AT
-
 Industrial Liaison Program to Provide Comprehensive Consultation Services
The ILP’s one-stop solutions target all industrial sectors including conglomerates, small and medium-sized enterprises, venture companies, venture capital (VC) firms, and government-affiliated organizations.
The Industrial Liaison Center at KAIST launched the Industrial Liaison Program (ILP) on September 28, an industry-academic cooperation project to provide comprehensive solutions to industry partners. The Industrial Liaison Center will recruit member companies for this service every year, targeting all industrial sectors including conglomerates, small and medium-sized enterprises, venture companies, venture capital (VC) firms, and government-affiliated organizations.
The program plans to build a one-stop support system that can systematically share and use excellent resource information from KAIST’s research teams, R&D achievements, and infrastructure to provide member companies with much-needed services.
More than 40 KAIST professors with abundant academic-industrial collaboration experience will participate in the program. Experts from various fields with different points of view and experiences will jointly provide solutions to ILP member companies. To actively participate in academic-industrial liaisons and joint consultations, KAIST assigned 10 professors from related fields as program directors.
The program directors will come from four different fields including AI/robots (Professor Alice Oh, School from the School of Computing, Professor Young Jae Jang from the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering, and Professor Yong-Hwa Park from Department of Mechanical Engineering), bio/medicine (Professor Daesoo Kim from Department of Biological Sciences and Professor YongKeun Park from Department of Physics), materials/electronics (Professor Sang Ouk Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professors Jun-Bo Yoon and Seonghwan Cho from the School of Electrical Engineering), and environment/energy (Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Professor Hoon Sohn from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering).
The transdisciplinary board of consulting professors that will lead technology innovation is composed of 30 professors including Professor Min-Soo Kim (School of Computing, AI), Professor Chan Hyuk Kim (Department of Biological Sciences, medicine), Professor Hae-Won Park (Department of Mechanical Engineering, robots), Professor Changho Suh (School of Electrical Engineering, electronics), Professor Haeshin Lee (Department of Chemistry, bio), Professor Il-Doo Kim (Department of Materials Science and Engineering, materials), Professor HyeJin Kim (School of Business Technology and Management), and Professor Byoung Pil Kim (School of Business Technology and Management, technology law)
The Head of the Industrial Liaison Center who is also in charge of the program, Professor Keon Jae Lee, said, “In a science and technology-oriented generation where technological supremacy determines national power, it is indispensable to build a new platform upon which innovative academic-industrial cooperation can be pushed forward in the fields of joint consultation, the development of academic-industrial projects, and the foundation of new industries.
He added, “KAIST professors carry out world-class research in many different fields and faculty members can come together through the ILP to communicate with representatives from industry to improve their corporations’ global competitiveness and further contribute to our nation’s interests by cultivating strong small enterprises
2021.09.30 View 7862
Industrial Liaison Program to Provide Comprehensive Consultation Services
The ILP’s one-stop solutions target all industrial sectors including conglomerates, small and medium-sized enterprises, venture companies, venture capital (VC) firms, and government-affiliated organizations.
The Industrial Liaison Center at KAIST launched the Industrial Liaison Program (ILP) on September 28, an industry-academic cooperation project to provide comprehensive solutions to industry partners. The Industrial Liaison Center will recruit member companies for this service every year, targeting all industrial sectors including conglomerates, small and medium-sized enterprises, venture companies, venture capital (VC) firms, and government-affiliated organizations.
The program plans to build a one-stop support system that can systematically share and use excellent resource information from KAIST’s research teams, R&D achievements, and infrastructure to provide member companies with much-needed services.
More than 40 KAIST professors with abundant academic-industrial collaboration experience will participate in the program. Experts from various fields with different points of view and experiences will jointly provide solutions to ILP member companies. To actively participate in academic-industrial liaisons and joint consultations, KAIST assigned 10 professors from related fields as program directors.
The program directors will come from four different fields including AI/robots (Professor Alice Oh, School from the School of Computing, Professor Young Jae Jang from the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering, and Professor Yong-Hwa Park from Department of Mechanical Engineering), bio/medicine (Professor Daesoo Kim from Department of Biological Sciences and Professor YongKeun Park from Department of Physics), materials/electronics (Professor Sang Ouk Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professors Jun-Bo Yoon and Seonghwan Cho from the School of Electrical Engineering), and environment/energy (Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Professor Hoon Sohn from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering).
The transdisciplinary board of consulting professors that will lead technology innovation is composed of 30 professors including Professor Min-Soo Kim (School of Computing, AI), Professor Chan Hyuk Kim (Department of Biological Sciences, medicine), Professor Hae-Won Park (Department of Mechanical Engineering, robots), Professor Changho Suh (School of Electrical Engineering, electronics), Professor Haeshin Lee (Department of Chemistry, bio), Professor Il-Doo Kim (Department of Materials Science and Engineering, materials), Professor HyeJin Kim (School of Business Technology and Management), and Professor Byoung Pil Kim (School of Business Technology and Management, technology law)
The Head of the Industrial Liaison Center who is also in charge of the program, Professor Keon Jae Lee, said, “In a science and technology-oriented generation where technological supremacy determines national power, it is indispensable to build a new platform upon which innovative academic-industrial cooperation can be pushed forward in the fields of joint consultation, the development of academic-industrial projects, and the foundation of new industries.
He added, “KAIST professors carry out world-class research in many different fields and faculty members can come together through the ILP to communicate with representatives from industry to improve their corporations’ global competitiveness and further contribute to our nation’s interests by cultivating strong small enterprises
2021.09.30 View 7862 -
 Deep Learning Framework to Enable Material Design in Unseen Domain
Researchers propose a deep neural network-based forward design space exploration using active transfer learning and data augmentation
A new study proposed a deep neural network-based forward design approach that enables an efficient search for superior materials far beyond the domain of the initial training set. This approach compensates for the weak predictive power of neural networks on an unseen domain through gradual updates of the neural network with active transfer learning and data augmentation methods.
Professor Seungwha Ryu believes that this study will help address a variety of optimization problems that have an astronomical number of possible design configurations. For the grid composite optimization problem, the proposed framework was able to provide excellent designs close to the global optima, even with the addition of a very small dataset corresponding to less than 0.5% of the initial training data-set size. This study was reported in npj Computational Materials last month.
“We wanted to mitigate the limitation of the neural network, weak predictive power beyond the training set domain for the material or structure design,” said Professor Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Neural network-based generative models have been actively investigated as an inverse design method for finding novel materials in a vast design space. However, the applicability of conventional generative models is limited because they cannot access data outside the range of training sets. Advanced generative models that were devised to overcome this limitation also suffer from weak predictive power for the unseen domain.
Professor Ryu’s team, in collaboration with researchers from Professor Grace Gu’s group at UC Berkeley, devised a design method that simultaneously expands the domain using the strong predictive power of a deep neural network and searches for the optimal design by repetitively performing three key steps.
First, it searches for few candidates with improved properties located close to the training set via genetic algorithms, by mixing superior designs within the training set. Then, it checks to see if the candidates really have improved properties, and expands the training set by duplicating the validated designs via a data augmentation method. Finally, they can expand the reliable prediction domain by updating the neural network with the new superior designs via transfer learning. Because the expansion proceeds along relatively narrow but correct routes toward the optimal design (depicted in the schematic of Fig. 1), the framework enables an efficient search.
As a data-hungry method, a deep neural network model tends to have reliable predictive power only within and near the domain of the training set. When the optimal configuration of materials and structures lies far beyond the initial training set, which frequently is the case, neural network-based design methods suffer from weak predictive power and become inefficient.
Researchers expect that the framework will be applicable for a wide range of optimization problems in other science and engineering disciplines with astronomically large design space, because it provides an efficient way of gradually expanding the reliable prediction domain toward the target design while avoiding the risk of being stuck in local minima. Especially, being a less-data-hungry method, design problems in which data generation is time-consuming and expensive will benefit most from this new framework.
