RNA
-
 Artificial Spore Production Technology Developed
The core technology needed in the development of ‘biosensors’ so crucial in diagnosing illnesses or pathogens was developed by Korean research team.
KAIST’s Professor Choi In Seung of the department of Chemistry developed the technology that allows for the production of Artificial Spore by selectively coating a live cell.
In the field of engineering the problem in developing the next generation bio sensor, the cell based sensor, was that it was difficult to keep a cell alive without division for a long time. Once a cell is taken out of the body, it will either divide or die easily.
Professor Choi’s research team mimicked the spore, which has the capability to survive harsh conditions without division, and chemically coated a live cell and artificially created a cell similar to that of a spore.
The physical and biological stabilities of the cell increased by coating an artificial shell over the yeast cell. The shell is composed with a protein similar to that of the protein that gives mussels its stickiness. In addition by controlling the thickness of the shell, the division rate of the yeast can be controlled.
Professor Choi commented that this technology will serve as the basis for the single cell based biosensor.
The research was conducted together with Professor Lee Hae Shin of KAIST department of Chemistry and Professor Jeong Taek Dong of Seoul National University’s department of Chemistry and was published as the cover paper of ‘Journal of the American Chemical Society’.
2011.04.01 View 14832
Artificial Spore Production Technology Developed
The core technology needed in the development of ‘biosensors’ so crucial in diagnosing illnesses or pathogens was developed by Korean research team.
KAIST’s Professor Choi In Seung of the department of Chemistry developed the technology that allows for the production of Artificial Spore by selectively coating a live cell.
In the field of engineering the problem in developing the next generation bio sensor, the cell based sensor, was that it was difficult to keep a cell alive without division for a long time. Once a cell is taken out of the body, it will either divide or die easily.
Professor Choi’s research team mimicked the spore, which has the capability to survive harsh conditions without division, and chemically coated a live cell and artificially created a cell similar to that of a spore.
The physical and biological stabilities of the cell increased by coating an artificial shell over the yeast cell. The shell is composed with a protein similar to that of the protein that gives mussels its stickiness. In addition by controlling the thickness of the shell, the division rate of the yeast can be controlled.
Professor Choi commented that this technology will serve as the basis for the single cell based biosensor.
The research was conducted together with Professor Lee Hae Shin of KAIST department of Chemistry and Professor Jeong Taek Dong of Seoul National University’s department of Chemistry and was published as the cover paper of ‘Journal of the American Chemical Society’.
2011.04.01 View 14832 -
 KAIST Design Week 2011 Held
KAIST designated a week (from March 27th to April 2nd) as KAIST Design Week 2011 and will be hosting a series of international conferences on engineering designs.
The 21st CIRP Design Conference, the 6th International Conference on Axiomatic Design, and the 1st Design in Civil and Environmental Engineering Workshop will be held in Fusion hall in the KI Building from the 27th of March.
The CIRP Design Conference was held on the 27th and the 28th and annually provides an opportunity for researchers and industry developers to exchange information and knowledge.
The International Conference on Axiomatic Design was held on the 30th to the 31st and dealt with various presentations and discussions on the axiomatic design theory. The Axiomatic Design Theory was thought up by KAIST President Seo Nam Pyo and deals with analyzing the wants of the consumers and solves the problems associated with the product through making altercations on the product design.
Last The Design in Civil and environmental Engineering Workshop will be held on the 1st and 2nd of April and will deal with sustainable city design and development.
The Design Week will also be featuring humanoid robot HUBO, the Online Electric Vehicle that can charge its battery wirelessly, and the Mobile Harbor, and therefore show off KAIST’s achievements.
2011.04.01 View 11392
KAIST Design Week 2011 Held
KAIST designated a week (from March 27th to April 2nd) as KAIST Design Week 2011 and will be hosting a series of international conferences on engineering designs.
The 21st CIRP Design Conference, the 6th International Conference on Axiomatic Design, and the 1st Design in Civil and Environmental Engineering Workshop will be held in Fusion hall in the KI Building from the 27th of March.
The CIRP Design Conference was held on the 27th and the 28th and annually provides an opportunity for researchers and industry developers to exchange information and knowledge.
