-
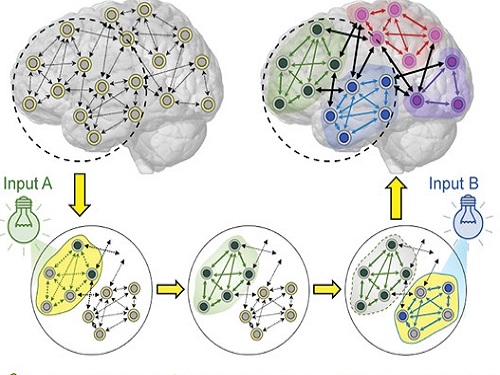 Energy-Efficient AI Hardware Technology Via a Brain-Inspired Stashing System
Researchers demonstrate neuromodulation-inspired stashing system for the energy-efficient learning of a spiking neural network using a self-rectifying memristor array
Researchers have proposed a novel system inspired by the neuromodulation of the brain, referred to as a ‘stashing system,’ that requires less energy consumption. The research group led by Professor Kyung Min Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a technology that can efficiently handle mathematical operations for artificial intelligence by imitating the continuous changes in the topology of the neural network according to the situation. The human brain changes its neural topology in real time, learning to store or recall memories as needed. The research group presented a new artificial intelligence learning method that directly implements these neural coordination circuit configurations.
Research on artificial intelligence is becoming very active, and the development of artificial intelligence-based electronic devices and product releases are accelerating, especially in the Fourth Industrial Revolution age. To implement artificial intelligence in electronic devices, customized hardware development should also be supported. However most electronic devices for artificial intelligence require high power consumption and highly integrated memory arrays for large-scale tasks. It has been challenging to solve these power consumption and integration limitations, and efforts have been made to find out how the human brain solves problems.
To prove the efficiency of the developed technology, the research group created artificial neural network hardware equipped with a self-rectifying synaptic array and algorithm called a ‘stashing system’ that was developed to conduct artificial intelligence learning. As a result, it was able to reduce energy by 37% within the stashing system without any accuracy degradation. This result proves that emulating the neuromodulation in humans is possible.
Professor Kim said, "In this study, we implemented the learning method of the human brain with only a simple circuit composition and through this we were able to reduce the energy needed by nearly 40 percent.”
This neuromodulation-inspired stashing system that mimics the brain’s neural activity is compatible with existing electronic devices and commercialized semiconductor hardware. It is expected to be used in the design of next-generation semiconductor chips for artificial intelligence.
This study was published in Advanced Functional Materials in March 2022 and supported by KAIST, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the National NanoFab Center, and SK Hynix.
-Publication:
Woon Hyung Cheong, Jae Bum Jeon†, Jae Hyun In, Geunyoung Kim, Hanchan Song, Janho An, Juseong Park, Young Seok Kim, Cheol Seong Hwang, and Kyung Min Kim (2022)
“Demonstration of Neuromodulation-inspired Stashing System for Energy-efficient Learning of Spiking Neural Network using a Self-Rectifying Memristor Array,” Advanced FunctionalMaterials March 31, 2022 (DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202200337)
-Profile:
Professor Kyung Min Kimhttp://semi.kaist.ac.kr https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=BGw8yDYAAAAJ&hl=ko
Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.18 View 11119
Energy-Efficient AI Hardware Technology Via a Brain-Inspired Stashing System
Researchers demonstrate neuromodulation-inspired stashing system for the energy-efficient learning of a spiking neural network using a self-rectifying memristor array
Researchers have proposed a novel system inspired by the neuromodulation of the brain, referred to as a ‘stashing system,’ that requires less energy consumption. The research group led by Professor Kyung Min Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a technology that can efficiently handle mathematical operations for artificial intelligence by imitating the continuous changes in the topology of the neural network according to the situation. The human brain changes its neural topology in real time, learning to store or recall memories as needed. The research group presented a new artificial intelligence learning method that directly implements these neural coordination circuit configurations.
Research on artificial intelligence is becoming very active, and the development of artificial intelligence-based electronic devices and product releases are accelerating, especially in the Fourth Industrial Revolution age. To implement artificial intelligence in electronic devices, customized hardware development should also be supported. However most electronic devices for artificial intelligence require high power consumption and highly integrated memory arrays for large-scale tasks. It has been challenging to solve these power consumption and integration limitations, and efforts have been made to find out how the human brain solves problems.
To prove the efficiency of the developed technology, the research group created artificial neural network hardware equipped with a self-rectifying synaptic array and algorithm called a ‘stashing system’ that was developed to conduct artificial intelligence learning. As a result, it was able to reduce energy by 37% within the stashing system without any accuracy degradation. This result proves that emulating the neuromodulation in humans is possible.
Professor Kim said, "In this study, we implemented the learning method of the human brain with only a simple circuit composition and through this we were able to reduce the energy needed by nearly 40 percent.”
This neuromodulation-inspired stashing system that mimics the brain’s neural activity is compatible with existing electronic devices and commercialized semiconductor hardware. It is expected to be used in the design of next-generation semiconductor chips for artificial intelligence.
This study was published in Advanced Functional Materials in March 2022 and supported by KAIST, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the National NanoFab Center, and SK Hynix.
-Publication:
Woon Hyung Cheong, Jae Bum Jeon†, Jae Hyun In, Geunyoung Kim, Hanchan Song, Janho An, Juseong Park, Young Seok Kim, Cheol Seong Hwang, and Kyung Min Kim (2022)
“Demonstration of Neuromodulation-inspired Stashing System for Energy-efficient Learning of Spiking Neural Network using a Self-Rectifying Memristor Array,” Advanced FunctionalMaterials March 31, 2022 (DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202200337)
-Profile:
Professor Kyung Min Kimhttp://semi.kaist.ac.kr https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=BGw8yDYAAAAJ&hl=ko
Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.18 View 11119 -
 Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center Opens
Distinguished visiting scholar soprano Sumi Jo gave a special lecture on May 13 at the KAIST auditorium. During the lecture, she talked about new technologies that will be introduced for future performing art stages while sharing some of the challenges she experienced before reaching to the stardom of the world stage. She also joined the KAIST student choral club ‘Chorus’ to perform the KAIST school song.
Professor Jo also opened the Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center on the same day along with President Kwang Hyung Lee and faculty members from the Graduate School of Culture Technology. The center will conduct AI and metaverse-based performing art technologies such as performer modeling via AI playing and motion creation, interactions between virtual and human players via sound analysis and motion recognition, as well as virtual stage and performing center modeling. The center will also carry out extensive stage production research applied to media convergence technologies.
Professor Juhan Nam, who heads the research center, said that the center is seeking collaborations with other universities such as Seoul National University and the Korea National University of Arts as well as top performing artists at home and abroad. He looks forward to the center growing into a collaborative center for future performing arts.
