Park
-
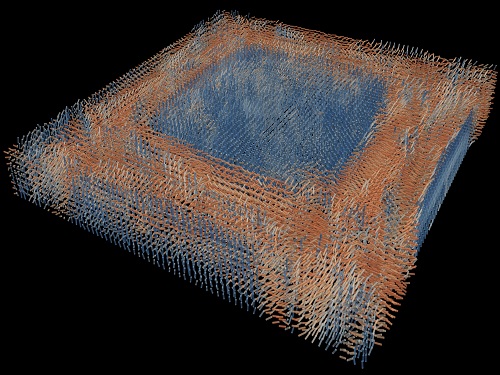 Tomographic Measurement of Dielectric Tensors
Dielectric tensor tomography allows the direct measurement of the 3D dielectric tensors of optically anisotropic structures
A research team reported the direct measurement of dielectric tensors of anisotropic structures including the spatial variations of principal refractive indices and directors. The group also demonstrated quantitative tomographic measurements of various nematic liquid-crystal structures and their fast 3D nonequilibrium dynamics using a 3D label-free tomographic method. The method was described in Nature Materials.
Light-matter interactions are described by the dielectric tensor. Despite their importance in basic science and applications, it has not been possible to measure 3D dielectric tensors directly. The main challenge was due to the vectorial nature of light scattering from a 3D anisotropic structure. Previous approaches only addressed 3D anisotropic information indirectly and were limited to two-dimensional, qualitative, strict sample conditions or assumptions.
The research team developed a method enabling the tomographic reconstruction of 3D dielectric tensors without any preparation or assumptions. A sample is illuminated with a laser beam with various angles and circularly polarization states. Then, the light fields scattered from a sample are holographically measured and converted into vectorial diffraction components. Finally, by inversely solving a vectorial wave equation, the 3D dielectric tensor is reconstructed.
Professor YongKeun Park said, “There were a greater number of unknowns in direct measuring than with the conventional approach. We applied our approach to measure additional holographic images by slightly tilting the incident angle.”
He said that the slightly tilted illumination provides an additional orthogonal polarization, which makes the underdetermined problem become the determined problem. “Although scattered fields are dependent on the illumination angle, the Fourier differentiation theorem enables the extraction of the same dielectric tensor for the slightly tilted illumination,” Professor Park added.
His team’s method was validated by reconstructing well-known liquid crystal (LC) structures, including the twisted nematic, hybrid aligned nematic, radial, and bipolar configurations. Furthermore, the research team demonstrated the experimental measurements of the non-equilibrium dynamics of annihilating, nucleating, and merging LC droplets, and the LC polymer network with repeating 3D topological defects.
“This is the first experimental measurement of non-equilibrium dynamics and 3D topological defects in LC structures in a label-free manner. Our method enables the exploration of inaccessible nematic structures and interactions in non-equilibrium dynamics,” first author Dr. Seungwoo Shin explained.
-PublicationSeungwoo Shin, Jonghee Eun, Sang Seok Lee, Changjae Lee, Herve Hugonnet, Dong Ki Yoon, Shin-Hyun Kim, Jongwoo Jeong, YongKeun Park, “Tomographic Measurement ofDielectric Tensors at Optical Frequency,” Nature Materials March 02, 2022 (https://doi.org/10/1038/s41563-022-01202-8)
-ProfileProfessor YongKeun ParkBiomedical Optics Laboratory (http://bmol.kaist.ac.kr)Department of PhysicsCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.03.22 View 9546
Tomographic Measurement of Dielectric Tensors
Dielectric tensor tomography allows the direct measurement of the 3D dielectric tensors of optically anisotropic structures
A research team reported the direct measurement of dielectric tensors of anisotropic structures including the spatial variations of principal refractive indices and directors. The group also demonstrated quantitative tomographic measurements of various nematic liquid-crystal structures and their fast 3D nonequilibrium dynamics using a 3D label-free tomographic method. The method was described in Nature Materials.
Light-matter interactions are described by the dielectric tensor. Despite their importance in basic science and applications, it has not been possible to measure 3D dielectric tensors directly. The main challenge was due to the vectorial nature of light scattering from a 3D anisotropic structure. Previous approaches only addressed 3D anisotropic information indirectly and were limited to two-dimensional, qualitative, strict sample conditions or assumptions.
The research team developed a method enabling the tomographic reconstruction of 3D dielectric tensors without any preparation or assumptions. A sample is illuminated with a laser beam with various angles and circularly polarization states. Then, the light fields scattered from a sample are holographically measured and converted into vectorial diffraction components. Finally, by inversely solving a vectorial wave equation, the 3D dielectric tensor is reconstructed.
Professor YongKeun Park said, “There were a greater number of unknowns in direct measuring than with the conventional approach. We applied our approach to measure additional holographic images by slightly tilting the incident angle.”
He said that the slightly tilted illumination provides an additional orthogonal polarization, which makes the underdetermined problem become the determined problem. “Although scattered fields are dependent on the illumination angle, the Fourier differentiation theorem enables the extraction of the same dielectric tensor for the slightly tilted illumination,” Professor Park added.
His team’s method was validated by reconstructing well-known liquid crystal (LC) structures, including the twisted nematic, hybrid aligned nematic, radial, and bipolar configurations. Furthermore, the research team demonstrated the experimental measurements of the non-equilibrium dynamics of annihilating, nucleating, and merging LC droplets, and the LC polymer network with repeating 3D topological defects.
“This is the first experimental measurement of non-equilibrium dynamics and 3D topological defects in LC structures in a label-free manner. Our method enables the exploration of inaccessible nematic structures and interactions in non-equilibrium dynamics,” first author Dr. Seungwoo Shin explained.
-PublicationSeungwoo Shin, Jonghee Eun, Sang Seok Lee, Changjae Lee, Herve Hugonnet, Dong Ki Yoon, Shin-Hyun Kim, Jongwoo Jeong, YongKeun Park, “Tomographic Measurement ofDielectric Tensors at Optical Frequency,” Nature Materials March 02, 2022 (https://doi.org/10/1038/s41563-022-01202-8)
-ProfileProfessor YongKeun ParkBiomedical Optics Laboratory (http://bmol.kaist.ac.kr)Department of PhysicsCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.03.22 View 9546 -
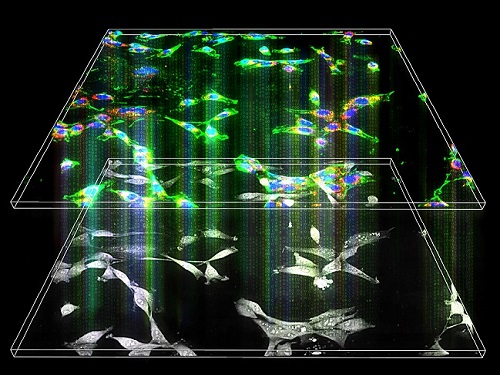 Label-Free Multiplexed Microtomography of Endogenous Subcellular Dynamics Using Deep Learning
AI-based holographic microscopy allows molecular imaging without introducing exogenous labeling agents
A research team upgraded the 3D microtomography observing dynamics of label-free live cells in multiplexed fluorescence imaging. The AI-powered 3D holotomographic microscopy extracts various molecular information from live unlabeled biological cells in real time without exogenous labeling or staining agents.