The International Conference on Axiomatic Design was held on the 30th to the 31st and dealt with various presentations and discussions on the axiomatic design theory. The Axiomatic Design Theory was thought up by KAIST President Seo Nam Pyo and deals with analyzing the wants of the consumers and solves the problems associated with the product through making altercations on the product design.
Last The Design in Civil and environmental Engineering Workshop will be held on the 1st and 2nd of April and will deal with sustainable city design and development.
The Design Week will also be featuring humanoid robot HUBO, the Online Electric Vehicle that can charge its battery wirelessly, and the Mobile Harbor, and therefore show off KAIST’s achievements.
2011.04.01 View 11392 -
 A Light Weight, Energy Effcient Household Polysomnography (PSG) System Developed
A smart ‘household polysomnography (PSG) system’ was developed by domestic research team.
Professor Yoo Hui Joon and his research team of KAIST’s department of Electricity and Electronic Engineering successfully developed a PSG system that is light weight and has high performance levels. The conventional PSG systems were complex with numerous lines and wires.
The PSG is used to monitor biological signals during sleep and the monitored results are used to diagnose and cure sleep-related illnesses and disorders. However because of restrictions like the size of the machine, impurities, and the change in environment, multiple trials over several days were required to obtain accurate data.
The system developed by the research team is lighter than a q-tip so as to not disturb the patient’s sleep. It also has Intelligent Circuit (IC) that detects when sensors come detached and automatically replaces the sensor with another sensor thereby allowing continual monitoring of the user.
A low-power consuming circuit was implemented allowing the entire system to run continuously on a single coin battery for 10 hours which effectively decreased the weight of the system and simultaneously allows for uninterrupted monitoring of the user over the entire sleep cycle.
Even a remote diagnosis system can be implemented. The user will don the PSG and sleep at home, ensuring that a normal heat beat rate, brain waves, breathing, etc. will be monitored. The data procured overnight can be sent to the experts online who will be able to diagnose remotely.
The research team plans on performing research in cooperation with the KAIST hospital and U-Healthcare research.
The research result is winning worldwide rave. The system was announced in the International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) and was published in ISSCC magazine and in Japan’s NIKKEI Electronics January edition.
2011.03.25 View 13703
A Light Weight, Energy Effcient Household Polysomnography (PSG) System Developed
A smart ‘household polysomnography (PSG) system’ was developed by domestic research team.
Professor Yoo Hui Joon and his research team of KAIST’s department of Electricity and Electronic Engineering successfully developed a PSG system that is light weight and has high performance levels. The conventional PSG systems were complex with numerous lines and wires.
The PSG is used to monitor biological signals during sleep and the monitored results are used to diagnose and cure sleep-related illnesses and disorders. However because of restrictions like the size of the machine, impurities, and the change in environment, multiple trials over several days were required to obtain accurate data.
The system developed by the research team is lighter than a q-tip so as to not disturb the patient’s sleep. It also has Intelligent Circuit (IC) that detects when sensors come detached and automatically replaces the sensor with another sensor thereby allowing continual monitoring of the user.
A low-power consuming circuit was implemented allowing the entire system to run continuously on a single coin battery for 10 hours which effectively decreased the weight of the system and simultaneously allows for uninterrupted monitoring of the user over the entire sleep cycle.
Even a remote diagnosis system can be implemented. The user will don the PSG and sleep at home, ensuring that a normal heat beat rate, brain waves, breathing, etc. will be monitored. The data procured overnight can be sent to the experts online who will be able to diagnose remotely.
The research team plans on performing research in cooperation with the KAIST hospital and U-Healthcare research.
The research result is winning worldwide rave. The system was announced in the International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) and was published in ISSCC magazine and in Japan’s NIKKEI Electronics January edition.
2011.03.25 View 13703 -
 Waking Up Is Hard to Do: Scientists have discovered a new mechanism in the core gears of the circadian clock.
The US News & World Report released an article (Feb. 18, 2011) on KAIST’s research collaboration with Northwestern University in the US to identify a gene that regulates the rhythm of a fruit fly’s circadian clock, which may be applied to explain human’s sleep-wake cycle. The research result was published February 17 in the journal Nature.
For the link of the US News & World Report article, please go to the following link:
http://www.usnews.com/science/articles/2011/02/18/waking-up-is-hard-to-do_print.html
2011.02.21 View 11925
Waking Up Is Hard to Do: Scientists have discovered a new mechanism in the core gears of the circadian clock.