Professor Jo added that she will spare no effort to offer her experience and advice for the center’s future-forward performing arts research projects.
2022.05.16 View 6687
Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center Opens
Distinguished visiting scholar soprano Sumi Jo gave a special lecture on May 13 at the KAIST auditorium. During the lecture, she talked about new technologies that will be introduced for future performing art stages while sharing some of the challenges she experienced before reaching to the stardom of the world stage. She also joined the KAIST student choral club ‘Chorus’ to perform the KAIST school song.
Professor Jo also opened the Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center on the same day along with President Kwang Hyung Lee and faculty members from the Graduate School of Culture Technology. The center will conduct AI and metaverse-based performing art technologies such as performer modeling via AI playing and motion creation, interactions between virtual and human players via sound analysis and motion recognition, as well as virtual stage and performing center modeling. The center will also carry out extensive stage production research applied to media convergence technologies.
Professor Juhan Nam, who heads the research center, said that the center is seeking collaborations with other universities such as Seoul National University and the Korea National University of Arts as well as top performing artists at home and abroad. He looks forward to the center growing into a collaborative center for future performing arts.
Professor Jo added that she will spare no effort to offer her experience and advice for the center’s future-forward performing arts research projects.
2022.05.16 View 6687 -
 Professor Hyo-Sang Shin at Cranfield University Named the 18th Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
Professor Hyo-Sang Shin at Cranfield University in the UK was named the 18th Jeong Hun Cho Award recipient. PhD candidate Kyu-Sob Kim from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, Master’s candidate from Korea University Kon-Hee Chang, Jae-Woo Chang from Kongju National University High School were also selected.
Professor Shin, a PhD graduate from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2016 works at Cranfield University. Professor Shin, whose main research focus covers guidance, navigation, and control, conducts research on information-based control. He has published 66 articles in SCI journals and presented approximately 70 papers at academic conference with more than 12 patent registrations. He is known for his expertise in areas related to unmanned aerospace systems and urban aero traffic automation. Professor Shin is participating in various aerospace engineering development projects run by the UK government.
The award recognizes promising young scientists who have made significant achievements in the field of aerospace engineering in honor of Jeong Hun Cho, the former PhD candidate in KAIST’s Department of Aerospace Engineering. Cho died in a lab accident in May 2003. Cho’s family endowed the award and scholarship to honor him and a recipient from each of his three alma maters (Kongju National High School, Korea University, and KAIST) are selected every year.
Professor Shin was awarded 25 million KRW in prize money. KAIST student Kim and Korea University student Chang received four million KRW while Kongju National University High School student Chang received three million KRW.
2022.05.16 View 6761
Professor Hyo-Sang Shin at Cranfield University Named the 18th Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
Professor Hyo-Sang Shin at Cranfield University in the UK was named the 18th Jeong Hun Cho Award recipient. PhD candidate Kyu-Sob Kim from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, Master’s candidate from Korea University Kon-Hee Chang, Jae-Woo Chang from Kongju National University High School were also selected.
Professor Shin, a PhD graduate from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2016 works at Cranfield University. Professor Shin, whose main research focus covers guidance, navigation, and control, conducts research on information-based control. He has published 66 articles in SCI journals and presented approximately 70 papers at academic conference with more than 12 patent registrations. He is known for his expertise in areas related to unmanned aerospace systems and urban aero traffic automation. Professor Shin is participating in various aerospace engineering development projects run by the UK government.
The award recognizes promising young scientists who have made significant achievements in the field of aerospace engineering in honor of Jeong Hun Cho, the former PhD candidate in KAIST’s Department of Aerospace Engineering. Cho died in a lab accident in May 2003. Cho’s family endowed the award and scholarship to honor him and a recipient from each of his three alma maters (Kongju National High School, Korea University, and KAIST) are selected every year.
Professor Shin was awarded 25 million KRW in prize money. KAIST student Kim and Korea University student Chang received four million KRW while Kongju National University High School student Chang received three million KRW.
2022.05.16 View 6761 -
 Anonymous Donor Makes a Gift of Property Valued at 30 Billion KRW
The KAIST Development Foundation announced on May 9 that an anonymous donor in his 50s made a gift of real estate valued at 30 billion KRW. This is the first donation from an anonymous benefactor on such a grand scale. The benefactor expressed his wishes to fund scholarships for students in need and R&D for medical and bio sciences.
According to the Development Foundation official, the benefactor is reported to have said that he felt burdened that he earned much more than he needed and was looking for the right way to share his assets. The benefactor refused to hold an official donation ceremony and meeting with high-level university administrators.
The donor believes that KAIST is filled with young and dynamic energy, saying, “I would like to help KAIST move forward and create breakthroughs that will benefit the nation as well as all humanity.”
Before making up his mind to give his asset to KAIST, he had planned to establish his own social foundation but he changed his mind. “I decided that an investment in education would be the best investment,” he said. He explained that he was inspired by his KAIST graduate friend who is running a company. He was deeply motivated to help KAIST after witnessing the KAIST graduate’s passion for conducting his business.
After receiving the gift, KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee was thankful for the full support and trust of the benefactor. “We will spare no effort to foster next-generation talents and advance science and technology in the field of biomedicine.”
2022.05.11 View 5576
Anonymous Donor Makes a Gift of Property Valued at 30 Billion KRW
The KAIST Development Foundation announced on May 9 that an anonymous donor in his 50s made a gift of real estate valued at 30 billion KRW. This is the first donation from an anonymous benefactor on such a grand scale. The benefactor expressed his wishes to fund scholarships for students in need and R&D for medical and bio sciences.
According to the Development Foundation official, the benefactor is reported to have said that he felt burdened that he earned much more than he needed and was looking for the right way to share his assets. The benefactor refused to hold an official donation ceremony and meeting with high-level university administrators.
The donor believes that KAIST is filled with young and dynamic energy, saying, “I would like to help KAIST move forward and create breakthroughs that will benefit the nation as well as all humanity.”
Before making up his mind to give his asset to KAIST, he had planned to establish his own social foundation but he changed his mind. “I decided that an investment in education would be the best investment,” he said. He explained that he was inspired by his KAIST graduate friend who is running a company. He was deeply motivated to help KAIST after witnessing the KAIST graduate’s passion for conducting his business.
After receiving the gift, KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee was thankful for the full support and trust of the benefactor. “We will spare no effort to foster next-generation talents and advance science and technology in the field of biomedicine.”
2022.05.11 View 5576 -
 Professor Sang Su Lee’s Team Wins Seven iF Design Awards 2022
Professor Sang Su Lee from the Department of Industrial Design and his team’s five apps made in collaboration with NH Investment and Securities won iF Design Awards in the fields of UI, UX, service design, product design, and communication. These apps are now offered as NH Investment and Securities mobile applications.