The research team is currently applying the optimization framework for the design task of metamaterial structures, segmented thermoelectric generators, and optimal sensor distributions. “From these sets of on-going studies, we expect to better recognize the pros and cons, and the potential of the suggested algorithm. Ultimately, we want to devise more efficient machine learning-based design approaches,” explained Professor Ryu.This study was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Project.
-Publication
Yongtae Kim, Youngsoo, Charles Yang, Kundo Park, Grace X. Gu, and Seunghwa Ryu, “Deep learning framework for material design space exploration using active transfer learning and data augmentation,” npj Computational Materials (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-021-00609-2)
-Profile
Professor Seunghwa Ryu
Mechanics & Materials Modeling Lab
Department of Mechanical Engineering
KAIST
2021.09.29 View 13539
Deep Learning Framework to Enable Material Design in Unseen Domain
Researchers propose a deep neural network-based forward design space exploration using active transfer learning and data augmentation
A new study proposed a deep neural network-based forward design approach that enables an efficient search for superior materials far beyond the domain of the initial training set. This approach compensates for the weak predictive power of neural networks on an unseen domain through gradual updates of the neural network with active transfer learning and data augmentation methods.
Professor Seungwha Ryu believes that this study will help address a variety of optimization problems that have an astronomical number of possible design configurations. For the grid composite optimization problem, the proposed framework was able to provide excellent designs close to the global optima, even with the addition of a very small dataset corresponding to less than 0.5% of the initial training data-set size. This study was reported in npj Computational Materials last month.
“We wanted to mitigate the limitation of the neural network, weak predictive power beyond the training set domain for the material or structure design,” said Professor Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Neural network-based generative models have been actively investigated as an inverse design method for finding novel materials in a vast design space. However, the applicability of conventional generative models is limited because they cannot access data outside the range of training sets. Advanced generative models that were devised to overcome this limitation also suffer from weak predictive power for the unseen domain.
Professor Ryu’s team, in collaboration with researchers from Professor Grace Gu’s group at UC Berkeley, devised a design method that simultaneously expands the domain using the strong predictive power of a deep neural network and searches for the optimal design by repetitively performing three key steps.
First, it searches for few candidates with improved properties located close to the training set via genetic algorithms, by mixing superior designs within the training set. Then, it checks to see if the candidates really have improved properties, and expands the training set by duplicating the validated designs via a data augmentation method. Finally, they can expand the reliable prediction domain by updating the neural network with the new superior designs via transfer learning. Because the expansion proceeds along relatively narrow but correct routes toward the optimal design (depicted in the schematic of Fig. 1), the framework enables an efficient search.
As a data-hungry method, a deep neural network model tends to have reliable predictive power only within and near the domain of the training set. When the optimal configuration of materials and structures lies far beyond the initial training set, which frequently is the case, neural network-based design methods suffer from weak predictive power and become inefficient.
Researchers expect that the framework will be applicable for a wide range of optimization problems in other science and engineering disciplines with astronomically large design space, because it provides an efficient way of gradually expanding the reliable prediction domain toward the target design while avoiding the risk of being stuck in local minima. Especially, being a less-data-hungry method, design problems in which data generation is time-consuming and expensive will benefit most from this new framework.
The research team is currently applying the optimization framework for the design task of metamaterial structures, segmented thermoelectric generators, and optimal sensor distributions. “From these sets of on-going studies, we expect to better recognize the pros and cons, and the potential of the suggested algorithm. Ultimately, we want to devise more efficient machine learning-based design approaches,” explained Professor Ryu.This study was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Project.
-Publication
Yongtae Kim, Youngsoo, Charles Yang, Kundo Park, Grace X. Gu, and Seunghwa Ryu, “Deep learning framework for material design space exploration using active transfer learning and data augmentation,” npj Computational Materials (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-021-00609-2)
-Profile
Professor Seunghwa Ryu
Mechanics & Materials Modeling Lab
Department of Mechanical Engineering
KAIST
2021.09.29 View 13539 -
 Two Researchers Designated as SUHF Fellows
Professor Taeyun Ku from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and Professor Hanseul Yang from the Department of Biological Sciences were nominated as 2021 fellows of the Suh Kyungbae Foundation (SUHF).
SUHF selected three young promising scientists from 53 researchers who are less than five years into their careers. A panel of judges comprised of scholars from home and abroad made the final selection based on the candidates’ innovativeness and power to influence. Professor You-Bong Hyun from Seoul National University also won the fellowship.
Professor Ku’s main topic is opto-connectomics. He will study ways to visualize the complex brain network using innovative technology that transforms neurons into optical elements.
Professor Yang will research the possibility of helping patients recover from skin diseases or injuries without scars by studying spiny mouse genes.
SUHF was established by Amorepacific Group Chairman Suh Kyungbae in 2016 with 300 billion KRW of his private funds. Under the vision of ‘contributing to humanity by supporting innovative discoveries of bioscience researchers,’ the foundation supports promising Korean scientists who pioneer new fields of research in biological sciences.
From 2017 to this year, SUHF has selected 20 promising scientists in the field of biological sciences. Selected scientists are provided with up to KRW 500 million each year for five years. The foundation has provided a total of KRW 48.5 billion in research funds to date.
2021.09.15 View 9864
Two Researchers Designated as SUHF Fellows
Professor Taeyun Ku from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and Professor Hanseul Yang from the Department of Biological Sciences were nominated as 2021 fellows of the Suh Kyungbae Foundation (SUHF).
SUHF selected three young promising scientists from 53 researchers who are less than five years into their careers. A panel of judges comprised of scholars from home and abroad made the final selection based on the candidates’ innovativeness and power to influence. Professor You-Bong Hyun from Seoul National University also won the fellowship.
Professor Ku’s main topic is opto-connectomics. He will study ways to visualize the complex brain network using innovative technology that transforms neurons into optical elements.
Professor Yang will research the possibility of helping patients recover from skin diseases or injuries without scars by studying spiny mouse genes.
SUHF was established by Amorepacific Group Chairman Suh Kyungbae in 2016 with 300 billion KRW of his private funds. Under the vision of ‘contributing to humanity by supporting innovative discoveries of bioscience researchers,’ the foundation supports promising Korean scientists who pioneer new fields of research in biological sciences.
From 2017 to this year, SUHF has selected 20 promising scientists in the field of biological sciences. Selected scientists are provided with up to KRW 500 million each year for five years. The foundation has provided a total of KRW 48.5 billion in research funds to date.
2021.09.15 View 9864 -
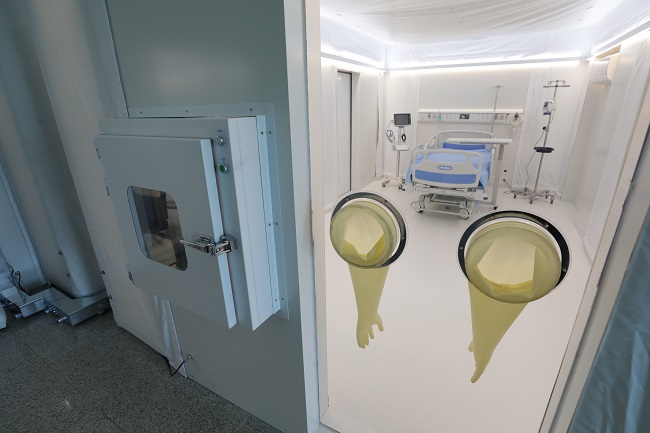 MCM Utilized at Residential Treatment Center in Gyeonggi
The Mobile Clinic Module (MCM) developed by the KAIST Action for Respiratory Epidemics was installed at special residential treatment center in Gyeonggi Province on September 13.
The MCM is an isolate negative pressure unit fitted with high-quality medical equipment, developed by Professor Taek-Jin Nam of the Department of Industrial Design under the KAIST New Deal R&D Initiative. This is also a part of the Korean Disease Control Package Development Project from last July.