The US News & World Report released an article (Feb. 18, 2011) on KAIST’s research collaboration with Northwestern University in the US to identify a gene that regulates the rhythm of a fruit fly’s circadian clock, which may be applied to explain human’s sleep-wake cycle. The research result was published February 17 in the journal Nature.
For the link of the US News & World Report article, please go to the following link:
http://www.usnews.com/science/articles/2011/02/18/waking-up-is-hard-to-do_print.html
2011.02.21 View 11925 -
 The 40th Anniversary of the Establishment of KAIST Commemoration Held
KAIST, aspiring to become the best Science and Technology University, has turned 40.
KAIST held the commemoration ceremony for the 40th Anniversary of the Establishment of KAIST in the auditorium.
Five awards (Scholar, Creative Lecture, Excellence in Lecture, International Cooperation, Experiment) were given to Professors Kim Eun Jun and Walton Jones (department of Biology), Professor Abigail Shin (department of Humanities and Social Sciences), Professor Shin Seong Chul (department of Physics), and Professor Lee Sang Yeop (department of Biological Chemical Engineering). Each recipient received a prize of five million won.
Professor Song Joon Hwa (department of Computer Sciences) received the ‘New Knowledge Award’ in recognition of his development of the Orchestrator Mobile platform. The new platform is different from Android or the IOS platform in that it allows a fluid relationship to be formed between the smartphone and the user.
KAIST also showed off its new emblem.
The emblem consists of a star which represents the KAIST’s goals of becoming the world leader, of training leaders, the center point, and hope. The main keywords are: ‘Leadership’, ‘Premium’, ‘Scientific’, and ‘Humanity’.
KAIST plans on having various events from May 9th when there will be the Vision Declaration.
2011.02.21 View 17172
The 40th Anniversary of the Establishment of KAIST Commemoration Held
KAIST, aspiring to become the best Science and Technology University, has turned 40.
KAIST held the commemoration ceremony for the 40th Anniversary of the Establishment of KAIST in the auditorium.
Five awards (Scholar, Creative Lecture, Excellence in Lecture, International Cooperation, Experiment) were given to Professors Kim Eun Jun and Walton Jones (department of Biology), Professor Abigail Shin (department of Humanities and Social Sciences), Professor Shin Seong Chul (department of Physics), and Professor Lee Sang Yeop (department of Biological Chemical Engineering). Each recipient received a prize of five million won.
Professor Song Joon Hwa (department of Computer Sciences) received the ‘New Knowledge Award’ in recognition of his development of the Orchestrator Mobile platform. The new platform is different from Android or the IOS platform in that it allows a fluid relationship to be formed between the smartphone and the user.
KAIST also showed off its new emblem.
The emblem consists of a star which represents the KAIST’s goals of becoming the world leader, of training leaders, the center point, and hope. The main keywords are: ‘Leadership’, ‘Premium’, ‘Scientific’, and ‘Humanity’.
KAIST plans on having various events from May 9th when there will be the Vision Declaration.
2011.02.21 View 17172 -
 KAIST establishes Indoor Location Recognition Industrial-Educational Research Center
KAIST has signed the memorandum of understanding on the 15th of February for the establishment of ‘KTNET-KAIST Industrial-Educational Research Center’ (Head of Center, Professor Han Dong Soo of department of Computer Sciences). Korea International Trade Association and KTNET will be working with KAIST to develop wi-fi based indoor location recognition service and applications of the developed technology.
The memorandum of understanding states that KTNET and Korea International Trade Association will be allowed access to the technology KAIST has in order to obtain competitive advantage in the field of location recognition.
In addition, KAIST will continue on making technological advances in the field of wi-fi based indoor location recognition for the next 5 years, develop new core technologies and applications, along with the export of related technologies abroad, under the support of the KITA and KTNET.
The KTNET-KAIST research center is special in that it has been derived off of the technology developed for the hosting of the G20 Global Summit. Last year, KAIST, KITA, and KTNET developed a wi-fi based Coex indoor navigation system and called it ‘myCoex’ and released it to the public in tandem with hosting G20 Summit.
‘myCoex’ application was the first of its kind in the world to provide wi-fi based indoor navigation system without problems. Despite ‘myCoex’ only useable within Coex, over 150,000 users have downloaded the application.
