Engineering
-
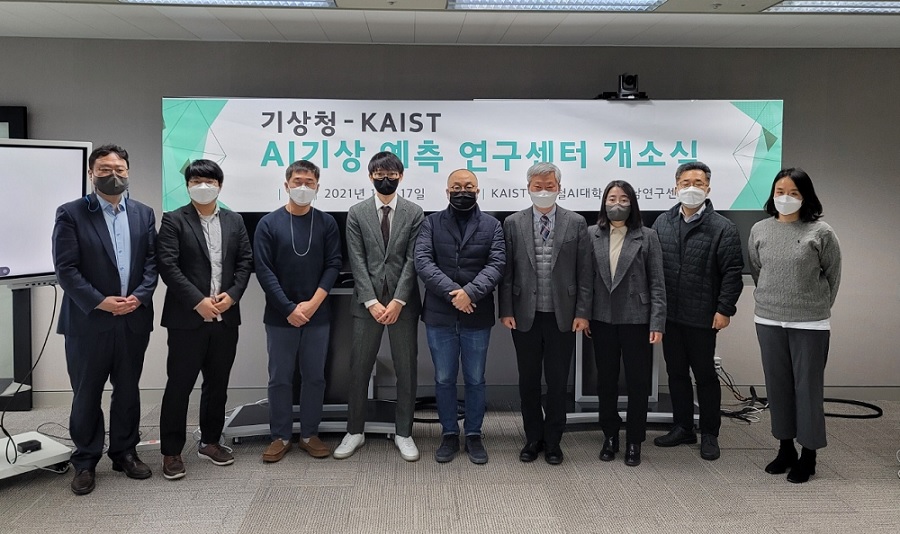 AI Weather Forecasting Research Center Opens
The Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI in collaboration with the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences (NIMS) under the National Meteorological Administration launched the AI Weather Forecasting Research Center last month.
The KAIST AI Weather Forecasting Research Center headed by Professor Seyoung Yoon was established with funding from from the AlphaWeather Development Research Project of the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences. KAIST was finally selected asas the project facilitator.
AlphaWeather is an AI system that utilizes and analyzes approximately approximately 150,000 ,000 pieces of weather information per hour to help weather forecasters produce accurate weather forecasts. The research center is composed of three research teams with the following goals: (a) developdevelop AI technology for precipitation nowcasting, (b) developdevelop AI technology for accelerating physical process-based numerical models, and (c) develop dAI technology for supporting weather forecasters. The teams consist of 15 staff member members from NIMS and 61 researchers from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST.
The research center is developing an AI algorithm for precipitation nowcasting (with up to six hours of lead time), which uses satellite images, radar reflectivity, and data collected from weather stations. It is also developing an AI algorithm for correcting biases in the prediction results from multiple numerical models. Finally, it is Finally, it is developing AI technology that supports weather forecasters by standardizing and automating repetitive manual processes. After verification, the the results obtained will be used by by the Korean National Weather Service as a next-generation forecasting/special-reporting system intelligence engine from 2026.
2022.01.10 View 7190
AI Weather Forecasting Research Center Opens
The Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI in collaboration with the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences (NIMS) under the National Meteorological Administration launched the AI Weather Forecasting Research Center last month.
The KAIST AI Weather Forecasting Research Center headed by Professor Seyoung Yoon was established with funding from from the AlphaWeather Development Research Project of the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences. KAIST was finally selected asas the project facilitator.
AlphaWeather is an AI system that utilizes and analyzes approximately approximately 150,000 ,000 pieces of weather information per hour to help weather forecasters produce accurate weather forecasts. The research center is composed of three research teams with the following goals: (a) developdevelop AI technology for precipitation nowcasting, (b) developdevelop AI technology for accelerating physical process-based numerical models, and (c) develop dAI technology for supporting weather forecasters. The teams consist of 15 staff member members from NIMS and 61 researchers from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST.
The research center is developing an AI algorithm for precipitation nowcasting (with up to six hours of lead time), which uses satellite images, radar reflectivity, and data collected from weather stations. It is also developing an AI algorithm for correcting biases in the prediction results from multiple numerical models. Finally, it is Finally, it is developing AI technology that supports weather forecasters by standardizing and automating repetitive manual processes. After verification, the the results obtained will be used by by the Korean National Weather Service as a next-generation forecasting/special-reporting system intelligence engine from 2026.
2022.01.10 View 7190 -
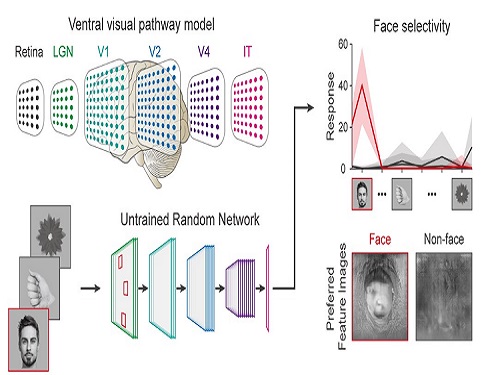 Face Detection in Untrained Deep Neural Networks
A KAIST team shows that primitive visual selectivity of faces can arise spontaneously in completely untrained deep neural networks
Researchers have found that higher visual cognitive functions can arise spontaneously in untrained neural networks. A KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has shown that visual selectivity of facial images can arise even in completely untrained deep neural networks.
This new finding has provided revelatory insights into mechanisms underlying the development of cognitive functions in both biological and artificial neural networks, also making a significant impact on our understanding of the origin of early brain functions before sensory experiences.
The study published in Nature Communications on December 16 demonstrates that neuronal activities selective to facial images are observed in randomly initialized deep neural networks in the complete absence of learning, and that they show the characteristics of those observed in biological brains.
The ability to identify and recognize faces is a crucial function for social behavior, and this ability is thought to originate from neuronal tuning at the single or multi-neuronal level. Neurons that selectively respond to faces are observed in young animals of various species, and this raises intense debate whether face-selective neurons can arise innately in the brain or if they require visual experience.
Using a model neural network that captures properties of the ventral stream of the visual cortex, the research team found that face-selectivity can emerge spontaneously from random feedforward wirings in untrained deep neural networks. The team showed that the character of this innate face-selectivity is comparable to that observed with face-selective neurons in the brain, and that this spontaneous neuronal tuning for faces enables the network to perform face detection tasks.
These results imply a possible scenario in which the random feedforward connections that develop in early, untrained networks may be sufficient for initializing primitive visual cognitive functions.
Professor Paik said, “Our findings suggest that innate cognitive functions can emerge spontaneously from the statistical complexity embedded in the hierarchical feedforward projection circuitry, even in the complete absence of learning”.
He continued, “Our results provide a broad conceptual advance as well as advanced insight into the mechanisms underlying the development of innate functions in both biological and artificial neural networks, which may unravel the mystery of the generation and evolution of intelligence.” This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and by the KAIST singularity research project.
-PublicationSeungdae Baek, Min Song, Jaeson Jang, Gwangsu Kim, and Se-Bum Baik, “Face detection in untrained deep neural network,” Nature Communications 12, 7328 on Dec.16, 2021
(https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27606-9)
-ProfileProfessor Se-Bum PaikVisual System and Neural Network LaboratoryProgram of Brain and Cognitive EngineeringDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.21 View 11232
Face Detection in Untrained Deep Neural Networks
A KAIST team shows that primitive visual selectivity of faces can arise spontaneously in completely untrained deep neural networks
Researchers have found that higher visual cognitive functions can arise spontaneously in untrained neural networks. A KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has shown that visual selectivity of facial images can arise even in completely untrained deep neural networks.
This new finding has provided revelatory insights into mechanisms underlying the development of cognitive functions in both biological and artificial neural networks, also making a significant impact on our understanding of the origin of early brain functions before sensory experiences.
The study published in Nature Communications on December 16 demonstrates that neuronal activities selective to facial images are observed in randomly initialized deep neural networks in the complete absence of learning, and that they show the characteristics of those observed in biological brains.
The ability to identify and recognize faces is a crucial function for social behavior, and this ability is thought to originate from neuronal tuning at the single or multi-neuronal level. Neurons that selectively respond to faces are observed in young animals of various species, and this raises intense debate whether face-selective neurons can arise innately in the brain or if they require visual experience.
