OT
-
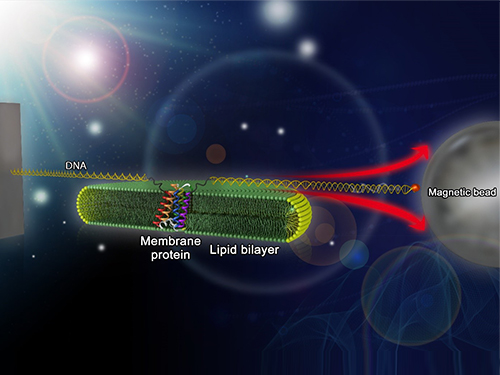 Mapping the Folding Process of a Single Membrane Protein
KAIST and UCLA scientists were able to observe an individual membrane protein fold and unfold by pulling and releasing magnetically trapped protein molecules.
Proteins are huge molecules containing hundreds to thousands of atoms that adopt a unique three dimensional structure, placing chemical groups in just the right place to catalyze reactions or build cellular structures. How all those atoms manage to find the right location - the so-called folding problem - has fascinated molecular biologists since the first structures were seen in the 1950s. Moreover, folding has important medical implications because most genetic defects cause protein misfolding.
About a third of all proteins float around in the cell membrane where they ensure the right chemicals get in the cell in the right amounts. Membrane proteins also provide key information links between the cell and its environment. Indeed, most drugs target membrane proteins. Nevertheless, the folding of membrane proteins has been particularly difficult to study and has rarely been studied in natural environments, leaving the folding process for a large fraction of the protein universe still largely cloaked in mystery.
In a recent issue of Nature Chemical Biology, published on October 19, 2015, a research team led by Tae-Young Yoon of the Department of Physics at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and James U. Bowie of the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), report a new method for manipulating the folding of membrane proteins in a membrane environment using a tool called a magnetic tweezer.
Researchers first attach long DNA handles to the ends of the protein. One handle is attached to a glass surface and the other to a magnetic bead. Using a magnet, they can essentially grab the protein and pull on it, inducing it to unfold. By playing with the bead attached to the protein, they can force the protein to unfold or allow it to refold, and watch all this happening by 3D-tracking of the magnetic bead. With this novel strategy, they were able to quantitatively map the folding energy landscape, the folding kinetic rate, and folding intermediates of a membrane protein in a membrane environment for the first time.
“I have been dreaming about this experiment for a decade. To see it work so well is really gratifying,” said Dr. Bowie.
One of the major surprises in the study was that essentially all the atoms of the protein jump into the correct structure together. The researchers expected that the protein structure would come together in a more piecemeal fashion, with different parts of the structure forming separately, but that was not the case. It is possible that nature evolved such a smooth, highly cooperative folding process to prevent partially folded forms that could get into trouble in the crowded cell membrane. On the other hand, the cooperative folding seen here might not apply to other membrane proteins.
“We need to look at more proteins. The technique developed here may allow us to do just that,” said Dr. Yoon.
The single molecule mechanical manipulation technique could enable detailed folding studies of many other membrane proteins. A major barrier to the study of membrane proteins previously is that the proteins tend to stick together and get tangled up, as computer cords lying at your feet tend to do. With the tweezer technique used in this work, the protein cords are held apart from other cords so they can’t get knotted up. It is hoped that the new approach will open up an important part of the protein universe to scrutiny, including many proteins that become misfolded in disease states.
The title of the research paper is “Mapping the energy landscape for second-stage folding of a single membrane protein” (DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1939).
Picture: Single-molecule magnetic tweezers that induce mechanical unfolding and refolding of a single membrane protein. Since the force applied is parallel to the biological lipid membrane, the unfolding and refolding processes occur within the membrane.
2015.10.20 View 10609
Mapping the Folding Process of a Single Membrane Protein
KAIST and UCLA scientists were able to observe an individual membrane protein fold and unfold by pulling and releasing magnetically trapped protein molecules.
Proteins are huge molecules containing hundreds to thousands of atoms that adopt a unique three dimensional structure, placing chemical groups in just the right place to catalyze reactions or build cellular structures. How all those atoms manage to find the right location - the so-called folding problem - has fascinated molecular biologists since the first structures were seen in the 1950s. Moreover, folding has important medical implications because most genetic defects cause protein misfolding.
About a third of all proteins float around in the cell membrane where they ensure the right chemicals get in the cell in the right amounts. Membrane proteins also provide key information links between the cell and its environment. Indeed, most drugs target membrane proteins. Nevertheless, the folding of membrane proteins has been particularly difficult to study and has rarely been studied in natural environments, leaving the folding process for a large fraction of the protein universe still largely cloaked in mystery.
In a recent issue of Nature Chemical Biology, published on October 19, 2015, a research team led by Tae-Young Yoon of the Department of Physics at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and James U. Bowie of the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), report a new method for manipulating the folding of membrane proteins in a membrane environment using a tool called a magnetic tweezer.
Researchers first attach long DNA handles to the ends of the protein. One handle is attached to a glass surface and the other to a magnetic bead. Using a magnet, they can essentially grab the protein and pull on it, inducing it to unfold. By playing with the bead attached to the protein, they can force the protein to unfold or allow it to refold, and watch all this happening by 3D-tracking of the magnetic bead. With this novel strategy, they were able to quantitatively map the folding energy landscape, the folding kinetic rate, and folding intermediates of a membrane protein in a membrane environment for the first time.
