 ultimately reduce the numbers of severe cases. This model suggests a clue as to when this pandemic will turn into an endemic.
With the future of the pandemic remaining uncertain, a research team of mathematicians and medical scientists analyzed a mathematical model that may predict how the changing transmission rate of COVID-19 would affect the settlement process of the virus as a mild respiratory virus.
The team led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the Department of Mathematical Science and Professor Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering used a new approach by dividing the human immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 into a shorter-term neutralizing antibody response and a longer-term T-cell immune response, and applying them each to a mathematical model. Additionally, the analysis was based on the fact that although breakthrough infection may occur frequently, the immune response of the patient will be boosted after recovery from each breakthrough infection.
The results showed that in an environment with a high vaccination rate, although COVID-19 cases may rise temporarily when the transmission rate increases, the ratio of critical cases would ultimately decline, thereby decreasing the total number of critical cases and in fact settling COVID-19 as a mild respiratory disease more quickly.
Conditions in which the number of cases may spike include relaxing social distancing measures or the rise of variants with higher transmission rates like the Omicron variant. This research did not take the less virulent characteristic of the Omicron variant into account but focused on the results of its high transmission rate, thereby predicting what may happen in the process of the endemic transition of COVID-19.
The research team pointed out the limitations of their mathematical model, such as the lack of consideration for age or patients with underlying diseases, and explained that the results of this study must be applied with care when compared against high-risk groups. Additionally, as medical systems may collapse when the number of cases rises sharply, this study must be interpreted with prudence and applied accordingly. The research team therefore emphasized that for policies that encourage a step-wise return to normality to succeed, the sustainable maintenance of public health systems is indispensable.
Professor Kim said, “We have drawn a counter-intuitive conclusion amid the unpredictable pandemic through an adequate mathematical model,” asserting the importance of applying mathematical models to medical research.
Professor Shin said, “Although the Omicron variant has become the dominant strain and the number of cases is rising rapidly in South Korea, it is important to use scientific approaches to predict the future and apply them to policies rather than fearing the current situation.”
The results of the research were published on medRxiv.org on February 11, under the title “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to severe COVID-19 during endemic transition.”
This research was funded by the Institute of Basic Science, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-PublicationHyukpyo Hong, Ji Yun Noh, Hyojung Lee, Sunhwa Choi, Boseung Choi, Jae Kyung Kim, Eui-Cheol Shin, “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to
severe COVID-19 during endemic transition,” medRxiv, February 9, 2022 (doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.09.22270633)
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
Professor Eui-Cheol ShinGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.02.22 View 11922
A Mathematical Model Shows High Viral Transmissions Reduce the Progression Rates for Severe Covid-19
The model suggests a clue as to when a pandemic will turn into an endemic
A mathematical model demonstrated that high transmission rates among highly vaccinated populations of COVID-19 ultimately reduce the numbers of severe cases. This model suggests a clue as to when this pandemic will turn into an endemic.
With the future of the pandemic remaining uncertain, a research team of mathematicians and medical scientists analyzed a mathematical model that may predict how the changing transmission rate of COVID-19 would affect the settlement process of the virus as a mild respiratory virus.
The team led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the Department of Mathematical Science and Professor Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering used a new approach by dividing the human immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 into a shorter-term neutralizing antibody response and a longer-term T-cell immune response, and applying them each to a mathematical model. Additionally, the analysis was based on the fact that although breakthrough infection may occur frequently, the immune response of the patient will be boosted after recovery from each breakthrough infection.
The results showed that in an environment with a high vaccination rate, although COVID-19 cases may rise temporarily when the transmission rate increases, the ratio of critical cases would ultimately decline, thereby decreasing the total number of critical cases and in fact settling COVID-19 as a mild respiratory disease more quickly.
Conditions in which the number of cases may spike include relaxing social distancing measures or the rise of variants with higher transmission rates like the Omicron variant. This research did not take the less virulent characteristic of the Omicron variant into account but focused on the results of its high transmission rate, thereby predicting what may happen in the process of the endemic transition of COVID-19.
The research team pointed out the limitations of their mathematical model, such as the lack of consideration for age or patients with underlying diseases, and explained that the results of this study must be applied with care when compared against high-risk groups. Additionally, as medical systems may collapse when the number of cases rises sharply, this study must be interpreted with prudence and applied accordingly. The research team therefore emphasized that for policies that encourage a step-wise return to normality to succeed, the sustainable maintenance of public health systems is indispensable.
Professor Kim said, “We have drawn a counter-intuitive conclusion amid the unpredictable pandemic through an adequate mathematical model,” asserting the importance of applying mathematical models to medical research.
Professor Shin said, “Although the Omicron variant has become the dominant strain and the number of cases is rising rapidly in South Korea, it is important to use scientific approaches to predict the future and apply them to policies rather than fearing the current situation.”
The results of the research were published on medRxiv.org on February 11, under the title “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to severe COVID-19 during endemic transition.”
This research was funded by the Institute of Basic Science, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-PublicationHyukpyo Hong, Ji Yun Noh, Hyojung Lee, Sunhwa Choi, Boseung Choi, Jae Kyung Kim, Eui-Cheol Shin, “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to
severe COVID-19 during endemic transition,” medRxiv, February 9, 2022 (doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.09.22270633)
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
Professor Eui-Cheol ShinGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.02.22 View 11922 -
 Commencement Ceremony Honors the Class of 2022
Third online commencement ceremony since the pandemic outbreak celebrates 2741 graduates
The 2022 commencement ceremony convened online on February 18 to celebrate and award degrees to the Class of 2022. The graduating class of 2022 included 663 PhDs, 1,383 Masters, and 695 Bachelors. The limited number of attendees included 86 graduate representatives and approximately 20 faculty members in senior leadership, as well as Korea’s Minister of Science and ICT Hyesook Lim. The ceremony was livestreamed on KAIST’s YouTube channel.
