ANG
-
 KAIST Hosts a Symposium on IPR
KAIST’s Graduate School of Future Strategy (http://futures.kaist.ac.kr) hosted a symposium entitled “Future Strategies to Grow Korea as the Hub for the World’s Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs)” under the theme of “Patent Laws and a Revised Bill for the Code of Civil Procedures” in the National Assembly’s Memorial Hall on April 9, 2015.
Experts who attended the symposium included Professor James Dator, Director of the Hawaii Research Center for Futures Studies, Sang-Wook Han, a lawyer and Vice President of Korea Intellectual Property Protection Association (KIPRA), and Min Seo, a former Chairman of Civil Law Revision Commission of the Ministry of Justice, Korea.
The event consisted of special lectures, patent law presentations, a revised bill for the code of civil procedures in patent law, and a general discussion forum. Professor Dator, the keynote speaker, addressed the future of intellectual property. San-Wook Han (KIPRA) talked about new and effective changes in Korean patent law such as the compensation against IPR violations and the reduction of legal burden of proof in IPR disputes. Min Seo from the Ministry of Justice moderated a panel of eight members, which offered an in-depth discussion on the revised bill.
A ceremony for “The Third Future Strategy Award” was also held at the symposium. Yeon-Soo Park, former Administrator of the National Emergency Management Agency, received the award for his work on the Northeast Asian International Business Center City Project which enabled the construction of Incheon International Airport and Songdo International City.
2015.04.09 View 11034
KAIST Hosts a Symposium on IPR
KAIST’s Graduate School of Future Strategy (http://futures.kaist.ac.kr) hosted a symposium entitled “Future Strategies to Grow Korea as the Hub for the World’s Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs)” under the theme of “Patent Laws and a Revised Bill for the Code of Civil Procedures” in the National Assembly’s Memorial Hall on April 9, 2015.
Experts who attended the symposium included Professor James Dator, Director of the Hawaii Research Center for Futures Studies, Sang-Wook Han, a lawyer and Vice President of Korea Intellectual Property Protection Association (KIPRA), and Min Seo, a former Chairman of Civil Law Revision Commission of the Ministry of Justice, Korea.
The event consisted of special lectures, patent law presentations, a revised bill for the code of civil procedures in patent law, and a general discussion forum. Professor Dator, the keynote speaker, addressed the future of intellectual property. San-Wook Han (KIPRA) talked about new and effective changes in Korean patent law such as the compensation against IPR violations and the reduction of legal burden of proof in IPR disputes. Min Seo from the Ministry of Justice moderated a panel of eight members, which offered an in-depth discussion on the revised bill.
A ceremony for “The Third Future Strategy Award” was also held at the symposium. Yeon-Soo Park, former Administrator of the National Emergency Management Agency, received the award for his work on the Northeast Asian International Business Center City Project which enabled the construction of Incheon International Airport and Songdo International City.
2015.04.09 View 11034 -
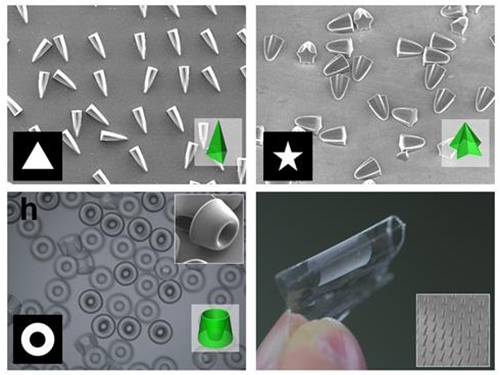 Novel Photolithographic Technology Enabling 3D Control over Functional Shapes of Microstructures
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim and his research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST have developed a novel photolithographic technology enabling control over the functional shapes of micropatterns using oxygen diffusion.
The research was published online in the March 13th issue of Nature Communications and was selected as a featured image for the journal.
Photolithography is a standard optical process for transferring micropatterns on to a substrate by exposing specific regions of the photoresist layer to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is used widely throughout industries that require micropatterns, especially in the semiconductor manufacturing industry.