Using a model neural network that captures properties of the ventral stream of the visual cortex, the research team found that face-selectivity can emerge spontaneously from random feedforward wirings in untrained deep neural networks. The team showed that the character of this innate face-selectivity is comparable to that observed with face-selective neurons in the brain, and that this spontaneous neuronal tuning for faces enables the network to perform face detection tasks.
These results imply a possible scenario in which the random feedforward connections that develop in early, untrained networks may be sufficient for initializing primitive visual cognitive functions.
Professor Paik said, “Our findings suggest that innate cognitive functions can emerge spontaneously from the statistical complexity embedded in the hierarchical feedforward projection circuitry, even in the complete absence of learning”.
He continued, “Our results provide a broad conceptual advance as well as advanced insight into the mechanisms underlying the development of innate functions in both biological and artificial neural networks, which may unravel the mystery of the generation and evolution of intelligence.” This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and by the KAIST singularity research project.
-PublicationSeungdae Baek, Min Song, Jaeson Jang, Gwangsu Kim, and Se-Bum Baik, “Face detection in untrained deep neural network,” Nature Communications 12, 7328 on Dec.16, 2021
(https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27606-9)
-ProfileProfessor Se-Bum PaikVisual System and Neural Network LaboratoryProgram of Brain and Cognitive EngineeringDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.21 View 11232 -
 Team KAIST to Race at CES 2022 Autonomous Challenge
Five top university autonomous racing teams will compete in a head-to-head passing competition in Las Vegas
A self-driving racing team from the KAIST Unmanned System Research Group (USRG) advised by Professor Hyunchul Shim will compete at the Autonomous Challenge at the Consumer Electronic Show (CES) on January 7, 2022. The head-to-head, high speed autonomous racecar passing competition at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway will feature the finalists and semifinalists from the Indy Autonomous Challenge in October of this year. Team KAIST qualified as a semifinalist at the Indy Autonomous Challenge and will join four other university teams including the winner of the competition, Technische Universität München.
Team KAIST’s AV-21 vehicle is capable of driving on its own at more than 200km/h will be expected to show a speed of more than 300 km/h at the race.The participating teams are:1. KAIST2. EuroRacing : University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), University of Pisa (Italy), ETH Zürich (Switzerland), Polish Academy of Sciences (Poland) 3. MIT-PITT-RW, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, University of Pittsburgh, Rochester Institute of Technology, University of Waterloo (Canada)4.PoliMOVE – Politecnico di Milano (Italy), University of Alabama 5.TUM Autonomous Motorsport – Technische Universität München (Germany)
Professor Shim’s team is dedicated to the development and validation of cutting edge technologies for highly autonomous vehicles. In recognition of his pioneering research in unmanned system technologies, Professor Shim was honored with the Grand Prize of the Minister of Science and ICT on December 9.
“We began autonomous vehicle research in 2009 when we signed up for Hyundai Motor Company’s Autonomous Driving Challenge. For this, we developed a complete set of in-house technologies such as low-level vehicle control, perception, localization, and decision making.” In 2019, the team came in third place in the Challenge and they finally won this year.
For years, his team has participated in many unmanned systems challenges at home and abroad, gaining recognition around the world. The team won the inaugural 2016 IROS autonomous drone racing and placed second in the 2018 IROS Autonomous Drone Racing Competition. They also competed in 2017 MBZIRC, ranking fourth in Missions 2 and 3, and fifth in the Grand Challenge.
Most recently, the team won the first round of Lockheed Martin’s Alpha Pilot AI Drone Innovation Challenge. The team is now participating in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge as a member of Team CoSTAR with NASA JPL, MIT, and Caltech.
“We have accumulated plenty of first-hand experience developing autonomous vehicles with the support of domestic companies such as Hyundai Motor Company, Samsung, LG, and NAVER. In 2017, the autonomous vehicle platform “EureCar” that we developed in-house was authorized by the Korean government to lawfully conduct autonomous driving experiment on public roads,” said Professor Shim.
The team has developed various key technologies and algorithms related to unmanned systems that can be categorized into three major components: perception, planning, and control. Considering the characteristics of the algorithms that make up each module, their technology operates using a distributed computing system.
Since 2015, the team has been actively using deep learning algorithms in the form of perception subsystems. Contextual information extracted from multi-modal sensory data gathered via cameras, lidar, radar, GPS, IMU, etc. is forwarded to the planning subsystem. The planning module is responsible for the decision making and planning required for autonomous driving such as lane change determination and trajectory planning, emergency stops, and velocity command generation. The results from the planner are fed into the controller to follow the planned high-level command. The team has also developed and verified the possibility of an end-to-end deep learning based autonomous driving approach that replaces a complex system with one single AI network.
2021.12.17 View 12417
Team KAIST to Race at CES 2022 Autonomous Challenge
Five top university autonomous racing teams will compete in a head-to-head passing competition in Las Vegas
A self-driving racing team from the KAIST Unmanned System Research Group (USRG) advised by Professor Hyunchul Shim will compete at the Autonomous Challenge at the Consumer Electronic Show (CES) on January 7, 2022. The head-to-head, high speed autonomous racecar passing competition at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway will feature the finalists and semifinalists from the Indy Autonomous Challenge in October of this year. Team KAIST qualified as a semifinalist at the Indy Autonomous Challenge and will join four other university teams including the winner of the competition, Technische Universität München.
Team KAIST’s AV-21 vehicle is capable of driving on its own at more than 200km/h will be expected to show a speed of more than 300 km/h at the race.The participating teams are:1. KAIST2. EuroRacing : University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), University of Pisa (Italy), ETH Zürich (Switzerland), Polish Academy of Sciences (Poland) 3. MIT-PITT-RW, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, University of Pittsburgh, Rochester Institute of Technology, University of Waterloo (Canada)4.PoliMOVE – Politecnico di Milano (Italy), University of Alabama 5.TUM Autonomous Motorsport – Technische Universität München (Germany)
Professor Shim’s team is dedicated to the development and validation of cutting edge technologies for highly autonomous vehicles. In recognition of his pioneering research in unmanned system technologies, Professor Shim was honored with the Grand Prize of the Minister of Science and ICT on December 9.
“We began autonomous vehicle research in 2009 when we signed up for Hyundai Motor Company’s Autonomous Driving Challenge. For this, we developed a complete set of in-house technologies such as low-level vehicle control, perception, localization, and decision making.” In 2019, the team came in third place in the Challenge and they finally won this year.
For years, his team has participated in many unmanned systems challenges at home and abroad, gaining recognition around the world. The team won the inaugural 2016 IROS autonomous drone racing and placed second in the 2018 IROS Autonomous Drone Racing Competition. They also competed in 2017 MBZIRC, ranking fourth in Missions 2 and 3, and fifth in the Grand Challenge.
Most recently, the team won the first round of Lockheed Martin’s Alpha Pilot AI Drone Innovation Challenge. The team is now participating in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge as a member of Team CoSTAR with NASA JPL, MIT, and Caltech.
“We have accumulated plenty of first-hand experience developing autonomous vehicles with the support of domestic companies such as Hyundai Motor Company, Samsung, LG, and NAVER. In 2017, the autonomous vehicle platform “EureCar” that we developed in-house was authorized by the Korean government to lawfully conduct autonomous driving experiment on public roads,” said Professor Shim.
The team has developed various key technologies and algorithms related to unmanned systems that can be categorized into three major components: perception, planning, and control. Considering the characteristics of the algorithms that make up each module, their technology operates using a distributed computing system.
Since 2015, the team has been actively using deep learning algorithms in the form of perception subsystems. Contextual information extracted from multi-modal sensory data gathered via cameras, lidar, radar, GPS, IMU, etc. is forwarded to the planning subsystem. The planning module is responsible for the decision making and planning required for autonomous driving such as lane change determination and trajectory planning, emergency stops, and velocity command generation. The results from the planner are fed into the controller to follow the planned high-level command. The team has also developed and verified the possibility of an end-to-end deep learning based autonomous driving approach that replaces a complex system with one single AI network.
2021.12.17 View 12417 -
 A Study Shows Reactive Electrolyte Additives Improve Lithium Metal Battery Performance
Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives provide an opportunity to improve high-performance lithium metal batteries
A research team showed that electrolyte additives increase the lifetime of lithium metal batteries and remarkably improve the performance of fast charging and discharging. Professor Nam-Soon Choi’s team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST hierarchized the solid electrolyte interphase to make a dual-layer structure and showed groundbreaking run times for lithium metal batteries.
