ICA
-
 A KAIST Team Wins the Chem-E-Car Competition 2016
A KAIST team consisted of four students from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering won the Chem-E-Car Competition 2016, which took place on November 13 at the Union Square in San Francisco. The students who participated were Young-Hyun Cha, Jin-Sol Shin, Dae-Seok Oh, and Wan-Tae Kim. Their adviser was Professor Doh Chang Lee of the same department.
Established in 1999, the Chem-E-Car is an annual worldwide college competition for students majoring in chemical engineering. The American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE), founded in 1908, is the world’s leading organization for chemical engineering professionals with more than 50,000 members from over 100 countries and hosts this competition every year.
A total of 41 university teams including Carnegie Mellon University and Purdue University participated in this year’s competition.
KAIST students competed in the event for the first time in 2014 and reached the rank of 28. In 2015, the students placed 16th, and finally, took the first place in last month’s competition, followed by the Georgia Institute of Technology.
In the competition, students must design small-scale (20x30x40 cm) automobiles that operate chemically, as well as describe their research and drive their car a fixed distance down a wedge-shaped course to demonstrate the car’s capabilities. In addition to driving a specified distance (15-30 meters), the car must hold a payload of 0-500 mL of water.
The organizers tell participants the exact distance and amount of payloads one hour before the competition begins. Winners are chosen based on their finishing time and how close their car reaches the finish line. Thus, students must show sophisticated coordination of chemical reactions to win.
The KAIST team designed their car to have a stable power output using a Vanadium redox flow battery developed by Professor Hee Tak Kim of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. They employed iodine clock reactions to induce quick and precise chemical reactions to control their car.
KAIST’s car finished with the best run coming within 11 cm of the target line; Georgia Tech’s car reached the finish line by 13 cm and New Jersey Institute of Technology’s car by 14 cm.
Young-Hyun Cha, one of the four students, said, “When we first designed our car, we had to deal with many issues such as stalls or connection errors. We kept working on fixing these problems through trial and error, which eventually led us to success.”
For a news article on KAIST’s win at 2016 Chemi-E-Car Competition by AIChE, see the link below:
http://www.aiche.org/chenected/2016/11/koreas-kaist-wins-1st-place-2016-chem-e-car-competition-photos
2016.12.08 View 11078
A KAIST Team Wins the Chem-E-Car Competition 2016
A KAIST team consisted of four students from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering won the Chem-E-Car Competition 2016, which took place on November 13 at the Union Square in San Francisco. The students who participated were Young-Hyun Cha, Jin-Sol Shin, Dae-Seok Oh, and Wan-Tae Kim. Their adviser was Professor Doh Chang Lee of the same department.
Established in 1999, the Chem-E-Car is an annual worldwide college competition for students majoring in chemical engineering. The American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE), founded in 1908, is the world’s leading organization for chemical engineering professionals with more than 50,000 members from over 100 countries and hosts this competition every year.
A total of 41 university teams including Carnegie Mellon University and Purdue University participated in this year’s competition.
KAIST students competed in the event for the first time in 2014 and reached the rank of 28. In 2015, the students placed 16th, and finally, took the first place in last month’s competition, followed by the Georgia Institute of Technology.
In the competition, students must design small-scale (20x30x40 cm) automobiles that operate chemically, as well as describe their research and drive their car a fixed distance down a wedge-shaped course to demonstrate the car’s capabilities. In addition to driving a specified distance (15-30 meters), the car must hold a payload of 0-500 mL of water.
The organizers tell participants the exact distance and amount of payloads one hour before the competition begins. Winners are chosen based on their finishing time and how close their car reaches the finish line. Thus, students must show sophisticated coordination of chemical reactions to win.
The KAIST team designed their car to have a stable power output using a Vanadium redox flow battery developed by Professor Hee Tak Kim of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. They employed iodine clock reactions to induce quick and precise chemical reactions to control their car.
KAIST’s car finished with the best run coming within 11 cm of the target line; Georgia Tech’s car reached the finish line by 13 cm and New Jersey Institute of Technology’s car by 14 cm.
Young-Hyun Cha, one of the four students, said, “When we first designed our car, we had to deal with many issues such as stalls or connection errors. We kept working on fixing these problems through trial and error, which eventually led us to success.”
For a news article on KAIST’s win at 2016 Chemi-E-Car Competition by AIChE, see the link below:
http://www.aiche.org/chenected/2016/11/koreas-kaist-wins-1st-place-2016-chem-e-car-competition-photos
2016.12.08 View 11078 -
 Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 10142
Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 10142 -
 Mystery of Biological Plastic Synthesis Machinery Unveiled
Plastics and other polymers are used every day. These polymers are mostly made from fossil resources by refining petrochemicals. On the other hand, many microorganisms naturally synthesize polyesters known as polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) as distinct granules inside cells.
PHAs are a family of microbial polyesters that have attracted much attention as biodegradable and biocompatible plastics and elastomers that can substitute petrochemical counterparts. There have been numerous papers and patents on gene cloning and metabolic engineering of PHA biosynthetic machineries, biochemical studies, and production of PHAs; simple Google search with “polyhydroxyalkanoates” yielded returns of 223,000 document pages. PHAs have always been considered amazing examples of biological polymer synthesis. It is astounding to see PHAs of 500 kDa to sometimes as high as 10,000 kDa can be synthesized in vivo by PHA synthase, the key polymerizing enzyme in PHA biosynthesis. They have attracted great interest in determining the crystal structure of PHA synthase over the last 30 years, but unfortunately without success. Thus, the characteristics and molecular mechanisms of PHA synthase were under a dark veil.
In two papers published back-to-back in Biotechnology Journal online on November 30, 2016, a Korean research team led by Professor Kyung-Jin Kim at Kyungpook National University and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) described the crystal structure of PHA synthase from Ralstonia eutropha, the best studied bacterium for PHA production, and reported the structural basis for the detailed molecular mechanisms of PHA biosynthesis. The crystal structure has been deposited to Protein Data Bank in February 2016. After deciphering the crystal structure of the catalytic domain of PHA synthase, in addition to other structural studies on whole enzyme and related proteins, the research team also performed experiments to elucidate the mechanisms of the enzyme reaction, validating detailed structures, enzyme engineering, and also N-terminal domain studies among others.
Through several biochemical studies based on crystal structure, the authors show that PHA synthase exists as a dimer and is divided into two distinct domains, the N-terminal domain (RePhaC1ND) and the C-terminal domain (RePhaC1CD). The RePhaC1CD catalyzes the polymerization reaction via a non-processive ping-pong mechanism using a Cys-His-Asp catalytic triad. The two catalytic sites of the RePhaC1CD dimer are positioned 33.4 Å apart, suggesting that the polymerization reaction occurs independently at each site. This study also presents the structure-based mechanisms for substrate specificities of various PHA synthases from different classes.
Professor Sang Yup Lee, who has worked on this topic for more than 20 years, said,
“The results and information presented in these two papers have long been awaited not only in the PHA community, but also metabolic engineering, bacteriology/microbiology, and in general biological sciences communities. The structural information on PHA synthase together with the recently deciphered reaction mechanisms will be valuable for understanding the detailed mechanisms of biosynthesizing this important energy/redox storage material, and also for the rational engineering of PHA synthases to produce designer bioplastics from various monomers more efficiently.”
Indeed, these two papers published in Biotechnology Journal finally reveal the 30-year mystery of machinery of biological polyester synthesis, and will serve as the essential compass in creating designer and more efficient bioplastic machineries.