Valedictorian Ji-Young Lee from the Department of Physics received the Minister of Science and ICT’s Award. Yu-Jin Bang from the School of Business and Technology Management was the Awardee of the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees and the KAIST Presidential Awardee was Jong-Hwan Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences.
KAIST conferred honorary doctorates to Honorary Chairman Jae-Chul Kim of Dongwon Group and Chairman Sung-Hwan Chang of Samsung Brush. Chairman Kim, whose donation funded the establishment of the Kim Jae-Chul Graduate School of AI, was awarded an honorary doctorate of science technology. Chairman Chang was awarded an honorary doctorate of business administration in recognition of his funding in the fields of medical science and engineering at KAIST.
This year’s undergraduate commencement speaker was Hye-Lin Park from the School of Computing. She has severe cerebral palsy and was the first student admitted to KAIST with a severe physical handicap.
“I loved mathematics and wanted to become a mathematician. When I learned programming in my second year, I was so mesmerized by it that I transferred to the School of Computing,” said Park, who plans to continue studying programming languages in graduate school at KAIST.
“I spent my entire life of 24 years in this beautiful wheelchair. Without the support and help of my parents, friends, and my special teachers who helped me move and study at the campus, I would not have made it this far,” said Park. For easier access to classrooms and facilities, KAIST started to remodel its facilities to make the entrance of buildings more wheelchair-friendly. Park made many suggestions to the Office of Student Life and the Facilities Management Office on how to ease mobility for handicapped people on campus. The physical education course that was required for graduation was also revised to stipulate exceptions.
Minister Lim stressed the role of young scientists and researchers in these times of digital transformation dominated by AI and the metaverse. She encouraged the graduates to carry out their dreams with warm hearts and challenging spirits.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee also stressed the power of dreams, calling for graduates to dream big even in times of uncertainty.
“Humanity stands at an inflection point in history. The fourth industrial revolution and outbreak of Covid-19 have unfolded the grand global transformation. Although the future gives us new opportunities, it also comes with anxiety regarding the uncertainties ahead.”
“Dreams make your heart race and push us to live life to the fullest. Dreams will help you keep moving forward even in the face of adversity,” he said.
2022.02.18 View 11432
Commencement Ceremony Honors the Class of 2022
Third online commencement ceremony since the pandemic outbreak celebrates 2741 graduates
The 2022 commencement ceremony convened online on February 18 to celebrate and award degrees to the Class of 2022. The graduating class of 2022 included 663 PhDs, 1,383 Masters, and 695 Bachelors. The limited number of attendees included 86 graduate representatives and approximately 20 faculty members in senior leadership, as well as Korea’s Minister of Science and ICT Hyesook Lim. The ceremony was livestreamed on KAIST’s YouTube channel.
Valedictorian Ji-Young Lee from the Department of Physics received the Minister of Science and ICT’s Award. Yu-Jin Bang from the School of Business and Technology Management was the Awardee of the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees and the KAIST Presidential Awardee was Jong-Hwan Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences.
KAIST conferred honorary doctorates to Honorary Chairman Jae-Chul Kim of Dongwon Group and Chairman Sung-Hwan Chang of Samsung Brush. Chairman Kim, whose donation funded the establishment of the Kim Jae-Chul Graduate School of AI, was awarded an honorary doctorate of science technology. Chairman Chang was awarded an honorary doctorate of business administration in recognition of his funding in the fields of medical science and engineering at KAIST.
This year’s undergraduate commencement speaker was Hye-Lin Park from the School of Computing. She has severe cerebral palsy and was the first student admitted to KAIST with a severe physical handicap.
“I loved mathematics and wanted to become a mathematician. When I learned programming in my second year, I was so mesmerized by it that I transferred to the School of Computing,” said Park, who plans to continue studying programming languages in graduate school at KAIST.
“I spent my entire life of 24 years in this beautiful wheelchair. Without the support and help of my parents, friends, and my special teachers who helped me move and study at the campus, I would not have made it this far,” said Park. For easier access to classrooms and facilities, KAIST started to remodel its facilities to make the entrance of buildings more wheelchair-friendly. Park made many suggestions to the Office of Student Life and the Facilities Management Office on how to ease mobility for handicapped people on campus. The physical education course that was required for graduation was also revised to stipulate exceptions.
Minister Lim stressed the role of young scientists and researchers in these times of digital transformation dominated by AI and the metaverse. She encouraged the graduates to carry out their dreams with warm hearts and challenging spirits.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee also stressed the power of dreams, calling for graduates to dream big even in times of uncertainty.
“Humanity stands at an inflection point in history. The fourth industrial revolution and outbreak of Covid-19 have unfolded the grand global transformation. Although the future gives us new opportunities, it also comes with anxiety regarding the uncertainties ahead.”
“Dreams make your heart race and push us to live life to the fullest. Dreams will help you keep moving forward even in the face of adversity,” he said.
2022.02.18 View 11432 -
 Five Projects Ranked in the Top 100 for National R&D Excellence
Five KAIST research projects were selected as the 2021 Top 100 for National R&D Excellence by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of Science & Technology Evaluation and Planning.
