Cancer
-
 Early Genome Catastrophes Can Cause Non-Smoking Lung Cancer
Some teenagers harbor catastrophic changes to their genomes that can lead to lung cancer later on in life, even if they never smoke
(Professor Young Seok Ju at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering)
Catastrophic rearrangements in the genome occurring as early as childhood and adolescence can lead to the development of lung cancer in later years in non-smokers. This finding, published in Cell, helps explain how some non-smoking-related lung cancers develop.
Researchers at KAIST, Seoul National University and their collaborators confirmed that gene fusions in non-smokers mostly occur early on, sometimes as early as childhood or adolescence, and on average about three decades before cancer is diagnosed. The study showed that these mutant lung cells, harboring oncogenic seeds, remain dormant for several decades until a number of further mutations accumulate sufficiently for progression into cancer. This is the first study to reveal the landscape of genome structural variations in lung adenocarcinoma.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, and lung adenocarcinoma is its most common type. Most lung adenocarcinomas are associated with chronic smoking, but about a fourth develop in non-smokers. Precisely what happens in non-smokers for this cancer to develop is not clearly understood.
Researchers analyzed the genomes of 138 lung adenocarcinoma patients, including smokers and non-smokers, with whole-genome sequencing technologies. They explored DNA damage that induced neoplastic transformation.
Lung adenocarcinomas that originated from chronic smoking, referred to as signature 4-high (S4-high) cancers in the study, showed several distinguishing features compared to smoking-unrelated cancers (S4-low).
People in the S4-high group were largely older, men and had more frequent mutations in a cancer-related gene called KRAS. Cancer genomes in the S4-high group were hypermutated with simple mutational classes, such as the substitution, insertion, or deletion of a single base, the building block of DNA.
But the story was very different in the S4-low group. Generally, mutational profiles in this group were much more silent than the S4-high group. However, all cancer-related gene fusions, which are abnormally activated from the merging of two originally separate genes, were exclusively observed in the S4-low group.
The patterns of genomic structural changes underlying gene fusions suggest that about three in four cases of gene fusions emerged from a single cellular crisis causing massive genomic fragmentation and subsequent imprecise repair in normal lung epithelium.
Most strikingly, these major genomic rearrangements, which led to the development of lung adenocarcinoma, are very likely to be acquired decades before cancer diagnosis. The researchers used genomic archaeology techniques to trace the timing of when the catastrophes took place.
Researchers started this study seven years ago when they discovered the expression of the KIF5B-RET gene fusion in lung adenocarcinoma for the first time. Professor Young-Seok Ju, co-lead author from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST says, “It is remarkable that oncogenesis can begin by a massive shattering of chromosomes early in life. Our study immediately raises a new question: What induces the mutational catastrophe in our normal lung epithelium.”
Professor Young Tae Kim, co-lead author from Seoul National University says, “We hope this work will help us get one step closer to precision medicine for lung cancer patients.”
The research team plans to further focus on the molecular mechanisms that stimulate complex rearrangements in the body, through screening the genomic structures of fusion genes in other cancer types.
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the College of Medicine Research Foundations at Seoul National University and others.
Figure.
(Smoking-unrelated oncogenesis of lung cancers by gene fusions)
Publication.
Jake June-Koo Lee, Seongyeol Park et al., Tracing Oncogene Rearrangements in the Mutational History of Lung Adenocarcinoma
Cell 177, June 13 2019, online publication ahead of print at May 30, 2019
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.013
Profile: Prof Young Seok Ju, MD, PhD
ysju@kaist.ac.kr
http://julab.kaist.ac.kr
Associate Professor
Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof Young Tae Kim, MD, PhD
ytkim@snu.ac.kr
Professor
Seoul National University Cancer Research Institute
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery
Seoul National University Hospital Seoul 03080, Korea
2019.05.31 View 56443
Early Genome Catastrophes Can Cause Non-Smoking Lung Cancer
Some teenagers harbor catastrophic changes to their genomes that can lead to lung cancer later on in life, even if they never smoke
(Professor Young Seok Ju at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering)
Catastrophic rearrangements in the genome occurring as early as childhood and adolescence can lead to the development of lung cancer in later years in non-smokers. This finding, published in Cell, helps explain how some non-smoking-related lung cancers develop.
Researchers at KAIST, Seoul National University and their collaborators confirmed that gene fusions in non-smokers mostly occur early on, sometimes as early as childhood or adolescence, and on average about three decades before cancer is diagnosed. The study showed that these mutant lung cells, harboring oncogenic seeds, remain dormant for several decades until a number of further mutations accumulate sufficiently for progression into cancer. This is the first study to reveal the landscape of genome structural variations in lung adenocarcinoma.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, and lung adenocarcinoma is its most common type. Most lung adenocarcinomas are associated with chronic smoking, but about a fourth develop in non-smokers. Precisely what happens in non-smokers for this cancer to develop is not clearly understood.
Researchers analyzed the genomes of 138 lung adenocarcinoma patients, including smokers and non-smokers, with whole-genome sequencing technologies. They explored DNA damage that induced neoplastic transformation.
Lung adenocarcinomas that originated from chronic smoking, referred to as signature 4-high (S4-high) cancers in the study, showed several distinguishing features compared to smoking-unrelated cancers (S4-low).
People in the S4-high group were largely older, men and had more frequent mutations in a cancer-related gene called KRAS. Cancer genomes in the S4-high group were hypermutated with simple mutational classes, such as the substitution, insertion, or deletion of a single base, the building block of DNA.
But the story was very different in the S4-low group. Generally, mutational profiles in this group were much more silent than the S4-high group. However, all cancer-related gene fusions, which are abnormally activated from the merging of two originally separate genes, were exclusively observed in the S4-low group.
The patterns of genomic structural changes underlying gene fusions suggest that about three in four cases of gene fusions emerged from a single cellular crisis causing massive genomic fragmentation and subsequent imprecise repair in normal lung epithelium.
Most strikingly, these major genomic rearrangements, which led to the development of lung adenocarcinoma, are very likely to be acquired decades before cancer diagnosis. The researchers used genomic archaeology techniques to trace the timing of when the catastrophes took place.
Researchers started this study seven years ago when they discovered the expression of the KIF5B-RET gene fusion in lung adenocarcinoma for the first time. Professor Young-Seok Ju, co-lead author from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST says, “It is remarkable that oncogenesis can begin by a massive shattering of chromosomes early in life. Our study immediately raises a new question: What induces the mutational catastrophe in our normal lung epithelium.”
Professor Young Tae Kim, co-lead author from Seoul National University says, “We hope this work will help us get one step closer to precision medicine for lung cancer patients.”
The research team plans to further focus on the molecular mechanisms that stimulate complex rearrangements in the body, through screening the genomic structures of fusion genes in other cancer types.
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the College of Medicine Research Foundations at Seoul National University and others.
Figure.
(Smoking-unrelated oncogenesis of lung cancers by gene fusions)
Publication.
