Campus/People
-
 'In KAIST, Administration Should Be Done Scientifically Too'
A university community is comprised of three actors; student, faculty, and staff members. Among them, in many cases, the staff remain the hidden group, always working behind the spotlight. However, the final pieces of the puzzle always go through the hands of staff members who facilitate students’ and faculty members’ studies and research.
The Office of Administration recently published two books: “In KAIST, Administration Should Be Done Scientifically Too,” and “A Life of Staff Called K.” The books describe ways to propel administrative innovation and organizational changes, seeking to increase the value of staff members’ working scope and their professionalism. These are the result of the 43-member Administration Advancement Committee’s year-long research to improve institutional efficiency. The 43 staff members voluntarily participated in the publication.
The books cite “the independent and self-motivating administration" as an ideal environment to make professional staff members. And the institution is responsible for creating such an inspiring environment through innovation.
“This will highlight the guiding role of our 550 staff members, who are at the frontline serving students and faculty. Based on the analysis of these valuable books, we will provide various educational systems and revise current HR system to enhance our staff’s career performance,” says Ki-Han Kim, Associate Vice President of Administration.
According to “In KAIST, Administration Should Be Done Scientifically Too,” 48% of students and faculty expressed negativity regarding the staff members’ performance in the administration offices. Meanwhile about 50% of them expressed satisfaction for the services provided by their department offices. The book analyzed which side current administration system should address more.
The book reports that 55% of staff members also cited professionalism as a priority for their career building. However, 65% of them confessed that they rarely have strong sense of ownership, which leads to passive working performance. Despite such passive attitude, 84% of them showed strong fellowship with their colleagues, a promising signal to the future administrative services and systems.
These books identify four prescriptions for advancing administration services: improving the HR system, building professionalism, establishing smart working systems, and creating an efficient organizational culture.
2019.04.23 View 3040
'In KAIST, Administration Should Be Done Scientifically Too'
A university community is comprised of three actors; student, faculty, and staff members. Among them, in many cases, the staff remain the hidden group, always working behind the spotlight. However, the final pieces of the puzzle always go through the hands of staff members who facilitate students’ and faculty members’ studies and research.
The Office of Administration recently published two books: “In KAIST, Administration Should Be Done Scientifically Too,” and “A Life of Staff Called K.” The books describe ways to propel administrative innovation and organizational changes, seeking to increase the value of staff members’ working scope and their professionalism. These are the result of the 43-member Administration Advancement Committee’s year-long research to improve institutional efficiency. The 43 staff members voluntarily participated in the publication.
The books cite “the independent and self-motivating administration" as an ideal environment to make professional staff members. And the institution is responsible for creating such an inspiring environment through innovation.
“This will highlight the guiding role of our 550 staff members, who are at the frontline serving students and faculty. Based on the analysis of these valuable books, we will provide various educational systems and revise current HR system to enhance our staff’s career performance,” says Ki-Han Kim, Associate Vice President of Administration.
According to “In KAIST, Administration Should Be Done Scientifically Too,” 48% of students and faculty expressed negativity regarding the staff members’ performance in the administration offices. Meanwhile about 50% of them expressed satisfaction for the services provided by their department offices. The book analyzed which side current administration system should address more.
The book reports that 55% of staff members also cited professionalism as a priority for their career building. However, 65% of them confessed that they rarely have strong sense of ownership, which leads to passive working performance. Despite such passive attitude, 84% of them showed strong fellowship with their colleagues, a promising signal to the future administrative services and systems.
These books identify four prescriptions for advancing administration services: improving the HR system, building professionalism, establishing smart working systems, and creating an efficient organizational culture.
2019.04.23 View 3040 -
 Next-Generation Small Satellite Starts Operations
Korea’s next generation small satellite developed by KAIST started its space observation missions after completing its performance checkup, the Ministry of Science and ICT announced on April 16.
The Ministry said that the Next Sat-1, launched on Dec. 4, has successfully deployed its solar panels, adjusted its posture and carried out internal checks to see if all system were functioning normally. The Next Sat-1, expected to be operation for some two years, is the first locally made satellite to have instruments for the Study of Space Storms (ISSS) that can check the impact of solar storms on the magnetic field of the pole areas. It can be further used to detect changes to the Earth's ionosphere in low longitude regions.
The ministry said the satellite's near-infrared imaging spectrometer (NISS) camera will be used to peer into space with one of tasks to determine the brightness of the M95 barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Leo.
KAIST built the large capacity memory and communication equipment with others, like Asia Pacific Satellite Inc., building star tracking sensors, computers and high speed data processors specifically designed for space.
The satellite weighs 100 kg and is in orbit 575 km from the surface of the Earth. “Everything has been checked to be in working order with initial tests utilizing its sensors and camera revealing positive results,” the Ministry said in a statement. (Yonhap News)
(The photos shows details of the Next Sat-1 satellite.)
2019.04.16 View 3168
Next-Generation Small Satellite Starts Operations
Korea’s next generation small satellite developed by KAIST started its space observation missions after completing its performance checkup, the Ministry of Science and ICT announced on April 16.
The Ministry said that the Next Sat-1, launched on Dec. 4, has successfully deployed its solar panels, adjusted its posture and carried out internal checks to see if all system were functioning normally. The Next Sat-1, expected to be operation for some two years, is the first locally made satellite to have instruments for the Study of Space Storms (ISSS) that can check the impact of solar storms on the magnetic field of the pole areas. It can be further used to detect changes to the Earth's ionosphere in low longitude regions.
The ministry said the satellite's near-infrared imaging spectrometer (NISS) camera will be used to peer into space with one of tasks to determine the brightness of the M95 barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Leo.
KAIST built the large capacity memory and communication equipment with others, like Asia Pacific Satellite Inc., building star tracking sensors, computers and high speed data processors specifically designed for space.
The satellite weighs 100 kg and is in orbit 575 km from the surface of the Earth. “Everything has been checked to be in working order with initial tests utilizing its sensors and camera revealing positive results,” the Ministry said in a statement. (Yonhap News)
(The photos shows details of the Next Sat-1 satellite.)
2019.04.16 View 3168 -
 Chair Professor Seong Honored with Don Miller Award
(Professor Poong-Hyun Seong)
Chair Professor Poong-Hyun Seong from the Department of Nuclear & Quantum Engineering was selected as the recipient of the Don Miller Award by the American Nuclear Society.
The award, established in 2009 by the American Nuclear Society in honor of former ANS President Don Miller, is given to an individual or team who has made a significant contribution to the advancement of one or both of the fields of nuclear instrumentation and control of human-machine interfaces through individual or combined activities. The award ceremony will be held on June 10 during the 2019 annual meeting of the ANS in Minneapolis in the US.
Professor Seong is being recognized for his pioneering research and training in the fields of nuclear instrumentation control and human factor engineering at Korea. His research significantly contributed to safety improvements in nuclear power plants and have been recognized worldwide. Professor Seong, a fellow of the ANS, now serves as the first vice chair of the International Nuclear Societies Council and will take up the role of chair in 2021.
Professor Seong said that, “ Korea is one of the most outstanding countries working on research in the fields of nuclear instrumentation control and human factors. KAIST PhDs are teaching at many universities at home and abroad. I look forward this award bringing new hope to our nuclear research and the domestic nuclear industry, which is now in difficult times.”
2019.04.11 View 5690
Chair Professor Seong Honored with Don Miller Award
(Professor Poong-Hyun Seong)
Chair Professor Poong-Hyun Seong from the Department of Nuclear & Quantum Engineering was selected as the recipient of the Don Miller Award by the American Nuclear Society.