“I have been dreaming about this experiment for a decade. To see it work so well is really gratifying,” said Dr. Bowie.
One of the major surprises in the study was that essentially all the atoms of the protein jump into the correct structure together. The researchers expected that the protein structure would come together in a more piecemeal fashion, with different parts of the structure forming separately, but that was not the case. It is possible that nature evolved such a smooth, highly cooperative folding process to prevent partially folded forms that could get into trouble in the crowded cell membrane. On the other hand, the cooperative folding seen here might not apply to other membrane proteins.
“We need to look at more proteins. The technique developed here may allow us to do just that,” said Dr. Yoon.
The single molecule mechanical manipulation technique could enable detailed folding studies of many other membrane proteins. A major barrier to the study of membrane proteins previously is that the proteins tend to stick together and get tangled up, as computer cords lying at your feet tend to do. With the tweezer technique used in this work, the protein cords are held apart from other cords so they can’t get knotted up. It is hoped that the new approach will open up an important part of the protein universe to scrutiny, including many proteins that become misfolded in disease states.
The title of the research paper is “Mapping the energy landscape for second-stage folding of a single membrane protein” (DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1939).
Picture: Single-molecule magnetic tweezers that induce mechanical unfolding and refolding of a single membrane protein. Since the force applied is parallel to the biological lipid membrane, the unfolding and refolding processes occur within the membrane.
2015.10.20 View 10609 -
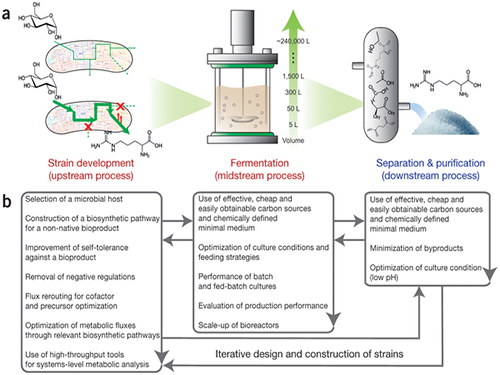 Establishment of System Metabolic Engineering Strategies
Although conventional petrochemical processes have generated chemicals and materials which have been useful to mankind, they have also triggered a variety of environmental problems including climate change and relied too much on nonrenewable natural resources. To ameliorate this, researchers have actively pursued the development of industrial microbial strains around the globe in order to overproduce industrially useful chemicals and materials from microbes using renewable biomass. This discipline is called metabolic engineering.
Thanks to advances in genetic engineering and our knowledge of cellular metabolism, conventional metabolic engineering efforts have succeeded to a certain extent in developing microbial strains that overproduce bioproducts at an industrial level. However, many metabolic engineering projects launched in academic labs do not reach commercial markets due to a failure to fully integrate industrial bioprocesses.
In response to this, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee and Dr. Hyun Uk Kim, both from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, have recently suggested ten general strategies of systems metabolic engineering to successfully develop industrial microbial strains. Systems metabolic engineering differs from conventional metabolic engineering by incorporating traditional metabolic engineering approaches along with tools of other fields, such as systems biology, synthetic biology, and molecular evolution.
The ten strategies of systems metabolic engineering have been featured in Nature Biotechnology released online in October 2015, which is entitled "Systems strategies for developing industrial microbial strains."
The strategies cover economic, state-of-the-art biological techniques and traditional bioprocess aspects. Specifically, they consist of: 1) project design including economic evaluation of a target bioproduct; 2) selection of host strains to be used for overproduction of a bioproduct; 3) metabolic pathway reconstruction for bioproducts that are not naturally produced in the selected host strains; 4) increasing tolerance of a host strain against the bioproduct; 5) removing negative regulatory circuits in the microbial host limiting overproduction of a bioproduct; 6) rerouting intracellular fluxes to optimize cofactor and precursor availability necessary for the bioproduct formation; 7) diagnosing and optimizing metabolic fluxes towards product formation; 8) diagnosis and optimization of microbial culture conditions including carbon sources; 9) system-wide gene manipulation to further increase the host strain's production performance using high-throughput genome-scale engineering and computational tools; and 10) scale-up fermentation of the developed strain and diagnosis for the reproducibility of the strain's production performance.
These ten strategies were articulated with successful examples of the production of L-arginine using Corynebacterium glutamicum, 1,4-butanediol using Escherichia coli, and L-lysine and bio-nylon using C. glutamicum.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "At the moment, the chance of commercializing microbial strains developed in academic labs is very low. The strategies of systems metabolic engineering outlined in this analysis can serve as guidelines when developing industrial microbial strains. We hope that these strategies contribute to improving opportunities to commercialize microbial strains developed in academic labs with drastically reduced costs and efforts, and that a large fraction of petroleum-based processes will be replaced with sustainable bioprocesses."
Lee S. Y. & Kim, H. U. Systems Strategies for Developing Industrial Microbial Strains. Nature Biotechnology (2015).
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556) and by the Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center through the Global Frontier Project (2011-0031963) from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP), Korea, and through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea. This work was also supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation.