Jake June-Koo Lee, Seongyeol Park et al., Tracing Oncogene Rearrangements in the Mutational History of Lung Adenocarcinoma
Cell 177, June 13 2019, online publication ahead of print at May 30, 2019
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.013
Profile: Prof Young Seok Ju, MD, PhD
ysju@kaist.ac.kr
http://julab.kaist.ac.kr
Associate Professor
Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof Young Tae Kim, MD, PhD
ytkim@snu.ac.kr
Professor
Seoul National University Cancer Research Institute
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery
Seoul National University Hospital Seoul 03080, Korea
2019.05.31 View 56443 -
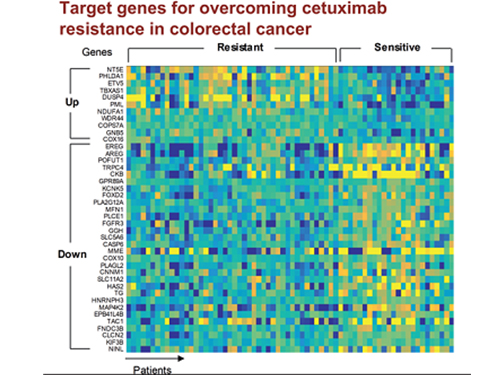 5 Biomarkers for Overcoming Colorectal Cancer Drug Resistance Identified
< Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's Team >
KAIST researchers have identified five biomarkers that will help them address resistance to cancer-targeting therapeutics. This new treatment strategy will bring us one step closer to precision medicine for patients who showed resistance.
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide. The number of patients has surpassed 1 million, and its five-year survival rate significantly drops to about 20 percent when metastasized. In Korea, the surge of colorectal cancer has been the highest in the last 10 years due to increasing Westernized dietary patterns and obesity. It is expected that the number and mortality rates of colorectal cancer patients will increase sharply as the nation is rapidly facing an increase in its aging population.
Recently, anticancer agents targeting only specific molecules of colon cancer cells have been developed. Unlike conventional anticancer medications, these selectively treat only specific target factors, so they can significantly reduce some of the side-effects of anticancer therapy while enhancing drug efficacy.
Cetuximab is the most well-known FDA approved anticancer medication. It is a biomarker that predicts drug reactivity and utilizes the presence of the ‘KRAS’ gene mutation. Cetuximab is prescribed to patients who don’t carry the KRAS gene mutation.
However, even in patients without the KRAS gene mutation, the response rate of Cetuximab is only about fifty percent, and there is also resistance to drugs after targeted chemotherapy. Compared with conventional chemotherapy alone, the life expectancy only lasts five months on average.
In research featured in the FEBS Journal as the cover paper for the April 7 edition, the KAIST research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering presented five additional biomarkers that could increase Cetuximab responsiveness using systems biology approach that combines genomic data analysis, mathematical modeling, and cell experiments. The experimental inhibition of newly discovered biomarkers DUSP4, ETV5, GNB5, NT5E, and PHLDA1 in colorectal cancer cells has been shown to overcome Cetuximab resistance in KRAS-normal genes. The research team confirmed that when suppressing GNB5, one of the new biomarkers, it was shown to overcome resistance to Cetuximab regardless of having a mutation in the KRAS gene.
Professor Cho said, “There has not been an example of colorectal cancer treatment involving regulation of the GNB5 gene.” He continued, “Identifying the principle of drug resistance in cancer cells through systems biology and discovering new biomarkers that could be a new molecular target to overcome drug resistance suggest real potential to actualize precision medicine.”
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (2017R1A2A1A17069642 and 2015M3A9A7067220).
Image 1. The cover of FEBS Journal for April 2019
2019.05.27 View 59003
5 Biomarkers for Overcoming Colorectal Cancer Drug Resistance Identified
< Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's Team >
KAIST researchers have identified five biomarkers that will help them address resistance to cancer-targeting therapeutics. This new treatment strategy will bring us one step closer to precision medicine for patients who showed resistance.
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide. The number of patients has surpassed 1 million, and its five-year survival rate significantly drops to about 20 percent when metastasized. In Korea, the surge of colorectal cancer has been the highest in the last 10 years due to increasing Westernized dietary patterns and obesity. It is expected that the number and mortality rates of colorectal cancer patients will increase sharply as the nation is rapidly facing an increase in its aging population.
Recently, anticancer agents targeting only specific molecules of colon cancer cells have been developed. Unlike conventional anticancer medications, these selectively treat only specific target factors, so they can significantly reduce some of the side-effects of anticancer therapy while enhancing drug efficacy.
Cetuximab is the most well-known FDA approved anticancer medication. It is a biomarker that predicts drug reactivity and utilizes the presence of the ‘KRAS’ gene mutation. Cetuximab is prescribed to patients who don’t carry the KRAS gene mutation.
However, even in patients without the KRAS gene mutation, the response rate of Cetuximab is only about fifty percent, and there is also resistance to drugs after targeted chemotherapy. Compared with conventional chemotherapy alone, the life expectancy only lasts five months on average.
In research featured in the FEBS Journal as the cover paper for the April 7 edition, the KAIST research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering presented five additional biomarkers that could increase Cetuximab responsiveness using systems biology approach that combines genomic data analysis, mathematical modeling, and cell experiments. The experimental inhibition of newly discovered biomarkers DUSP4, ETV5, GNB5, NT5E, and PHLDA1 in colorectal cancer cells has been shown to overcome Cetuximab resistance in KRAS-normal genes. The research team confirmed that when suppressing GNB5, one of the new biomarkers, it was shown to overcome resistance to Cetuximab regardless of having a mutation in the KRAS gene.
Professor Cho said, “There has not been an example of colorectal cancer treatment involving regulation of the GNB5 gene.” He continued, “Identifying the principle of drug resistance in cancer cells through systems biology and discovering new biomarkers that could be a new molecular target to overcome drug resistance suggest real potential to actualize precision medicine.”
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (2017R1A2A1A17069642 and 2015M3A9A7067220).
Image 1. The cover of FEBS Journal for April 2019
2019.05.27 View 59003 -
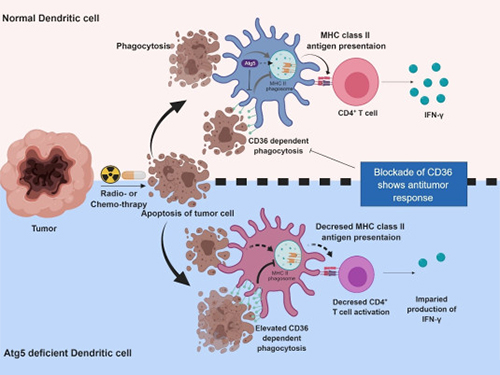 Autophagy in Dendritic Cells Helps Anticancer Activity
Autophagy contributes to the homeostasis of a cell and recently another function of autophagy has been reported. A KAIST research team found that the autophagy of dendritic cells supports T-cell anticancer activity.
Autophagy is a process of maintaining cell homeostasis by removing cellular waste and damaged cellular organelles; nevertheless, its role in the presentation of phagocytized tumor-associated antigens remains vague.
Meanwhile, dendritic cells are the ones that recognize pathogens or cancer antigens, and induce immune responses in T cells. When cancer cells are killed by radiation or an anticancer drug, dendritic cells absorb and remove them and present antigens on their surface to transfer them to T-cells.