References:
Jieun Kim, Yeo-Jin Kim, So Young Choi, Sang Yup Lee and Kyung-Jin Kim. “Crystal structure of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase C-terminal domain and reaction mechanisms” Biotechnology Journal DOI: 10.1002/biot.201600648
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/biot.201600648/abstract
Yeo-Jin Kim, So Young Choi, Jieun Kim, Kyeong Sik Jin, Sang Yup Lee and Kyung-Jin Kim. “Structure and function of the N-terminal domain of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase, and the proposed structure and mechanisms of the whole enzyme” Biotechnology Journal DOI: 10.1002/biot.201600649
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/biot.201600649/abstract
2016.12.02 View 10439
Mystery of Biological Plastic Synthesis Machinery Unveiled
Plastics and other polymers are used every day. These polymers are mostly made from fossil resources by refining petrochemicals. On the other hand, many microorganisms naturally synthesize polyesters known as polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) as distinct granules inside cells.
PHAs are a family of microbial polyesters that have attracted much attention as biodegradable and biocompatible plastics and elastomers that can substitute petrochemical counterparts. There have been numerous papers and patents on gene cloning and metabolic engineering of PHA biosynthetic machineries, biochemical studies, and production of PHAs; simple Google search with “polyhydroxyalkanoates” yielded returns of 223,000 document pages. PHAs have always been considered amazing examples of biological polymer synthesis. It is astounding to see PHAs of 500 kDa to sometimes as high as 10,000 kDa can be synthesized in vivo by PHA synthase, the key polymerizing enzyme in PHA biosynthesis. They have attracted great interest in determining the crystal structure of PHA synthase over the last 30 years, but unfortunately without success. Thus, the characteristics and molecular mechanisms of PHA synthase were under a dark veil.
In two papers published back-to-back in Biotechnology Journal online on November 30, 2016, a Korean research team led by Professor Kyung-Jin Kim at Kyungpook National University and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) described the crystal structure of PHA synthase from Ralstonia eutropha, the best studied bacterium for PHA production, and reported the structural basis for the detailed molecular mechanisms of PHA biosynthesis. The crystal structure has been deposited to Protein Data Bank in February 2016. After deciphering the crystal structure of the catalytic domain of PHA synthase, in addition to other structural studies on whole enzyme and related proteins, the research team also performed experiments to elucidate the mechanisms of the enzyme reaction, validating detailed structures, enzyme engineering, and also N-terminal domain studies among others.
Through several biochemical studies based on crystal structure, the authors show that PHA synthase exists as a dimer and is divided into two distinct domains, the N-terminal domain (RePhaC1ND) and the C-terminal domain (RePhaC1CD). The RePhaC1CD catalyzes the polymerization reaction via a non-processive ping-pong mechanism using a Cys-His-Asp catalytic triad. The two catalytic sites of the RePhaC1CD dimer are positioned 33.4 Å apart, suggesting that the polymerization reaction occurs independently at each site. This study also presents the structure-based mechanisms for substrate specificities of various PHA synthases from different classes.
Professor Sang Yup Lee, who has worked on this topic for more than 20 years, said,
“The results and information presented in these two papers have long been awaited not only in the PHA community, but also metabolic engineering, bacteriology/microbiology, and in general biological sciences communities. The structural information on PHA synthase together with the recently deciphered reaction mechanisms will be valuable for understanding the detailed mechanisms of biosynthesizing this important energy/redox storage material, and also for the rational engineering of PHA synthases to produce designer bioplastics from various monomers more efficiently.”
Indeed, these two papers published in Biotechnology Journal finally reveal the 30-year mystery of machinery of biological polyester synthesis, and will serve as the essential compass in creating designer and more efficient bioplastic machineries.
References:
Jieun Kim, Yeo-Jin Kim, So Young Choi, Sang Yup Lee and Kyung-Jin Kim. “Crystal structure of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase C-terminal domain and reaction mechanisms” Biotechnology Journal DOI: 10.1002/biot.201600648
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/biot.201600648/abstract
Yeo-Jin Kim, So Young Choi, Jieun Kim, Kyeong Sik Jin, Sang Yup Lee and Kyung-Jin Kim. “Structure and function of the N-terminal domain of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase, and the proposed structure and mechanisms of the whole enzyme” Biotechnology Journal DOI: 10.1002/biot.201600649
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/biot.201600649/abstract
2016.12.02 View 10439 -
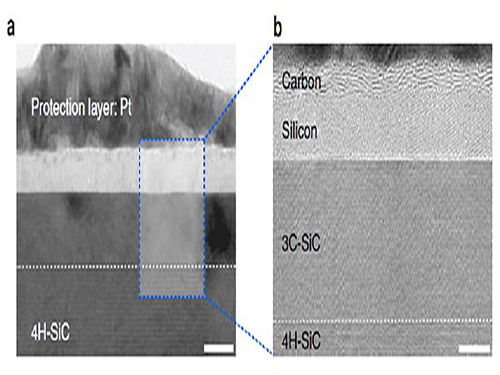 Making Graphene Using Laser-induced Phase Separation
IBS & KAIST researchers clarify how laser annealing technology can lead to the production of ultrathin nanomaterials
All our smart phones have shiny flat AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays. Behind each single pixel of these displays hides at least two silicon transistors which are mass-manufactured using laser annealing technology. While the traditional methods to make the transistors use temperature above 1,000°C, the laser technique reaches the same results at low temperatures even on plastic substrates (melting temperature below 300°C). Interestingly, a similar procedure can be used to generate crystals of graphene. Graphene is a strong and thin nano-material made of carbon, its electric and heat-conductive properties have attracted the attention of scientists worldwide.
Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and his research group at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), as well as Professor Sung-Yool Choi of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team discovered graphene synthesis mechanism using laser-induced solid-state phase separation of single-crystal silicon carbide (SiC). This study, available in Nature Communications, clarifies how this laser technology can separate a complex compound (SiC) into its ultrathin elements of carbon and silicon.
Although several fundamental studies presented the effect of excimer lasers in transforming elemental materials like silicon, the laser interaction with more complex compounds like SiC has rarely been studied due to the complexity of compound phase transition and ultra-short processing time.
With high resolution microscope images and molecular dynamic simulations, scientists found that a single-pulse irradiation of xenon chloride excimer laser of 30 nanoseconds melts SiC, leading to the separation of a liquid SiC layer, a disordered carbon layer with graphitic domains (about 2.5 nm thick) on top surface and a polycrystalline silicon layer (about 5 nm) below carbon layer. Giving additional pulses causes the sublimation of the separated silicon, while the disordered carbon layer is transformed into a multilayer graphene.
"This research shows that the laser material interaction technology can be a powerful tool for the next generation of two dimensional nanomaterials," said Professor Lee.
Professor Choi added: "Using laser-induced phase separation of complex compounds, new types of two dimensional materials can be synthesized in the future."
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy shows that after just one laser pulse of 30 nanoseconds, the silicon carbide (SiC) substrate is melted and separates into a carbon and a silicon layer. More pulses cause the carbon layer to organize into graphene and the silicon to leave as gas.
Molecular dynamics simulates the graphene formation mechanism. The carbon layer on the top forms because the laser-induced liquid SiC (SiC (l)) is unstable.