The team applied two electrolyte additives that have different reduction and adsorption properties to improve the functionality of the dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase. In addition, the team has confirmed that the structural stability of the nickel-rich cathode was achieved through the formation of a thin protective layer on the cathode. This study was reported in Energy Storage Materials.
Securing high-energy-density lithium metal batteries with a long lifespan and fast charging performance is vital for realizing their ubiquitous use as superior power sources for electric vehicles. Lithium metal batteries comprise a lithium metal anode that delivers 10 times higher capacity than the graphite anodes in lithium-ion batteries. Therefore, lithium metal is an indispensable anode material for realizing high-energy rechargeable batteries. However, undesirable reactions among the electrolytes with lithium metal anodes can reduce the power and this remains an impediment to achieving a longer battery lifespan. Previous studies only focused on the formation of the solid electrolyte interphase on the surface of the lithium metal anode.
The team designed a way to create a dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase to resolve the instability of the lithium metal anode by using electrolyte additives, depending on their electron accepting ability and adsorption tendencies. This hierarchical structure of the solid electrolyte interphase on the lithium metal anode has the potential to be further applied to lithium-alloy anodes, lithium storage structures, and anode-free technology to meet market expectations for electrolyte technology.
The batteries with lithium metal anodes and nickel-rich cathodes represented 80.9% of the initial capacity after 600 cycles and achieved a high Coulombic efficiency of 99.94%. These remarkable results contributed to the development of protective dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase technology for lithium metal anodes.
Professor Choi said that the research suggests a new direction for the development of electrolyte additives to regulate the unstable lithium metal anode-electrolyte interface, the biggest hurdle in research on lithium metal batteries.
She added that anode-free secondary battery technology is expected to be a game changer in the secondary battery market and electrolyte additive technology will contribute to the enhancement of anode-free secondary batteries through the stabilization of lithium metal anodes.
This research was funded by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change of the National Research Foundation in Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning and the Technology Innovation Program funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, and Hyundai Motor Company.
- PublicationSaehun Kim, Sung O Park, Min-Young Lee, Jeong-A Lee, Imanuel Kristanto, Tae Kyung Lee, Daeyeon Hwang, Juyoung Kim, Tae-Ung Wi, Hyun-Wook Lee, Sang Kyu Kwak, and NamSoon Choi, “Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives for high-performance lithium metal batteries,” Energy Storage Materials,45, 1-13 (2022), (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.10.031)
- ProfileProfessor Nam-Soon ChoiEnergy Materials LaboratoryDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.16 View 10330
A Study Shows Reactive Electrolyte Additives Improve Lithium Metal Battery Performance
Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives provide an opportunity to improve high-performance lithium metal batteries
A research team showed that electrolyte additives increase the lifetime of lithium metal batteries and remarkably improve the performance of fast charging and discharging. Professor Nam-Soon Choi’s team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST hierarchized the solid electrolyte interphase to make a dual-layer structure and showed groundbreaking run times for lithium metal batteries.
The team applied two electrolyte additives that have different reduction and adsorption properties to improve the functionality of the dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase. In addition, the team has confirmed that the structural stability of the nickel-rich cathode was achieved through the formation of a thin protective layer on the cathode. This study was reported in Energy Storage Materials.
Securing high-energy-density lithium metal batteries with a long lifespan and fast charging performance is vital for realizing their ubiquitous use as superior power sources for electric vehicles. Lithium metal batteries comprise a lithium metal anode that delivers 10 times higher capacity than the graphite anodes in lithium-ion batteries. Therefore, lithium metal is an indispensable anode material for realizing high-energy rechargeable batteries. However, undesirable reactions among the electrolytes with lithium metal anodes can reduce the power and this remains an impediment to achieving a longer battery lifespan. Previous studies only focused on the formation of the solid electrolyte interphase on the surface of the lithium metal anode.
The team designed a way to create a dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase to resolve the instability of the lithium metal anode by using electrolyte additives, depending on their electron accepting ability and adsorption tendencies. This hierarchical structure of the solid electrolyte interphase on the lithium metal anode has the potential to be further applied to lithium-alloy anodes, lithium storage structures, and anode-free technology to meet market expectations for electrolyte technology.
The batteries with lithium metal anodes and nickel-rich cathodes represented 80.9% of the initial capacity after 600 cycles and achieved a high Coulombic efficiency of 99.94%. These remarkable results contributed to the development of protective dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase technology for lithium metal anodes.
Professor Choi said that the research suggests a new direction for the development of electrolyte additives to regulate the unstable lithium metal anode-electrolyte interface, the biggest hurdle in research on lithium metal batteries.
She added that anode-free secondary battery technology is expected to be a game changer in the secondary battery market and electrolyte additive technology will contribute to the enhancement of anode-free secondary batteries through the stabilization of lithium metal anodes.
This research was funded by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change of the National Research Foundation in Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning and the Technology Innovation Program funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, and Hyundai Motor Company.
- PublicationSaehun Kim, Sung O Park, Min-Young Lee, Jeong-A Lee, Imanuel Kristanto, Tae Kyung Lee, Daeyeon Hwang, Juyoung Kim, Tae-Ung Wi, Hyun-Wook Lee, Sang Kyu Kwak, and NamSoon Choi, “Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives for high-performance lithium metal batteries,” Energy Storage Materials,45, 1-13 (2022), (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.10.031)
- ProfileProfessor Nam-Soon ChoiEnergy Materials LaboratoryDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.16 View 10330 -
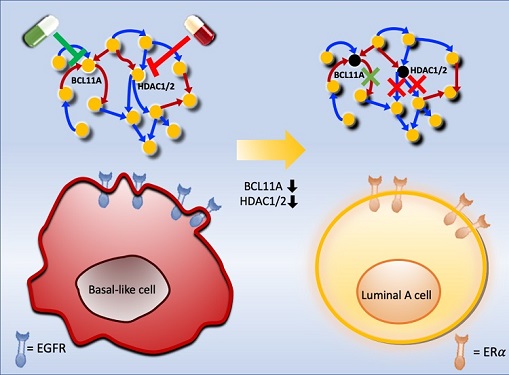 Connecting the Dots to Find New Treatments for Breast Cancer
Systems biologists uncovered new ways of cancer cell reprogramming to treat drug-resistant cancers
Scientists at KAIST believe they may have found a way to reverse an aggressive, treatment-resistant type of breast cancer into a less dangerous kind that responds well to treatment. The study involved the use of mathematical models to untangle the complex genetic and molecular interactions that occur in the two types of breast cancer, but could be extended to find ways for treating many others. The study’s findings were published in the journal Cancer Research.
Basal-like tumours are the most aggressive type of breast cancer, with the worst prognosis. Chemotherapy is the only available treatment option, but patients experience high recurrence rates. On the other hand, luminal-A breast cancer responds well to drugs that specifically target a receptor on their cell surfaces, called estrogen receptor alpha (ERα).
KAIST systems biologist Kwang-Hyun Cho and colleagues analyzed the complex molecular and genetic interactions of basal-like and luminal-A breast cancers to find out if there might be a way to switch the former to the latter and give patients a better chance to respond to treatment.
To do this, they accessed large amounts of cancer and patient data to understand which genes and molecules are involved in the two types. They then input this data into a mathematical model that represents genes, proteins and molecules as dots and the interactions between them as lines. The model can be used to conduct simulations and see how interactions change when certain genes are turned on or off.
“There have been a tremendous number of studies trying to find therapeutic targets for treating basal-like breast cancer patients,” says Cho. “But clinical trials have failed due to the complex and dynamic nature of cancer. To overcome this issue, we looked at breast cancer cells as a complex network system and implemented a systems biological approach to unravel the underlying mechanisms that would allow us to reprogram basal-like into luminal-A breast cancer cells.”
Using this approach, followed by experimental validation on real breast cancer cells, the team found that turning off two key gene regulators, called BCL11A and HDAC1/2, switched a basal-like cancer signalling pathway into a different one used by luminal-A cancer cells. The switch reprograms the cancer cells and makes them more responsive to drugs that target ERα receptors. However, further tests will be needed to confirm that this also works in animal models and eventually humans.
“Our study demonstrates that the systems biological approach can be useful for identifying novel therapeutic targets,” says Cho.
The researchers are now expanding its breast cancer network model to include all breast cancer subtypes. Their ultimate aim is to identify more drug targets and to understand the mechanisms that could drive drug-resistant cells to turn into drug-sensitive ones.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Ministry of Science and ICT, Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute, and the KAIST Grand Challenge 30 Project.