Professor Heung Kyu Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and his team found that the autophagy of dendritic cells plays a key role in T-cell activation and they proposed the principles of enhancing anti-cancer effects.
Their experiments showed that T-cell activation of dendritic cells as well as anticancer immune response dropped when there is a deficiency of Atg5 (autophagy-related) in dendritic cells.
Interestingly, Atg5-deficient dendritic cells significantly elevated receptor CD36 on the surface of the cells, which increased the phagocytosis of apoptotic tumor cells yet restricted the activation of T-cells.
At this time, when introducing antibodies into the system in order to block the receptor CD36, the anti-tumor T-cell response increased substantially while tumor growth declined.
Professor Lee said, “This study allowed us to explore the role of autophagy in the anti-cancer immune response of T-cells. We look forward to developing targeted anti-cancer therapies using the receptor CD36.”
This research was published in Autophagy (10.1080/15548627.2019.1596493) on March 22, 2019.
Figure 1.Mechanism of autophagy in dendritic cells
Figure 2. A role of autophagy in dendritic cells
2019.05.13 View 50838
Autophagy in Dendritic Cells Helps Anticancer Activity
Autophagy contributes to the homeostasis of a cell and recently another function of autophagy has been reported. A KAIST research team found that the autophagy of dendritic cells supports T-cell anticancer activity.
Autophagy is a process of maintaining cell homeostasis by removing cellular waste and damaged cellular organelles; nevertheless, its role in the presentation of phagocytized tumor-associated antigens remains vague.
Meanwhile, dendritic cells are the ones that recognize pathogens or cancer antigens, and induce immune responses in T cells. When cancer cells are killed by radiation or an anticancer drug, dendritic cells absorb and remove them and present antigens on their surface to transfer them to T-cells.
Professor Heung Kyu Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and his team found that the autophagy of dendritic cells plays a key role in T-cell activation and they proposed the principles of enhancing anti-cancer effects.
Their experiments showed that T-cell activation of dendritic cells as well as anticancer immune response dropped when there is a deficiency of Atg5 (autophagy-related) in dendritic cells.
Interestingly, Atg5-deficient dendritic cells significantly elevated receptor CD36 on the surface of the cells, which increased the phagocytosis of apoptotic tumor cells yet restricted the activation of T-cells.
At this time, when introducing antibodies into the system in order to block the receptor CD36, the anti-tumor T-cell response increased substantially while tumor growth declined.
Professor Lee said, “This study allowed us to explore the role of autophagy in the anti-cancer immune response of T-cells. We look forward to developing targeted anti-cancer therapies using the receptor CD36.”
This research was published in Autophagy (10.1080/15548627.2019.1596493) on March 22, 2019.
Figure 1.Mechanism of autophagy in dendritic cells
Figure 2. A role of autophagy in dendritic cells
2019.05.13 View 50838 -
 'K-FLEX' Makes a Splash as a Flexible Endoscopic Surgical Robot
( Robot arms perform an incision during an ex-vivo test on a porcine gallbladder.)
K-FLEX, a flexible endoscopic surgical robot developed by the KAIST Future Medical Robotics Research Center, opens a new chapter for minimally invasive robot-assisted surgery with its precision control of 3.7 mm diameter robotic arms. The two arms, placing at the end of flexible endoscopes, highlight impeccable precision control and robust mini-joint design technologies. While cruising through the complicated inner body pliably, it carries out procedures on the spot with its robotic arms.
The research team under Professor Dong-Soo Kwon recently tested the device in-vivo, conducting a complicated endoscopic procedure dissecting a porcine gallbladder in collaboration with Professor Dae-Kyung Son of the National Cancer Center. The arms successfully manipulated the tissue safely.
During the test, K-FLEX, inserted through an incision in the navel, snaked through the narrow passages of the complicated inner organs. When reaching the desired spot, one of the robot arms pushed aside and held up the nearby tissue to secure proper vision and space for the procedure. Meanwhile, a cautery needle mounted at the tip of the other hand removed the lesion tissue on the gallbladder. The tiny camera installed at the front of the robot arms relayed the internal conditions. The full procedure was able to be monitored from the master console.
The two arms are placed onto 4.2 mm internal channels of an endoscope which is 17 mm in diameter. The arms can be deployable forward and backward and are extendable up to 7 cm for performing procedures.
K-FLEX is made of domestically produced components, except for the endoscopic module. It will expand new medical robotics research while offering novel therapeutic capabilities for endoscopes.
Flexible endoscopes are very promising for surgical applications because they can treat areas thought to be difficult to reach, such as the posterior side of an organ. Current rigid-type laparoscopic tools could not reach a lesion if it occurs in such serpentine and complicated areas. However, this flexible endoscopic surgery robot will bypass obstacles to reach the troubled area.
The ability to seamlessly integrate effective actuation into millimeter-scale deployable mechanisms fits well with minimally invasive surgical procedures. This flexible endoscopic surgery robot, only half the size of current laparoscopic surgical robots, is deployable into natural orifices such as the mouth, anus, and vagina without requiring external incisions. Laparoscopic devices and robots require at least three to four external incisions to insert the devices; however, the applicability of internal incisions reduces the possibility of complications arousing from excessive bleeding and bacterial infections.
Despite these advantages, it has remained challenging to manipulate the robotic arms of flexible endoscopes with integrated grabbing force, flexibility, and multiple degrees of freedom for clinical environments.
The team focused on smaller but smarter devices. Dr. Min-Ho Hwang, a principal researcher of K-FLEX, said that developing tiny robots that are able to generate the necessary forces without compromising safety was the challenge. They created a robust but smaller-joint technology that can exert a relatively greater force even into millimeter scale.
Professor Kwon said, “K-FLEX is the first flexible endoscopic surgery robot in Korea. We already confirmed the clinical adaptation through ex vivo tests and will see complete commercialization in two to three years.” The team believes K-FLEX will be very effective for surgery on incipient cancer cells in the stomach, colon, and thyroid.
Professor Kwon and his eight researchers recently established a tech start-up called EasyEndo Surgical Inc. with these core technologies. In June, K-FLEX won the ‘Best Application Award’ and the ‘Overall Winner’ at the Surgical Robot Challenge 2018 held at Imperial College London. The Korea Research Foundation funded the research on K-FLEX.
(The team conducts a procedure using K-FLEX, flexible endoscopic surgical robot.)
2018.08.17 View 8632
'K-FLEX' Makes a Splash as a Flexible Endoscopic Surgical Robot
( Robot arms perform an incision during an ex-vivo test on a porcine gallbladder.)
K-FLEX, a flexible endoscopic surgical robot developed by the KAIST Future Medical Robotics Research Center, opens a new chapter for minimally invasive robot-assisted surgery with its precision control of 3.7 mm diameter robotic arms. The two arms, placing at the end of flexible endoscopes, highlight impeccable precision control and robust mini-joint design technologies. While cruising through the complicated inner body pliably, it carries out procedures on the spot with its robotic arms.
The research team under Professor Dong-Soo Kwon recently tested the device in-vivo, conducting a complicated endoscopic procedure dissecting a porcine gallbladder in collaboration with Professor Dae-Kyung Son of the National Cancer Center. The arms successfully manipulated the tissue safely.