In January, a ward with four beds for critical care was installed at the Korea Institute for Radiological & Medical Sciences in Seoul for a trial operation, and two mild cases were treated there. It was also implemented as an isolated negative pressure unit in the Daejeon Konyang University Hospital emergency room in June, and has treated 138 cases since.
The special residential treatment center installed in the Gyeonggi Provincial Academy gymnasium, which consists of 28 beds in 14 rooms (double occupancy) and a multipurpose room (for X-rays and treatment), is to remain open through October 10. Unlike existing treatment centers that have quarantined COVID-19 patients for two weeks, the Gyeonggi MCM will act as a self-treatment-associated short-term treatment center. While in self-treatment, patients showing symptoms requiring special attention will be moved to the MCM, followed by short-term hospitalization of 1-3 days for observation before further measures are taken.
Patients can be treated using the MCM’s own treatment capacities, including in-person and oxygen treatment, X-rays, and IVs. There are individual bathrooms in each room, and the pressure, ventilation, and the automatic opening and closing of the entrance can be centrally monitored and controlled. Patients showing symptoms during treatment will be moved to a specially designated hospital for critical care, and will return to the self-treatment center if no further abnormalities are reported.
The Gyeonggi Provincial Medical Center’s Ansung Hospital will take charge of operating the special treatment center. Each day, one or two doctors, three nurses, two nursing assistants, one administrative staff member, two or three disinfection specialists, and a medical imaging engineer will work in three shifts. There will also be about 20 additional specially designated staff members including KAIST researchers, firefighters, and police officers.
The MCM was internationally recognized as an excellent medical facility not only for its functionality, economic feasibility, and utility, but also for its unique design and aesthetics. It received two Best of Best awards at the Red Dot Award in product design and Communication Design in user interface.
By running this special treatment center, KAIST will conduct research on how to build an optimized model for efficient negative pressure medical units. This research is expected to lead to advances in waste water treatment systems, mobile bathrooms optimized for infectious cases, and MCM user interfaces for electronic devices, etc.
Professor Taek-Jin Nam, the general director of the project and design, said “if there is a gymnasium available, we can convert it into a special treatment center fitted with a waste water treatment system, and pressure equipment in two weeks even without additional infrastructure.”
The head of the KAIST New Deal R&D Initiative Choongsik Bae said, “our MCM research started in July of last year, and in just over a year, it has become a successful and innovative case that has undergone trials and become commercialized in a short period of time.” He added, “In response to COVID-19, KAIST is conducting research and empirical studies, not just in relation to the MCM, but in other areas of disease control as well.”
Based on the excellent disease control technologies developed by KAIST research teams, the KAIST Action for Respiratory Epidemics is conducting technology transfers and industrialization, and is developing a Korean disease control package model
2021.09.15 View 13017
MCM Utilized at Residential Treatment Center in Gyeonggi
The Mobile Clinic Module (MCM) developed by the KAIST Action for Respiratory Epidemics was installed at special residential treatment center in Gyeonggi Province on September 13.
The MCM is an isolate negative pressure unit fitted with high-quality medical equipment, developed by Professor Taek-Jin Nam of the Department of Industrial Design under the KAIST New Deal R&D Initiative. This is also a part of the Korean Disease Control Package Development Project from last July.
In January, a ward with four beds for critical care was installed at the Korea Institute for Radiological & Medical Sciences in Seoul for a trial operation, and two mild cases were treated there. It was also implemented as an isolated negative pressure unit in the Daejeon Konyang University Hospital emergency room in June, and has treated 138 cases since.
The special residential treatment center installed in the Gyeonggi Provincial Academy gymnasium, which consists of 28 beds in 14 rooms (double occupancy) and a multipurpose room (for X-rays and treatment), is to remain open through October 10. Unlike existing treatment centers that have quarantined COVID-19 patients for two weeks, the Gyeonggi MCM will act as a self-treatment-associated short-term treatment center. While in self-treatment, patients showing symptoms requiring special attention will be moved to the MCM, followed by short-term hospitalization of 1-3 days for observation before further measures are taken.
Patients can be treated using the MCM’s own treatment capacities, including in-person and oxygen treatment, X-rays, and IVs. There are individual bathrooms in each room, and the pressure, ventilation, and the automatic opening and closing of the entrance can be centrally monitored and controlled. Patients showing symptoms during treatment will be moved to a specially designated hospital for critical care, and will return to the self-treatment center if no further abnormalities are reported.
The Gyeonggi Provincial Medical Center’s Ansung Hospital will take charge of operating the special treatment center. Each day, one or two doctors, three nurses, two nursing assistants, one administrative staff member, two or three disinfection specialists, and a medical imaging engineer will work in three shifts. There will also be about 20 additional specially designated staff members including KAIST researchers, firefighters, and police officers.
The MCM was internationally recognized as an excellent medical facility not only for its functionality, economic feasibility, and utility, but also for its unique design and aesthetics. It received two Best of Best awards at the Red Dot Award in product design and Communication Design in user interface.
By running this special treatment center, KAIST will conduct research on how to build an optimized model for efficient negative pressure medical units. This research is expected to lead to advances in waste water treatment systems, mobile bathrooms optimized for infectious cases, and MCM user interfaces for electronic devices, etc.
Professor Taek-Jin Nam, the general director of the project and design, said “if there is a gymnasium available, we can convert it into a special treatment center fitted with a waste water treatment system, and pressure equipment in two weeks even without additional infrastructure.”
The head of the KAIST New Deal R&D Initiative Choongsik Bae said, “our MCM research started in July of last year, and in just over a year, it has become a successful and innovative case that has undergone trials and become commercialized in a short period of time.” He added, “In response to COVID-19, KAIST is conducting research and empirical studies, not just in relation to the MCM, but in other areas of disease control as well.”
Based on the excellent disease control technologies developed by KAIST research teams, the KAIST Action for Respiratory Epidemics is conducting technology transfers and industrialization, and is developing a Korean disease control package model
2021.09.15 View 13017 -
 Genomic Data Reveals New Insights into Human Embryonic Development
KAIST researchers have used whole-genome sequencing to track the development from a single fertilized-egg to a human body
Genomic scientists at KAIST have revealed new insights into the process of human embryonic development using large-scale, whole-genome sequencing of cells and tissues from adult humans. The study, published in Nature on Aug.25, is the first to analyse somatic mutations in normal tissue across multiple organs within and between humans.
An adult human body comprises trillions of cells of more than 200 types. How a human develops from a single fertilized egg to a fully grown adult is a fundamental question in biomedical science. Due to the ethical challenges of performing studies on human embryos, however, the details of this process remain largely unknown.
To overcome these issues, the research team took a different approach. They analysed genetic mutations in cells taken from adult human post-mortem tissue. Specifically, they identified mutations that occur spontaneously in early developmental cell divisions. These mutations, also called genomic scars, act like unique genetic fingerprints that can be used to trace the embryonic development process.
The study, which looked at 334 single-cell colonies and 379 tissue samples from seven recently deceased human body donors, is the largest single-cell, whole-genome analysis carried out to date. The researchers examined the genomic scars of each individual in order to reconstruct their early embryonic cellular dynamics.
The result revealed several key characteristics of the human embryonic development process. Firstly, mutation rates are higher in the first cell division, but then decrease to approximately one mutation per cell during later cell division. Secondly, early cells contributed unequally to the development of the embryo in all informative donors, for example, at the two-cell stage, one of the cells always left more progeny cells than the other. The ratio of this was different from person to person, implying that the process varies between individuals and is not fully deterministic.
The researchers were also able to deduce the timing of when cells begin to differentiate into individual organ-specific cells. They found that within three days of fertilization, embryonic cells began to be distributed asymmetrically into tissues for the left and right sides of the body, followed by differentiation into three germ layers, and then differentiation into specific tissues and organs.
“It is an impressive scientific achievement that, within 20 years of the completion of human genome project, genomic technology has advanced to the extent that we are now able to accurately identify mutations in a single-cell genome,” said Professor Young Seok Ju from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST. “This technology will enable us to track human embryogenesis at even higher resolutions in the future.”