Conventional photolithography relied on photomasks which protected certain regions of the substrate from the input UV light. Areas covered by the photomasks remain intact with the base layer while the areas exposed to the UV light are washed away, thus creating a micropattern. This technology was limited to a two-dimensional, disc-shaped design as the boundaries between the exposed and roofed regions are always in a parallel arrangement with the direction of the light.
Professor Kim’s research team discovered that: 1) the areas exposed to UV light lowered the concentration of oxygen and thus resulted in oxygen diffusion; and 2) manipulation of the diffusion speed and direction allowed control of the growth, shape and size of the polymers. Based on these findings, the team developed a new photolithographic technology that enabled the production of micropatterns with three-dimensional structures in various shapes and sizes.
Oxygen was considered an inhibitor during photopolymerization. Photoresist under UV light creates radicals which initialize a chemical reaction. These radicals are eliminated with the presence of oxygen and thus prevents the reaction. This suggests that the photoresist must be exposed to UV light for an extended time to completely remove oxygen for a chemical reaction to begin.
The research team, however, exploited the presence of oxygen. While the region affected by the UV light lowered oxygen concentration, the concentration in the untouched region remained unchanged. This difference in the concentrations caused a diffusion of oxygen to the region under UV light.
When the speed of the oxygen flow is slow, the diffusion occurs in parallel with the direction of the UV light. When fast, the diffusion process develops horizontally, outward from the area affected by the UV light. Professor Kim and his team proved this phenomenon both empirically and theoretically. Furthermore, by injecting an external oxygen source, the team was able to manipulate diffusion strength and direction, and thus control the shape and size of the polymer. The use of the polymerization inhibitors enabled and facilitated the fabrication of complex, three-dimensional micropatterns.
Professor Kim said, “While 3D printing is considered an innovative manufacturing technology, it cannot be used for mass-production of microscopic products. The new photolithographic technology will have a broad impact on both the academia and industry especially because existing, conventional photolithographic equipment can be used for the development of more complex micropatterns.” His newest technology will enhance the manufacturing process of three-dimensional polymers which were considered difficult to be commercialized.
The research was also dedicated to the late Professor Seung-Man Yang of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. He was considered one of the greatest scholars in Korea in the field of hydrodynamics and colloids.
Picture 1: Featured Image of Nature Communications, March 2015
Picture 2: Polymers with various shapes and sizes produced with the new photolithographic technology developed by Professor Kim
2015.04.06 View 10745
Novel Photolithographic Technology Enabling 3D Control over Functional Shapes of Microstructures
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim and his research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST have developed a novel photolithographic technology enabling control over the functional shapes of micropatterns using oxygen diffusion.
The research was published online in the March 13th issue of Nature Communications and was selected as a featured image for the journal.
Photolithography is a standard optical process for transferring micropatterns on to a substrate by exposing specific regions of the photoresist layer to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is used widely throughout industries that require micropatterns, especially in the semiconductor manufacturing industry.
Conventional photolithography relied on photomasks which protected certain regions of the substrate from the input UV light. Areas covered by the photomasks remain intact with the base layer while the areas exposed to the UV light are washed away, thus creating a micropattern. This technology was limited to a two-dimensional, disc-shaped design as the boundaries between the exposed and roofed regions are always in a parallel arrangement with the direction of the light.
Professor Kim’s research team discovered that: 1) the areas exposed to UV light lowered the concentration of oxygen and thus resulted in oxygen diffusion; and 2) manipulation of the diffusion speed and direction allowed control of the growth, shape and size of the polymers. Based on these findings, the team developed a new photolithographic technology that enabled the production of micropatterns with three-dimensional structures in various shapes and sizes.
Oxygen was considered an inhibitor during photopolymerization. Photoresist under UV light creates radicals which initialize a chemical reaction. These radicals are eliminated with the presence of oxygen and thus prevents the reaction. This suggests that the photoresist must be exposed to UV light for an extended time to completely remove oxygen for a chemical reaction to begin.