-Publication Sea R. Choi, Chae Young Hwang, Jonghoon Lee, and Kwang-Hyun Cho, “Network Analysis Identifies Regulators of Basal-like Breast Cancer Reprogramming and Endocrine TherapyVulnerability,” Cancer Research, November 30. (doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0621)
-ProfileProfessor Kwang-Hyun ChoLaboratory for Systems Biology and Bio-Inspired EngineeringDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.07 View 12028
Connecting the Dots to Find New Treatments for Breast Cancer
Systems biologists uncovered new ways of cancer cell reprogramming to treat drug-resistant cancers
Scientists at KAIST believe they may have found a way to reverse an aggressive, treatment-resistant type of breast cancer into a less dangerous kind that responds well to treatment. The study involved the use of mathematical models to untangle the complex genetic and molecular interactions that occur in the two types of breast cancer, but could be extended to find ways for treating many others. The study’s findings were published in the journal Cancer Research.
Basal-like tumours are the most aggressive type of breast cancer, with the worst prognosis. Chemotherapy is the only available treatment option, but patients experience high recurrence rates. On the other hand, luminal-A breast cancer responds well to drugs that specifically target a receptor on their cell surfaces, called estrogen receptor alpha (ERα).
KAIST systems biologist Kwang-Hyun Cho and colleagues analyzed the complex molecular and genetic interactions of basal-like and luminal-A breast cancers to find out if there might be a way to switch the former to the latter and give patients a better chance to respond to treatment.
To do this, they accessed large amounts of cancer and patient data to understand which genes and molecules are involved in the two types. They then input this data into a mathematical model that represents genes, proteins and molecules as dots and the interactions between them as lines. The model can be used to conduct simulations and see how interactions change when certain genes are turned on or off.
“There have been a tremendous number of studies trying to find therapeutic targets for treating basal-like breast cancer patients,” says Cho. “But clinical trials have failed due to the complex and dynamic nature of cancer. To overcome this issue, we looked at breast cancer cells as a complex network system and implemented a systems biological approach to unravel the underlying mechanisms that would allow us to reprogram basal-like into luminal-A breast cancer cells.”
Using this approach, followed by experimental validation on real breast cancer cells, the team found that turning off two key gene regulators, called BCL11A and HDAC1/2, switched a basal-like cancer signalling pathway into a different one used by luminal-A cancer cells. The switch reprograms the cancer cells and makes them more responsive to drugs that target ERα receptors. However, further tests will be needed to confirm that this also works in animal models and eventually humans.
“Our study demonstrates that the systems biological approach can be useful for identifying novel therapeutic targets,” says Cho.
The researchers are now expanding its breast cancer network model to include all breast cancer subtypes. Their ultimate aim is to identify more drug targets and to understand the mechanisms that could drive drug-resistant cells to turn into drug-sensitive ones.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Ministry of Science and ICT, Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute, and the KAIST Grand Challenge 30 Project.
-Publication Sea R. Choi, Chae Young Hwang, Jonghoon Lee, and Kwang-Hyun Cho, “Network Analysis Identifies Regulators of Basal-like Breast Cancer Reprogramming and Endocrine TherapyVulnerability,” Cancer Research, November 30. (doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0621)
-ProfileProfessor Kwang-Hyun ChoLaboratory for Systems Biology and Bio-Inspired EngineeringDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.07 View 12028 -
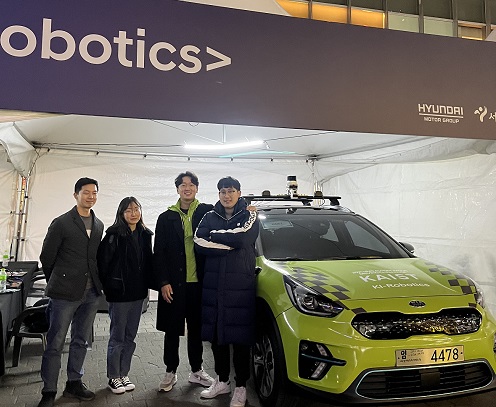 KI-Robotics Wins the 2021 Hyundai Motor Autonomous Driving Challenge
Professor Hyunchul Shim’s autonomous driving team topped the challenge
KI-Robotics, a KAIST autonomous driving research team led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electric Engineering won the 2021 Hyundai Motor Autonomous Driving Challenge held in Seoul on November 29. The KI-Robotics team received 100 million won in prize money and a field trip to the US.
Out of total 23 teams, the six teams competed in the finals by simultaneously driving through a 4km section within the test operation region, where other traffic was constrained. The challenge included avoiding and overtaking vehicles, crossing intersections, and keeping to traffic laws including traffic lights, lanes, speed limit, and school zones. The contestants were ranked by their order of course completion, but points were deducted every time they violated a traffic rule. A driver and an invigilator rode in each car in case of an emergency, and the race was broadcasted live on a large screen on stage and via YouTube.
In the first round, KI-Robotics came in first with a score of 11 minutes and 27 seconds after a tight race with Incheon University. Although the team’s result in the second round exceeded 16 minutes due to traffic conditions like traffic lights, the 11 minutes and 27 seconds ultimately ranked first out of the six universities. It is worth noting that KI-Robotics focused on its vehicle’s perception and judgement rather than speed when building its algorithm. Out of the six universities that made it to the final round, KI-Robotics was the only team that excluded GPS from the vehicle to minimize its risk.
The team considered the fact that GPS signals are not accurate in urban settings, meaning location errors can cause problems while driving. As an alternative, the team added three radar sensors and cameras in the front and the back of the vehicle. They also used the urban-specific SLAM technology they developed to construct a precise map and were more successful in location determination.
As opposed to other teams that focused on speed, the KAIST team also developed overtaking route construction technology, taking into consideration the locations of surrounding cars, which gave them an advantage in responding to obstacles while keeping to real urban traffic rules. Through this, the KAIST team could score highest in rounds one and two combined.
Professor Shim said, “I am very glad that the autonomous driving technology our research team has been developing over the last ten years has borne fruit. I would like to thank the leader, Daegyu Lee, and all the students that participated in the development, as they did more than their best under difficult conditions.”
Dae-Gyu Lee, the leader of KI-Robotics and a Ph.D. candidate in the School of Electrical Engineering, explained, “Since we came in fourth in the preliminary round, we were further behind than we expected. But we were able to overtake the cars ahead of us and shorten our record.”
2021.12.07 View 7639
KI-Robotics Wins the 2021 Hyundai Motor Autonomous Driving Challenge
Professor Hyunchul Shim’s autonomous driving team topped the challenge
KI-Robotics, a KAIST autonomous driving research team led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electric Engineering won the 2021 Hyundai Motor Autonomous Driving Challenge held in Seoul on November 29. The KI-Robotics team received 100 million won in prize money and a field trip to the US.
Out of total 23 teams, the six teams competed in the finals by simultaneously driving through a 4km section within the test operation region, where other traffic was constrained. The challenge included avoiding and overtaking vehicles, crossing intersections, and keeping to traffic laws including traffic lights, lanes, speed limit, and school zones. The contestants were ranked by their order of course completion, but points were deducted every time they violated a traffic rule. A driver and an invigilator rode in each car in case of an emergency, and the race was broadcasted live on a large screen on stage and via YouTube.
In the first round, KI-Robotics came in first with a score of 11 minutes and 27 seconds after a tight race with Incheon University. Although the team’s result in the second round exceeded 16 minutes due to traffic conditions like traffic lights, the 11 minutes and 27 seconds ultimately ranked first out of the six universities. It is worth noting that KI-Robotics focused on its vehicle’s perception and judgement rather than speed when building its algorithm. Out of the six universities that made it to the final round, KI-Robotics was the only team that excluded GPS from the vehicle to minimize its risk.
The team considered the fact that GPS signals are not accurate in urban settings, meaning location errors can cause problems while driving. As an alternative, the team added three radar sensors and cameras in the front and the back of the vehicle. They also used the urban-specific SLAM technology they developed to construct a precise map and were more successful in location determination.
As opposed to other teams that focused on speed, the KAIST team also developed overtaking route construction technology, taking into consideration the locations of surrounding cars, which gave them an advantage in responding to obstacles while keeping to real urban traffic rules. Through this, the KAIST team could score highest in rounds one and two combined.