During the test, K-FLEX, inserted through an incision in the navel, snaked through the narrow passages of the complicated inner organs. When reaching the desired spot, one of the robot arms pushed aside and held up the nearby tissue to secure proper vision and space for the procedure. Meanwhile, a cautery needle mounted at the tip of the other hand removed the lesion tissue on the gallbladder. The tiny camera installed at the front of the robot arms relayed the internal conditions. The full procedure was able to be monitored from the master console.
The two arms are placed onto 4.2 mm internal channels of an endoscope which is 17 mm in diameter. The arms can be deployable forward and backward and are extendable up to 7 cm for performing procedures.
K-FLEX is made of domestically produced components, except for the endoscopic module. It will expand new medical robotics research while offering novel therapeutic capabilities for endoscopes.
Flexible endoscopes are very promising for surgical applications because they can treat areas thought to be difficult to reach, such as the posterior side of an organ. Current rigid-type laparoscopic tools could not reach a lesion if it occurs in such serpentine and complicated areas. However, this flexible endoscopic surgery robot will bypass obstacles to reach the troubled area.
The ability to seamlessly integrate effective actuation into millimeter-scale deployable mechanisms fits well with minimally invasive surgical procedures. This flexible endoscopic surgery robot, only half the size of current laparoscopic surgical robots, is deployable into natural orifices such as the mouth, anus, and vagina without requiring external incisions. Laparoscopic devices and robots require at least three to four external incisions to insert the devices; however, the applicability of internal incisions reduces the possibility of complications arousing from excessive bleeding and bacterial infections.
Despite these advantages, it has remained challenging to manipulate the robotic arms of flexible endoscopes with integrated grabbing force, flexibility, and multiple degrees of freedom for clinical environments.
The team focused on smaller but smarter devices. Dr. Min-Ho Hwang, a principal researcher of K-FLEX, said that developing tiny robots that are able to generate the necessary forces without compromising safety was the challenge. They created a robust but smaller-joint technology that can exert a relatively greater force even into millimeter scale.
Professor Kwon said, “K-FLEX is the first flexible endoscopic surgery robot in Korea. We already confirmed the clinical adaptation through ex vivo tests and will see complete commercialization in two to three years.” The team believes K-FLEX will be very effective for surgery on incipient cancer cells in the stomach, colon, and thyroid.
Professor Kwon and his eight researchers recently established a tech start-up called EasyEndo Surgical Inc. with these core technologies. In June, K-FLEX won the ‘Best Application Award’ and the ‘Overall Winner’ at the Surgical Robot Challenge 2018 held at Imperial College London. The Korea Research Foundation funded the research on K-FLEX.
(The team conducts a procedure using K-FLEX, flexible endoscopic surgical robot.)
2018.08.17 View 8632 -
 Professor Hee-Sung Park Named Scientist of May
(Professor Hee-Sung Park)
Professor Hee-Sung Park from the Department of Chemistry was named ‘Scientist of May’ sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Park was honored in recognition of his developing a tool to engineer designer proteins via diverse chemical modifications. This approach provides a novel platform for investigating numerous diseases such as cancer and dementia.
His research focuses on the production of synthetic proteins and the generation of diverse protein functions as well as the designing and engineering of new translation machinery for genetic code expansion, and the application of synthetic biology techniques for basic cell biology and applied medical science.
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are constantly taking place during or after protein biosynthesis. PTMs play a vital role in expanding protein functional diversity and, as a result, critically affect numerous biological processes. Abnormal PTMs have been known to trigger various diseases including cancer and dementia. Therefore, this technology enables proteins to reproduce with specific modifications at selected residues and will significantly help establish experimental strategies to investigate fundamental biological mechanisms including the development of targeted cancer therapies.
Professor Park also received 10 million KRW in prize money.
2018.05.04 View 9716
Professor Hee-Sung Park Named Scientist of May
(Professor Hee-Sung Park)
Professor Hee-Sung Park from the Department of Chemistry was named ‘Scientist of May’ sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Park was honored in recognition of his developing a tool to engineer designer proteins via diverse chemical modifications. This approach provides a novel platform for investigating numerous diseases such as cancer and dementia.
His research focuses on the production of synthetic proteins and the generation of diverse protein functions as well as the designing and engineering of new translation machinery for genetic code expansion, and the application of synthetic biology techniques for basic cell biology and applied medical science.
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are constantly taking place during or after protein biosynthesis. PTMs play a vital role in expanding protein functional diversity and, as a result, critically affect numerous biological processes. Abnormal PTMs have been known to trigger various diseases including cancer and dementia. Therefore, this technology enables proteins to reproduce with specific modifications at selected residues and will significantly help establish experimental strategies to investigate fundamental biological mechanisms including the development of targeted cancer therapies.
Professor Park also received 10 million KRW in prize money.
2018.05.04 View 9716 -
 Professor Ju, to Receive Grants from HFSP
(Professor Young Seok Ju)
Professor Young Seok Ju from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was selected as a young investigator to receive research funds from the Human Frontiers Science Program.
The Human Frontiers Science Program (HFSP) was founded in 1989 with members of the G7 and European Union to stimulate innovative research in the field of life sciences.
Professor Ju placed third out of the eight teams that were selected from 158 applicants representing 60 countries. He is now the fourth Korean to receive a research grant as a young investigator. Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the Department of Mathematical Sciences also received this prize last year, hence KAIST has produced grant recipients for two consecutive years.
Professor Ju is a medical doctor specializing in cancer genomics and computer biology. He has been studying somatic mutations and their functional consequences in human cancer in a bioinformatics way. He has published papers in international journals including Nature, Science, Genome Research, and Journal of Clinical Oncology.
With a title ‘Tracing AID/APOBEC- and MSI-mediated hyper-mutagenesis in the clonal evolution of gastric cancer,’ Professor Ju will receive 1.05 million dollars for three years along with Professor Bon-Kyoung Koo from the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology at Austrian Academy of Sciences, and Sinppert Hugo from University Medical Center Utrecht.
Professor Ju said, “As a young investigator, it is my great honor to receive this research fund from this organization. Through this internationally collaborative research, I will carry out groundbreaking research to understand the pathophysiology of cancers at a molecular level.”
2018.04.24 View 8429
Professor Ju, to Receive Grants from HFSP
(Professor Young Seok Ju)
Professor Young Seok Ju from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was selected as a young investigator to receive research funds from the Human Frontiers Science Program.
The Human Frontiers Science Program (HFSP) was founded in 1989 with members of the G7 and European Union to stimulate innovative research in the field of life sciences.
Professor Ju placed third out of the eight teams that were selected from 158 applicants representing 60 countries. He is now the fourth Korean to receive a research grant as a young investigator. Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the Department of Mathematical Sciences also received this prize last year, hence KAIST has produced grant recipients for two consecutive years.
Professor Ju is a medical doctor specializing in cancer genomics and computer biology. He has been studying somatic mutations and their functional consequences in human cancer in a bioinformatics way. He has published papers in international journals including Nature, Science, Genome Research, and Journal of Clinical Oncology.