The research team, however, exploited the presence of oxygen. While the region affected by the UV light lowered oxygen concentration, the concentration in the untouched region remained unchanged. This difference in the concentrations caused a diffusion of oxygen to the region under UV light.
When the speed of the oxygen flow is slow, the diffusion occurs in parallel with the direction of the UV light. When fast, the diffusion process develops horizontally, outward from the area affected by the UV light. Professor Kim and his team proved this phenomenon both empirically and theoretically. Furthermore, by injecting an external oxygen source, the team was able to manipulate diffusion strength and direction, and thus control the shape and size of the polymer. The use of the polymerization inhibitors enabled and facilitated the fabrication of complex, three-dimensional micropatterns.
Professor Kim said, “While 3D printing is considered an innovative manufacturing technology, it cannot be used for mass-production of microscopic products. The new photolithographic technology will have a broad impact on both the academia and industry especially because existing, conventional photolithographic equipment can be used for the development of more complex micropatterns.” His newest technology will enhance the manufacturing process of three-dimensional polymers which were considered difficult to be commercialized.
The research was also dedicated to the late Professor Seung-Man Yang of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. He was considered one of the greatest scholars in Korea in the field of hydrodynamics and colloids.
Picture 1: Featured Image of Nature Communications, March 2015
Picture 2: Polymers with various shapes and sizes produced with the new photolithographic technology developed by Professor Kim
2015.04.06 View 10745 -
 KVIP Opened in Pangyo
KAIST has opened the KAIST Venture Innovation Program (KVIP) in its Center for Industry Outreach, designed for executive and high-ranking officers of venture companies. Located in Pangyo Techno Valley, KAIST’s Center for Industry Outreach was established in collaboration with the government of Gyeonggi Province to support venture companies in Pangyo for business management training, venture networking, and university-industry cooperation.
The program will be held every Monday for 12 weeks from April 13 to July 6 in KAIST’s Center for Industry Outreach. This executive education program mainly focuses on solving problems that arise when a medium-sized venture company is in the course of growing into a global corporation. The program is divided into four courses which will cover business management, competition in the global market, transformation of a company, and technological innovation.
Professors from various departments at KAIST will give lectures on their fields. Professor Jaeseung Jeong from the Bio and Brain Engineering Department, Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the Electrical Engineering Department, Professor Sangmin Bae from the Industrial Design Department, and Professor Kwangjae Sung from the Business and Technology Management Department will each deliver lectures on brain engineering, semiconductor, design, and restructuring.
Industry experts are also invited to give talks, including Dr. Dae-Gyu Byun, the Chief Executive Officer and President of HUMAX Electronics, Dr. Gwang-Cheol Choi, the Chief Executive Officer of SK Engineering & Construction, Mr. Il-young Kim, the former Chief Executive Officer of KT, Dr. Jae-hoon Jeong, the President of the Korea Institute for the Advancement of Technology (KIAT), Dr. Intak Bae, the Chief Executive Officer of Summit Partners, and Mr. Kyung-taek Kwak, a film director.
The department has started recruiting first round applicants for the program, targeting executive and high-ranking officers of middle-sized venture companies. The details of the program can be found on its website, kvip.kaist.ac.kr.
2015.03.23 View 10869
KVIP Opened in Pangyo
KAIST has opened the KAIST Venture Innovation Program (KVIP) in its Center for Industry Outreach, designed for executive and high-ranking officers of venture companies. Located in Pangyo Techno Valley, KAIST’s Center for Industry Outreach was established in collaboration with the government of Gyeonggi Province to support venture companies in Pangyo for business management training, venture networking, and university-industry cooperation.
The program will be held every Monday for 12 weeks from April 13 to July 6 in KAIST’s Center for Industry Outreach. This executive education program mainly focuses on solving problems that arise when a medium-sized venture company is in the course of growing into a global corporation. The program is divided into four courses which will cover business management, competition in the global market, transformation of a company, and technological innovation.
Professors from various departments at KAIST will give lectures on their fields. Professor Jaeseung Jeong from the Bio and Brain Engineering Department, Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the Electrical Engineering Department, Professor Sangmin Bae from the Industrial Design Department, and Professor Kwangjae Sung from the Business and Technology Management Department will each deliver lectures on brain engineering, semiconductor, design, and restructuring.
