research
-
 Every Moment of Ultrafast Chemical Bonding Now Captured on Film
- The emerging moment of bond formation, two separate bonding steps, and subsequent vibrational motions were visualized. -
< Emergence of molecular vibrations and the evolution to covalent bonds observed in the research. Video Credit: KEK IMSS >
A team of South Korean researchers led by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST reported the direct observation of the birthing moment of chemical bonds by tracking real-time atomic positions in the molecule. Professor Ihee, who also serves as Associate Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Chemical Reactions at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), conducted this study in collaboration with scientists at the Institute of Materials Structure Science of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK IMSS, Japan), RIKEN (Japan), and Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL, South Korea). This work was published in Nature on June 24.
Targeted cancer drugs work by striking a tight bond between cancer cell and specific molecular targets that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer. Detailed images of such chemical bonding sites or pathways can provide key information necessary for maximizing the efficacy of oncogene treatments. However, atomic movements in a molecule have never been captured in the middle of the action, not even for an extremely simple molecule such as a triatomic molecule, made of only three atoms.
Professor Ihee's group and their international collaborators finally succeeded in capturing the ongoing reaction process of the chemical bond formation in the gold trimer. "The femtosecond-resolution images revealed that such molecular events took place in two separate stages, not simultaneously as previously assumed," says Professor Ihee, the corresponding author of the study. "The atoms in the gold trimer complex atoms remain in motion even after the chemical bonding is complete. The distance between the atoms increased and decreased periodically, exhibiting the molecular vibration. These visualized molecular vibrations allowed us to name the characteristic motion of each observed vibrational mode." adds Professor Ihee.
Atoms move extremely fast at a scale of femtosecond (fs) ― quadrillionths (or millionths of a billionth) of a second. Its movement is minute in the level of angstrom equal to one ten-billionth of a meter. They are especially elusive during the transition state where reaction intermediates are transitioning from reactants to products in a flash. The KAIST-IBS research team made this experimentally challenging task possible by using femtosecond x-ray liquidography (solution scattering). This experimental technique combines laser photolysis and x-ray scattering techniques. When a laser pulse strikes the sample, X-rays scatter and initiate the chemical bond formation reaction in the gold trimer complex. Femtosecond x-ray pulses obtained from a special light source called an x-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) were used to interrogate the bond-forming process. The experiments were performed at two XFEL facilities (4th generation linear accelerator) that are PAL-XFEL in South Korea and SACLA in Japan, and this study was conducted in collaboration with researchers from KEK IMSS, PAL, RIKEN, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI).
Scattered waves from each atom interfere with each other and thus their x-ray scattering images are characterized by specific travel directions. The KAIST-IBS research team traced real-time positions of the three gold atoms over time by analyzing x-ray scattering images, which are determined by a three-dimensional structure of a molecule. Structural changes in the molecule complex resulted in multiple characteristic scattering images over time. When a molecule is excited by a laser pulse, multiple vibrational quantum states are simultaneously excited. The superposition of several excited vibrational quantum states is called a wave packet. The researchers tracked the wave packet in three-dimensional nuclear coordinates and found that the first half round of chemical bonding was formed within 35 fs after photoexcitation. The second half of the reaction followed within 360 fs to complete the entire reaction dynamics.
They also accurately illustrated molecular vibration motions in both temporal- and spatial-wise. This is quite a remarkable feat considering that such an ultrafast speed and a minute length of motion are quite challenging conditions for acquiring precise experimental data.
In this study, the KAIST-IBS research team improved upon their 2015 study published by Nature. In the previous study in 2015, the speed of the x-ray camera (time resolution) was limited to 500 fs, and the molecular structure had already changed to be linear with two chemical bonds within 500 fs. In this study, the progress of the bond formation and bent-to-linear structural transformation could be observed in real time, thanks to the improvement time resolution down to 100 fs. Thereby, the asynchronous bond formation mechanism in which two chemical bonds are formed in 35 fs and 360 fs, respectively, and the bent-to-linear transformation completed in 335 fs were visualized. In short, in addition to observing the beginning and end of chemical reactions, they reported every moment of the intermediate, ongoing rearrangement of nuclear configurations with dramatically improved experimental and analytical methods.
They will push this method of 'real-time tracking of atomic positions in a molecule and molecular vibration using femtosecond x-ray scattering' to reveal the mechanisms of organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and reactions involving proteins in the human body. "By directly tracking the molecular vibrations and real-time positions of all atoms in a molecule in the middle of reaction, we will be able to uncover mechanisms of various unknown organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and biochemical reactions," notes Dr. Jong Goo Kim, the lead author of the study.
Publications:
Kim, J. G., et al. (2020) ‘Mapping the emergence of molecular vibrations mediating bond formation’. Nature. Volume 582. Page 520-524. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2417-3
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.24 View 17895
Every Moment of Ultrafast Chemical Bonding Now Captured on Film
- The emerging moment of bond formation, two separate bonding steps, and subsequent vibrational motions were visualized. -
< Emergence of molecular vibrations and the evolution to covalent bonds observed in the research. Video Credit: KEK IMSS >
A team of South Korean researchers led by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST reported the direct observation of the birthing moment of chemical bonds by tracking real-time atomic positions in the molecule. Professor Ihee, who also serves as Associate Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Chemical Reactions at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), conducted this study in collaboration with scientists at the Institute of Materials Structure Science of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK IMSS, Japan), RIKEN (Japan), and Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL, South Korea). This work was published in Nature on June 24.
Targeted cancer drugs work by striking a tight bond between cancer cell and specific molecular targets that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer. Detailed images of such chemical bonding sites or pathways can provide key information necessary for maximizing the efficacy of oncogene treatments. However, atomic movements in a molecule have never been captured in the middle of the action, not even for an extremely simple molecule such as a triatomic molecule, made of only three atoms.
Professor Ihee's group and their international collaborators finally succeeded in capturing the ongoing reaction process of the chemical bond formation in the gold trimer. "The femtosecond-resolution images revealed that such molecular events took place in two separate stages, not simultaneously as previously assumed," says Professor Ihee, the corresponding author of the study. "The atoms in the gold trimer complex atoms remain in motion even after the chemical bonding is complete. The distance between the atoms increased and decreased periodically, exhibiting the molecular vibration. These visualized molecular vibrations allowed us to name the characteristic motion of each observed vibrational mode." adds Professor Ihee.
Atoms move extremely fast at a scale of femtosecond (fs) ― quadrillionths (or millionths of a billionth) of a second. Its movement is minute in the level of angstrom equal to one ten-billionth of a meter. They are especially elusive during the transition state where reaction intermediates are transitioning from reactants to products in a flash. The KAIST-IBS research team made this experimentally challenging task possible by using femtosecond x-ray liquidography (solution scattering). This experimental technique combines laser photolysis and x-ray scattering techniques. When a laser pulse strikes the sample, X-rays scatter and initiate the chemical bond formation reaction in the gold trimer complex. Femtosecond x-ray pulses obtained from a special light source called an x-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) were used to interrogate the bond-forming process. The experiments were performed at two XFEL facilities (4th generation linear accelerator) that are PAL-XFEL in South Korea and SACLA in Japan, and this study was conducted in collaboration with researchers from KEK IMSS, PAL, RIKEN, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI).
Scattered waves from each atom interfere with each other and thus their x-ray scattering images are characterized by specific travel directions. The KAIST-IBS research team traced real-time positions of the three gold atoms over time by analyzing x-ray scattering images, which are determined by a three-dimensional structure of a molecule. Structural changes in the molecule complex resulted in multiple characteristic scattering images over time. When a molecule is excited by a laser pulse, multiple vibrational quantum states are simultaneously excited. The superposition of several excited vibrational quantum states is called a wave packet. The researchers tracked the wave packet in three-dimensional nuclear coordinates and found that the first half round of chemical bonding was formed within 35 fs after photoexcitation. The second half of the reaction followed within 360 fs to complete the entire reaction dynamics.
They also accurately illustrated molecular vibration motions in both temporal- and spatial-wise. This is quite a remarkable feat considering that such an ultrafast speed and a minute length of motion are quite challenging conditions for acquiring precise experimental data.
In this study, the KAIST-IBS research team improved upon their 2015 study published by Nature. In the previous study in 2015, the speed of the x-ray camera (time resolution) was limited to 500 fs, and the molecular structure had already changed to be linear with two chemical bonds within 500 fs. In this study, the progress of the bond formation and bent-to-linear structural transformation could be observed in real time, thanks to the improvement time resolution down to 100 fs. Thereby, the asynchronous bond formation mechanism in which two chemical bonds are formed in 35 fs and 360 fs, respectively, and the bent-to-linear transformation completed in 335 fs were visualized. In short, in addition to observing the beginning and end of chemical reactions, they reported every moment of the intermediate, ongoing rearrangement of nuclear configurations with dramatically improved experimental and analytical methods.
They will push this method of 'real-time tracking of atomic positions in a molecule and molecular vibration using femtosecond x-ray scattering' to reveal the mechanisms of organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and reactions involving proteins in the human body. "By directly tracking the molecular vibrations and real-time positions of all atoms in a molecule in the middle of reaction, we will be able to uncover mechanisms of various unknown organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and biochemical reactions," notes Dr. Jong Goo Kim, the lead author of the study.
Publications:
Kim, J. G., et al. (2020) ‘Mapping the emergence of molecular vibrations mediating bond formation’. Nature. Volume 582. Page 520-524. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2417-3
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.24 View 17895 -
 A New Strategy for Early Evaluations of CO2 Utilization Technologies
- A three-step evaluation procedure based on technology readiness levels helps find the most efficient technology before allocating R&D manpower and investments in CO2 utilization technologies. -
Researchers presented a unified framework for early-stage evaluations of a variety of emerging CO2 utilization (CU) technologies. The three-step procedure allows a large number of potential CU technologies to be screened in order to identify the most promising ones, including those at low level of technical maturity, before allocating R&D manpower and investments.
When evaluating new technology, various aspects of the new technology should be considered. Its feasibility, efficiency, economic competitiveness, and environmental friendliness are crucial, and its level of technical maturity is also an important component for further consideration. However, most technology evaluation procedures are data-driven, and the amount of reliable data in the early stages of technology development has been often limited.