Professor YongKeum Park’s team and the startup Tomocube encoded 3D refractive index tomograms using the refractive index as a means of measurement. Then they decoded the information with a deep learning-based model that infers multiple 3D fluorescence tomograms from the refractive index measurements of the corresponding subcellular targets, thereby achieving multiplexed micro tomography. This study was reported in Nature Cell Biology online on December 7, 2021.
Fluorescence microscopy is the most widely used optical microscopy technique due to its high biochemical specificity. However, it needs to genetically manipulate or to stain cells with fluorescent labels in order to express fluorescent proteins. These labeling processes inevitably affect the intrinsic physiology of cells. It also has challenges in long-term measuring due to photobleaching and phototoxicity. The overlapped spectra of multiplexed fluorescence signals also hinder the viewing of various structures at the same time. More critically, it took several hours to observe the cells after preparing them.
3D holographic microscopy, also known as holotomography, is providing new ways to quantitatively image live cells without pretreatments such as staining. Holotomography can accurately and quickly measure the morphological and structural information of cells, but only provides limited biochemical and molecular information.
The 'AI microscope' created in this process takes advantage of the features of both holographic microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. That is, a specific image from a fluorescence microscope can be obtained without a fluorescent label. Therefore, the microscope can observe many types of cellular structures in their natural state in 3D and at the same time as fast as one millisecond, and long-term measurements over several days are also possible.
The Tomocube-KAIST team showed that fluorescence images can be directly and precisely predicted from holotomographic images in various cells and conditions. Using the quantitative relationship between the spatial distribution of the refractive index found by AI and the major structures in cells, it was possible to decipher the spatial distribution of the refractive index. And surprisingly, it confirmed that this relationship is constant regardless of cell type.
Professor Park said, “We were able to develop a new concept microscope that combines the advantages of several microscopes with the multidisciplinary research of AI, optics, and biology. It will be immediately applicable for new types of cells not included in the existing data and is expected to be widely applicable for various biological and medical research.”
When comparing the molecular image information extracted by AI with the molecular image information physically obtained by fluorescence staining in 3D space, it showed a 97% or more conformity, which is a level that is difficult to distinguish with the naked eye.
“Compared to the sub-60% accuracy of the fluorescence information extracted from the model developed by the Google AI team, it showed significantly higher performance,” Professor Park added.
This work was supported by the KAIST Up program, the BK21+ program, Tomocube, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Health & Welfare.
-Publication
Hyun-seok Min, Won-Do Heo, YongKeun Park, et al. “Label-free multiplexed microtomography of endogenous subcellular dynamics using generalizable deep learning,” Nature Cell Biology (doi.org/10.1038/s41556-021-00802-x) published online December 07 2021.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
Department of Physics
KAIST
2022.02.09 View 12582
Label-Free Multiplexed Microtomography of Endogenous Subcellular Dynamics Using Deep Learning
AI-based holographic microscopy allows molecular imaging without introducing exogenous labeling agents
A research team upgraded the 3D microtomography observing dynamics of label-free live cells in multiplexed fluorescence imaging. The AI-powered 3D holotomographic microscopy extracts various molecular information from live unlabeled biological cells in real time without exogenous labeling or staining agents.
Professor YongKeum Park’s team and the startup Tomocube encoded 3D refractive index tomograms using the refractive index as a means of measurement. Then they decoded the information with a deep learning-based model that infers multiple 3D fluorescence tomograms from the refractive index measurements of the corresponding subcellular targets, thereby achieving multiplexed micro tomography. This study was reported in Nature Cell Biology online on December 7, 2021.
Fluorescence microscopy is the most widely used optical microscopy technique due to its high biochemical specificity. However, it needs to genetically manipulate or to stain cells with fluorescent labels in order to express fluorescent proteins. These labeling processes inevitably affect the intrinsic physiology of cells. It also has challenges in long-term measuring due to photobleaching and phototoxicity. The overlapped spectra of multiplexed fluorescence signals also hinder the viewing of various structures at the same time. More critically, it took several hours to observe the cells after preparing them.
3D holographic microscopy, also known as holotomography, is providing new ways to quantitatively image live cells without pretreatments such as staining. Holotomography can accurately and quickly measure the morphological and structural information of cells, but only provides limited biochemical and molecular information.
The 'AI microscope' created in this process takes advantage of the features of both holographic microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. That is, a specific image from a fluorescence microscope can be obtained without a fluorescent label. Therefore, the microscope can observe many types of cellular structures in their natural state in 3D and at the same time as fast as one millisecond, and long-term measurements over several days are also possible.
The Tomocube-KAIST team showed that fluorescence images can be directly and precisely predicted from holotomographic images in various cells and conditions. Using the quantitative relationship between the spatial distribution of the refractive index found by AI and the major structures in cells, it was possible to decipher the spatial distribution of the refractive index. And surprisingly, it confirmed that this relationship is constant regardless of cell type.
Professor Park said, “We were able to develop a new concept microscope that combines the advantages of several microscopes with the multidisciplinary research of AI, optics, and biology. It will be immediately applicable for new types of cells not included in the existing data and is expected to be widely applicable for various biological and medical research.”
When comparing the molecular image information extracted by AI with the molecular image information physically obtained by fluorescence staining in 3D space, it showed a 97% or more conformity, which is a level that is difficult to distinguish with the naked eye.
“Compared to the sub-60% accuracy of the fluorescence information extracted from the model developed by the Google AI team, it showed significantly higher performance,” Professor Park added.
This work was supported by the KAIST Up program, the BK21+ program, Tomocube, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Health & Welfare.
-Publication
Hyun-seok Min, Won-Do Heo, YongKeun Park, et al. “Label-free multiplexed microtomography of endogenous subcellular dynamics using generalizable deep learning,” Nature Cell Biology (doi.org/10.1038/s41556-021-00802-x) published online December 07 2021.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
Department of Physics
KAIST
2022.02.09 View 12582 -
 Flexible Sensor-Integrated RFA Needle Leads to Smarter Medical Treatment
Clinical trial of flexible sensor-integrated radiofrequency ablation (RFA) needle tip monitors physical changes and steam pop
Researchers have designed a thin polymeric sensor platform on a radiofrequency ablation needle to monitor temperature and pressure in real time. The sensors integrated onto 1.5 mm diameter needle tip have proven their efficacy during clinical tests and expect to provide a new opportunity for safer and more effective medical practices. The research was reported in Advanced Science as the frontispiece on August 5.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a minimally invasive surgery technique for removing tumors and treating cardiovascular disease. During a procedure, an unintended audible explosion called ‘steam pop’ can occur due to the increased internal steam pressure in the ablation region. This phenomenon has been cited as a cause of various negative thermal and mechanical effects on neighboring tissue. Even more, the relationship between steam pop and cancer recurrence is still being investigated.
Professor Inkyu Park said that his team’s integrated sensors reliably detected the occurrence of steam pop. The sensors also monitor rapidly spreading hot steam in tissue. It is expected that the diverse properties of tissue undergoing RFA could be checked by utilizing the physical sensors integrated on the needle.
“We believe that the integrated sensors can provide useful information about a variety of medical procedures and accompanying environmental changes in the human body, and help develop more effective and safer surgical procedures,” said Professor Park.
Professor Park’s team built a thin film type pressure and temperature sensor stack with a thickness of less than 10 μm using a microfabrication process. For the pressure sensor, the team used contact resistance changes between metal electrodes and a carbon nanotube coated polymeric membrane. The entire sensor array was thoroughly insulated with medical tubes to minimize any exposure of the sensor materials to external tissue and maximize its biocompatibility.