Industry experts are also invited to give talks, including Dr. Dae-Gyu Byun, the Chief Executive Officer and President of HUMAX Electronics, Dr. Gwang-Cheol Choi, the Chief Executive Officer of SK Engineering & Construction, Mr. Il-young Kim, the former Chief Executive Officer of KT, Dr. Jae-hoon Jeong, the President of the Korea Institute for the Advancement of Technology (KIAT), Dr. Intak Bae, the Chief Executive Officer of Summit Partners, and Mr. Kyung-taek Kwak, a film director.
The department has started recruiting first round applicants for the program, targeting executive and high-ranking officers of middle-sized venture companies. The details of the program can be found on its website, kvip.kaist.ac.kr.
2015.03.23 View 10869 -
 KAIST Welcomes Freshmen at the 2015 Convocation Ceremony
Around 1,600 freshmen and their parents gathered on March 12, 2015 at the main auditorium on campus for the KAIST convocation ceremony. A total of 796 freshmen joined the convocation ceremony.
The ceremony proceeded with the freshmen oath, administered by freshmen representatives Ja-Young Ryu (a graduate of the Korea Science Academy) and Yun-Min Song (a graduate of Changwon Science High School). Vice Minister Jae-Yoo Choi of Science, ICT and Future Planning, the Republic of Korea, and President Steve Kang of KAIST delivered congratulatory messages, respectively. Members of KAIST student clubs performed a music concert to celebrate the event.
In his message, Vice Minister Choi said, “Scientists should not be afraid of failure but have a challenging spirit. As always, the Korean government will provide students with generous support by creating an environment for education and research, in which students can reach their potential and realize imagination into reality.”
President Kang urged students to be respectful and thankful to others, to master their expertise in depth, to take social responsibilities, and to improve on global communication skills. He continued, “With all the best intellectuals you will meet at KAIST, you will face a much more challenging environment compared to high school. Even if it gets too difficult and you fail, do not be discouraged but please have the heart to get back up and try again.”
Freshmen representatives, Ja-Young Ryu (a female student) and Yun-Min Song (a male student), are administering the student oath in front of President Sung-Mo Kang in the picture below.
2015.03.02 View 6277
KAIST Welcomes Freshmen at the 2015 Convocation Ceremony
Around 1,600 freshmen and their parents gathered on March 12, 2015 at the main auditorium on campus for the KAIST convocation ceremony. A total of 796 freshmen joined the convocation ceremony.
The ceremony proceeded with the freshmen oath, administered by freshmen representatives Ja-Young Ryu (a graduate of the Korea Science Academy) and Yun-Min Song (a graduate of Changwon Science High School). Vice Minister Jae-Yoo Choi of Science, ICT and Future Planning, the Republic of Korea, and President Steve Kang of KAIST delivered congratulatory messages, respectively. Members of KAIST student clubs performed a music concert to celebrate the event.
In his message, Vice Minister Choi said, “Scientists should not be afraid of failure but have a challenging spirit. As always, the Korean government will provide students with generous support by creating an environment for education and research, in which students can reach their potential and realize imagination into reality.”
President Kang urged students to be respectful and thankful to others, to master their expertise in depth, to take social responsibilities, and to improve on global communication skills. He continued, “With all the best intellectuals you will meet at KAIST, you will face a much more challenging environment compared to high school. Even if it gets too difficult and you fail, do not be discouraged but please have the heart to get back up and try again.”
Freshmen representatives, Ja-Young Ryu (a female student) and Yun-Min Song (a male student), are administering the student oath in front of President Sung-Mo Kang in the picture below.
2015.03.02 View 6277 -
 Ethiopian Minister of Education Visits KAIST
An Ethiopian delegation headed by the Minister of Education visited the KAIST campus on February 26, 2015. The delegation consisted of Mr. Demitu Hambisa, Minister of Education, Mr. Dibaba Abdetta, Ethiopian Ambassador to Korea, Dr. Jang-Kyu Lee, President of Adama Science and Technology University (ASTU), and Mr. Nurelegne Tefera, President of Addis Ababa Science and Technology University (AASTU).