The five projects are:-The development of E. coli that proliferates with only formic acid and carbon dioxide by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-An original reverse aging technology that restores an old human skin cell into a younger one by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering-The development of next-generation high-efficiency perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells by Professor Byungha Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering-Research on the effects of ultrafine dust in the atmosphere has on energy consumption by Professor Jiyong Eom from the School of Business and Technology Management-Research on a molecular trigger that controls the phase transformation of bio materials by Professor Myungchul Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Started in 2006, an Evaluation Committee composed of experts in industries, universities, and research institutes has made the preliminary selections of the most outstanding research projects based on their significance as a scientific and technological development and their socioeconomic effects. The finalists went through an open public evaluation. The final 100 studies are from six fields: 18 from mechanics & materials, 26 from biology & marine sciences, 19 from ICT & electronics, 10 from interdisciplinary research, and nine from natural science and infrastructure.
The selected 100 studies will receive a certificate and an award plaque from the minister of MSIT as well as additional points for business and institutional evaluations according to appropriate regulations, and the selected researchers will be strongly recommended as candidates for national meritorious awards.
In particular, to help the 100 selected research projects become more accessible for the general public, their main contents will be provided in a free e-book ‘The Top 100 for National R&D Excellence of 2021’ that will be available from online booksellers.
2022.02.17 View 12010
Five Projects Ranked in the Top 100 for National R&D Excellence
Five KAIST research projects were selected as the 2021 Top 100 for National R&D Excellence by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of Science & Technology Evaluation and Planning.
The five projects are:-The development of E. coli that proliferates with only formic acid and carbon dioxide by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-An original reverse aging technology that restores an old human skin cell into a younger one by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering-The development of next-generation high-efficiency perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells by Professor Byungha Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering-Research on the effects of ultrafine dust in the atmosphere has on energy consumption by Professor Jiyong Eom from the School of Business and Technology Management-Research on a molecular trigger that controls the phase transformation of bio materials by Professor Myungchul Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Started in 2006, an Evaluation Committee composed of experts in industries, universities, and research institutes has made the preliminary selections of the most outstanding research projects based on their significance as a scientific and technological development and their socioeconomic effects. The finalists went through an open public evaluation. The final 100 studies are from six fields: 18 from mechanics & materials, 26 from biology & marine sciences, 19 from ICT & electronics, 10 from interdisciplinary research, and nine from natural science and infrastructure.
The selected 100 studies will receive a certificate and an award plaque from the minister of MSIT as well as additional points for business and institutional evaluations according to appropriate regulations, and the selected researchers will be strongly recommended as candidates for national meritorious awards.
In particular, to help the 100 selected research projects become more accessible for the general public, their main contents will be provided in a free e-book ‘The Top 100 for National R&D Excellence of 2021’ that will be available from online booksellers.
2022.02.17 View 12010 -
 President Lee Presents Plans to Nurture Next-Generation Talents
President Lee stressed that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during a news conference
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during an online news conference marking the 1st anniversary of him becoming the president on February 15.
He said that nurturing physician-scientists is the most critical mission for KAIST to help the nation create a new growth engine. He said KAIST will help the nation drive the bio-industry and provide medical science resources for the nation’s health sector. To this end, he said that KAIST will open its Medical Science and Technology School by 2026.
“We plan to expand the current Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering into a new Medical Science and Technology School that will focus entirely on a condensed MD-PhD course converging the fields of AI, bio, and physics,” he said.
The school aims to foster medical scientists whose research results will eventually be commercialized. He said that the university is now discussing revisions to related laws and regulations with the government and other universities.
To supply human resources to the semiconductor industry, President Lee said the university will add a campus in Pyongtaek City that will serve as an advanced convergence research hub in the field of next generation semiconductors in collaboration with Samsung Electronics and the city of Pyongtaek. The three-stage opening plan projected the final opening of the campus by 2036. During the first stage, which will be completed by 2026, it will construct the campus infrastructure in Pyongtaek city where Samsung Semiconductors runs two massive semiconductor complexes. By 2031, it plans to launch the open research platform including a future cities research center and future vehicles research center. The campus will open the global industrial collaboration cluster hub by 2036.
In the global arena, President Lee said he is working to open the New York campus with stakeholders in the United States. He announced the plan last December that was endorsed by New York-based entrepreneur Hee-Nam Bae, the chairman of Big Continent Inc. President Lee and Chairman Lee signed an MOU for the funding to open the campus in New York.
“We are discussing how to facilitate the plan and best accommodate the interests and potential of our students. Many ideas and plans are on the table and we think it will take longer than expected to finalize the plan,” explained President Lee.
However, he added that the basic idea is to offer art tech and health technology programs as well as an AI-based finance MBA at the New York campus, in addition to it serving as the startup accelerator of KAIST.
President Lee stressed the importance of technology commercialization when successfully launching KAIST Holdings last month to help spinoffs of KAIST labs accelerate their end results. He said that KAIST Holdings will build a virtuous supporting system to commercialize the technology startups coming from KAIST.
“We plan to list at least 10 KAIST startups on the KOSDAQ and two on the NASDAQ by 2031. KAIST Holdings also aims to nurture companies valued at a total of one billion KRW and earn 100 billion KRW in technology fees by 2031.
2022.02.17 View 12749
President Lee Presents Plans to Nurture Next-Generation Talents
President Lee stressed that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during a news conference
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during an online news conference marking the 1st anniversary of him becoming the president on February 15.
He said that nurturing physician-scientists is the most critical mission for KAIST to help the nation create a new growth engine. He said KAIST will help the nation drive the bio-industry and provide medical science resources for the nation’s health sector. To this end, he said that KAIST will open its Medical Science and Technology School by 2026.
“We plan to expand the current Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering into a new Medical Science and Technology School that will focus entirely on a condensed MD-PhD course converging the fields of AI, bio, and physics,” he said.
The school aims to foster medical scientists whose research results will eventually be commercialized. He said that the university is now discussing revisions to related laws and regulations with the government and other universities.