The research center plans on developing the necessary technology that will allow the application of such an app like ‘mCoex’ to large indoor spaces like Incheon International Airport, subway, shopping malls, and etc.
In addition the addition of a social commerce service to ‘myCoex’ is being looked into which will be the marriage of navigation services and social commerce services.
The KTNET KAIST research center will develop a wi-fi based indoor location recognition service platform that can be widely used and open it so that numerous other developers can develop personalized services.
Han Dong Soo Head od Center commented, “The wi-fi based indoor location recognition technology is still found wanting in its accuracy, response time, and energy consumption efficiency making further research imperative in this particular field. The establishment of KTNET-KAIST research center has created a research friendly environment and KAIST will do its utmost to become the leader in the field”.
2011.02.21 View 13818
KAIST establishes Indoor Location Recognition Industrial-Educational Research Center
KAIST has signed the memorandum of understanding on the 15th of February for the establishment of ‘KTNET-KAIST Industrial-Educational Research Center’ (Head of Center, Professor Han Dong Soo of department of Computer Sciences). Korea International Trade Association and KTNET will be working with KAIST to develop wi-fi based indoor location recognition service and applications of the developed technology.
The memorandum of understanding states that KTNET and Korea International Trade Association will be allowed access to the technology KAIST has in order to obtain competitive advantage in the field of location recognition.
In addition, KAIST will continue on making technological advances in the field of wi-fi based indoor location recognition for the next 5 years, develop new core technologies and applications, along with the export of related technologies abroad, under the support of the KITA and KTNET.
The KTNET-KAIST research center is special in that it has been derived off of the technology developed for the hosting of the G20 Global Summit. Last year, KAIST, KITA, and KTNET developed a wi-fi based Coex indoor navigation system and called it ‘myCoex’ and released it to the public in tandem with hosting G20 Summit.
‘myCoex’ application was the first of its kind in the world to provide wi-fi based indoor navigation system without problems. Despite ‘myCoex’ only useable within Coex, over 150,000 users have downloaded the application.
The research center plans on developing the necessary technology that will allow the application of such an app like ‘mCoex’ to large indoor spaces like Incheon International Airport, subway, shopping malls, and etc.
In addition the addition of a social commerce service to ‘myCoex’ is being looked into which will be the marriage of navigation services and social commerce services.
The KTNET KAIST research center will develop a wi-fi based indoor location recognition service platform that can be widely used and open it so that numerous other developers can develop personalized services.
Han Dong Soo Head od Center commented, “The wi-fi based indoor location recognition technology is still found wanting in its accuracy, response time, and energy consumption efficiency making further research imperative in this particular field. The establishment of KTNET-KAIST research center has created a research friendly environment and KAIST will do its utmost to become the leader in the field”.
2011.02.21 View 13818 -
 Soyeon's Odyssey by Space Travel, Feb. 1, 2011
Soyeon Yi, an alumna of KAIST who joined the Soyuz TMA-12 mission to the International Space Station in 2008 and successfully returned to the Earth after completion of her mission. She is often cited as the first Korean astronaut who had spaceflight. She recently had an interview with an Australian based online newspaper that publishes space related news stories. For the interview, please go to the link.
http://www.space-travel.com/reports/Soyeon_Odyssey_999.html
2011.02.02 View 11453
Soyeon's Odyssey by Space Travel, Feb. 1, 2011
Soyeon Yi, an alumna of KAIST who joined the Soyuz TMA-12 mission to the International Space Station in 2008 and successfully returned to the Earth after completion of her mission. She is often cited as the first Korean astronaut who had spaceflight. She recently had an interview with an Australian based online newspaper that publishes space related news stories. For the interview, please go to the link.
http://www.space-travel.com/reports/Soyeon_Odyssey_999.html
2011.02.02 View 11453 -
 Korean researchers reveal new sea defense model by EurekAlert
The Journal of Defense Modeling and Simulation, a peer review journal devoted to advancing the practice, science and art of modeling and simulation that relate to military and defense purposes.