With a title ‘Tracing AID/APOBEC- and MSI-mediated hyper-mutagenesis in the clonal evolution of gastric cancer,’ Professor Ju will receive 1.05 million dollars for three years along with Professor Bon-Kyoung Koo from the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology at Austrian Academy of Sciences, and Sinppert Hugo from University Medical Center Utrecht.
Professor Ju said, “As a young investigator, it is my great honor to receive this research fund from this organization. Through this internationally collaborative research, I will carry out groundbreaking research to understand the pathophysiology of cancers at a molecular level.”
2018.04.24 View 8429 -
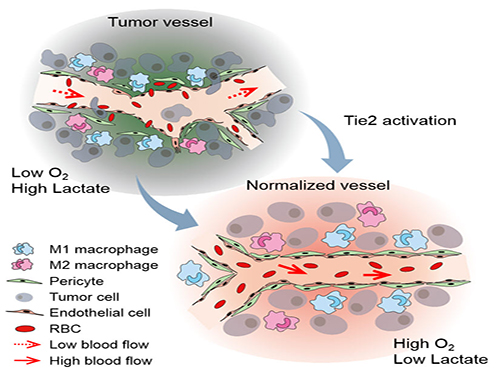 The Antibody That Normalizes Tumor Vessels
Researchers also discover that their antisepsis antibody reduces glioma, lung and breast cancer progression in mice.
A research team at the Center for Vascular Research within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) discovered that the antisepsis antibody ABTAA (Ang2-Binding and Tie2-Activating Antibody) reduces tumor volume and improves the delivery of anti-cancer drugs. Published in Cancer Cell, this study demonstrates that ABTAA restores the structural and functional integrity of tumor blood vessels in three different tumor models: breast, lungs, and brain.
Blood vessels inside and around an established tumor can be described as a chaotic and dysfunctional labyrinth. While the inner walls of healthy blood vessels are surrounded and supported by endothelial cells and other cells called pericytes, in the established tumor, the endothelial junctions are broken apart and pericytes are also detached. Blood flow into and from the tumor is severely retarded and tumor vessels lacking an intact vessel wall become leaky. This microenvironment causes limited drug delivery to the tumor and leads to inadequate oxygen supply (hypoxia) and even metastasis.
The research team led by Professor Gou-Young Koh at KAIST’s Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering found that the antibody ABTAA normalizes the tumor vessels and hence, change the whole tumor microenvironment. “We call it normalization of tumor vessels, because it resembles closely the wall architecture of healthy, normal vessels,” explains PARK Jin-Sung, first author of the study. And continues: “Tumor can adapt to hypoxia and get more aggressive, so we tried to prevent this transition by normalizing tumor vessels. ABTAA changes the whole tumor environment, oxygenation status and level of lactate, so that the immune cells and drugs can reach the core regions of the tumor more easily. In this way, we create a favorable ground for tumor treatment.”
In an attempt to generate antibodies targeting the protein Ang2, which is specifically expressed by endothelial cells in stressful conditions like in tumor, the team unexpectedly discovered that ABTAA has a peculiar way of working and a dual function. ABTAA indeed not only blocks Ang2, but also activates Tie2 at the same time. Tie2 is a receptor present on the cell membrane of endothelial cells. ABTAA causes Ang2 to cluster together and to strongly activate Tie2 receptors. “If we activate Tie2, we can efficiently normalize tumor vessels, enhance drug delivery and change the whole microenvironment,” explains KOH Gou Young, Director of the Center for Vascular Research.
Several pharmaceutical companies are developing Ang2-blocking antibodies to cure cancer. However, even if these antibodies significantly inhibit tumor progression, they do not stop tumor hypoxia. Moreover, most of the anti-cancer drugs target the tumor at its early stage, when tumors are still hard to diagnose. ABTAA, instead, works with tumors that are already rooted: “When the tumor is established, hypoxia is the main driver of tumor progression. So, if we eliminate hypoxia, we make the tumor milder, by reducing its progression and metastasis,” comments Koh.
Figure: Schematic drawing of a blood vessel around tumors before and after treatment with ABTAA. The picture above shows a typical tumor vasculature characterized by damaged walls, red blood cells leakage and detached pericytes. Activating Tie2 on endothelial cells with the antibody ABTAA restores the normal vessel architecture: endothelial and pericytes on the vessel walls are stabilized, the delivery of blood is improved, and the anticancer drugs are more likely to reach the tumor core.
The researchers tested ABTAA in mice with three different types of tumors that show high levels of Ang2: glioma (a type of a brain tumor), lung carcinoma, and breast cancer. They also compared the effect of ABTAA with ABA, another antibody that blocks Ang2 but misses the Tie2 activating properties. In all three cases, ABTAA was superior to ABA in inducing tumor vessel normalization, which led to a better delivery of the anti-cancer drugs into the tumor core region.
Glioma is one of the so-called intractable diseases, because of its poor prognosis and treatment. Professor Koh’s team found that the glioma volume was reduced 39% by ABTAA and 17% by ABA. ABTAA profoundly reduced vascular leakage and edema formation in glioma through promoting vascular tightening. Moreover, when ABTAA was administered together with the chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide (TMZ), the tumor volume reduces further (76% by ABTAA+TMZ, 51% by ABA+TMZ, and 36% by TMZ).
In the Lewis Lung Carcinoma (LLC) tumor model, the team administered ABTAA together with a chemotherapeutic drug called cisplatin (Cpt) and observed a greater suppression of tumor growth (52%) compared with the controls and increased overall survival. Moreover, ABTAA+Cpt led to a marked increase in necrotic area within tumors.
Finally, in a spontaneous breast cancer model, ABTAA delayed tumor growth and enhanced the anti-tumor effect of Cpt.
Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Sciences (IBS)
Figure: The antibody ABTAA alone and in combination with other anti-cancer drugs have a beneficial effect in reducing tumor volume. ABTAA was tested in mice with brain tumor (glioma), lung or breast cancer. The image shows the improvements: reduction in glioma tumor size, reduction in metastatic colonies in lung tumor and decrease in necrotic regions in breast tumor.
In the future, the team would like to further understand the underlying relationship between faulty blood vessels and diseases. “We would like to apply this antibody to an organ that is rich in blood vessels, that is the eye, and see if this antibody can be useful to treat eye diseases such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy,” concludes Koh.
Professor Gou-Young Koh (left) and Jin-Sung Park (right)
2016.12.16 View 8876
The Antibody That Normalizes Tumor Vessels
Researchers also discover that their antisepsis antibody reduces glioma, lung and breast cancer progression in mice.
A research team at the Center for Vascular Research within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) discovered that the antisepsis antibody ABTAA (Ang2-Binding and Tie2-Activating Antibody) reduces tumor volume and improves the delivery of anti-cancer drugs. Published in Cancer Cell, this study demonstrates that ABTAA restores the structural and functional integrity of tumor blood vessels in three different tumor models: breast, lungs, and brain.
