AT
-
 Mathematicians Identify a Key Source of Cell-to-Cell Variability in Cell Signaling
Systematic inferences identify a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics
Why do genetically identical cells respond differently to the same external stimuli, such as antibiotics? This long-standing mystery has been solved by KAIST and IBS mathematicians who have developed a new framework for analyzing cell responses to some stimuli. The team found that the cell-to-cell variability in antibiotic stress response increases as the effective length of the cell signaling pathway (i.e., the number of rate-limiting steps) increases. This finding could identify more effective chemotherapies to overcome the fractional killing of cancer cells caused by cell-to-cell variability.
Cells in the human body contain signal transduction systems that respond to various external stimuli such as antibiotics and changes in osmotic pressure. When an external stimulus is detected, various biochemical reactions occur sequentially. This leads to the expression of relevant genes, allowing the cells to respond to the perturbed external environment. Furthermore, signal transduction leads to a drug response (e.g., antibiotic resistance genes are expressed when antibiotic drugs are given).
However, even when the same external stimuli are detected, the responses of individual cells are greatly heterogeneous. This leads to the emergence of persister cells that are highly resistant to drugs. To identify potential sources of this cell-to cell variability, many studies have been conducted. However, most of the intermediate signal transduction reactions are unobservable with current experimental techniques.
A group of researchers including Dae Wook Kim and Hyukpyo Hong and led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences and IBS Biomedical Mathematics Group solved the mystery by exploiting queueing theory and Bayesian inference methodology. They proposed a queueing process that describes the signal transduction system in cells. Based on this, they developed Bayesian inference computational software using MBI (the Moment-based Bayesian Inference method). This enables the analysis of the signal transduction system without a direct observation of the intermediate steps. This study was published in Science Advances.
By analyzing experimental data from Escherichia coli using MBI, the research team found that cell-to-cell variability increases as the number of rate-limiting steps in the signaling pathway increases.
The rate-limiting steps denote the slowest steps (i.e., bottlenecks) in sequential biochemical reaction steps composing cell signaling pathways and thus dominates most of the signaling time. As the number of the rate-limiting steps increases, the intensity of the transduced signal becomes greatly heterogeneous even in a population of genetically identical cells. This finding is expected to provide a new paradigm for studying the heterogeneous antibiotic resistance of cells, which is a big challenge in cancer medicine.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help advance the understanding of cell-to-cell variability in response to external stimuli. I hope this finding facilitates the development of more effective chemotherapies.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Institute for Basic Science.
-Publication:Dae Wook Kim, Hyukpyo Hong, and Jae Kyoung Kim (2022) “Systematic inference identifies a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics: the rate-limiting step number,”Science Advances March 18, 2022 (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl4598)
-Profile:Professor Jae Kyoung Kimhttp://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr@umichkim on TwitterDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.03.29 View 11457
Mathematicians Identify a Key Source of Cell-to-Cell Variability in Cell Signaling
Systematic inferences identify a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics
Why do genetically identical cells respond differently to the same external stimuli, such as antibiotics? This long-standing mystery has been solved by KAIST and IBS mathematicians who have developed a new framework for analyzing cell responses to some stimuli. The team found that the cell-to-cell variability in antibiotic stress response increases as the effective length of the cell signaling pathway (i.e., the number of rate-limiting steps) increases. This finding could identify more effective chemotherapies to overcome the fractional killing of cancer cells caused by cell-to-cell variability.
Cells in the human body contain signal transduction systems that respond to various external stimuli such as antibiotics and changes in osmotic pressure. When an external stimulus is detected, various biochemical reactions occur sequentially. This leads to the expression of relevant genes, allowing the cells to respond to the perturbed external environment. Furthermore, signal transduction leads to a drug response (e.g., antibiotic resistance genes are expressed when antibiotic drugs are given).
However, even when the same external stimuli are detected, the responses of individual cells are greatly heterogeneous. This leads to the emergence of persister cells that are highly resistant to drugs. To identify potential sources of this cell-to cell variability, many studies have been conducted. However, most of the intermediate signal transduction reactions are unobservable with current experimental techniques.
A group of researchers including Dae Wook Kim and Hyukpyo Hong and led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences and IBS Biomedical Mathematics Group solved the mystery by exploiting queueing theory and Bayesian inference methodology. They proposed a queueing process that describes the signal transduction system in cells. Based on this, they developed Bayesian inference computational software using MBI (the Moment-based Bayesian Inference method). This enables the analysis of the signal transduction system without a direct observation of the intermediate steps. This study was published in Science Advances.
By analyzing experimental data from Escherichia coli using MBI, the research team found that cell-to-cell variability increases as the number of rate-limiting steps in the signaling pathway increases.
The rate-limiting steps denote the slowest steps (i.e., bottlenecks) in sequential biochemical reaction steps composing cell signaling pathways and thus dominates most of the signaling time. As the number of the rate-limiting steps increases, the intensity of the transduced signal becomes greatly heterogeneous even in a population of genetically identical cells. This finding is expected to provide a new paradigm for studying the heterogeneous antibiotic resistance of cells, which is a big challenge in cancer medicine.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help advance the understanding of cell-to-cell variability in response to external stimuli. I hope this finding facilitates the development of more effective chemotherapies.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Institute for Basic Science.
-Publication:Dae Wook Kim, Hyukpyo Hong, and Jae Kyoung Kim (2022) “Systematic inference identifies a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics: the rate-limiting step number,”Science Advances March 18, 2022 (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl4598)
-Profile:Professor Jae Kyoung Kimhttp://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr@umichkim on TwitterDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.03.29 View 11457 -
 Baemin CEO Endows a Scholarship in Honor of the Late Professor Chwa
CEO Beom-Jun Kim of Woowa Brothers also known as ‘Baemin,’ a leading meal delivery app company, made a donation of 100 million KRW in honor of the late Professor Kyong-Yong Chwa from the School of Computing who passed away last year. The fund will be established for the “Kyong-Yong Chwa - Beom-Jun Kim Scholarship” to provide scholarships for four students over five years.
Kim finished his BS in 1997 and MS in 1999 at the School of Computing and Professor Chwa was his advisor. The late Professor Chwa was a pioneering scholar who brought the concept of computer algorithms to Korea. After graduating from Seoul National University in electric engineering, Professor Chwa earned his PhD at Northwestern University and began teaching at KAIST in 1980. Professor Chwa served as the President of the Korean Institute of Information Scientists and Engineers and a fellow emeritus at the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
Professor Chwa encouraged younger students to participate in international computer programming contests. Under his wing, Team Korea, which was comprised of four high school students, including Kim, placed fourth in the International Olympiad Informatics (IOI). Kim, who participated in the contest as high school junior, won an individual gold medal in the fourth IOI competition in 1992. Since then, Korean students have actively participated in many competitions including the International Collegiate Programming Contest (ICPC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery.
Kim said, “I feel fortunate to have met so many good friends and distinguished professors. With them, I had opportunities to grow. I would like to provide such opportunities to my juniors at KAIST. Professor Chwa was a larger than life figure in the field of computer programming. He was always caring and supported us with a warm heart. I want this donation to help carry on his legacy for our students and for them to seek greater challenges and bigger dreams.”
2022.03.25 View 9328
Baemin CEO Endows a Scholarship in Honor of the Late Professor Chwa
CEO Beom-Jun Kim of Woowa Brothers also known as ‘Baemin,’ a leading meal delivery app company, made a donation of 100 million KRW in honor of the late Professor Kyong-Yong Chwa from the School of Computing who passed away last year. The fund will be established for the “Kyong-Yong Chwa - Beom-Jun Kim Scholarship” to provide scholarships for four students over five years.