To supply human resources to the semiconductor industry, President Lee said the university will add a campus in Pyongtaek City that will serve as an advanced convergence research hub in the field of next generation semiconductors in collaboration with Samsung Electronics and the city of Pyongtaek. The three-stage opening plan projected the final opening of the campus by 2036. During the first stage, which will be completed by 2026, it will construct the campus infrastructure in Pyongtaek city where Samsung Semiconductors runs two massive semiconductor complexes. By 2031, it plans to launch the open research platform including a future cities research center and future vehicles research center. The campus will open the global industrial collaboration cluster hub by 2036.
In the global arena, President Lee said he is working to open the New York campus with stakeholders in the United States. He announced the plan last December that was endorsed by New York-based entrepreneur Hee-Nam Bae, the chairman of Big Continent Inc. President Lee and Chairman Lee signed an MOU for the funding to open the campus in New York.
“We are discussing how to facilitate the plan and best accommodate the interests and potential of our students. Many ideas and plans are on the table and we think it will take longer than expected to finalize the plan,” explained President Lee.
However, he added that the basic idea is to offer art tech and health technology programs as well as an AI-based finance MBA at the New York campus, in addition to it serving as the startup accelerator of KAIST.
President Lee stressed the importance of technology commercialization when successfully launching KAIST Holdings last month to help spinoffs of KAIST labs accelerate their end results. He said that KAIST Holdings will build a virtuous supporting system to commercialize the technology startups coming from KAIST.
“We plan to list at least 10 KAIST startups on the KOSDAQ and two on the NASDAQ by 2031. KAIST Holdings also aims to nurture companies valued at a total of one billion KRW and earn 100 billion KRW in technology fees by 2031.
2022.02.17 View 12749 -
 Research Finds Digital Music Streaming Consumption Dropped as a Result of Covid-19 and Lockdowns
Decline in human mobility has stunning consequences for content streaming
The Covid-19 pandemic and lockdowns significantly reduced the consumption of audio music streaming in many countries as people turned to video platforms. On average, audio music consumption decreased by 12.5% after the World Health Organization’s (WHO) pandemic declaration in March 2020.
Music streaming services were an unlikely area hit hard by the Covid-19 pandemic. New research in Marketing Science found that the drop in people’s mobility during the pandemic significantly reduced the consumption of audio music streaming. Instead, people turned more to video platforms.
“On average, audio music consumption decreased by more than 12% after the World Health Organization’s (WHO) pandemic declaration on March 11, 2020. As a result, during the pandemic, Spotify lost 838 million dollars of revenue in the first three quarters of 2020,” said Jaeung Sim, a PhD candidate in management engineering at KAIST and one of the authors of the research study on this phenomenon. “Our results showed that human mobility plays a much larger role in the audio consumption of music than previously thought.”
The study, “Frontiers: Virus Shook the Streaming Star: Estimating the Covid-19 Impact on Music Consumption,” conducted by Sim and Professor Daegon Cho of KAIST, Youngdeok Hwang of City University of New York, and Rahul Telang of Carnegie Mellon University, looked at online music streaming data for top songs for two years in 60 countries, as well as Covid-19 cases, lockdown statistics, and daily mobility data, to determine the nature of the changes.
The study showed how the pandemic adversely impacted music streaming services despite the common expectation that the pandemic would universally benefit online medias platforms. This implies that the substantially changing media consumption environment can place streaming music in fiercer competition with other media forms that offer more dynamic and vivid experiences to consumers.
The researchers found that music consumption through video platforms was positively associated with the severity of Covid-19, lockdown policies, and time spent at home.
-PublicationJaeung Sim, Daegon Cho, Youngdeok Hwang, and Rahul Telang,“Frontiers: Virus Shook the Streaming Star: Estimating the Covid-19 Impact on Music Consumption,” November 30 in Marketing Science online (doi.org/10.1287/mksc.2021.1321)
-Profile Professor Daegon ChoGraduate School of Information and Media ManagementCollege of BusinessKAIST
2022.02.15 View 11111
Research Finds Digital Music Streaming Consumption Dropped as a Result of Covid-19 and Lockdowns
Decline in human mobility has stunning consequences for content streaming
The Covid-19 pandemic and lockdowns significantly reduced the consumption of audio music streaming in many countries as people turned to video platforms. On average, audio music consumption decreased by 12.5% after the World Health Organization’s (WHO) pandemic declaration in March 2020.
Music streaming services were an unlikely area hit hard by the Covid-19 pandemic. New research in Marketing Science found that the drop in people’s mobility during the pandemic significantly reduced the consumption of audio music streaming. Instead, people turned more to video platforms.
“On average, audio music consumption decreased by more than 12% after the World Health Organization’s (WHO) pandemic declaration on March 11, 2020. As a result, during the pandemic, Spotify lost 838 million dollars of revenue in the first three quarters of 2020,” said Jaeung Sim, a PhD candidate in management engineering at KAIST and one of the authors of the research study on this phenomenon. “Our results showed that human mobility plays a much larger role in the audio consumption of music than previously thought.”
The study, “Frontiers: Virus Shook the Streaming Star: Estimating the Covid-19 Impact on Music Consumption,” conducted by Sim and Professor Daegon Cho of KAIST, Youngdeok Hwang of City University of New York, and Rahul Telang of Carnegie Mellon University, looked at online music streaming data for top songs for two years in 60 countries, as well as Covid-19 cases, lockdown statistics, and daily mobility data, to determine the nature of the changes.
The study showed how the pandemic adversely impacted music streaming services despite the common expectation that the pandemic would universally benefit online medias platforms. This implies that the substantially changing media consumption environment can place streaming music in fiercer competition with other media forms that offer more dynamic and vivid experiences to consumers.