(Press Release by Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS))
2016.12.01 View 11631
Making Graphene Using Laser-induced Phase Separation
IBS & KAIST researchers clarify how laser annealing technology can lead to the production of ultrathin nanomaterials
All our smart phones have shiny flat AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays. Behind each single pixel of these displays hides at least two silicon transistors which are mass-manufactured using laser annealing technology. While the traditional methods to make the transistors use temperature above 1,000°C, the laser technique reaches the same results at low temperatures even on plastic substrates (melting temperature below 300°C). Interestingly, a similar procedure can be used to generate crystals of graphene. Graphene is a strong and thin nano-material made of carbon, its electric and heat-conductive properties have attracted the attention of scientists worldwide.
Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and his research group at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), as well as Professor Sung-Yool Choi of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team discovered graphene synthesis mechanism using laser-induced solid-state phase separation of single-crystal silicon carbide (SiC). This study, available in Nature Communications, clarifies how this laser technology can separate a complex compound (SiC) into its ultrathin elements of carbon and silicon.
Although several fundamental studies presented the effect of excimer lasers in transforming elemental materials like silicon, the laser interaction with more complex compounds like SiC has rarely been studied due to the complexity of compound phase transition and ultra-short processing time.
With high resolution microscope images and molecular dynamic simulations, scientists found that a single-pulse irradiation of xenon chloride excimer laser of 30 nanoseconds melts SiC, leading to the separation of a liquid SiC layer, a disordered carbon layer with graphitic domains (about 2.5 nm thick) on top surface and a polycrystalline silicon layer (about 5 nm) below carbon layer. Giving additional pulses causes the sublimation of the separated silicon, while the disordered carbon layer is transformed into a multilayer graphene.
"This research shows that the laser material interaction technology can be a powerful tool for the next generation of two dimensional nanomaterials," said Professor Lee.
Professor Choi added: "Using laser-induced phase separation of complex compounds, new types of two dimensional materials can be synthesized in the future."
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy shows that after just one laser pulse of 30 nanoseconds, the silicon carbide (SiC) substrate is melted and separates into a carbon and a silicon layer. More pulses cause the carbon layer to organize into graphene and the silicon to leave as gas.
Molecular dynamics simulates the graphene formation mechanism. The carbon layer on the top forms because the laser-induced liquid SiC (SiC (l)) is unstable.
(Press Release by Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS))
2016.12.01 View 11631 -
 KAIST's Doctoral Student Receives a Hoffman Scholarship Award
Hyo-Sun Lee, a doctoral student at the Graduate School of EEWS (Environment, Energy, Water and Sustainability), KAIST, is a recipient of the 2016 Dorothy M. and Earl S. Hoffman Scholarships presented by the American Vacuum Society (AVS). The award ceremony took place during the Society’s 63rd International Symposium and Exhibition on November 6-11, 2016 in Nashville, Tennessee.
Lee is the first Korean and foreign student to receive this scholarship.
The Hoffman Scholarships were established in 2002 to recognize and encourage excellence in graduate studies in the sciences and technologies of interest to AVS. The scholarships are funded by a bequest from Dorothy M. Hoffman, who was a pioneering member of the Society of Women Engineers and served as the president of AVS in 1974.
Lee received the scholarship for her research that detects hot electrons from chemical reactions on catalytic surface using nanodevices. Nano Letters, an academic journal published by the American Chemical Society, described her work in its February 2016 issue as a technology that allows quantitative analysis of hot electrons by employing a new nanodevice and therefore helps researchers understand better the mechanism of chemical reactions on nanocatalytic surface. She also published her work to detect the flow of hot electrons that occur on metal nanocatalytic surface during hydrogen oxidation reactions in Angewandte Chemie.
Lee said, “I am pleased to receive this honor from such a world-renowned academic society. Certainly, this will be a great support for my future study and research.”
Founded in 1953, AVS is an interdisciplinary, professional society composed of approximately 4,500 members worldwide. It supports networking among academic, industrial, government, and consulting professionals involved in a range of established and emerging science and technology areas such as chemistry, physics, engineering, business, and technology development.
2016.11.17 View 10042
KAIST's Doctoral Student Receives a Hoffman Scholarship Award
Hyo-Sun Lee, a doctoral student at the Graduate School of EEWS (Environment, Energy, Water and Sustainability), KAIST, is a recipient of the 2016 Dorothy M. and Earl S. Hoffman Scholarships presented by the American Vacuum Society (AVS). The award ceremony took place during the Society’s 63rd International Symposium and Exhibition on November 6-11, 2016 in Nashville, Tennessee.
Lee is the first Korean and foreign student to receive this scholarship.
The Hoffman Scholarships were established in 2002 to recognize and encourage excellence in graduate studies in the sciences and technologies of interest to AVS. The scholarships are funded by a bequest from Dorothy M. Hoffman, who was a pioneering member of the Society of Women Engineers and served as the president of AVS in 1974.
Lee received the scholarship for her research that detects hot electrons from chemical reactions on catalytic surface using nanodevices. Nano Letters, an academic journal published by the American Chemical Society, described her work in its February 2016 issue as a technology that allows quantitative analysis of hot electrons by employing a new nanodevice and therefore helps researchers understand better the mechanism of chemical reactions on nanocatalytic surface. She also published her work to detect the flow of hot electrons that occur on metal nanocatalytic surface during hydrogen oxidation reactions in Angewandte Chemie.
Lee said, “I am pleased to receive this honor from such a world-renowned academic society. Certainly, this will be a great support for my future study and research.”
Founded in 1953, AVS is an interdisciplinary, professional society composed of approximately 4,500 members worldwide. It supports networking among academic, industrial, government, and consulting professionals involved in a range of established and emerging science and technology areas such as chemistry, physics, engineering, business, and technology development.
2016.11.17 View 10042 -
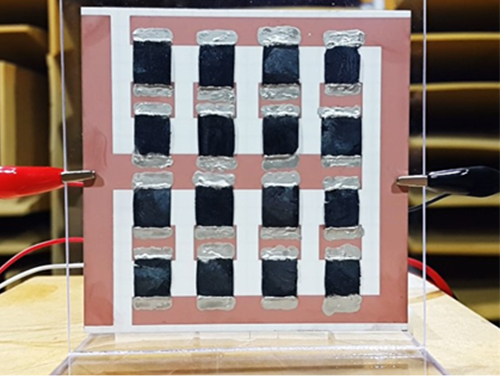 Extremely Thin and Highly Flexible Graphene-Based Thermoacoustic Speakers
A joint research team led by Professors Jung-Woo Choi and Byung Jin Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim of the Material Science and Engineering Department, all on the faculty of the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), has developed a simpler way to mass-produce ultra-thin graphene thermosacoustic speakers.
Their research results were published online on August 17, 2016 in a journal called Applied Materials & Interfaces. The IEEE Spectrum, a monthly magazine published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, reported on the research on September 9, 2016, in an article titled, “Graphene Enables Flat Speakers for Mobile Audio Systems.” The American Chemical Society also drew attention to the team’s work in its article dated September 7, 2016, “Bringing Graphene Speakers to the Mobile Market.”
Thermoacoustic speakers generate sound waves from temperature fluctuations by rapidly heating and cooling conducting materials. Unlike conventional voice-coil speakers, thermoacoustic speakers do not rely on vibrations to produce sound, and thus do not need bulky acoustic boxes to keep complicated mechanical parts for sound production. They also generate good quality sound in all directions, enabling them to be placed on any surface including curved ones without canceling out sounds generated from opposite sides.