The techniques used in this study could be used to improve our understanding of rare diseases caused by abnormalities in embryonic development, and to design new precision diagnostics and treatments for patients.
The research was completed in collaboration with Kyungpook National University Hospital, the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information, Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Genome Insights Inc, and Immune Square Inc. This work was supported by the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea, the National Research Foundastion of Korea.
-PublicationSeongyeol Park, Nanda Mali, Ryul Kim et al. ‘Clonal dynamics in early human embryogenesis inferred from somatic mutation’ Nature Online ahead of print, Aug. 25, 2021 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03786-8)
-ProfileProfessor Young Seok JuLab of Cancer Genomics (https://www.julab.kaist.ac.kr/)Graduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2021.08.31 View 10247
Genomic Data Reveals New Insights into Human Embryonic Development
KAIST researchers have used whole-genome sequencing to track the development from a single fertilized-egg to a human body
Genomic scientists at KAIST have revealed new insights into the process of human embryonic development using large-scale, whole-genome sequencing of cells and tissues from adult humans. The study, published in Nature on Aug.25, is the first to analyse somatic mutations in normal tissue across multiple organs within and between humans.
An adult human body comprises trillions of cells of more than 200 types. How a human develops from a single fertilized egg to a fully grown adult is a fundamental question in biomedical science. Due to the ethical challenges of performing studies on human embryos, however, the details of this process remain largely unknown.
To overcome these issues, the research team took a different approach. They analysed genetic mutations in cells taken from adult human post-mortem tissue. Specifically, they identified mutations that occur spontaneously in early developmental cell divisions. These mutations, also called genomic scars, act like unique genetic fingerprints that can be used to trace the embryonic development process.
The study, which looked at 334 single-cell colonies and 379 tissue samples from seven recently deceased human body donors, is the largest single-cell, whole-genome analysis carried out to date. The researchers examined the genomic scars of each individual in order to reconstruct their early embryonic cellular dynamics.
The result revealed several key characteristics of the human embryonic development process. Firstly, mutation rates are higher in the first cell division, but then decrease to approximately one mutation per cell during later cell division. Secondly, early cells contributed unequally to the development of the embryo in all informative donors, for example, at the two-cell stage, one of the cells always left more progeny cells than the other. The ratio of this was different from person to person, implying that the process varies between individuals and is not fully deterministic.
The researchers were also able to deduce the timing of when cells begin to differentiate into individual organ-specific cells. They found that within three days of fertilization, embryonic cells began to be distributed asymmetrically into tissues for the left and right sides of the body, followed by differentiation into three germ layers, and then differentiation into specific tissues and organs.
“It is an impressive scientific achievement that, within 20 years of the completion of human genome project, genomic technology has advanced to the extent that we are now able to accurately identify mutations in a single-cell genome,” said Professor Young Seok Ju from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST. “This technology will enable us to track human embryogenesis at even higher resolutions in the future.”
The techniques used in this study could be used to improve our understanding of rare diseases caused by abnormalities in embryonic development, and to design new precision diagnostics and treatments for patients.
The research was completed in collaboration with Kyungpook National University Hospital, the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information, Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Genome Insights Inc, and Immune Square Inc. This work was supported by the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea, the National Research Foundastion of Korea.
-PublicationSeongyeol Park, Nanda Mali, Ryul Kim et al. ‘Clonal dynamics in early human embryogenesis inferred from somatic mutation’ Nature Online ahead of print, Aug. 25, 2021 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03786-8)
-ProfileProfessor Young Seok JuLab of Cancer Genomics (https://www.julab.kaist.ac.kr/)Graduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2021.08.31 View 10247 -
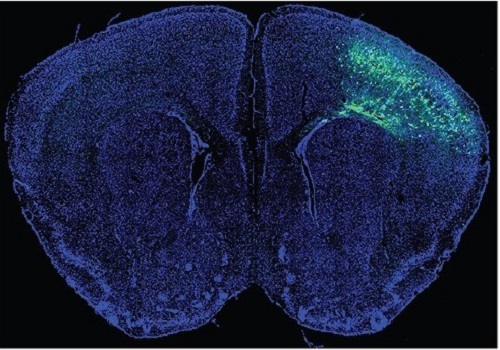 A Mechanism Underlying Most Common Cause of Epileptic Seizures Revealed
An interdisciplinary study shows that neurons carrying somatic mutations in MTOR can lead to focal epileptogenesis via non-cell-autonomous hyperexcitability of nearby nonmutated neurons
During fetal development, cells should migrate to the outer edge of the brain to form critical connections for information transfer and regulation in the body. When even a few cells fail to move to the correct location, the neurons become disorganized and this results in focal cortical dysplasia. This condition is the most common cause of seizures that cannot be controlled with medication in children and the second most common cause in adults.
Now, an interdisciplinary team studying neurogenetics, neural networks, and neurophysiology at KAIST has revealed how dysfunctions in even a small percentage of cells can cause disorder across the entire brain. They published their results on June 28 in Annals of Neurology.
The work builds on a previous finding, also by a KAIST scientists, who found that focal cortical dysplasia was caused by mutations in the cells involved in mTOR, a pathway that regulates signaling between neurons in the brain.
“Only 1 to 2% of neurons carrying mutations in the mTOR signaling pathway that regulates cell signaling in the brain have been found to include seizures in animal models of focal cortical dysplasia,” said Professor Jong-Woo Sohn from the Department of Biological Sciences. “The main challenge of this study was to explain how nearby non-mutated neurons are hyperexcitable.”
Initially, the researchers hypothesized that the mutated cells affected the number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in all neurons, mutated or not. These neural gates can trigger or halt activity, respectively, in other neurons. Seizures are a result of extreme activity, called hyperexcitability. If the mutated cells upend the balance and result in more excitatory cells, the researchers thought, it made sense that the cells would be more susceptible to hyperexcitability and, as a result, seizures.
“Contrary to our expectations, the synaptic input balance was not changed in either the mutated or non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. “We turned our attention to a protein overproduced by mutated neurons.”
The protein is adenosine kinase, which lowers the concentration of adenosine. This naturally occurring compound is an anticonvulsant and works to relax vessels. In mice engineered to have focal cortical dysplasia, the researchers injected adenosine to replace the levels lowered by the protein. It worked and the neurons became less excitable.
“We demonstrated that augmentation of adenosine signaling could attenuate the excitability of non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering.
The effect on the non-mutated neurons was the surprising part, according to Paik. “The seizure-triggering hyperexcitability originated not in the mutation-carrying neurons, but instead in the nearby non-mutated neurons,” he said.
The mutated neurons excreted more adenosine kinase, reducing the adenosine levels in the local environment of all the cells. With less adenosine, the non-mutated neurons became hyperexcitable, leading to seizures.
“While we need further investigate into the relationship between the concentration of adenosine and the increased excitation of nearby neurons, our results support the medical use of drugs to activate adenosine signaling as a possible treatment pathway for focal cortical dysplasia,” Professor Lee said.
The Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Korea Health Technology Research and Development Project, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation in Korea funded this work.