A research team led by Professor Jay Hyung Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST proposed a new procedure for evaluating the early development stages of emerging CU technologies which are applicable at various technology readiness levels (TRLs).
The procedure obtains performance indicators via primary data preparation, secondary data calculation, and performance indicator calculation, and the lead author of the study Dr. Kosan Roh and his colleagues presented a number of databases, methods, and computer-aided tools that can effectively facilitate the procedure.
The research team demonstrated the procedure through four case studies involving novel CU technologies of different types and at various TRLs. They confirmed the electrochemical CO2 reduction for the production of ten chemicals, the co-electrolysis of CO2 and water for ethylene production, the direct oxidation of CO2 -based methanol for oxymethylene dimethyl production, and the microalgal biomass co-firing for power generation.
The expected range of the performance indicators for low TRL technologies is broader than that for high TRL technologies, however, it is not the case for high TRL technologies as they are already at an optimized state. The research team believes that low TRL technologies will be significantly improved through future R&D until they are commercialized. “We plan to develop a systematic approach for such a comparison to help avoid misguided decision-making,” Professor Lee explained.
Professor Lee added, “This procedure allows us to conduct a comprehensive and systematic evaluation of new technology. On top of that, it helps make efficient and reliable assessment possible.”
The research team collaborated with Professor Alexander Mitsos, Professor André Bardow, and Professor Matthias Wessling at RWTH Aachen University in Germany. Their findings were reported in Green Chemistry on May 21. This work was supported by the Korea Carbon Capture and Sequestration R&D Center (KCRC).
Publications:
Roh, K., et al. (2020) ‘Early-stage evaluation of emerging CO2 utilization technologies at low technology readiness levels’ Green Chemistry. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1039/c9gc04440j
Profile: Jay Hyung Lee, Ph.D.
Professor
jayhlee@kaist.ac.kr
http://lense.kaist.ac.kr/
Laboratory for Energy System Engineering (LENSE)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.22 View 10793
A New Strategy for Early Evaluations of CO2 Utilization Technologies
- A three-step evaluation procedure based on technology readiness levels helps find the most efficient technology before allocating R&D manpower and investments in CO2 utilization technologies. -
Researchers presented a unified framework for early-stage evaluations of a variety of emerging CO2 utilization (CU) technologies. The three-step procedure allows a large number of potential CU technologies to be screened in order to identify the most promising ones, including those at low level of technical maturity, before allocating R&D manpower and investments.
When evaluating new technology, various aspects of the new technology should be considered. Its feasibility, efficiency, economic competitiveness, and environmental friendliness are crucial, and its level of technical maturity is also an important component for further consideration. However, most technology evaluation procedures are data-driven, and the amount of reliable data in the early stages of technology development has been often limited.
A research team led by Professor Jay Hyung Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST proposed a new procedure for evaluating the early development stages of emerging CU technologies which are applicable at various technology readiness levels (TRLs).
The procedure obtains performance indicators via primary data preparation, secondary data calculation, and performance indicator calculation, and the lead author of the study Dr. Kosan Roh and his colleagues presented a number of databases, methods, and computer-aided tools that can effectively facilitate the procedure.
The research team demonstrated the procedure through four case studies involving novel CU technologies of different types and at various TRLs. They confirmed the electrochemical CO2 reduction for the production of ten chemicals, the co-electrolysis of CO2 and water for ethylene production, the direct oxidation of CO2 -based methanol for oxymethylene dimethyl production, and the microalgal biomass co-firing for power generation.
The expected range of the performance indicators for low TRL technologies is broader than that for high TRL technologies, however, it is not the case for high TRL technologies as they are already at an optimized state. The research team believes that low TRL technologies will be significantly improved through future R&D until they are commercialized. “We plan to develop a systematic approach for such a comparison to help avoid misguided decision-making,” Professor Lee explained.
Professor Lee added, “This procedure allows us to conduct a comprehensive and systematic evaluation of new technology. On top of that, it helps make efficient and reliable assessment possible.”
The research team collaborated with Professor Alexander Mitsos, Professor André Bardow, and Professor Matthias Wessling at RWTH Aachen University in Germany. Their findings were reported in Green Chemistry on May 21. This work was supported by the Korea Carbon Capture and Sequestration R&D Center (KCRC).
Publications:
Roh, K., et al. (2020) ‘Early-stage evaluation of emerging CO2 utilization technologies at low technology readiness levels’ Green Chemistry. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1039/c9gc04440j
Profile: Jay Hyung Lee, Ph.D.
Professor
jayhlee@kaist.ac.kr
http://lense.kaist.ac.kr/
Laboratory for Energy System Engineering (LENSE)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.22 View 10793 -
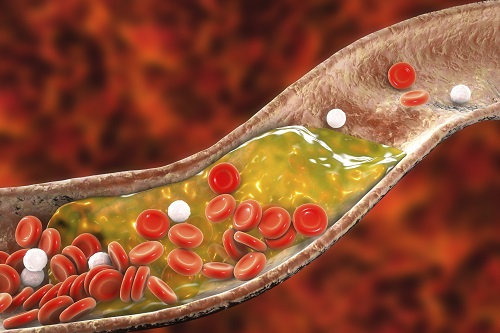 New Nanoparticle Drug Combination For Atherosclerosis
Physicochemical cargo-switching nanoparticles (CSNP) designed by KAIST can help significantly reduce cholesterol and macrophage foam cells in arteries, which are the two main triggers for atherosclerotic plaque and inflammation.
The CSNP-based combination drug delivery therapy was proved to exert cholesterol-lowering, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative functions of two common medications for treating and preventing atherosclerosis that are cyclodextrin and statin. Professor Ji-Ho Park and Dr. Heegon Kim from KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering said their study has shown great potential for future applications with reduced side effects.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory vascular disease that is characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol and cholesterol-loaded macrophage foam cells in the intima. When this atherosclerotic plaque clogs and narrows the artery walls, they restrict blood flow and cause various cardiovascular conditions such as heart attacks and strokes. Heart attacks and strokes are the world’s first and fifth causes of death respectively.
Oral statin administration has been used in clinics as a standard care for atherosclerosis, which is prescribed to lower blood cholesterol and inhibit its accumulation within the plaque. Although statins can effectively prevent the progression of plaque growth, they have only shown modest efficacy in eliminating the already-established plaque. Therefore, patients are required to take statin drugs for the rest of their lives and will always carry the risk of plaque ruptures that can trigger a blood clot.
To address these issues, Professor Park and Dr. Kim exploited another antiatherogenic agent called cyclodextrin. In their paper published in the Journal of Controlled Release on March 10, Professor Park and Dr. Kim reported that the polymeric formulation of cyclodextrin with a diameter of approximately 10 nanometers(nm) can accumulate within the atherosclerotic plaque 14 times more and effectively reduce the plaque even at lower doses, compared to cyclodextrin in a non-polymer structure.
Moreover, although cyclodextrin is known to have a cytotoxic effect on hair cells in the cochlea, which can lead to hearing loss, cyclodextrin polymers developed by Professor Park’s research group exhibited a varying biodistribution profile and did not have this side effect.
In the follow-up study reported in ACS Nano on April 28, the researchers exploited both cyclodextrin and statin and form the cyclodextrin-statin self-assembly drug complex, based on previous findings that each drug can exert local anti-atherosclerosis effect within the plaque. The complex formation processes were optimized to obtain homogeneous and stable nanoparticles with a diameter of about 100 nm for systematic injection.
The therapeutic synergy of cyclodextrin and statin could reportedly enhance plaque-targeted drug delivery and anti-inflammation. Cyclodextrin led to the regression of cholesterol in the established plaque, and the statins were shown to inhibit the proliferation of macrophage foam cells. The study suggested that combination therapy is required to resolve the complex inflammatory cholesterol-rich microenvironment within the plaque.
Professor Park said, “While nanomedicine has been mainly developed for the treatment of cancers, our studies show that nanomedicine can also play a significant role in treating and preventing atherosclerosis, which causes various cardiovascular diseases that are the leading causes of death worldwide.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publications:
1. Heegon Kim, Junhee Han, and Ji-Ho Park. (2020) ‘Cyclodextrin polymer improves atherosclerosis therapy and reduces ototoxicity’ Journal of Controlled Release. Volume 319. Page 77-86. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.12.021
2. Kim, H., et al. (2020) ‘Affinity-Driven Design of Cargo-Switching Nanoparticles to Leverage a Cholesterol-Rich Microenvironment for Atherosclerosis Therapy’ ACS Nano. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b08216
Profile: Ji-Ho Park, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jihopark@kaist.ac.kr
http://openwetware.org/wiki/Park_Lab
Biomaterials Engineering Laboratory (BEL)
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering (BIOENG)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Heegon Kim, Ph.D.
Postdoctoral Researcher
heegon@kaist.ac.kr
BEL, BIOENG, KAIST
(END)
2020.06.16 View 14047
New Nanoparticle Drug Combination For Atherosclerosis
Physicochemical cargo-switching nanoparticles (CSNP) designed by KAIST can help significantly reduce cholesterol and macrophage foam cells in arteries, which are the two main triggers for atherosclerotic plaque and inflammation.
The CSNP-based combination drug delivery therapy was proved to exert cholesterol-lowering, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative functions of two common medications for treating and preventing atherosclerosis that are cyclodextrin and statin. Professor Ji-Ho Park and Dr. Heegon Kim from KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering said their study has shown great potential for future applications with reduced side effects.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory vascular disease that is characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol and cholesterol-loaded macrophage foam cells in the intima. When this atherosclerotic plaque clogs and narrows the artery walls, they restrict blood flow and cause various cardiovascular conditions such as heart attacks and strokes. Heart attacks and strokes are the world’s first and fifth causes of death respectively.
Oral statin administration has been used in clinics as a standard care for atherosclerosis, which is prescribed to lower blood cholesterol and inhibit its accumulation within the plaque. Although statins can effectively prevent the progression of plaque growth, they have only shown modest efficacy in eliminating the already-established plaque. Therefore, patients are required to take statin drugs for the rest of their lives and will always carry the risk of plaque ruptures that can trigger a blood clot.