The award, established in 2009 by the American Nuclear Society in honor of former ANS President Don Miller, is given to an individual or team who has made a significant contribution to the advancement of one or both of the fields of nuclear instrumentation and control of human-machine interfaces through individual or combined activities. The award ceremony will be held on June 10 during the 2019 annual meeting of the ANS in Minneapolis in the US.
Professor Seong is being recognized for his pioneering research and training in the fields of nuclear instrumentation control and human factor engineering at Korea. His research significantly contributed to safety improvements in nuclear power plants and have been recognized worldwide. Professor Seong, a fellow of the ANS, now serves as the first vice chair of the International Nuclear Societies Council and will take up the role of chair in 2021.
Professor Seong said that, “ Korea is one of the most outstanding countries working on research in the fields of nuclear instrumentation control and human factors. KAIST PhDs are teaching at many universities at home and abroad. I look forward this award bringing new hope to our nuclear research and the domestic nuclear industry, which is now in difficult times.”
2019.04.11 View 5690 -
 KAIST-THE Innovation & Impact Summit Touts New Roles of Higher Education
Global leaders from 115 institutions across 35 countries reaffirmed that the roles of universities are evolving to become much broader and more diverse, and redefined the impact of higher education last week at KAIST. During the THE Innovation and Impact Summit hosted by KAIST in partnership with the Times Higher Education, global leaders in higher education, industry, and government all agreed that universities should respond better in order to have a lasting and sustainable impact on society.
In an effort to encourage social responsibility and boost the impact of universities, the THE first launched the University Impact Rankings based on the Sustainable Developed Goals declared during the 2015 UN summit. The THE’s University Impact Rankings are the first global attempt to evaluate universities’ impact on society, rather than only focusing on research and teaching performance.
The new metrics include universities’ policies and outcomes based on 11 of the 17 UN SDGs. More than 500 institutions from 75 countries submitted data for the new rankings. The top three scores from ten of the SDGs were combined with SDG 17 to calculate the final score. The University of Auckland placed first in this new ranking while KAIST ranked fourth in the category of SDG 9 on Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure.
President Shin said, “KAIST has dedicated itself to producing knowledge that could serve as a growth engine for national development over the past half century. Now, taking on the UN’s 17 SDGs as new indicators, we will do our utmost to become a leading university in creating global value and better serving the world.”
(Phil Baty, chief knowledge officer of THE)
Phil Baty, chief knowledge officer at THE said, “I would like to applaud KAIST for being a pioneer, taking a new way of looking at university excellence. KAIST’s performance was strong overall, but especially outstanding in SDG 9. Its data proves that the university is fully engaged in knowledge creation and entrepreneur activities.”
Keynote speakers all shared their views on disruptive knowledge and how to adjust to the new AI technology-driven, socio-economic culture.
(from left: Lino Guzzella, former ETH Zurich President and Sung-Chul Shin, KAIST President)
Lino Guzzella, former ETH Zurich President, argued in his keynote speech that there has been amazing growth in university enrollments, coupled with a substantial mismatch between what universities teach and what society needs. He went on to say that universities should look beyond the classical university model and find a way to train the next generation in a way that ensures society has a role for them.
“The likelihood of each generation having a higher income at the age of 30 than their parents has diminished dramatically,” he said. He provided data that showed that middle-income professions have been declining, and between 2000 and 2010 the number of very high-skilled jobs and very low-skilled jobs doubled, whereas the number of those in the middle increased far more slowly. He expected that this trend will continue, saying that universities should focus on instilling critical thinking, interdisciplinary studies, and ‘productive failure’ to students in the new era.
He also shared the secret recipe for the reduced youth unemployment statistics in Switzerland. He said that the education system in Switzerland was designed so that only 20 percent of an age cohort undertakes a classical university education, while 80 percent do vocational training run by companies. They learn what is really needed by industry and society from the early stages of their careers, so no mismatch exists.
(Young Suk Chi, chairman of Elsevier)
Meanwhile, Young Suk Chi, chairman of Elsevier, claimed in his keynote speech that universities should stop evaluating researchers only on their publication and citation counts. He said that doing so was driving academics to turn out multiple papers based on a single study in a practice called ‘salami publishing.’ Chi said, “It’s a responsibility we bear together, and we certainly, as industry associates, have to work hard to educate the world that publishing isn’t everything, but the impact is. But the impact is not just citations, either.”
Chi said that there is a global ‘tech-lash’ that has arisen due to falling trust in major IT companies. On the other hand, universities are trustworthy. People perceive that universities are not merely seeking profits, and they can take advantage of it for fostering next generation researchers and CEOs, which can stand for ‘Chief Ethics Officers’.
“Universities are collaborative,” said Chi. Universities’ research will flourish with more collaboration at a global scale. Collaborative research shows higher citation and impact rates. Instead of competing against one another, universities and industries should collaborate for advancing research. He argued further saying, “If they can uphold this reputation, universities, not companies, will be the institutions that people trust to influence and educate the next generation. Universities, in contrast to industry, have long-term vision, can facilitate collaborative research, and are trustworthy.”
(President Joseph Aoun, Northeastern University)
In the last day’s keynote speech, President Joseph Aoun of Northeastern University said that higher education risks becoming obsolete if it does not fully embrace lifelong learning. He also talked about preparing learners to succeed in the AI age.
He said that lifelong learners made up 74 percent of learners in the US, and only 34 percent of universities in the country fill their seats, but higher education has not yet incorporated lifelong learning as part of its core mission. He said that lifelong learning is going to require that we listen to the needs of society, of both individuals and organizations.
He also called for institutions to create curricula based on what he termed ‘humanics’ – the integration of technological literacy, data literacy, and human literacy, and said that this should be combined with experiential learning.
(from left: So Young Kim, Guohua Chen, Aqil Jamal, Mooyoung Jung and Max Lu)
(from left: Hubo and Duncan Ross, chief data officer of THE)
2019.04.09 View 5411
KAIST-THE Innovation & Impact Summit Touts New Roles of Higher Education
Global leaders from 115 institutions across 35 countries reaffirmed that the roles of universities are evolving to become much broader and more diverse, and redefined the impact of higher education last week at KAIST. During the THE Innovation and Impact Summit hosted by KAIST in partnership with the Times Higher Education, global leaders in higher education, industry, and government all agreed that universities should respond better in order to have a lasting and sustainable impact on society.
In an effort to encourage social responsibility and boost the impact of universities, the THE first launched the University Impact Rankings based on the Sustainable Developed Goals declared during the 2015 UN summit. The THE’s University Impact Rankings are the first global attempt to evaluate universities’ impact on society, rather than only focusing on research and teaching performance.
The new metrics include universities’ policies and outcomes based on 11 of the 17 UN SDGs. More than 500 institutions from 75 countries submitted data for the new rankings. The top three scores from ten of the SDGs were combined with SDG 17 to calculate the final score. The University of Auckland placed first in this new ranking while KAIST ranked fourth in the category of SDG 9 on Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure.
President Shin said, “KAIST has dedicated itself to producing knowledge that could serve as a growth engine for national development over the past half century. Now, taking on the UN’s 17 SDGs as new indicators, we will do our utmost to become a leading university in creating global value and better serving the world.”
(Phil Baty, chief knowledge officer of THE)
Phil Baty, chief knowledge officer at THE said, “I would like to applaud KAIST for being a pioneer, taking a new way of looking at university excellence. KAIST’s performance was strong overall, but especially outstanding in SDG 9. Its data proves that the university is fully engaged in knowledge creation and entrepreneur activities.”