The iF Design Awards recognize top quality creativity in product design, communication, packaging, service design and concepts, and architecture and interior design, as well as user experience (UX) and interface for digital media (UI).
In the field of UI, ‘Gretell’ is a mobile stock investment app service designed by Lee and his team to support investors struggling to learn about investing by archiving personalized information. Gretell provides investment information including news and reports. Users learn, evaluate, and leave comments. This shows both quantitative and qualitative indications, leading to rational decision-making. Other user’s comments are shared to reduce confirmation bias. Through this process, Gretell helps users who are impulsive or easily swayed by others’ opinions to grow as independent investors.
‘Bright’ is another app created by Lee’s team. It helps people exercise their rights as shareholders. As the need to exercise shareholders’ rights increases, many people are frustrated that investors with a small number of shares don’t have a lot of power. Bright provides a space for shareholders to share their opinions and brings people together so that individuals can be more proactive as shareholders. The Integrated Power of Attorney System (IPAS) expands the chances for shareholders to exercise their rights and allows users to submit proposals that can be communicated during the general meeting. Bright fosters influential shareholders, responsible companies, and a healthy society.
For communications, ‘Rewind’ is a stock information services app that visualizes past stock charts through sentiment analysis. Existing services focus on numbers, while Rewind takes a qualitative approach. Rewind analyzes public sentiment toward each event by collecting opinions on social media and then visualizes them chronologically along with the stock chart. Rewind allows users to review stock market movements and record their thoughts. Users can gain their own insights into current events in the stock market and make wiser investment decisions. The intuitive color gradient design provides a pleasant and simplified information experience.
In the area of interfaces for digital media and service design, ‘Groo’ is a green bond investing service app that helps users participate in green investment though investing in green bonds that support green projects for environmental improvement. Not restricted to trading bonds, Groo joins users in the holistic experience of green investing, from taking an interest in environmental issues to confirming the impact of the investment.
Next, ‘Modu’ is a story-based empathy expression training game for children with intellectual disabilities. Modu was developed to support emotion recognition and empathy behavior training in children with mild intellectual disabilities (MID) and borderline intellectual functioning (BIF).
Finally, the diving VR device for neutral buoyancy training, ‘Blow-yancy’, also made winner’s list. The device mimics scuba diving training without having to go into the water, therefore beginner divers are able getting feeling of diving while remaining perfectly safe and not harming any corals. It is expected that the device will be able to help protect at-risk underwater ecosystems.
2022.05.10 View 8528
Professor Sang Su Lee’s Team Wins Seven iF Design Awards 2022
Professor Sang Su Lee from the Department of Industrial Design and his team’s five apps made in collaboration with NH Investment and Securities won iF Design Awards in the fields of UI, UX, service design, product design, and communication. These apps are now offered as NH Investment and Securities mobile applications.
The iF Design Awards recognize top quality creativity in product design, communication, packaging, service design and concepts, and architecture and interior design, as well as user experience (UX) and interface for digital media (UI).
In the field of UI, ‘Gretell’ is a mobile stock investment app service designed by Lee and his team to support investors struggling to learn about investing by archiving personalized information. Gretell provides investment information including news and reports. Users learn, evaluate, and leave comments. This shows both quantitative and qualitative indications, leading to rational decision-making. Other user’s comments are shared to reduce confirmation bias. Through this process, Gretell helps users who are impulsive or easily swayed by others’ opinions to grow as independent investors.
‘Bright’ is another app created by Lee’s team. It helps people exercise their rights as shareholders. As the need to exercise shareholders’ rights increases, many people are frustrated that investors with a small number of shares don’t have a lot of power. Bright provides a space for shareholders to share their opinions and brings people together so that individuals can be more proactive as shareholders. The Integrated Power of Attorney System (IPAS) expands the chances for shareholders to exercise their rights and allows users to submit proposals that can be communicated during the general meeting. Bright fosters influential shareholders, responsible companies, and a healthy society.
For communications, ‘Rewind’ is a stock information services app that visualizes past stock charts through sentiment analysis. Existing services focus on numbers, while Rewind takes a qualitative approach. Rewind analyzes public sentiment toward each event by collecting opinions on social media and then visualizes them chronologically along with the stock chart. Rewind allows users to review stock market movements and record their thoughts. Users can gain their own insights into current events in the stock market and make wiser investment decisions. The intuitive color gradient design provides a pleasant and simplified information experience.
In the area of interfaces for digital media and service design, ‘Groo’ is a green bond investing service app that helps users participate in green investment though investing in green bonds that support green projects for environmental improvement. Not restricted to trading bonds, Groo joins users in the holistic experience of green investing, from taking an interest in environmental issues to confirming the impact of the investment.
Next, ‘Modu’ is a story-based empathy expression training game for children with intellectual disabilities. Modu was developed to support emotion recognition and empathy behavior training in children with mild intellectual disabilities (MID) and borderline intellectual functioning (BIF).
Finally, the diving VR device for neutral buoyancy training, ‘Blow-yancy’, also made winner’s list. The device mimics scuba diving training without having to go into the water, therefore beginner divers are able getting feeling of diving while remaining perfectly safe and not harming any corals. It is expected that the device will be able to help protect at-risk underwater ecosystems.
2022.05.10 View 8528 -
 Machine Learning-Based Algorithm to Speed up DNA Sequencing
The algorithm presents the first full-fledged, short-read alignment software that leverages learned indices for solving the exact match search problem for efficient seeding
The human genome consists of a complete set of DNA, which is about 6.4 billion letters long. Because of its size, reading the whole genome sequence at once is challenging. So scientists use DNA sequencers to produce hundreds of millions of DNA sequence fragments, or short reads, up to 300 letters long. Then the DNA sequencer assembles all the short reads like a giant jigsaw puzzle to reconstruct the entire genome sequence. Even with very fast computers, this job can take hours to complete.
A research team at KAIST has achieved up to 3.45x faster speeds by developing the first short-read alignment software that uses a recent advance in machine-learning called a learned index.
The research team reported their findings on March 7, 2022 in the journal Bioinformatics. The software has been released as open source and can be found on github (https://github.com/kaist-ina/BWA-MEME).
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a state-of-the-art DNA sequencing method. Projects are underway with the goal of producing genome sequencing at population scale. Modern NGS hardware is capable of generating billions of short reads in a single run. Then the short reads have to be aligned with the reference DNA sequence. With large-scale DNA sequencing operations running hundreds of next-generation sequences, the need for an efficient short read alignment tool has become even more critical. Accelerating the DNA sequence alignment would be a step toward achieving the goal of population-scale sequencing. However, existing algorithms are limited in their performance because of their frequent memory accesses.