Based on a two-step, template-free fabrication method that involved freeze-drying a solution of graphene oxide flakes and the reduction/doping of oxidized graphene to improve electrical properties, the research team produced a N-doped, three-dimensional (3D), reduced graphene oxide aerogel (N-rGOA) with a porous macroscopic structure that permitted easy modulation for many potential applications.
Using 3D graphene aerogels, the team succeeded in fabricating an array of loudspeakers that were able to withstand over 40 W input power and that showed excellent sound pressure level (SPL), comparable to those of previously reported 2D and 3D graphene loudspeakers.
Choong Sun Kim, the lead author of the research paper and a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, said:
“Thermoacoustic speakers have a higher efficiency when conducting materials have a smaller heat capacity. Nanomaterials such as graphene are an ideal candidate for conductors, but they require a substrate to support their extremely thinness. The substrate’s tendency to lose heat lowers the speakers’ efficiency. Here, we developed 3D graphene aerogels without a substrate by using a simple two-step process. With graphene aerogels, we have fabricated an array of loudspeakers that demonstrated stable performance. This is a practical technology that will enable mass-production of thermosacoustic speakers including on mobile platforms.”
The research paper is entitled “Application of N-Doped Three-Dimensional Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel to Thin Film Loudspeaker.” (DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b03618)
Figure 1: A Thermoacoustic Loudspeaker Consisted of an Array of 16 3D Graphene Aerogels
Figure 2: Two-step Fabrication Process of 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel Using Freeze-Drying and Reduction/Doping
Figure 3: X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Graph of the 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel and Its Scanning Electron Microscope Image
2016.10.05 View 14111
Extremely Thin and Highly Flexible Graphene-Based Thermoacoustic Speakers
A joint research team led by Professors Jung-Woo Choi and Byung Jin Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim of the Material Science and Engineering Department, all on the faculty of the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), has developed a simpler way to mass-produce ultra-thin graphene thermosacoustic speakers.
Their research results were published online on August 17, 2016 in a journal called Applied Materials & Interfaces. The IEEE Spectrum, a monthly magazine published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, reported on the research on September 9, 2016, in an article titled, “Graphene Enables Flat Speakers for Mobile Audio Systems.” The American Chemical Society also drew attention to the team’s work in its article dated September 7, 2016, “Bringing Graphene Speakers to the Mobile Market.”
Thermoacoustic speakers generate sound waves from temperature fluctuations by rapidly heating and cooling conducting materials. Unlike conventional voice-coil speakers, thermoacoustic speakers do not rely on vibrations to produce sound, and thus do not need bulky acoustic boxes to keep complicated mechanical parts for sound production. They also generate good quality sound in all directions, enabling them to be placed on any surface including curved ones without canceling out sounds generated from opposite sides.
Based on a two-step, template-free fabrication method that involved freeze-drying a solution of graphene oxide flakes and the reduction/doping of oxidized graphene to improve electrical properties, the research team produced a N-doped, three-dimensional (3D), reduced graphene oxide aerogel (N-rGOA) with a porous macroscopic structure that permitted easy modulation for many potential applications.
Using 3D graphene aerogels, the team succeeded in fabricating an array of loudspeakers that were able to withstand over 40 W input power and that showed excellent sound pressure level (SPL), comparable to those of previously reported 2D and 3D graphene loudspeakers.
Choong Sun Kim, the lead author of the research paper and a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, said:
“Thermoacoustic speakers have a higher efficiency when conducting materials have a smaller heat capacity. Nanomaterials such as graphene are an ideal candidate for conductors, but they require a substrate to support their extremely thinness. The substrate’s tendency to lose heat lowers the speakers’ efficiency. Here, we developed 3D graphene aerogels without a substrate by using a simple two-step process. With graphene aerogels, we have fabricated an array of loudspeakers that demonstrated stable performance. This is a practical technology that will enable mass-production of thermosacoustic speakers including on mobile platforms.”
The research paper is entitled “Application of N-Doped Three-Dimensional Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel to Thin Film Loudspeaker.” (DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b03618)
Figure 1: A Thermoacoustic Loudspeaker Consisted of an Array of 16 3D Graphene Aerogels
Figure 2: Two-step Fabrication Process of 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel Using Freeze-Drying and Reduction/Doping
Figure 3: X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Graph of the 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel and Its Scanning Electron Microscope Image
2016.10.05 View 14111 -
 Continuous Roll-Process Technology for Transferring and Packaging Flexible Large-Scale Integrated Circuits
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from KAIST and by Dr. Jae-Hyun Kim from the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) has jointly developed a continuous roll-processing technology that transfers and packages flexible large-scale integrated circuits (LSI), the key element in constructing the computer’s brain such as CPU, on plastics to realize flexible electronics.
Professor Lee previously demonstrated the silicon-based flexible LSIs using 0.18 CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) process in 2013 (ACS Nano, “In Vivo Silicon-based Flexible Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Monolithically Encapsulated with Biocompatible Liquid Crystal Polymers”) and presented the work in an invited talk of 2015 International Electron Device Meeting (IEDM), the world’s premier semiconductor forum.
Highly productive roll-processing is considered a core technology for accelerating the commercialization of wearable computers using flexible LSI. However, realizing it has been a difficult challenge not only from the roll-based manufacturing perspective but also for creating roll-based packaging for the interconnection of flexible LSI with flexible displays, batteries, and other peripheral devices.
To overcome these challenges, the research team started fabricating NAND flash memories on a silicon wafer using conventional semiconductor processes, and then removed a sacrificial wafer leaving a top hundreds-nanometer-thick circuit layer. Next, they simultaneously transferred and interconnected the ultrathin device on a flexible substrate through the continuous roll-packaging technology using anisotropic conductive film (ACF). The final silicon-based flexible NAND memory successfully demonstrated stable memory operations and interconnections even under severe bending conditions. This roll-based flexible LSI technology can be potentially utilized to produce flexible application processors (AP), high-density memories, and high-speed communication devices for mass manufacture.
Professor Lee said, “Highly productive roll-process was successfully applied to flexible LSIs to continuously transfer and interconnect them onto plastics. For example, we have confirmed the reliable operation of our flexible NAND memory at the circuit level by programming and reading letters in ASCII codes. Out results may open up new opportunities to integrate silicon-based flexible LSIs on plastics with the ACF packing for roll-based manufacturing.”
Dr. Kim added, “We employed the roll-to-plate ACF packaging, which showed outstanding bonding capability for continuous roll-based transfer and excellent flexibility of interconnecting core and peripheral devices. This can be a key process to the new era of flexible computers combining the already developed flexible displays and batteries.”
The team’s results will be published on the front cover of Advanced Materials (August 31, 2016) in an article entitled “Simultaneous Roll Transfer and Interconnection of Silicon NAND Flash Memory.” (DOI: 10.1002/adma.201602339)
YouTube Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8OJjAEm27sw
Picture 1: This schematic image shows the flexible silicon NAND flash memory produced by the simultaneous roll-transfer and interconnection process.
Picture 2: The flexible silicon NAND flash memory is attached to a 7 mm diameter glass rod.
2016.09.01 View 11723
Continuous Roll-Process Technology for Transferring and Packaging Flexible Large-Scale Integrated Circuits
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from KAIST and by Dr. Jae-Hyun Kim from the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) has jointly developed a continuous roll-processing technology that transfers and packages flexible large-scale integrated circuits (LSI), the key element in constructing the computer’s brain such as CPU, on plastics to realize flexible electronics.