During the clinical trial, the research team found that the accumulated hot steam is suddenly released during steam pops and this hot air spreads to neighboring tissue, which accelerates the ablation process. Furthermore, using in-situ ultrasound imaging and computational simulations, the research team could confirm the non-uniform temperature distribution around the RFA needle can be one of the primary reasons for the steam popping.
Professor Park explained that various physical and chemical sensors for different targets can be added to create other medical devices and industrial tools.
“This result will expand the usability and applicability of current flexible sensor technologies. We are also trying to integrate this sensor onto a 0.3mm diameter needle for in-vivo diagnosis applications and expect that this approach can be applied to other medical treatments as well as the industrial field,” added Professor Park. This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-PublicationJaeho Park, Jinwoo Lee, Hyo Keun Lim, Inkyu Park et al. “Real-Time Internal Steam Pop Detection during Radiofrequency Ablation with a Radiofrequency Ablation Needle Integrated with a Temperature and Pressure Sensor: Preclinical and clinical pilot tests," Advanced Science (https://doi/org/10.1002/advs.202100725) on August 5, 2021
-ProfileProfessor Inkyu ParkMicro & Nano Tranducers Laboratory http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Mechanical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2021.10.20 View 10012
Flexible Sensor-Integrated RFA Needle Leads to Smarter Medical Treatment
Clinical trial of flexible sensor-integrated radiofrequency ablation (RFA) needle tip monitors physical changes and steam pop
Researchers have designed a thin polymeric sensor platform on a radiofrequency ablation needle to monitor temperature and pressure in real time. The sensors integrated onto 1.5 mm diameter needle tip have proven their efficacy during clinical tests and expect to provide a new opportunity for safer and more effective medical practices. The research was reported in Advanced Science as the frontispiece on August 5.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a minimally invasive surgery technique for removing tumors and treating cardiovascular disease. During a procedure, an unintended audible explosion called ‘steam pop’ can occur due to the increased internal steam pressure in the ablation region. This phenomenon has been cited as a cause of various negative thermal and mechanical effects on neighboring tissue. Even more, the relationship between steam pop and cancer recurrence is still being investigated.
Professor Inkyu Park said that his team’s integrated sensors reliably detected the occurrence of steam pop. The sensors also monitor rapidly spreading hot steam in tissue. It is expected that the diverse properties of tissue undergoing RFA could be checked by utilizing the physical sensors integrated on the needle.
“We believe that the integrated sensors can provide useful information about a variety of medical procedures and accompanying environmental changes in the human body, and help develop more effective and safer surgical procedures,” said Professor Park.
Professor Park’s team built a thin film type pressure and temperature sensor stack with a thickness of less than 10 μm using a microfabrication process. For the pressure sensor, the team used contact resistance changes between metal electrodes and a carbon nanotube coated polymeric membrane. The entire sensor array was thoroughly insulated with medical tubes to minimize any exposure of the sensor materials to external tissue and maximize its biocompatibility.
During the clinical trial, the research team found that the accumulated hot steam is suddenly released during steam pops and this hot air spreads to neighboring tissue, which accelerates the ablation process. Furthermore, using in-situ ultrasound imaging and computational simulations, the research team could confirm the non-uniform temperature distribution around the RFA needle can be one of the primary reasons for the steam popping.
Professor Park explained that various physical and chemical sensors for different targets can be added to create other medical devices and industrial tools.
“This result will expand the usability and applicability of current flexible sensor technologies. We are also trying to integrate this sensor onto a 0.3mm diameter needle for in-vivo diagnosis applications and expect that this approach can be applied to other medical treatments as well as the industrial field,” added Professor Park. This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-PublicationJaeho Park, Jinwoo Lee, Hyo Keun Lim, Inkyu Park et al. “Real-Time Internal Steam Pop Detection during Radiofrequency Ablation with a Radiofrequency Ablation Needle Integrated with a Temperature and Pressure Sensor: Preclinical and clinical pilot tests," Advanced Science (https://doi/org/10.1002/advs.202100725) on August 5, 2021
-ProfileProfessor Inkyu ParkMicro & Nano Tranducers Laboratory http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Mechanical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2021.10.20 View 10012 -
 A Study Reveals What Triggers Lung Damage during COVID-19
A longitudinal study of macrophages from SARS-CoV-2 infected lungs offers new insights into dynamic immunological changes
A KAIST immunology research team found that a specific subtype of macrophages that originated from blood monocytes plays a key role in the hyper-inflammatory response in SARS-CoV-2 infected lungs, by performing single-cell RNA sequencing of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cells. This study provides new insights for understanding dynamic changes in immune responses to COVID-19.
In the early phase of COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 infected lung tissue and the immediate defense system is activated. This early and fast response is called ‘innate immunity,’ provided by immune cells residing in lungs. Macrophages are major cell types of the innate immune system of the lungs, and newly differentiated macrophages originating from the bloodstream also contribute to early defenses against viruses.
Professor Su-Hyung Park and his collaborators investigated the quantitative and qualitative evaluation of immune responses in the lungs of SARS-CoV-2 infected ferrets. To overcome the limitations of research using patient-originated specimens, the researchers used a ferret infection model to obtain SARS-CoV-2 infected lungs sequentially with a defined time interval.
The researchers analyzed the 10 subtypes of macrophages during the five-day course of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and found that infiltrating macrophages originating from activated monocytes in the blood were key players for viral clearance as well as damaged lung tissue. Moreover, they found that the differentiation process of these inflammatory macrophages resembled the immune responses in the lung tissue of severe COVID-19 patients.
Currently, the research team is conducting a follow-up study to identify the dynamic changes in immune responses during the use of immunosuppressive agents to control hyper-inflammatory response called ‘cytokine storm’ in patients with COVID-19.
Dr. Jeong Seok Lee, the chief medical officer at Genome Insight Inc., explained, “Our analysis will enhance the understanding of the early features of COVID-19 immunity and provide a scientific background for the more precise use of immunosuppressive agents targeting specific macrophage subtypes.”
“This study is the first longitudinal study using sequentially obtained immune cells originating from SARS-CoV-2 infected lungs. The research describes the innate immune response to COVID-19 using single cell transcriptome data and enhances our understanding of the two phases of inflammatory responses,” Professor Park said.
This work was supported by the Ministry of Health and Welfare and KAIST, and was published in Nature Communications on July 28.
-PublicationSu-Hyung Park, Jeong Seok Lee, Su-Hyung Park et al. “Single-cell transcriptome of bronchoalverolar lavage fluid reveals sequential change of macrophages during SARS-CoV-2 infection in ferrets” Nature Communications (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24807-0)
-ProfileProfessor Su-Hyung ParkLaboratory of Translational Immunology and Vaccinologyhttps://ltiv.kaist.ac.kr/
Graduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2021.08.04 View 14000
A Study Reveals What Triggers Lung Damage during COVID-19
A longitudinal study of macrophages from SARS-CoV-2 infected lungs offers new insights into dynamic immunological changes
A KAIST immunology research team found that a specific subtype of macrophages that originated from blood monocytes plays a key role in the hyper-inflammatory response in SARS-CoV-2 infected lungs, by performing single-cell RNA sequencing of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cells. This study provides new insights for understanding dynamic changes in immune responses to COVID-19.