BWA-MEM2 is a popular short-read alignment software package currently used to sequence the DNA. However, it has its limitations. The state-of-the-art alignment has two phases – seeding and extending. During the seeding phase, searches find exact matches of short reads in the reference DNA sequence. During the extending phase, the short reads from the seeding phase are extended. In the current process, bottlenecks occur in the seeding phase. Finding the exact matches slows the process.
The researchers set out to solve the problem of accelerating the DNA sequence alignment. To speed the process, they applied machine learning techniques to create an algorithmic improvement. Their algorithm, BWA-MEME (BWA-MEM emulated) leverages learned indices to solve the exact match search problem. The original software compared one character at a time for an exact match search. The team’s new algorithm achieves up to 3.45x faster speeds in seeding throughput over BWA-MEM2 by reducing the number of instructions by 4.60x and memory accesses by 8.77x. “Through this study, it has been shown that full genome big data analysis can be performed faster and less costly than conventional methods by applying machine learning technology,” said Professor Dongsu Han from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
The researchers’ ultimate goal was to develop efficient software that scientists from academia and industry could use on a daily basis for analyzing big data in genomics. “With the recent advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning, we see so many opportunities for designing better software for genomic data analysis. The potential is there for accelerating existing analysis as well as enabling new types of analysis, and our goal is to develop such software,” added Han.
Whole genome sequencing has traditionally been used for discovering genomic mutations and identifying the root causes of diseases, which leads to the discovery and development of new drugs and cures. There could be many potential applications. Whole genome sequencing is used not only for research, but also for clinical purposes. “The science and technology for analyzing genomic data is making rapid progress to make it more accessible for scientists and patients. This will enhance our understanding about diseases and develop a better cure for patients of various diseases.”
The research was funded by the National Research Foundation of the Korean government’s Ministry of Science and ICT.
-PublicationYoungmok Jung, Dongsu Han, “BWA-MEME:BWA-MEM emulated with a machine learning approach,” Bioinformatics, Volume 38, Issue 9, May 2022
(https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac137)
-ProfileProfessor Dongsu HanSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.10 View 9284
Machine Learning-Based Algorithm to Speed up DNA Sequencing
The algorithm presents the first full-fledged, short-read alignment software that leverages learned indices for solving the exact match search problem for efficient seeding
The human genome consists of a complete set of DNA, which is about 6.4 billion letters long. Because of its size, reading the whole genome sequence at once is challenging. So scientists use DNA sequencers to produce hundreds of millions of DNA sequence fragments, or short reads, up to 300 letters long. Then the DNA sequencer assembles all the short reads like a giant jigsaw puzzle to reconstruct the entire genome sequence. Even with very fast computers, this job can take hours to complete.
A research team at KAIST has achieved up to 3.45x faster speeds by developing the first short-read alignment software that uses a recent advance in machine-learning called a learned index.
The research team reported their findings on March 7, 2022 in the journal Bioinformatics. The software has been released as open source and can be found on github (https://github.com/kaist-ina/BWA-MEME).
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a state-of-the-art DNA sequencing method. Projects are underway with the goal of producing genome sequencing at population scale. Modern NGS hardware is capable of generating billions of short reads in a single run. Then the short reads have to be aligned with the reference DNA sequence. With large-scale DNA sequencing operations running hundreds of next-generation sequences, the need for an efficient short read alignment tool has become even more critical. Accelerating the DNA sequence alignment would be a step toward achieving the goal of population-scale sequencing. However, existing algorithms are limited in their performance because of their frequent memory accesses.
BWA-MEM2 is a popular short-read alignment software package currently used to sequence the DNA. However, it has its limitations. The state-of-the-art alignment has two phases – seeding and extending. During the seeding phase, searches find exact matches of short reads in the reference DNA sequence. During the extending phase, the short reads from the seeding phase are extended. In the current process, bottlenecks occur in the seeding phase. Finding the exact matches slows the process.
The researchers set out to solve the problem of accelerating the DNA sequence alignment. To speed the process, they applied machine learning techniques to create an algorithmic improvement. Their algorithm, BWA-MEME (BWA-MEM emulated) leverages learned indices to solve the exact match search problem. The original software compared one character at a time for an exact match search. The team’s new algorithm achieves up to 3.45x faster speeds in seeding throughput over BWA-MEM2 by reducing the number of instructions by 4.60x and memory accesses by 8.77x. “Through this study, it has been shown that full genome big data analysis can be performed faster and less costly than conventional methods by applying machine learning technology,” said Professor Dongsu Han from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
The researchers’ ultimate goal was to develop efficient software that scientists from academia and industry could use on a daily basis for analyzing big data in genomics. “With the recent advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning, we see so many opportunities for designing better software for genomic data analysis. The potential is there for accelerating existing analysis as well as enabling new types of analysis, and our goal is to develop such software,” added Han.
Whole genome sequencing has traditionally been used for discovering genomic mutations and identifying the root causes of diseases, which leads to the discovery and development of new drugs and cures. There could be many potential applications. Whole genome sequencing is used not only for research, but also for clinical purposes. “The science and technology for analyzing genomic data is making rapid progress to make it more accessible for scientists and patients. This will enhance our understanding about diseases and develop a better cure for patients of various diseases.”
The research was funded by the National Research Foundation of the Korean government’s Ministry of Science and ICT.
-PublicationYoungmok Jung, Dongsu Han, “BWA-MEME:BWA-MEM emulated with a machine learning approach,” Bioinformatics, Volume 38, Issue 9, May 2022
(https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac137)
-ProfileProfessor Dongsu HanSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.10 View 9284 -
 VP Sang Yup Lee Receives Honorary Doctorate from DTU
Vice President for Research, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, was awarded an honorary doctorate from the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) during the DTU Commemoration Day 2022 on April 29. The event drew distinguished guests, students, and faculty including HRH The Crown Prince Frederik Andre Henrik Christian and DTU President Anders Bjarklev.
Professor Lee was recognized for his exceptional scholarship in the field of systems metabolic engineering, which led to the development of microcell factories capable of producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds, many for the first time.
Professor Lee said in his acceptance speech that KAIST’s continued partnership with DTU in the field of biotechnology will lead to significant contributions in the global efforts to respond to climate change and promote green growth.
DTU CPO and CSO Dina Petronovic Nielson, who heads DTU Biosustain, also lauded Professor Lee saying, “It is not only a great honor for Professor Lee to be induced at DTU but also great honor for DTU to have him.”
Professor Lee also gave commemorative lectures at DTU Biosustain in Lingby and the Bio Innovation Research Institute at the Novo Nordisk Foundation in Copenhagen while in Denmark.
DTU, one of the leading science and technology universities in Europe, has been awarding honorary doctorates since 1921, including to Nobel laureate in chemistry Professor Frances Arnold at Caltech. Professor Lee is the first Korean to receive an honorary doctorate from DTU.