Keynote speakers all shared their views on disruptive knowledge and how to adjust to the new AI technology-driven, socio-economic culture.
(from left: Lino Guzzella, former ETH Zurich President and Sung-Chul Shin, KAIST President)
Lino Guzzella, former ETH Zurich President, argued in his keynote speech that there has been amazing growth in university enrollments, coupled with a substantial mismatch between what universities teach and what society needs. He went on to say that universities should look beyond the classical university model and find a way to train the next generation in a way that ensures society has a role for them.
“The likelihood of each generation having a higher income at the age of 30 than their parents has diminished dramatically,” he said. He provided data that showed that middle-income professions have been declining, and between 2000 and 2010 the number of very high-skilled jobs and very low-skilled jobs doubled, whereas the number of those in the middle increased far more slowly. He expected that this trend will continue, saying that universities should focus on instilling critical thinking, interdisciplinary studies, and ‘productive failure’ to students in the new era.
He also shared the secret recipe for the reduced youth unemployment statistics in Switzerland. He said that the education system in Switzerland was designed so that only 20 percent of an age cohort undertakes a classical university education, while 80 percent do vocational training run by companies. They learn what is really needed by industry and society from the early stages of their careers, so no mismatch exists.
(Young Suk Chi, chairman of Elsevier)
Meanwhile, Young Suk Chi, chairman of Elsevier, claimed in his keynote speech that universities should stop evaluating researchers only on their publication and citation counts. He said that doing so was driving academics to turn out multiple papers based on a single study in a practice called ‘salami publishing.’ Chi said, “It’s a responsibility we bear together, and we certainly, as industry associates, have to work hard to educate the world that publishing isn’t everything, but the impact is. But the impact is not just citations, either.”
Chi said that there is a global ‘tech-lash’ that has arisen due to falling trust in major IT companies. On the other hand, universities are trustworthy. People perceive that universities are not merely seeking profits, and they can take advantage of it for fostering next generation researchers and CEOs, which can stand for ‘Chief Ethics Officers’.
“Universities are collaborative,” said Chi. Universities’ research will flourish with more collaboration at a global scale. Collaborative research shows higher citation and impact rates. Instead of competing against one another, universities and industries should collaborate for advancing research. He argued further saying, “If they can uphold this reputation, universities, not companies, will be the institutions that people trust to influence and educate the next generation. Universities, in contrast to industry, have long-term vision, can facilitate collaborative research, and are trustworthy.”
(President Joseph Aoun, Northeastern University)
In the last day’s keynote speech, President Joseph Aoun of Northeastern University said that higher education risks becoming obsolete if it does not fully embrace lifelong learning. He also talked about preparing learners to succeed in the AI age.
He said that lifelong learners made up 74 percent of learners in the US, and only 34 percent of universities in the country fill their seats, but higher education has not yet incorporated lifelong learning as part of its core mission. He said that lifelong learning is going to require that we listen to the needs of society, of both individuals and organizations.
He also called for institutions to create curricula based on what he termed ‘humanics’ – the integration of technological literacy, data literacy, and human literacy, and said that this should be combined with experiential learning.
(from left: So Young Kim, Guohua Chen, Aqil Jamal, Mooyoung Jung and Max Lu)
(from left: Hubo and Duncan Ross, chief data officer of THE)
2019.04.09 View 5411 -
 KAIST-KU Joint Research Center for Smart Healthcare & Transportation
(President Shin shakes hands with KU acting Presidedent Arif Al Hammdi at the KAIST-KU Joint Research Center opening ceremony on April 8.)
KAIST opened the KAIST-Khalifa University Joint Research Center with Khalifa University on April 8. The opening ceremony was held at Khalifa University and was attended by President Sung-Chul Shin and Khalifa University Acting President Arif Al Hammadi.
The new research center reflects the evolution of the long-established partnership between the two institutions. The two universities have already made very close collaborations in research and education in the fields of nuclear and quantum engineering.
The launch of this center expanded their fields of collaboration to smart healthcare and smart transportation, key emerging sectors in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. President Shin signed an MOU with the UAE Minister of State for Advanced Science Sarah Amiri and Khalifa University to expand mutual collaboration in technology development and fostering human capital last year.
The center will conduct research and education on autonomous vehicles, infrastructure for autonomous vehicle operation, wireless charging for electric vehicles, and infrastructure for electric autonomous vehicles. As for smart healthcare, the center will focus on healthcare robotics as well as sensors and wearable devices for personal healthcare services.
President Shin, who accompanied a research team from the Graduate School of Green Transportation, said, “We are very delighted to enter into this expanded collaboration with KU. This partnership justifies our long-standing collaboration in the areas of emerging technologies in the Fourth Industrial Revolution while fostering human capital.”
KU Acting President Arif Al Hammadi added, “The outcome of these research projects will establish the status of both institutions as champions of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, bringing benefits to our communities. We believe the new research center will further consolidate our status as a globally active, research-intensive academic institution, developing international collaborations that benefit the community in general.”
2019.04.09 View 8700
KAIST-KU Joint Research Center for Smart Healthcare & Transportation
(President Shin shakes hands with KU acting Presidedent Arif Al Hammdi at the KAIST-KU Joint Research Center opening ceremony on April 8.)
KAIST opened the KAIST-Khalifa University Joint Research Center with Khalifa University on April 8. The opening ceremony was held at Khalifa University and was attended by President Sung-Chul Shin and Khalifa University Acting President Arif Al Hammadi.
The new research center reflects the evolution of the long-established partnership between the two institutions. The two universities have already made very close collaborations in research and education in the fields of nuclear and quantum engineering.
The launch of this center expanded their fields of collaboration to smart healthcare and smart transportation, key emerging sectors in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. President Shin signed an MOU with the UAE Minister of State for Advanced Science Sarah Amiri and Khalifa University to expand mutual collaboration in technology development and fostering human capital last year.
The center will conduct research and education on autonomous vehicles, infrastructure for autonomous vehicle operation, wireless charging for electric vehicles, and infrastructure for electric autonomous vehicles. As for smart healthcare, the center will focus on healthcare robotics as well as sensors and wearable devices for personal healthcare services.
President Shin, who accompanied a research team from the Graduate School of Green Transportation, said, “We are very delighted to enter into this expanded collaboration with KU. This partnership justifies our long-standing collaboration in the areas of emerging technologies in the Fourth Industrial Revolution while fostering human capital.”
KU Acting President Arif Al Hammadi added, “The outcome of these research projects will establish the status of both institutions as champions of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, bringing benefits to our communities. We believe the new research center will further consolidate our status as a globally active, research-intensive academic institution, developing international collaborations that benefit the community in general.”
2019.04.09 View 8700 -
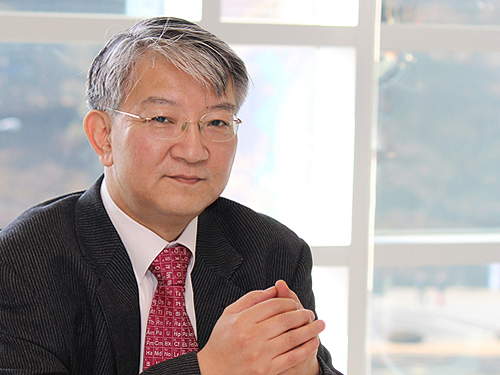 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Honored with the 23rd NAEK Award
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was honored to be the laureate of the 23rd NAEK Award.