To address these issues, Professor Park and Dr. Kim exploited another antiatherogenic agent called cyclodextrin. In their paper published in the Journal of Controlled Release on March 10, Professor Park and Dr. Kim reported that the polymeric formulation of cyclodextrin with a diameter of approximately 10 nanometers(nm) can accumulate within the atherosclerotic plaque 14 times more and effectively reduce the plaque even at lower doses, compared to cyclodextrin in a non-polymer structure.
Moreover, although cyclodextrin is known to have a cytotoxic effect on hair cells in the cochlea, which can lead to hearing loss, cyclodextrin polymers developed by Professor Park’s research group exhibited a varying biodistribution profile and did not have this side effect.
In the follow-up study reported in ACS Nano on April 28, the researchers exploited both cyclodextrin and statin and form the cyclodextrin-statin self-assembly drug complex, based on previous findings that each drug can exert local anti-atherosclerosis effect within the plaque. The complex formation processes were optimized to obtain homogeneous and stable nanoparticles with a diameter of about 100 nm for systematic injection.
The therapeutic synergy of cyclodextrin and statin could reportedly enhance plaque-targeted drug delivery and anti-inflammation. Cyclodextrin led to the regression of cholesterol in the established plaque, and the statins were shown to inhibit the proliferation of macrophage foam cells. The study suggested that combination therapy is required to resolve the complex inflammatory cholesterol-rich microenvironment within the plaque.
Professor Park said, “While nanomedicine has been mainly developed for the treatment of cancers, our studies show that nanomedicine can also play a significant role in treating and preventing atherosclerosis, which causes various cardiovascular diseases that are the leading causes of death worldwide.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publications:
1. Heegon Kim, Junhee Han, and Ji-Ho Park. (2020) ‘Cyclodextrin polymer improves atherosclerosis therapy and reduces ototoxicity’ Journal of Controlled Release. Volume 319. Page 77-86. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.12.021
2. Kim, H., et al. (2020) ‘Affinity-Driven Design of Cargo-Switching Nanoparticles to Leverage a Cholesterol-Rich Microenvironment for Atherosclerosis Therapy’ ACS Nano. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b08216
Profile: Ji-Ho Park, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jihopark@kaist.ac.kr
http://openwetware.org/wiki/Park_Lab
Biomaterials Engineering Laboratory (BEL)
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering (BIOENG)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Heegon Kim, Ph.D.
Postdoctoral Researcher
heegon@kaist.ac.kr
BEL, BIOENG, KAIST
(END)
2020.06.16 View 14047 -
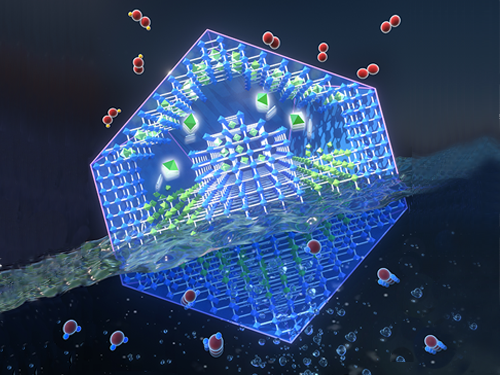 Energy Storage Using Oxygen to Boost Battery Performance
Researchers have presented a novel electrode material for advanced energy storage device that is directly charged with oxygen from the air. Professor Jeung Ku Kang’s team synthesized and preserved the sub-nanometric particles of atomic cluster sizes at high mass loadings within metal-organic frameworks (MOF) by controlling the behavior of reactants at the molecular level. This new strategy ensures high performance for lithium-oxygen batteries, acclaimed as a next-generation energy storage technology and widely used in electric vehicles.
Lithium-oxygen batteries in principle can generate ten times higher energy densities than conventional lithium-ion batteries, but they suffer from very poor cyclability. One of the methods to improve cycle stability is to reduce the overpotential of electrocatalysts in cathode electrodes. When the size of an electrocatalyst material is reduced to the atomic level, the increased surface energy leads to increased activity while significantly accelerating the material’s agglomeration.
As a solution to this challenge, Professor Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering aimed to maintain the improved activity by stabilizing atomic-scale sized electrocatalysts into the sub-nanometric spaces. This is a novel strategy for simultaneously producing and stabilizing atomic-level electrocatalysts within metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
Metal-organic frameworks continuously assemble metal ions and organic linkers.
The team controlled hydrogen affinities between water molecules to separate them and transfer the isolated water molecules one by one through the sub-nanometric pores of MOFs. The transferred water molecules reacted with cobalt ions to form di-nuclear cobalt hydroxide under precisely controlled synthetic conditions, then the atomic-level cobalt hydroxide is stabilized inside the sub-nanometric pores.
The di-nuclear cobalt hydroxide that is stabilized in the sub-nanometric pores of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) reduced the overpotential by 63.9% and showed ten-fold improvements in the life cycle.
Professor Kang said, “Simultaneously generating and stabilizing atomic-level electrocatalysts within MOFs can diversify materials according to numerous combinations of metal and organic linkers. It can expand not only the development of electrocatalysts, but also various research fields such as photocatalysts, medicine, the environment, and petrochemicals.”
This study was reported in Advanced Science (Title: Autogenous Production and Stabilization of Highly Loaded Sub-Nanometric Particles within Multishell Hollow Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Utilization for High Performance in Li-O2 Batteries).
This research was mainly supported by the Global Frontier R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT & Planning (Grant No. 2013M3A6B1078884) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning, and the National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant No. 2019M3E6A1104196).
Profile:Professor Jeung Ku Kang
jeungku@kaist.ac.kr
http://nanosf.kaist.ac.kr/
Nano Materials Simulation and Fabrication Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2020.06.15 View 13253
Energy Storage Using Oxygen to Boost Battery Performance
Researchers have presented a novel electrode material for advanced energy storage device that is directly charged with oxygen from the air. Professor Jeung Ku Kang’s team synthesized and preserved the sub-nanometric particles of atomic cluster sizes at high mass loadings within metal-organic frameworks (MOF) by controlling the behavior of reactants at the molecular level. This new strategy ensures high performance for lithium-oxygen batteries, acclaimed as a next-generation energy storage technology and widely used in electric vehicles.
Lithium-oxygen batteries in principle can generate ten times higher energy densities than conventional lithium-ion batteries, but they suffer from very poor cyclability. One of the methods to improve cycle stability is to reduce the overpotential of electrocatalysts in cathode electrodes. When the size of an electrocatalyst material is reduced to the atomic level, the increased surface energy leads to increased activity while significantly accelerating the material’s agglomeration.
As a solution to this challenge, Professor Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering aimed to maintain the improved activity by stabilizing atomic-scale sized electrocatalysts into the sub-nanometric spaces. This is a novel strategy for simultaneously producing and stabilizing atomic-level electrocatalysts within metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
Metal-organic frameworks continuously assemble metal ions and organic linkers.
The team controlled hydrogen affinities between water molecules to separate them and transfer the isolated water molecules one by one through the sub-nanometric pores of MOFs. The transferred water molecules reacted with cobalt ions to form di-nuclear cobalt hydroxide under precisely controlled synthetic conditions, then the atomic-level cobalt hydroxide is stabilized inside the sub-nanometric pores.
The di-nuclear cobalt hydroxide that is stabilized in the sub-nanometric pores of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) reduced the overpotential by 63.9% and showed ten-fold improvements in the life cycle.
Professor Kang said, “Simultaneously generating and stabilizing atomic-level electrocatalysts within MOFs can diversify materials according to numerous combinations of metal and organic linkers. It can expand not only the development of electrocatalysts, but also various research fields such as photocatalysts, medicine, the environment, and petrochemicals.”
This study was reported in Advanced Science (Title: Autogenous Production and Stabilization of Highly Loaded Sub-Nanometric Particles within Multishell Hollow Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Utilization for High Performance in Li-O2 Batteries).
This research was mainly supported by the Global Frontier R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT & Planning (Grant No. 2013M3A6B1078884) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning, and the National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant No. 2019M3E6A1104196).
Profile:Professor Jeung Ku Kang
jeungku@kaist.ac.kr
http://nanosf.kaist.ac.kr/
Nano Materials Simulation and Fabrication Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2020.06.15 View 13253 -
 A Deep-Learned E-Skin Decodes Complex Human Motion
A deep-learning powered single-strained electronic skin sensor can capture human motion from a distance. The single strain sensor placed on the wrist decodes complex five-finger motions in real time with a virtual 3D hand that mirrors the original motions. The deep neural network boosted by rapid situation learning (RSL) ensures stable operation regardless of its position on the surface of the skin.
Conventional approaches require many sensor networks that cover the entire curvilinear surfaces of the target area. Unlike conventional wafer-based fabrication, this laser fabrication provides a new sensing paradigm for motion tracking.
The research team, led by Professor Sungho Jo from the School of Computing, collaborated with Professor Seunghwan Ko from Seoul National University to design this new measuring system that extracts signals corresponding to multiple finger motions by generating cracks in metal nanoparticle films using laser technology. The sensor patch was then attached to a user’s wrist to detect the movement of the fingers.
The concept of this research started from the idea that pinpointing a single area would be more efficient for identifying movements than affixing sensors to every joint and muscle. To make this targeting strategy work, it needs to accurately capture the signals from different areas at the point where they all converge, and then decoupling the information entangled in the converged signals. To maximize users’ usability and mobility, the research team used a single-channeled sensor to generate the signals corresponding to complex hand motions.
The rapid situation learning (RSL) system collects data from arbitrary parts on the wrist and automatically trains the model in a real-time demonstration with a virtual 3D hand that mirrors the original motions. To enhance the sensitivity of the sensor, researchers used laser-induced nanoscale cracking.
This sensory system can track the motion of the entire body with a small sensory network and facilitate the indirect remote measurement of human motions, which is applicable for wearable VR/AR systems.
The research team said they focused on two tasks while developing the sensor. First, they analyzed the sensor signal patterns into a latent space encapsulating temporal sensor behavior and then they mapped the latent vectors to finger motion metric spaces.
Professor Jo said, “Our system is expandable to other body parts. We already confirmed that the sensor is also capable of extracting gait motions from a pelvis. This technology is expected to provide a turning point in health-monitoring, motion tracking, and soft robotics.”