Picture: Concept of the Systems Metabolic Engineering Framework
(a) Three major bioprocess stages (b) Considerations in systems metabolic engineering to optimize the whole bioprocess. List of considerations for the strain development and fermentation contribute to improving microbial strain's production performance (red), whereas those for the separation and purification help in reducing overall operation costs by facilitating the downstream process (blue). Some of the considerations can be repeated in the course of systems metabolic engineering.
2015.10.19 View 11929
Establishment of System Metabolic Engineering Strategies
Although conventional petrochemical processes have generated chemicals and materials which have been useful to mankind, they have also triggered a variety of environmental problems including climate change and relied too much on nonrenewable natural resources. To ameliorate this, researchers have actively pursued the development of industrial microbial strains around the globe in order to overproduce industrially useful chemicals and materials from microbes using renewable biomass. This discipline is called metabolic engineering.
Thanks to advances in genetic engineering and our knowledge of cellular metabolism, conventional metabolic engineering efforts have succeeded to a certain extent in developing microbial strains that overproduce bioproducts at an industrial level. However, many metabolic engineering projects launched in academic labs do not reach commercial markets due to a failure to fully integrate industrial bioprocesses.
In response to this, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee and Dr. Hyun Uk Kim, both from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, have recently suggested ten general strategies of systems metabolic engineering to successfully develop industrial microbial strains. Systems metabolic engineering differs from conventional metabolic engineering by incorporating traditional metabolic engineering approaches along with tools of other fields, such as systems biology, synthetic biology, and molecular evolution.
The ten strategies of systems metabolic engineering have been featured in Nature Biotechnology released online in October 2015, which is entitled "Systems strategies for developing industrial microbial strains."
The strategies cover economic, state-of-the-art biological techniques and traditional bioprocess aspects. Specifically, they consist of: 1) project design including economic evaluation of a target bioproduct; 2) selection of host strains to be used for overproduction of a bioproduct; 3) metabolic pathway reconstruction for bioproducts that are not naturally produced in the selected host strains; 4) increasing tolerance of a host strain against the bioproduct; 5) removing negative regulatory circuits in the microbial host limiting overproduction of a bioproduct; 6) rerouting intracellular fluxes to optimize cofactor and precursor availability necessary for the bioproduct formation; 7) diagnosing and optimizing metabolic fluxes towards product formation; 8) diagnosis and optimization of microbial culture conditions including carbon sources; 9) system-wide gene manipulation to further increase the host strain's production performance using high-throughput genome-scale engineering and computational tools; and 10) scale-up fermentation of the developed strain and diagnosis for the reproducibility of the strain's production performance.
These ten strategies were articulated with successful examples of the production of L-arginine using Corynebacterium glutamicum, 1,4-butanediol using Escherichia coli, and L-lysine and bio-nylon using C. glutamicum.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "At the moment, the chance of commercializing microbial strains developed in academic labs is very low. The strategies of systems metabolic engineering outlined in this analysis can serve as guidelines when developing industrial microbial strains. We hope that these strategies contribute to improving opportunities to commercialize microbial strains developed in academic labs with drastically reduced costs and efforts, and that a large fraction of petroleum-based processes will be replaced with sustainable bioprocesses."
Lee S. Y. & Kim, H. U. Systems Strategies for Developing Industrial Microbial Strains. Nature Biotechnology (2015).
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556) and by the Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center through the Global Frontier Project (2011-0031963) from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP), Korea, and through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea. This work was also supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation.
Picture: Concept of the Systems Metabolic Engineering Framework
(a) Three major bioprocess stages (b) Considerations in systems metabolic engineering to optimize the whole bioprocess. List of considerations for the strain development and fermentation contribute to improving microbial strain's production performance (red), whereas those for the separation and purification help in reducing overall operation costs by facilitating the downstream process (blue). Some of the considerations can be repeated in the course of systems metabolic engineering.
2015.10.19 View 11929 -
 Professor Ki-Jun Jeong Wins the 2015 Dam Yeun Academic Award
The 11th Dam Yeun Academic Award presented by the Korean Society for Biotechnology and Bioengineering (KSBB) to a biologist under 45 years old went to Professor Ki-Jun Jeong of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST.
The award ceremony took place on October 13, 2015, at the annual conference of KSBB held at Songdo Convensia in Incheon City.
Each year KSBB announces the recipient of the award based on the publications by researchers in the last five years at peer-reviewed international journals or KSBB Journal as well as the record of patent registration and technology transfers.
Professor Jeong is recognized for his pioneering research in protein, antibody, cellular engineering, and protein displays and chips.
2015.10.19 View 10691
Professor Ki-Jun Jeong Wins the 2015 Dam Yeun Academic Award
The 11th Dam Yeun Academic Award presented by the Korean Society for Biotechnology and Bioengineering (KSBB) to a biologist under 45 years old went to Professor Ki-Jun Jeong of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST.
The award ceremony took place on October 13, 2015, at the annual conference of KSBB held at Songdo Convensia in Incheon City.
Each year KSBB announces the recipient of the award based on the publications by researchers in the last five years at peer-reviewed international journals or KSBB Journal as well as the record of patent registration and technology transfers.
Professor Jeong is recognized for his pioneering research in protein, antibody, cellular engineering, and protein displays and chips.