Kim finished his BS in 1997 and MS in 1999 at the School of Computing and Professor Chwa was his advisor. The late Professor Chwa was a pioneering scholar who brought the concept of computer algorithms to Korea. After graduating from Seoul National University in electric engineering, Professor Chwa earned his PhD at Northwestern University and began teaching at KAIST in 1980. Professor Chwa served as the President of the Korean Institute of Information Scientists and Engineers and a fellow emeritus at the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
Professor Chwa encouraged younger students to participate in international computer programming contests. Under his wing, Team Korea, which was comprised of four high school students, including Kim, placed fourth in the International Olympiad Informatics (IOI). Kim, who participated in the contest as high school junior, won an individual gold medal in the fourth IOI competition in 1992. Since then, Korean students have actively participated in many competitions including the International Collegiate Programming Contest (ICPC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery.
Kim said, “I feel fortunate to have met so many good friends and distinguished professors. With them, I had opportunities to grow. I would like to provide such opportunities to my juniors at KAIST. Professor Chwa was a larger than life figure in the field of computer programming. He was always caring and supported us with a warm heart. I want this donation to help carry on his legacy for our students and for them to seek greater challenges and bigger dreams.”
2022.03.25 View 9328 -
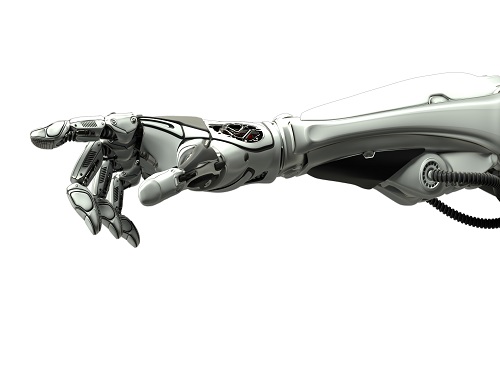 Decoding Brain Signals to Control a Robotic Arm
Advanced brain-machine interface system successfully interprets arm movement directions from neural signals in the brain
Researchers have developed a mind-reading system for decoding neural signals from the brain during arm movement. The method, described in the journal Applied Soft Computing, can be used by a person to control a robotic arm through a brain-machine interface (BMI).
A BMI is a device that translates nerve signals into commands to control a machine, such as a computer or a robotic limb. There are two main techniques for monitoring neural signals in BMIs: electroencephalography (EEG) and electrocorticography (ECoG).
The EEG exhibits signals from electrodes on the surface of the scalp and is widely employed because it is non-invasive, relatively cheap, safe and easy to use. However, the EEG has low spatial resolution and detects irrelevant neural signals, which makes it difficult to interpret the intentions of individuals from the EEG.
On the other hand, the ECoG is an invasive method that involves placing electrodes directly on the surface of the cerebral cortex below the scalp. Compared with the EEG, the ECoG can monitor neural signals with much higher spatial resolution and less background noise. However, this technique has several drawbacks.
“The ECoG is primarily used to find potential sources of epileptic seizures, meaning the electrodes are placed in different locations for different patients and may not be in the optimal regions of the brain for detecting sensory and movement signals,” explained Professor Jaeseung Jeong, a brain scientist at KAIST. “This inconsistency makes it difficult to decode brain signals to predict movements.”
To overcome these problems, Professor Jeong’s team developed a new method for decoding ECoG neural signals during arm movement. The system is based on a machine-learning system for analysing and predicting neural signals called an ‘echo-state network’ and a mathematical probability model called the Gaussian distribution.
In the study, the researchers recorded ECoG signals from four individuals with epilepsy while they were performing a reach-and-grasp task. Because the ECoG electrodes were placed according to the potential sources of each patient’s epileptic seizures, only 22% to 44% of the electrodes were located in the regions of the brain responsible for controlling movement.
During the movement task, the participants were given visual cues, either by placing a real tennis ball in front of them, or via a virtual reality headset showing a clip of a human arm reaching forward in first-person view. They were asked to reach forward, grasp an object, then return their hand and release the object, while wearing motion sensors on their wrists and fingers. In a second task, they were instructed to imagine reaching forward without moving their arms.
The researchers monitored the signals from the ECoG electrodes during real and imaginary arm movements, and tested whether the new system could predict the direction of this movement from the neural signals. They found that the novel decoder successfully classified arm movements in 24 directions in three-dimensional space, both in the real and virtual tasks, and that the results were at least five times more accurate than chance. They also used a computer simulation to show that the novel ECoG decoder could control the movements of a robotic arm.
Overall, the results suggest that the new machine learning-based BCI system successfully used ECoG signals to interpret the direction of the intended movements. The next steps will be to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the decoder. In the future, it could be used in a real-time BMI device to help people with movement or sensory impairments.
This research was supported by the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program of 2021, Brain Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning, and the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education.
-PublicationHoon-Hee Kim, Jaeseung Jeong, “An electrocorticographic decoder for arm movement for brain-machine interface using an echo state network and Gaussian readout,” Applied SoftComputing online December 31, 2021 (doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.108393)
-ProfileProfessor Jaeseung JeongDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.03.18 View 13495
Decoding Brain Signals to Control a Robotic Arm
Advanced brain-machine interface system successfully interprets arm movement directions from neural signals in the brain
Researchers have developed a mind-reading system for decoding neural signals from the brain during arm movement. The method, described in the journal Applied Soft Computing, can be used by a person to control a robotic arm through a brain-machine interface (BMI).
A BMI is a device that translates nerve signals into commands to control a machine, such as a computer or a robotic limb. There are two main techniques for monitoring neural signals in BMIs: electroencephalography (EEG) and electrocorticography (ECoG).
The EEG exhibits signals from electrodes on the surface of the scalp and is widely employed because it is non-invasive, relatively cheap, safe and easy to use. However, the EEG has low spatial resolution and detects irrelevant neural signals, which makes it difficult to interpret the intentions of individuals from the EEG.
On the other hand, the ECoG is an invasive method that involves placing electrodes directly on the surface of the cerebral cortex below the scalp. Compared with the EEG, the ECoG can monitor neural signals with much higher spatial resolution and less background noise. However, this technique has several drawbacks.
“The ECoG is primarily used to find potential sources of epileptic seizures, meaning the electrodes are placed in different locations for different patients and may not be in the optimal regions of the brain for detecting sensory and movement signals,” explained Professor Jaeseung Jeong, a brain scientist at KAIST. “This inconsistency makes it difficult to decode brain signals to predict movements.”
To overcome these problems, Professor Jeong’s team developed a new method for decoding ECoG neural signals during arm movement. The system is based on a machine-learning system for analysing and predicting neural signals called an ‘echo-state network’ and a mathematical probability model called the Gaussian distribution.
In the study, the researchers recorded ECoG signals from four individuals with epilepsy while they were performing a reach-and-grasp task. Because the ECoG electrodes were placed according to the potential sources of each patient’s epileptic seizures, only 22% to 44% of the electrodes were located in the regions of the brain responsible for controlling movement.
During the movement task, the participants were given visual cues, either by placing a real tennis ball in front of them, or via a virtual reality headset showing a clip of a human arm reaching forward in first-person view. They were asked to reach forward, grasp an object, then return their hand and release the object, while wearing motion sensors on their wrists and fingers. In a second task, they were instructed to imagine reaching forward without moving their arms.
The researchers monitored the signals from the ECoG electrodes during real and imaginary arm movements, and tested whether the new system could predict the direction of this movement from the neural signals. They found that the novel decoder successfully classified arm movements in 24 directions in three-dimensional space, both in the real and virtual tasks, and that the results were at least five times more accurate than chance. They also used a computer simulation to show that the novel ECoG decoder could control the movements of a robotic arm.
Overall, the results suggest that the new machine learning-based BCI system successfully used ECoG signals to interpret the direction of the intended movements. The next steps will be to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the decoder. In the future, it could be used in a real-time BMI device to help people with movement or sensory impairments.
This research was supported by the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program of 2021, Brain Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning, and the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education.