In the early phase of COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 infected lung tissue and the immediate defense system is activated. This early and fast response is called ‘innate immunity,’ provided by immune cells residing in lungs. Macrophages are major cell types of the innate immune system of the lungs, and newly differentiated macrophages originating from the bloodstream also contribute to early defenses against viruses.
Professor Su-Hyung Park and his collaborators investigated the quantitative and qualitative evaluation of immune responses in the lungs of SARS-CoV-2 infected ferrets. To overcome the limitations of research using patient-originated specimens, the researchers used a ferret infection model to obtain SARS-CoV-2 infected lungs sequentially with a defined time interval.
The researchers analyzed the 10 subtypes of macrophages during the five-day course of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and found that infiltrating macrophages originating from activated monocytes in the blood were key players for viral clearance as well as damaged lung tissue. Moreover, they found that the differentiation process of these inflammatory macrophages resembled the immune responses in the lung tissue of severe COVID-19 patients.
Currently, the research team is conducting a follow-up study to identify the dynamic changes in immune responses during the use of immunosuppressive agents to control hyper-inflammatory response called ‘cytokine storm’ in patients with COVID-19.
Dr. Jeong Seok Lee, the chief medical officer at Genome Insight Inc., explained, “Our analysis will enhance the understanding of the early features of COVID-19 immunity and provide a scientific background for the more precise use of immunosuppressive agents targeting specific macrophage subtypes.”
“This study is the first longitudinal study using sequentially obtained immune cells originating from SARS-CoV-2 infected lungs. The research describes the innate immune response to COVID-19 using single cell transcriptome data and enhances our understanding of the two phases of inflammatory responses,” Professor Park said.
This work was supported by the Ministry of Health and Welfare and KAIST, and was published in Nature Communications on July 28.
-PublicationSu-Hyung Park, Jeong Seok Lee, Su-Hyung Park et al. “Single-cell transcriptome of bronchoalverolar lavage fluid reveals sequential change of macrophages during SARS-CoV-2 infection in ferrets” Nature Communications (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24807-0)
-ProfileProfessor Su-Hyung ParkLaboratory of Translational Immunology and Vaccinologyhttps://ltiv.kaist.ac.kr/
Graduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2021.08.04 View 14000 -
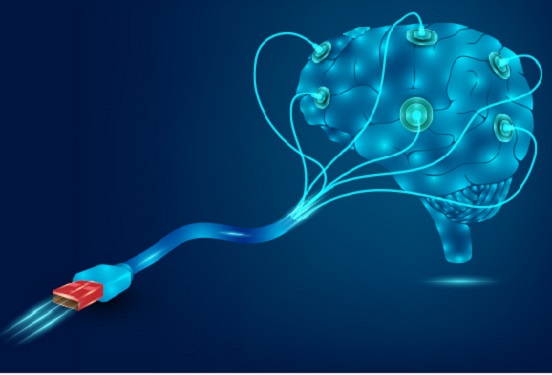 Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-PublicationPark, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-ProfileProfessor Seongjun ParkBio and Neural Interfaces LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.13 View 13015
Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-PublicationPark, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-ProfileProfessor Seongjun ParkBio and Neural Interfaces LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.13 View 13015 -
 ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 34325
ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 34325 -
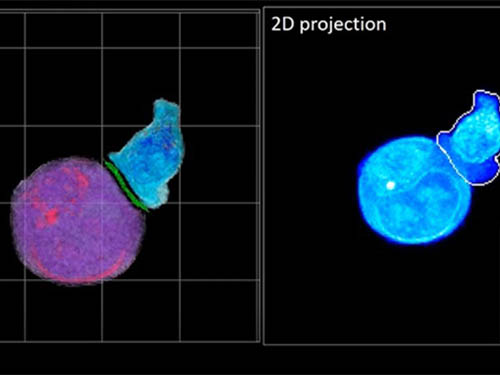 Deep-Learning and 3D Holographic Microscopy Beats Scientists at Analyzing Cancer Immunotherapy
Live tracking and analyzing of the dynamics of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells targeting cancer cells can open new avenues for the development of cancer immunotherapy. However, imaging via conventional microscopy approaches can result in cellular damage, and assessments of cell-to-cell interactions are extremely difficult and labor-intensive. When researchers applied deep learning and 3D holographic microscopy to the task, however, they not only avoided these difficultues but found that AI was better at it than humans were.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is helping researchers decipher images from a new holographic microscopy technique needed to investigate a key process in cancer immunotherapy “live” as it takes place. The AI transformed work that, if performed manually by scientists, would otherwise be incredibly labor-intensive and time-consuming into one that is not only effortless but done better than they could have done it themselves. The research, conducted by the team of Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics, appeared in the journal eLife last December.
A critical stage in the development of the human immune system’s ability to respond not just generally to any invader (such as pathogens or cancer cells) but specifically to that particular type of invader and remember it should it attempt to invade again is the formation of a junction between an immune cell called a T-cell and a cell that presents the antigen, or part of the invader that is causing the problem, to it. This process is like when a picture of a suspect is sent to a police car so that the officers can recognize the criminal they are trying to track down. The junction between the two cells, called the immunological synapse, or IS, is the key process in teaching the immune system how to recognize a specific type of invader.
Since the formation of the IS junction is such a critical step for the initiation of an antigen-specific immune response, various techniques allowing researchers to observe the process as it happens have been used to study its dynamics. Most of these live imaging techniques rely on fluorescence microscopy, where genetic tweaking causes part of a protein from a cell to fluoresce, in turn allowing the subject to be tracked via fluorescence rather than via the reflected light used in many conventional microscopy techniques.
However, fluorescence-based imaging can suffer from effects such as photo-bleaching and photo-toxicity, preventing the assessment of dynamic changes in the IS junction process over the long term. Fluorescence-based imaging still involves illumination, whereupon the fluorophores (chemical compounds that cause the fluorescence) emit light of a different color. Photo-bleaching or photo-toxicity occur when the subject is exposed to too much illumination, resulting in chemical alteration or cellular damage.
One recent option that does away with fluorescent labelling and thereby avoids such problems is 3D holographic microscopy or holotomography (HT). In this technique, the refractive index (the way that light changes direction when encountering a substance with a different density—why a straw looks like it bends in a glass of water) is recorded in 3D as a hologram.
Until now, HT has been used to study single cells, but never cell-cell interactions involved in immune responses. One of the main reasons is the difficulty of “segmentation,” or distinguishing the different parts of a cell and thus distinguishing between the interacting cells; in other words, deciphering which part belongs to which cell.
Manual segmentation, or marking out the different parts manually, is one option, but it is difficult and time-consuming, especially in three dimensions. To overcome this problem, automatic segmentation has been developed in which simple computer algorithms perform the identification.
“But these basic algorithms often make mistakes,” explained Professor YongKeun Park, “particularly with respect to adjoining segmentation, which of course is exactly what is occurring here in the immune response we’re most interested in.”
So, the researchers applied a deep learning framework to the HT segmentation problem. Deep learning is a type of machine learning in which artificial neural networks based on the human brain recognize patterns in a way that is similar to how humans do this. Regular machine learning requires data as an input that has already been labelled. The AI “learns” by understanding the labeled data and then recognizes the concept that has been labelled when it is fed novel data. For example, AI trained on a thousand images of cats labelled “cat” should be able to recognize a cat the next time it encounters an image with a cat in it. Deep learning involves multiple layers of artificial neural networks attacking much larger, but unlabeled datasets, in which the AI develops its own ‘labels’ for concepts it encounters.