2015.10.19 View 10691 -
 Brain Cognitive Engineering Experts from Korea and Abroad Gather at KAIST
The symposium presents recent and future research trends in brain and cognitive engineering.
KAIST hosted the Brain Cognitive Engineering Symposium on September 24, 2015, at the Dream Hall of the Chung Moon Soul building on campus. Around 100 experts in the field of neuroscience participated.
Organized by the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, the symposium celebrated the establishment of the Brain Cognitive Engineering Program at the university and examined the recent research trends in neuroscience.
Six neuroscience experts presented their research and held discussions.
Professor Paul M. Thompson of the University of Southern California (USC), a renowned scientist in neurology imaging genetics, gave a speech entitled “The ENIGMA Project: Mapping Disease and Genetic Effects on the Human Brain in 30,000 People Worldwide.”
Professor Jae-seung Jeong of KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, Director Sung-Gi Kim of IBS Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research, Professor Sung-Hwan Lee of Korea University’s Department of Brain Engineering, Professor Cheil-Moon of DGIST’s Department of Brain and Cognitive Science, and Professor Jun-Tani of KAIST’s Department of Electrical Engineering also participated in the symposium.
Participants discussed the most recent findings in the field of brain science such as the education and research trends of brain cognitive engineering, trends of the world’s brain integrated science, the prospects of brain cognitive engineering program, brain activities that induce blood flow and fMRI, activity production in the brain cortex model as well as the development of functional hierarchy for the motor visual perception, and the neurorobotics research.
Professor Jeong said that “this symposium is a place for examination of the most recent research findings in the field of neuroscience as well as for discussion of its education,”and that “it would be an important opportunity for learning research on brain’s basic mechanisms as well as its applications.”
2015.09.25 View 9821
Brain Cognitive Engineering Experts from Korea and Abroad Gather at KAIST
The symposium presents recent and future research trends in brain and cognitive engineering.
KAIST hosted the Brain Cognitive Engineering Symposium on September 24, 2015, at the Dream Hall of the Chung Moon Soul building on campus. Around 100 experts in the field of neuroscience participated.
Organized by the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, the symposium celebrated the establishment of the Brain Cognitive Engineering Program at the university and examined the recent research trends in neuroscience.
Six neuroscience experts presented their research and held discussions.
Professor Paul M. Thompson of the University of Southern California (USC), a renowned scientist in neurology imaging genetics, gave a speech entitled “The ENIGMA Project: Mapping Disease and Genetic Effects on the Human Brain in 30,000 People Worldwide.”
Professor Jae-seung Jeong of KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, Director Sung-Gi Kim of IBS Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research, Professor Sung-Hwan Lee of Korea University’s Department of Brain Engineering, Professor Cheil-Moon of DGIST’s Department of Brain and Cognitive Science, and Professor Jun-Tani of KAIST’s Department of Electrical Engineering also participated in the symposium.
Participants discussed the most recent findings in the field of brain science such as the education and research trends of brain cognitive engineering, trends of the world’s brain integrated science, the prospects of brain cognitive engineering program, brain activities that induce blood flow and fMRI, activity production in the brain cortex model as well as the development of functional hierarchy for the motor visual perception, and the neurorobotics research.
Professor Jeong said that “this symposium is a place for examination of the most recent research findings in the field of neuroscience as well as for discussion of its education,”and that “it would be an important opportunity for learning research on brain’s basic mechanisms as well as its applications.”
2015.09.25 View 9821 -
 KAIST and Oberthur Technologies Agree for Research and Development in Mobile Security
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the School of Computing at KAIST has signed a research and development (R&D) agreement with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (OT), a French security solutions firm, on September 18, 2015 in Paris.
Under the agreement, KAIST and OT will conduct joint research on mobile security as well as implement an internship program for KAIST graduate students to work either at OT’s R&D center in Korea or in France.
OT has established a research center in Korea in July 2014, which was the fourth of its research centers in Asia.
Professor Kim said, “Our goal at KAIST is to cultivate top-level security experts in security technologies. By partnering with such a leader in security technologies as OT, we know that we will both help shape tomorrow’s security solution for the IoT (Internet of Things) space.”
In the picture, Professor Kwangjo Kim (left) shakes hands with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (right), after the signing of a memorandum of understanding.
2015.09.24 View 8666
KAIST and Oberthur Technologies Agree for Research and Development in Mobile Security
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the School of Computing at KAIST has signed a research and development (R&D) agreement with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (OT), a French security solutions firm, on September 18, 2015 in Paris.
Under the agreement, KAIST and OT will conduct joint research on mobile security as well as implement an internship program for KAIST graduate students to work either at OT’s R&D center in Korea or in France.
OT has established a research center in Korea in July 2014, which was the fourth of its research centers in Asia.
Professor Kim said, “Our goal at KAIST is to cultivate top-level security experts in security technologies. By partnering with such a leader in security technologies as OT, we know that we will both help shape tomorrow’s security solution for the IoT (Internet of Things) space.”
In the picture, Professor Kwangjo Kim (left) shakes hands with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (right), after the signing of a memorandum of understanding.
2015.09.24 View 8666 -
 Nature Biotechnology Nominates Sang Yup Lee of KAIST for Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014
Nature Biotechnology, recognized as the most prestigious journal in the field of biotechnology, has released today its list of the Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014. Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST (Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology) ranked seventh in the list. He is the only Asian researcher listed.