-PublicationHoon-Hee Kim, Jaeseung Jeong, “An electrocorticographic decoder for arm movement for brain-machine interface using an echo state network and Gaussian readout,” Applied SoftComputing online December 31, 2021 (doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.108393)
-ProfileProfessor Jaeseung JeongDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.03.18 View 13495 -
 CXL-Based Memory Disaggregation Technology Opens Up a New Direction for Big Data Solution Frameworks
A KAIST team’s compute express link (CXL) provides new insights on memory disaggregation and ensures direct access and high-performance capabilities
A team from the Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL) at KAIST presented a new compute express link (CXL) solution whose directly accessible, and high-performance memory disaggregation opens new directions for big data memory processing. Professor Myoungsoo Jung said the team’s technology significantly improves performance compared to existing remote direct memory access (RDMA)-based memory disaggregation.
CXL is a peripheral component interconnect-express (PCIe)-based new dynamic multi-protocol made for efficiently utilizing memory devices and accelerators. Many enterprise data centers and memory vendors are paying attention to it as the next-generation multi-protocol for the era of big data.
Emerging big data applications such as machine learning, graph analytics, and in-memory databases require large memory capacities. However, scaling out the memory capacity via a prior memory interface like double data rate (DDR) is limited by the number of the central processing units (CPUs) and memory controllers. Therefore, memory disaggregation, which allows connecting a host to another host’s memory or memory nodes, has appeared.
RDMA is a way that a host can directly access another host’s memory via InfiniBand, the commonly used network protocol in data centers. Nowadays, most existing memory disaggregation technologies employ RDMA to get a large memory capacity. As a result, a host can share another host’s memory by transferring the data between local and remote memory.
Although RDMA-based memory disaggregation provides a large memory capacity to a host, two critical problems exist. First, scaling out the memory still needs an extra CPU to be added. Since passive memory such as dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), cannot operate by itself, it should be controlled by the CPU. Second, redundant data copies and software fabric interventions for RDMA-based memory disaggregation cause longer access latency. For example, remote memory access latency in RDMA-based memory disaggregation is multiple orders of magnitude longer than local memory access.
To address these issues, Professor Jung’s team developed the CXL-based memory disaggregation framework, including CXL-enabled customized CPUs, CXL devices, CXL switches, and CXL-aware operating system modules. The team’s CXL device is a pure passive and directly accessible memory node that contains multiple DRAM dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) and a CXL memory controller. Since the CXL memory controller supports the memory in the CXL device, a host can utilize the memory node without processor or software intervention. The team’s CXL switch enables scaling out a host’s memory capacity by hierarchically connecting multiple CXL devices to the CXL switch allowing more than hundreds of devices. Atop the switches and devices, the team’s CXL-enabled operating system removes redundant data copy and protocol conversion exhibited by conventional RDMA, which can significantly decrease access latency to the memory nodes.
In a test comparing loading 64B (cacheline) data from memory pooling devices, CXL-based memory disaggregation showed 8.2 times higher data load performance than RDMA-based memory disaggregation and even similar performance to local DRAM memory. In the team’s evaluations for a big data benchmark such as a machine learning-based test, CXL-based memory disaggregation technology also showed a maximum of 3.7 times higher performance than prior RDMA-based memory disaggregation technologies.
“Escaping from the conventional RDMA-based memory disaggregation, our CXL-based memory disaggregation framework can provide high scalability and performance for diverse datacenters and cloud service infrastructures,” said Professor Jung. He went on to stress, “Our CXL-based memory disaggregation research will bring about a new paradigm for memory solutions that will lead the era of big data.”
-Profile: Professor Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL)http://camelab.org School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.03.16 View 24114
CXL-Based Memory Disaggregation Technology Opens Up a New Direction for Big Data Solution Frameworks
A KAIST team’s compute express link (CXL) provides new insights on memory disaggregation and ensures direct access and high-performance capabilities
A team from the Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL) at KAIST presented a new compute express link (CXL) solution whose directly accessible, and high-performance memory disaggregation opens new directions for big data memory processing. Professor Myoungsoo Jung said the team’s technology significantly improves performance compared to existing remote direct memory access (RDMA)-based memory disaggregation.
CXL is a peripheral component interconnect-express (PCIe)-based new dynamic multi-protocol made for efficiently utilizing memory devices and accelerators. Many enterprise data centers and memory vendors are paying attention to it as the next-generation multi-protocol for the era of big data.
Emerging big data applications such as machine learning, graph analytics, and in-memory databases require large memory capacities. However, scaling out the memory capacity via a prior memory interface like double data rate (DDR) is limited by the number of the central processing units (CPUs) and memory controllers. Therefore, memory disaggregation, which allows connecting a host to another host’s memory or memory nodes, has appeared.
RDMA is a way that a host can directly access another host’s memory via InfiniBand, the commonly used network protocol in data centers. Nowadays, most existing memory disaggregation technologies employ RDMA to get a large memory capacity. As a result, a host can share another host’s memory by transferring the data between local and remote memory.
Although RDMA-based memory disaggregation provides a large memory capacity to a host, two critical problems exist. First, scaling out the memory still needs an extra CPU to be added. Since passive memory such as dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), cannot operate by itself, it should be controlled by the CPU. Second, redundant data copies and software fabric interventions for RDMA-based memory disaggregation cause longer access latency. For example, remote memory access latency in RDMA-based memory disaggregation is multiple orders of magnitude longer than local memory access.
To address these issues, Professor Jung’s team developed the CXL-based memory disaggregation framework, including CXL-enabled customized CPUs, CXL devices, CXL switches, and CXL-aware operating system modules. The team’s CXL device is a pure passive and directly accessible memory node that contains multiple DRAM dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) and a CXL memory controller. Since the CXL memory controller supports the memory in the CXL device, a host can utilize the memory node without processor or software intervention. The team’s CXL switch enables scaling out a host’s memory capacity by hierarchically connecting multiple CXL devices to the CXL switch allowing more than hundreds of devices. Atop the switches and devices, the team’s CXL-enabled operating system removes redundant data copy and protocol conversion exhibited by conventional RDMA, which can significantly decrease access latency to the memory nodes.
In a test comparing loading 64B (cacheline) data from memory pooling devices, CXL-based memory disaggregation showed 8.2 times higher data load performance than RDMA-based memory disaggregation and even similar performance to local DRAM memory. In the team’s evaluations for a big data benchmark such as a machine learning-based test, CXL-based memory disaggregation technology also showed a maximum of 3.7 times higher performance than prior RDMA-based memory disaggregation technologies.
“Escaping from the conventional RDMA-based memory disaggregation, our CXL-based memory disaggregation framework can provide high scalability and performance for diverse datacenters and cloud service infrastructures,” said Professor Jung. He went on to stress, “Our CXL-based memory disaggregation research will bring about a new paradigm for memory solutions that will lead the era of big data.”
-Profile: Professor Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL)http://camelab.org School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.03.16 View 24114 -
 SM CEP Soo-Man Lee to Teach at the KAIST School of Computing
The Founder and Chief Executive Producer of SM Entertainment Soo-Man Lee was appointed as a distinguished visiting professor in the KAIST School of Computing. His three-year term starts on March 1.
KAIST and the SM Entertainment signed an MOU on joint research on the metaverse last year and Lee’s appointment is the extension of their mutual collaborations in fields where technologies converge and will encourage innovative advancements in engineering technology and the entertainment industry.
Lee, who completed a graduate program in computer science at California State University Northridge will give special leadership lectures for both undergraduate and graduate students, and will participate in metaverse-related research as a consultant.
In particular, Professor Lee will participate in joint research with the tentatively named Metaverse Institute affiliated with the KAIST Institute for Artificial Intelligence. The institute will help SM Entertainment stay ahead of the global metaverse market by using the avatars of celebrities, and lend itself to raising the already strong brand power of the K-pop leader.