-Publication:Koh, H.Y., Jang, J., Ju, S.H., Kim, R., Cho, G.-B., Kim, D.S., Sohn, J.-W., Paik, S.-B. and Lee, J.H. (2021), ‘Non–Cell Autonomous Epileptogenesis in Focal Cortical Dysplasia’ Annals of Neurology, 90: 285 299. (https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26149)
-ProfileProfessor Jeong Ho Lee Translational Neurogenetics Labhttps://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/ Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering KAIST
Professor Se-Bum Paik Visual System and Neural Network Laboratory http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/ Department of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Jong-Woo Sohn Laboratory for Neurophysiology, https://sites.google.com/site/sohnlab2014/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
Dr. Hyun Yong Koh Translational Neurogenetics LabGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
Dr. Jaeson Jang Ph.D.Visual System and Neural Network LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST
Sang Hyeon Ju M.D.Laboratory for NeurophysiologyDepartment of Biological SciencesKAIST
2021.08.26 View 14979
A Mechanism Underlying Most Common Cause of Epileptic Seizures Revealed
An interdisciplinary study shows that neurons carrying somatic mutations in MTOR can lead to focal epileptogenesis via non-cell-autonomous hyperexcitability of nearby nonmutated neurons
During fetal development, cells should migrate to the outer edge of the brain to form critical connections for information transfer and regulation in the body. When even a few cells fail to move to the correct location, the neurons become disorganized and this results in focal cortical dysplasia. This condition is the most common cause of seizures that cannot be controlled with medication in children and the second most common cause in adults.
Now, an interdisciplinary team studying neurogenetics, neural networks, and neurophysiology at KAIST has revealed how dysfunctions in even a small percentage of cells can cause disorder across the entire brain. They published their results on June 28 in Annals of Neurology.
The work builds on a previous finding, also by a KAIST scientists, who found that focal cortical dysplasia was caused by mutations in the cells involved in mTOR, a pathway that regulates signaling between neurons in the brain.
“Only 1 to 2% of neurons carrying mutations in the mTOR signaling pathway that regulates cell signaling in the brain have been found to include seizures in animal models of focal cortical dysplasia,” said Professor Jong-Woo Sohn from the Department of Biological Sciences. “The main challenge of this study was to explain how nearby non-mutated neurons are hyperexcitable.”
Initially, the researchers hypothesized that the mutated cells affected the number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in all neurons, mutated or not. These neural gates can trigger or halt activity, respectively, in other neurons. Seizures are a result of extreme activity, called hyperexcitability. If the mutated cells upend the balance and result in more excitatory cells, the researchers thought, it made sense that the cells would be more susceptible to hyperexcitability and, as a result, seizures.
“Contrary to our expectations, the synaptic input balance was not changed in either the mutated or non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. “We turned our attention to a protein overproduced by mutated neurons.”
The protein is adenosine kinase, which lowers the concentration of adenosine. This naturally occurring compound is an anticonvulsant and works to relax vessels. In mice engineered to have focal cortical dysplasia, the researchers injected adenosine to replace the levels lowered by the protein. It worked and the neurons became less excitable.
“We demonstrated that augmentation of adenosine signaling could attenuate the excitability of non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering.
The effect on the non-mutated neurons was the surprising part, according to Paik. “The seizure-triggering hyperexcitability originated not in the mutation-carrying neurons, but instead in the nearby non-mutated neurons,” he said.
The mutated neurons excreted more adenosine kinase, reducing the adenosine levels in the local environment of all the cells. With less adenosine, the non-mutated neurons became hyperexcitable, leading to seizures.
“While we need further investigate into the relationship between the concentration of adenosine and the increased excitation of nearby neurons, our results support the medical use of drugs to activate adenosine signaling as a possible treatment pathway for focal cortical dysplasia,” Professor Lee said.
The Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Korea Health Technology Research and Development Project, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation in Korea funded this work.
-Publication:Koh, H.Y., Jang, J., Ju, S.H., Kim, R., Cho, G.-B., Kim, D.S., Sohn, J.-W., Paik, S.-B. and Lee, J.H. (2021), ‘Non–Cell Autonomous Epileptogenesis in Focal Cortical Dysplasia’ Annals of Neurology, 90: 285 299. (https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26149)
-ProfileProfessor Jeong Ho Lee Translational Neurogenetics Labhttps://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/ Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering KAIST
Professor Se-Bum Paik Visual System and Neural Network Laboratory http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/ Department of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Jong-Woo Sohn Laboratory for Neurophysiology, https://sites.google.com/site/sohnlab2014/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
Dr. Hyun Yong Koh Translational Neurogenetics LabGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
Dr. Jaeson Jang Ph.D.Visual System and Neural Network LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST
Sang Hyeon Ju M.D.Laboratory for NeurophysiologyDepartment of Biological SciencesKAIST
2021.08.26 View 14979 -
 KAIST KPC4IR Presents the AI Global Guide for Healthcare
The benchmark for the responsible usage of AI technology in the healthcare sector will promote clarity and high standards for technological applications
The KAIST Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) published 'Using AI to Support Healthcare Decisions: A Guide for Society.' This global guide is designed to serve as a benchmark for the responsible usage of AI technologies, and will promote clarity and high standards for technological applications in the healthcare sector. The guide details what should be considered when making clinical decisions to help reduce the chances of the AI giving false or misleading results.
The KPC4IR presented the guide in collaboration with the Lloyd’s Register Foundation Institute for the Public Understanding of Risk at the National University of Singapore (NUS IPUR) and Sense about Science, a non-profit organization in the UK specialized in science communication, during the 2021 SIG-KDD (Special Interest Group on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining) Conference on August 15.
AI technology is being widely used in the healthcare sector and has already proved its accuracy and efficiency in diagnosing and predicting diseases. Despite its huge impact on our daily lives in every sector of society, AI technology has some drawbacks and comes with risks, especially due to biased algorithms.
“We focused on the ‘reliability’ of AI applications in the healthcare sector to make all data well represented, in good quality. The technology will eventually innovate to better serve the people’s new demand, especially critical demands for safety and precision in healthcare services. This global guide will help both developers and people’s understanding of the appropriate technology applications,” says Director So Young Kim at the KPC4IR.
The guide, for instance, says that to scrutinize quality and reliability, the source of the data must be clearly known; the data must have been collected or selected for the purpose it’s being used for; the limitations and assumptions for that purpose have been clearly stated; the biases have been addressed; and it has been properly tested in the real world. It also reflects the importance of the representativeness of data that will affect the accuracy of the AI applications.
“By being transparent and demonstrating the steps taken to check that the AI is reliable, researchers and developers can help give people confidence about providing their data,” the guide states.
For this guide, the KPC4IR and its collaborators collected data after working with numerous experts from the Graduate School of AI at KAIST, the Science and Technology Policy Institute in Korea, Asan Medical Center in Seoul, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, and AI solution companies.
2021.08.17 View 9465
KAIST KPC4IR Presents the AI Global Guide for Healthcare
The benchmark for the responsible usage of AI technology in the healthcare sector will promote clarity and high standards for technological applications
The KAIST Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) published 'Using AI to Support Healthcare Decisions: A Guide for Society.' This global guide is designed to serve as a benchmark for the responsible usage of AI technologies, and will promote clarity and high standards for technological applications in the healthcare sector. The guide details what should be considered when making clinical decisions to help reduce the chances of the AI giving false or misleading results.
The KPC4IR presented the guide in collaboration with the Lloyd’s Register Foundation Institute for the Public Understanding of Risk at the National University of Singapore (NUS IPUR) and Sense about Science, a non-profit organization in the UK specialized in science communication, during the 2021 SIG-KDD (Special Interest Group on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining) Conference on August 15.
AI technology is being widely used in the healthcare sector and has already proved its accuracy and efficiency in diagnosing and predicting diseases. Despite its huge impact on our daily lives in every sector of society, AI technology has some drawbacks and comes with risks, especially due to biased algorithms.
“We focused on the ‘reliability’ of AI applications in the healthcare sector to make all data well represented, in good quality. The technology will eventually innovate to better serve the people’s new demand, especially critical demands for safety and precision in healthcare services. This global guide will help both developers and people’s understanding of the appropriate technology applications,” says Director So Young Kim at the KPC4IR.
The guide, for instance, says that to scrutinize quality and reliability, the source of the data must be clearly known; the data must have been collected or selected for the purpose it’s being used for; the limitations and assumptions for that purpose have been clearly stated; the biases have been addressed; and it has been properly tested in the real world. It also reflects the importance of the representativeness of data that will affect the accuracy of the AI applications.
“By being transparent and demonstrating the steps taken to check that the AI is reliable, researchers and developers can help give people confidence about providing their data,” the guide states.