The journal, in partnership with IP Checkups, a patent analytics firm, presents an annual ranking of researchers based on their paper and patent output. The list includes, among others, each researcher’s most-cited patent in the past five years and their H index, a measurement to evaluate the impact of a researcher’s published work utilizing citation analysis. (More details can be found at http://www.nature.com/bioent/2015/150801/full/bioe.2015.9.html.)
American institutions made up the majority of the list, with 18 universities and research institutes, and the remainder was filled by KAIST in Korea and the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) in Australia.
Globally known as a leading researcher in systems metabolic engineering, Professor Lee has published more than 500 journal papers and 580 patents. He has received many awards, including the Citation Classic Award, Elmer Gaden Award, Merck Metabolic Engineering Award, ACS Marvin Johnson Award, SIMB Charles Thom Award, POSCO TJ Park Prize, Amgen Biochemical Engineering Award, and the Ho Am Prize in Engineering.
2015.08.27 View 12176
Nature Biotechnology Nominates Sang Yup Lee of KAIST for Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014
Nature Biotechnology, recognized as the most prestigious journal in the field of biotechnology, has released today its list of the Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014. Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST (Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology) ranked seventh in the list. He is the only Asian researcher listed.
The journal, in partnership with IP Checkups, a patent analytics firm, presents an annual ranking of researchers based on their paper and patent output. The list includes, among others, each researcher’s most-cited patent in the past five years and their H index, a measurement to evaluate the impact of a researcher’s published work utilizing citation analysis. (More details can be found at http://www.nature.com/bioent/2015/150801/full/bioe.2015.9.html.)
American institutions made up the majority of the list, with 18 universities and research institutes, and the remainder was filled by KAIST in Korea and the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO) in Australia.
Globally known as a leading researcher in systems metabolic engineering, Professor Lee has published more than 500 journal papers and 580 patents. He has received many awards, including the Citation Classic Award, Elmer Gaden Award, Merck Metabolic Engineering Award, ACS Marvin Johnson Award, SIMB Charles Thom Award, POSCO TJ Park Prize, Amgen Biochemical Engineering Award, and the Ho Am Prize in Engineering.
2015.08.27 View 12176 -
 KAIST holds the 2015 KAIST-MIT-Technion International Symposium on Nano Science
The 2015 KAIST-MIT-Technion International Symposium on Nano Science was held on August 11, 2015 at the KAIST campus. The event took place under three subtopics: Materials for Production and Storage of Renewable Energy, Functional Materials, and Multiferroic Materials.
The joint symposium invited more than 300 experts in material science and engineering including ten speakers and panelists. From MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), Professors Harry L. Tuller and Geoffrey S. Beach in the Department of Material Engineering, as well as Professor Gregory Rutledge in the Department of Chemical Engineering joined the symposium. Professor Avner Rothschild in the Department of Material Engineering and Professor Yair Ein-Eli in the Department of Chemical Engineering at Technion Institute of Technology in Israel also participated.
From KAIST, Professors Il-Doo Kim, Byong-Guk Park, and Yeon-Sik Jung in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Chan-Ho Yang in the Department of Physics, and Professor Doh-Chang Lee in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering spoke at the event. The list of topics included “Next Generation Lithium-Air Battery,” “Nano Materials for High Performance Energy Storage System,” and “Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Photoelectrode for the Conversion and Storage of Solar Energy.”
In its efforts to promote cooperation among the three universities, KAIST plans to send six students to MIT and one student to Technion for joint research.
Professor Il-Doo Kim, who organized the symposium said, “We believe this kind of international gathering will serve as an opportunity for scholars from leading universities to share their expertise in material science and help them better understand on the recent trends in nanoscience and its related technology.”
2015.08.12 View 9623
KAIST holds the 2015 KAIST-MIT-Technion International Symposium on Nano Science
The 2015 KAIST-MIT-Technion International Symposium on Nano Science was held on August 11, 2015 at the KAIST campus. The event took place under three subtopics: Materials for Production and Storage of Renewable Energy, Functional Materials, and Multiferroic Materials.
The joint symposium invited more than 300 experts in material science and engineering including ten speakers and panelists. From MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), Professors Harry L. Tuller and Geoffrey S. Beach in the Department of Material Engineering, as well as Professor Gregory Rutledge in the Department of Chemical Engineering joined the symposium. Professor Avner Rothschild in the Department of Material Engineering and Professor Yair Ein-Eli in the Department of Chemical Engineering at Technion Institute of Technology in Israel also participated.
From KAIST, Professors Il-Doo Kim, Byong-Guk Park, and Yeon-Sik Jung in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Chan-Ho Yang in the Department of Physics, and Professor Doh-Chang Lee in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering spoke at the event. The list of topics included “Next Generation Lithium-Air Battery,” “Nano Materials for High Performance Energy Storage System,” and “Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Photoelectrode for the Conversion and Storage of Solar Energy.”
In its efforts to promote cooperation among the three universities, KAIST plans to send six students to MIT and one student to Technion for joint research.
Professor Il-Doo Kim, who organized the symposium said, “We believe this kind of international gathering will serve as an opportunity for scholars from leading universities to share their expertise in material science and help them better understand on the recent trends in nanoscience and its related technology.”