Professor Lee previously demonstrated the silicon-based flexible LSIs using 0.18 CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) process in 2013 (ACS Nano, “In Vivo Silicon-based Flexible Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Monolithically Encapsulated with Biocompatible Liquid Crystal Polymers”) and presented the work in an invited talk of 2015 International Electron Device Meeting (IEDM), the world’s premier semiconductor forum.
Highly productive roll-processing is considered a core technology for accelerating the commercialization of wearable computers using flexible LSI. However, realizing it has been a difficult challenge not only from the roll-based manufacturing perspective but also for creating roll-based packaging for the interconnection of flexible LSI with flexible displays, batteries, and other peripheral devices.
To overcome these challenges, the research team started fabricating NAND flash memories on a silicon wafer using conventional semiconductor processes, and then removed a sacrificial wafer leaving a top hundreds-nanometer-thick circuit layer. Next, they simultaneously transferred and interconnected the ultrathin device on a flexible substrate through the continuous roll-packaging technology using anisotropic conductive film (ACF). The final silicon-based flexible NAND memory successfully demonstrated stable memory operations and interconnections even under severe bending conditions. This roll-based flexible LSI technology can be potentially utilized to produce flexible application processors (AP), high-density memories, and high-speed communication devices for mass manufacture.
Professor Lee said, “Highly productive roll-process was successfully applied to flexible LSIs to continuously transfer and interconnect them onto plastics. For example, we have confirmed the reliable operation of our flexible NAND memory at the circuit level by programming and reading letters in ASCII codes. Out results may open up new opportunities to integrate silicon-based flexible LSIs on plastics with the ACF packing for roll-based manufacturing.”
Dr. Kim added, “We employed the roll-to-plate ACF packaging, which showed outstanding bonding capability for continuous roll-based transfer and excellent flexibility of interconnecting core and peripheral devices. This can be a key process to the new era of flexible computers combining the already developed flexible displays and batteries.”
The team’s results will be published on the front cover of Advanced Materials (August 31, 2016) in an article entitled “Simultaneous Roll Transfer and Interconnection of Silicon NAND Flash Memory.” (DOI: 10.1002/adma.201602339)
YouTube Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8OJjAEm27sw
Picture 1: This schematic image shows the flexible silicon NAND flash memory produced by the simultaneous roll-transfer and interconnection process.
Picture 2: The flexible silicon NAND flash memory is attached to a 7 mm diameter glass rod.
2016.09.01 View 11723 -
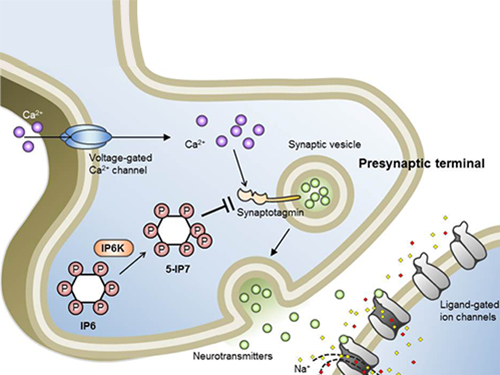 Professor Seyun Kim Identifies a Neuron Signal Controlling Molecule
A research team led by Professor Seyun Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has identified inositol pyrophosphates as the molecule that strongly controls neuron signaling via synaptotagmin.
Professors Tae-Young Yoon of Yonsei University’s Y-IBS and Sung-Hyun Kim of Kyung Hee University’s Department of Biomedical Science also joined the team.
The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30, 2016.
This interdisciplinary research project was conducted by six research teams from four different countries and covered a wide scope of academic fields, from neurobiology to super resolution optic imaging.
Inositol pyrophosphates such as 5-diphosphoinositol pentakisphos-phate (5-IP7), which naturally occur in corns and beans, are essential metabolites in the body. In particular, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) has anti-cancer properties and is thought to have an important role in cell signaling.
Inositol pentakisphosphate (IP7) differs from IP6 by having an additional phosphate group, which was first discovered 20 years ago. IP7 has recently been identified as playing a key role in diabetes and obesity.
Psychopathy and neurodegenerative diseases are known to result from the disrupted balance of inositol pyrophosphates. However, the role and the mechanism of action of IP7 in brain neurons and nerve transmission remained unknown.
Professor Kim’s team has worked on inositol pyrophosphates for several years and discovered that very small quantities of IP7 control cell-signaling transduction. Professor Yoon of Yonsei University identified IP7 as a much stronger inhibitor of neuron signaling compared to IP6. In particular, IP7 directly suppresses synaptotagmin, one of the key proteins in neuron signaling. Moreover, Professor Kim of Kyung Hee University observed IP7 inhibition in sea horse neurons.
Together, the joint research team identified inositol pyrophosphates as the key switch metabolite of brain-signaling transduction.
The researchers hope that future research on synaptotagmin and IP7 will reveal the mechanism of neuron-signal transduction and thus enable the treatment of neurological disorders.
These research findings were the result of cooperation of various science and technology institutes: KAIST, Yonsei-IBS (Institute for Basic Science), Kyung Hee University, Sungkyunkwan University, KIST, University of Zurich in Switzerland, and Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg in Germany.
Schematic Image of Controlling the Synaptic Exocytotic Pathway by 5-IP7 , Helping the Understanding of the Signaling Mechanisms of Inositol Pyrophosphates
2016.07.21 View 12014
Professor Seyun Kim Identifies a Neuron Signal Controlling Molecule
A research team led by Professor Seyun Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has identified inositol pyrophosphates as the molecule that strongly controls neuron signaling via synaptotagmin.
Professors Tae-Young Yoon of Yonsei University’s Y-IBS and Sung-Hyun Kim of Kyung Hee University’s Department of Biomedical Science also joined the team.
The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30, 2016.
This interdisciplinary research project was conducted by six research teams from four different countries and covered a wide scope of academic fields, from neurobiology to super resolution optic imaging.
Inositol pyrophosphates such as 5-diphosphoinositol pentakisphos-phate (5-IP7), which naturally occur in corns and beans, are essential metabolites in the body. In particular, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) has anti-cancer properties and is thought to have an important role in cell signaling.
Inositol pentakisphosphate (IP7) differs from IP6 by having an additional phosphate group, which was first discovered 20 years ago. IP7 has recently been identified as playing a key role in diabetes and obesity.
Psychopathy and neurodegenerative diseases are known to result from the disrupted balance of inositol pyrophosphates. However, the role and the mechanism of action of IP7 in brain neurons and nerve transmission remained unknown.
Professor Kim’s team has worked on inositol pyrophosphates for several years and discovered that very small quantities of IP7 control cell-signaling transduction. Professor Yoon of Yonsei University identified IP7 as a much stronger inhibitor of neuron signaling compared to IP6. In particular, IP7 directly suppresses synaptotagmin, one of the key proteins in neuron signaling. Moreover, Professor Kim of Kyung Hee University observed IP7 inhibition in sea horse neurons.
Together, the joint research team identified inositol pyrophosphates as the key switch metabolite of brain-signaling transduction.
The researchers hope that future research on synaptotagmin and IP7 will reveal the mechanism of neuron-signal transduction and thus enable the treatment of neurological disorders.
These research findings were the result of cooperation of various science and technology institutes: KAIST, Yonsei-IBS (Institute for Basic Science), Kyung Hee University, Sungkyunkwan University, KIST, University of Zurich in Switzerland, and Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg in Germany.