Professor Shim said, “I am very glad that the autonomous driving technology our research team has been developing over the last ten years has borne fruit. I would like to thank the leader, Daegyu Lee, and all the students that participated in the development, as they did more than their best under difficult conditions.”
Dae-Gyu Lee, the leader of KI-Robotics and a Ph.D. candidate in the School of Electrical Engineering, explained, “Since we came in fourth in the preliminary round, we were further behind than we expected. But we were able to overtake the cars ahead of us and shorten our record.”
2021.12.07 View 7639 -
 A Team of Three PhD Candidates Wins the Korea Semiconductor Design Contest
“We felt a sense of responsibility to help the nation advance its semiconductor design technology”
A CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor)-based “ultra-low noise signal chip” for 6G communications designed by three PhD candidates at the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering won the Presidential Award at the 22nd Korea Semiconductor Design Contest.
The winners are PhD candidates Sun-Eui Park, Yoon-Seo Cho, and Ju-Eun Bang from the Integrated Circuits and System Lab run by Professor Jaehyouk Choi. The contest, which is hosted by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy and the Korea Semiconductors Industry Association, is one of the top national semiconductor design contests for college students.
Park said the team felt a sense of responsibility to help advance semiconductor design technology in Korea when deciding to participate the contest. The team expressed deep gratitude to Professor Choi for guiding their research on 6G communications.
“Our colleagues from other labs and seniors who already graduated helped us a great deal, so we owe them a lot,” explained Park. Cho added that their hard work finally got recognized and that acknowledgement pushes her to move forward with her research. Meanwhile, Bang said she is delighted to see that many people seem to be interested in her research topic.
Research for 6G is attempting to reach 1 tera bps (Tbps), 50 times faster than 5G communications with transmission speeds of up to 20 gigabytes. In general, the wider the communication frequency band, the higher the data transmission speed. Thus, the use of frequency bands above 100 gigahertz is essential for delivering high data transmission speeds for 6G communications.
However, it remains a big challenge to make a precise benchmark signal that can be used as a carrier wave in a high frequency band. Despite the advantages of CMOS’s ultra-small and low-power design, it still has limitations at high frequency bands and its operating frequency. Thus, it was difficult to achieve a frequency band above 100 gigahertz.
To overcome these challenges, the three students introduced ultra-low noise signal generation technology that can support high-order modulation technologies. This technology is expected to contribute to increasing the price competitiveness and density of 6G communication chips that will be used in the future.
5G just got started in 2020 and still has long way to go for full commercialization. Nevertheless, many researchers have started preparing for 6G technology, targeting 2030 since a new cellular communication appears in every other decade.
Professor Choi said, “Generating ultra-high frequency signals in bands above 100 GHz with highly accurate timing is one of the key technologies for implementing 6G communication hardware. Our research is significant for the development of the world’s first semiconductor chip that will use the CMOS process to achieve noise performance of less than 80fs in a frequency band above 100 GHz.”
The team members plan to work as circuit designers in Korean semiconductor companies after graduation. “We will continue to research the development of signal generators on the topic of award-winning 6G. We would like to continue our research on high-speed circuit designs such as ultra-fast analog-to-digital converters,” Park added.
2021.11.30 View 10296
A Team of Three PhD Candidates Wins the Korea Semiconductor Design Contest
“We felt a sense of responsibility to help the nation advance its semiconductor design technology”
A CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor)-based “ultra-low noise signal chip” for 6G communications designed by three PhD candidates at the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering won the Presidential Award at the 22nd Korea Semiconductor Design Contest.
The winners are PhD candidates Sun-Eui Park, Yoon-Seo Cho, and Ju-Eun Bang from the Integrated Circuits and System Lab run by Professor Jaehyouk Choi. The contest, which is hosted by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy and the Korea Semiconductors Industry Association, is one of the top national semiconductor design contests for college students.
Park said the team felt a sense of responsibility to help advance semiconductor design technology in Korea when deciding to participate the contest. The team expressed deep gratitude to Professor Choi for guiding their research on 6G communications.
“Our colleagues from other labs and seniors who already graduated helped us a great deal, so we owe them a lot,” explained Park. Cho added that their hard work finally got recognized and that acknowledgement pushes her to move forward with her research. Meanwhile, Bang said she is delighted to see that many people seem to be interested in her research topic.
Research for 6G is attempting to reach 1 tera bps (Tbps), 50 times faster than 5G communications with transmission speeds of up to 20 gigabytes. In general, the wider the communication frequency band, the higher the data transmission speed. Thus, the use of frequency bands above 100 gigahertz is essential for delivering high data transmission speeds for 6G communications.
However, it remains a big challenge to make a precise benchmark signal that can be used as a carrier wave in a high frequency band. Despite the advantages of CMOS’s ultra-small and low-power design, it still has limitations at high frequency bands and its operating frequency. Thus, it was difficult to achieve a frequency band above 100 gigahertz.
To overcome these challenges, the three students introduced ultra-low noise signal generation technology that can support high-order modulation technologies. This technology is expected to contribute to increasing the price competitiveness and density of 6G communication chips that will be used in the future.
5G just got started in 2020 and still has long way to go for full commercialization. Nevertheless, many researchers have started preparing for 6G technology, targeting 2030 since a new cellular communication appears in every other decade.
Professor Choi said, “Generating ultra-high frequency signals in bands above 100 GHz with highly accurate timing is one of the key technologies for implementing 6G communication hardware. Our research is significant for the development of the world’s first semiconductor chip that will use the CMOS process to achieve noise performance of less than 80fs in a frequency band above 100 GHz.”
The team members plan to work as circuit designers in Korean semiconductor companies after graduation. “We will continue to research the development of signal generators on the topic of award-winning 6G. We would like to continue our research on high-speed circuit designs such as ultra-fast analog-to-digital converters,” Park added.
2021.11.30 View 10296 -
 Scientists Develop Wireless Networks that Allow Brain Circuits to Be Controlled Remotely through the Internet
Wireless implantable devices and IoT could manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world due to their minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility
A new study shows that researchers can remotely control the brain circuits of numerous animals simultaneously and independently through the internet. The scientists believe this newly developed technology can speed up brain research and various neuroscience studies to uncover basic brain functions as well as the underpinnings of various neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers at KAIST, Washington University in St. Louis, and the University of Colorado, Boulder, created a wireless ecosystem with its own wireless implantable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure to enable high-throughput neuroscience experiments over the internet. This innovative technology could enable scientists to manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world. The study was published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering on November 25
“This novel technology is highly versatile and adaptive. It can remotely control numerous neural implants and laboratory tools in real-time or in a scheduled way without direct human interactions,” said Professor Jae-Woong Jeong of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and a senior author of the study. “These wireless neural devices and equipment integrated with IoT technology have enormous potential for science and medicine.”
The wireless ecosystem only requires a mini-computer that can be purchased for under $45, which connects to the internet and communicates with wireless multifunctional brain probes or other types of conventional laboratory equipment using IoT control modules. By optimally integrating the versatility and modular construction of both unique IoT hardware and software within a single ecosystem, this wireless technology offers new applications that have not been demonstrated before by a single standalone technology. This includes, but is not limited to minimalistic hardware, global remote access, selective and scheduled experiments, customizable automation, and high-throughput scalability.
“As long as researchers have internet access, they are able to trigger, customize, stop, validate, and store the outcomes of large experiments at any time and from anywhere in the world. They can remotely perform large-scale neuroscience experiments in animals deployed in multiple countries,” said one of the lead authors, Dr. Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado, Boulder. “The low cost of this system allows it to be easily adopted and can further fuel innovation across many laboratories,” Dr. Qazi added.
One of the significant advantages of this IoT neurotechnology is its ability to be mass deployed across the globe due to its minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility. Scientists across the world can quickly implement this technology within their existing laboratories with minimal budget concerns to achieve globally remote access, scalable experimental automation, or both, thus potentially reducing the time needed to unravel various neuroscientific challenges such as those associated with intractable neurological conditions.
Another senior author on the study, Professor Jordan McCall from the Department of Anesthesiology and Center for Clinical Pharmacology at Washington University in St. Louis, said this technology has the potential to change how basic neuroscience studies are performed. “One of the biggest limitations when trying to understand how the mammalian brain works is that we have to study these functions in unnatural conditions. This technology brings us one step closer to performing important studies without direct human interaction with the study subjects.”