2015.08.12 View 9623 -
 Dr. Se-Jung Kim Receives the Grand Prize at the International Photo and Image Contest on Light
Dr. Se-Jung Kim of the Physics Department at KAIST received the Grand Prize at the 2015 Photo and Image Contest of the International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies.
The United Nations has designated the year 2015 as the International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies.
The Optical Society of Korea celebrated the UN’s designation by hosting an international photo and image contest on the theme of light and optics related technology.
Dr. Kim presented a photo of images taken from a liquid crystal, which was entitled “A Micro Pinwheel.” She took pictures of liquid crystal images with a polarizing microscope and then colored the pictures. The liquid crystal has self-assembled circle domain structures, and each domain can form vortex optics. Her adviser for the project is Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Physics Department.
Her work was exhibited during the annual conference of the Optical Society of Korea, which was held on July 13-15, 2015 at Gyeong-Ju Hwabaek International Convention Center. It will also be exhibited at the National Science Museum in Gwacheon and the Kim Dae-Jung Convention Center in Gwangju.
Picture: A Micro Pinwheel
2015.07.31 View 11944
Dr. Se-Jung Kim Receives the Grand Prize at the International Photo and Image Contest on Light
Dr. Se-Jung Kim of the Physics Department at KAIST received the Grand Prize at the 2015 Photo and Image Contest of the International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies.
The United Nations has designated the year 2015 as the International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies.
The Optical Society of Korea celebrated the UN’s designation by hosting an international photo and image contest on the theme of light and optics related technology.
Dr. Kim presented a photo of images taken from a liquid crystal, which was entitled “A Micro Pinwheel.” She took pictures of liquid crystal images with a polarizing microscope and then colored the pictures. The liquid crystal has self-assembled circle domain structures, and each domain can form vortex optics. Her adviser for the project is Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Physics Department.
Her work was exhibited during the annual conference of the Optical Society of Korea, which was held on July 13-15, 2015 at Gyeong-Ju Hwabaek International Convention Center. It will also be exhibited at the National Science Museum in Gwacheon and the Kim Dae-Jung Convention Center in Gwangju.
Picture: A Micro Pinwheel
2015.07.31 View 11944 -
 A Technology Holding Company Establishes Two Companies Based on Technologies Developed at KAIST
Mirae Holdings is a technology holding company created by four science and technology universities, KAIST, DIGIST (Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology), GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology), and UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology) in 2014 to commercialize the universities’ research achievements. The company identifies promising technologies for commercialization, makes business plans, establishes venture capitals, and invests in startup companies.
Over the past year, Mirae Holdings has established two venture companies based on the technologies developed at KAIST. In September 2014, it founded Cresem Inc., a company used the anisotropic conductive film (ACF) bonding technology, which was developed by Professor Kyung-Wook Paik of the Material Science and Engineering Department at KAIST. Cresem provides a technology to bond electronic parts ultrasonically. The company is expected to have 860,000 USD worth of sales within the first year of its launching.
Last June, Mirae Holdings created another company, Doctor Kitchen, with the technology developed by Professor Gwan-Su Yi of the Bio and Brain Engineering Department at KAIST. Doctor Kitchen supplies precooked food, which helps diabetic patients regulate their diet. The company offers a personalized diet plan to customers so that they can effectively manage their disease and monitor their blood sugar level efficiently.
The Chief Executive Officer of Mirae Holdings, Young-Ho Kim, said, “We can assist KAIST researchers who aspire to create a company based on their research outcomes through various stages of startup services such as making business plans, securing venture capitals, and networking with existing businesses.”
Young-Ho Kim (left in the picture), the Chief Executive Officer of Mirae Holdings, holds a certificate of company registration with Sang-Min Oh (right in the picture), the Chief Executive Officer of Cresem.
Young-Ho Kim (left in the picture), the Chief Executive Officer of Mirae Holdings, holds a certificate of company registration with Jae-Yeun Park (right in the picture), the Chief Executive Officer of Dr. Kitchen.
2015.07.29 View 14548
A Technology Holding Company Establishes Two Companies Based on Technologies Developed at KAIST
Mirae Holdings is a technology holding company created by four science and technology universities, KAIST, DIGIST (Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology), GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology), and UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology) in 2014 to commercialize the universities’ research achievements. The company identifies promising technologies for commercialization, makes business plans, establishes venture capitals, and invests in startup companies.
Over the past year, Mirae Holdings has established two venture companies based on the technologies developed at KAIST. In September 2014, it founded Cresem Inc., a company used the anisotropic conductive film (ACF) bonding technology, which was developed by Professor Kyung-Wook Paik of the Material Science and Engineering Department at KAIST. Cresem provides a technology to bond electronic parts ultrasonically. The company is expected to have 860,000 USD worth of sales within the first year of its launching.
Last June, Mirae Holdings created another company, Doctor Kitchen, with the technology developed by Professor Gwan-Su Yi of the Bio and Brain Engineering Department at KAIST. Doctor Kitchen supplies precooked food, which helps diabetic patients regulate their diet. The company offers a personalized diet plan to customers so that they can effectively manage their disease and monitor their blood sugar level efficiently.
The Chief Executive Officer of Mirae Holdings, Young-Ho Kim, said, “We can assist KAIST researchers who aspire to create a company based on their research outcomes through various stages of startup services such as making business plans, securing venture capitals, and networking with existing businesses.”