The researchers found that music consumption through video platforms was positively associated with the severity of Covid-19, lockdown policies, and time spent at home.
-PublicationJaeung Sim, Daegon Cho, Youngdeok Hwang, and Rahul Telang,“Frontiers: Virus Shook the Streaming Star: Estimating the Covid-19 Impact on Music Consumption,” November 30 in Marketing Science online (doi.org/10.1287/mksc.2021.1321)
-Profile Professor Daegon ChoGraduate School of Information and Media ManagementCollege of BusinessKAIST
2022.02.15 View 11111 -
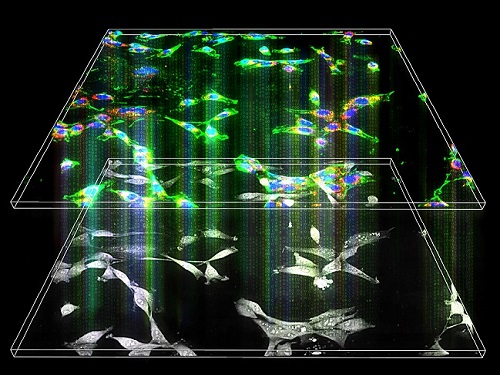 Label-Free Multiplexed Microtomography of Endogenous Subcellular Dynamics Using Deep Learning
AI-based holographic microscopy allows molecular imaging without introducing exogenous labeling agents
A research team upgraded the 3D microtomography observing dynamics of label-free live cells in multiplexed fluorescence imaging. The AI-powered 3D holotomographic microscopy extracts various molecular information from live unlabeled biological cells in real time without exogenous labeling or staining agents.
Professor YongKeum Park’s team and the startup Tomocube encoded 3D refractive index tomograms using the refractive index as a means of measurement. Then they decoded the information with a deep learning-based model that infers multiple 3D fluorescence tomograms from the refractive index measurements of the corresponding subcellular targets, thereby achieving multiplexed micro tomography. This study was reported in Nature Cell Biology online on December 7, 2021.
Fluorescence microscopy is the most widely used optical microscopy technique due to its high biochemical specificity. However, it needs to genetically manipulate or to stain cells with fluorescent labels in order to express fluorescent proteins. These labeling processes inevitably affect the intrinsic physiology of cells. It also has challenges in long-term measuring due to photobleaching and phototoxicity. The overlapped spectra of multiplexed fluorescence signals also hinder the viewing of various structures at the same time. More critically, it took several hours to observe the cells after preparing them.
3D holographic microscopy, also known as holotomography, is providing new ways to quantitatively image live cells without pretreatments such as staining. Holotomography can accurately and quickly measure the morphological and structural information of cells, but only provides limited biochemical and molecular information.
The 'AI microscope' created in this process takes advantage of the features of both holographic microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. That is, a specific image from a fluorescence microscope can be obtained without a fluorescent label. Therefore, the microscope can observe many types of cellular structures in their natural state in 3D and at the same time as fast as one millisecond, and long-term measurements over several days are also possible.
The Tomocube-KAIST team showed that fluorescence images can be directly and precisely predicted from holotomographic images in various cells and conditions. Using the quantitative relationship between the spatial distribution of the refractive index found by AI and the major structures in cells, it was possible to decipher the spatial distribution of the refractive index. And surprisingly, it confirmed that this relationship is constant regardless of cell type.
Professor Park said, “We were able to develop a new concept microscope that combines the advantages of several microscopes with the multidisciplinary research of AI, optics, and biology. It will be immediately applicable for new types of cells not included in the existing data and is expected to be widely applicable for various biological and medical research.”
When comparing the molecular image information extracted by AI with the molecular image information physically obtained by fluorescence staining in 3D space, it showed a 97% or more conformity, which is a level that is difficult to distinguish with the naked eye.
“Compared to the sub-60% accuracy of the fluorescence information extracted from the model developed by the Google AI team, it showed significantly higher performance,” Professor Park added.
This work was supported by the KAIST Up program, the BK21+ program, Tomocube, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Health & Welfare.
-Publication
Hyun-seok Min, Won-Do Heo, YongKeun Park, et al. “Label-free multiplexed microtomography of endogenous subcellular dynamics using generalizable deep learning,” Nature Cell Biology (doi.org/10.1038/s41556-021-00802-x) published online December 07 2021.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
Department of Physics
KAIST
2022.02.09 View 12707
Label-Free Multiplexed Microtomography of Endogenous Subcellular Dynamics Using Deep Learning
AI-based holographic microscopy allows molecular imaging without introducing exogenous labeling agents
A research team upgraded the 3D microtomography observing dynamics of label-free live cells in multiplexed fluorescence imaging. The AI-powered 3D holotomographic microscopy extracts various molecular information from live unlabeled biological cells in real time without exogenous labeling or staining agents.
Professor YongKeum Park’s team and the startup Tomocube encoded 3D refractive index tomograms using the refractive index as a means of measurement. Then they decoded the information with a deep learning-based model that infers multiple 3D fluorescence tomograms from the refractive index measurements of the corresponding subcellular targets, thereby achieving multiplexed micro tomography. This study was reported in Nature Cell Biology online on December 7, 2021.
Fluorescence microscopy is the most widely used optical microscopy technique due to its high biochemical specificity. However, it needs to genetically manipulate or to stain cells with fluorescent labels in order to express fluorescent proteins. These labeling processes inevitably affect the intrinsic physiology of cells. It also has challenges in long-term measuring due to photobleaching and phototoxicity. The overlapped spectra of multiplexed fluorescence signals also hinder the viewing of various structures at the same time. More critically, it took several hours to observe the cells after preparing them.