The NAEK (National Academy of Engineering of Korea) Award was instituted in 1997 to honor and recognize engineers who have made significant contributions to the development of the engineering and technology field at universities, industries, and institutions. Every year, it is conferred to only one person who has achieved original and world-leading research that has led to national development.
Distinguished Professor Lee is a pioneering scholar of the field of systems metabolic engineering and he was recognized for his significant achievements in the biochemical industry by developing novel microbial bioprocesses. In particular, he is globally renowned for biological plastic synthesis, making or decomposing polymers with microorganisms instead of using fossil resources.
He has produced numerous high-quality research breakthroughs in metabolic and systems engineering. In 2016, he produced an easily degradable plastic with Escherichia coli (E. coli). In 2018, he successfully produced aromatic polyesters, the main material for PET (poly ethylene terephthalate) from E. coli strains. He also identified microorganism structures for PET degradation and improved its degradability with a novel variant.
His research was ranked number one in the research and development division of Top Ten Science and Technology News 2018 announced by Korean Federation of Science & Technology Societies. He is one of highly cited researchers (HCR) ranked in the top 1% by citations for their field by the Clarivate Analytics.
2019.03.21 View 9001
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Honored with the 23rd NAEK Award
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was honored to be the laureate of the 23rd NAEK Award.
The NAEK (National Academy of Engineering of Korea) Award was instituted in 1997 to honor and recognize engineers who have made significant contributions to the development of the engineering and technology field at universities, industries, and institutions. Every year, it is conferred to only one person who has achieved original and world-leading research that has led to national development.
Distinguished Professor Lee is a pioneering scholar of the field of systems metabolic engineering and he was recognized for his significant achievements in the biochemical industry by developing novel microbial bioprocesses. In particular, he is globally renowned for biological plastic synthesis, making or decomposing polymers with microorganisms instead of using fossil resources.
He has produced numerous high-quality research breakthroughs in metabolic and systems engineering. In 2016, he produced an easily degradable plastic with Escherichia coli (E. coli). In 2018, he successfully produced aromatic polyesters, the main material for PET (poly ethylene terephthalate) from E. coli strains. He also identified microorganism structures for PET degradation and improved its degradability with a novel variant.
His research was ranked number one in the research and development division of Top Ten Science and Technology News 2018 announced by Korean Federation of Science & Technology Societies. He is one of highly cited researchers (HCR) ranked in the top 1% by citations for their field by the Clarivate Analytics.
2019.03.21 View 9001 -
 The Future Mobility of the Year 2019
KAIST announced the Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) 2019. The winners are Volvo 360C, Toyota e-Palette, and Toyota Concept-i WALK.
FMOTY are the first awards that recognizes concept cars that exhibit innovative services and practical transportation technology in three categories: private mobility, public and commercial mobility, and personal mobility.
Figure 1. The winner in the private mobility division, the Volvo 360C
In the private mobility division, the award went to the Volvo 360C. With targeted routes of roughly 186 miles, this vehicle has an ambitious service goal to replace airplanes by traveling these routes with great comfort. Goro Okazaki, a journalist with Car and Driver Japan, said, “The Volvo 360C clearly shows how highly personalized autonomous driving can change the future.”
Figure 2. The winner in the public mobility division, the Toyota e-Palette
The Toyota e-Palette was the winning car in commercial mobility division. This vehicle provides the best solution as a mobile service platform by transforming itself into mobile hospitals, hotels, stores and food trucks. Carlo Calderón, a journalist for Autopista Spain, said, “It has a great strength in remodeling its indoor and outdoor spaces according to various commercial uses.”
Figure 3. The winner in the personal mobility division, the Toyota Concept-i WALK
In the personal mobility division, the award went to the Toyota Concept-i WALK. It was recognized for having an exquisite user environment and artificial intelligent agent, along with an excellent completion. Jun Miao, a journalist with MJ CarShow China, said, “It is aesthetically pleasing. Beyond the upright control of conventional personal mobility, it allows agile control with a joystick.”
FMOTY conducted a screening process for 45 concept cars over three months and 16 renowned automotive experts from 11 countries participated as judges for this award, including Editor in Chief of BBC Top Gear Magazine Charlie Turner and European Bureau Chief of Automobile Magazine Georg Kacher. The judges said that FMOTY was born to propose a new aspect of future mobility, and in terms of evaluating technical and social values of concept cars, FMOTY carries great significance.
Kyung-soo Kim, Dean of the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation said, “Globally renowned experts in the automotive field participated as judges to elevate the prestige and fairness of the awards. KAIST members were excluded from the entire judging process. I believe that the FMOTY Awards will expand public attention from the present to the future.”
Details can be found on the official website of FMOTY ( www.fmoty.org ).
2019.03.11 View 7486
The Future Mobility of the Year 2019
KAIST announced the Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) 2019. The winners are Volvo 360C, Toyota e-Palette, and Toyota Concept-i WALK.
FMOTY are the first awards that recognizes concept cars that exhibit innovative services and practical transportation technology in three categories: private mobility, public and commercial mobility, and personal mobility.
Figure 1. The winner in the private mobility division, the Volvo 360C
In the private mobility division, the award went to the Volvo 360C. With targeted routes of roughly 186 miles, this vehicle has an ambitious service goal to replace airplanes by traveling these routes with great comfort. Goro Okazaki, a journalist with Car and Driver Japan, said, “The Volvo 360C clearly shows how highly personalized autonomous driving can change the future.”
Figure 2. The winner in the public mobility division, the Toyota e-Palette
The Toyota e-Palette was the winning car in commercial mobility division. This vehicle provides the best solution as a mobile service platform by transforming itself into mobile hospitals, hotels, stores and food trucks. Carlo Calderón, a journalist for Autopista Spain, said, “It has a great strength in remodeling its indoor and outdoor spaces according to various commercial uses.”
Figure 3. The winner in the personal mobility division, the Toyota Concept-i WALK
In the personal mobility division, the award went to the Toyota Concept-i WALK. It was recognized for having an exquisite user environment and artificial intelligent agent, along with an excellent completion. Jun Miao, a journalist with MJ CarShow China, said, “It is aesthetically pleasing. Beyond the upright control of conventional personal mobility, it allows agile control with a joystick.”
FMOTY conducted a screening process for 45 concept cars over three months and 16 renowned automotive experts from 11 countries participated as judges for this award, including Editor in Chief of BBC Top Gear Magazine Charlie Turner and European Bureau Chief of Automobile Magazine Georg Kacher. The judges said that FMOTY was born to propose a new aspect of future mobility, and in terms of evaluating technical and social values of concept cars, FMOTY carries great significance.
Kyung-soo Kim, Dean of the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation said, “Globally renowned experts in the automotive field participated as judges to elevate the prestige and fairness of the awards. KAIST members were excluded from the entire judging process. I believe that the FMOTY Awards will expand public attention from the present to the future.”
Details can be found on the official website of FMOTY ( www.fmoty.org ).
2019.03.11 View 7486 -
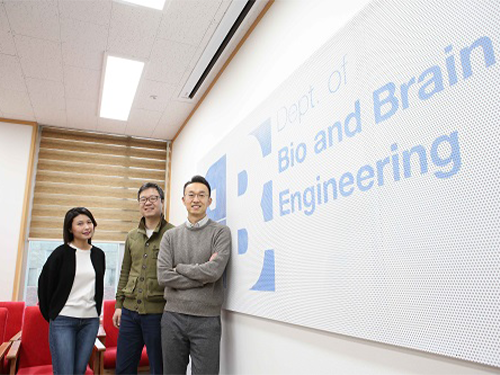 Brain-inspired Artificial Intelligence in Robots
(from left: PhD candidate Su Jin An, Dr. Jee Hang Lee and Professor Sang Wan Lee)
Research groups in KAIST, the University of Cambridge, Japan’s National Institute for Information and Communications Technology, and Google DeepMind argue that our understanding of how humans make intelligent decisions has now reached a critical point in which robot intelligence can be significantly enhanced by mimicking strategies that the human brain uses when we make decisions in our everyday lives.