This study was featured in Nature Communications.
Publication:
Kim, K. K., et al. (2020) A deep-learned skin sensor decoding the epicentral human motions. Nature Communications. 11. 2149. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16040-y29
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-16040-y.pdf
Profile: Professor Sungho Jo
shjo@kaist.ac.kr
http://nmail.kaist.ac.kr
Neuro-Machine Augmented Intelligence Lab
School of Computing
College of Engineering
KAIST
2020.06.10 View 12808
A Deep-Learned E-Skin Decodes Complex Human Motion
A deep-learning powered single-strained electronic skin sensor can capture human motion from a distance. The single strain sensor placed on the wrist decodes complex five-finger motions in real time with a virtual 3D hand that mirrors the original motions. The deep neural network boosted by rapid situation learning (RSL) ensures stable operation regardless of its position on the surface of the skin.
Conventional approaches require many sensor networks that cover the entire curvilinear surfaces of the target area. Unlike conventional wafer-based fabrication, this laser fabrication provides a new sensing paradigm for motion tracking.
The research team, led by Professor Sungho Jo from the School of Computing, collaborated with Professor Seunghwan Ko from Seoul National University to design this new measuring system that extracts signals corresponding to multiple finger motions by generating cracks in metal nanoparticle films using laser technology. The sensor patch was then attached to a user’s wrist to detect the movement of the fingers.
The concept of this research started from the idea that pinpointing a single area would be more efficient for identifying movements than affixing sensors to every joint and muscle. To make this targeting strategy work, it needs to accurately capture the signals from different areas at the point where they all converge, and then decoupling the information entangled in the converged signals. To maximize users’ usability and mobility, the research team used a single-channeled sensor to generate the signals corresponding to complex hand motions.
The rapid situation learning (RSL) system collects data from arbitrary parts on the wrist and automatically trains the model in a real-time demonstration with a virtual 3D hand that mirrors the original motions. To enhance the sensitivity of the sensor, researchers used laser-induced nanoscale cracking.
This sensory system can track the motion of the entire body with a small sensory network and facilitate the indirect remote measurement of human motions, which is applicable for wearable VR/AR systems.
The research team said they focused on two tasks while developing the sensor. First, they analyzed the sensor signal patterns into a latent space encapsulating temporal sensor behavior and then they mapped the latent vectors to finger motion metric spaces.
Professor Jo said, “Our system is expandable to other body parts. We already confirmed that the sensor is also capable of extracting gait motions from a pelvis. This technology is expected to provide a turning point in health-monitoring, motion tracking, and soft robotics.”
This study was featured in Nature Communications.
Publication:
Kim, K. K., et al. (2020) A deep-learned skin sensor decoding the epicentral human motions. Nature Communications. 11. 2149. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16040-y29
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-16040-y.pdf
Profile: Professor Sungho Jo
shjo@kaist.ac.kr
http://nmail.kaist.ac.kr
Neuro-Machine Augmented Intelligence Lab
School of Computing
College of Engineering
KAIST
2020.06.10 View 12808 -
 Unravelling Complex Brain Networks with Automated 3-D Neural Mapping
-Automated 3-D brain imaging data analysis technology offers more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of complex neural circuits.-
KAIST researchers developed a new algorithm for brain imaging data analysis that enables the precise and quantitative mapping of complex neural circuits onto a standardized 3-D reference atlas.
Brain imaging data analysis is indispensable in the studies of neuroscience. However, analysis of obtained brain imaging data has been heavily dependent on manual processing, which cannot guarantee the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of the results.
Conventional brain imaging data analysis typically begins with finding a 2-D brain atlas image that is visually similar to the experimentally obtained brain image. Then, the region-of-interest (ROI) of the atlas image is matched manually with the obtained image, and the number of labeled neurons in the ROI is counted.
Such a visual matching process between experimentally obtained brain images and 2-D brain atlas images has been one of the major sources of error in brain imaging data analysis, as the process is highly subjective, sample-specific, and susceptible to human error. Manual analysis processes for brain images are also laborious, and thus studying the complete 3-D neuronal organization on a whole-brain scale is a formidable task.
To address these issues, a KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering developed new brain imaging data analysis software named 'AMaSiNe (Automated 3-D Mapping of Single Neurons)', and introduced the algorithm in the May 26 issue of Cell Reports.
AMaSiNe automatically detects the positions of single neurons from multiple brain images, and accurately maps all the data onto a common standard 3-D reference space. The algorithm allows the direct comparison of brain data from different animals by automatically matching similar features from the images, and computing the image similarity score.
This feature-based quantitative image-to-image comparison technology improves the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of analysis results using only a small number of brain slice image samples, and helps standardize brain imaging data analyses.
Unlike other existing brain imaging data analysis methods, AMaSiNe can also automatically find the alignment conditions from misaligned and distorted brain images, and draw an accurate ROI, without any cumbersome manual validation process.
AMaSiNe has been further proved to produce consistent results with brain slice images stained utilizing various methods including DAPI, Nissl, and autofluorescence.
The two co-lead authors of this study, Jun Ho Song and Woochul Choi, exploited these benefits of AMaSiNe to investigate the topographic organization of neurons that project to the primary visual area (VISp) in various ROIs, such as the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGd), which could hardly be addressed without proper calibration and standardization of the brain slice image samples.
In collaboration with Professor Seung-Hee Lee's group of the Department of Biological Science, the researchers successfully observed the 3-D topographic neural projections to the VISp from LGd, and also demonstrated that these projections could not be observed when the slicing angle was not properly corrected by AMaSiNe. The results suggest that the precise correction of a slicing angle is essential for the investigation of complex and important brain structures.
AMaSiNe is widely applicable in the studies of various brain regions and other experimental conditions. For example, in the research team’s previous study jointly conducted with Professor Yang Dan’s group at UC Berkeley, the algorithm enabled the accurate analysis of the neuronal subsets in the substantia nigra and their projections to the whole brain. Their findings were published in Science on January 24.
AMaSiNe is of great interest to many neuroscientists in Korea and abroad, and is being actively used by a number of other research groups at KAIST, MIT, Harvard, Caltech, and UC San Diego.
Professor Paik said, “Our new algorithm allows the spatial organization of complex neural circuits to be found in a standardized 3-D reference atlas on a whole-brain scale. This will bring brain imaging data analysis to a new level.”
He continued, “More in-depth insights for understanding the function of brain circuits can be achieved by facilitating more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of neural circuits in various regions of the brain.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Figure and Image Credit: Professor Se-Bum Paik, KAIST
Figure and Image Usage Restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and images, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Song, J. H., et al. (2020). Precise Mapping of Single Neurons by Calibrated 3D Reconstruction of Brain Slices Reveals Topographic Projection in Mouse Visual Cortex. Cell Reports. Volume 31, 107682. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107682
Profile:
Se-Bum Paik
Assistant Professor
sbpaik@kaist.ac.kr
http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/
VSNN Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.06.08 View 14163
Unravelling Complex Brain Networks with Automated 3-D Neural Mapping
-Automated 3-D brain imaging data analysis technology offers more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of complex neural circuits.-
KAIST researchers developed a new algorithm for brain imaging data analysis that enables the precise and quantitative mapping of complex neural circuits onto a standardized 3-D reference atlas.
Brain imaging data analysis is indispensable in the studies of neuroscience. However, analysis of obtained brain imaging data has been heavily dependent on manual processing, which cannot guarantee the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of the results.
Conventional brain imaging data analysis typically begins with finding a 2-D brain atlas image that is visually similar to the experimentally obtained brain image. Then, the region-of-interest (ROI) of the atlas image is matched manually with the obtained image, and the number of labeled neurons in the ROI is counted.
Such a visual matching process between experimentally obtained brain images and 2-D brain atlas images has been one of the major sources of error in brain imaging data analysis, as the process is highly subjective, sample-specific, and susceptible to human error. Manual analysis processes for brain images are also laborious, and thus studying the complete 3-D neuronal organization on a whole-brain scale is a formidable task.
To address these issues, a KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering developed new brain imaging data analysis software named 'AMaSiNe (Automated 3-D Mapping of Single Neurons)', and introduced the algorithm in the May 26 issue of Cell Reports.
AMaSiNe automatically detects the positions of single neurons from multiple brain images, and accurately maps all the data onto a common standard 3-D reference space. The algorithm allows the direct comparison of brain data from different animals by automatically matching similar features from the images, and computing the image similarity score.
This feature-based quantitative image-to-image comparison technology improves the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of analysis results using only a small number of brain slice image samples, and helps standardize brain imaging data analyses.
Unlike other existing brain imaging data analysis methods, AMaSiNe can also automatically find the alignment conditions from misaligned and distorted brain images, and draw an accurate ROI, without any cumbersome manual validation process.
AMaSiNe has been further proved to produce consistent results with brain slice images stained utilizing various methods including DAPI, Nissl, and autofluorescence.
The two co-lead authors of this study, Jun Ho Song and Woochul Choi, exploited these benefits of AMaSiNe to investigate the topographic organization of neurons that project to the primary visual area (VISp) in various ROIs, such as the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGd), which could hardly be addressed without proper calibration and standardization of the brain slice image samples.
In collaboration with Professor Seung-Hee Lee's group of the Department of Biological Science, the researchers successfully observed the 3-D topographic neural projections to the VISp from LGd, and also demonstrated that these projections could not be observed when the slicing angle was not properly corrected by AMaSiNe. The results suggest that the precise correction of a slicing angle is essential for the investigation of complex and important brain structures.
AMaSiNe is widely applicable in the studies of various brain regions and other experimental conditions. For example, in the research team’s previous study jointly conducted with Professor Yang Dan’s group at UC Berkeley, the algorithm enabled the accurate analysis of the neuronal subsets in the substantia nigra and their projections to the whole brain. Their findings were published in Science on January 24.
AMaSiNe is of great interest to many neuroscientists in Korea and abroad, and is being actively used by a number of other research groups at KAIST, MIT, Harvard, Caltech, and UC San Diego.
Professor Paik said, “Our new algorithm allows the spatial organization of complex neural circuits to be found in a standardized 3-D reference atlas on a whole-brain scale. This will bring brain imaging data analysis to a new level.”