Blood vessels inside and around an established tumor can be described as a chaotic and dysfunctional labyrinth. While the inner walls of healthy blood vessels are surrounded and supported by endothelial cells and other cells called pericytes, in the established tumor, the endothelial junctions are broken apart and pericytes are also detached. Blood flow into and from the tumor is severely retarded and tumor vessels lacking an intact vessel wall become leaky. This microenvironment causes limited drug delivery to the tumor and leads to inadequate oxygen supply (hypoxia) and even metastasis.
The research team led by Professor Gou-Young Koh at KAIST’s Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering found that the antibody ABTAA normalizes the tumor vessels and hence, change the whole tumor microenvironment. “We call it normalization of tumor vessels, because it resembles closely the wall architecture of healthy, normal vessels,” explains PARK Jin-Sung, first author of the study. And continues: “Tumor can adapt to hypoxia and get more aggressive, so we tried to prevent this transition by normalizing tumor vessels. ABTAA changes the whole tumor environment, oxygenation status and level of lactate, so that the immune cells and drugs can reach the core regions of the tumor more easily. In this way, we create a favorable ground for tumor treatment.”
In an attempt to generate antibodies targeting the protein Ang2, which is specifically expressed by endothelial cells in stressful conditions like in tumor, the team unexpectedly discovered that ABTAA has a peculiar way of working and a dual function. ABTAA indeed not only blocks Ang2, but also activates Tie2 at the same time. Tie2 is a receptor present on the cell membrane of endothelial cells. ABTAA causes Ang2 to cluster together and to strongly activate Tie2 receptors. “If we activate Tie2, we can efficiently normalize tumor vessels, enhance drug delivery and change the whole microenvironment,” explains KOH Gou Young, Director of the Center for Vascular Research.
Several pharmaceutical companies are developing Ang2-blocking antibodies to cure cancer. However, even if these antibodies significantly inhibit tumor progression, they do not stop tumor hypoxia. Moreover, most of the anti-cancer drugs target the tumor at its early stage, when tumors are still hard to diagnose. ABTAA, instead, works with tumors that are already rooted: “When the tumor is established, hypoxia is the main driver of tumor progression. So, if we eliminate hypoxia, we make the tumor milder, by reducing its progression and metastasis,” comments Koh.
Figure: Schematic drawing of a blood vessel around tumors before and after treatment with ABTAA. The picture above shows a typical tumor vasculature characterized by damaged walls, red blood cells leakage and detached pericytes. Activating Tie2 on endothelial cells with the antibody ABTAA restores the normal vessel architecture: endothelial and pericytes on the vessel walls are stabilized, the delivery of blood is improved, and the anticancer drugs are more likely to reach the tumor core.
The researchers tested ABTAA in mice with three different types of tumors that show high levels of Ang2: glioma (a type of a brain tumor), lung carcinoma, and breast cancer. They also compared the effect of ABTAA with ABA, another antibody that blocks Ang2 but misses the Tie2 activating properties. In all three cases, ABTAA was superior to ABA in inducing tumor vessel normalization, which led to a better delivery of the anti-cancer drugs into the tumor core region.
Glioma is one of the so-called intractable diseases, because of its poor prognosis and treatment. Professor Koh’s team found that the glioma volume was reduced 39% by ABTAA and 17% by ABA. ABTAA profoundly reduced vascular leakage and edema formation in glioma through promoting vascular tightening. Moreover, when ABTAA was administered together with the chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide (TMZ), the tumor volume reduces further (76% by ABTAA+TMZ, 51% by ABA+TMZ, and 36% by TMZ).
In the Lewis Lung Carcinoma (LLC) tumor model, the team administered ABTAA together with a chemotherapeutic drug called cisplatin (Cpt) and observed a greater suppression of tumor growth (52%) compared with the controls and increased overall survival. Moreover, ABTAA+Cpt led to a marked increase in necrotic area within tumors.
Finally, in a spontaneous breast cancer model, ABTAA delayed tumor growth and enhanced the anti-tumor effect of Cpt.
Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Sciences (IBS)
Figure: The antibody ABTAA alone and in combination with other anti-cancer drugs have a beneficial effect in reducing tumor volume. ABTAA was tested in mice with brain tumor (glioma), lung or breast cancer. The image shows the improvements: reduction in glioma tumor size, reduction in metastatic colonies in lung tumor and decrease in necrotic regions in breast tumor.
In the future, the team would like to further understand the underlying relationship between faulty blood vessels and diseases. “We would like to apply this antibody to an organ that is rich in blood vessels, that is the eye, and see if this antibody can be useful to treat eye diseases such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy,” concludes Koh.
Professor Gou-Young Koh (left) and Jin-Sung Park (right)
2016.12.16 View 8876 -
 Visit by Sir Paul Maxime Nurse, President of the Royal Society
Sir Paul Maxime
Nurse, who is an English geneticist and cell biologist, visited KAIST and gave
a lecture entitled The Great Ideas of
Biology on March 11, 2014.
Sir Paul was awarded the 2001 Nobel Prize in
Physiology or Medicine with Leland H. Hartwell and R. Timothy Hunt for their discoveries
of protein molecules that control the division of cells in the cell cycle.
He was Professor of Microbiology at the University
of Oxford, CEO of the Imperial Cancer Research Fund and Cancer Research UK, and
President of Rockefeller University in New York. Sir Paul is currently the President of
the Royal Society as well as Director and Chief Executive of the Francis Crick
Institute.
Founded in London in 1660, the Royal Society is composed of the world’s most distinguished scientists drawn from all areas of
science, engineering, and medicine.
Below is a summary of his lecture, The Great Ideas of Biology:
Four major ideas of biology
are the theory of genes, evolution by natural selection, the proposal that the
cell is the fundamental unit of all life, and the chemical composition of a cell.
When considering the
question “what is life?” these ideas come together. The special way cells reproduce
provides the conditions by which natural selection takes place, allowing living
organisms to evolve. The organization of chemistry within the cell provides
explanations for life’s phenomena.
In addition, an emerging idea
is the nature of biological self-organization with which living cells and organisms
process information and acquire specific forms. These great ideas have
influenced one another and changed the way we perceive biology and science
today.
2014.03.11 View 10565
Visit by Sir Paul Maxime Nurse, President of the Royal Society
Sir Paul Maxime
Nurse, who is an English geneticist and cell biologist, visited KAIST and gave
a lecture entitled The Great Ideas of
Biology on March 11, 2014.
Sir Paul was awarded the 2001 Nobel Prize in
Physiology or Medicine with Leland H. Hartwell and R. Timothy Hunt for their discoveries
of protein molecules that control the division of cells in the cell cycle.
He was Professor of Microbiology at the University
of Oxford, CEO of the Imperial Cancer Research Fund and Cancer Research UK, and
President of Rockefeller University in New York. Sir Paul is currently the President of
the Royal Society as well as Director and Chief Executive of the Francis Crick
Institute.
Founded in London in 1660, the Royal Society is composed of the world’s most distinguished scientists drawn from all areas of
science, engineering, and medicine.
Below is a summary of his lecture, The Great Ideas of Biology:
Four major ideas of biology
are the theory of genes, evolution by natural selection, the proposal that the
cell is the fundamental unit of all life, and the chemical composition of a cell.