In our rapidly changing world, both humans and autonomous robots constantly need to learn and adapt to new environments. But the difference is that humans are capable of making decisions according to the unique situations, whereas robots still rely on predetermined data to make decisions.
Despite the rapid progress being made in strengthening the physical capability of robots, their central control systems, which govern how robots decide what to do at any one time, are still inferior to those of humans. In particular, they often rely on pre-programmed instructions to direct their behavior, and lack the hallmark of human behavior, that is, the flexibility and capacity to quickly learn and adapt.
Applying neuroscience in robotics, Professor Sang Wan Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST and Professor Ben Seymour from the University of Cambridge and Japan’s National Institute for Information and Communications Technology proposed a case in which robots should be designed based on the principles of the human brain. They argue that robot intelligence can be significantly enhanced by mimicking strategies that the human brain uses during decision-making processes in everyday life.
The problem with importing human-like intelligence into robots has always been a difficult task without knowing the computational principles for how the human brain makes decisions –in other words, how to translate brain activity into computer code for the robots’ ‘brains’.
However, researchers now argue that, following a series of recent discoveries in the field of computational neuroscience, there is enough of this code to effectively write it into robots. One of the examples discovered is the human brain’s ‘meta-controller’, a mechanism by which the brain decides how to switch between different subsystems to carry out complex tasks. Another example is the human pain system, which allows them to protect themselves in potentially hazardous environments. “Copying the brain’s code for these could greatly enhance the flexibility, efficiency, and safety of robots,” Professor Lee said.
The team argued that this inter-disciplinary approach will provide just as many benefits to neuroscience as to robotics. The recent explosion of interest in what lies behind psychiatric disorders such as anxiety, depression, and addiction has given rise to a set of sophisticated theories that are complex and difficult to test without some sort of advanced situation platform.
Professor Seymour explained, “We need a way of modelling the human brain to find how it interacts with the world in real-life to test whether and how different abnormalities in these models give rise to certain disorders. For instance, if we could reproduce anxiety behavior or obsessive-compulsive disorder in a robot, we could then predict what we need to do to treat it in humans.”
The team expects that producing robot models of different psychiatric disorders, in a similar way to how researchers use animal models now, will become a key future technology in clinical research.
The team also stated that there may also be other benefits to humans and intelligent robots learning, acting, and behaving in the same way. In future societies in which humans and robots live and work amongst each other, the ability to cooperate and empathize with robots might be much greater if we feel they think like us.
Professor Seymour said, “We might think that having robots with the human traits of being a bit impulsive or overcautious would be a detriment, but these traits are an unavoidable by-product of human-like intelligence. And it turns out that this is helping us to understand human behavior as human.”
The framework for achieving this brain-inspired artificial intelligence was published in two journals, Science Robotics (10.1126/scirobotics.aav2975) on January 16 and Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences (10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.12.012) on February 6, 2019.
Figure 1. Overview of neuroscience - robotics approach for decision-making. The figure details key areas for interdisciplinary study (Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences)
Figure 2. Brain-inspired solutions to robot learning. Neuroscientific views on various aspects of learning and cognition converge and create a new idea called prefrontal metacontrol, which can inspire researchers to design learning agents that can address various key challenges in robotics such as performance-efficiency-speed, cooperation-competition, and exploration-exploitation trade-offs (Science Robotics)
2019.02.20 View 6359
Brain-inspired Artificial Intelligence in Robots
(from left: PhD candidate Su Jin An, Dr. Jee Hang Lee and Professor Sang Wan Lee)
Research groups in KAIST, the University of Cambridge, Japan’s National Institute for Information and Communications Technology, and Google DeepMind argue that our understanding of how humans make intelligent decisions has now reached a critical point in which robot intelligence can be significantly enhanced by mimicking strategies that the human brain uses when we make decisions in our everyday lives.
In our rapidly changing world, both humans and autonomous robots constantly need to learn and adapt to new environments. But the difference is that humans are capable of making decisions according to the unique situations, whereas robots still rely on predetermined data to make decisions.
Despite the rapid progress being made in strengthening the physical capability of robots, their central control systems, which govern how robots decide what to do at any one time, are still inferior to those of humans. In particular, they often rely on pre-programmed instructions to direct their behavior, and lack the hallmark of human behavior, that is, the flexibility and capacity to quickly learn and adapt.
Applying neuroscience in robotics, Professor Sang Wan Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST and Professor Ben Seymour from the University of Cambridge and Japan’s National Institute for Information and Communications Technology proposed a case in which robots should be designed based on the principles of the human brain. They argue that robot intelligence can be significantly enhanced by mimicking strategies that the human brain uses during decision-making processes in everyday life.
The problem with importing human-like intelligence into robots has always been a difficult task without knowing the computational principles for how the human brain makes decisions –in other words, how to translate brain activity into computer code for the robots’ ‘brains’.
However, researchers now argue that, following a series of recent discoveries in the field of computational neuroscience, there is enough of this code to effectively write it into robots. One of the examples discovered is the human brain’s ‘meta-controller’, a mechanism by which the brain decides how to switch between different subsystems to carry out complex tasks. Another example is the human pain system, which allows them to protect themselves in potentially hazardous environments. “Copying the brain’s code for these could greatly enhance the flexibility, efficiency, and safety of robots,” Professor Lee said.
The team argued that this inter-disciplinary approach will provide just as many benefits to neuroscience as to robotics. The recent explosion of interest in what lies behind psychiatric disorders such as anxiety, depression, and addiction has given rise to a set of sophisticated theories that are complex and difficult to test without some sort of advanced situation platform.
Professor Seymour explained, “We need a way of modelling the human brain to find how it interacts with the world in real-life to test whether and how different abnormalities in these models give rise to certain disorders. For instance, if we could reproduce anxiety behavior or obsessive-compulsive disorder in a robot, we could then predict what we need to do to treat it in humans.”
The team expects that producing robot models of different psychiatric disorders, in a similar way to how researchers use animal models now, will become a key future technology in clinical research.
The team also stated that there may also be other benefits to humans and intelligent robots learning, acting, and behaving in the same way. In future societies in which humans and robots live and work amongst each other, the ability to cooperate and empathize with robots might be much greater if we feel they think like us.
Professor Seymour said, “We might think that having robots with the human traits of being a bit impulsive or overcautious would be a detriment, but these traits are an unavoidable by-product of human-like intelligence. And it turns out that this is helping us to understand human behavior as human.”
The framework for achieving this brain-inspired artificial intelligence was published in two journals, Science Robotics (10.1126/scirobotics.aav2975) on January 16 and Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences (10.1016/j.cobeha.2018.12.012) on February 6, 2019.