Professor Lee said, “I am grateful that KAIST, the very cradle of Korea’s science and technology, has given me the opportunity to meet its students as a visiting professor. We will lead the metaverse world, in which Korea is emerging as a market leader, with the excellent contents and technology unique to our country, and work together to lead the future global entertainment market.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “The ability to expand our limitless creativity in the metaverse is indispensable for us as we adapt to this new era. We hope that the vision and creative insights of Executive Producer Lee, which have allowed him to look ahead into the future of the entertainment contents market, will have a positive and fresh impact on the members of KAIST.”
The global influence and reputation of Executive Producer Lee has been well established through his various awards. He was the first Korean to be listed on Variety500 for five consecutive years from 2017 to 2021. He was also the first Korean awardee of the Asia Game Changer Awards in 2016, the first cultural figure to receive the YoungSan Diplomacy Award in 2017, the only Korean to be listed on the 2020 Billboard Impact List, and he has also received the K-pop Contribution Award at the 10th Gaon Chart Music Awards. He recently introduced Play2Create (P2C), a new interactive and creative culture in which re-creation can be enjoyed like a game using IP, and is leading the establishment of the P2C ecosystem.
2022.03.03 View 6730
SM CEP Soo-Man Lee to Teach at the KAIST School of Computing
The Founder and Chief Executive Producer of SM Entertainment Soo-Man Lee was appointed as a distinguished visiting professor in the KAIST School of Computing. His three-year term starts on March 1.
KAIST and the SM Entertainment signed an MOU on joint research on the metaverse last year and Lee’s appointment is the extension of their mutual collaborations in fields where technologies converge and will encourage innovative advancements in engineering technology and the entertainment industry.
Lee, who completed a graduate program in computer science at California State University Northridge will give special leadership lectures for both undergraduate and graduate students, and will participate in metaverse-related research as a consultant.
In particular, Professor Lee will participate in joint research with the tentatively named Metaverse Institute affiliated with the KAIST Institute for Artificial Intelligence. The institute will help SM Entertainment stay ahead of the global metaverse market by using the avatars of celebrities, and lend itself to raising the already strong brand power of the K-pop leader.
Professor Lee said, “I am grateful that KAIST, the very cradle of Korea’s science and technology, has given me the opportunity to meet its students as a visiting professor. We will lead the metaverse world, in which Korea is emerging as a market leader, with the excellent contents and technology unique to our country, and work together to lead the future global entertainment market.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “The ability to expand our limitless creativity in the metaverse is indispensable for us as we adapt to this new era. We hope that the vision and creative insights of Executive Producer Lee, which have allowed him to look ahead into the future of the entertainment contents market, will have a positive and fresh impact on the members of KAIST.”
The global influence and reputation of Executive Producer Lee has been well established through his various awards. He was the first Korean to be listed on Variety500 for five consecutive years from 2017 to 2021. He was also the first Korean awardee of the Asia Game Changer Awards in 2016, the first cultural figure to receive the YoungSan Diplomacy Award in 2017, the only Korean to be listed on the 2020 Billboard Impact List, and he has also received the K-pop Contribution Award at the 10th Gaon Chart Music Awards. He recently introduced Play2Create (P2C), a new interactive and creative culture in which re-creation can be enjoyed like a game using IP, and is leading the establishment of the P2C ecosystem.
2022.03.03 View 6730 -
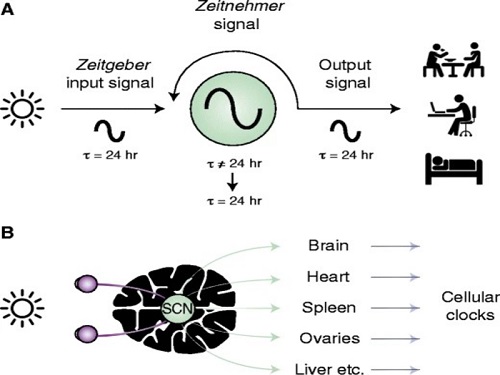 Scientist Discover How Circadian Rhythm Can Be Both Strong and Flexible
Study reveals that master and slave oscillators function via different molecular mechanisms
From tiny fruit flies to human beings, all animals on Earth maintain their daily rhythms based on their internal circadian clock. The circadian clock enables organisms to undergo rhythmic changes in behavior and physiology based on a 24-hour circadian cycle. For example, our own biological clock tells our brain to release melatonin, a sleep-inducing hormone, at night time.
The discovery of the molecular mechanism of the circadian clock was bestowed the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2017. From what we know, no one centralized clock is responsible for our circadian cycles. Instead, it operates in a hierarchical network where there are “master pacemaker” and “slave oscillator”.
The master pacemaker receives various input signals from the environment such as light. The master then drives the slave oscillator that regulates various outputs such as sleep, feeding, and metabolism. Despite the different roles of the pacemaker neurons, they are known to share common molecular mechanisms that are well conserved in all lifeforms. For example, interlocked systems of multiple transcriptional-translational feedback loops (TTFLs) composed of core clock proteins have been deeply studied in fruit flies.
However, there is still much that we need to learn about our own biological clock. The hierarchically-organized nature of master and slave clock neurons leads to a prevailing belief that they share an identical molecular clockwork. At the same time, the different roles they serve in regulating bodily rhythms also raise the question of whether they might function under different molecular clockworks.
Research team led by Professor Kim Jae Kyoung from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, a chief investigator at the Biomedical Mathematics Group at the Institute for Basic Science, used a combination of mathematical and experimental approaches using fruit flies to answer this question. The team found that the master clock and the slave clock operate via different molecular mechanisms.
In both master and slave neurons of fruit flies, a circadian rhythm-related protein called PER is produced and degraded at different rates depending on the time of the day. Previously, the team found that the master clock neuron (sLNvs) and the slave clock neuron (DN1ps) have different profiles of PER in wild-type and Clk-Δ mutant Drosophila. This hinted that there might be a potential difference in molecular clockworks between the master and slave clock neurons.
However, due to the complexity of the molecular clockwork, it was challenging to identify the source of such differences. Thus, the team developed a mathematical model describing the molecular clockworks of the master and slave clocks. Then, all possible molecular differences between the master and slave clock neurons were systematically investigated by using computer simulations. The model predicted that PER is more efficiently produced and then rapidly degraded in the master clock compared to the slave clock neurons. This prediction was then confirmed by the follow-up experiments using animal.
Then, why do the master clock neurons have such different molecular properties from the slave clock neurons? To answer this question, the research team again used the combination of mathematical model simulation and experiments. It was found that the faster rate of synthesis of PER in the master clock neurons allows them to generate synchronized rhythms with a high level of amplitude. Generation of such a strong rhythm with high amplitude is critical to delivering clear signals to slave clock neurons.
However, such strong rhythms would typically be unfavorable when it comes to adapting to environmental changes. These include natural causes such as different daylight hours across summer and winter seasons, up to more extreme artificial cases such as jet lag that occurs after international travel. Thanks to the distinct property of the master clock neurons, it is able to undergo phase dispersion when the standard light-dark cycle is disrupted, drastically reducing the level of PER. The master clock neurons can then easily adapt to the new diurnal cycle. Our master pacemaker’s plasticity explains how we can quickly adjust to the new time zones after international flights after just a brief period of jet lag.
It is hoped that the findings of this study can have future clinical implications when it comes to treating various disorders that affect our circadian rhythm. Professor Kim notes, “When the circadian clock loses its robustness and flexibility, the circadian rhythms sleep disorders can occur. As this study identifies the molecular mechanism that generates robustness and flexibility of the circadian clock, it can facilitate the identification of the cause of and treatment strategy for the circadian rhythm sleep disorders.” This work was supported by the Human Frontier Science Program.