Schematic Image of Controlling the Synaptic Exocytotic Pathway by 5-IP7 , Helping the Understanding of the Signaling Mechanisms of Inositol Pyrophosphates
2016.07.21 View 12014 -
 'The 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea'
The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) of Korea recently released a list of the 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea. The list included the work of KAIST Professors Dong-Ho Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering, Jeung Ku Kang of the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS), and Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department.
Experts from academia, universities, and industries selected the 100 research projects, among 620 projects recommended by various government offices, in consideration of their contribution to the growth of science and technology in the nation.
Professor Cho conducts research on the development of 5G mobile communication systems based on the pattern polarization beam-division multiple access method.
Professor Kang works on the production of highly efficient energy materials and equipment by controlling them at the electron and atomic level.
Professor Lee focuses on the creation of strategies to produce important chemicals through a biological approach, i.e., microorganisms, which will help develop the means to mitigate climate change.
The MISP will publish a book that describes in detail each research project and will distribute copies of it to the National Assembly of Korea, libraries, and other public organizations.
For more information on the list, please go to www.ntis.go.kr.
Pictured from left to right are Professors Dong-Ho Cho, Jeung Ku Kang, and Sang Yup Lee.
2016.07.21 View 5286
'The 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea'
The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) of Korea recently released a list of the 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea. The list included the work of KAIST Professors Dong-Ho Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering, Jeung Ku Kang of the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS), and Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department.
Experts from academia, universities, and industries selected the 100 research projects, among 620 projects recommended by various government offices, in consideration of their contribution to the growth of science and technology in the nation.
Professor Cho conducts research on the development of 5G mobile communication systems based on the pattern polarization beam-division multiple access method.
Professor Kang works on the production of highly efficient energy materials and equipment by controlling them at the electron and atomic level.
Professor Lee focuses on the creation of strategies to produce important chemicals through a biological approach, i.e., microorganisms, which will help develop the means to mitigate climate change.
The MISP will publish a book that describes in detail each research project and will distribute copies of it to the National Assembly of Korea, libraries, and other public organizations.
For more information on the list, please go to www.ntis.go.kr.
Pictured from left to right are Professors Dong-Ho Cho, Jeung Ku Kang, and Sang Yup Lee.
2016.07.21 View 5286 -
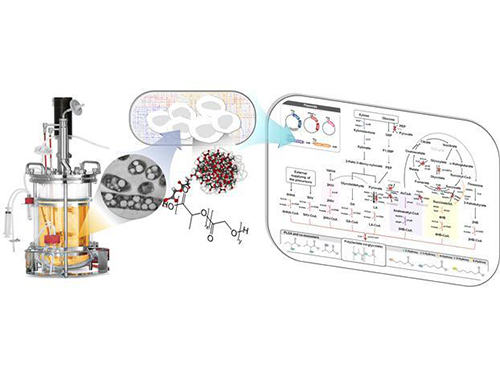 Top 10 Emerging Technologies by World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum’s Meta-Council on Emerging Technologies announced its annual list of breakthrough technologies, the “Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016,” on June 23, 2016. The Meta-Council chose the top ten technologies based on the technologies’ potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet. The research field of systems metabolic engineering, founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST, was also citied. Systems metabolic engineering, which combines elements of synthetic biology, systems biology, and evolutionary engineering, offers a sustainable process for the production of useful chemicals in an environmentally friendly way from plants such as inedible biomass, reducing the need of using fossil fuels. Details about the list follow below:
https://www.weforum.org/press/2016/06/battery-powered-villages-sociable-robots-rank-among-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2016
The picture below shows the “systems metabolic engineering of E. coli for the production of PLGA." PLGA is poly(lactate-co-glycolate), which is widely used for biomedical applications, and has been made by chemical synthesis. Now it is possible to produce PLGA eco-friendly by one-step fermentation of a gut bacterium which is developed through systems metabolic engineering.
2016.06.27 View 11336
Top 10 Emerging Technologies by World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum’s Meta-Council on Emerging Technologies announced its annual list of breakthrough technologies, the “Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016,” on June 23, 2016. The Meta-Council chose the top ten technologies based on the technologies’ potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet. The research field of systems metabolic engineering, founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST, was also citied. Systems metabolic engineering, which combines elements of synthetic biology, systems biology, and evolutionary engineering, offers a sustainable process for the production of useful chemicals in an environmentally friendly way from plants such as inedible biomass, reducing the need of using fossil fuels. Details about the list follow below:
https://www.weforum.org/press/2016/06/battery-powered-villages-sociable-robots-rank-among-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2016
The picture below shows the “systems metabolic engineering of E. coli for the production of PLGA." PLGA is poly(lactate-co-glycolate), which is widely used for biomedical applications, and has been made by chemical synthesis. Now it is possible to produce PLGA eco-friendly by one-step fermentation of a gut bacterium which is developed through systems metabolic engineering.
2016.06.27 View 11336 -
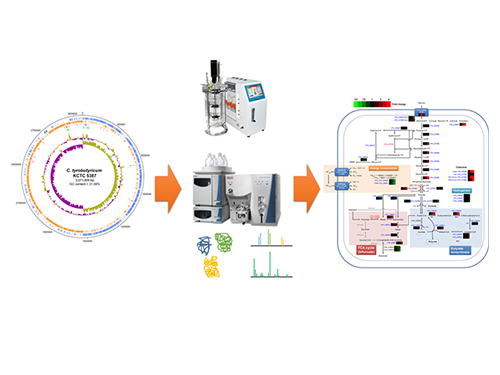 Unveiling the Distinctive Features of Industrial Microorganism
KAIST researchers have sequenced the whole genome of Clostridium tyrobutyricum, which has a higher tolerance to toxic chemicals, such as 1-butanol, compared to other clostridial bacterial strains.
Clostridium tyrobutyricum, a Gram-positive, anaerobic spore-forming bacterium, is considered a promising industrial host strain for the production of various chemicals including butyric acid which has many applications in different industries such as a precursor to biofuels. Despite such potential, C. tyrobutyricum has received little attention, mainly due to a limited understanding of its genotypic and metabolic characteristics at the genome level.
A Korean research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) deciphered the genome sequence of C. tyrobutyricum and its proteome profiles during the course of batch fermentation. As a result, the research team learned that the bacterium is not only capable of producing a large amount of butyric acid but also can tolerate toxic compounds such as 1-butanol. The research results were published in mBio on June 14, 2016.
The team adopted a genoproteomic approach, combining genomics and proteomics, to investigate the metabolic features of C. tyrobutyricum. Unlike Clostridium acetobutylicum, the most widely used organism for 1-butanol production, C. tyrobutyricum has a novel butyrate-producing pathway and various mechanisms for energy conservation under anaerobic conditions. The expression of various metabolic genes, including those involved in butyrate formation, was analyzed using the “shotgun” proteome approach.
To date, the bio-based production of 1-butanol, a next-generation biofuel, has relied on several clostridial hosts including C. acetobutylicum and C. beijerinckii. However, these organisms have a low tolerance against 1-butanol even though they are naturally capable of producing it. C. tyrobutyricum cannot produce 1-butanol itself, but has a higher 1-butanol-tolerance and rapid uptake of monosaccharides, compared to those two species.
The team identified most of the genes involved in the central metabolism of C. tyrobutyricum from the whole-genome and shotgun proteome data, and this study will accelerate the bacterium’s engineering to produce useful chemicals including butyric acid and 1-butanol, replacing traditional bacterial hosts.