He continued, “More in-depth insights for understanding the function of brain circuits can be achieved by facilitating more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of neural circuits in various regions of the brain.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Figure and Image Credit: Professor Se-Bum Paik, KAIST
Figure and Image Usage Restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and images, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Song, J. H., et al. (2020). Precise Mapping of Single Neurons by Calibrated 3D Reconstruction of Brain Slices Reveals Topographic Projection in Mouse Visual Cortex. Cell Reports. Volume 31, 107682. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107682
Profile:
Se-Bum Paik
Assistant Professor
sbpaik@kaist.ac.kr
http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/
VSNN Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.06.08 View 14163 -
 ‘Mole-bot’ Optimized for Underground and Space Exploration
Biomimetic drilling robot provides new insights into the development of efficient drilling technologies
Mole-bot, a drilling biomimetic robot designed by KAIST, boasts a stout scapula, a waist inclinable on all sides, and powerful forelimbs. Most of all, the powerful torque from the expandable drilling bit mimicking the chiseling ability of a mole’s front teeth highlights the best feature of the drilling robot.
The Mole-bot is expected to be used for space exploration and mining for underground resources such as coalbed methane and Rare Earth Elements (REE), which require highly advanced drilling technologies in complex environments.
The research team, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the School of Electrical Engineering, found inspiration for their drilling bot from two striking features of the African mole-rat and European mole.
“The crushing power of the African mole-rat’s teeth is so powerful that they can dig a hole with 48 times more power than their body weight. We used this characteristic for building the main excavation tool. And its expandable drill is designed not to collide with its forelimbs,” said Professor Myung.
The 25-cm wide and 84-cm long Mole-bot can excavate three times faster with six times higher directional accuracy than conventional models. The Mole-bot weighs 26 kg.
After digging, the robot removes the excavated soil and debris using its forelimbs. This embedded muscle feature, inspired by the European mole’s scapula, converts linear motion into a powerful rotational force. For directional drilling, the robot’s elongated waist changes its direction 360° like living mammals.
For exploring underground environments, the research team developed and applied new sensor systems and algorithms to identify the robot’s position and orientation using graph-based 3D Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) technology that matches the Earth’s magnetic field sequence, which enables 3D autonomous navigation underground.
According to Market & Market’s survey, the directional drilling market in 2016 is estimated to be 83.3 billion USD and is expected to grow to 103 billion USD in 2021. The growth of the drilling market, starting with the Shale Revolution, is likely to expand into the future development of space and polar resources. As initiated by Space X recently, more attention for planetary exploration will be on the rise and its related technology and equipment market will also increase.
The Mole-bot is a huge step forward for efficient underground drilling and exploration technologies. Unlike conventional drilling processes that use environmentally unfriendly mud compounds for cleaning debris, Mole-bot can mitigate environmental destruction. The researchers said their system saves on cost and labor and does not require additional pipelines or other ancillary equipment.
“We look forward to a more efficient resource exploration with this type of drilling robot. We also hope Mole-bot will have a very positive impact on the robotics market in terms of its extensive application spectra and economic feasibility,” said Professor Myung.
This research, made in collaboration with Professor Jung-Wuk Hong and Professor Tae-Hyuk Kwon’s team in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering for robot structure analysis and geotechnical experiments, was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy’s Industrial Technology Innovation Project.
Profile
Professor Hyun Myung
Urban Robotics Lab
http://urobot.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2020.06.05 View 11189
‘Mole-bot’ Optimized for Underground and Space Exploration
Biomimetic drilling robot provides new insights into the development of efficient drilling technologies
Mole-bot, a drilling biomimetic robot designed by KAIST, boasts a stout scapula, a waist inclinable on all sides, and powerful forelimbs. Most of all, the powerful torque from the expandable drilling bit mimicking the chiseling ability of a mole’s front teeth highlights the best feature of the drilling robot.
The Mole-bot is expected to be used for space exploration and mining for underground resources such as coalbed methane and Rare Earth Elements (REE), which require highly advanced drilling technologies in complex environments.
The research team, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the School of Electrical Engineering, found inspiration for their drilling bot from two striking features of the African mole-rat and European mole.
“The crushing power of the African mole-rat’s teeth is so powerful that they can dig a hole with 48 times more power than their body weight. We used this characteristic for building the main excavation tool. And its expandable drill is designed not to collide with its forelimbs,” said Professor Myung.
The 25-cm wide and 84-cm long Mole-bot can excavate three times faster with six times higher directional accuracy than conventional models. The Mole-bot weighs 26 kg.
After digging, the robot removes the excavated soil and debris using its forelimbs. This embedded muscle feature, inspired by the European mole’s scapula, converts linear motion into a powerful rotational force. For directional drilling, the robot’s elongated waist changes its direction 360° like living mammals.
For exploring underground environments, the research team developed and applied new sensor systems and algorithms to identify the robot’s position and orientation using graph-based 3D Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) technology that matches the Earth’s magnetic field sequence, which enables 3D autonomous navigation underground.
According to Market & Market’s survey, the directional drilling market in 2016 is estimated to be 83.3 billion USD and is expected to grow to 103 billion USD in 2021. The growth of the drilling market, starting with the Shale Revolution, is likely to expand into the future development of space and polar resources. As initiated by Space X recently, more attention for planetary exploration will be on the rise and its related technology and equipment market will also increase.
The Mole-bot is a huge step forward for efficient underground drilling and exploration technologies. Unlike conventional drilling processes that use environmentally unfriendly mud compounds for cleaning debris, Mole-bot can mitigate environmental destruction. The researchers said their system saves on cost and labor and does not require additional pipelines or other ancillary equipment.
“We look forward to a more efficient resource exploration with this type of drilling robot. We also hope Mole-bot will have a very positive impact on the robotics market in terms of its extensive application spectra and economic feasibility,” said Professor Myung.
This research, made in collaboration with Professor Jung-Wuk Hong and Professor Tae-Hyuk Kwon’s team in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering for robot structure analysis and geotechnical experiments, was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy’s Industrial Technology Innovation Project.
Profile
Professor Hyun Myung
Urban Robotics Lab
http://urobot.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2020.06.05 View 11189 -
 A New Strategy for the Optimal Electroreduction of CO2 to High-Value Products
-Researchers suggest that modulation of local CO2 concentration improves the selectivity, conversion rate, and electrode stability, and shed a new light on the electrochemical CO2 reduction technology for controlling emissions at a low cost.-
A KAIST research team presented three novel approaches for modulating local carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration in gas-diffusion electrode (GDE)-based flow electrolyzers. Their study also empirically demonstrated that providing a moderate local CO2 concentration is effective in promoting Carbon–Carbon (C–C) coupling reactions toward the production of multi-carbon molecules. This work, featured in the May 20th issue of Joule, serves as a rational guide to tune CO2 mass transport for the optimal production of valuable multi-carbon products.
Amid global efforts to reduce and recycle anthropogenic CO2 emissions, CO2 electrolysis holds great promise for converting CO2 into useful chemicals that were traditionally derived from fossil fuels. Many researches have been attempting to improve the selectivity of CO2 for commercially and industrially high-value multi-carbon products such as ethylene, ethanol, and 1-propanol, due to their high energy density and large market size.
In order to achieve the highly-selective conversion of CO2 into valuable multi-carbon products, past studies have focused on the design of catalysts and the tuning of local environment related to pH, cations, and molecular additives.
Conventional CO2 electrolytic systems relied heavily on an alkaline electrolyte that is often consumed in large quantities when reacting with CO2, and thus led to an increase in the operational costs. Moreover, the life span of a catalyst electrode was short, due to its inherent chemical reactivity.
In their recent study, a group of KAIST researchers led by Professor Jihun Oh from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering reported that the local CO2 concentration has been an overlooked factor that largely affects the selectivity toward multi-carbon products.
Professor Oh and his researchers Dr. Ying Chuan Tan, Hakhyeon Song, and Kelvin Berm Lee proposed that there is an intimate relation between local CO2 and multi-carbon product selectivity during electrochemical CO2 reduction reactions. The team employed the mass-transport modeling of a GDE-based flow electrolyzer that utilizes copper oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles as model catalysts. They then identified and applied three approaches to modulate the local CO2 concentration within a GDE-based electrolytic system, including 1) controlling the catalyst layer structure, 2) CO2 feed concentration, and 3) feed flow rate.
Contrary to common intuition, the study showed that providing a maximum CO2 transport leads to suboptimal multi-carbon product faradaic efficiency. Instead, by restricting and providing a moderate local CO2 concentration, C–C coupling can be significantly enhanced.
The researchers demonstrated experimentally that the selectivity rate increased from 25.4% to 61.9%, and from 5.9% to 22.6% for the CO2 conversion rate. When a cheap milder near-neutral electrolyte was used, the stability of the CO2 electrolytic system improved to a great extent, allowing over 10 hours of steady selective production of multi-carbon products.
Dr. Tan, the lead author of the paper, said, “Our research clearly revealed that the optimization of the local CO2 concentration is the key to maximizing the efficiency of converting CO2 into high-value multi-carbon products.”
Professor Oh added, “This finding is expected to deliver new insights to the research community that variables affecting local CO2 concentration are also influential factors in the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction performance. My colleagues and I hope that our study becomes a cornerstone for related technologies and their industrial applications.”
This work was supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) Creative Materials Discovery Program.
Publication:
Tan, Y. C et al. (2020) ‘Modulating Local CO2 Concentration as a General Strategy for Enhancing C−C Coupling in CO2 Electroreduction’, Joule, Vol. 4, Issue 5, pp. 1104-1120. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2020.03.013
Profile: Jihun Oh, PhD
Associate Professor
jihun.oh@kaist.ac.kr
http://les.kaist.ac.kr/
Laboratory for Energy and Sustainability (LE&S)
Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Republic of Korea
Profile: Ying Chuan Tan, PhD
tanyc@kaist.ac.kr
LE&S, MSE, KAIST
Profile: Hakhyeon Song, PhD Candidate
hyeon0401@kaist.ac.kr
LE&S, MSE, KAIST
Profile: Kelvin Berm Lee, M.S. Candidate
kbl9105@kaist.ac.kr
LE&S, MSE, KAIST
(END)
2020.06.03 View 12393
A New Strategy for the Optimal Electroreduction of CO2 to High-Value Products
-Researchers suggest that modulation of local CO2 concentration improves the selectivity, conversion rate, and electrode stability, and shed a new light on the electrochemical CO2 reduction technology for controlling emissions at a low cost.-
A KAIST research team presented three novel approaches for modulating local carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration in gas-diffusion electrode (GDE)-based flow electrolyzers. Their study also empirically demonstrated that providing a moderate local CO2 concentration is effective in promoting Carbon–Carbon (C–C) coupling reactions toward the production of multi-carbon molecules. This work, featured in the May 20th issue of Joule, serves as a rational guide to tune CO2 mass transport for the optimal production of valuable multi-carbon products.