Young-Ho Kim (left in the picture), the Chief Executive Officer of Mirae Holdings, holds a certificate of company registration with Sang-Min Oh (right in the picture), the Chief Executive Officer of Cresem.
Young-Ho Kim (left in the picture), the Chief Executive Officer of Mirae Holdings, holds a certificate of company registration with Jae-Yeun Park (right in the picture), the Chief Executive Officer of Dr. Kitchen.
2015.07.29 View 14548 -
 Professor Kyoungsik Yu Receives the Young IT Engineer Award from IEEE and IEIE of Korea
Professor Kyoungsik Yu of KAIST’s Department of Electrical Engineering is the recipient of this year’s Young IT (Information Technology) Engineer Award that was co-hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), the Institute of Electronics Engineers of Korea (IEIE), and Haedong Science Culture Foundation in Korea. The award was presented on June 22, 2015 at The Ramada Plaza Jeju Hotel on Jeju Island, Korea.
The Young IT Engineer Award is given to emerging scientists who have made significant contributions to the advancement of technology, society, environment, and creative education.
Professor Yu's main research interests are IT, energy, and imaging through miniaturization and integration of optoelectronic devices. His contribution to academic and technological development is reflected in his publication of more than 100 papers in international journals and conferences, which were cited over 2,200 times.
Professor Yu said, “I’m honored to receive this award and am encouraged by it. I also find the award meaningful because the United Nations has designated this year as the “International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies,” the field I have been involved in as a researcher.”
In addition to Korea, the IEEE has jointly hosted and presented this award to researchers in countries such as Chile, Ecuador, Peru, Singapore, and Italy.
2015.06.22 View 13988
Professor Kyoungsik Yu Receives the Young IT Engineer Award from IEEE and IEIE of Korea
Professor Kyoungsik Yu of KAIST’s Department of Electrical Engineering is the recipient of this year’s Young IT (Information Technology) Engineer Award that was co-hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), the Institute of Electronics Engineers of Korea (IEIE), and Haedong Science Culture Foundation in Korea. The award was presented on June 22, 2015 at The Ramada Plaza Jeju Hotel on Jeju Island, Korea.
The Young IT Engineer Award is given to emerging scientists who have made significant contributions to the advancement of technology, society, environment, and creative education.
Professor Yu's main research interests are IT, energy, and imaging through miniaturization and integration of optoelectronic devices. His contribution to academic and technological development is reflected in his publication of more than 100 papers in international journals and conferences, which were cited over 2,200 times.
Professor Yu said, “I’m honored to receive this award and am encouraged by it. I also find the award meaningful because the United Nations has designated this year as the “International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies,” the field I have been involved in as a researcher.”
In addition to Korea, the IEEE has jointly hosted and presented this award to researchers in countries such as Chile, Ecuador, Peru, Singapore, and Italy.
2015.06.22 View 13988 -
 KAIST's DRC-HUBO Wins the DARPA Robotics Challenge 2015
DRC-HUBO finished all eight assignments in less than 45 minutes, taking first place among 24 international teams and claiming the USD 2 million prize offered by a US defense research agency.
The Robotics Challenge Finals 2015 hosted by the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) took place on June 5-6, 2015 at the Fairplex in Pomona, California.
Team KAIST of the Republic of Korea led by Professor Jun-Ho Oh of the Mechanical Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Professor In-So Kweon of the Electrical Engineering Department, and researchers from Rainbow Co., the university’s spin-off company that builds the robots, won the DARPA Finals. The team received USD 2 million as a prize.
The DARPA’s Robotics Challenge (DRC) promotes a competition of robot systems and software teams which seek to develop robots capable of assisting humans in responding to natural and man-made disasters such as the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear incident in 2011. The DRC consists of three competitions: a software-based Virtual Robotics Challenge which took place in June 2013; the Robotics Challenge Trials in Homestead, Florida, in December 2013; and the Finals in June 2015.
A total of 24 teams from universities and private and public research institutes from Korea, the US, Hong Kong, Germany, Japan, and Italy participated in the Finals. The participating teams had to finish eight assignments in 60 minutes, during which their robots were untethered and operated wirelessly without communication from their engineers.
Each team was assigned a series of tasks: they included driving a vehicle, getting out of a vehicle, opening a door, turning a valve, drilling a hole in a wall, a surprise task such as pushing a button or turning on a switch, walking over rubble or debris, and climbing stairs. Robots scored a point each time they completed their missions. To win, a team had to complete all the tasks successfully in the shortest amount of time possible.
Team KAIST completed the entire course in 44 minutes and 28 seconds, followed by the Institute of Human and Machine Cognition (IHMC) Robotics in Pensacola, Florida in 50:26, and Team TARTAN Rescue of the National Robotics Engineering Center at Carnegie Mellon University in 55:15.
For details, see an article below from the New York Times:
New York Times, June 6, 2015
“Korean Robot Makers Walk Off With $2 Million Prize”
http://www.nytimes.com/2015/06/07/science/korean-robot-makers-walk-off-with-2-million-prize.html?_r=1
DRC-HUBO sticks a plug into an outlet for the surprise task at the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge on June 5-6, 2015, in Pomona, California.