In essence, the deep learning framework that KAIST researchers developed, called DeepIS, came up with its own concepts by which it distinguishes the different parts of the IS junction process. To validate this method, the research team applied it to the dynamics of a particular IS junction formed between chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells and target cancer cells. They then compared the results to what they would normally have done: the laborious process of performing the segmentation manually. They found not only that DeepIS was able to define areas within the IS with high accuracy, but that the technique was even able to capture information about the total distribution of proteins within the IS that may not have been easily measured using conventional techniques.
“In addition to allowing us to avoid the drudgery of manual segmentation and the problems of photo-bleaching and photo-toxicity, we found that the AI actually did a better job,” Professor Park added.
The next step will be to combine the technique with methods of measuring how much physical force is applied by different parts of the IS junction, such as holographic optical tweezers or traction force microscopy.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Department of Physics
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
http://bmol.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
2021.02.24 View 14015
Deep-Learning and 3D Holographic Microscopy Beats Scientists at Analyzing Cancer Immunotherapy
Live tracking and analyzing of the dynamics of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells targeting cancer cells can open new avenues for the development of cancer immunotherapy. However, imaging via conventional microscopy approaches can result in cellular damage, and assessments of cell-to-cell interactions are extremely difficult and labor-intensive. When researchers applied deep learning and 3D holographic microscopy to the task, however, they not only avoided these difficultues but found that AI was better at it than humans were.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is helping researchers decipher images from a new holographic microscopy technique needed to investigate a key process in cancer immunotherapy “live” as it takes place. The AI transformed work that, if performed manually by scientists, would otherwise be incredibly labor-intensive and time-consuming into one that is not only effortless but done better than they could have done it themselves. The research, conducted by the team of Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics, appeared in the journal eLife last December.
A critical stage in the development of the human immune system’s ability to respond not just generally to any invader (such as pathogens or cancer cells) but specifically to that particular type of invader and remember it should it attempt to invade again is the formation of a junction between an immune cell called a T-cell and a cell that presents the antigen, or part of the invader that is causing the problem, to it. This process is like when a picture of a suspect is sent to a police car so that the officers can recognize the criminal they are trying to track down. The junction between the two cells, called the immunological synapse, or IS, is the key process in teaching the immune system how to recognize a specific type of invader.
Since the formation of the IS junction is such a critical step for the initiation of an antigen-specific immune response, various techniques allowing researchers to observe the process as it happens have been used to study its dynamics. Most of these live imaging techniques rely on fluorescence microscopy, where genetic tweaking causes part of a protein from a cell to fluoresce, in turn allowing the subject to be tracked via fluorescence rather than via the reflected light used in many conventional microscopy techniques.
However, fluorescence-based imaging can suffer from effects such as photo-bleaching and photo-toxicity, preventing the assessment of dynamic changes in the IS junction process over the long term. Fluorescence-based imaging still involves illumination, whereupon the fluorophores (chemical compounds that cause the fluorescence) emit light of a different color. Photo-bleaching or photo-toxicity occur when the subject is exposed to too much illumination, resulting in chemical alteration or cellular damage.
One recent option that does away with fluorescent labelling and thereby avoids such problems is 3D holographic microscopy or holotomography (HT). In this technique, the refractive index (the way that light changes direction when encountering a substance with a different density—why a straw looks like it bends in a glass of water) is recorded in 3D as a hologram.
Until now, HT has been used to study single cells, but never cell-cell interactions involved in immune responses. One of the main reasons is the difficulty of “segmentation,” or distinguishing the different parts of a cell and thus distinguishing between the interacting cells; in other words, deciphering which part belongs to which cell.
Manual segmentation, or marking out the different parts manually, is one option, but it is difficult and time-consuming, especially in three dimensions. To overcome this problem, automatic segmentation has been developed in which simple computer algorithms perform the identification.
“But these basic algorithms often make mistakes,” explained Professor YongKeun Park, “particularly with respect to adjoining segmentation, which of course is exactly what is occurring here in the immune response we’re most interested in.”
So, the researchers applied a deep learning framework to the HT segmentation problem. Deep learning is a type of machine learning in which artificial neural networks based on the human brain recognize patterns in a way that is similar to how humans do this. Regular machine learning requires data as an input that has already been labelled. The AI “learns” by understanding the labeled data and then recognizes the concept that has been labelled when it is fed novel data. For example, AI trained on a thousand images of cats labelled “cat” should be able to recognize a cat the next time it encounters an image with a cat in it. Deep learning involves multiple layers of artificial neural networks attacking much larger, but unlabeled datasets, in which the AI develops its own ‘labels’ for concepts it encounters.
In essence, the deep learning framework that KAIST researchers developed, called DeepIS, came up with its own concepts by which it distinguishes the different parts of the IS junction process. To validate this method, the research team applied it to the dynamics of a particular IS junction formed between chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells and target cancer cells. They then compared the results to what they would normally have done: the laborious process of performing the segmentation manually. They found not only that DeepIS was able to define areas within the IS with high accuracy, but that the technique was even able to capture information about the total distribution of proteins within the IS that may not have been easily measured using conventional techniques.
“In addition to allowing us to avoid the drudgery of manual segmentation and the problems of photo-bleaching and photo-toxicity, we found that the AI actually did a better job,” Professor Park added.
The next step will be to combine the technique with methods of measuring how much physical force is applied by different parts of the IS junction, such as holographic optical tweezers or traction force microscopy.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Department of Physics
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
http://bmol.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
2021.02.24 View 14015 -
 KAIST Showcases Healthcare Technologies at K-Hospital Fair 2020
KAIST Pavilion showcased its innovative medical and healthcare technologies and their advanced applications at the K-Hospital Fair 2020. Five KAIST research groups who teamed up for the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project participated in the fair held in Seoul last week.
The K-Hospital Fair is a yearly event organized by the Korean Hospital Association to present the latest research and practical innovations to help the medical industry better serve the patients. This year, 120 healthcare organizations participated in the fair and operated 320 booths.
At the fair, a research group led by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering demonstrated the manufacturing process of orthogonal nanofibers used to develop their ‘recyclable nano-fiber filtered face mask’ introduced in March of this year. This mask has garnered immense international attention for maintaining its sturdy frame and filtering function even after being washed more than 20 times. Professor Kim is now extending his facilities for the mass production of this mask at his start-up company. While awaiting final approval from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety to bring his product into the market, Professor Kim is developing other mask variations such as eco-friendly biodegradable masks and transparent masks to aid the hearing-impaired who rely on lip reading to communicate.
The team working under Professor Wonho Choe from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering presented two low-temperature plasma sterilizers for medical use, co-developed with Plasmapp, a start-up company founded by a KAIST alumnus. Their sterilizers are the first ones that can sterilize medical devices by diffusing hydrogen peroxide vapor into the pouch. They rapidly sterilize medical instruments and materials in just seven minutes without leaving toxic residue, while reducing sterilization time and costs by 90%.
Professor Hyung-Soon Park and his researchers from the Department of Mechanical Engineering introduced a smart protective suit ventilation system that features high cooling capacity and a slimmed-down design. For comfortable use, the suit is equipped with a technique that monitors its inner temperature and humidity and automatically controls its inner circulation accordingly. The group also presented a new system that helps a person in a contaminated suit undress without coming into contact with the contaminated outer part of the suit.