For this guide, the KPC4IR and its collaborators collected data after working with numerous experts from the Graduate School of AI at KAIST, the Science and Technology Policy Institute in Korea, Asan Medical Center in Seoul, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, and AI solution companies.
2021.08.17 View 9465 -
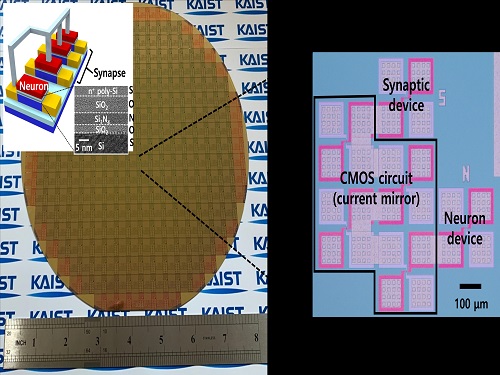 Brain-Inspired Highly Scalable Neuromorphic Hardware Presented
Neurons and synapses based on single transistor can dramatically reduce the hardware cost and accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware
KAIST researchers fabricated a brain-inspired highly scalable neuromorphic hardware by co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses. Using standard silicon complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, the neuromorphic hardware is expected to reduce chip cost and simplify fabrication procedures.
The research team led by Yang-Kyu Choi and Sung-Yool Choi produced a neurons and synapses based on single transistor for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware and showed the ability to recognize text and face images. This research was featured in Science Advances on August 4.
Neuromorphic hardware has attracted a great deal of attention because of its artificial intelligence functions, but consuming ultra-low power of less than 20 watts by mimicking the human brain. To make neuromorphic hardware work, a neuron that generates a spike when integrating a certain signal, and a synapse remembering the connection between two neurons are necessary, just like the biological brain. However, since neurons and synapses constructed on digital or analog circuits occupy a large space, there is a limit in terms of hardware efficiency and costs. Since the human brain consists of about 1011 neurons and 1014 synapses, it is necessary to improve the hardware cost in order to apply it to mobile and IoT devices.
To solve the problem, the research team mimicked the behavior of biological neurons and synapses with a single transistor, and co-integrated them onto an 8-inch wafer. The manufactured neuromorphic transistors have the same structure as the transistors for memory and logic that are currently mass-produced. In addition, the neuromorphic transistors proved for the first time that they can be implemented with a ‘Janus structure’ that functions as both neuron and synapse, just like coins have heads and tails.
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi said that this work can dramatically reduce the hardware cost by replacing the neurons and synapses that were based on complex digital and analog circuits with a single transistor. "We have demonstrated that neurons and synapses can be implemented using a single transistor," said Joon-Kyu Han, the first author. "By co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses on the same wafer using a standard CMOS process, the hardware cost of the neuromorphic hardware has been improved, which will accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware,” Han added.This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) and IC Design Education Center (IDEC).
-PublicationJoon-Kyu Han, Sung-Yool Choi, Yang-Kyu Choi, et al.“Cointegration of single-transistor neurons and synapses by nanoscale CMOS fabrication for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware,” Science Advances (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg8836)
-ProfileProfessor Yang-Kyu ChoiNano-Oriented Bio-Electronics Labhttps://sites.google.com/view/nobelab/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
Professor Sung-Yool ChoiMolecular and Nano Device Laboratoryhttps://www.mndl.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.08.05 View 12505
Brain-Inspired Highly Scalable Neuromorphic Hardware Presented
Neurons and synapses based on single transistor can dramatically reduce the hardware cost and accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware
KAIST researchers fabricated a brain-inspired highly scalable neuromorphic hardware by co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses. Using standard silicon complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, the neuromorphic hardware is expected to reduce chip cost and simplify fabrication procedures.
The research team led by Yang-Kyu Choi and Sung-Yool Choi produced a neurons and synapses based on single transistor for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware and showed the ability to recognize text and face images. This research was featured in Science Advances on August 4.
Neuromorphic hardware has attracted a great deal of attention because of its artificial intelligence functions, but consuming ultra-low power of less than 20 watts by mimicking the human brain. To make neuromorphic hardware work, a neuron that generates a spike when integrating a certain signal, and a synapse remembering the connection between two neurons are necessary, just like the biological brain. However, since neurons and synapses constructed on digital or analog circuits occupy a large space, there is a limit in terms of hardware efficiency and costs. Since the human brain consists of about 1011 neurons and 1014 synapses, it is necessary to improve the hardware cost in order to apply it to mobile and IoT devices.
To solve the problem, the research team mimicked the behavior of biological neurons and synapses with a single transistor, and co-integrated them onto an 8-inch wafer. The manufactured neuromorphic transistors have the same structure as the transistors for memory and logic that are currently mass-produced. In addition, the neuromorphic transistors proved for the first time that they can be implemented with a ‘Janus structure’ that functions as both neuron and synapse, just like coins have heads and tails.
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi said that this work can dramatically reduce the hardware cost by replacing the neurons and synapses that were based on complex digital and analog circuits with a single transistor. "We have demonstrated that neurons and synapses can be implemented using a single transistor," said Joon-Kyu Han, the first author. "By co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses on the same wafer using a standard CMOS process, the hardware cost of the neuromorphic hardware has been improved, which will accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware,” Han added.This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) and IC Design Education Center (IDEC).
-PublicationJoon-Kyu Han, Sung-Yool Choi, Yang-Kyu Choi, et al.“Cointegration of single-transistor neurons and synapses by nanoscale CMOS fabrication for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware,” Science Advances (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg8836)
-ProfileProfessor Yang-Kyu ChoiNano-Oriented Bio-Electronics Labhttps://sites.google.com/view/nobelab/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
Professor Sung-Yool ChoiMolecular and Nano Device Laboratoryhttps://www.mndl.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.08.05 View 12505 -
 KPC4IR Helping to Create Global Standards for Virtual Transactions
KPC4IR will join the task force for the Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards
The KAIST Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will participate in a global initiative to create global standards for virtual asset transactions. As a member of the GI-TRUST (Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards) task force, the KPC4IR will develop technical standards and relevant policies that support the global implementation of the travel rule for virtual assets in compliance with the recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF).
The FATF is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1989 by the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering. In June 2019, the FATF extended its Recommendation 16, commonly known as the “travel rule,” to virtual asset services providers (VASPs), requiring both financial institutions and VASPs to aggregate information on the senders and recipients of wire transfers and exchange this information between parties to create a suitable audit trail.
According to the FATF’s recommendation and the G20’s support, jurisdictions, especially G20 member countries, have now applied the travel rule to their respective local laws. Korea also amended the Act on Reporting and Using Specified Financial Transaction Information in March 2020 to include virtual assets in their regulatory scope by March 2022.
The GI-TRUST task force will collaborate with global and local organizations developing travel rule technologies and offer a neutral assessment of proposed solutions. Their activities are aimed at standardizing related authentication protocols and security technologies that help VASPs comply with the travel rule.
The task force will also aid in the pilot testing of travel rule solutions for certain VASPs in Korea. Afterwards, the task force will report on the performance and reliability of the tested travel rule solutions for actual virtual asset transactions, in compliance with the FATF’s guidance.
Besides the KPC4IR, the GI-TRUST task force includes the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC), International Digital Asset Exchange Association (IDAXA), and Korea Blockchain Association (KBCA).
Director of the KPC4IR Professor So Young Kim will co-chair the task force. Professor Kim said their approach should be prudential in dealing with the regulations that rely on secure real-name data on top of the opposing governance style of pseudonymization, distribution, and recombination.
She explained, “KAIST has designed the co-evolution of technologies and institutions in conjunction with the global leaders’ groups such as the World Economic Forum and the EC Joint Research Center.”
She expects KAIST’s interdisciplinary, global cooperation to untie the entangled problem between regulations and technologies that obstruct future pathways.