Amid global efforts to reduce and recycle anthropogenic CO2 emissions, CO2 electrolysis holds great promise for converting CO2 into useful chemicals that were traditionally derived from fossil fuels. Many researches have been attempting to improve the selectivity of CO2 for commercially and industrially high-value multi-carbon products such as ethylene, ethanol, and 1-propanol, due to their high energy density and large market size.
In order to achieve the highly-selective conversion of CO2 into valuable multi-carbon products, past studies have focused on the design of catalysts and the tuning of local environment related to pH, cations, and molecular additives.
Conventional CO2 electrolytic systems relied heavily on an alkaline electrolyte that is often consumed in large quantities when reacting with CO2, and thus led to an increase in the operational costs. Moreover, the life span of a catalyst electrode was short, due to its inherent chemical reactivity.
In their recent study, a group of KAIST researchers led by Professor Jihun Oh from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering reported that the local CO2 concentration has been an overlooked factor that largely affects the selectivity toward multi-carbon products.
Professor Oh and his researchers Dr. Ying Chuan Tan, Hakhyeon Song, and Kelvin Berm Lee proposed that there is an intimate relation between local CO2 and multi-carbon product selectivity during electrochemical CO2 reduction reactions. The team employed the mass-transport modeling of a GDE-based flow electrolyzer that utilizes copper oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles as model catalysts. They then identified and applied three approaches to modulate the local CO2 concentration within a GDE-based electrolytic system, including 1) controlling the catalyst layer structure, 2) CO2 feed concentration, and 3) feed flow rate.
Contrary to common intuition, the study showed that providing a maximum CO2 transport leads to suboptimal multi-carbon product faradaic efficiency. Instead, by restricting and providing a moderate local CO2 concentration, C–C coupling can be significantly enhanced.
The researchers demonstrated experimentally that the selectivity rate increased from 25.4% to 61.9%, and from 5.9% to 22.6% for the CO2 conversion rate. When a cheap milder near-neutral electrolyte was used, the stability of the CO2 electrolytic system improved to a great extent, allowing over 10 hours of steady selective production of multi-carbon products.
Dr. Tan, the lead author of the paper, said, “Our research clearly revealed that the optimization of the local CO2 concentration is the key to maximizing the efficiency of converting CO2 into high-value multi-carbon products.”
Professor Oh added, “This finding is expected to deliver new insights to the research community that variables affecting local CO2 concentration are also influential factors in the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction performance. My colleagues and I hope that our study becomes a cornerstone for related technologies and their industrial applications.”
This work was supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) Creative Materials Discovery Program.
Publication:
Tan, Y. C et al. (2020) ‘Modulating Local CO2 Concentration as a General Strategy for Enhancing C−C Coupling in CO2 Electroreduction’, Joule, Vol. 4, Issue 5, pp. 1104-1120. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2020.03.013
Profile: Jihun Oh, PhD
Associate Professor
jihun.oh@kaist.ac.kr
http://les.kaist.ac.kr/
Laboratory for Energy and Sustainability (LE&S)
Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Republic of Korea
Profile: Ying Chuan Tan, PhD
tanyc@kaist.ac.kr
LE&S, MSE, KAIST
Profile: Hakhyeon Song, PhD Candidate
hyeon0401@kaist.ac.kr
LE&S, MSE, KAIST
Profile: Kelvin Berm Lee, M.S. Candidate
kbl9105@kaist.ac.kr
LE&S, MSE, KAIST
(END)
2020.06.03 View 12393 -
 From Dark to Light in a Flash: Smart Film Lets Windows Switch Autonomously
Researchers have developed a new easy-to-use smart optical film technology that allows smart window devices to autonomously switch between transparent and opaque states in response to the surrounding light conditions.
The proposed 3D hybrid nanocomposite film with a highly periodic network structure has empirically demonstrated its high speed and performance, enabling the smart window to quantify and self-regulate its high-contrast optical transmittance. As a proof of concept, a mobile-app-enabled smart window device for Internet of Things (IoT) applications has been realized using the proposed smart optical film with successful expansion to the 3-by-3-inch scale. This energy-efficient and cost-effective technology holds great promise for future use in various applications that require active optical transmission modulation.
Flexible optical transmission modulation technologies for smart applications including privacy-protection windows, zero-energy buildings, and beam projection screens have been in the spotlight in recent years. Conventional technologies that used external stimuli such as electricity, heat, or light to modulate optical transmission had only limited applications due to their slow response speeds, unnecessary color switching, and low durability, stability, and safety.
The optical transmission modulation contrast achieved by controlling the light scattering interfaces on non-periodic 2D surface structures that often have low optical density such as cracks, wrinkles, and pillars is also generally low. In addition, since the light scattering interfaces are exposed and not subject to any passivation, they can be vulnerable to external damage and may lose optical transmission modulation functions. Furthermore, in-plane scattering interfaces that randomly exist on the surface make large-area modulation with uniformity difficult.
Inspired by these limitations, a KAIST research team led by Professor Seokwoo Jeon from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Jung-Wuk Hong of the Civil and Environmental Engineering Department used proximity-field nanopatterning (PnP) technology that effectively produces highly periodic 3D hybrid nanostructures, and an atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique that allows the precise control of oxide deposition and the high-quality fabrication of semiconductor devices.
The team then successfully produced a large-scale smart optical film with a size of 3 by 3 inches in which ultrathin alumina nanoshells are inserted between the elastomers in a periodic 3D nanonetwork.
This “mechano-responsive” 3D hybrid nanocomposite film with a highly periodic network structure is the largest smart optical transmission modulation film that exists. The film has been shown to have state-of-the-art optical transmission modulation of up to 74% at visible wavelengths from 90% initial transmission to 16% in the scattering state under strain. Its durability and stability were proved by more than 10,000 tests of harsh mechanical deformation including stretching, releasing, bending, and being placed under high temperatures of up to 70°C. When this film was used, the transmittance of the smart window device was adjusted promptly and automatically within one second in response to the surrounding light conditions. Through these experiments, the underlying physics of optical scattering phenomena occurring in the heterogeneous interfaces were identified. Their findings were reported in the online edition of Advanced Science on April 26. KAIST Professor Jong-Hwa Shin’s group and Professor Young-Seok Shim at Silla University also collaborated on this project.
Donghwi Cho, a PhD candidate in materials science and engineering at KAIST and co-lead author of the study, said, “Our smart optical film technology can better control high-contrast optical transmittance by relatively simple operating principles and with low energy consumption and costs.”
“When this technology is applied by simply attaching the film to a conventional smart window glass surface without replacing the existing window system, fast switching and uniform tinting are possible while also securing durability, stability, and safety. In addition, its wide range of applications for stretchable or rollable devices such as wall-type displays for a beam projection screen will also fulfill aesthetic needs,” he added.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), and the Korean Ministries of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP), and Science and ICT (MSIT).
Publication:
Cho, D, et al. (2020) ‘High-Contrast Optical Modulation from Strain-Indicated Nanogaps at 3D Heterogeneous Interfaces’ Advanced Science, 1903708. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201903708
Profile: Seokwoo Jeon, PhD
Professor
jeon39@kaist.ac.kr
https://fdml.kaist.ac.kr/
Flexible Device and Metamaterials Lab (FDML)
Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.krDaejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Jung-Wuk Hong, PhD
Associate Professor
j.hong@kaist.ac.kr
http://aaml.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Applied Mechanics Laboratory (AAML)
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
KAIST
Profile: Donghwi Cho
PhD Candidate
roy0202@kaist.ac.krFDML, MSE, KAIST
Profile: Young-Seok Shim, PhD
Assistant Professor
ysshim@silla.ac.kr
Division of Materials Science and Engineering Silla University
https://www.silla.ac.kr
Busan 46958, Korea
(END)
2020.06.02 View 13737
From Dark to Light in a Flash: Smart Film Lets Windows Switch Autonomously
Researchers have developed a new easy-to-use smart optical film technology that allows smart window devices to autonomously switch between transparent and opaque states in response to the surrounding light conditions.
The proposed 3D hybrid nanocomposite film with a highly periodic network structure has empirically demonstrated its high speed and performance, enabling the smart window to quantify and self-regulate its high-contrast optical transmittance. As a proof of concept, a mobile-app-enabled smart window device for Internet of Things (IoT) applications has been realized using the proposed smart optical film with successful expansion to the 3-by-3-inch scale. This energy-efficient and cost-effective technology holds great promise for future use in various applications that require active optical transmission modulation.
Flexible optical transmission modulation technologies for smart applications including privacy-protection windows, zero-energy buildings, and beam projection screens have been in the spotlight in recent years. Conventional technologies that used external stimuli such as electricity, heat, or light to modulate optical transmission had only limited applications due to their slow response speeds, unnecessary color switching, and low durability, stability, and safety.
The optical transmission modulation contrast achieved by controlling the light scattering interfaces on non-periodic 2D surface structures that often have low optical density such as cracks, wrinkles, and pillars is also generally low. In addition, since the light scattering interfaces are exposed and not subject to any passivation, they can be vulnerable to external damage and may lose optical transmission modulation functions. Furthermore, in-plane scattering interfaces that randomly exist on the surface make large-area modulation with uniformity difficult.
Inspired by these limitations, a KAIST research team led by Professor Seokwoo Jeon from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Jung-Wuk Hong of the Civil and Environmental Engineering Department used proximity-field nanopatterning (PnP) technology that effectively produces highly periodic 3D hybrid nanostructures, and an atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique that allows the precise control of oxide deposition and the high-quality fabrication of semiconductor devices.