When considering the
question “what is life?” these ideas come together. The special way cells reproduce
provides the conditions by which natural selection takes place, allowing living
organisms to evolve. The organization of chemistry within the cell provides
explanations for life’s phenomena.
In addition, an emerging idea
is the nature of biological self-organization with which living cells and organisms
process information and acquire specific forms. These great ideas have
influenced one another and changed the way we perceive biology and science
today.
2014.03.11 View 10565 -
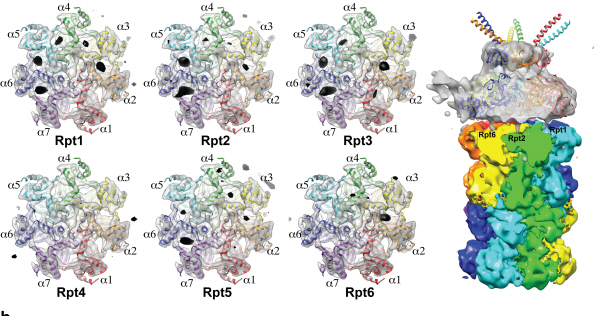 Complex responsible for protein breakdown in cells identified using Bio TEM
Professor Ho-Min Kim
- High resolution 3D structure analysis success using Bio Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), a giant step towards new anticancer treatment development
- Published in Nature on May 5th
Using TEM to observe protein molecules and analysing its high resolution 3D structure is now possible. KAIST Biomedical Science and Engineering Department’s Professor Ho-Min Kim has identified the high resolution structure of proteasome complexes, which is responsible for protein breakdown in cells, using Bio TEM.
This research has been published on the world"s most prestigious journal, Nature, online on May 5th. Our body controls many cellular processes through production and degradation of proteins to maintain homeostasis. A proteasome complex acts as a garbage disposal system and degrades cellular proteins when needed for regulation, which is one of the central roles of the body.
However, a mutation in proteasome complex leads to diseases such as cancer, degenerative brain diseases, and autoimmune diseases.
Currently, the anticancer drug Velcade is used to decrease proteasome function to treat Multiple Myeloma, a form of blood cancer. Research concerning proteasome complexes for more effective anticancer drugs and treatments with fewer side effects has been taking place for more than 20 years. There have been many difficulties in understanding proteasome function through 3D structure analysis since a proteasome complex, consisting of around 30 different proteins, has a great size and complexity.
The research team used Bio TEM instead of conventionally used protein crystallography technique. The protein sample was inserted into Bio TEM, hundreds of photographs were taken from various angles, and then a high–performance computer was used to analyse its structure. Bio TEM requires a smaller sample and can analyse the complexes of great size of proteins.
Professor Ho-Min Kim said, “Identifying proteasome complex assembly process and 3D structure will increase our understanding of cellular protein degradation process and hence assist in new drug development using this knowledge.” He added, “High resolution protein structure analysis using Bio TEM, used for the first time in Korea, will enable us to observe structure analysis of large protein complexes that were difficult to approach using protein crystallography.” Professor Kim continued, “If protein crystallography technology and Bio TEM could be used together to complement one another, it would bring a great synergetic effect to protein complex 3D structure analysis research in the future.”
Professor Ho-Min Kim has conducted this research since his post-doctorate at the University of California, San Francisco, under the advice of Professor Yifan Cheng; in co-operation with Harvard University and Colorado University.
Figure 1: A picture taken by Bio TEM of open state protein sample (proteasome complex)
Figure 2: Bio TEM image analysis showing protein 3D structure
2013.05.25 View 11040
Complex responsible for protein breakdown in cells identified using Bio TEM
Professor Ho-Min Kim
- High resolution 3D structure analysis success using Bio Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), a giant step towards new anticancer treatment development
- Published in Nature on May 5th
Using TEM to observe protein molecules and analysing its high resolution 3D structure is now possible. KAIST Biomedical Science and Engineering Department’s Professor Ho-Min Kim has identified the high resolution structure of proteasome complexes, which is responsible for protein breakdown in cells, using Bio TEM.
This research has been published on the world"s most prestigious journal, Nature, online on May 5th. Our body controls many cellular processes through production and degradation of proteins to maintain homeostasis. A proteasome complex acts as a garbage disposal system and degrades cellular proteins when needed for regulation, which is one of the central roles of the body.
However, a mutation in proteasome complex leads to diseases such as cancer, degenerative brain diseases, and autoimmune diseases.
Currently, the anticancer drug Velcade is used to decrease proteasome function to treat Multiple Myeloma, a form of blood cancer. Research concerning proteasome complexes for more effective anticancer drugs and treatments with fewer side effects has been taking place for more than 20 years. There have been many difficulties in understanding proteasome function through 3D structure analysis since a proteasome complex, consisting of around 30 different proteins, has a great size and complexity.
The research team used Bio TEM instead of conventionally used protein crystallography technique. The protein sample was inserted into Bio TEM, hundreds of photographs were taken from various angles, and then a high–performance computer was used to analyse its structure. Bio TEM requires a smaller sample and can analyse the complexes of great size of proteins.
Professor Ho-Min Kim said, “Identifying proteasome complex assembly process and 3D structure will increase our understanding of cellular protein degradation process and hence assist in new drug development using this knowledge.” He added, “High resolution protein structure analysis using Bio TEM, used for the first time in Korea, will enable us to observe structure analysis of large protein complexes that were difficult to approach using protein crystallography.” Professor Kim continued, “If protein crystallography technology and Bio TEM could be used together to complement one another, it would bring a great synergetic effect to protein complex 3D structure analysis research in the future.”
Professor Ho-Min Kim has conducted this research since his post-doctorate at the University of California, San Francisco, under the advice of Professor Yifan Cheng; in co-operation with Harvard University and Colorado University.
Figure 1: A picture taken by Bio TEM of open state protein sample (proteasome complex)
Figure 2: Bio TEM image analysis showing protein 3D structure
2013.05.25 View 11040 -
 Bio Pharmaceutical Business Center: Now Open
The Signboard Hanging Ceremony for the Bio Pharmaceutical Business Center for the Integrated Research for the field of Bio Pharmaceutics. 150 representatives from various bio pharmaceutics related businesses and institutes were present for this ceremony.
The Ministry of Education, Science and Technology placed the Molecular Process research team, Personalized Drug Delivery Medium research team, and the newly formed Cancer Cell Detection using Blood research team at the Bio Pharmaceutical Business Center at KAIST.
2012.01.31 View 8982
Bio Pharmaceutical Business Center: Now Open
The Signboard Hanging Ceremony for the Bio Pharmaceutical Business Center for the Integrated Research for the field of Bio Pharmaceutics. 150 representatives from various bio pharmaceutics related businesses and institutes were present for this ceremony.
The Ministry of Education, Science and Technology placed the Molecular Process research team, Personalized Drug Delivery Medium research team, and the newly formed Cancer Cell Detection using Blood research team at the Bio Pharmaceutical Business Center at KAIST.