The SAGE Publication that issues the journal released a press release on January 18, 2011, announcing that KAIST researchers in collaboration with other intuitions in Korea devised “improved methods to model underwater warfare, which could aid future decisions about weapons and defense purchases.” Details of the article follow below: http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2011-01/sp-krr011811.php
2011.01.19 View 10484
Korean researchers reveal new sea defense model by EurekAlert
The Journal of Defense Modeling and Simulation, a peer review journal devoted to advancing the practice, science and art of modeling and simulation that relate to military and defense purposes.
The SAGE Publication that issues the journal released a press release on January 18, 2011, announcing that KAIST researchers in collaboration with other intuitions in Korea devised “improved methods to model underwater warfare, which could aid future decisions about weapons and defense purchases.” Details of the article follow below: http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2011-01/sp-krr011811.php
2011.01.19 View 10484 -
 Success in differentiating Functional Vascular Progenitor Cells (VPC)
KAIST’s Professor Han Yong Man successfully differentiated vascular progenitor cells from human embryonic stem cells and reversed differentiated stem cells.
The research went beyond the current method of synthesis of embryonic body or mice cell ball culture and used the careful alteration of signal transmission system of the human embryonic stem cells to differentiate the formation of vascular progenitor cells.
The team controlled the MEK/ERK and BMP signal transmission system that serves an important role in the self replication of human embryonic stem cells and successfully differentiated 20% of the cells experimented on to vascular progenitor cells.
The vascular progenitor cells produced with such a method successfully differentiated into cells forming the endodermis of the blood vessel, vascular smooth muscle cells and hematopoietic cells in an environment outside of the human body and also successfully differentiated into blood vessels in nude mice.
In addition, the vascular progenitor cell derived from human embryonic cells successfully formed blood vessels or secreted vascular growth factors and increased the blood flow and the necrosis of blood vessels when injected into an animal with limb ischemic illness.
The research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, 21st Century Frontier Research and Development Institution’s Cell Application Research Department and Professor Ko Kyu Young (KAIST), Professor Choi Chul Hee (KAIST), Professor Jeong Hyung Min (Cha Medical School) and Doctor Jo Lee Sook (Researcher in Korea Bio Engineering Institute) participated in it.
The results of the research was published as the cover paper of the September edition of “Blood (IF:10.55)”, the American Blood Journal and has been patented domestically and has finished registration of foreign PCT.
The results of the experiment opened the possibility of providing a patient specific cure using stem cells in the field of blood vessel illness.
2011.01.18 View 16257
Success in differentiating Functional Vascular Progenitor Cells (VPC)
KAIST’s Professor Han Yong Man successfully differentiated vascular progenitor cells from human embryonic stem cells and reversed differentiated stem cells.
The research went beyond the current method of synthesis of embryonic body or mice cell ball culture and used the careful alteration of signal transmission system of the human embryonic stem cells to differentiate the formation of vascular progenitor cells.
The team controlled the MEK/ERK and BMP signal transmission system that serves an important role in the self replication of human embryonic stem cells and successfully differentiated 20% of the cells experimented on to vascular progenitor cells.
The vascular progenitor cells produced with such a method successfully differentiated into cells forming the endodermis of the blood vessel, vascular smooth muscle cells and hematopoietic cells in an environment outside of the human body and also successfully differentiated into blood vessels in nude mice.
In addition, the vascular progenitor cell derived from human embryonic cells successfully formed blood vessels or secreted vascular growth factors and increased the blood flow and the necrosis of blood vessels when injected into an animal with limb ischemic illness.
The research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, 21st Century Frontier Research and Development Institution’s Cell Application Research Department and Professor Ko Kyu Young (KAIST), Professor Choi Chul Hee (KAIST), Professor Jeong Hyung Min (Cha Medical School) and Doctor Jo Lee Sook (Researcher in Korea Bio Engineering Institute) participated in it.
The results of the research was published as the cover paper of the September edition of “Blood (IF:10.55)”, the American Blood Journal and has been patented domestically and has finished registration of foreign PCT.
The results of the experiment opened the possibility of providing a patient specific cure using stem cells in the field of blood vessel illness.
2011.01.18 View 16257 -
 Explanation for the polymerized nucleic acid enzyme's abnormal activation found
KAIST’s Professor Park Hyun Kyu of the Department of Bio Chemical Engineering revealed on the 23rd of December 2010 that his team had successfully developed the technology that uses the metal ions to control the abnormal activation of nucleic acids’ enzymes and using this, created a logic gate, which is a core technology in the field of future bio electrons.