Minister Hambisa explained the purpose of his visit, “We would like to learn about what KAIST has achieved over the years for Korea and its people and increase exchanges and cooperation between our universities and KAIST.”
KAIST and the two Ethiopian universities, ASTU and AASTU, signed memoranda of understanding for cooperative programs in science and engineering education.
Established in 1993, ASTU appointed Dr. Jang-Kyu Lee, a former professor from Seoul National University, Korea, to become its president since 2011. President Lee is the first Korean ever to have served the institution.
2015.02.26 View 8147
Ethiopian Minister of Education Visits KAIST
An Ethiopian delegation headed by the Minister of Education visited the KAIST campus on February 26, 2015. The delegation consisted of Mr. Demitu Hambisa, Minister of Education, Mr. Dibaba Abdetta, Ethiopian Ambassador to Korea, Dr. Jang-Kyu Lee, President of Adama Science and Technology University (ASTU), and Mr. Nurelegne Tefera, President of Addis Ababa Science and Technology University (AASTU).
Minister Hambisa explained the purpose of his visit, “We would like to learn about what KAIST has achieved over the years for Korea and its people and increase exchanges and cooperation between our universities and KAIST.”
KAIST and the two Ethiopian universities, ASTU and AASTU, signed memoranda of understanding for cooperative programs in science and engineering education.
Established in 1993, ASTU appointed Dr. Jang-Kyu Lee, a former professor from Seoul National University, Korea, to become its president since 2011. President Lee is the first Korean ever to have served the institution.
2015.02.26 View 8147 -
 KAIST Signs MOU with Jeonju City
KAIST signed a memorandum of understanding for the development of new industries based on convergence technology with the government of Jeonju City on February 26, 2015. Located in the south west portion of the Korean peninsula, Jeonju City is home to a rich historical and cultural heritage.
Taking advantage of its proximity to the university's campus, the city will cooperate with KAIST to develop the local economy through creating new industries and jobs. To that end, KAIST and Jeonju will foster carbon-based industry, 3D printing technology, the Internet of Things, and emerging technologies. The two organizations also hope this cooperation will produce highly educated manpower for research and development in the city and offer the city to conduct national research projects.
President Sung-Mo Kang and Mayor Seung-Soo Kim pose after signing in the picture below.
2015.02.26 View 7921
KAIST Signs MOU with Jeonju City
KAIST signed a memorandum of understanding for the development of new industries based on convergence technology with the government of Jeonju City on February 26, 2015. Located in the south west portion of the Korean peninsula, Jeonju City is home to a rich historical and cultural heritage.
Taking advantage of its proximity to the university's campus, the city will cooperate with KAIST to develop the local economy through creating new industries and jobs. To that end, KAIST and Jeonju will foster carbon-based industry, 3D printing technology, the Internet of Things, and emerging technologies. The two organizations also hope this cooperation will produce highly educated manpower for research and development in the city and offer the city to conduct national research projects.
President Sung-Mo Kang and Mayor Seung-Soo Kim pose after signing in the picture below.
2015.02.26 View 7921 -
 The Number of KAIST Doctoral Graduates to Reach Over Ten Thousands
The ten-thousandth doctoral graduate received her degree in the commencement ceremony on February 13, 2015.
KAIST has contributed to the development of science, technology, and industry in Korea by fostering talents in advanced science and engineering.
Since its establishment forty-four years ago, more than ten-thousand KAIST alumni have received their doctorates. This year’s graduation ceremony took place on February 13, 2015, at the Sports Complex on campus, awarding the ten-thousandth doctoral degree.
Dr. Sun-Mi Cho of the Department of Biological Sciences received the ten-thousandth doctoral degree. A graduate of Jeon-Nam Science High School, Dr. Cho also received her Bachelor of Science degree from KAIST.
Dr. Cho wrote a dissertation entitled “GABA from reactive astrocytes impairs learning and memory in Alzheimer disease.” Her dissertation adviser was Professor Daesoo Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences.