2012.01.31 View 8982 -
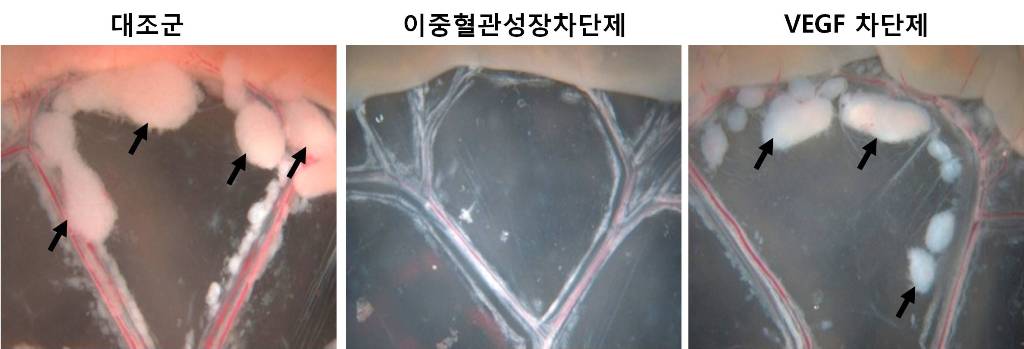 An internationally renowned academic journal published the research result produced by a KAST research team on its cover.
Fc DAAP VEGF-Trap
Photograph showing the gross features of tumor growth along the mesentery-intestinal border. T: tumor. Scale bars represent 5 mm.
Professor Gou-Young Koh of the Biological Sciences Department, KAIST, and his research team published their research result in Cancer Cell, a peer-review scientific journal, as a cover article dated August 17, 2010. It is the first time for the journal to pick up a paper written by a Korean research team and publish it as the cover.
It has been known that a vascular growth factor (VEGF) is closely related to the growth of a tumor. The research team recently discovered that in addition to VEGF, another growth factor, angiopoietin-2 (Ang2), is also engaged with the increase of tumors.
Professor Koh said, “VEGF and the angiopoietins play critical roles in tumor progression and metastasis, and a single inhibitor targeting both factors have not been available.”
The team led by Professor Koh has developed a double anti-angiogenic protein (DAAP) that can simultaneously bind VEGF-A and the angiopoietins and block their actions.
Professor Koh said in his paper, “DAAP is a highly effective molecule for regressing tumor angiogenesis and metastasis in implanted and spontaneous solid tumor; it can also effectively reduce ascites formation and vascular leakage in an ovarian carcinoma model. Thus, simultaneous blockade of VEGF-A and angiopoietins with DAAP is an effective therapeutic strategy for blocking tumor angiogenesis, metastasis, and vascular leakage.”
So far, cancer patients have received Avastin, anticancer drug, to inhibit VEGF, but the drug has not successfully restrained the growth of cancer tumors and brought to some of the patients with serious side effects instead.
Professor Koh said, “DAAP will be very effective to control the expansion of tumor growth factors, which will open up a new possibility for the development of more helpful cancer medicine with low side effects.”
2010.08.20 View 12520
An internationally renowned academic journal published the research result produced by a KAST research team on its cover.
Fc DAAP VEGF-Trap
Photograph showing the gross features of tumor growth along the mesentery-intestinal border. T: tumor. Scale bars represent 5 mm.
Professor Gou-Young Koh of the Biological Sciences Department, KAIST, and his research team published their research result in Cancer Cell, a peer-review scientific journal, as a cover article dated August 17, 2010. It is the first time for the journal to pick up a paper written by a Korean research team and publish it as the cover.
It has been known that a vascular growth factor (VEGF) is closely related to the growth of a tumor. The research team recently discovered that in addition to VEGF, another growth factor, angiopoietin-2 (Ang2), is also engaged with the increase of tumors.
Professor Koh said, “VEGF and the angiopoietins play critical roles in tumor progression and metastasis, and a single inhibitor targeting both factors have not been available.”
The team led by Professor Koh has developed a double anti-angiogenic protein (DAAP) that can simultaneously bind VEGF-A and the angiopoietins and block their actions.
Professor Koh said in his paper, “DAAP is a highly effective molecule for regressing tumor angiogenesis and metastasis in implanted and spontaneous solid tumor; it can also effectively reduce ascites formation and vascular leakage in an ovarian carcinoma model. Thus, simultaneous blockade of VEGF-A and angiopoietins with DAAP is an effective therapeutic strategy for blocking tumor angiogenesis, metastasis, and vascular leakage.”
So far, cancer patients have received Avastin, anticancer drug, to inhibit VEGF, but the drug has not successfully restrained the growth of cancer tumors and brought to some of the patients with serious side effects instead.
Professor Koh said, “DAAP will be very effective to control the expansion of tumor growth factors, which will open up a new possibility for the development of more helpful cancer medicine with low side effects.”
2010.08.20 View 12520 -
 KAIST Opens Cell Bench Research Center
KAIST opened a cell bench research center on the campus on Monday, Nov. 17, as a joint project with Samsung Electric Co. and Samsung Medical Center.
On hand at the opening ceremony were about 100 persons from the three organizations, including KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh, Samsung Electric"s Chief Technology Officer (CTO) Byung-Cheon Koh and Samsung Medical Center Vice President Hyo-Geun Lim.
The newly-opened research center will be involved in the development of individually-tailored anti-cancer medicine using bio-inspired cell chips and technologies for clinical applications. Prof. Young-Ho Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was named director of the research center.
"Top-notch professionals from the electronic industry, academia and the medical community have gathered together to establish this research center. We expect the center will open a new path for the science and technology community and the industry to combine their strengths and develop innovative anti-cancer therapeutics," said KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh at the opening ceremony.
"The development of bio-cell chip technology represents a new challenge for the Samsung Electric which has focused on information technologies thus far. Through cooperation with KAIST and Samsung Medical Center, we expect to be able to develop a simple and efficient cure for cancer patients," commented Samsung Electric CTO Byung-Cheon Koh.
The research center will be initially concentrating on the development of cell chips for lung cancer, one of the primary causes of death for Koreans.
2008.11.17 View 16412
KAIST Opens Cell Bench Research Center
KAIST opened a cell bench research center on the campus on Monday, Nov. 17, as a joint project with Samsung Electric Co. and Samsung Medical Center.
On hand at the opening ceremony were about 100 persons from the three organizations, including KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh, Samsung Electric"s Chief Technology Officer (CTO) Byung-Cheon Koh and Samsung Medical Center Vice President Hyo-Geun Lim.
The newly-opened research center will be involved in the development of individually-tailored anti-cancer medicine using bio-inspired cell chips and technologies for clinical applications. Prof. Young-Ho Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was named director of the research center.
"Top-notch professionals from the electronic industry, academia and the medical community have gathered together to establish this research center. We expect the center will open a new path for the science and technology community and the industry to combine their strengths and develop innovative anti-cancer therapeutics," said KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh at the opening ceremony.
"The development of bio-cell chip technology represents a new challenge for the Samsung Electric which has focused on information technologies thus far. Through cooperation with KAIST and Samsung Medical Center, we expect to be able to develop a simple and efficient cure for cancer patients," commented Samsung Electric CTO Byung-Cheon Koh.
The research center will be initially concentrating on the development of cell chips for lung cancer, one of the primary causes of death for Koreans.
2008.11.17 View 16412