Professor Jong Chul Ye's group from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering demonstrated AI software that can quickly diagnose an infectious disease based on chest X-ray imaging. The technique compares the differences in the severity of pneumonia in individual patients to distinguish whether their conditions fall under viral pneumonia including COVID-19, bacterial pneumonia, tuberculosis, other diseases, or normal conditions. The AI software visualizes the basis of its reasoning for each of the suspected diseases and provides them as information that can be utilized by medical personnel.
Finally, researchers of Professor Ki-Hun Jeong’s team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering demonstrated their ultra-high-speed sub-miniature molecular diagnostic system for the on-site diagnosis of diseases. The existing Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) diagnostic usually takes from 30 minutes to an hour to provide results, but their new technique using an LED light source can present results within just three minutes and it is expected to be used actively for on-site diagnosis.
Professor Choongsik Bae, the Director of the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project, said, “KAIST will build a healthy relationship amongst researchers, enterprises, and hospitals to contribute to the end of COVID-19 and build a new paradigm of Korean disease prevention and control.”
KAIST launched the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative in July with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea. This unit was created to overcome the pandemic crisis by using science and technology, and to contribute to economic development by creating a new antiviral drug industry. The unit is comprised of 464 KAIST members including professors, researchers, and students as well as 503 professionals from enterprises, hospitals, and research centers.
(END)
2020.10.26 View 16106
KAIST Showcases Healthcare Technologies at K-Hospital Fair 2020
KAIST Pavilion showcased its innovative medical and healthcare technologies and their advanced applications at the K-Hospital Fair 2020. Five KAIST research groups who teamed up for the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project participated in the fair held in Seoul last week.
The K-Hospital Fair is a yearly event organized by the Korean Hospital Association to present the latest research and practical innovations to help the medical industry better serve the patients. This year, 120 healthcare organizations participated in the fair and operated 320 booths.
At the fair, a research group led by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering demonstrated the manufacturing process of orthogonal nanofibers used to develop their ‘recyclable nano-fiber filtered face mask’ introduced in March of this year. This mask has garnered immense international attention for maintaining its sturdy frame and filtering function even after being washed more than 20 times. Professor Kim is now extending his facilities for the mass production of this mask at his start-up company. While awaiting final approval from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety to bring his product into the market, Professor Kim is developing other mask variations such as eco-friendly biodegradable masks and transparent masks to aid the hearing-impaired who rely on lip reading to communicate.
The team working under Professor Wonho Choe from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering presented two low-temperature plasma sterilizers for medical use, co-developed with Plasmapp, a start-up company founded by a KAIST alumnus. Their sterilizers are the first ones that can sterilize medical devices by diffusing hydrogen peroxide vapor into the pouch. They rapidly sterilize medical instruments and materials in just seven minutes without leaving toxic residue, while reducing sterilization time and costs by 90%.
Professor Hyung-Soon Park and his researchers from the Department of Mechanical Engineering introduced a smart protective suit ventilation system that features high cooling capacity and a slimmed-down design. For comfortable use, the suit is equipped with a technique that monitors its inner temperature and humidity and automatically controls its inner circulation accordingly. The group also presented a new system that helps a person in a contaminated suit undress without coming into contact with the contaminated outer part of the suit.
Professor Jong Chul Ye's group from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering demonstrated AI software that can quickly diagnose an infectious disease based on chest X-ray imaging. The technique compares the differences in the severity of pneumonia in individual patients to distinguish whether their conditions fall under viral pneumonia including COVID-19, bacterial pneumonia, tuberculosis, other diseases, or normal conditions. The AI software visualizes the basis of its reasoning for each of the suspected diseases and provides them as information that can be utilized by medical personnel.
Finally, researchers of Professor Ki-Hun Jeong’s team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering demonstrated their ultra-high-speed sub-miniature molecular diagnostic system for the on-site diagnosis of diseases. The existing Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) diagnostic usually takes from 30 minutes to an hour to provide results, but their new technique using an LED light source can present results within just three minutes and it is expected to be used actively for on-site diagnosis.
Professor Choongsik Bae, the Director of the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project, said, “KAIST will build a healthy relationship amongst researchers, enterprises, and hospitals to contribute to the end of COVID-19 and build a new paradigm of Korean disease prevention and control.”
KAIST launched the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative in July with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea. This unit was created to overcome the pandemic crisis by using science and technology, and to contribute to economic development by creating a new antiviral drug industry. The unit is comprised of 464 KAIST members including professors, researchers, and students as well as 503 professionals from enterprises, hospitals, and research centers.
(END)
2020.10.26 View 16106 -
 Deep Learning-Based Cough Recognition Model Helps Detect the Location of Coughing Sounds in Real Time
The Center for Noise and Vibration Control at KAIST announced that their coughing detection camera recognizes where coughing happens, visualizing the locations. The resulting cough recognition camera can track and record information about the person who coughed, their location, and the number of coughs on a real-time basis.
Professor Yong-Hwa Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a deep learning-based cough recognition model to classify a coughing sound in real time. The coughing event classification model is combined with a sound camera that visualizes their locations in public places. The research team said they achieved a best test accuracy of 87.4 %.
Professor Park said that it will be useful medical equipment during epidemics in public places such as schools, offices, and restaurants, and to constantly monitor patients’ conditions in a hospital room.
Fever and coughing are the most relevant respiratory disease symptoms, among which fever can be recognized remotely using thermal cameras. This new technology is expected to be very helpful for detecting epidemic transmissions in a non-contact way. The cough event classification model is combined with a sound camera that visualizes the cough event and indicates the location in the video image.
To develop a cough recognition model, a supervised learning was conducted with a convolutional neural network (CNN). The model performs binary classification with an input of a one-second sound profile feature, generating output to be either a cough event or something else.
In the training and evaluation, various datasets were collected from Audioset, DEMAND, ETSI, and TIMIT. Coughing and others sounds were extracted from Audioset, and the rest of the datasets were used as background noises for data augmentation so that this model could be generalized for various background noises in public places.
The dataset was augmented by mixing coughing sounds and other sounds from Audioset and background noises with the ratio of 0.15 to 0.75, then the overall volume was adjusted to 0.25 to 1.0 times to generalize the model for various distances.
The training and evaluation datasets were constructed by dividing the augmented dataset by 9:1, and the test dataset was recorded separately in a real office environment.
In the optimization procedure of the network model, training was conducted with various combinations of five acoustic features including spectrogram, Mel-scaled spectrogram and Mel-frequency cepstrum coefficients with seven optimizers. The performance of each combination was compared with the test dataset. The best test accuracy of 87.4% was achieved with Mel-scaled Spectrogram as the acoustic feature and ASGD as the optimizer.
The trained cough recognition model was combined with a sound camera. The sound camera is composed of a microphone array and a camera module. A beamforming process is applied to a collected set of acoustic data to find out the direction of incoming sound source. The integrated cough recognition model determines whether the sound is cough or not. If it is, the location of cough is visualized as a contour image with a ‘cough’ label at the location of the coughing sound source in a video image.
A pilot test of the cough recognition camera in an office environment shows that it successfully distinguishes cough events and other events even in a noisy environment. In addition, it can track the location of the person who coughed and count the number of coughs in real time. The performance will be improved further with additional training data obtained from other real environments such as hospitals and classrooms.