-PublicationEui Min Jeong, Miri Kwon, Eunjoo Cho, Sang Hyuk Lee, Hyun Kim, Eun Young Kim, and Jae Kyoung Kim, “Systematic modeling-driven experiments identify distinct molecularclockworks underlying hierarchically organized pacemaker neurons,” February 22, 2022, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyoung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.02.23 View 11460
Scientist Discover How Circadian Rhythm Can Be Both Strong and Flexible
Study reveals that master and slave oscillators function via different molecular mechanisms
From tiny fruit flies to human beings, all animals on Earth maintain their daily rhythms based on their internal circadian clock. The circadian clock enables organisms to undergo rhythmic changes in behavior and physiology based on a 24-hour circadian cycle. For example, our own biological clock tells our brain to release melatonin, a sleep-inducing hormone, at night time.
The discovery of the molecular mechanism of the circadian clock was bestowed the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2017. From what we know, no one centralized clock is responsible for our circadian cycles. Instead, it operates in a hierarchical network where there are “master pacemaker” and “slave oscillator”.
The master pacemaker receives various input signals from the environment such as light. The master then drives the slave oscillator that regulates various outputs such as sleep, feeding, and metabolism. Despite the different roles of the pacemaker neurons, they are known to share common molecular mechanisms that are well conserved in all lifeforms. For example, interlocked systems of multiple transcriptional-translational feedback loops (TTFLs) composed of core clock proteins have been deeply studied in fruit flies.
However, there is still much that we need to learn about our own biological clock. The hierarchically-organized nature of master and slave clock neurons leads to a prevailing belief that they share an identical molecular clockwork. At the same time, the different roles they serve in regulating bodily rhythms also raise the question of whether they might function under different molecular clockworks.
Research team led by Professor Kim Jae Kyoung from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, a chief investigator at the Biomedical Mathematics Group at the Institute for Basic Science, used a combination of mathematical and experimental approaches using fruit flies to answer this question. The team found that the master clock and the slave clock operate via different molecular mechanisms.
In both master and slave neurons of fruit flies, a circadian rhythm-related protein called PER is produced and degraded at different rates depending on the time of the day. Previously, the team found that the master clock neuron (sLNvs) and the slave clock neuron (DN1ps) have different profiles of PER in wild-type and Clk-Δ mutant Drosophila. This hinted that there might be a potential difference in molecular clockworks between the master and slave clock neurons.
However, due to the complexity of the molecular clockwork, it was challenging to identify the source of such differences. Thus, the team developed a mathematical model describing the molecular clockworks of the master and slave clocks. Then, all possible molecular differences between the master and slave clock neurons were systematically investigated by using computer simulations. The model predicted that PER is more efficiently produced and then rapidly degraded in the master clock compared to the slave clock neurons. This prediction was then confirmed by the follow-up experiments using animal.
Then, why do the master clock neurons have such different molecular properties from the slave clock neurons? To answer this question, the research team again used the combination of mathematical model simulation and experiments. It was found that the faster rate of synthesis of PER in the master clock neurons allows them to generate synchronized rhythms with a high level of amplitude. Generation of such a strong rhythm with high amplitude is critical to delivering clear signals to slave clock neurons.
However, such strong rhythms would typically be unfavorable when it comes to adapting to environmental changes. These include natural causes such as different daylight hours across summer and winter seasons, up to more extreme artificial cases such as jet lag that occurs after international travel. Thanks to the distinct property of the master clock neurons, it is able to undergo phase dispersion when the standard light-dark cycle is disrupted, drastically reducing the level of PER. The master clock neurons can then easily adapt to the new diurnal cycle. Our master pacemaker’s plasticity explains how we can quickly adjust to the new time zones after international flights after just a brief period of jet lag.
It is hoped that the findings of this study can have future clinical implications when it comes to treating various disorders that affect our circadian rhythm. Professor Kim notes, “When the circadian clock loses its robustness and flexibility, the circadian rhythms sleep disorders can occur. As this study identifies the molecular mechanism that generates robustness and flexibility of the circadian clock, it can facilitate the identification of the cause of and treatment strategy for the circadian rhythm sleep disorders.” This work was supported by the Human Frontier Science Program.
-PublicationEui Min Jeong, Miri Kwon, Eunjoo Cho, Sang Hyuk Lee, Hyun Kim, Eun Young Kim, and Jae Kyoung Kim, “Systematic modeling-driven experiments identify distinct molecularclockworks underlying hierarchically organized pacemaker neurons,” February 22, 2022, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyoung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.02.23 View 11460 -
 A Mathematical Model Shows High Viral Transmissions Reduce the Progression Rates for Severe Covid-19
The model suggests a clue as to when a pandemic will turn into an endemic
A mathematical model demonstrated that high transmission rates among highly vaccinated populations of COVID-19 ultimately reduce the numbers of severe cases. This model suggests a clue as to when this pandemic will turn into an endemic.
With the future of the pandemic remaining uncertain, a research team of mathematicians and medical scientists analyzed a mathematical model that may predict how the changing transmission rate of COVID-19 would affect the settlement process of the virus as a mild respiratory virus.
The team led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the Department of Mathematical Science and Professor Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering used a new approach by dividing the human immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 into a shorter-term neutralizing antibody response and a longer-term T-cell immune response, and applying them each to a mathematical model. Additionally, the analysis was based on the fact that although breakthrough infection may occur frequently, the immune response of the patient will be boosted after recovery from each breakthrough infection.
The results showed that in an environment with a high vaccination rate, although COVID-19 cases may rise temporarily when the transmission rate increases, the ratio of critical cases would ultimately decline, thereby decreasing the total number of critical cases and in fact settling COVID-19 as a mild respiratory disease more quickly.
Conditions in which the number of cases may spike include relaxing social distancing measures or the rise of variants with higher transmission rates like the Omicron variant. This research did not take the less virulent characteristic of the Omicron variant into account but focused on the results of its high transmission rate, thereby predicting what may happen in the process of the endemic transition of COVID-19.
The research team pointed out the limitations of their mathematical model, such as the lack of consideration for age or patients with underlying diseases, and explained that the results of this study must be applied with care when compared against high-risk groups. Additionally, as medical systems may collapse when the number of cases rises sharply, this study must be interpreted with prudence and applied accordingly. The research team therefore emphasized that for policies that encourage a step-wise return to normality to succeed, the sustainable maintenance of public health systems is indispensable.
Professor Kim said, “We have drawn a counter-intuitive conclusion amid the unpredictable pandemic through an adequate mathematical model,” asserting the importance of applying mathematical models to medical research.
Professor Shin said, “Although the Omicron variant has become the dominant strain and the number of cases is rising rapidly in South Korea, it is important to use scientific approaches to predict the future and apply them to policies rather than fearing the current situation.”
The results of the research were published on medRxiv.org on February 11, under the title “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to severe COVID-19 during endemic transition.”
This research was funded by the Institute of Basic Science, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-PublicationHyukpyo Hong, Ji Yun Noh, Hyojung Lee, Sunhwa Choi, Boseung Choi, Jae Kyung Kim, Eui-Cheol Shin, “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to
severe COVID-19 during endemic transition,” medRxiv, February 9, 2022 (doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.09.22270633)
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
Professor Eui-Cheol ShinGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.02.22 View 11776
A Mathematical Model Shows High Viral Transmissions Reduce the Progression Rates for Severe Covid-19
The model suggests a clue as to when a pandemic will turn into an endemic
A mathematical model demonstrated that high transmission rates among highly vaccinated populations of COVID-19 ultimately reduce the numbers of severe cases. This model suggests a clue as to when this pandemic will turn into an endemic.
With the future of the pandemic remaining uncertain, a research team of mathematicians and medical scientists analyzed a mathematical model that may predict how the changing transmission rate of COVID-19 would affect the settlement process of the virus as a mild respiratory virus.