3D holographic microscopy, also known as holotomography, is providing new ways to quantitatively image live cells without pretreatments such as staining. Holotomography can accurately and quickly measure the morphological and structural information of cells, but only provides limited biochemical and molecular information.
The 'AI microscope' created in this process takes advantage of the features of both holographic microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. That is, a specific image from a fluorescence microscope can be obtained without a fluorescent label. Therefore, the microscope can observe many types of cellular structures in their natural state in 3D and at the same time as fast as one millisecond, and long-term measurements over several days are also possible.
The Tomocube-KAIST team showed that fluorescence images can be directly and precisely predicted from holotomographic images in various cells and conditions. Using the quantitative relationship between the spatial distribution of the refractive index found by AI and the major structures in cells, it was possible to decipher the spatial distribution of the refractive index. And surprisingly, it confirmed that this relationship is constant regardless of cell type.
Professor Park said, “We were able to develop a new concept microscope that combines the advantages of several microscopes with the multidisciplinary research of AI, optics, and biology. It will be immediately applicable for new types of cells not included in the existing data and is expected to be widely applicable for various biological and medical research.”
When comparing the molecular image information extracted by AI with the molecular image information physically obtained by fluorescence staining in 3D space, it showed a 97% or more conformity, which is a level that is difficult to distinguish with the naked eye.
“Compared to the sub-60% accuracy of the fluorescence information extracted from the model developed by the Google AI team, it showed significantly higher performance,” Professor Park added.
This work was supported by the KAIST Up program, the BK21+ program, Tomocube, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Health & Welfare.
-Publication
Hyun-seok Min, Won-Do Heo, YongKeun Park, et al. “Label-free multiplexed microtomography of endogenous subcellular dynamics using generalizable deep learning,” Nature Cell Biology (doi.org/10.1038/s41556-021-00802-x) published online December 07 2021.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
Department of Physics
KAIST
2022.02.09 View 12707 -
 Thermal Superconductor Lab Becomes the 7th Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab
The Thermal Superconductor Lab led by Senior Professor Sung Jin Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering will team up with Junior Professor Youngsuk Nam to develop next-generation superconductors. The two professor team was selected as the 7th Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab last week and will sustain the academic legacy of Professor Kim’s three decades of research on superconductors. The team will continue to develop thin, next-generation superconductors that carry super thermal conductivity using phase transition control technology and thin film packaging.
Thin-filmed, next-generation superconductors can be used in various high-temperature flexible electronic devices. The superconductors built inside of the semiconductor device packages will also be used for managing the low-powered but high-performance temperatures of semiconductor and electronic equipment.
Professor Kim said, “I am very pleased that my research, know-how, and knowledge from over 30 years of work will continue through the Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab system with Professor Nam. We will spare no effort to advance superconductor technology and play a part in KAIST leading global technology fields.” Junior Professor Nam also stressed that the team is excited to continue its research on crucial technology for managing the temperatures of semiconductors and other electronic equipment.
KAIST started this innovative research system in 2018, and in 2021 it established the steering committee to select new labs based on: originality, differentiation, and excellence; academic, social, economic impact; the urgency of cross-generation research; the senior professor’s academic excellence and international reputation; and the senior professor’s research vision. Selected labs receive 500 million KRW in research funding over five years.
2022.01.27 View 7326
Thermal Superconductor Lab Becomes the 7th Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab
The Thermal Superconductor Lab led by Senior Professor Sung Jin Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering will team up with Junior Professor Youngsuk Nam to develop next-generation superconductors. The two professor team was selected as the 7th Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab last week and will sustain the academic legacy of Professor Kim’s three decades of research on superconductors. The team will continue to develop thin, next-generation superconductors that carry super thermal conductivity using phase transition control technology and thin film packaging.
Thin-filmed, next-generation superconductors can be used in various high-temperature flexible electronic devices. The superconductors built inside of the semiconductor device packages will also be used for managing the low-powered but high-performance temperatures of semiconductor and electronic equipment.
Professor Kim said, “I am very pleased that my research, know-how, and knowledge from over 30 years of work will continue through the Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab system with Professor Nam. We will spare no effort to advance superconductor technology and play a part in KAIST leading global technology fields.” Junior Professor Nam also stressed that the team is excited to continue its research on crucial technology for managing the temperatures of semiconductors and other electronic equipment.
KAIST started this innovative research system in 2018, and in 2021 it established the steering committee to select new labs based on: originality, differentiation, and excellence; academic, social, economic impact; the urgency of cross-generation research; the senior professor’s academic excellence and international reputation; and the senior professor’s research vision. Selected labs receive 500 million KRW in research funding over five years.
2022.01.27 View 7326 -
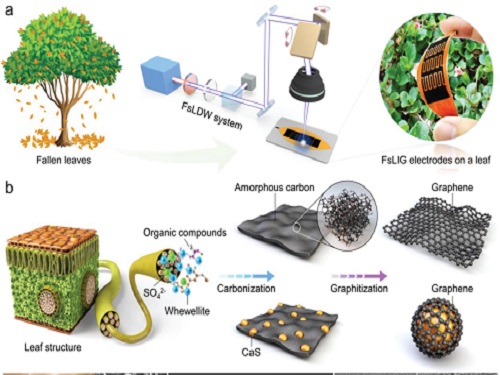 Eco-Friendly Micro-Supercapacitors Using Fallen Leaves
Green micro-supercapacitors on a single leaf could easily be applied in wearable electronics, smart houses, and IoTs
A KAIST research team has developed graphene-inorganic-hybrid micro-supercapacitors made of fallen leaves using femtosecond laser direct writing. The rapid development of wearable electronics requires breakthrough innovations in flexible energy storage devices in which micro-supercapacitors have drawn a great deal of interest due to their high power density, long lifetimes, and short charging times. Recently, there has been an enormous increase in waste batteries owing to the growing demand and the shortened replacement cycle in consumer electronics. The safety and environmental issues involved in the collection, recycling, and processing of such waste batteries are creating a number of challenges.