2022.05.03 View 10277
VP Sang Yup Lee Receives Honorary Doctorate from DTU
Vice President for Research, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, was awarded an honorary doctorate from the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) during the DTU Commemoration Day 2022 on April 29. The event drew distinguished guests, students, and faculty including HRH The Crown Prince Frederik Andre Henrik Christian and DTU President Anders Bjarklev.
Professor Lee was recognized for his exceptional scholarship in the field of systems metabolic engineering, which led to the development of microcell factories capable of producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds, many for the first time.
Professor Lee said in his acceptance speech that KAIST’s continued partnership with DTU in the field of biotechnology will lead to significant contributions in the global efforts to respond to climate change and promote green growth.
DTU CPO and CSO Dina Petronovic Nielson, who heads DTU Biosustain, also lauded Professor Lee saying, “It is not only a great honor for Professor Lee to be induced at DTU but also great honor for DTU to have him.”
Professor Lee also gave commemorative lectures at DTU Biosustain in Lingby and the Bio Innovation Research Institute at the Novo Nordisk Foundation in Copenhagen while in Denmark.
DTU, one of the leading science and technology universities in Europe, has been awarding honorary doctorates since 1921, including to Nobel laureate in chemistry Professor Frances Arnold at Caltech. Professor Lee is the first Korean to receive an honorary doctorate from DTU.
2022.05.03 View 10277 -
 A New Strategy for Active Metasurface Design Provides a Full 360° Phase Tunable Metasurface
The new strategy displays an unprecedented upper limit of dynamic phase modulation with no significant variations in optical amplitude
An international team of researchers led by Professor Min Seok Jang of KAIST and Professor Victor W. Brar of the University of Wisconsin-Madison has demonstrated a widely applicable methodology enabling a full 360° active phase modulation for metasurfaces while maintaining significant levels of uniform light amplitude. This strategy can be fundamentally applied to any spectral region with any structures and resonances that fit the bill.
Metasurfaces are optical components with specialized functionalities indispensable for real-life applications ranging from LIDAR and spectroscopy to futuristic technologies such as invisibility cloaks and holograms. They are known for their compact and micro/nano-sized nature, which enables them to be integrated into electronic computerized systems with sizes that are ever decreasing as predicted by Moore’s law.
In order to allow for such innovations, metasurfaces must be capable of manipulating the impinging light, doing so by manipulating either the light’s amplitude or phase (or both) and emitting it back out. However, dynamically modulating the phase with the full circle range has been a notoriously difficult task, with very few works managing to do so by sacrificing a substantial amount of amplitude control.
Challenged by these limitations, the team proposed a general methodology that enables metasurfaces to implement a dynamic phase modulation with the complete 360° phase range, all the while uniformly maintaining significant levels of amplitude.
The underlying reason for the difficulty achieving such a feat is that there is a fundamental trade-off regarding dynamically controlling the optical phase of light. Metasurfaces generally perform such a function through optical resonances, an excitation of electrons inside the metasurface structure that harmonically oscillate together with the incident light. In order to be able to modulate through the entire range of 0-360°, the optical resonance frequency (the center of the spectrum) must be tuned by a large amount while the linewidth (the width of the spectrum) is kept to a minimum. However, to electrically tune the optical resonance frequency of the metasurface on demand, there needs to be a controllable influx and outflux of electrons into the metasurface and this inevitably leads to a larger linewidth of the aforementioned optical resonance.
The problem is further compounded by the fact that the phase and the amplitude of optical resonances are closely correlated in a complex, non-linear fashion, making it very difficult to hold substantial control over the amplitude while changing the phase.
The team’s work circumvented both problems by using two optical resonances, each with specifically designated properties. One resonance provides the decoupling between the phase and amplitude so that the phase is able to be tuned while significant and uniform levels of amplitude are maintained, as well as providing a narrow linewidth.
The other resonance provides the capability of being sufficiently tuned to a large degree so that the complete full circle range of phase modulation is achievable. The quintessence of the work is then to combine the different properties of the two resonances through a phenomenon called avoided crossing, so that the interactions between the two resonances lead to an amalgamation of the desired traits that achieves and even surpasses the full 360° phase modulation with uniform amplitude.
Professor Jang said, “Our research proposes a new methodology in dynamic phase modulation that breaks through the conventional limits and trade-offs, while being broadly applicable in diverse types of metasurfaces. We hope that this idea helps researchers implement and realize many key applications of metasurfaces, such as LIDAR and holograms, so that the nanophotonics industry keeps growing and provides a brighter technological future.”
The research paper authored by Ju Young Kim and Juho Park, et al., and titled "Full 2π Tunable Phase Modulation Using Avoided Crossing of Resonances" was published in Nature Communications on April 19. The research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
-Publication:Ju Young Kim, Juho Park, Gregory R. Holdman, Jacob T. Heiden, Shinho Kim, Victor W. Brar, and Min Seok Jang, “Full 2π Tunable Phase Modulation Using Avoided Crossing ofResonances” Nature Communications on April 19 (2022). doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29721-7
-ProfileProfessor Min Seok JangSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.02 View 7885
A New Strategy for Active Metasurface Design Provides a Full 360° Phase Tunable Metasurface
The new strategy displays an unprecedented upper limit of dynamic phase modulation with no significant variations in optical amplitude
An international team of researchers led by Professor Min Seok Jang of KAIST and Professor Victor W. Brar of the University of Wisconsin-Madison has demonstrated a widely applicable methodology enabling a full 360° active phase modulation for metasurfaces while maintaining significant levels of uniform light amplitude. This strategy can be fundamentally applied to any spectral region with any structures and resonances that fit the bill.
Metasurfaces are optical components with specialized functionalities indispensable for real-life applications ranging from LIDAR and spectroscopy to futuristic technologies such as invisibility cloaks and holograms. They are known for their compact and micro/nano-sized nature, which enables them to be integrated into electronic computerized systems with sizes that are ever decreasing as predicted by Moore’s law.
In order to allow for such innovations, metasurfaces must be capable of manipulating the impinging light, doing so by manipulating either the light’s amplitude or phase (or both) and emitting it back out. However, dynamically modulating the phase with the full circle range has been a notoriously difficult task, with very few works managing to do so by sacrificing a substantial amount of amplitude control.
Challenged by these limitations, the team proposed a general methodology that enables metasurfaces to implement a dynamic phase modulation with the complete 360° phase range, all the while uniformly maintaining significant levels of amplitude.