The polymerized nucleic acid enzyme works to increase the synthesis of DNA and kicks into action only when the target DNA and primers form complimentary pairs (A and T, C and G).
Professor Park broke the common conception and found that it is possible for none complimentary pairs like T-T and C-C to initiate the activation of the enzyme and thus increase the nucleic acid production, given that there are certain metal ions present.
What Professor Park realized is that the enzymes mistake the uncomplimentary T-T and C-C pairs (with stabilized structures due to the bonding with mercury and silver ions) as being complimentary base pairs. Professor Park described this phenomenon as the “illusionary polymerase activity.”
The research team developed a logic gate based on the “illusionary polymerase activity’ phenomenon.” The logic gate paves the way to the development of future bio electron needed for bio computers and high performance memories.
Professor Park commented, “The research is an advancement of the previous research carried on about metal ions and nucleic acid synthesis. Our research is the first attempt at merging the concepts of the two previously separately carried out researches and can be adapted for testing presence of metal ions and development of a new single nucleotide polymorphic gene analysis technology.”
Professor Park added that, “Our research is a great stride in the field of nano scale electron element research as the results made possible the formation of accurate logic gates through relatively cost efficient and simple system designs.”
On a side note, the research was funded by Korea Research Foundation (Chairman: Park Chan Mo) and was selected as the cover paper for the December issue of ‘Angewandte Chemie International Edition’.
2011.01.18 View 13471
Explanation for the polymerized nucleic acid enzyme's abnormal activation found
KAIST’s Professor Park Hyun Kyu of the Department of Bio Chemical Engineering revealed on the 23rd of December 2010 that his team had successfully developed the technology that uses the metal ions to control the abnormal activation of nucleic acids’ enzymes and using this, created a logic gate, which is a core technology in the field of future bio electrons.
The polymerized nucleic acid enzyme works to increase the synthesis of DNA and kicks into action only when the target DNA and primers form complimentary pairs (A and T, C and G).
Professor Park broke the common conception and found that it is possible for none complimentary pairs like T-T and C-C to initiate the activation of the enzyme and thus increase the nucleic acid production, given that there are certain metal ions present.
What Professor Park realized is that the enzymes mistake the uncomplimentary T-T and C-C pairs (with stabilized structures due to the bonding with mercury and silver ions) as being complimentary base pairs. Professor Park described this phenomenon as the “illusionary polymerase activity.”
The research team developed a logic gate based on the “illusionary polymerase activity’ phenomenon.” The logic gate paves the way to the development of future bio electron needed for bio computers and high performance memories.
Professor Park commented, “The research is an advancement of the previous research carried on about metal ions and nucleic acid synthesis. Our research is the first attempt at merging the concepts of the two previously separately carried out researches and can be adapted for testing presence of metal ions and development of a new single nucleotide polymorphic gene analysis technology.”
Professor Park added that, “Our research is a great stride in the field of nano scale electron element research as the results made possible the formation of accurate logic gates through relatively cost efficient and simple system designs.”
On a side note, the research was funded by Korea Research Foundation (Chairman: Park Chan Mo) and was selected as the cover paper for the December issue of ‘Angewandte Chemie International Edition’.