The ability to remotely schedule experiments moves toward automating these types of experiments. Dr. Kyle Parker, an instructor at Washington University in St. Louis and another lead author on the study added, “This experimental automation can potentially help us reduce the number of animals used in biomedical research by reducing the variability introduced by various experimenters. This is especially important given our moral imperative to seek research designs that enable this reduction.”
The researchers believe this wireless technology may open new opportunities for many applications including brain research, pharmaceuticals, and telemedicine to treat diseases in the brain and other organs remotely. This remote automation technology could become even more valuable when many labs need to shut down, such as during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This work was supported by grants from the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the United States National Institute of Health, and Oak Ridge Associated Universities.
-PublicationRaza Qazi, Kyle Parker, Choong Yeon Kim, Jordan McCall, Jae-Woong Jeong et al. “Scalable and modular wireless-network infrastructure for large-scale behavioral neuroscience,” Nature Biomedical Engineering, November 25 2021 (doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00814-w)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Woong JeongBio-Integrated Electronics and Systems LabSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.11.29 View 16828
Scientists Develop Wireless Networks that Allow Brain Circuits to Be Controlled Remotely through the Internet
Wireless implantable devices and IoT could manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world due to their minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility
A new study shows that researchers can remotely control the brain circuits of numerous animals simultaneously and independently through the internet. The scientists believe this newly developed technology can speed up brain research and various neuroscience studies to uncover basic brain functions as well as the underpinnings of various neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers at KAIST, Washington University in St. Louis, and the University of Colorado, Boulder, created a wireless ecosystem with its own wireless implantable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure to enable high-throughput neuroscience experiments over the internet. This innovative technology could enable scientists to manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world. The study was published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering on November 25
“This novel technology is highly versatile and adaptive. It can remotely control numerous neural implants and laboratory tools in real-time or in a scheduled way without direct human interactions,” said Professor Jae-Woong Jeong of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and a senior author of the study. “These wireless neural devices and equipment integrated with IoT technology have enormous potential for science and medicine.”
The wireless ecosystem only requires a mini-computer that can be purchased for under $45, which connects to the internet and communicates with wireless multifunctional brain probes or other types of conventional laboratory equipment using IoT control modules. By optimally integrating the versatility and modular construction of both unique IoT hardware and software within a single ecosystem, this wireless technology offers new applications that have not been demonstrated before by a single standalone technology. This includes, but is not limited to minimalistic hardware, global remote access, selective and scheduled experiments, customizable automation, and high-throughput scalability.
“As long as researchers have internet access, they are able to trigger, customize, stop, validate, and store the outcomes of large experiments at any time and from anywhere in the world. They can remotely perform large-scale neuroscience experiments in animals deployed in multiple countries,” said one of the lead authors, Dr. Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado, Boulder. “The low cost of this system allows it to be easily adopted and can further fuel innovation across many laboratories,” Dr. Qazi added.
One of the significant advantages of this IoT neurotechnology is its ability to be mass deployed across the globe due to its minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility. Scientists across the world can quickly implement this technology within their existing laboratories with minimal budget concerns to achieve globally remote access, scalable experimental automation, or both, thus potentially reducing the time needed to unravel various neuroscientific challenges such as those associated with intractable neurological conditions.
Another senior author on the study, Professor Jordan McCall from the Department of Anesthesiology and Center for Clinical Pharmacology at Washington University in St. Louis, said this technology has the potential to change how basic neuroscience studies are performed. “One of the biggest limitations when trying to understand how the mammalian brain works is that we have to study these functions in unnatural conditions. This technology brings us one step closer to performing important studies without direct human interaction with the study subjects.”
The ability to remotely schedule experiments moves toward automating these types of experiments. Dr. Kyle Parker, an instructor at Washington University in St. Louis and another lead author on the study added, “This experimental automation can potentially help us reduce the number of animals used in biomedical research by reducing the variability introduced by various experimenters. This is especially important given our moral imperative to seek research designs that enable this reduction.”
The researchers believe this wireless technology may open new opportunities for many applications including brain research, pharmaceuticals, and telemedicine to treat diseases in the brain and other organs remotely. This remote automation technology could become even more valuable when many labs need to shut down, such as during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This work was supported by grants from the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the United States National Institute of Health, and Oak Ridge Associated Universities.
-PublicationRaza Qazi, Kyle Parker, Choong Yeon Kim, Jordan McCall, Jae-Woong Jeong et al. “Scalable and modular wireless-network infrastructure for large-scale behavioral neuroscience,” Nature Biomedical Engineering, November 25 2021 (doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00814-w)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Woong JeongBio-Integrated Electronics and Systems LabSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.11.29 View 16828 -
 Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s Team Wins the Best Paper and the Methods Recognition Awards at the ACM CSCW
A research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee at the School of Electrical Engineering won the Best Paper Award and the Methods Recognition Award from ACM CSCW (International Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing) 2021 for their paper “Reflect, not Regret: Understanding Regretful Smartphone Use with App Feature-Level Analysis”.
Founded in 1986, CSCW has been a premier conference on HCI (Human Computer Interaction) and Social Computing. This year, 340 full papers were presented and the best paper awards are given to the top 1% papers of the submitted. Methods Recognition, which is a new award, is given “for strong examples of work that includes well developed, explained, or implemented methods, and methodological innovation.”
Hyunsung Cho (KAIST alumus and currently a PhD candidate at Carnegie Mellon University), Daeun Choi (KAIST undergraduate researcher), Donghwi Kim (KAIST PhD Candidate), Wan Ju Kang (KAIST PhD Candidate), and Professor Eun Kyoung Choe (University of Maryland and KAIST alumna) collaborated on this research.
The authors developed a tool that tracks and analyzes which features of a mobile app (e.g., Instagram’s following post, following story, recommended post, post upload, direct messaging, etc.) are in use based on a smartphone’s User Interface (UI) layout. Utilizing this novel method, the authors revealed which feature usage patterns result in regretful smartphone use.
Professor Lee said, “Although many people enjoy the benefits of smartphones, issues have emerged from the overuse of smartphones. With this feature level analysis, users can reflect on their smartphone usage based on finer grained analysis and this could contribute to digital wellbeing.”
2021.11.22 View 8807
Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s Team Wins the Best Paper and the Methods Recognition Awards at the ACM CSCW
A research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee at the School of Electrical Engineering won the Best Paper Award and the Methods Recognition Award from ACM CSCW (International Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing) 2021 for their paper “Reflect, not Regret: Understanding Regretful Smartphone Use with App Feature-Level Analysis”.
Founded in 1986, CSCW has been a premier conference on HCI (Human Computer Interaction) and Social Computing. This year, 340 full papers were presented and the best paper awards are given to the top 1% papers of the submitted. Methods Recognition, which is a new award, is given “for strong examples of work that includes well developed, explained, or implemented methods, and methodological innovation.”
Hyunsung Cho (KAIST alumus and currently a PhD candidate at Carnegie Mellon University), Daeun Choi (KAIST undergraduate researcher), Donghwi Kim (KAIST PhD Candidate), Wan Ju Kang (KAIST PhD Candidate), and Professor Eun Kyoung Choe (University of Maryland and KAIST alumna) collaborated on this research.
The authors developed a tool that tracks and analyzes which features of a mobile app (e.g., Instagram’s following post, following story, recommended post, post upload, direct messaging, etc.) are in use based on a smartphone’s User Interface (UI) layout. Utilizing this novel method, the authors revealed which feature usage patterns result in regretful smartphone use.
Professor Lee said, “Although many people enjoy the benefits of smartphones, issues have emerged from the overuse of smartphones. With this feature level analysis, users can reflect on their smartphone usage based on finer grained analysis and this could contribute to digital wellbeing.”
2021.11.22 View 8807 -
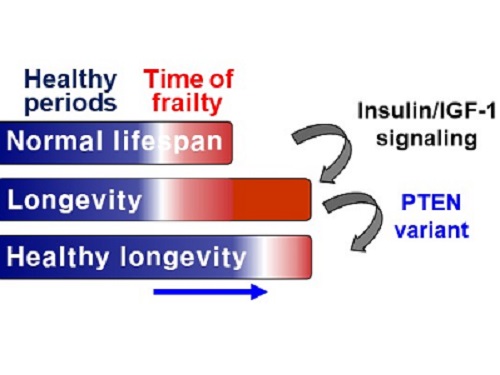 A Genetic Change for Achieving a Long and Healthy Life
Researchers identified a single amino acid change in the tumor suppressor protein in PTEN that extends healthy periods while maintaining longevity
Living a long, healthy life is everyone’s wish, but it is not an easy one to achieve. Many aging studies are developing strategies to increase health spans, the period of life spent with good health, without chronic diseases and disabilities. Researchers at KAIST presented new insights for improving the health span by just regulating the activity of a protein.