The underlying reason for the difficulty achieving such a feat is that there is a fundamental trade-off regarding dynamically controlling the optical phase of light. Metasurfaces generally perform such a function through optical resonances, an excitation of electrons inside the metasurface structure that harmonically oscillate together with the incident light. In order to be able to modulate through the entire range of 0-360°, the optical resonance frequency (the center of the spectrum) must be tuned by a large amount while the linewidth (the width of the spectrum) is kept to a minimum. However, to electrically tune the optical resonance frequency of the metasurface on demand, there needs to be a controllable influx and outflux of electrons into the metasurface and this inevitably leads to a larger linewidth of the aforementioned optical resonance.
The problem is further compounded by the fact that the phase and the amplitude of optical resonances are closely correlated in a complex, non-linear fashion, making it very difficult to hold substantial control over the amplitude while changing the phase.
The team’s work circumvented both problems by using two optical resonances, each with specifically designated properties. One resonance provides the decoupling between the phase and amplitude so that the phase is able to be tuned while significant and uniform levels of amplitude are maintained, as well as providing a narrow linewidth.
The other resonance provides the capability of being sufficiently tuned to a large degree so that the complete full circle range of phase modulation is achievable. The quintessence of the work is then to combine the different properties of the two resonances through a phenomenon called avoided crossing, so that the interactions between the two resonances lead to an amalgamation of the desired traits that achieves and even surpasses the full 360° phase modulation with uniform amplitude.
Professor Jang said, “Our research proposes a new methodology in dynamic phase modulation that breaks through the conventional limits and trade-offs, while being broadly applicable in diverse types of metasurfaces. We hope that this idea helps researchers implement and realize many key applications of metasurfaces, such as LIDAR and holograms, so that the nanophotonics industry keeps growing and provides a brighter technological future.”
The research paper authored by Ju Young Kim and Juho Park, et al., and titled "Full 2π Tunable Phase Modulation Using Avoided Crossing of Resonances" was published in Nature Communications on April 19. The research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
-Publication:Ju Young Kim, Juho Park, Gregory R. Holdman, Jacob T. Heiden, Shinho Kim, Victor W. Brar, and Min Seok Jang, “Full 2π Tunable Phase Modulation Using Avoided Crossing ofResonances” Nature Communications on April 19 (2022). doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29721-7
-ProfileProfessor Min Seok JangSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.02 View 7885 -
 President-Elect Suk-Yeol Yoon Meets and Talks with KAIST Students
President-Elect Yoon stresses science and technology-powered economic growth during his visit to KAIST
Korean President-elect Suk-Yeol Yoon stressed that semiconductors are the key strategical industry that will take the lead during the fourth industrial revolution powered by AI and data during a meeting with KAIST graduate students on April 29. President-elect Yoon promised systemic policy support for making science and technology breakthroughs possible and better rewarding young researchers who are devoted to advances in R&D during his meeting at KAIST.
Before he met with the students, he toured the National Nanofab Center, which is affiliated with KAIST, and was briefed on the center’s role and responsibilities.
President-elect Yoon, who will take office on May 10, said that the best way to ensure prompt growth in Korea’s aging society hinges on advances in science and technology. “All-out investments in science and technology will help us move forward to improve people’s quality of life and lessen the social divide,” he explained.
Eight Master’s and PhD candidates majoring in nuclear engineering, AI robotics, semiconductors, electrical engineering, aerospace, and bioengineering attended the meeting with President-elect Yoon. The students asked for help dealing with the challenges they are experiencing while researching and called for deregulation in the process of forming startups.
PhD candidate Jae Wan Cho from the Department Nuclear and Quantum Engineering stressed the importance of energy security. He asked for the prompt development of new types of nuclear reactors such as small modular reactors, adding, “Korea has very excellent technologies in nuclear plant construction and parts manufacturing, but lags behind in the new types of nuclear reactors. This sector will develop new energy markets and create synergy along with the shipbuilding industry, which will emerge as new pillars of our export.”
Student entrepreneurs such as PhD candidate Kwang Min Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and PhD candidate Dong Yoon Shin from the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering asked for more deregulation in the process of creating startups. PhD candidate Dong Hon Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering pointed out the insecure future caused by the ‘special research fellow system,’ where the number of fellows who have been designated alternative military service has drastically decreased.
2022.05.02 View 6174
President-Elect Suk-Yeol Yoon Meets and Talks with KAIST Students
President-Elect Yoon stresses science and technology-powered economic growth during his visit to KAIST
Korean President-elect Suk-Yeol Yoon stressed that semiconductors are the key strategical industry that will take the lead during the fourth industrial revolution powered by AI and data during a meeting with KAIST graduate students on April 29. President-elect Yoon promised systemic policy support for making science and technology breakthroughs possible and better rewarding young researchers who are devoted to advances in R&D during his meeting at KAIST.
Before he met with the students, he toured the National Nanofab Center, which is affiliated with KAIST, and was briefed on the center’s role and responsibilities.
President-elect Yoon, who will take office on May 10, said that the best way to ensure prompt growth in Korea’s aging society hinges on advances in science and technology. “All-out investments in science and technology will help us move forward to improve people’s quality of life and lessen the social divide,” he explained.
Eight Master’s and PhD candidates majoring in nuclear engineering, AI robotics, semiconductors, electrical engineering, aerospace, and bioengineering attended the meeting with President-elect Yoon. The students asked for help dealing with the challenges they are experiencing while researching and called for deregulation in the process of forming startups.
PhD candidate Jae Wan Cho from the Department Nuclear and Quantum Engineering stressed the importance of energy security. He asked for the prompt development of new types of nuclear reactors such as small modular reactors, adding, “Korea has very excellent technologies in nuclear plant construction and parts manufacturing, but lags behind in the new types of nuclear reactors. This sector will develop new energy markets and create synergy along with the shipbuilding industry, which will emerge as new pillars of our export.”
Student entrepreneurs such as PhD candidate Kwang Min Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and PhD candidate Dong Yoon Shin from the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering asked for more deregulation in the process of creating startups. PhD candidate Dong Hon Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering pointed out the insecure future caused by the ‘special research fellow system,’ where the number of fellows who have been designated alternative military service has drastically decreased.
2022.05.02 View 6174 -
 LightPC Presents a Resilient System Using Only Non-Volatile Memory
Lightweight Persistence Centric System (LightPC) ensures both data and execution persistence for energy-efficient full system persistence
A KAIST research team has developed hardware and software technology that ensures both data and execution persistence. The Lightweight Persistence Centric System (LightPC) makes the systems resilient against power failures by utilizing only non-volatile memory as the main memory.
“We mounted non-volatile memory on a system board prototype and created an operating system to verify the effectiveness of LightPC,” said Professor Myoungsoo Jung. The team confirmed that LightPC validated its execution while powering up and down in the middle of execution, showing up to eight times more memory, 4.3 times faster application execution, and 73% lower power consumption compared to traditional systems.
Professor Jung said that LightPC can be utilized in a variety of fields such as data centers and high-performance computing to provide large-capacity memory, high performance, low power consumption, and service reliability.