The team then successfully produced a large-scale smart optical film with a size of 3 by 3 inches in which ultrathin alumina nanoshells are inserted between the elastomers in a periodic 3D nanonetwork.
This “mechano-responsive” 3D hybrid nanocomposite film with a highly periodic network structure is the largest smart optical transmission modulation film that exists. The film has been shown to have state-of-the-art optical transmission modulation of up to 74% at visible wavelengths from 90% initial transmission to 16% in the scattering state under strain. Its durability and stability were proved by more than 10,000 tests of harsh mechanical deformation including stretching, releasing, bending, and being placed under high temperatures of up to 70°C. When this film was used, the transmittance of the smart window device was adjusted promptly and automatically within one second in response to the surrounding light conditions. Through these experiments, the underlying physics of optical scattering phenomena occurring in the heterogeneous interfaces were identified. Their findings were reported in the online edition of Advanced Science on April 26. KAIST Professor Jong-Hwa Shin’s group and Professor Young-Seok Shim at Silla University also collaborated on this project.
Donghwi Cho, a PhD candidate in materials science and engineering at KAIST and co-lead author of the study, said, “Our smart optical film technology can better control high-contrast optical transmittance by relatively simple operating principles and with low energy consumption and costs.”
“When this technology is applied by simply attaching the film to a conventional smart window glass surface without replacing the existing window system, fast switching and uniform tinting are possible while also securing durability, stability, and safety. In addition, its wide range of applications for stretchable or rollable devices such as wall-type displays for a beam projection screen will also fulfill aesthetic needs,” he added.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), and the Korean Ministries of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP), and Science and ICT (MSIT).
Publication:
Cho, D, et al. (2020) ‘High-Contrast Optical Modulation from Strain-Indicated Nanogaps at 3D Heterogeneous Interfaces’ Advanced Science, 1903708. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201903708
Profile: Seokwoo Jeon, PhD
Professor
jeon39@kaist.ac.kr
https://fdml.kaist.ac.kr/
Flexible Device and Metamaterials Lab (FDML)
Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.krDaejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Jung-Wuk Hong, PhD
Associate Professor
j.hong@kaist.ac.kr
http://aaml.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Applied Mechanics Laboratory (AAML)
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
KAIST
Profile: Donghwi Cho
PhD Candidate
roy0202@kaist.ac.krFDML, MSE, KAIST
Profile: Young-Seok Shim, PhD
Assistant Professor
ysshim@silla.ac.kr
Division of Materials Science and Engineering Silla University
https://www.silla.ac.kr
Busan 46958, Korea
(END)
2020.06.02 View 13737 -
 Universal Virus Detection Platform to Expedite Viral Diagnosis
Reactive polymer-based tester pre-screens dsRNAs of a wide range of viruses without their genome sequences
The prompt, precise, and massive detection of a virus is the key to combat infectious diseases such as Covid-19. A new viral diagnostic strategy using reactive polymer-grafted, double-stranded RNAs will serve as a pre-screening tester for a wide range of viruses with enhanced sensitivity.
Currently, the most widely using viral detection methodology is polymerase chain reaction (PCR) diagnosis, which amplifies and detects a piece of the viral genome. Prior knowledge of the relevant primer nucleic acids of the virus is quintessential for this test.
The detection platform developed by KAIST researchers identifies viral activities without amplifying specific nucleic acid targets. The research team, co-led by Professor Sheng Li and Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, constructed a universal virus detection platform by utilizing the distinct features of the PPFPA-grafted surface and double-stranded RNAs.
The key principle of this platform is utilizing the distinct feature of reactive polymer-grafted surfaces, which serve as a versatile platform for the immobilization of functional molecules. These activated surfaces can be used in a wide range of applications including separation, delivery, and detection. As long double-stranded RNAs are common byproducts of viral transcription and replication, these PPFPA-grafted surfaces can detect the presence of different kinds of viruses without prior knowledge of their genomic sequences.
“We employed the PPFPA-grafted silicon surface to develop a universal virus detection platform by immobilizing antibodies that recognize double-stranded RNAs,” said Professor Kim.
To increase detection sensitivity, the research team devised two-step detection process analogues to sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay where the bound double-stranded RNAs are then visualized using fluorophore-tagged antibodies that also recognize the RNAs’ double-stranded secondary structure.
By utilizing the developed platform, long double-stranded RNAs can be detected and visualized from an RNA mixture as well as from total cell lysates, which contain a mixture of various abundant contaminants such as DNAs and proteins.
The research team successfully detected elevated levels of hepatitis C and A viruses with this tool.
“This new technology allows us to take on virus detection from a new perspective. By targeting a common biomarker, viral double-stranded RNAs, we can develop a pre-screening platform that can quickly differentiate infected populations from non-infected ones,” said Professor Li.
“This detection platform provides new perspectives for diagnosing infectious diseases. This will provide fast and accurate diagnoses for an infected population and prevent the influx of massive outbreaks,” said Professor Kim.
This work is featured in Biomacromolecules. This work was supported by the Agency for Defense Development (Grant UD170039ID), the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2017R1D1A1B03034660, NRF-2019R1C1C1006672), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project from the Ministry of Science and ICT (KAISTHEALTHCARE42).
Profile:-Professor Yoosik KimDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineeringhttps://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST-Professor Sheng LiDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineeringhttps://bcpolymer.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
Publication:Ku et al., 2020. Reactive Polymer Targeting dsRNA as Universal Virus Detection Platform with Enhanced Sensitivity. Biomacromolecules (https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00379).
2020.06.01 View 19120
Universal Virus Detection Platform to Expedite Viral Diagnosis
Reactive polymer-based tester pre-screens dsRNAs of a wide range of viruses without their genome sequences
The prompt, precise, and massive detection of a virus is the key to combat infectious diseases such as Covid-19. A new viral diagnostic strategy using reactive polymer-grafted, double-stranded RNAs will serve as a pre-screening tester for a wide range of viruses with enhanced sensitivity.
Currently, the most widely using viral detection methodology is polymerase chain reaction (PCR) diagnosis, which amplifies and detects a piece of the viral genome. Prior knowledge of the relevant primer nucleic acids of the virus is quintessential for this test.
The detection platform developed by KAIST researchers identifies viral activities without amplifying specific nucleic acid targets. The research team, co-led by Professor Sheng Li and Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, constructed a universal virus detection platform by utilizing the distinct features of the PPFPA-grafted surface and double-stranded RNAs.
The key principle of this platform is utilizing the distinct feature of reactive polymer-grafted surfaces, which serve as a versatile platform for the immobilization of functional molecules. These activated surfaces can be used in a wide range of applications including separation, delivery, and detection. As long double-stranded RNAs are common byproducts of viral transcription and replication, these PPFPA-grafted surfaces can detect the presence of different kinds of viruses without prior knowledge of their genomic sequences.
“We employed the PPFPA-grafted silicon surface to develop a universal virus detection platform by immobilizing antibodies that recognize double-stranded RNAs,” said Professor Kim.
To increase detection sensitivity, the research team devised two-step detection process analogues to sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay where the bound double-stranded RNAs are then visualized using fluorophore-tagged antibodies that also recognize the RNAs’ double-stranded secondary structure.
By utilizing the developed platform, long double-stranded RNAs can be detected and visualized from an RNA mixture as well as from total cell lysates, which contain a mixture of various abundant contaminants such as DNAs and proteins.
The research team successfully detected elevated levels of hepatitis C and A viruses with this tool.
“This new technology allows us to take on virus detection from a new perspective. By targeting a common biomarker, viral double-stranded RNAs, we can develop a pre-screening platform that can quickly differentiate infected populations from non-infected ones,” said Professor Li.
“This detection platform provides new perspectives for diagnosing infectious diseases. This will provide fast and accurate diagnoses for an infected population and prevent the influx of massive outbreaks,” said Professor Kim.
This work is featured in Biomacromolecules. This work was supported by the Agency for Defense Development (Grant UD170039ID), the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2017R1D1A1B03034660, NRF-2019R1C1C1006672), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project from the Ministry of Science and ICT (KAISTHEALTHCARE42).
Profile:-Professor Yoosik KimDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineeringhttps://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST-Professor Sheng LiDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineeringhttps://bcpolymer.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
Publication:Ku et al., 2020. Reactive Polymer Targeting dsRNA as Universal Virus Detection Platform with Enhanced Sensitivity. Biomacromolecules (https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00379).
2020.06.01 View 19120 -
 Visualization of Functional Components to Characterize Optimal Composite Electrodes
Researchers have developed a visualization method that will determine the distribution of components in battery electrodes using atomic force microscopy. The method provides insights into the optimal conditions of composite electrodes and takes us one step closer to being able to manufacture next-generation all-solid-state batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in smart devices and vehicles. However, their flammability makes them a safety concern, arising from potential leakage of liquid electrolytes.
All-solid-state lithium ion batteries have emerged as an alternative because of their better safety and wider electrochemical stability. Despite their advantages, all-solid-state lithium ion batteries still have drawbacks such as limited ion conductivity, insufficient contact areas, and high interfacial resistance between the electrode and solid electrolyte.
To solve these issues, studies have been conducted on composite electrodes in which lithium ion conducting additives are dispersed as a medium to provide ion conductive paths at the interface and increase the overall ionic conductivity.
It is very important to identify the shape and distribution of the components used in active materials, ion conductors, binders, and conductive additives on a microscopic scale for significantly improving the battery operation performance.
The developed method is able to distinguish regions of each component based on detected signal sensitivity, by using various modes of atomic force microscopy on a multiscale basis, including electrochemical strain microscopy and lateral force microscopy.
For this research project, both conventional electrodes and composite electrodes were tested, and the results were compared. Individual regions were distinguished and nanoscale correlation between ion reactivity distribution and friction force distribution within a single region was determined to examine the effect of the distribution of binder on the electrochemical strain.
The research team explored the electrochemical strain microscopy amplitude/phase and lateral force microscopy friction force dependence on the AC drive voltage and the tip loading force, and used their sensitivities as markers for each component in the composite anode.