Figure 1. Overview of neuroscience - robotics approach for decision-making. The figure details key areas for interdisciplinary study (Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences)
Figure 2. Brain-inspired solutions to robot learning. Neuroscientific views on various aspects of learning and cognition converge and create a new idea called prefrontal metacontrol, which can inspire researchers to design learning agents that can address various key challenges in robotics such as performance-efficiency-speed, cooperation-competition, and exploration-exploitation trade-offs (Science Robotics)
2019.02.20 View 6359 -
 Kimchi Toolkit by Costa Rican Summa Cum Laude Helps Make the Best Flavor
(Maria Jose Reyes Castro with her kimchi toolkit application)
Every graduate feels a special attachment to their school, but for Maria Jose Reyes Castro who graduated summa cum laude in the Department of Industrial Design this year, KAIST will be remembered for more than just academics. She appreciates KAIST for not only giving her great professional opportunities, but also helping her find the love of her life.
During her master’s course, she completed an electronic kimchi toolkit, which optimizes kimchi’s flavor. Her kit uses a mobile application and smart sensor to find the fermentation level of kimchi by measuring its pH level, which is closely related to its fermentation. A user can set a desired fermentation level or salinity on the mobile application, and it provides the best date to serve it.
Under the guidance of Professor Daniel Saakes, she conducted research on developing a kimchi toolkit for beginners (Qualified Kimchi: Improving the experience of inexperienced kimchi makers by developing a monitoring toolkit for kimchi).
“I’ve seen many foreigners saying it’s quite difficult to make kimchi. So I chose to study kimchi to help people, especially those who are first-experienced making kimchi more easily,” she said. She got recipes from YouTube and studied fermentation through academic journals. She also asked kimchi experts to have a more profound understanding of it.
Extending her studies, she now works for a startup specializing in smart farms after starting last month. She conducts research on biology and applies it to designs that can be used practically in daily life.
Her tie with KAIST goes back to 2011 when she attended an international science camp in Germany. She met Sunghan Ro (’19 PhD in Nanoscience and Technology), a student from KAIST and now her husband. He recommended for her to enroll at KAIST because the school offers an outstanding education and research infrastructure along with support for foreign students.
At that time, Castro had just begun her first semester in electrical engineering at the University of Costa Rica, but she decided to apply to KAIST and seek a better opportunity in a new environment. One year later, she began her fresh start at KAIST in the fall semester of 2012.
Instead of choosing her original major, electrical engineering, she decided to pursue her studies in the Department of Industrial Design, because it is an interdisciplinary field where students get to study design while learning business models and making prototypes.
She said, “I felt encouraged by my professors and colleagues in my department to be creative and follow my passion. I never regret entering this major.”
When Castro was pursuing her master’s program in the same department, she became interested in interaction designs with food and biological designs by Professor Saakes, who is her advisor specializing in these areas.
After years of following her passion in design, she now graduates with academic honors in her department.
It is a bittersweet moment to close her journey at KAIST, but “I want to thank KAIST for the opportunity to change my life for the better. I also thank my parents for being supportive and encouraging me. I really appreciate the professors from the Department of Industrial Design who guided and shaped who I am,” she said.
Figure 1. The concept of the kimchi toolkit
Figure 2. The scenario of the kimchi toolkit
2019.02.19 View 5906
Kimchi Toolkit by Costa Rican Summa Cum Laude Helps Make the Best Flavor
(Maria Jose Reyes Castro with her kimchi toolkit application)
Every graduate feels a special attachment to their school, but for Maria Jose Reyes Castro who graduated summa cum laude in the Department of Industrial Design this year, KAIST will be remembered for more than just academics. She appreciates KAIST for not only giving her great professional opportunities, but also helping her find the love of her life.
During her master’s course, she completed an electronic kimchi toolkit, which optimizes kimchi’s flavor. Her kit uses a mobile application and smart sensor to find the fermentation level of kimchi by measuring its pH level, which is closely related to its fermentation. A user can set a desired fermentation level or salinity on the mobile application, and it provides the best date to serve it.
Under the guidance of Professor Daniel Saakes, she conducted research on developing a kimchi toolkit for beginners (Qualified Kimchi: Improving the experience of inexperienced kimchi makers by developing a monitoring toolkit for kimchi).
“I’ve seen many foreigners saying it’s quite difficult to make kimchi. So I chose to study kimchi to help people, especially those who are first-experienced making kimchi more easily,” she said. She got recipes from YouTube and studied fermentation through academic journals. She also asked kimchi experts to have a more profound understanding of it.
Extending her studies, she now works for a startup specializing in smart farms after starting last month. She conducts research on biology and applies it to designs that can be used practically in daily life.
Her tie with KAIST goes back to 2011 when she attended an international science camp in Germany. She met Sunghan Ro (’19 PhD in Nanoscience and Technology), a student from KAIST and now her husband. He recommended for her to enroll at KAIST because the school offers an outstanding education and research infrastructure along with support for foreign students.
At that time, Castro had just begun her first semester in electrical engineering at the University of Costa Rica, but she decided to apply to KAIST and seek a better opportunity in a new environment. One year later, she began her fresh start at KAIST in the fall semester of 2012.
Instead of choosing her original major, electrical engineering, she decided to pursue her studies in the Department of Industrial Design, because it is an interdisciplinary field where students get to study design while learning business models and making prototypes.
She said, “I felt encouraged by my professors and colleagues in my department to be creative and follow my passion. I never regret entering this major.”
When Castro was pursuing her master’s program in the same department, she became interested in interaction designs with food and biological designs by Professor Saakes, who is her advisor specializing in these areas.
After years of following her passion in design, she now graduates with academic honors in her department.
It is a bittersweet moment to close her journey at KAIST, but “I want to thank KAIST for the opportunity to change my life for the better. I also thank my parents for being supportive and encouraging me. I really appreciate the professors from the Department of Industrial Design who guided and shaped who I am,” she said.
Figure 1. The concept of the kimchi toolkit
Figure 2. The scenario of the kimchi toolkit
2019.02.19 View 5906 -
 KAIST 2019 Commencement at a Glance
(KAIST 2019 Commencement Ceremony)
This year, KAIST awarded a total of 2,705 degrees: 654 PhD degrees, 1,255 master’s degrees, and 796 bachelor’s degrees. Including this year’s numbers, KAIST has conferred a total of 63,830 degrees since its foundation in 1971.
Parents, family, and friends came to campus to congratulate the graduates with big smiles and hugs. Faculty and staff members also attended the ceremony to celebrate their graduation. This year, distinguished guests including National Assembly Member Kyung-Jin Kim and Vice Minister for Science, Technology and Innovation Dae-sik came to celebrate the day with the KAIST community.
During the commencement, KAIST also announced the recipients of its undergraduate academic awards. The Minister of Science and ICT Award was won by Do-Yoon Kim from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, the KAIST Board of Trustee Chairperson Award went to Se-rin Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, the KAIST Presidential Award was won by Hee-Ju Kim from the Department of Physics, the KAIST Alumni Association President Award went to Hyeon-Seong Park from the School of Electrical Engineering, and finally the KAIST Development Foundation Chairperson Award was won by Gyeong-Hoon Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences.
This year’s valedictorian Eun-Seok Jeong from the School of Computing said, “I believe that we are able to stand here today because we challenged ourselves to confront our shortcomings and our uncertainty. If we continue to develop, we will become a better person than we were yesterday.”
(KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and Woo-Seok Jeong, '19 PhD in Aerospace Engineering)
As a KAIST alumnus and fellow scientist, President Sung-Chul Shin offered his congratulations and emphasized that graduates should continue to pursue the C³ spirit. “In this age of great transformation, embrace challenges and exercise creativity as you have learnt through your education and research at KAIST. And keep in mind the importance of caring for others. Please remember that challenge and creativity will have more meaning if rendered with a caring spirit,” he said.