In general, power failures on legacy systems can lead to the loss of data stored in the DRAM-based main memory. Unlike volatile memory such as DRAM, non-volatile memory can retain its data without power. Although non-volatile memory has the characteristics of lower power consumption and larger capacity than DRAM, non-volatile memory is typically used for the task of secondary storage due to its lower write performance. For this reason, nonvolatile memory is often used with DRAM. However, modern systems employing non-volatile memory-based main memory experience unexpected performance degradation due to the complicated memory microarchitecture.
To enable both data and execution persistent in legacy systems, it is necessary to transfer the data from the volatile memory to the non-volatile memory. Checkpointing is one possible solution. It periodically transfers the data in preparation for a sudden power failure. While this technology is essential for ensuring high mobility and reliability for users, checkpointing also has fatal drawbacks. It takes additional time and power to move data and requires a data recovery process as well as restarting the system.
In order to address these issues, the research team developed a processor and memory controller to raise the performance of non-volatile memory-only memory. LightPC matches the performance of DRAM by minimizing the internal volatile memory components from non-volatile memory, exposing the non-volatile memory (PRAM) media to the host, and increasing parallelism to service on-the-fly requests as soon as possible.
The team also presented operating system technology that quickly makes execution states of running processes persistent without the need for a checkpointing process. The operating system prevents all modifications to execution states and data by keeping all program executions idle before transferring data in order to support consistency within a period much shorter than the standard power hold-up time of about 16 minutes. For consistency, when the power is recovered, the computer almost immediately revives itself and re-executes all the offline processes immediately without the need for a boot process.
The researchers will present their work (LightPC: Hardware and Software Co-Design for Energy-Efficient Full System Persistence) at the International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA) 2022 in New York in June. More information is available at the CAMELab website (http://camelab.org).
-Profile: Professor Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL)http://camelab.org School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.04.25 View 22984
LightPC Presents a Resilient System Using Only Non-Volatile Memory
Lightweight Persistence Centric System (LightPC) ensures both data and execution persistence for energy-efficient full system persistence
A KAIST research team has developed hardware and software technology that ensures both data and execution persistence. The Lightweight Persistence Centric System (LightPC) makes the systems resilient against power failures by utilizing only non-volatile memory as the main memory.
“We mounted non-volatile memory on a system board prototype and created an operating system to verify the effectiveness of LightPC,” said Professor Myoungsoo Jung. The team confirmed that LightPC validated its execution while powering up and down in the middle of execution, showing up to eight times more memory, 4.3 times faster application execution, and 73% lower power consumption compared to traditional systems.
Professor Jung said that LightPC can be utilized in a variety of fields such as data centers and high-performance computing to provide large-capacity memory, high performance, low power consumption, and service reliability.
In general, power failures on legacy systems can lead to the loss of data stored in the DRAM-based main memory. Unlike volatile memory such as DRAM, non-volatile memory can retain its data without power. Although non-volatile memory has the characteristics of lower power consumption and larger capacity than DRAM, non-volatile memory is typically used for the task of secondary storage due to its lower write performance. For this reason, nonvolatile memory is often used with DRAM. However, modern systems employing non-volatile memory-based main memory experience unexpected performance degradation due to the complicated memory microarchitecture.
To enable both data and execution persistent in legacy systems, it is necessary to transfer the data from the volatile memory to the non-volatile memory. Checkpointing is one possible solution. It periodically transfers the data in preparation for a sudden power failure. While this technology is essential for ensuring high mobility and reliability for users, checkpointing also has fatal drawbacks. It takes additional time and power to move data and requires a data recovery process as well as restarting the system.
In order to address these issues, the research team developed a processor and memory controller to raise the performance of non-volatile memory-only memory. LightPC matches the performance of DRAM by minimizing the internal volatile memory components from non-volatile memory, exposing the non-volatile memory (PRAM) media to the host, and increasing parallelism to service on-the-fly requests as soon as possible.
The team also presented operating system technology that quickly makes execution states of running processes persistent without the need for a checkpointing process. The operating system prevents all modifications to execution states and data by keeping all program executions idle before transferring data in order to support consistency within a period much shorter than the standard power hold-up time of about 16 minutes. For consistency, when the power is recovered, the computer almost immediately revives itself and re-executes all the offline processes immediately without the need for a boot process.
The researchers will present their work (LightPC: Hardware and Software Co-Design for Energy-Efficient Full System Persistence) at the International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA) 2022 in New York in June. More information is available at the CAMELab website (http://camelab.org).
-Profile: Professor Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL)http://camelab.org School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.04.25 View 22984 -
 Quantum Technology: the Next Game Changer?
The 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute Forum explores how quantum technology has evolved into a new growth engine for the future
The participants of the 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute (GSI) Forum on April 20 agreed that the emerging technology of quantum computing will be a game changer of the future. As KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said in his opening remarks, the future is quantum and that future is rapidly approaching. Keynote speakers and panelists presented their insights on the disruptive innovations we are already experiencing.
The three keynote speakers included Dr. Jerry M. Chow, IBM fellow and director of quantum infrastructure, Professor John Preskill from Caltech, and Professor Jungsang Kim from Duke University. They discussed the academic impact and industrial applications of quantum technology, and its prospects for the future.
Dr. Chow leads IBM Quantum’s hardware system development efforts, focusing on research and system deployment. Professor Preskill is one of the leading quantum information science and quantum computation scholars. He coined the term “quantum supremacy.” Professor Kim is the co-founder and CTO of IonQ Inc., which develops general-purpose trapped ion quantum computers and software to generate, optimize, and execute quantum circuits.
Two leading quantum scholars from KAIST, Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Youngik Sohn, and Professor Andreas Heinrich from the IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience also participated in the forum as panelists. Professor Rhee is the founder of the nation’s first quantum computing software company and leads the AI Quantum Computing IT Research Center at KAIST.
During the panel session, Professor Rhee said that although it is undeniable the quantum computing will be a game changer, there are several challenges. For instance, the first actual quantum computer is NISQ (Noisy intermediate-scale quantum era), which is still incomplete. However, it is expected to outperform a supercomputer. Until then, it is important to advance the accuracy of quantum computation in order to offer super computation speeds.
Professor Sohn, who worked at PsiQuantum, detailed how quantum computers will affect our society. He said that PsiQuantum is developing silicon photonics that will control photons. We can’t begin to imagine how silicon photonics will transform our society. Things will change slowly but the scale would be massive.
The keynote speakers presented how quantum cryptography communications and its sensing technology will serve as disruptive innovations. Dr. Chow stressed that to realize the potential growth and innovation, additional R&D is needed. More research groups and scholars should be nurtured. Only then will the rich R&D resources be able to create breakthroughs in quantum-related industries. Lastly, the commercialization of quantum computing must be advanced, which will enable the provision of diverse services. In addition, more technological and industrial infrastructure must be built to better accommodate quantum computing.