A research group under Professor Seung-Jae V. Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences identified a single amino acid change in the tumor suppressor protein phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) that dramatically extends healthy periods while maintaining longevity. This study highlights the importance of the well-conserved tumor suppressor protein PTEN in health span regulation, which can be targeted to develop therapies for promoting healthy longevity in humans. The research was published in Nature Communications on September 24, 2021.
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) signaling (IIS) is one of the evolutionarily conserved aging-modulatory pathways present in life forms ranging from tiny roundworms to humans. The proper reduction of IIS leads to longevity in animals but often causes defects in multiple health parameters including impaired motility, reproduction, and growth.
The research team found that a specific amino acid change in the PTEN protein improves health status while retaining the longevity conferred by reduced IIS. They used the roundworm C. elegans, an excellent model animal that has been widely used for aging research, mainly because of its very short normal lifespan of about two to three weeks. The PTEN protein is a phosphatase that removes phosphate from lipids as well as proteins. Interestingly, the newly identified amino acid change delicately recalibrated the IIS by partially maintaining protein phosphatase activity while reducing lipid phosphatase activity.
As a result, the amino acid change in the PTEN protein maintained the activity of the longevity-promoting transcription factor Forkhead Box O (FOXO) protein while restricting the detrimental upregulation of another transcription factor, NRF2, leading to long and healthy life in animals with reduced IIS.
Professor Lee said, “Our study raises the exciting possibility of simultaneously promoting longevity and health in humans by slightly tweaking the activity of one protein, PTEN.”
This work was supported by the MInistry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication:Hae-Eun H. Park, Wooseon Hwang, Seokjin Ham, Eunah Kim, Ozlem Altintas, Sangsoon Park, Heehwa G. Son, Yujin Lee, Dongyeop Lee, Won Do Heo, and Seung-Jae V. Lee. 2021. “A PTEN variant uncouples longevity from impaired fitness in Caenorhabditis elegans with reduced insulin/IGF-1 signaling,” Nature Communications, 12(1), 5631. (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25920-w)
-ProfileProfessor Seung-Jae V. LeeMolecular Genetics of Aging LaboratoryDepartment of Biological Sciences KAIST
2021.11.19 View 9566
A Genetic Change for Achieving a Long and Healthy Life
Researchers identified a single amino acid change in the tumor suppressor protein in PTEN that extends healthy periods while maintaining longevity
Living a long, healthy life is everyone’s wish, but it is not an easy one to achieve. Many aging studies are developing strategies to increase health spans, the period of life spent with good health, without chronic diseases and disabilities. Researchers at KAIST presented new insights for improving the health span by just regulating the activity of a protein.
A research group under Professor Seung-Jae V. Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences identified a single amino acid change in the tumor suppressor protein phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) that dramatically extends healthy periods while maintaining longevity. This study highlights the importance of the well-conserved tumor suppressor protein PTEN in health span regulation, which can be targeted to develop therapies for promoting healthy longevity in humans. The research was published in Nature Communications on September 24, 2021.
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) signaling (IIS) is one of the evolutionarily conserved aging-modulatory pathways present in life forms ranging from tiny roundworms to humans. The proper reduction of IIS leads to longevity in animals but often causes defects in multiple health parameters including impaired motility, reproduction, and growth.
The research team found that a specific amino acid change in the PTEN protein improves health status while retaining the longevity conferred by reduced IIS. They used the roundworm C. elegans, an excellent model animal that has been widely used for aging research, mainly because of its very short normal lifespan of about two to three weeks. The PTEN protein is a phosphatase that removes phosphate from lipids as well as proteins. Interestingly, the newly identified amino acid change delicately recalibrated the IIS by partially maintaining protein phosphatase activity while reducing lipid phosphatase activity.
As a result, the amino acid change in the PTEN protein maintained the activity of the longevity-promoting transcription factor Forkhead Box O (FOXO) protein while restricting the detrimental upregulation of another transcription factor, NRF2, leading to long and healthy life in animals with reduced IIS.
Professor Lee said, “Our study raises the exciting possibility of simultaneously promoting longevity and health in humans by slightly tweaking the activity of one protein, PTEN.”
This work was supported by the MInistry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication:Hae-Eun H. Park, Wooseon Hwang, Seokjin Ham, Eunah Kim, Ozlem Altintas, Sangsoon Park, Heehwa G. Son, Yujin Lee, Dongyeop Lee, Won Do Heo, and Seung-Jae V. Lee. 2021. “A PTEN variant uncouples longevity from impaired fitness in Caenorhabditis elegans with reduced insulin/IGF-1 signaling,” Nature Communications, 12(1), 5631. (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25920-w)
-ProfileProfessor Seung-Jae V. LeeMolecular Genetics of Aging LaboratoryDepartment of Biological Sciences KAIST
2021.11.19 View 9566 -
 Nanoscale Self-Assembling Salt-Crystal ‘Origami’ Balls Envelop Liquids
Mechanical engineers have devised a ‘crystal capillary origami’ technique where salt crystals spontaneously encapsulate liquid droplets
Researchers have developed a technique whereby they can spontaneously encapsulate microscopic droplets of water and oil emulsion in a tiny sphere made of salt crystals—sort of like a minute, self-constructing origami soccer ball filled with liquid. The process, which they are calling ‘crystal capillary origami,’ could be used in a range of fields from more precise drug delivery to nanoscale medical devices.The technique is described in a paper appearing in the journal Nanoscale on September 21.
Capillary action, or ‘capillarity,’ will be familiar to most people as the way that water or other liquids can move up narrow tubes or other porous materials seemingly in defiance of gravity (for example within the vascular systems of plants, or even more simply, the drawing up of paint between the hairs of a paintbrush). This effect is due to the forces of cohesion (the tendency of a liquid’s molecules to stick together), which results in surface tension, and adhesion (their tendency to stick to the surface of other substances). The strength of the capillarity depends on the chemistry of the liquid, the chemistry of the porous material, and on the other forces acting on them both. For example, a liquid with lower surface tension than water would not be able to hold up a water strider insect.
Less well known is a related phenomenon, elasto-capillarity, that takes advantage of the relationship between capillarity and the elasticity of a very tiny flat sheet of a solid material. In certain circumstances, the capillary forces can overcome the elastic bending resistance of the sheet.
This relationship can be exploited to create ‘capillary origami,’ or three-dimensional structures. When a liquid droplet is placed on the flat sheet, the latter can spontaneously encapsulate the former due to surface tension. Capillary origami can take on other forms including wrinkling, buckling, or self-folding into other shapes. The specific geometrical shape that the 3D capillary origami structure ends up taking is determined by both the chemistry of the flat sheet and that of the liquid, and by carefully designing the shape and size of the sheet.
There is one big problem with these small devices, however. “These conventional self-assembled origami structures cannot be completely spherical and will always have discontinuous boundaries, or what you might call ‘edges,’ as a result of the original two-dimensional shape of the sheet,” said Kwangseok Park, a lead researcher on the project. He added, “These edges could turn out to be future defects with the potential for failure in the face of increased stress.” Non-spherical particles are also known to be more disadvantageous than spherical particles in terms of cellular uptake.
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering explained, “This is why researchers have long been on the hunt for substances that could produce a fully spherical capillary origami structure.”
The authors of the study have demonstrated such an origami sphere for the first time. They showed how instead of a flat sheet, the growth of salt-crystals can perform capillary origami action in a similar manner. What they call ‘crystal capillary origami’ spontaneously constructs a smooth spherical shell capsule from these same surface tension effects, but now the spontaneous encapsulation of a liquid is determined by the elasto-capillary conditions of growing crystals.
Here, the term ‘salt’ refers to a compound of one positively charged ion and another negatively charged. Table salt, or sodium chloride, is just one example of a salt. The researchers used four other salts: calcium propionate, sodium salicylate, calcium nitrate tetrahydrate, and sodium bicarbonate to envelop a water-oil emulsion. Normally, a salt such as sodium chloride has a cubical crystal structure, but these four salts form plate-like structures as crystallites or ‘grains’ (the microscopic shape that forms when a crystal first starts to grow) instead. These plates then self-assemble into perfect spheres.