Dr. Cho, who will be a post-doctorate researcher at the Biological Sciences Department, said, “It was my childhood dream to receive a doctorate from KAIST. I cannot believe that I’m the ten-thousandth doctoral graduate, for which I’m very grateful.” She continued, “I hope to become a neuroscientist where I can be of help to the sick.”
In 1978, KAIST only had two doctoral graduates, but since 1987 there have been more than one hundred graduates each year, two hundred since 1994, and four hundred since 2000. In 2015, 522 doctoral students graduated.
One of the first doctoral graduates, Dong-Yol Yang (class of 1978 in the Mechanical Engineering Department), became a professor at the same department of KAIST. Professor Yang expressed his thoughts on the news, “There was a trend in Korea to go overseas for Ph.D. degrees in the early 1970s, but it changed when KAIST began to select candidates for Master’s degrees in 1973 and Doctoral degrees in 1975. Talented Korean students came to KAIST laboratories, and its graduates were known for their knowledge and skills. Now, we see that the talent is coming from overseas.”
At the 2015 Commencement, KAIST conferred 522 Doctoral, 1,241 Master’s, and 915 Bachelor of Science (B.S.) degrees.
Since its inception in 1971, KAIST has granted 10,403 doctor's, 26,402 master's, and 51,412 bachelor's degrees.
In the picture below, Professor Dong-Yol Yang (left) seats next to Dr. Sun-Mi Cho (right), the recipient of 10,000th doctoral degree.
2015.02.16 View 10360
The Number of KAIST Doctoral Graduates to Reach Over Ten Thousands
The ten-thousandth doctoral graduate received her degree in the commencement ceremony on February 13, 2015.
KAIST has contributed to the development of science, technology, and industry in Korea by fostering talents in advanced science and engineering.
Since its establishment forty-four years ago, more than ten-thousand KAIST alumni have received their doctorates. This year’s graduation ceremony took place on February 13, 2015, at the Sports Complex on campus, awarding the ten-thousandth doctoral degree.
Dr. Sun-Mi Cho of the Department of Biological Sciences received the ten-thousandth doctoral degree. A graduate of Jeon-Nam Science High School, Dr. Cho also received her Bachelor of Science degree from KAIST.
Dr. Cho wrote a dissertation entitled “GABA from reactive astrocytes impairs learning and memory in Alzheimer disease.” Her dissertation adviser was Professor Daesoo Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences.
Dr. Cho, who will be a post-doctorate researcher at the Biological Sciences Department, said, “It was my childhood dream to receive a doctorate from KAIST. I cannot believe that I’m the ten-thousandth doctoral graduate, for which I’m very grateful.” She continued, “I hope to become a neuroscientist where I can be of help to the sick.”
In 1978, KAIST only had two doctoral graduates, but since 1987 there have been more than one hundred graduates each year, two hundred since 1994, and four hundred since 2000. In 2015, 522 doctoral students graduated.
One of the first doctoral graduates, Dong-Yol Yang (class of 1978 in the Mechanical Engineering Department), became a professor at the same department of KAIST. Professor Yang expressed his thoughts on the news, “There was a trend in Korea to go overseas for Ph.D. degrees in the early 1970s, but it changed when KAIST began to select candidates for Master’s degrees in 1973 and Doctoral degrees in 1975. Talented Korean students came to KAIST laboratories, and its graduates were known for their knowledge and skills. Now, we see that the talent is coming from overseas.”
At the 2015 Commencement, KAIST conferred 522 Doctoral, 1,241 Master’s, and 915 Bachelor of Science (B.S.) degrees.
Since its inception in 1971, KAIST has granted 10,403 doctor's, 26,402 master's, and 51,412 bachelor's degrees.
In the picture below, Professor Dong-Yol Yang (left) seats next to Dr. Sun-Mi Cho (right), the recipient of 10,000th doctoral degree.