Professor Park said, “In a pandemic situation like we are experiencing with COVID-19, a cough detection camera can contribute to the prevention and early detection of epidemics in public places. Especially when applied to a hospital room, the patient's condition can be tracked 24 hours a day and support more accurate diagnoses while reducing the effort of the medical staff."
This study was conducted in collaboration with SM Instruments Inc.
Profile: Yong-Hwa Park, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
yhpark@kaist.ac.kr
http://human.kaist.ac.kr/
Human-Machine Interaction Laboratory (HuMaN Lab.)
Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr/en/
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Gyeong Tae Lee
PhD Candidate
hansaram@kaist.ac.kr
HuMaN Lab., ME, KAIST
Profile: Seong Hu Kim
PhD Candidate
tjdgnkim@kaist.ac.kr
HuMaN Lab., ME, KAIST
Profile: Hyeonuk Nam
PhD Candidate
frednam@kaist.ac.kr
HuMaN Lab., ME, KAIST
Profile: Young-Key Kim
CEO
sales@smins.co.kr
http://en.smins.co.kr/
SM Instruments Inc.
Daejeon 34109, Korea
(END)
2020.08.13 View 18316
Deep Learning-Based Cough Recognition Model Helps Detect the Location of Coughing Sounds in Real Time
The Center for Noise and Vibration Control at KAIST announced that their coughing detection camera recognizes where coughing happens, visualizing the locations. The resulting cough recognition camera can track and record information about the person who coughed, their location, and the number of coughs on a real-time basis.
Professor Yong-Hwa Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a deep learning-based cough recognition model to classify a coughing sound in real time. The coughing event classification model is combined with a sound camera that visualizes their locations in public places. The research team said they achieved a best test accuracy of 87.4 %.
Professor Park said that it will be useful medical equipment during epidemics in public places such as schools, offices, and restaurants, and to constantly monitor patients’ conditions in a hospital room.
Fever and coughing are the most relevant respiratory disease symptoms, among which fever can be recognized remotely using thermal cameras. This new technology is expected to be very helpful for detecting epidemic transmissions in a non-contact way. The cough event classification model is combined with a sound camera that visualizes the cough event and indicates the location in the video image.
To develop a cough recognition model, a supervised learning was conducted with a convolutional neural network (CNN). The model performs binary classification with an input of a one-second sound profile feature, generating output to be either a cough event or something else.
In the training and evaluation, various datasets were collected from Audioset, DEMAND, ETSI, and TIMIT. Coughing and others sounds were extracted from Audioset, and the rest of the datasets were used as background noises for data augmentation so that this model could be generalized for various background noises in public places.
The dataset was augmented by mixing coughing sounds and other sounds from Audioset and background noises with the ratio of 0.15 to 0.75, then the overall volume was adjusted to 0.25 to 1.0 times to generalize the model for various distances.
The training and evaluation datasets were constructed by dividing the augmented dataset by 9:1, and the test dataset was recorded separately in a real office environment.
In the optimization procedure of the network model, training was conducted with various combinations of five acoustic features including spectrogram, Mel-scaled spectrogram and Mel-frequency cepstrum coefficients with seven optimizers. The performance of each combination was compared with the test dataset. The best test accuracy of 87.4% was achieved with Mel-scaled Spectrogram as the acoustic feature and ASGD as the optimizer.
The trained cough recognition model was combined with a sound camera. The sound camera is composed of a microphone array and a camera module. A beamforming process is applied to a collected set of acoustic data to find out the direction of incoming sound source. The integrated cough recognition model determines whether the sound is cough or not. If it is, the location of cough is visualized as a contour image with a ‘cough’ label at the location of the coughing sound source in a video image.
A pilot test of the cough recognition camera in an office environment shows that it successfully distinguishes cough events and other events even in a noisy environment. In addition, it can track the location of the person who coughed and count the number of coughs in real time. The performance will be improved further with additional training data obtained from other real environments such as hospitals and classrooms.
Professor Park said, “In a pandemic situation like we are experiencing with COVID-19, a cough detection camera can contribute to the prevention and early detection of epidemics in public places. Especially when applied to a hospital room, the patient's condition can be tracked 24 hours a day and support more accurate diagnoses while reducing the effort of the medical staff."
This study was conducted in collaboration with SM Instruments Inc.
Profile: Yong-Hwa Park, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
yhpark@kaist.ac.kr
http://human.kaist.ac.kr/
Human-Machine Interaction Laboratory (HuMaN Lab.)
Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr/en/
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Gyeong Tae Lee
PhD Candidate
hansaram@kaist.ac.kr
HuMaN Lab., ME, KAIST
Profile: Seong Hu Kim
PhD Candidate
tjdgnkim@kaist.ac.kr
HuMaN Lab., ME, KAIST
Profile: Hyeonuk Nam
PhD Candidate
frednam@kaist.ac.kr
HuMaN Lab., ME, KAIST
Profile: Young-Key Kim
CEO
sales@smins.co.kr
http://en.smins.co.kr/
SM Instruments Inc.
Daejeon 34109, Korea
(END)
2020.08.13 View 18316 -
 Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-Publication
Park, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-Profile
Professor Seongjun Park
Bio and Neural Interfaces Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
2020.07.13 View 8904
Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-Publication
Park, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-Profile
Professor Seongjun Park
Bio and Neural Interfaces Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
2020.07.13 View 8904 -
 New Nanoparticle Drug Combination For Atherosclerosis
Physicochemical cargo-switching nanoparticles (CSNP) designed by KAIST can help significantly reduce cholesterol and macrophage foam cells in arteries, which are the two main triggers for atherosclerotic plaque and inflammation.
The CSNP-based combination drug delivery therapy was proved to exert cholesterol-lowering, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative functions of two common medications for treating and preventing atherosclerosis that are cyclodextrin and statin. Professor Ji-Ho Park and Dr. Heegon Kim from KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering said their study has shown great potential for future applications with reduced side effects.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory vascular disease that is characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol and cholesterol-loaded macrophage foam cells in the intima. When this atherosclerotic plaque clogs and narrows the artery walls, they restrict blood flow and cause various cardiovascular conditions such as heart attacks and strokes. Heart attacks and strokes are the world’s first and fifth causes of death respectively.
Oral statin administration has been used in clinics as a standard care for atherosclerosis, which is prescribed to lower blood cholesterol and inhibit its accumulation within the plaque. Although statins can effectively prevent the progression of plaque growth, they have only shown modest efficacy in eliminating the already-established plaque. Therefore, patients are required to take statin drugs for the rest of their lives and will always carry the risk of plaque ruptures that can trigger a blood clot.
To address these issues, Professor Park and Dr. Kim exploited another antiatherogenic agent called cyclodextrin. In their paper published in the Journal of Controlled Release on March 10, Professor Park and Dr. Kim reported that the polymeric formulation of cyclodextrin with a diameter of approximately 10 nanometers(nm) can accumulate within the atherosclerotic plaque 14 times more and effectively reduce the plaque even at lower doses, compared to cyclodextrin in a non-polymer structure.
Moreover, although cyclodextrin is known to have a cytotoxic effect on hair cells in the cochlea, which can lead to hearing loss, cyclodextrin polymers developed by Professor Park’s research group exhibited a varying biodistribution profile and did not have this side effect.
In the follow-up study reported in ACS Nano on April 28, the researchers exploited both cyclodextrin and statin and form the cyclodextrin-statin self-assembly drug complex, based on previous findings that each drug can exert local anti-atherosclerosis effect within the plaque. The complex formation processes were optimized to obtain homogeneous and stable nanoparticles with a diameter of about 100 nm for systematic injection.