DRC-HUBO turns a valve in a clockwise direction.
DRC-HUBO drills to cut a circle into the wall.
Members of Team KAIST pose together after the award ceremony on June 6, 2015.
2015.06.07 View 25578
KAIST's DRC-HUBO Wins the DARPA Robotics Challenge 2015
DRC-HUBO finished all eight assignments in less than 45 minutes, taking first place among 24 international teams and claiming the USD 2 million prize offered by a US defense research agency.
The Robotics Challenge Finals 2015 hosted by the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) took place on June 5-6, 2015 at the Fairplex in Pomona, California.
Team KAIST of the Republic of Korea led by Professor Jun-Ho Oh of the Mechanical Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Professor In-So Kweon of the Electrical Engineering Department, and researchers from Rainbow Co., the university’s spin-off company that builds the robots, won the DARPA Finals. The team received USD 2 million as a prize.
The DARPA’s Robotics Challenge (DRC) promotes a competition of robot systems and software teams which seek to develop robots capable of assisting humans in responding to natural and man-made disasters such as the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear incident in 2011. The DRC consists of three competitions: a software-based Virtual Robotics Challenge which took place in June 2013; the Robotics Challenge Trials in Homestead, Florida, in December 2013; and the Finals in June 2015.
A total of 24 teams from universities and private and public research institutes from Korea, the US, Hong Kong, Germany, Japan, and Italy participated in the Finals. The participating teams had to finish eight assignments in 60 minutes, during which their robots were untethered and operated wirelessly without communication from their engineers.
Each team was assigned a series of tasks: they included driving a vehicle, getting out of a vehicle, opening a door, turning a valve, drilling a hole in a wall, a surprise task such as pushing a button or turning on a switch, walking over rubble or debris, and climbing stairs. Robots scored a point each time they completed their missions. To win, a team had to complete all the tasks successfully in the shortest amount of time possible.
Team KAIST completed the entire course in 44 minutes and 28 seconds, followed by the Institute of Human and Machine Cognition (IHMC) Robotics in Pensacola, Florida in 50:26, and Team TARTAN Rescue of the National Robotics Engineering Center at Carnegie Mellon University in 55:15.
For details, see an article below from the New York Times:
New York Times, June 6, 2015
“Korean Robot Makers Walk Off With $2 Million Prize”
http://www.nytimes.com/2015/06/07/science/korean-robot-makers-walk-off-with-2-million-prize.html?_r=1
DRC-HUBO sticks a plug into an outlet for the surprise task at the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge on June 5-6, 2015, in Pomona, California.
DRC-HUBO turns a valve in a clockwise direction.
DRC-HUBO drills to cut a circle into the wall.
Members of Team KAIST pose together after the award ceremony on June 6, 2015.
2015.06.07 View 25578 -
 Professor Sang-Yup Lee Receives the Order of Service Merit Red Stripes from the Korean Government
The government of the Republic of Korea named Professor Sang-Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Bio-molecular Engineering at KAIST as the fiftieth recipient of the Order of Service Merit Red Stripes on May 19, 2015.
This medal is awarded to government employees, officials, and teachers in recognition of their contributions to public services including education.
Professor Lee is regarded as a leading scientist in the field of metabolic engineering, genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and bioinformatics on microorganism producing various primary and secondary metabolites. He contributed significantly to the advancement of bio-based engineering research in Korea.
In addition, his research in microorganism metabolic engineering propelled him to the front of his field, making him the world’s founder of systems metabolic engineering, inventing numerous technologies in strain development.
Professor Lee has received many patent rights in bioprocess engineering. While at KAIST, he applied for 585 patents and registered 227 patents. In particular, he has applied for 135 patents and registered 99 patents in the past five years, successfully turning research results into commercial applications.
Professor Lee said, “I’m glad to contribute to the development of Korean science and technology as a researcher and teacher. I would like to share this honor with my students, master’s and doctoral students in particular, because without their support, it wouldn’t have been possible to pull off the highest level of research results recognized by this medal.”
2015.05.21 View 9706
Professor Sang-Yup Lee Receives the Order of Service Merit Red Stripes from the Korean Government
The government of the Republic of Korea named Professor Sang-Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Bio-molecular Engineering at KAIST as the fiftieth recipient of the Order of Service Merit Red Stripes on May 19, 2015.
This medal is awarded to government employees, officials, and teachers in recognition of their contributions to public services including education.
Professor Lee is regarded as a leading scientist in the field of metabolic engineering, genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and bioinformatics on microorganism producing various primary and secondary metabolites. He contributed significantly to the advancement of bio-based engineering research in Korea.
In addition, his research in microorganism metabolic engineering propelled him to the front of his field, making him the world’s founder of systems metabolic engineering, inventing numerous technologies in strain development.
Professor Lee has received many patent rights in bioprocess engineering. While at KAIST, he applied for 585 patents and registered 227 patents. In particular, he has applied for 135 patents and registered 99 patents in the past five years, successfully turning research results into commercial applications.
Professor Lee said, “I’m glad to contribute to the development of Korean science and technology as a researcher and teacher. I would like to share this honor with my students, master’s and doctoral students in particular, because without their support, it wouldn’t have been possible to pull off the highest level of research results recognized by this medal.”
2015.05.21 View 9706