Forests cover about 30 percent of the Earth’s surface and produce a huge amount of fallen leaves. This naturally occurring biomass comes in large quantities and is completely biodegradable, which makes it an attractive sustainable resource. Nevertheless, if the fallen leaves are left neglected instead of being used efficiently, they can contribute to fire hazards, air pollution, and global warming.
To solve both problems at once, a research team led by Professor Young-Jin Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Hana Yoon from the Korea Institute of Energy Research developed a novel technology that can create 3D porous graphene microelectrodes with high electrical conductivity by irradiating femtosecond laser pulses on the leaves in ambient air. This one-step fabrication does not require any additional materials or pre-treatment.
They showed that this technique could quickly and easily produce porous graphene electrodes at a low price, and demonstrated potential applications by fabricating graphene micro-supercapacitors to power an LED and an electronic watch. These results open up a new possibility for the mass production of flexible and green graphene-based electronic devices.
Professor Young-Jin Kim said, “Leaves create forest biomass that comes in unmanageable quantities, so using them for next-generation energy storage devices makes it possible for us to reuse waste resources, thereby establishing a virtuous cycle.”
This research was published in Advanced Functional Materials last month and was sponsored by the Ministry of Agriculture Food and Rural Affairs, the Korea Forest Service, and the Korea Institute of Energy Research.
-Publication
Truong-Son Dinh Le, Yeong A. Lee, Han Ku Nam, Kyu Yeon Jang, Dongwook Yang, Byunggi Kim, Kanghoon Yim, Seung Woo Kim, Hana Yoon, and Young-jin Kim, “Green Flexible Graphene-Inorganic-Hybrid Micro-Supercapacitors Made of Fallen Leaves Enabled by Ultrafast Laser Pulses," December 05, 2021, Advanced Functional Materials (doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202107768)
-ProfileProfessor Young-Jin KimUltra-Precision Metrology and Manufacturing (UPM2) LaboratoryDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2022.01.27 View 13993
Eco-Friendly Micro-Supercapacitors Using Fallen Leaves
Green micro-supercapacitors on a single leaf could easily be applied in wearable electronics, smart houses, and IoTs
A KAIST research team has developed graphene-inorganic-hybrid micro-supercapacitors made of fallen leaves using femtosecond laser direct writing. The rapid development of wearable electronics requires breakthrough innovations in flexible energy storage devices in which micro-supercapacitors have drawn a great deal of interest due to their high power density, long lifetimes, and short charging times. Recently, there has been an enormous increase in waste batteries owing to the growing demand and the shortened replacement cycle in consumer electronics. The safety and environmental issues involved in the collection, recycling, and processing of such waste batteries are creating a number of challenges.
Forests cover about 30 percent of the Earth’s surface and produce a huge amount of fallen leaves. This naturally occurring biomass comes in large quantities and is completely biodegradable, which makes it an attractive sustainable resource. Nevertheless, if the fallen leaves are left neglected instead of being used efficiently, they can contribute to fire hazards, air pollution, and global warming.
To solve both problems at once, a research team led by Professor Young-Jin Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Hana Yoon from the Korea Institute of Energy Research developed a novel technology that can create 3D porous graphene microelectrodes with high electrical conductivity by irradiating femtosecond laser pulses on the leaves in ambient air. This one-step fabrication does not require any additional materials or pre-treatment.
They showed that this technique could quickly and easily produce porous graphene electrodes at a low price, and demonstrated potential applications by fabricating graphene micro-supercapacitors to power an LED and an electronic watch. These results open up a new possibility for the mass production of flexible and green graphene-based electronic devices.
Professor Young-Jin Kim said, “Leaves create forest biomass that comes in unmanageable quantities, so using them for next-generation energy storage devices makes it possible for us to reuse waste resources, thereby establishing a virtuous cycle.”
This research was published in Advanced Functional Materials last month and was sponsored by the Ministry of Agriculture Food and Rural Affairs, the Korea Forest Service, and the Korea Institute of Energy Research.
-Publication
Truong-Son Dinh Le, Yeong A. Lee, Han Ku Nam, Kyu Yeon Jang, Dongwook Yang, Byunggi Kim, Kanghoon Yim, Seung Woo Kim, Hana Yoon, and Young-jin Kim, “Green Flexible Graphene-Inorganic-Hybrid Micro-Supercapacitors Made of Fallen Leaves Enabled by Ultrafast Laser Pulses," December 05, 2021, Advanced Functional Materials (doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202107768)
-ProfileProfessor Young-Jin KimUltra-Precision Metrology and Manufacturing (UPM2) LaboratoryDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2022.01.27 View 13993 -
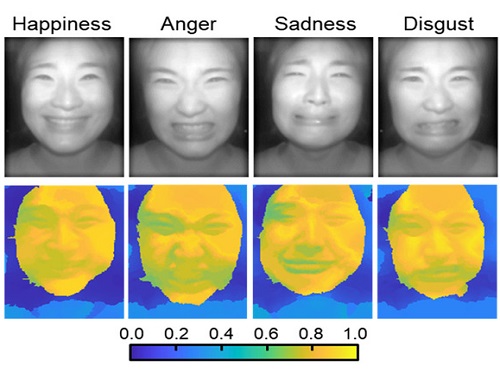 AI Light-Field Camera Reads 3D Facial Expressions
Machine-learned, light-field camera reads facial expressions from high-contrast illumination invariant 3D facial images
A joint research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong and Doheon Lee from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering reported the development of a technique for facial expression detection by merging near-infrared light-field camera techniques with artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
Unlike a conventional camera, the light-field camera contains micro-lens arrays in front of the image sensor, which makes the camera small enough to fit into a smart phone, while allowing it to acquire the spatial and directional information of the light with a single shot. The technique has received attention as it can reconstruct images in a variety of ways including multi-views, refocusing, and 3D image acquisition, giving rise to many potential applications.