The therapeutic synergy of cyclodextrin and statin could reportedly enhance plaque-targeted drug delivery and anti-inflammation. Cyclodextrin led to the regression of cholesterol in the established plaque, and the statins were shown to inhibit the proliferation of macrophage foam cells. The study suggested that combination therapy is required to resolve the complex inflammatory cholesterol-rich microenvironment within the plaque.
Professor Park said, “While nanomedicine has been mainly developed for the treatment of cancers, our studies show that nanomedicine can also play a significant role in treating and preventing atherosclerosis, which causes various cardiovascular diseases that are the leading causes of death worldwide.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publications:
1. Heegon Kim, Junhee Han, and Ji-Ho Park. (2020) ‘Cyclodextrin polymer improves atherosclerosis therapy and reduces ototoxicity’ Journal of Controlled Release. Volume 319. Page 77-86. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.12.021
2. Kim, H., et al. (2020) ‘Affinity-Driven Design of Cargo-Switching Nanoparticles to Leverage a Cholesterol-Rich Microenvironment for Atherosclerosis Therapy’ ACS Nano. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b08216
Profile: Ji-Ho Park, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jihopark@kaist.ac.kr
http://openwetware.org/wiki/Park_Lab
Biomaterials Engineering Laboratory (BEL)
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering (BIOENG)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Heegon Kim, Ph.D.
Postdoctoral Researcher
heegon@kaist.ac.kr
BEL, BIOENG, KAIST
(END)
2020.06.16 View 15406
New Nanoparticle Drug Combination For Atherosclerosis
Physicochemical cargo-switching nanoparticles (CSNP) designed by KAIST can help significantly reduce cholesterol and macrophage foam cells in arteries, which are the two main triggers for atherosclerotic plaque and inflammation.
The CSNP-based combination drug delivery therapy was proved to exert cholesterol-lowering, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative functions of two common medications for treating and preventing atherosclerosis that are cyclodextrin and statin. Professor Ji-Ho Park and Dr. Heegon Kim from KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering said their study has shown great potential for future applications with reduced side effects.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory vascular disease that is characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol and cholesterol-loaded macrophage foam cells in the intima. When this atherosclerotic plaque clogs and narrows the artery walls, they restrict blood flow and cause various cardiovascular conditions such as heart attacks and strokes. Heart attacks and strokes are the world’s first and fifth causes of death respectively.
Oral statin administration has been used in clinics as a standard care for atherosclerosis, which is prescribed to lower blood cholesterol and inhibit its accumulation within the plaque. Although statins can effectively prevent the progression of plaque growth, they have only shown modest efficacy in eliminating the already-established plaque. Therefore, patients are required to take statin drugs for the rest of their lives and will always carry the risk of plaque ruptures that can trigger a blood clot.
To address these issues, Professor Park and Dr. Kim exploited another antiatherogenic agent called cyclodextrin. In their paper published in the Journal of Controlled Release on March 10, Professor Park and Dr. Kim reported that the polymeric formulation of cyclodextrin with a diameter of approximately 10 nanometers(nm) can accumulate within the atherosclerotic plaque 14 times more and effectively reduce the plaque even at lower doses, compared to cyclodextrin in a non-polymer structure.
Moreover, although cyclodextrin is known to have a cytotoxic effect on hair cells in the cochlea, which can lead to hearing loss, cyclodextrin polymers developed by Professor Park’s research group exhibited a varying biodistribution profile and did not have this side effect.
In the follow-up study reported in ACS Nano on April 28, the researchers exploited both cyclodextrin and statin and form the cyclodextrin-statin self-assembly drug complex, based on previous findings that each drug can exert local anti-atherosclerosis effect within the plaque. The complex formation processes were optimized to obtain homogeneous and stable nanoparticles with a diameter of about 100 nm for systematic injection.
The therapeutic synergy of cyclodextrin and statin could reportedly enhance plaque-targeted drug delivery and anti-inflammation. Cyclodextrin led to the regression of cholesterol in the established plaque, and the statins were shown to inhibit the proliferation of macrophage foam cells. The study suggested that combination therapy is required to resolve the complex inflammatory cholesterol-rich microenvironment within the plaque.
Professor Park said, “While nanomedicine has been mainly developed for the treatment of cancers, our studies show that nanomedicine can also play a significant role in treating and preventing atherosclerosis, which causes various cardiovascular diseases that are the leading causes of death worldwide.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publications:
1. Heegon Kim, Junhee Han, and Ji-Ho Park. (2020) ‘Cyclodextrin polymer improves atherosclerosis therapy and reduces ototoxicity’ Journal of Controlled Release. Volume 319. Page 77-86. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.12.021
2. Kim, H., et al. (2020) ‘Affinity-Driven Design of Cargo-Switching Nanoparticles to Leverage a Cholesterol-Rich Microenvironment for Atherosclerosis Therapy’ ACS Nano. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b08216
Profile: Ji-Ho Park, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jihopark@kaist.ac.kr
http://openwetware.org/wiki/Park_Lab
Biomaterials Engineering Laboratory (BEL)
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering (BIOENG)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Heegon Kim, Ph.D.
Postdoctoral Researcher
heegon@kaist.ac.kr
BEL, BIOENG, KAIST
(END)
2020.06.16 View 15406 -
 Professor Sukyung Park Named Presidential Science and Technology Adviser
Professor Sukyung Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was appointed as the science and technology adviser to the President Jae-in Moon on May 4. Professor Park, at the age of 47, became the youngest member of the president’s senior aide team at Chong Wa Dae.
A Chong Wa Dae spokesman said on May 4 while announcing the appointment, “Professor Park, a talent with a great deal of policymaking participation in science and technology, will contribute to accelerating the government’s push for science and technology innovation, especially in the information and communications technology (ICT) sector.”
Professor Park joined KAIST in 2004 as the first female professor of mechanical engineering. She is a biomechanics expert who has conducted extensive research on biometric mechanical behaviors. Professor Park is also a member of the KAIST Board of Trustees. Before that, she served as a senior researcher at the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) as well as a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology.
After graduating from Seoul Science High School as the first ever two-year graduate, Professor Park earned a bachelor and master’s degrees in mechanical engineering at KAIST. She then finished her Ph.D. from the University of Michigan.
(END)
2020.05.06 View 15271
Professor Sukyung Park Named Presidential Science and Technology Adviser
Professor Sukyung Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was appointed as the science and technology adviser to the President Jae-in Moon on May 4. Professor Park, at the age of 47, became the youngest member of the president’s senior aide team at Chong Wa Dae.
A Chong Wa Dae spokesman said on May 4 while announcing the appointment, “Professor Park, a talent with a great deal of policymaking participation in science and technology, will contribute to accelerating the government’s push for science and technology innovation, especially in the information and communications technology (ICT) sector.”
Professor Park joined KAIST in 2004 as the first female professor of mechanical engineering. She is a biomechanics expert who has conducted extensive research on biometric mechanical behaviors. Professor Park is also a member of the KAIST Board of Trustees. Before that, she served as a senior researcher at the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) as well as a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology.
After graduating from Seoul Science High School as the first ever two-year graduate, Professor Park earned a bachelor and master’s degrees in mechanical engineering at KAIST. She then finished her Ph.D. from the University of Michigan.
(END)
2020.05.06 View 15271