2011.01.18 View 13471 -
 Korea should find niche in space race, Korea Herald, December 20, 2010
A proud alumna of KAIST, Dr. Yi So-Yeon, who went to the International Space Station in the outer space for the first time as a Korean in 2009, had an interview with the Korea Herald. In the interview, she talks about her experience in working at the space station and her personal plans for the future as a researcher and astronaut. For the article, please click the link:
http://www.koreaherald.com/lifestyle/Detail.jsp?newsMLId=20101220000999
2010.12.21 View 12060
Korea should find niche in space race, Korea Herald, December 20, 2010
A proud alumna of KAIST, Dr. Yi So-Yeon, who went to the International Space Station in the outer space for the first time as a Korean in 2009, had an interview with the Korea Herald. In the interview, she talks about her experience in working at the space station and her personal plans for the future as a researcher and astronaut. For the article, please click the link:
http://www.koreaherald.com/lifestyle/Detail.jsp?newsMLId=20101220000999
2010.12.21 View 12060 -
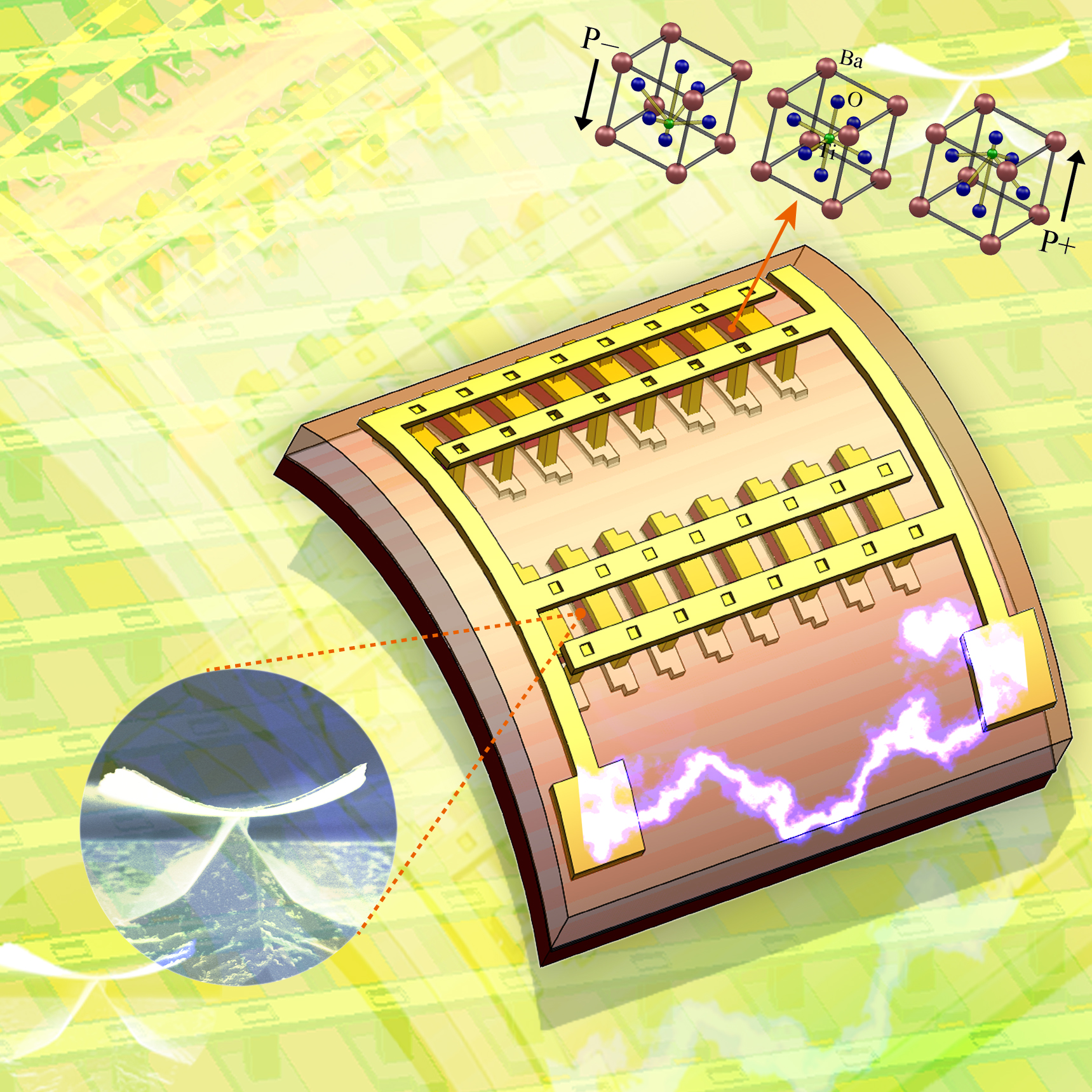 The KAIST & GIT team developed a power generation technology using bendable thin film nano-materials.
Figure description: Flexible thin film nanomaterials produce electricity.
Can a heart implanted micro robot operate permanently?
Can cell phones and tiny robots implanted in the heart operate permanently without having their batteries charged?
It might sound like science fiction, but these things seem to be possible in the near future. The team of Prof. Keon Jae Lee (KAIST, Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering) and Prof. Zhong Lin Wang (Georgia Institute of Technology, Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering) has developed new forms of highly efficient, flexible nanogenerator technology using the freely bendable piezoelectric ceramic thin film nano-materials that can convert tiny movements of the human body (such as heart beats and blood flow) into electrical energy.