2019.02.15 View 11024
KAIST 2019 Commencement at a Glance
(KAIST 2019 Commencement Ceremony)
This year, KAIST awarded a total of 2,705 degrees: 654 PhD degrees, 1,255 master’s degrees, and 796 bachelor’s degrees. Including this year’s numbers, KAIST has conferred a total of 63,830 degrees since its foundation in 1971.
Parents, family, and friends came to campus to congratulate the graduates with big smiles and hugs. Faculty and staff members also attended the ceremony to celebrate their graduation. This year, distinguished guests including National Assembly Member Kyung-Jin Kim and Vice Minister for Science, Technology and Innovation Dae-sik came to celebrate the day with the KAIST community.
During the commencement, KAIST also announced the recipients of its undergraduate academic awards. The Minister of Science and ICT Award was won by Do-Yoon Kim from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, the KAIST Board of Trustee Chairperson Award went to Se-rin Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, the KAIST Presidential Award was won by Hee-Ju Kim from the Department of Physics, the KAIST Alumni Association President Award went to Hyeon-Seong Park from the School of Electrical Engineering, and finally the KAIST Development Foundation Chairperson Award was won by Gyeong-Hoon Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences.
This year’s valedictorian Eun-Seok Jeong from the School of Computing said, “I believe that we are able to stand here today because we challenged ourselves to confront our shortcomings and our uncertainty. If we continue to develop, we will become a better person than we were yesterday.”
(KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and Woo-Seok Jeong, '19 PhD in Aerospace Engineering)
As a KAIST alumnus and fellow scientist, President Sung-Chul Shin offered his congratulations and emphasized that graduates should continue to pursue the C³ spirit. “In this age of great transformation, embrace challenges and exercise creativity as you have learnt through your education and research at KAIST. And keep in mind the importance of caring for others. Please remember that challenge and creativity will have more meaning if rendered with a caring spirit,” he said.
2019.02.15 View 11024 -
 The First Award for Concept Cars, Future Mobility of the Year
KAIST will host an award to recognize the most visionary and inspiring concept cars of the year.
The ‘Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY)’ Awards recognize concept cars that have made outstanding contributions to future mobility. The first awards ceremony will take place in Korea in March 2019.
The awards will be given to concept cars that exhibit innovative services and practical transportation technology in three categories: private mobility, public and commercial mobility, and personal mobility.
To ensure a fair judging process, the contest invited influential and eminent journalists in the automotive field. They will evaluate the social values and innovative contributions of the concept cars that will pave the way for next-generation transportation.
Concept cars have been neglected in existing automobile awards, such as the ‘Car of the Year’ because they have been considered experimental prototypes only built for showcasing a new vision for the quite far future.
The FMOTY Awards will brings concept cars back into the spotlight and showcase the best ideas and social values of mind-blowing concept cars.
Among 45 concept cars, fifteen candidates were selected as finalists after the initial screening that took place over the last three months: including models from Audi, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Peugeot, Porsche, Renault, Toyota, Volkswagen, and Volvo. The winners will be announced and awarded in Seoul on March 28th.
Kyung-soo Kim, Dean of the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation which organizes the award said, “As the automobile industry undergoes an era of transformation, it is crucial to recognize the efforts of automobile companies who are making attempts to create novel forms of mobility. That is why we launched the FMOTY Awards, hoping to add a future-oriented spirit to the existing awards that consider finished vehicles only. By selecting the best concept car, the FMOTY Awards will expand public attention from the present to the future.”
Details can be found on the official website of FMOTY ( www.fmoty.org), where photos of the finalists are also available for download ( http://bitly.kr/JTUUp).
Figure 1. Finalists for the 'Future Mobility of the Year'
2019.02.13 View 8002
The First Award for Concept Cars, Future Mobility of the Year
KAIST will host an award to recognize the most visionary and inspiring concept cars of the year.
The ‘Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY)’ Awards recognize concept cars that have made outstanding contributions to future mobility. The first awards ceremony will take place in Korea in March 2019.
The awards will be given to concept cars that exhibit innovative services and practical transportation technology in three categories: private mobility, public and commercial mobility, and personal mobility.
To ensure a fair judging process, the contest invited influential and eminent journalists in the automotive field. They will evaluate the social values and innovative contributions of the concept cars that will pave the way for next-generation transportation.
Concept cars have been neglected in existing automobile awards, such as the ‘Car of the Year’ because they have been considered experimental prototypes only built for showcasing a new vision for the quite far future.
The FMOTY Awards will brings concept cars back into the spotlight and showcase the best ideas and social values of mind-blowing concept cars.
Among 45 concept cars, fifteen candidates were selected as finalists after the initial screening that took place over the last three months: including models from Audi, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Peugeot, Porsche, Renault, Toyota, Volkswagen, and Volvo. The winners will be announced and awarded in Seoul on March 28th.
Kyung-soo Kim, Dean of the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation which organizes the award said, “As the automobile industry undergoes an era of transformation, it is crucial to recognize the efforts of automobile companies who are making attempts to create novel forms of mobility. That is why we launched the FMOTY Awards, hoping to add a future-oriented spirit to the existing awards that consider finished vehicles only. By selecting the best concept car, the FMOTY Awards will expand public attention from the present to the future.”
Details can be found on the official website of FMOTY ( www.fmoty.org), where photos of the finalists are also available for download ( http://bitly.kr/JTUUp).
Figure 1. Finalists for the 'Future Mobility of the Year'
2019.02.13 View 8002 -
 Kenya-KAIST Kicks off with a 95-Million USD Funding from the Korean Government
KAIST, founded through a six-million USD loan from USAID in 1971, to provide turnkey-based education consultancy for Kenya’s first advanced science and technology institute.
KAIST and the Konza Technopolis Development Authority (KoTDA) announced the official establishment of Kenya-KAIST by 2021 during a kickoff ceremony on February 12 in Kenya. The KAIST delegation headed by President Sung-Chul Shin and Kenyan cabinet members and dignitaries including Minister of Education Amina Mohamed, the Chairman of the KoTDA Reuben Mutiso, and the CEO of KoTDA John Tanui attended the ceremony.
With this kickoff held at Konza Technopolis Malili, KAIST, the first and top science and technology university in Korea, will participate in Kenya’s strategic economic development plan with the provision of a turnkey-based science and technology education consultancy for the establishment of Kenya’s first advanced institute of science and technology. KAIST, which won preferred bidder status in consortium with Samwoo and Sunjin architecture and engineering companies, signed the contract with the KoTDA last November.
Korea Eximbank will offer a 95-million USD economic development cooperation fund loan to the Kenyan government. The campus will be constructed in the Konza Techno City located near Nairobi by 2021, with the first batch of 200 graduate students starting classes in 2022.
KAIST will develop academic curricula for six initial departments (Mechanical Engineering, Electrical/Electronic Engineering, ICT Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Civil Engineering, and Agricultural Biotechnology), which will lay the groundwork for engineering research and education in Kenya to meet emerging socioeconomic demands. In addition, KAIST will provide education in the basic science areas of math, physics, chemistry, and biology for students.
The Kenyan government plans to transform Kenya into a middle-income country under Vision 2030 through the promotion of science, technology, and innovation for national economic growth. Nicknamed Africa’s Silicon Savannah, Konza Techno City is a strategic science and technology hub constructed to realize this vision. To this end, the medium-term plan set a goal to provide specialized research and training in various cutting-edge engineering and advanced science fields.
It is also notable that the Kenyan government asked to develop an industry-academy cooperation program in the Konza Techno City. This reflects the high expectations for Kenya-KAIST and its role as a growth engine in the center of the Konza Technopolis. It is anticipated that the technopolis will create 16,675 jobs in the medium term and over 200,000 upon completion, positioning Kenya as an ICT hub within the region.