Professor Lee said,
“The unique metabolic features and energy conservation mechanisms of C. tyrobutyricum can be employed in the various microbial hosts we have previously developed to further improve their productivity and yield. Moreover, findings on C. tyrobutyricum revealed by this study will be the first step to directly engineer this bacterium.”
Director Jin-Woo Kim at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said,
“Over the years, Professor Lee’s team has researched the development of a bio-refinery system to produce natural and non-natural chemicals with the systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms. They were able to design strategies for the development of diverse industrial microbial strains to produce useful chemicals from inedible biomass-based carbon dioxide fixation. We believe the efficient production of butyric acid using a metabolic engineering approach will play an important role in the establishment of a bioprocess for chemical production.”
The title of the research paper is “Deciphering Clostridium tyrobutyricum Metabolism Based on the Who-Genome Sequence and Proteome Analyses.” (DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00743-16)
The lead authors are Joungmin Lee, a post-doctoral fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working in CJ CheilJedang Research Institute; Yu-Sin Jang, a research fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working at Gyeongsang National University as an assistant professor; and Mee-Jung Han, an assistant professor in the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Dongyang University. Jin Young Kim, a senior researcher at the Korea Basic Science Institute, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project entitled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
Schematic Diagram of C. tyrobutyricum’s Genome Sequence and Its Proteome Profiles
The picture below shows the complete genome sequence, global protein expression profiles, and the genome-based metabolic characteristics during batch fermentation of C. tyrobutyricum.
2016.06.20 View 10859
Unveiling the Distinctive Features of Industrial Microorganism
KAIST researchers have sequenced the whole genome of Clostridium tyrobutyricum, which has a higher tolerance to toxic chemicals, such as 1-butanol, compared to other clostridial bacterial strains.
Clostridium tyrobutyricum, a Gram-positive, anaerobic spore-forming bacterium, is considered a promising industrial host strain for the production of various chemicals including butyric acid which has many applications in different industries such as a precursor to biofuels. Despite such potential, C. tyrobutyricum has received little attention, mainly due to a limited understanding of its genotypic and metabolic characteristics at the genome level.
A Korean research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) deciphered the genome sequence of C. tyrobutyricum and its proteome profiles during the course of batch fermentation. As a result, the research team learned that the bacterium is not only capable of producing a large amount of butyric acid but also can tolerate toxic compounds such as 1-butanol. The research results were published in mBio on June 14, 2016.
The team adopted a genoproteomic approach, combining genomics and proteomics, to investigate the metabolic features of C. tyrobutyricum. Unlike Clostridium acetobutylicum, the most widely used organism for 1-butanol production, C. tyrobutyricum has a novel butyrate-producing pathway and various mechanisms for energy conservation under anaerobic conditions. The expression of various metabolic genes, including those involved in butyrate formation, was analyzed using the “shotgun” proteome approach.
To date, the bio-based production of 1-butanol, a next-generation biofuel, has relied on several clostridial hosts including C. acetobutylicum and C. beijerinckii. However, these organisms have a low tolerance against 1-butanol even though they are naturally capable of producing it. C. tyrobutyricum cannot produce 1-butanol itself, but has a higher 1-butanol-tolerance and rapid uptake of monosaccharides, compared to those two species.
The team identified most of the genes involved in the central metabolism of C. tyrobutyricum from the whole-genome and shotgun proteome data, and this study will accelerate the bacterium’s engineering to produce useful chemicals including butyric acid and 1-butanol, replacing traditional bacterial hosts.
Professor Lee said,
“The unique metabolic features and energy conservation mechanisms of C. tyrobutyricum can be employed in the various microbial hosts we have previously developed to further improve their productivity and yield. Moreover, findings on C. tyrobutyricum revealed by this study will be the first step to directly engineer this bacterium.”
Director Jin-Woo Kim at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said,
“Over the years, Professor Lee’s team has researched the development of a bio-refinery system to produce natural and non-natural chemicals with the systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms. They were able to design strategies for the development of diverse industrial microbial strains to produce useful chemicals from inedible biomass-based carbon dioxide fixation. We believe the efficient production of butyric acid using a metabolic engineering approach will play an important role in the establishment of a bioprocess for chemical production.”
The title of the research paper is “Deciphering Clostridium tyrobutyricum Metabolism Based on the Who-Genome Sequence and Proteome Analyses.” (DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00743-16)
The lead authors are Joungmin Lee, a post-doctoral fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working in CJ CheilJedang Research Institute; Yu-Sin Jang, a research fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working at Gyeongsang National University as an assistant professor; and Mee-Jung Han, an assistant professor in the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Dongyang University. Jin Young Kim, a senior researcher at the Korea Basic Science Institute, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project entitled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
Schematic Diagram of C. tyrobutyricum’s Genome Sequence and Its Proteome Profiles
The picture below shows the complete genome sequence, global protein expression profiles, and the genome-based metabolic characteristics during batch fermentation of C. tyrobutyricum.
2016.06.20 View 10859 -
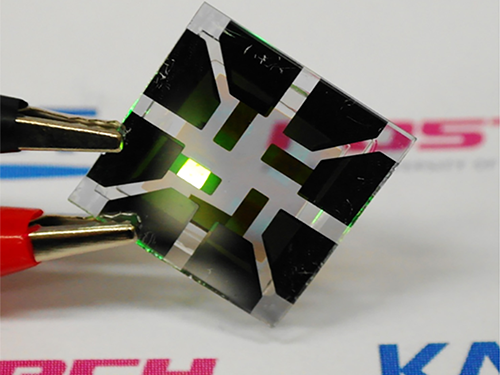 Graphene-Based Transparent Electrodes for Highly Efficient Flexible OLEDs
A Korean research team developed an ideal electrode structure composed of graphene and layers of titanium dioxide and conducting polymers, resulting in highly flexible and efficient OLEDs.
The arrival of a thin and lightweight computer that even rolls up like a piece of paper will not be in the far distant future. Flexible organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), built upon a plastic substrate, have received greater attention lately for their use in next-generation displays that can be bent or rolled while still operating.
A Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering, KAIST and Professor Tae-Woo Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has developed highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE) which is placed in between titanium dioxide (TiO2) and conducting polymer layers. The research results were published online on June 2, 2016 in Nature Communications.
OLEDs are stacked in several ultra-thin layers on glass, foil, or plastic substrates, in which multi-layers of organic compounds are sandwiched between two electrodes (cathode and anode). When voltage is applied across the electrodes, electrons from the cathode and holes (positive charges) from the anode draw toward each other and meet in the emissive layer. OLEDs emit light as an electron recombines with a positive hole, releasing energy in the form of a photon. One of the electrodes in OLEDs is usually transparent, and depending on which electrode is transparent, OLEDs can either emit from the top or bottom.
In conventional bottom-emission OLEDs, an anode is transparent in order for the emitted photons to exit the device through its substrate. Indium-tin-oxide (ITO) is commonly used as a transparent anode because of its high transparency, low sheet resistance, and well-established manufacturing process. However, ITO can potentially be expensive, and moreover, is brittle, being susceptible to bending-induced formation of cracks.
Graphene, a two-dimensional thin layer of carbon atoms tightly bonded together in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice, has recently emerged as an alternative to ITO. With outstanding electrical, physical, and chemical properties, its atomic thinness leading to a high degree of flexibility and transparency makes it an ideal candidate for TEs. Nonetheless, the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs reported to date has been, at best, about the same level of ITO-based OLEDs.