The team led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the Department of Mathematical Science and Professor Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering used a new approach by dividing the human immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 into a shorter-term neutralizing antibody response and a longer-term T-cell immune response, and applying them each to a mathematical model. Additionally, the analysis was based on the fact that although breakthrough infection may occur frequently, the immune response of the patient will be boosted after recovery from each breakthrough infection.
The results showed that in an environment with a high vaccination rate, although COVID-19 cases may rise temporarily when the transmission rate increases, the ratio of critical cases would ultimately decline, thereby decreasing the total number of critical cases and in fact settling COVID-19 as a mild respiratory disease more quickly.
Conditions in which the number of cases may spike include relaxing social distancing measures or the rise of variants with higher transmission rates like the Omicron variant. This research did not take the less virulent characteristic of the Omicron variant into account but focused on the results of its high transmission rate, thereby predicting what may happen in the process of the endemic transition of COVID-19.
The research team pointed out the limitations of their mathematical model, such as the lack of consideration for age or patients with underlying diseases, and explained that the results of this study must be applied with care when compared against high-risk groups. Additionally, as medical systems may collapse when the number of cases rises sharply, this study must be interpreted with prudence and applied accordingly. The research team therefore emphasized that for policies that encourage a step-wise return to normality to succeed, the sustainable maintenance of public health systems is indispensable.
Professor Kim said, “We have drawn a counter-intuitive conclusion amid the unpredictable pandemic through an adequate mathematical model,” asserting the importance of applying mathematical models to medical research.
Professor Shin said, “Although the Omicron variant has become the dominant strain and the number of cases is rising rapidly in South Korea, it is important to use scientific approaches to predict the future and apply them to policies rather than fearing the current situation.”
The results of the research were published on medRxiv.org on February 11, under the title “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to severe COVID-19 during endemic transition.”
This research was funded by the Institute of Basic Science, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-PublicationHyukpyo Hong, Ji Yun Noh, Hyojung Lee, Sunhwa Choi, Boseung Choi, Jae Kyung Kim, Eui-Cheol Shin, “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to
severe COVID-19 during endemic transition,” medRxiv, February 9, 2022 (doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.09.22270633)
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
Professor Eui-Cheol ShinGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.02.22 View 11776 -
 Commencement Ceremony Honors the Class of 2022
Third online commencement ceremony since the pandemic outbreak celebrates 2741 graduates
The 2022 commencement ceremony convened online on February 18 to celebrate and award degrees to the Class of 2022. The graduating class of 2022 included 663 PhDs, 1,383 Masters, and 695 Bachelors. The limited number of attendees included 86 graduate representatives and approximately 20 faculty members in senior leadership, as well as Korea’s Minister of Science and ICT Hyesook Lim. The ceremony was livestreamed on KAIST’s YouTube channel.
Valedictorian Ji-Young Lee from the Department of Physics received the Minister of Science and ICT’s Award. Yu-Jin Bang from the School of Business and Technology Management was the Awardee of the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees and the KAIST Presidential Awardee was Jong-Hwan Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences.
KAIST conferred honorary doctorates to Honorary Chairman Jae-Chul Kim of Dongwon Group and Chairman Sung-Hwan Chang of Samsung Brush. Chairman Kim, whose donation funded the establishment of the Kim Jae-Chul Graduate School of AI, was awarded an honorary doctorate of science technology. Chairman Chang was awarded an honorary doctorate of business administration in recognition of his funding in the fields of medical science and engineering at KAIST.
This year’s undergraduate commencement speaker was Hye-Lin Park from the School of Computing. She has severe cerebral palsy and was the first student admitted to KAIST with a severe physical handicap.
“I loved mathematics and wanted to become a mathematician. When I learned programming in my second year, I was so mesmerized by it that I transferred to the School of Computing,” said Park, who plans to continue studying programming languages in graduate school at KAIST.
“I spent my entire life of 24 years in this beautiful wheelchair. Without the support and help of my parents, friends, and my special teachers who helped me move and study at the campus, I would not have made it this far,” said Park. For easier access to classrooms and facilities, KAIST started to remodel its facilities to make the entrance of buildings more wheelchair-friendly. Park made many suggestions to the Office of Student Life and the Facilities Management Office on how to ease mobility for handicapped people on campus. The physical education course that was required for graduation was also revised to stipulate exceptions.
Minister Lim stressed the role of young scientists and researchers in these times of digital transformation dominated by AI and the metaverse. She encouraged the graduates to carry out their dreams with warm hearts and challenging spirits.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee also stressed the power of dreams, calling for graduates to dream big even in times of uncertainty.
“Humanity stands at an inflection point in history. The fourth industrial revolution and outbreak of Covid-19 have unfolded the grand global transformation. Although the future gives us new opportunities, it also comes with anxiety regarding the uncertainties ahead.”
“Dreams make your heart race and push us to live life to the fullest. Dreams will help you keep moving forward even in the face of adversity,” he said.
2022.02.18 View 11312
Commencement Ceremony Honors the Class of 2022
Third online commencement ceremony since the pandemic outbreak celebrates 2741 graduates
The 2022 commencement ceremony convened online on February 18 to celebrate and award degrees to the Class of 2022. The graduating class of 2022 included 663 PhDs, 1,383 Masters, and 695 Bachelors. The limited number of attendees included 86 graduate representatives and approximately 20 faculty members in senior leadership, as well as Korea’s Minister of Science and ICT Hyesook Lim. The ceremony was livestreamed on KAIST’s YouTube channel.
Valedictorian Ji-Young Lee from the Department of Physics received the Minister of Science and ICT’s Award. Yu-Jin Bang from the School of Business and Technology Management was the Awardee of the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees and the KAIST Presidential Awardee was Jong-Hwan Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences.
KAIST conferred honorary doctorates to Honorary Chairman Jae-Chul Kim of Dongwon Group and Chairman Sung-Hwan Chang of Samsung Brush. Chairman Kim, whose donation funded the establishment of the Kim Jae-Chul Graduate School of AI, was awarded an honorary doctorate of science technology. Chairman Chang was awarded an honorary doctorate of business administration in recognition of his funding in the fields of medical science and engineering at KAIST.
This year’s undergraduate commencement speaker was Hye-Lin Park from the School of Computing. She has severe cerebral palsy and was the first student admitted to KAIST with a severe physical handicap.
“I loved mathematics and wanted to become a mathematician. When I learned programming in my second year, I was so mesmerized by it that I transferred to the School of Computing,” said Park, who plans to continue studying programming languages in graduate school at KAIST.
“I spent my entire life of 24 years in this beautiful wheelchair. Without the support and help of my parents, friends, and my special teachers who helped me move and study at the campus, I would not have made it this far,” said Park. For easier access to classrooms and facilities, KAIST started to remodel its facilities to make the entrance of buildings more wheelchair-friendly. Park made many suggestions to the Office of Student Life and the Facilities Management Office on how to ease mobility for handicapped people on campus. The physical education course that was required for graduation was also revised to stipulate exceptions.
Minister Lim stressed the role of young scientists and researchers in these times of digital transformation dominated by AI and the metaverse. She encouraged the graduates to carry out their dreams with warm hearts and challenging spirits.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee also stressed the power of dreams, calling for graduates to dream big even in times of uncertainty.
“Humanity stands at an inflection point in history. The fourth industrial revolution and outbreak of Covid-19 have unfolded the grand global transformation. Although the future gives us new opportunities, it also comes with anxiety regarding the uncertainties ahead.”
“Dreams make your heart race and push us to live life to the fullest. Dreams will help you keep moving forward even in the face of adversity,” he said.
2022.02.18 View 11312 -
 President Lee Presents Plans to Nurture Next-Generation Talents
President Lee stressed that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during a news conference
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during an online news conference marking the 1st anniversary of him becoming the president on February 15.
He said that nurturing physician-scientists is the most critical mission for KAIST to help the nation create a new growth engine. He said KAIST will help the nation drive the bio-industry and provide medical science resources for the nation’s health sector. To this end, he said that KAIST will open its Medical Science and Technology School by 2026.