The piezoelectric effect refers to voltage generation when pressure or bending strength is applied to piezoelectric materials. The ceramics, containing a perovskite structure, have a high piezoelectric efficiency. Until now, it has been very difficult to use these ceramic materials to fabricate flexible electronic systems due to their brittle property.
The research team, however, has succeeded in developing a bio-eco-friendly ceramic thin film nanogenerator that is freely bendable without breakdown.
Nanogenerator technology, a power generating system without wires or batteries, combines nanotechnology with piezoelectrics that can be used not only in personal mobile electronics but also in bio-implantable sensors or as an energy source for micro robots. Energy sources in nature (wind, vibration, and sound) and biomechanical forces produced by the human body (heart beats, blood flow, and muscle contraction/relaxation) can infinitely produce nonpolluting energy. (Nanogenerator produces electricity by external forces: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tvj0SsBqpBw)
Prof. Keon Jae Lee (KAIST) was involved in the first co-invention of “High Performance Flexible Single Crystal Electronics” during his PhD course at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. This nanogenerator technology, based on the previous invention, utilized the similar protocol of transferring ceramic thin film nano-materials on flexible substrates and produced voltage generation between electrodes.
Prof. Zhong Lin Wang (Georgia Tech, inventor of the nanogenerator) said, “This technology can be used to turn on an LED by slightly modifying circuits and operate touchable flexible displays. In addition, thin film nano-materials (‘barium titanate’) of this research have the property of both high efficiency and lead-free bio compatibility, which can be used in future medical applications.” This result is published in November online issue of ‘Nano Letters’ ACS journal.
<Video>
Youtube link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tvj0SsBqpBw
Thin Film Nanogenerator produces electricity by external forces.
2010.11.23 View 17267
The KAIST & GIT team developed a power generation technology using bendable thin film nano-materials.
Figure description: Flexible thin film nanomaterials produce electricity.
Can a heart implanted micro robot operate permanently?
Can cell phones and tiny robots implanted in the heart operate permanently without having their batteries charged?
It might sound like science fiction, but these things seem to be possible in the near future. The team of Prof. Keon Jae Lee (KAIST, Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering) and Prof. Zhong Lin Wang (Georgia Institute of Technology, Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering) has developed new forms of highly efficient, flexible nanogenerator technology using the freely bendable piezoelectric ceramic thin film nano-materials that can convert tiny movements of the human body (such as heart beats and blood flow) into electrical energy.
The piezoelectric effect refers to voltage generation when pressure or bending strength is applied to piezoelectric materials. The ceramics, containing a perovskite structure, have a high piezoelectric efficiency. Until now, it has been very difficult to use these ceramic materials to fabricate flexible electronic systems due to their brittle property.
The research team, however, has succeeded in developing a bio-eco-friendly ceramic thin film nanogenerator that is freely bendable without breakdown.
Nanogenerator technology, a power generating system without wires or batteries, combines nanotechnology with piezoelectrics that can be used not only in personal mobile electronics but also in bio-implantable sensors or as an energy source for micro robots. Energy sources in nature (wind, vibration, and sound) and biomechanical forces produced by the human body (heart beats, blood flow, and muscle contraction/relaxation) can infinitely produce nonpolluting energy. (Nanogenerator produces electricity by external forces: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tvj0SsBqpBw)
Prof. Keon Jae Lee (KAIST) was involved in the first co-invention of “High Performance Flexible Single Crystal Electronics” during his PhD course at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. This nanogenerator technology, based on the previous invention, utilized the similar protocol of transferring ceramic thin film nano-materials on flexible substrates and produced voltage generation between electrodes.
Prof. Zhong Lin Wang (Georgia Tech, inventor of the nanogenerator) said, “This technology can be used to turn on an LED by slightly modifying circuits and operate touchable flexible displays. In addition, thin film nano-materials (‘barium titanate’) of this research have the property of both high efficiency and lead-free bio compatibility, which can be used in future medical applications.” This result is published in November online issue of ‘Nano Letters’ ACS journal.
<Video>
Youtube link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tvj0SsBqpBw
Thin Film Nanogenerator produces electricity by external forces.
2010.11.23 View 17267