This method allows for direct multiscale observation of the composite electrode in ambient condition, distinguishing various components and measuring their properties simultaneously.
Lead author Dr. Hongjun Kim said, “It is easy to prepare the test sample for observation while providing much higher spatial resolution and intensity resolution for detected signals.” He added, “The method also has the advantage of providing 3D surface morphology information for the observed specimens.”
Professor Seungbum Hong from the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering said, “This analytical technique using atomic force microscopy will be useful for quantitatively understanding what role each component of a composite material plays in the final properties.”
“Our method not only will suggest the new direction for next-generation all-solid-state battery design on a multiscale basis but also lay the groundwork for innovation in the manufacturing process of other electrochemical materials.”
This study is published in ACS Applied Energy Materials and supported by the Big Science Research and Development Project under the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Basic Research Project under the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center, and KAIST Global Singularity Research Program for 2019 and 2020.
Publication:Kim, H, et al. (2020) ‘Visualization of Functional Components in a Lithium Silicon Titanium Phosphate-Natural Graphite Composite Anode’. ACS Applied Energy Materials, Volume 3, Issue 4, pp. 3253-3261. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b02045
Profile:
Seungbum Hong
Professor
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Materials Imaging and Integration Laboratory
Department of Material Sciences and Engineering
KAIST
2020.05.22 View 10397
Visualization of Functional Components to Characterize Optimal Composite Electrodes
Researchers have developed a visualization method that will determine the distribution of components in battery electrodes using atomic force microscopy. The method provides insights into the optimal conditions of composite electrodes and takes us one step closer to being able to manufacture next-generation all-solid-state batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in smart devices and vehicles. However, their flammability makes them a safety concern, arising from potential leakage of liquid electrolytes.
All-solid-state lithium ion batteries have emerged as an alternative because of their better safety and wider electrochemical stability. Despite their advantages, all-solid-state lithium ion batteries still have drawbacks such as limited ion conductivity, insufficient contact areas, and high interfacial resistance between the electrode and solid electrolyte.
To solve these issues, studies have been conducted on composite electrodes in which lithium ion conducting additives are dispersed as a medium to provide ion conductive paths at the interface and increase the overall ionic conductivity.
It is very important to identify the shape and distribution of the components used in active materials, ion conductors, binders, and conductive additives on a microscopic scale for significantly improving the battery operation performance.
The developed method is able to distinguish regions of each component based on detected signal sensitivity, by using various modes of atomic force microscopy on a multiscale basis, including electrochemical strain microscopy and lateral force microscopy.
For this research project, both conventional electrodes and composite electrodes were tested, and the results were compared. Individual regions were distinguished and nanoscale correlation between ion reactivity distribution and friction force distribution within a single region was determined to examine the effect of the distribution of binder on the electrochemical strain.
The research team explored the electrochemical strain microscopy amplitude/phase and lateral force microscopy friction force dependence on the AC drive voltage and the tip loading force, and used their sensitivities as markers for each component in the composite anode.
This method allows for direct multiscale observation of the composite electrode in ambient condition, distinguishing various components and measuring their properties simultaneously.
Lead author Dr. Hongjun Kim said, “It is easy to prepare the test sample for observation while providing much higher spatial resolution and intensity resolution for detected signals.” He added, “The method also has the advantage of providing 3D surface morphology information for the observed specimens.”
Professor Seungbum Hong from the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering said, “This analytical technique using atomic force microscopy will be useful for quantitatively understanding what role each component of a composite material plays in the final properties.”
“Our method not only will suggest the new direction for next-generation all-solid-state battery design on a multiscale basis but also lay the groundwork for innovation in the manufacturing process of other electrochemical materials.”
This study is published in ACS Applied Energy Materials and supported by the Big Science Research and Development Project under the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Basic Research Project under the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center, and KAIST Global Singularity Research Program for 2019 and 2020.
Publication:Kim, H, et al. (2020) ‘Visualization of Functional Components in a Lithium Silicon Titanium Phosphate-Natural Graphite Composite Anode’. ACS Applied Energy Materials, Volume 3, Issue 4, pp. 3253-3261. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.9b02045
Profile:
Seungbum Hong
Professor
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Materials Imaging and Integration Laboratory
Department of Material Sciences and Engineering
KAIST
2020.05.22 View 10397 -
 Highly Efficient Charge-to-Spin Interconversion in Graphene Heterostructures
Researchers present a new route for designing a graphene-based active spintronic component
KAIST physicists described a route to design the energy-efficient generation, manipulation and detection of spin currents using nonmagnetic two-dimensional materials. The research team, led by Professor Sungjae Cho, observed highly efficient charge-to-spin interconversion via the gate-tunable Rashba-Edelstien effect (REE) in graphene heterostructures.
This research paves the way for the application of graphene as an active spintronic component for generating, controlling, and detecting spin current without ferromagnetic electrodes or magnetic fields.
Graphene is a promising spintronic component owing to its long spin diffusion length. However, its small spin-orbit coupling limits the potential of graphene in spintronic applications since graphene cannot be used to generate, control, or detect spin current.
“We successfully increased the spin-orbit coupling of graphene by stacking graphene on top of 2H-TaS2, which is one of the transition metal dichalcogenide materials with the largest spin-orbit coupling. Graphene now can be used to generate, control, and detect spin current,” Professor Cho said.
The Rashba-Edelstein effect is a physical mechanism that enables charge current-to-spin current interconversion by spin-dependent band structure induced by the Rashba effect, a momentum-dependent splitting of spin bands in low-dimensional condensed matter systems.
Professor Cho’s group demonstrated the gate-tunable Rashba-Edelstein effect in a multilayer graphene for the first time. The Rahsba-Edelstein effect allows the two-dimensional conduction electrons of graphene to be magnetized by an applied charge current and form a spin current. Furthermore, as the Fermi level of graphene, tuned by gate voltage, moves from the valence to conduction band, the spin current generated by graphene reversed its spin direction.
This spin reversal is useful in the design of low-power-consumption transistors utilizing spins in that it provides the carrier “On” state with spin up holes (or spin down electrons) and the "Off" state with zero net spin polarization at so called “charge neutrality point” where numbers of electrons and holes are equal.
“Our work is the first demonstration of charge-to-spin interconversion in a metallic TMD (transition-metal dichalcogenides) and graphene heterostructure with a spin polarization state controlled by a gate. We expect that the all-electrical spin-switching effect and the reversal of non-equilibrium spin polarization by the application of gate voltage is applicable for the energy-efficient generation and manipulation of spin currents using nonmagnetic van der Waals materials,” explained Professor Cho.
This study (https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.0c01037) was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Lijun Li, Jin Zhang, Gyuho Myeong, Wongil Shin, Hongsik Lim, Boram Kim, Seungho Kim, Taehyeok Jin, Stuart Cavill, Beom Seo Kim, Changyoung Kim, Johannes Lischner, Aires Ferreira, and Sungjae Cho, Gate-Tunable Reversible Rashba−Edelstein Effect in a Few-Layer Graphene/2H-TaS2 Heterostructure at Room Temperature. ACS Nano 2020. Link to download the paper: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.0c01037
Profile:
Professor Sungjae Cho, PhD
sungjae.cho@kaist.ac.kr
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
2020.05.18 View 10207
Highly Efficient Charge-to-Spin Interconversion in Graphene Heterostructures
Researchers present a new route for designing a graphene-based active spintronic component
KAIST physicists described a route to design the energy-efficient generation, manipulation and detection of spin currents using nonmagnetic two-dimensional materials. The research team, led by Professor Sungjae Cho, observed highly efficient charge-to-spin interconversion via the gate-tunable Rashba-Edelstien effect (REE) in graphene heterostructures.
This research paves the way for the application of graphene as an active spintronic component for generating, controlling, and detecting spin current without ferromagnetic electrodes or magnetic fields.
Graphene is a promising spintronic component owing to its long spin diffusion length. However, its small spin-orbit coupling limits the potential of graphene in spintronic applications since graphene cannot be used to generate, control, or detect spin current.
“We successfully increased the spin-orbit coupling of graphene by stacking graphene on top of 2H-TaS2, which is one of the transition metal dichalcogenide materials with the largest spin-orbit coupling. Graphene now can be used to generate, control, and detect spin current,” Professor Cho said.
The Rashba-Edelstein effect is a physical mechanism that enables charge current-to-spin current interconversion by spin-dependent band structure induced by the Rashba effect, a momentum-dependent splitting of spin bands in low-dimensional condensed matter systems.
Professor Cho’s group demonstrated the gate-tunable Rashba-Edelstein effect in a multilayer graphene for the first time. The Rahsba-Edelstein effect allows the two-dimensional conduction electrons of graphene to be magnetized by an applied charge current and form a spin current. Furthermore, as the Fermi level of graphene, tuned by gate voltage, moves from the valence to conduction band, the spin current generated by graphene reversed its spin direction.
This spin reversal is useful in the design of low-power-consumption transistors utilizing spins in that it provides the carrier “On” state with spin up holes (or spin down electrons) and the "Off" state with zero net spin polarization at so called “charge neutrality point” where numbers of electrons and holes are equal.
“Our work is the first demonstration of charge-to-spin interconversion in a metallic TMD (transition-metal dichalcogenides) and graphene heterostructure with a spin polarization state controlled by a gate. We expect that the all-electrical spin-switching effect and the reversal of non-equilibrium spin polarization by the application of gate voltage is applicable for the energy-efficient generation and manipulation of spin currents using nonmagnetic van der Waals materials,” explained Professor Cho.
This study (https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.0c01037) was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Lijun Li, Jin Zhang, Gyuho Myeong, Wongil Shin, Hongsik Lim, Boram Kim, Seungho Kim, Taehyeok Jin, Stuart Cavill, Beom Seo Kim, Changyoung Kim, Johannes Lischner, Aires Ferreira, and Sungjae Cho, Gate-Tunable Reversible Rashba−Edelstein Effect in a Few-Layer Graphene/2H-TaS2 Heterostructure at Room Temperature. ACS Nano 2020. Link to download the paper: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.0c01037
Profile:
Professor Sungjae Cho, PhD
sungjae.cho@kaist.ac.kr
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
2020.05.18 View 10207