Saying that the partnership through Kenya-KAIST will bring a new future to Kenya as well as KAIST at the ceremony, President Shin reflected that the project will be a significant milestone for KAIST’s history and global competitiveness. He added, “With this Kenya project, we come to share the past, present, and future of KAIST. And I am very pleased to celebrate our shared vision: the empowerment of science, technology, and education.”
In particular, President Shin was accompanied by Dr. Kun-Mo Chung, a founding provost who served as the Minister of Science and Technology in Korea twice. He now serves as an advisor to Kenyan President Uhuru Kenyatta.
Dr. Chung had played a crucial role in securing a six-million USD loan from US AID to the Korean government to establish KAIST in 1971. He proposed the idea to establish an advanced science and technology institute in Korea to Dr. John Hannah, then the director of US AID.
The seed that was sowed five decades ago in Korea by Dr. Chung has now fully bloomed in Kenya. In only a half century, KAIST has become a donor institution that passes on science and technology education systems including the construction of campuses to developing countries.
KAIST has been acclaimed as US AID’s most successful foreign aid project. A report from the National Academy of Sciences in the US described KAIST as an exemplary case in which a former recipient of international aid has grown to become a science, technology and innovation leader.
The kickoff of Kenya-KAIST drew the attention of both media and local universities in Kenya, attesting to their strong interest to drive economic growth through advanced science and technology.
The University of Nairobi also hosted a special lecture by President Shin, asking him to share the recipe for the success of KAIST in Korea. In a lecture titled “A Crucial Engine for Rapid National Development,” President Shin presented the vision, innovation, and passion of the Korean people that led to the phenomenal results we can see today.
The successful case of KAIST has been benchmarked by many countries for years. For instance, KAIST set up the curriculum for the nuclear engineering program at the Khalifa University of Science and Technology in UAE in 2010. Since 2015, Chongquing University of Technology in China has been running its electrical engineering and computer science programs based on the educational systems and curricula offered by KAIST.
Last October, KAIST also signed an MOU with the Prince Mohammad Bin Salman College of Cyber Security, AI, and Advanced Technologies in Saudi Arabia to provide the undergraduate program for robotics.
Among all these programs benchmarking KAIST, Kenya-KAIST clearly stands out, as it carries out a turnkey-based project that encompasses every aspect of institution building, ranging from educational curricular development to campus construction and supervision.
Figure 1. KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and Principal Secretary of Ministry of Education Collette A. Suda
Figure 2. Kickoff Ceremony of Kenya-KAIST
Figure 3. Conceptual image of Kenya KAIST
2019.02.13 View 8033
Kenya-KAIST Kicks off with a 95-Million USD Funding from the Korean Government
KAIST, founded through a six-million USD loan from USAID in 1971, to provide turnkey-based education consultancy for Kenya’s first advanced science and technology institute.
KAIST and the Konza Technopolis Development Authority (KoTDA) announced the official establishment of Kenya-KAIST by 2021 during a kickoff ceremony on February 12 in Kenya. The KAIST delegation headed by President Sung-Chul Shin and Kenyan cabinet members and dignitaries including Minister of Education Amina Mohamed, the Chairman of the KoTDA Reuben Mutiso, and the CEO of KoTDA John Tanui attended the ceremony.
With this kickoff held at Konza Technopolis Malili, KAIST, the first and top science and technology university in Korea, will participate in Kenya’s strategic economic development plan with the provision of a turnkey-based science and technology education consultancy for the establishment of Kenya’s first advanced institute of science and technology. KAIST, which won preferred bidder status in consortium with Samwoo and Sunjin architecture and engineering companies, signed the contract with the KoTDA last November.
Korea Eximbank will offer a 95-million USD economic development cooperation fund loan to the Kenyan government. The campus will be constructed in the Konza Techno City located near Nairobi by 2021, with the first batch of 200 graduate students starting classes in 2022.
KAIST will develop academic curricula for six initial departments (Mechanical Engineering, Electrical/Electronic Engineering, ICT Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Civil Engineering, and Agricultural Biotechnology), which will lay the groundwork for engineering research and education in Kenya to meet emerging socioeconomic demands. In addition, KAIST will provide education in the basic science areas of math, physics, chemistry, and biology for students.
The Kenyan government plans to transform Kenya into a middle-income country under Vision 2030 through the promotion of science, technology, and innovation for national economic growth. Nicknamed Africa’s Silicon Savannah, Konza Techno City is a strategic science and technology hub constructed to realize this vision. To this end, the medium-term plan set a goal to provide specialized research and training in various cutting-edge engineering and advanced science fields.
It is also notable that the Kenyan government asked to develop an industry-academy cooperation program in the Konza Techno City. This reflects the high expectations for Kenya-KAIST and its role as a growth engine in the center of the Konza Technopolis. It is anticipated that the technopolis will create 16,675 jobs in the medium term and over 200,000 upon completion, positioning Kenya as an ICT hub within the region.
Saying that the partnership through Kenya-KAIST will bring a new future to Kenya as well as KAIST at the ceremony, President Shin reflected that the project will be a significant milestone for KAIST’s history and global competitiveness. He added, “With this Kenya project, we come to share the past, present, and future of KAIST. And I am very pleased to celebrate our shared vision: the empowerment of science, technology, and education.”
In particular, President Shin was accompanied by Dr. Kun-Mo Chung, a founding provost who served as the Minister of Science and Technology in Korea twice. He now serves as an advisor to Kenyan President Uhuru Kenyatta.
Dr. Chung had played a crucial role in securing a six-million USD loan from US AID to the Korean government to establish KAIST in 1971. He proposed the idea to establish an advanced science and technology institute in Korea to Dr. John Hannah, then the director of US AID.
The seed that was sowed five decades ago in Korea by Dr. Chung has now fully bloomed in Kenya. In only a half century, KAIST has become a donor institution that passes on science and technology education systems including the construction of campuses to developing countries.
KAIST has been acclaimed as US AID’s most successful foreign aid project. A report from the National Academy of Sciences in the US described KAIST as an exemplary case in which a former recipient of international aid has grown to become a science, technology and innovation leader.
The kickoff of Kenya-KAIST drew the attention of both media and local universities in Kenya, attesting to their strong interest to drive economic growth through advanced science and technology.
The University of Nairobi also hosted a special lecture by President Shin, asking him to share the recipe for the success of KAIST in Korea. In a lecture titled “A Crucial Engine for Rapid National Development,” President Shin presented the vision, innovation, and passion of the Korean people that led to the phenomenal results we can see today.
The successful case of KAIST has been benchmarked by many countries for years. For instance, KAIST set up the curriculum for the nuclear engineering program at the Khalifa University of Science and Technology in UAE in 2010. Since 2015, Chongquing University of Technology in China has been running its electrical engineering and computer science programs based on the educational systems and curricula offered by KAIST.
Last October, KAIST also signed an MOU with the Prince Mohammad Bin Salman College of Cyber Security, AI, and Advanced Technologies in Saudi Arabia to provide the undergraduate program for robotics.
Among all these programs benchmarking KAIST, Kenya-KAIST clearly stands out, as it carries out a turnkey-based project that encompasses every aspect of institution building, ranging from educational curricular development to campus construction and supervision.
Figure 1. KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and Principal Secretary of Ministry of Education Collette A. Suda
Figure 2. Kickoff Ceremony of Kenya-KAIST
Figure 3. Conceptual image of Kenya KAIST
2019.02.13 View 8033