2015.02.16 View 10360 -
 Light Driven Drug-Enzyme Reaction Catalytic Platform Developed
Low Cost Dye Used, Hope for Future Development of High Value Medicinal Products to Treat Cardiovascular Disease and Gastric Ulcers
A KAIST research team from the Departments of Materials Science and Engineering and of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, led respectively by Professors Chan Beum Park and Ki Jun Jeong, has developed a new reaction platform to induce drug-enzyme reaction using light.
The research results were published in the journal Angewandte Chemie, International Edition, as the back cover on 12 January 2015.
Applications of this technology may enable production of high value products such as medicine for cardiovascular disease and gastric ulcers, for example Omeprazole, using an inexpensive dye.
Cytochrome P450 is an enzyme involved in oxidative response which has an important role in drug and hormone metabolism in organisms. It is known to be responsible for metabolism of 75% of drugs in humans and is considered a fundamental factor in new drug development.
To activate cytochrome P450, the enzyme must receive an electron by reducing the enzyme. In addition, NADPH (a coenzyme) needs to be present. However, since NADPH is expensive, the use of cytochrome P450 was limited to the laboratory and has not yet been commercialized.
The research team used photosensitizer eosin Y instead of NADPH to develop “Whole Cell Photo-Biocatalysis” in bacteria E. coli. By exposing inexpensive eosin Y to light, cytochrome P450 reaction was catalyzed to produce the expensive metabolic material.
Professor Park said, “This research enabled industrial application of cytochrome P450 enzyme, which was previous limited.” He continued, “This technology will help greatly in producing high value medical products using cytochrome P450 enzyme.”
The research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and KAIST's High Risk High Return Project (HRHRP).
Figure 1: Mimetic Diagram of Electron Transfer from Light to Cytochrome P450 Enzyme via Eosin Y, EY
Figure 2: The back cover of Angewandte Chemie published on 12 January 2015, showing the research results
2015.01.26 View 10732
Light Driven Drug-Enzyme Reaction Catalytic Platform Developed
Low Cost Dye Used, Hope for Future Development of High Value Medicinal Products to Treat Cardiovascular Disease and Gastric Ulcers
A KAIST research team from the Departments of Materials Science and Engineering and of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, led respectively by Professors Chan Beum Park and Ki Jun Jeong, has developed a new reaction platform to induce drug-enzyme reaction using light.
The research results were published in the journal Angewandte Chemie, International Edition, as the back cover on 12 January 2015.
Applications of this technology may enable production of high value products such as medicine for cardiovascular disease and gastric ulcers, for example Omeprazole, using an inexpensive dye.
Cytochrome P450 is an enzyme involved in oxidative response which has an important role in drug and hormone metabolism in organisms. It is known to be responsible for metabolism of 75% of drugs in humans and is considered a fundamental factor in new drug development.
To activate cytochrome P450, the enzyme must receive an electron by reducing the enzyme. In addition, NADPH (a coenzyme) needs to be present. However, since NADPH is expensive, the use of cytochrome P450 was limited to the laboratory and has not yet been commercialized.
The research team used photosensitizer eosin Y instead of NADPH to develop “Whole Cell Photo-Biocatalysis” in bacteria E. coli. By exposing inexpensive eosin Y to light, cytochrome P450 reaction was catalyzed to produce the expensive metabolic material.
Professor Park said, “This research enabled industrial application of cytochrome P450 enzyme, which was previous limited.” He continued, “This technology will help greatly in producing high value medical products using cytochrome P450 enzyme.”
The research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and KAIST's High Risk High Return Project (HRHRP).
Figure 1: Mimetic Diagram of Electron Transfer from Light to Cytochrome P450 Enzyme via Eosin Y, EY
Figure 2: The back cover of Angewandte Chemie published on 12 January 2015, showing the research results
2015.01.26 View 10732 -
 The Graduate School of Green Growth at KAIST Holds a Student Conference
The Graduate School of Green Growth at KAIST hosted a student conference on December 22, 2014 at the Seoul campus of the College of Business. About 100 master’s and doctoral students joined the conference held under the theme of “Green Knowledge Hub” and presented their research papers.