Using scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction analysis, they investigated the mechanism of such formation and concluded that it was ‘Laplace pressure’ that drives the crystallite plates to cover the emulsion surface. Laplace pressure describes the pressure difference between the interior and exterior of a curved surface caused by the surface tension at the interface between the two substances, in this case between the salt water and the oil.
The researchers hope that these self-assembling nanostructures can be used for encapsulation applications in a range of sectors, from the food industry and cosmetics to drug delivery and even tiny medical devices.
-Publication
Kwangseok Park, Hyoungsoo Kim “Crystal capillary origami capsule with self-assembled nanostructure,” Nanoscale, 13(35), 14656-14665 (DOI: 10.1039/d1nr02456f)
-Profile
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim
Fluid and Interface Laboratory
http://fil.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Mechanical Engineering
KAIST
2021.11.04 View 10677
Nanoscale Self-Assembling Salt-Crystal ‘Origami’ Balls Envelop Liquids
Mechanical engineers have devised a ‘crystal capillary origami’ technique where salt crystals spontaneously encapsulate liquid droplets
Researchers have developed a technique whereby they can spontaneously encapsulate microscopic droplets of water and oil emulsion in a tiny sphere made of salt crystals—sort of like a minute, self-constructing origami soccer ball filled with liquid. The process, which they are calling ‘crystal capillary origami,’ could be used in a range of fields from more precise drug delivery to nanoscale medical devices.The technique is described in a paper appearing in the journal Nanoscale on September 21.
Capillary action, or ‘capillarity,’ will be familiar to most people as the way that water or other liquids can move up narrow tubes or other porous materials seemingly in defiance of gravity (for example within the vascular systems of plants, or even more simply, the drawing up of paint between the hairs of a paintbrush). This effect is due to the forces of cohesion (the tendency of a liquid’s molecules to stick together), which results in surface tension, and adhesion (their tendency to stick to the surface of other substances). The strength of the capillarity depends on the chemistry of the liquid, the chemistry of the porous material, and on the other forces acting on them both. For example, a liquid with lower surface tension than water would not be able to hold up a water strider insect.
Less well known is a related phenomenon, elasto-capillarity, that takes advantage of the relationship between capillarity and the elasticity of a very tiny flat sheet of a solid material. In certain circumstances, the capillary forces can overcome the elastic bending resistance of the sheet.
This relationship can be exploited to create ‘capillary origami,’ or three-dimensional structures. When a liquid droplet is placed on the flat sheet, the latter can spontaneously encapsulate the former due to surface tension. Capillary origami can take on other forms including wrinkling, buckling, or self-folding into other shapes. The specific geometrical shape that the 3D capillary origami structure ends up taking is determined by both the chemistry of the flat sheet and that of the liquid, and by carefully designing the shape and size of the sheet.
There is one big problem with these small devices, however. “These conventional self-assembled origami structures cannot be completely spherical and will always have discontinuous boundaries, or what you might call ‘edges,’ as a result of the original two-dimensional shape of the sheet,” said Kwangseok Park, a lead researcher on the project. He added, “These edges could turn out to be future defects with the potential for failure in the face of increased stress.” Non-spherical particles are also known to be more disadvantageous than spherical particles in terms of cellular uptake.
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering explained, “This is why researchers have long been on the hunt for substances that could produce a fully spherical capillary origami structure.”
The authors of the study have demonstrated such an origami sphere for the first time. They showed how instead of a flat sheet, the growth of salt-crystals can perform capillary origami action in a similar manner. What they call ‘crystal capillary origami’ spontaneously constructs a smooth spherical shell capsule from these same surface tension effects, but now the spontaneous encapsulation of a liquid is determined by the elasto-capillary conditions of growing crystals.
Here, the term ‘salt’ refers to a compound of one positively charged ion and another negatively charged. Table salt, or sodium chloride, is just one example of a salt. The researchers used four other salts: calcium propionate, sodium salicylate, calcium nitrate tetrahydrate, and sodium bicarbonate to envelop a water-oil emulsion. Normally, a salt such as sodium chloride has a cubical crystal structure, but these four salts form plate-like structures as crystallites or ‘grains’ (the microscopic shape that forms when a crystal first starts to grow) instead. These plates then self-assemble into perfect spheres.
Using scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction analysis, they investigated the mechanism of such formation and concluded that it was ‘Laplace pressure’ that drives the crystallite plates to cover the emulsion surface. Laplace pressure describes the pressure difference between the interior and exterior of a curved surface caused by the surface tension at the interface between the two substances, in this case between the salt water and the oil.
The researchers hope that these self-assembling nanostructures can be used for encapsulation applications in a range of sectors, from the food industry and cosmetics to drug delivery and even tiny medical devices.
-Publication
Kwangseok Park, Hyoungsoo Kim “Crystal capillary origami capsule with self-assembled nanostructure,” Nanoscale, 13(35), 14656-14665 (DOI: 10.1039/d1nr02456f)
-Profile
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim
Fluid and Interface Laboratory
http://fil.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Mechanical Engineering
KAIST
2021.11.04 View 10677 -
 Hubo Professor Jun-Ho Oh Donates Startup Shares Worth 5 Billion KRW
Rainbow Robotics stock used to endow the development fund
Emeritus Professor Jun-Ho Oh, who developed the 2015 DARPA Challenge winning humanoid robot DRC-Hubo, donated 5 billion KRW on October 25 during a ceremony held at the KAIST campus in Daejeon.
Professor Oh donated his 20% share (400 shares) of his startup Rainbow Robotics, which was established in 2011. Rainbow Robotics was listed on the KOSDAQ this February. The 400 shares were converted to 200,000 shares with a value of approximately 5 billion KRW when listed this year.
KAIST sold the stocks and endowed the Jun-Ho Oh Fund, which will be used for the development of the university. He was the 39th faculty member who launched a startup with technology from his lab and became the biggest faculty entrepreneur donor.
“I have received huge support and funding for my research. Fortunately, the research had a good result and led to the startup. Now I am very delighted to pay back the university. I feel that I have played a part in building the school’s startup ecosystem and creating a virtuous circle,” said Professor Oh during the ceremony.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee declared, “Professor Oh has been a very impressive exemplary model for our aspiring faculty and student tech startups. We will spare no effort to support startups at KAIST.”
Professor Oh, who retired from the Department of Mechanical Engineering last year, now serves as the CTO at Rainbow Robotics. The company is developing humanoid bipedal robots and collaborative robots, and advancing robot technology including parts for astronomical observations.
Professor Hae-Won Park and Professor Je Min Hwangbo, who are now responsible for the Hubo Lab, also joined the ceremony along with employees of Rainbow Robotics.
2021.10.26 View 10608
Hubo Professor Jun-Ho Oh Donates Startup Shares Worth 5 Billion KRW
Rainbow Robotics stock used to endow the development fund
Emeritus Professor Jun-Ho Oh, who developed the 2015 DARPA Challenge winning humanoid robot DRC-Hubo, donated 5 billion KRW on October 25 during a ceremony held at the KAIST campus in Daejeon.
Professor Oh donated his 20% share (400 shares) of his startup Rainbow Robotics, which was established in 2011. Rainbow Robotics was listed on the KOSDAQ this February. The 400 shares were converted to 200,000 shares with a value of approximately 5 billion KRW when listed this year.
KAIST sold the stocks and endowed the Jun-Ho Oh Fund, which will be used for the development of the university. He was the 39th faculty member who launched a startup with technology from his lab and became the biggest faculty entrepreneur donor.
“I have received huge support and funding for my research. Fortunately, the research had a good result and led to the startup. Now I am very delighted to pay back the university. I feel that I have played a part in building the school’s startup ecosystem and creating a virtuous circle,” said Professor Oh during the ceremony.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee declared, “Professor Oh has been a very impressive exemplary model for our aspiring faculty and student tech startups. We will spare no effort to support startups at KAIST.”
Professor Oh, who retired from the Department of Mechanical Engineering last year, now serves as the CTO at Rainbow Robotics. The company is developing humanoid bipedal robots and collaborative robots, and advancing robot technology including parts for astronomical observations.
Professor Hae-Won Park and Professor Je Min Hwangbo, who are now responsible for the Hubo Lab, also joined the ceremony along with employees of Rainbow Robotics.
2021.10.26 View 10608