2021.07.30 View 10038
KPC4IR Helping to Create Global Standards for Virtual Transactions
KPC4IR will join the task force for the Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards
The KAIST Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will participate in a global initiative to create global standards for virtual asset transactions. As a member of the GI-TRUST (Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards) task force, the KPC4IR will develop technical standards and relevant policies that support the global implementation of the travel rule for virtual assets in compliance with the recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF).
The FATF is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1989 by the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering. In June 2019, the FATF extended its Recommendation 16, commonly known as the “travel rule,” to virtual asset services providers (VASPs), requiring both financial institutions and VASPs to aggregate information on the senders and recipients of wire transfers and exchange this information between parties to create a suitable audit trail.
According to the FATF’s recommendation and the G20’s support, jurisdictions, especially G20 member countries, have now applied the travel rule to their respective local laws. Korea also amended the Act on Reporting and Using Specified Financial Transaction Information in March 2020 to include virtual assets in their regulatory scope by March 2022.
The GI-TRUST task force will collaborate with global and local organizations developing travel rule technologies and offer a neutral assessment of proposed solutions. Their activities are aimed at standardizing related authentication protocols and security technologies that help VASPs comply with the travel rule.
The task force will also aid in the pilot testing of travel rule solutions for certain VASPs in Korea. Afterwards, the task force will report on the performance and reliability of the tested travel rule solutions for actual virtual asset transactions, in compliance with the FATF’s guidance.
Besides the KPC4IR, the GI-TRUST task force includes the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC), International Digital Asset Exchange Association (IDAXA), and Korea Blockchain Association (KBCA).
Director of the KPC4IR Professor So Young Kim will co-chair the task force. Professor Kim said their approach should be prudential in dealing with the regulations that rely on secure real-name data on top of the opposing governance style of pseudonymization, distribution, and recombination.
She explained, “KAIST has designed the co-evolution of technologies and institutions in conjunction with the global leaders’ groups such as the World Economic Forum and the EC Joint Research Center.”
She expects KAIST’s interdisciplinary, global cooperation to untie the entangled problem between regulations and technologies that obstruct future pathways.
2021.07.30 View 10038 -
 3D Visualization and Quantification of Bioplastic PHA in a Living Bacterial Cell
3D holographic microscopy leads to in-depth analysis of bacterial cells accumulating the bacterial bioplastic, polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)
A research team at KAIST has observed how bioplastic granule is being accumulated in living bacteria cells through 3D holographic microscopy. Their 3D imaging and quantitative analysis of the bioplastic ‘polyhydroxyalkanoate’ (PHA) via optical diffraction tomography provides insights into biosynthesizing sustainable substitutes for petroleum-based plastics.
The bio-degradable polyester polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) is being touted as an eco-friendly bioplastic to replace existing synthetic plastics. While carrying similar properties to general-purpose plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene, PHA can be used in various industrial applications such as container packaging and disposable products.
PHA is synthesized by numerous bacteria as an energy and carbon storage material under unbalanced growth conditions in the presence of excess carbon sources. PHA exists in the form of insoluble granules in the cytoplasm. Previous studies on investigating in vivo PHA granules have been performed by using fluorescence microscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and electron cryotomography.
These techniques have generally relied on the statistical analysis of multiple 2D snapshots of fixed cells or the short-time monitoring of the cells. For the TEM analysis, cells need to be fixed and sectioned, and thus the investigation of living cells was not possible. Fluorescence-based techniques require fluorescence labeling or dye staining. Thus, indirect imaging with the use of reporter proteins cannot show the native state of PHAs or cells, and invasive exogenous dyes can affect the physiology and viability of the cells. Therefore, it was difficult to fully understand the formation of PHA granules in cells due to the technical limitations, and thus several mechanism models based on the observations have been only proposed.
The team of metabolic engineering researchers led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee and Physics Professor YongKeun Park, who established the startup Tomocube with his 3D holographic microscopy, reported the results of 3D quantitative label-free analysis of PHA granules in individual live bacterial cells by measuring the refractive index distributions using optical diffraction tomography. The formation and growth of PHA granules in the cells of Cupriavidus necator, the most-studied native PHA (specifically, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), also known as PHB) producer, and recombinant Escherichia coli harboring C. necator PHB biosynthesis pathway were comparatively examined.
From the reconstructed 3D refractive index distribution of the cells, the team succeeded in the 3D visualization and quantitative analysis of cells and intracellular PHA granules at a single-cell level. In particular, the team newly presented the concept of “in vivo PHA granule density.” Through the statistical analysis of hundreds of single cells accumulating PHA granules, the distinctive differences of density and localization of PHA granules in the two micro-organisms were found. Furthermore, the team identified the key protein that plays a major role in making the difference that enabled the characteristics of PHA granules in the recombinant E. coli to become similar to those of C. necator.
The research team also presented 3D time-lapse movies showing the actual processes of PHA granule formation combined with cell growth and division. Movies showing the living cells synthesizing and accumulating PHA granules in their native state had never been reported before.
Professor Lee said, “This study provides insights into the morphological and physical characteristics of in vivo PHA as well as the unique mechanisms of PHA granule formation that undergo the phase transition from soluble monomers into the insoluble polymer, followed by granule formation. Through this study, a deeper understanding of PHA granule formation within the bacterial cells is now possible, which has great significance in that a convergence study of biology and physics was achieved. This study will help develop various bioplastics production processes in the future.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (Grants NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program (Grant No. 2021M3A9I4022740) from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea to S.Y.L. This work was also supported by the KAIST Cross-Generation Collaborative Laboratory project.
-PublicationSo Young Choi, Jeonghun Oh, JaeHwang Jung, YongKeun Park, and Sang Yup Lee. Three-dimensional label-free visualization and quantification of polyhydroxyalkanoates in individualbacterial cell in its native state. PNAS(https://doi.org./10.1073/pnas.2103956118)
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic Engineering and Synthetic Biologyhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering KAIST
Endowed Chair Professor YongKeun ParkBiomedical Optics Laboratoryhttps://bmokaist.wordpress.com/
Department of PhysicsKAIST
2021.07.28 View 15315
3D Visualization and Quantification of Bioplastic PHA in a Living Bacterial Cell
3D holographic microscopy leads to in-depth analysis of bacterial cells accumulating the bacterial bioplastic, polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)
A research team at KAIST has observed how bioplastic granule is being accumulated in living bacteria cells through 3D holographic microscopy. Their 3D imaging and quantitative analysis of the bioplastic ‘polyhydroxyalkanoate’ (PHA) via optical diffraction tomography provides insights into biosynthesizing sustainable substitutes for petroleum-based plastics.
The bio-degradable polyester polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) is being touted as an eco-friendly bioplastic to replace existing synthetic plastics. While carrying similar properties to general-purpose plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene, PHA can be used in various industrial applications such as container packaging and disposable products.
PHA is synthesized by numerous bacteria as an energy and carbon storage material under unbalanced growth conditions in the presence of excess carbon sources. PHA exists in the form of insoluble granules in the cytoplasm. Previous studies on investigating in vivo PHA granules have been performed by using fluorescence microscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and electron cryotomography.
These techniques have generally relied on the statistical analysis of multiple 2D snapshots of fixed cells or the short-time monitoring of the cells. For the TEM analysis, cells need to be fixed and sectioned, and thus the investigation of living cells was not possible. Fluorescence-based techniques require fluorescence labeling or dye staining. Thus, indirect imaging with the use of reporter proteins cannot show the native state of PHAs or cells, and invasive exogenous dyes can affect the physiology and viability of the cells. Therefore, it was difficult to fully understand the formation of PHA granules in cells due to the technical limitations, and thus several mechanism models based on the observations have been only proposed.