“We plan to expand the current Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering into a new Medical Science and Technology School that will focus entirely on a condensed MD-PhD course converging the fields of AI, bio, and physics,” he said.
The school aims to foster medical scientists whose research results will eventually be commercialized. He said that the university is now discussing revisions to related laws and regulations with the government and other universities.
To supply human resources to the semiconductor industry, President Lee said the university will add a campus in Pyongtaek City that will serve as an advanced convergence research hub in the field of next generation semiconductors in collaboration with Samsung Electronics and the city of Pyongtaek. The three-stage opening plan projected the final opening of the campus by 2036. During the first stage, which will be completed by 2026, it will construct the campus infrastructure in Pyongtaek city where Samsung Semiconductors runs two massive semiconductor complexes. By 2031, it plans to launch the open research platform including a future cities research center and future vehicles research center. The campus will open the global industrial collaboration cluster hub by 2036.
In the global arena, President Lee said he is working to open the New York campus with stakeholders in the United States. He announced the plan last December that was endorsed by New York-based entrepreneur Hee-Nam Bae, the chairman of Big Continent Inc. President Lee and Chairman Lee signed an MOU for the funding to open the campus in New York.
“We are discussing how to facilitate the plan and best accommodate the interests and potential of our students. Many ideas and plans are on the table and we think it will take longer than expected to finalize the plan,” explained President Lee.
However, he added that the basic idea is to offer art tech and health technology programs as well as an AI-based finance MBA at the New York campus, in addition to it serving as the startup accelerator of KAIST.
President Lee stressed the importance of technology commercialization when successfully launching KAIST Holdings last month to help spinoffs of KAIST labs accelerate their end results. He said that KAIST Holdings will build a virtuous supporting system to commercialize the technology startups coming from KAIST.
“We plan to list at least 10 KAIST startups on the KOSDAQ and two on the NASDAQ by 2031. KAIST Holdings also aims to nurture companies valued at a total of one billion KRW and earn 100 billion KRW in technology fees by 2031.
2022.02.17 View 12567
President Lee Presents Plans to Nurture Next-Generation Talents
President Lee stressed that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during a news conference
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during an online news conference marking the 1st anniversary of him becoming the president on February 15.
He said that nurturing physician-scientists is the most critical mission for KAIST to help the nation create a new growth engine. He said KAIST will help the nation drive the bio-industry and provide medical science resources for the nation’s health sector. To this end, he said that KAIST will open its Medical Science and Technology School by 2026.
“We plan to expand the current Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering into a new Medical Science and Technology School that will focus entirely on a condensed MD-PhD course converging the fields of AI, bio, and physics,” he said.
The school aims to foster medical scientists whose research results will eventually be commercialized. He said that the university is now discussing revisions to related laws and regulations with the government and other universities.
To supply human resources to the semiconductor industry, President Lee said the university will add a campus in Pyongtaek City that will serve as an advanced convergence research hub in the field of next generation semiconductors in collaboration with Samsung Electronics and the city of Pyongtaek. The three-stage opening plan projected the final opening of the campus by 2036. During the first stage, which will be completed by 2026, it will construct the campus infrastructure in Pyongtaek city where Samsung Semiconductors runs two massive semiconductor complexes. By 2031, it plans to launch the open research platform including a future cities research center and future vehicles research center. The campus will open the global industrial collaboration cluster hub by 2036.
In the global arena, President Lee said he is working to open the New York campus with stakeholders in the United States. He announced the plan last December that was endorsed by New York-based entrepreneur Hee-Nam Bae, the chairman of Big Continent Inc. President Lee and Chairman Lee signed an MOU for the funding to open the campus in New York.
“We are discussing how to facilitate the plan and best accommodate the interests and potential of our students. Many ideas and plans are on the table and we think it will take longer than expected to finalize the plan,” explained President Lee.
However, he added that the basic idea is to offer art tech and health technology programs as well as an AI-based finance MBA at the New York campus, in addition to it serving as the startup accelerator of KAIST.
President Lee stressed the importance of technology commercialization when successfully launching KAIST Holdings last month to help spinoffs of KAIST labs accelerate their end results. He said that KAIST Holdings will build a virtuous supporting system to commercialize the technology startups coming from KAIST.
“We plan to list at least 10 KAIST startups on the KOSDAQ and two on the NASDAQ by 2031. KAIST Holdings also aims to nurture companies valued at a total of one billion KRW and earn 100 billion KRW in technology fees by 2031.
2022.02.17 View 12567 -
 Research Finds Digital Music Streaming Consumption Dropped as a Result of Covid-19 and Lockdowns
Decline in human mobility has stunning consequences for content streaming
The Covid-19 pandemic and lockdowns significantly reduced the consumption of audio music streaming in many countries as people turned to video platforms. On average, audio music consumption decreased by 12.5% after the World Health Organization’s (WHO) pandemic declaration in March 2020.
Music streaming services were an unlikely area hit hard by the Covid-19 pandemic. New research in Marketing Science found that the drop in people’s mobility during the pandemic significantly reduced the consumption of audio music streaming. Instead, people turned more to video platforms.
“On average, audio music consumption decreased by more than 12% after the World Health Organization’s (WHO) pandemic declaration on March 11, 2020. As a result, during the pandemic, Spotify lost 838 million dollars of revenue in the first three quarters of 2020,” said Jaeung Sim, a PhD candidate in management engineering at KAIST and one of the authors of the research study on this phenomenon. “Our results showed that human mobility plays a much larger role in the audio consumption of music than previously thought.”
The study, “Frontiers: Virus Shook the Streaming Star: Estimating the Covid-19 Impact on Music Consumption,” conducted by Sim and Professor Daegon Cho of KAIST, Youngdeok Hwang of City University of New York, and Rahul Telang of Carnegie Mellon University, looked at online music streaming data for top songs for two years in 60 countries, as well as Covid-19 cases, lockdown statistics, and daily mobility data, to determine the nature of the changes.
The study showed how the pandemic adversely impacted music streaming services despite the common expectation that the pandemic would universally benefit online medias platforms. This implies that the substantially changing media consumption environment can place streaming music in fiercer competition with other media forms that offer more dynamic and vivid experiences to consumers.
The researchers found that music consumption through video platforms was positively associated with the severity of Covid-19, lockdown policies, and time spent at home.
-PublicationJaeung Sim, Daegon Cho, Youngdeok Hwang, and Rahul Telang,“Frontiers: Virus Shook the Streaming Star: Estimating the Covid-19 Impact on Music Consumption,” November 30 in Marketing Science online (doi.org/10.1287/mksc.2021.1321)
-Profile Professor Daegon ChoGraduate School of Information and Media ManagementCollege of BusinessKAIST
2022.02.15 View 11009
Research Finds Digital Music Streaming Consumption Dropped as a Result of Covid-19 and Lockdowns
Decline in human mobility has stunning consequences for content streaming
The Covid-19 pandemic and lockdowns significantly reduced the consumption of audio music streaming in many countries as people turned to video platforms. On average, audio music consumption decreased by 12.5% after the World Health Organization’s (WHO) pandemic declaration in March 2020.
Music streaming services were an unlikely area hit hard by the Covid-19 pandemic. New research in Marketing Science found that the drop in people’s mobility during the pandemic significantly reduced the consumption of audio music streaming. Instead, people turned more to video platforms.
“On average, audio music consumption decreased by more than 12% after the World Health Organization’s (WHO) pandemic declaration on March 11, 2020. As a result, during the pandemic, Spotify lost 838 million dollars of revenue in the first three quarters of 2020,” said Jaeung Sim, a PhD candidate in management engineering at KAIST and one of the authors of the research study on this phenomenon. “Our results showed that human mobility plays a much larger role in the audio consumption of music than previously thought.”