Professor Preskill believes that quantum computing will benefit humanity. He cited two basic reasons for his optimistic prediction: quantum complexity and quantum error corrections. He explained why quantum computing is so powerful: quantum computer can easily solve the problems classically considered difficult, such as factorization. In addition, quantum computer has the potential to efficiently simulate all of the physical processes taking place in nature.
Despite such dramatic advantages, why does it seem so difficult? Professor Preskill believes this is because we want qubits (quantum bits or ‘qubits’ are the basic unit of quantum information) to interact very strongly with each other. Because computations can fail, we don’t want qubits to interact with the environment unless we can control and predict them.
As for quantum computing in the NISQ era, he said that NISQ will be an exciting tool for exploring physics. Professor Preskill does not believe that NISQ will change the world alone, rather it is a step forward toward more powerful quantum technologies in the future. He added that a potentially transformable, scalable quantum computer could still be decades away.
Professor Preskill said that a large number of qubits, higher accuracy, and better quality will require a significant investment. He said if we expand with better ideas, we can make a better system. In the longer term, quantum technology will bring significant benefits to the technological sectors and society in the fields of materials, physics, chemistry, and energy production.
Professor Kim from Duke University presented on the practical applications of quantum computing, especially in the startup environment. He said that although there is no right answer for the early applications of quantum computing, developing new approaches to solve difficult problems and raising the accessibility of the technology will be important for ensuring the growth of technology-based startups.
2022.04.21 View 11499
Quantum Technology: the Next Game Changer?
The 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute Forum explores how quantum technology has evolved into a new growth engine for the future
The participants of the 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute (GSI) Forum on April 20 agreed that the emerging technology of quantum computing will be a game changer of the future. As KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said in his opening remarks, the future is quantum and that future is rapidly approaching. Keynote speakers and panelists presented their insights on the disruptive innovations we are already experiencing.
The three keynote speakers included Dr. Jerry M. Chow, IBM fellow and director of quantum infrastructure, Professor John Preskill from Caltech, and Professor Jungsang Kim from Duke University. They discussed the academic impact and industrial applications of quantum technology, and its prospects for the future.
Dr. Chow leads IBM Quantum’s hardware system development efforts, focusing on research and system deployment. Professor Preskill is one of the leading quantum information science and quantum computation scholars. He coined the term “quantum supremacy.” Professor Kim is the co-founder and CTO of IonQ Inc., which develops general-purpose trapped ion quantum computers and software to generate, optimize, and execute quantum circuits.
Two leading quantum scholars from KAIST, Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Youngik Sohn, and Professor Andreas Heinrich from the IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience also participated in the forum as panelists. Professor Rhee is the founder of the nation’s first quantum computing software company and leads the AI Quantum Computing IT Research Center at KAIST.
During the panel session, Professor Rhee said that although it is undeniable the quantum computing will be a game changer, there are several challenges. For instance, the first actual quantum computer is NISQ (Noisy intermediate-scale quantum era), which is still incomplete. However, it is expected to outperform a supercomputer. Until then, it is important to advance the accuracy of quantum computation in order to offer super computation speeds.
Professor Sohn, who worked at PsiQuantum, detailed how quantum computers will affect our society. He said that PsiQuantum is developing silicon photonics that will control photons. We can’t begin to imagine how silicon photonics will transform our society. Things will change slowly but the scale would be massive.
The keynote speakers presented how quantum cryptography communications and its sensing technology will serve as disruptive innovations. Dr. Chow stressed that to realize the potential growth and innovation, additional R&D is needed. More research groups and scholars should be nurtured. Only then will the rich R&D resources be able to create breakthroughs in quantum-related industries. Lastly, the commercialization of quantum computing must be advanced, which will enable the provision of diverse services. In addition, more technological and industrial infrastructure must be built to better accommodate quantum computing.
Professor Preskill believes that quantum computing will benefit humanity. He cited two basic reasons for his optimistic prediction: quantum complexity and quantum error corrections. He explained why quantum computing is so powerful: quantum computer can easily solve the problems classically considered difficult, such as factorization. In addition, quantum computer has the potential to efficiently simulate all of the physical processes taking place in nature.
Despite such dramatic advantages, why does it seem so difficult? Professor Preskill believes this is because we want qubits (quantum bits or ‘qubits’ are the basic unit of quantum information) to interact very strongly with each other. Because computations can fail, we don’t want qubits to interact with the environment unless we can control and predict them.
As for quantum computing in the NISQ era, he said that NISQ will be an exciting tool for exploring physics. Professor Preskill does not believe that NISQ will change the world alone, rather it is a step forward toward more powerful quantum technologies in the future. He added that a potentially transformable, scalable quantum computer could still be decades away.
Professor Preskill said that a large number of qubits, higher accuracy, and better quality will require a significant investment. He said if we expand with better ideas, we can make a better system. In the longer term, quantum technology will bring significant benefits to the technological sectors and society in the fields of materials, physics, chemistry, and energy production.
Professor Kim from Duke University presented on the practical applications of quantum computing, especially in the startup environment. He said that although there is no right answer for the early applications of quantum computing, developing new approaches to solve difficult problems and raising the accessibility of the technology will be important for ensuring the growth of technology-based startups.
2022.04.21 View 11499 -
 Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee to Co-Chair IEEE MEMS 2025
Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering has been appointed General Chair of the 38th IEEE MEMS 2025 (International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems). Professor Lee, who is 40, is the conference’s youngest General Chair to date and will work jointly with Professor Sheng-Shian Li of Taiwan’s National Tsing Hua University as co-chairs in 2025.
IEEE MEMS is a top-tier international conference on microelectromechanical systems and it serves as a core academic showcase for MEMS research and technology in areas such as microsensors and actuators.
With over 800 MEMS paper submissions each year, the conference only accepts and publishes about 250 of them after a rigorous review process recognized for its world-class prestige. Of all the submissions, fewer than 10% are chosen for oral presentations.
2022.04.18 View 7070
Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee to Co-Chair IEEE MEMS 2025
Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering has been appointed General Chair of the 38th IEEE MEMS 2025 (International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems). Professor Lee, who is 40, is the conference’s youngest General Chair to date and will work jointly with Professor Sheng-Shian Li of Taiwan’s National Tsing Hua University as co-chairs in 2025.
IEEE MEMS is a top-tier international conference on microelectromechanical systems and it serves as a core academic showcase for MEMS research and technology in areas such as microsensors and actuators.
With over 800 MEMS paper submissions each year, the conference only accepts and publishes about 250 of them after a rigorous review process recognized for its world-class prestige. Of all the submissions, fewer than 10% are chosen for oral presentations.
2022.04.18 View 7070