However, the optical crosstalk between shadows caused by external light sources in the environment and the micro-lens has limited existing light-field cameras from being able to provide accurate image contrast and 3D reconstruction.
The joint research team applied a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) in the near-IR range to stabilize the accuracy of 3D image reconstruction that previously depended on environmental light. When an external light source is shone on a face at 0-, 30-, and 60-degree angles, the light field camera reduces 54% of image reconstruction errors. Additionally, by inserting a light-absorbing layer for visible and near-IR wavelengths between the micro-lens arrays, the team could minimize optical crosstalk while increasing the image contrast by 2.1 times.
Through this technique, the team could overcome the limitations of existing light-field cameras and was able to develop their NIR-based light-field camera (NIR-LFC), optimized for the 3D image reconstruction of facial expressions. Using the NIR-LFC, the team acquired high-quality 3D reconstruction images of facial expressions expressing various emotions regardless of the lighting conditions of the surrounding environment.
The facial expressions in the acquired 3D images were distinguished through machine learning with an average of 85% accuracy – a statistically significant figure compared to when 2D images were used. Furthermore, by calculating the interdependency of distance information that varies with facial expression in 3D images, the team could identify the information a light-field camera utilizes to distinguish human expressions.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong said, “The sub-miniature light-field camera developed by the research team has the potential to become the new platform to quantitatively analyze the facial expressions and emotions of humans.” To highlight the significance of this research, he added, “It could be applied in various fields including mobile healthcare, field diagnosis, social cognition, and human-machine interactions.”
This research was published in Advanced Intelligent Systems online on December 16, under the title, “Machine-Learned Light-field Camera that Reads Facial Expression from High-Contrast and Illumination Invariant 3D Facial Images.” This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
-Publication“Machine-learned light-field camera that reads fascial expression from high-contrast and illumination invariant 3D facial images,” Sang-In Bae, Sangyeon Lee, Jae-Myeong Kwon, Hyun-Kyung Kim. Kyung-Won Jang, Doheon Lee, Ki-Hun Jeong, Advanced Intelligent Systems, December 16, 2021 (doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202100182)
ProfileProfessor Ki-Hun JeongBiophotonic LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Doheon LeeDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2022.01.21 View 13958
AI Light-Field Camera Reads 3D Facial Expressions
Machine-learned, light-field camera reads facial expressions from high-contrast illumination invariant 3D facial images
A joint research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong and Doheon Lee from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering reported the development of a technique for facial expression detection by merging near-infrared light-field camera techniques with artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
Unlike a conventional camera, the light-field camera contains micro-lens arrays in front of the image sensor, which makes the camera small enough to fit into a smart phone, while allowing it to acquire the spatial and directional information of the light with a single shot. The technique has received attention as it can reconstruct images in a variety of ways including multi-views, refocusing, and 3D image acquisition, giving rise to many potential applications.
However, the optical crosstalk between shadows caused by external light sources in the environment and the micro-lens has limited existing light-field cameras from being able to provide accurate image contrast and 3D reconstruction.
The joint research team applied a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) in the near-IR range to stabilize the accuracy of 3D image reconstruction that previously depended on environmental light. When an external light source is shone on a face at 0-, 30-, and 60-degree angles, the light field camera reduces 54% of image reconstruction errors. Additionally, by inserting a light-absorbing layer for visible and near-IR wavelengths between the micro-lens arrays, the team could minimize optical crosstalk while increasing the image contrast by 2.1 times.
Through this technique, the team could overcome the limitations of existing light-field cameras and was able to develop their NIR-based light-field camera (NIR-LFC), optimized for the 3D image reconstruction of facial expressions. Using the NIR-LFC, the team acquired high-quality 3D reconstruction images of facial expressions expressing various emotions regardless of the lighting conditions of the surrounding environment.
The facial expressions in the acquired 3D images were distinguished through machine learning with an average of 85% accuracy – a statistically significant figure compared to when 2D images were used. Furthermore, by calculating the interdependency of distance information that varies with facial expression in 3D images, the team could identify the information a light-field camera utilizes to distinguish human expressions.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong said, “The sub-miniature light-field camera developed by the research team has the potential to become the new platform to quantitatively analyze the facial expressions and emotions of humans.” To highlight the significance of this research, he added, “It could be applied in various fields including mobile healthcare, field diagnosis, social cognition, and human-machine interactions.”
This research was published in Advanced Intelligent Systems online on December 16, under the title, “Machine-Learned Light-field Camera that Reads Facial Expression from High-Contrast and Illumination Invariant 3D Facial Images.” This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
-Publication“Machine-learned light-field camera that reads fascial expression from high-contrast and illumination invariant 3D facial images,” Sang-In Bae, Sangyeon Lee, Jae-Myeong Kwon, Hyun-Kyung Kim. Kyung-Won Jang, Doheon Lee, Ki-Hun Jeong, Advanced Intelligent Systems, December 16, 2021 (doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202100182)
ProfileProfessor Ki-Hun JeongBiophotonic LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Doheon LeeDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2022.01.21 View 13958