The study, “Frontiers: Virus Shook the Streaming Star: Estimating the Covid-19 Impact on Music Consumption,” conducted by Sim and Professor Daegon Cho of KAIST, Youngdeok Hwang of City University of New York, and Rahul Telang of Carnegie Mellon University, looked at online music streaming data for top songs for two years in 60 countries, as well as Covid-19 cases, lockdown statistics, and daily mobility data, to determine the nature of the changes.
The study showed how the pandemic adversely impacted music streaming services despite the common expectation that the pandemic would universally benefit online medias platforms. This implies that the substantially changing media consumption environment can place streaming music in fiercer competition with other media forms that offer more dynamic and vivid experiences to consumers.
The researchers found that music consumption through video platforms was positively associated with the severity of Covid-19, lockdown policies, and time spent at home.
-PublicationJaeung Sim, Daegon Cho, Youngdeok Hwang, and Rahul Telang,“Frontiers: Virus Shook the Streaming Star: Estimating the Covid-19 Impact on Music Consumption,” November 30 in Marketing Science online (doi.org/10.1287/mksc.2021.1321)
-Profile Professor Daegon ChoGraduate School of Information and Media ManagementCollege of BusinessKAIST
2022.02.15 View 11009 -
 Thermal Superconductor Lab Becomes the 7th Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab
The Thermal Superconductor Lab led by Senior Professor Sung Jin Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering will team up with Junior Professor Youngsuk Nam to develop next-generation superconductors. The two professor team was selected as the 7th Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab last week and will sustain the academic legacy of Professor Kim’s three decades of research on superconductors. The team will continue to develop thin, next-generation superconductors that carry super thermal conductivity using phase transition control technology and thin film packaging.
Thin-filmed, next-generation superconductors can be used in various high-temperature flexible electronic devices. The superconductors built inside of the semiconductor device packages will also be used for managing the low-powered but high-performance temperatures of semiconductor and electronic equipment.
Professor Kim said, “I am very pleased that my research, know-how, and knowledge from over 30 years of work will continue through the Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab system with Professor Nam. We will spare no effort to advance superconductor technology and play a part in KAIST leading global technology fields.” Junior Professor Nam also stressed that the team is excited to continue its research on crucial technology for managing the temperatures of semiconductors and other electronic equipment.
KAIST started this innovative research system in 2018, and in 2021 it established the steering committee to select new labs based on: originality, differentiation, and excellence; academic, social, economic impact; the urgency of cross-generation research; the senior professor’s academic excellence and international reputation; and the senior professor’s research vision. Selected labs receive 500 million KRW in research funding over five years.
2022.01.27 View 7253
Thermal Superconductor Lab Becomes the 7th Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab
The Thermal Superconductor Lab led by Senior Professor Sung Jin Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering will team up with Junior Professor Youngsuk Nam to develop next-generation superconductors. The two professor team was selected as the 7th Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab last week and will sustain the academic legacy of Professor Kim’s three decades of research on superconductors. The team will continue to develop thin, next-generation superconductors that carry super thermal conductivity using phase transition control technology and thin film packaging.
Thin-filmed, next-generation superconductors can be used in various high-temperature flexible electronic devices. The superconductors built inside of the semiconductor device packages will also be used for managing the low-powered but high-performance temperatures of semiconductor and electronic equipment.
Professor Kim said, “I am very pleased that my research, know-how, and knowledge from over 30 years of work will continue through the Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab system with Professor Nam. We will spare no effort to advance superconductor technology and play a part in KAIST leading global technology fields.” Junior Professor Nam also stressed that the team is excited to continue its research on crucial technology for managing the temperatures of semiconductors and other electronic equipment.
KAIST started this innovative research system in 2018, and in 2021 it established the steering committee to select new labs based on: originality, differentiation, and excellence; academic, social, economic impact; the urgency of cross-generation research; the senior professor’s academic excellence and international reputation; and the senior professor’s research vision. Selected labs receive 500 million KRW in research funding over five years.
2022.01.27 View 7253 -
 Seven Faculty Members Elected to Join the National Academy of Engineering of Korea
< Clockwise from top left: Professor Doo-Hwan Bae, Professor Seung Seob Lee, Professor Kyung Cheol Choi, Professor JaeYong Choung >
Seven KAIST faculty members have been elected as National Academy of Engineering of Korea (NAEK) members and associate members. NAEK, the most prestigious engineering society in Korea, elects new members with a minimum of 15 years of experience in engineering in academia and business every year.
In 2022, 24 members were newly elected from academia, including four KAIST faculty members: Professor Doo-Hwan Bae from the SW Education Center, KAIST Provost and Executive Vice President Seung Seob Lee, Professor JaeYong Choung from the School of Business and Technology Management, and Professor Kyung Cheol Choi of the School of Electrical Engineering. In the business sector, 21 members were elected as members in business, including Vice Chairman Jong-hee Han of Samsung Electronics, CEO Hyeon-Mo Ku of KT, President Sang-Ryul Lee of the Korea Aerospace Research Institute, President Kyo Won Jin of SK Hynix, CEO Eunkang Song of Capstone Partners, and Executive Vice President Se-hoon Kim of Hyundai Motor Company.
Among the newly elected 40 associate members from academia, three KAIST professors were listed: Professor Sukyoung Ryu from the School of Computing, Professor Joongmyeon Bae from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Professor EunAe Cho from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. Another 44 members were elected as associate members in business, including Vice Chairman Hag-Dong Kim of POSCO, President Seong-Hyeon Cho of Mando Corp, President Siyoung Choi of Samsung Electronics, President Joo Sun Choi of Samsung Display, and Chairman Byung-Gyu Chang of Krafton.
NAEK evaluates candidates not only on their academic achievements, but on various other criteria including technological achievements, patents, the nurturing of talents, and contributions to the advancements of the industry. Candidates are then elected through written ballots by the members of NAEK. There are now 294 members and 360 associate members of NAEK.
2022.01.14 View 7095
Seven Faculty Members Elected to Join the National Academy of Engineering of Korea
< Clockwise from top left: Professor Doo-Hwan Bae, Professor Seung Seob Lee, Professor Kyung Cheol Choi, Professor JaeYong Choung >
Seven KAIST faculty members have been elected as National Academy of Engineering of Korea (NAEK) members and associate members. NAEK, the most prestigious engineering society in Korea, elects new members with a minimum of 15 years of experience in engineering in academia and business every year.
In 2022, 24 members were newly elected from academia, including four KAIST faculty members: Professor Doo-Hwan Bae from the SW Education Center, KAIST Provost and Executive Vice President Seung Seob Lee, Professor JaeYong Choung from the School of Business and Technology Management, and Professor Kyung Cheol Choi of the School of Electrical Engineering. In the business sector, 21 members were elected as members in business, including Vice Chairman Jong-hee Han of Samsung Electronics, CEO Hyeon-Mo Ku of KT, President Sang-Ryul Lee of the Korea Aerospace Research Institute, President Kyo Won Jin of SK Hynix, CEO Eunkang Song of Capstone Partners, and Executive Vice President Se-hoon Kim of Hyundai Motor Company.
Among the newly elected 40 associate members from academia, three KAIST professors were listed: Professor Sukyoung Ryu from the School of Computing, Professor Joongmyeon Bae from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Professor EunAe Cho from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. Another 44 members were elected as associate members in business, including Vice Chairman Hag-Dong Kim of POSCO, President Seong-Hyeon Cho of Mando Corp, President Siyoung Choi of Samsung Electronics, President Joo Sun Choi of Samsung Display, and Chairman Byung-Gyu Chang of Krafton.
NAEK evaluates candidates not only on their academic achievements, but on various other criteria including technological achievements, patents, the nurturing of talents, and contributions to the advancements of the industry. Candidates are then elected through written ballots by the members of NAEK. There are now 294 members and 360 associate members of NAEK.
2022.01.14 View 7095