As a solution, the Korean research team, which further includes Professors Sung-Yool Choi (Electrical Engineering) and Taek-Soo Kim (Mechanical Engineering) of KAIST and their students, proposed a new device architecture that can maximize the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs. They fabricated a transparent anode in a composite structure in which a TiO2 layer with a high refractive index (high-n) and a hole-injection layer (HIL) of conducting polymers with a low refractive index (low-n) sandwich graphene electrodes. This is an optical design that induces a synergistic collaboration between the high-n and low-n layers to increase the effective reflectance of TEs. As a result, the enhancement of the optical cavity resonance is maximized. The optical cavity resonance is related to the improvement of efficiency and color gamut in OLEDs. At the same time, the loss from surface plasmon polariton (SPP), a major cause for weak photon emissions in OLEDs, is also reduced due to the presence of the low-n conducting polymers.
Under this approach, graphene-based OLEDs exhibit 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency, which is unprecedented in those using graphene as a TE. Furthermore, these devices remain intact and operate well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm. This is a remarkable result for OLEDs containing oxide layers such as TiO2 because oxides are typically brittle and prone to bending-induced fractures even at a relatively low strain. The research team discovered that TiO2 has a crack-deflection toughening mechanism that tends to prevent bending-induced cracks from being formed easily.
Professor Yoo said, “What’s unique and advanced about this technology, compared with previous graphene-based OLEDs, is the synergistic collaboration of high- and low-index layers that enables optical management of both resonance effect and SPP loss, leading to significant enhancement in efficiency, all with little compromise in flexibility.” He added, “Our work was the achievement of collaborative research, transcending the boundaries of different fields, through which we have often found meaningful breakthroughs.”
Professor Lee said, “We expect that our technology will pave the way to develop an OLED light source for highly flexible and wearable displays, or flexible sensors that can be attached to the human body for health monitoring, for instance.”
The research paper is entitled “Synergistic Electrode Architecture for Efficient Graphene-based Flexible Organic Light-emitting Diodes” (DOI. 10.1038/NCOMMS11791). The lead authors are Jae-Ho Lee, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST; Tae-Hee Han, a Ph.D. researcher at POSTECH; and Min-Ho Park, a Ph.D. candidate at POSTECH.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Center for Advanced Flexible Display (CAFDC) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP); by the Center for Advanced Soft-Electronics funded by the MSIP as a Global Frontier Project; by the Graphene Research Center Program of KAIST; and by grants from the IT R&D Program of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy of Korea (MOTIE).
Figure 1: Application of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows an OLED with the composite structure of TiO2/graphene/conducting polymer electrode in operation. The OLED exhibits 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency. The device prepared on a plastic substrate shown in the right remains intact and operates well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm.
Figure 2: Schematic Device Structure of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows the new architecture to develop highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE).
2016.06.07 View 14266
Graphene-Based Transparent Electrodes for Highly Efficient Flexible OLEDs
A Korean research team developed an ideal electrode structure composed of graphene and layers of titanium dioxide and conducting polymers, resulting in highly flexible and efficient OLEDs.
The arrival of a thin and lightweight computer that even rolls up like a piece of paper will not be in the far distant future. Flexible organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), built upon a plastic substrate, have received greater attention lately for their use in next-generation displays that can be bent or rolled while still operating.
A Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering, KAIST and Professor Tae-Woo Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has developed highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE) which is placed in between titanium dioxide (TiO2) and conducting polymer layers. The research results were published online on June 2, 2016 in Nature Communications.
OLEDs are stacked in several ultra-thin layers on glass, foil, or plastic substrates, in which multi-layers of organic compounds are sandwiched between two electrodes (cathode and anode). When voltage is applied across the electrodes, electrons from the cathode and holes (positive charges) from the anode draw toward each other and meet in the emissive layer. OLEDs emit light as an electron recombines with a positive hole, releasing energy in the form of a photon. One of the electrodes in OLEDs is usually transparent, and depending on which electrode is transparent, OLEDs can either emit from the top or bottom.
In conventional bottom-emission OLEDs, an anode is transparent in order for the emitted photons to exit the device through its substrate. Indium-tin-oxide (ITO) is commonly used as a transparent anode because of its high transparency, low sheet resistance, and well-established manufacturing process. However, ITO can potentially be expensive, and moreover, is brittle, being susceptible to bending-induced formation of cracks.
Graphene, a two-dimensional thin layer of carbon atoms tightly bonded together in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice, has recently emerged as an alternative to ITO. With outstanding electrical, physical, and chemical properties, its atomic thinness leading to a high degree of flexibility and transparency makes it an ideal candidate for TEs. Nonetheless, the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs reported to date has been, at best, about the same level of ITO-based OLEDs.
As a solution, the Korean research team, which further includes Professors Sung-Yool Choi (Electrical Engineering) and Taek-Soo Kim (Mechanical Engineering) of KAIST and their students, proposed a new device architecture that can maximize the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs. They fabricated a transparent anode in a composite structure in which a TiO2 layer with a high refractive index (high-n) and a hole-injection layer (HIL) of conducting polymers with a low refractive index (low-n) sandwich graphene electrodes. This is an optical design that induces a synergistic collaboration between the high-n and low-n layers to increase the effective reflectance of TEs. As a result, the enhancement of the optical cavity resonance is maximized. The optical cavity resonance is related to the improvement of efficiency and color gamut in OLEDs. At the same time, the loss from surface plasmon polariton (SPP), a major cause for weak photon emissions in OLEDs, is also reduced due to the presence of the low-n conducting polymers.
Under this approach, graphene-based OLEDs exhibit 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency, which is unprecedented in those using graphene as a TE. Furthermore, these devices remain intact and operate well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm. This is a remarkable result for OLEDs containing oxide layers such as TiO2 because oxides are typically brittle and prone to bending-induced fractures even at a relatively low strain. The research team discovered that TiO2 has a crack-deflection toughening mechanism that tends to prevent bending-induced cracks from being formed easily.
Professor Yoo said, “What’s unique and advanced about this technology, compared with previous graphene-based OLEDs, is the synergistic collaboration of high- and low-index layers that enables optical management of both resonance effect and SPP loss, leading to significant enhancement in efficiency, all with little compromise in flexibility.” He added, “Our work was the achievement of collaborative research, transcending the boundaries of different fields, through which we have often found meaningful breakthroughs.”
Professor Lee said, “We expect that our technology will pave the way to develop an OLED light source for highly flexible and wearable displays, or flexible sensors that can be attached to the human body for health monitoring, for instance.”
The research paper is entitled “Synergistic Electrode Architecture for Efficient Graphene-based Flexible Organic Light-emitting Diodes” (DOI. 10.1038/NCOMMS11791). The lead authors are Jae-Ho Lee, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST; Tae-Hee Han, a Ph.D. researcher at POSTECH; and Min-Ho Park, a Ph.D. candidate at POSTECH.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Center for Advanced Flexible Display (CAFDC) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP); by the Center for Advanced Soft-Electronics funded by the MSIP as a Global Frontier Project; by the Graphene Research Center Program of KAIST; and by grants from the IT R&D Program of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy of Korea (MOTIE).
Figure 1: Application of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows an OLED with the composite structure of TiO2/graphene/conducting polymer electrode in operation. The OLED exhibits 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency. The device prepared on a plastic substrate shown in the right remains intact and operates well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm.
Figure 2: Schematic Device Structure of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows the new architecture to develop highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE).
2016.06.07 View 14266