The team of metabolic engineering researchers led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee and Physics Professor YongKeun Park, who established the startup Tomocube with his 3D holographic microscopy, reported the results of 3D quantitative label-free analysis of PHA granules in individual live bacterial cells by measuring the refractive index distributions using optical diffraction tomography. The formation and growth of PHA granules in the cells of Cupriavidus necator, the most-studied native PHA (specifically, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), also known as PHB) producer, and recombinant Escherichia coli harboring C. necator PHB biosynthesis pathway were comparatively examined.
From the reconstructed 3D refractive index distribution of the cells, the team succeeded in the 3D visualization and quantitative analysis of cells and intracellular PHA granules at a single-cell level. In particular, the team newly presented the concept of “in vivo PHA granule density.” Through the statistical analysis of hundreds of single cells accumulating PHA granules, the distinctive differences of density and localization of PHA granules in the two micro-organisms were found. Furthermore, the team identified the key protein that plays a major role in making the difference that enabled the characteristics of PHA granules in the recombinant E. coli to become similar to those of C. necator.
The research team also presented 3D time-lapse movies showing the actual processes of PHA granule formation combined with cell growth and division. Movies showing the living cells synthesizing and accumulating PHA granules in their native state had never been reported before.
Professor Lee said, “This study provides insights into the morphological and physical characteristics of in vivo PHA as well as the unique mechanisms of PHA granule formation that undergo the phase transition from soluble monomers into the insoluble polymer, followed by granule formation. Through this study, a deeper understanding of PHA granule formation within the bacterial cells is now possible, which has great significance in that a convergence study of biology and physics was achieved. This study will help develop various bioplastics production processes in the future.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (Grants NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program (Grant No. 2021M3A9I4022740) from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea to S.Y.L. This work was also supported by the KAIST Cross-Generation Collaborative Laboratory project.
-PublicationSo Young Choi, Jeonghun Oh, JaeHwang Jung, YongKeun Park, and Sang Yup Lee. Three-dimensional label-free visualization and quantification of polyhydroxyalkanoates in individualbacterial cell in its native state. PNAS(https://doi.org./10.1073/pnas.2103956118)
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic Engineering and Synthetic Biologyhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering KAIST
Endowed Chair Professor YongKeun ParkBiomedical Optics Laboratoryhttps://bmokaist.wordpress.com/
Department of PhysicsKAIST
2021.07.28 View 15315 -
 Prof. Changho Suh Named the 2021 James L. Massey Awardee
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering was named the recipient of the 2021 James L.Massey Award. The award recognizes outstanding achievement in research and teaching by young scholars in the information theory community. The award is named in honor of James L. Massey, who was an internationally acclaimed pioneer in digital communications and revered teacher and mentor to communications engineers.
Professor Suh is a recipient of numerous awards, including the 2021 James L. Massey Research & Teaching Award for Young Scholars from the IEEE Information Theory Society, the 2019 AFOSR Grant, the 2019 Google Education Grant, the 2018 IEIE/IEEE Joint Award, the 2015 IEIE Haedong Young Engineer Award, the 2013 IEEE Communications Society Stephen O. Rice Prize, the 2011 David J. Sakrison Memorial Prize (the best dissertation award in UC Berkeley EECS), the 2009 IEEE ISIT Best Student Paper Award, the 2020 LINKGENESIS Best Teacher Award (the campus-wide Grand Prize in Teaching), and the four Departmental Teaching Awards (2013, 2019, 2020, 2021).
Dr. Suh is an IEEE Information Theory Society Distinguished Lecturer, the General Chair of the Inaugural IEEE East Asian School of Information Theory, and a Member of the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology. He is also an Associate Editor of Machine Learning for the IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, the Editor for the IEEE Information Theory Newsletter, a Column Editor for IEEE BITS the Information Theory Magazine, an Area Chair of NeurIPS 2021, and on the Senior Program Committee of IJCAI 2019–2021.
2021.07.27 View 9530
Prof. Changho Suh Named the 2021 James L. Massey Awardee
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering was named the recipient of the 2021 James L.Massey Award. The award recognizes outstanding achievement in research and teaching by young scholars in the information theory community. The award is named in honor of James L. Massey, who was an internationally acclaimed pioneer in digital communications and revered teacher and mentor to communications engineers.
Professor Suh is a recipient of numerous awards, including the 2021 James L. Massey Research & Teaching Award for Young Scholars from the IEEE Information Theory Society, the 2019 AFOSR Grant, the 2019 Google Education Grant, the 2018 IEIE/IEEE Joint Award, the 2015 IEIE Haedong Young Engineer Award, the 2013 IEEE Communications Society Stephen O. Rice Prize, the 2011 David J. Sakrison Memorial Prize (the best dissertation award in UC Berkeley EECS), the 2009 IEEE ISIT Best Student Paper Award, the 2020 LINKGENESIS Best Teacher Award (the campus-wide Grand Prize in Teaching), and the four Departmental Teaching Awards (2013, 2019, 2020, 2021).
Dr. Suh is an IEEE Information Theory Society Distinguished Lecturer, the General Chair of the Inaugural IEEE East Asian School of Information Theory, and a Member of the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology. He is also an Associate Editor of Machine Learning for the IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, the Editor for the IEEE Information Theory Newsletter, a Column Editor for IEEE BITS the Information Theory Magazine, an Area Chair of NeurIPS 2021, and on the Senior Program Committee of IJCAI 2019–2021.
2021.07.27 View 9530 -
 Jungheung to Donate 30B KRW for Semiconductor Research and Education
Jungheung Group, a construction company in Korea, made a pledge to donate 30 billion KRW for semiconductor research and education at KAIST. Junghueng will spend 20 billion KRW to construct the semiconductor education and research facilities that will be established in Pyeongtaek City in collaboration with Samsung Electronics, and 10 billion will go for supporting the educational training program. The pledge ceremony was held at the Daejeon campus with Jungheung Group Chairman Chang-Sun Jung, KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, and Pyeongtaek City Mayor Jang-Seon Jung in attendance.
Chairman said, “The only way to earn a competitive edge in this era of technology hegemony is to invest in young talents in the science and technology fields. They will grow up to be excellent experts who will feed tens of thousands of people.” He added, “Donating to nurture future talents is the most rewarding investment we can make for the future.”
President Lee said, “Jungheung’s donation is an investment in the semiconductor industry in Korea, which will be the growth engine for the nation. We will make every effort to foster the world’s best workforce in the semiconductor sector.”
Mayor Jung also expressed high hopes for the advancement of KAIST into ‘Brain City,’ a complex designated with Samsung Electronics for the semiconductor industry.
“The city government will fully support the semiconductor industry and KAIST. In doing so, we look forward to becoming the center of the semiconductor industry in the nation,” announced Mayor Jung.
2021.07.20 View 6541
Jungheung to Donate 30B KRW for Semiconductor Research and Education
Jungheung Group, a construction company in Korea, made a pledge to donate 30 billion KRW for semiconductor research and education at KAIST. Junghueng will spend 20 billion KRW to construct the semiconductor education and research facilities that will be established in Pyeongtaek City in collaboration with Samsung Electronics, and 10 billion will go for supporting the educational training program. The pledge ceremony was held at the Daejeon campus with Jungheung Group Chairman Chang-Sun Jung, KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, and Pyeongtaek City Mayor Jang-Seon Jung in attendance.
Chairman said, “The only way to earn a competitive edge in this era of technology hegemony is to invest in young talents in the science and technology fields. They will grow up to be excellent experts who will feed tens of thousands of people.” He added, “Donating to nurture future talents is the most rewarding investment we can make for the future.”
President Lee said, “Jungheung’s donation is an investment in the semiconductor industry in Korea, which will be the growth engine for the nation. We will make every effort to foster the world’s best workforce in the semiconductor sector.”
Mayor Jung also expressed high hopes for the advancement of KAIST into ‘Brain City,’ a complex designated with Samsung Electronics for the semiconductor industry.
“The city government will fully support the semiconductor industry and KAIST. In doing so, we look forward to becoming the center of the semiconductor industry in the nation,” announced Mayor Jung.
2021.07.20 View 6541