At the conference, three students received awards. The author of a paper entitled “Development and Analysis of Climate Change Vulnerability Index Applicable to Developing Countries” received the grand prize. The authors of “Green IT and Its Case Study on the Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Industry” and “Analysis of Correlation between Consumers’ Subjective Happiness and Their Green Purchasing” were selected for runner-up prizes, respectively.
Dean Jae-Kyu Lee of the Green Growth Graduate School said, “We offered the conference to our students to engage with their peers and share ideas and knowledge in their majors. I hope students become more motivated, and we will continue holding this event in the future.”
2015.01.05 View 7164
The Graduate School of Green Growth at KAIST Holds a Student Conference
The Graduate School of Green Growth at KAIST hosted a student conference on December 22, 2014 at the Seoul campus of the College of Business. About 100 master’s and doctoral students joined the conference held under the theme of “Green Knowledge Hub” and presented their research papers.
At the conference, three students received awards. The author of a paper entitled “Development and Analysis of Climate Change Vulnerability Index Applicable to Developing Countries” received the grand prize. The authors of “Green IT and Its Case Study on the Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Industry” and “Analysis of Correlation between Consumers’ Subjective Happiness and Their Green Purchasing” were selected for runner-up prizes, respectively.
Dean Jae-Kyu Lee of the Green Growth Graduate School said, “We offered the conference to our students to engage with their peers and share ideas and knowledge in their majors. I hope students become more motivated, and we will continue holding this event in the future.”
2015.01.05 View 7164 -
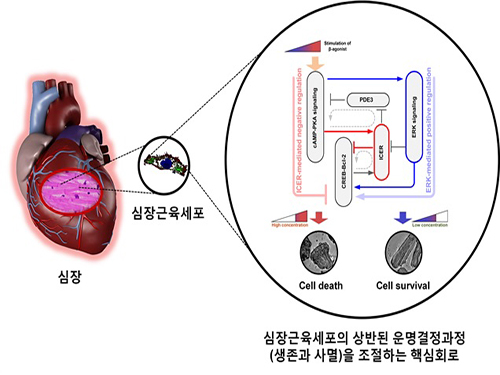 A Key Signal Transduction Pathway Switch in Cardiomyocyte Identified
A KAIST research team has identified the fundamental principle in deciding the fate of cardiomyocyte or heart muscle cells. They have determined that it depends on the degree of stimulus in β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway in the cardiomyocyte to control cells' survival or death. The findings, the team hopes, can be used to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.
The research was led by KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering Chair Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and conducted by Dr. Sung-Young Shin (lead author) and Ph.D. candidates Ho-Sung Lee and Joon-Hyuk Kang. The research was conducted jointly with GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology) Department of Biological Sciences Professor Do-Han Kim’s team. The research was supported by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The paper was published in Nature Communications on December 17, 2014 with the title, “The switching role of β-adrenergic receptor signalling in cell survival or death decision of cardiomyocytes.”
The β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway can promote cell survival (mediated by β2 receptors), but also can result in cell death by inducing toxin (mediated by β1 receptors) that leads to various heart diseases including heart failure. Past attempts to identify the fundamental principle in the fate determining process of cardiomyocyte based on β-adrenergic receptor signalling concluded without much success.
The β-adrenergic receptor is a type of protein on the cell membrane of cardiomyocyte (heart muscle cell) that when stimulated by neurohormones such as epinephrine or norepinephrine would transduce signals making the cardiomyocyte contract faster and stronger.
The research team used large-scale computer simulation analysis and systems biology to identify ERK* and ICER** signal transduction pathways mediated by a feed-forward circuit as a key molecular switch that decides between cell survival and death.
Weak β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ERK signal transduction pathway, increasing Bcl-2*** protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte survival. On the other hand, strong β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ICER signal transduction pathway, reducing Bcl-2 protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte death.
Researchers used a systems biology approach to identify the mechanism of B-blocker****, a common drug prescribed for heart failure. When cardiomyocyte is treated with β1 inhibitor, strong stimulation on β-adrenergic receptor increases Bcl-2 expression, improving the chance of cardiomyocyte survival, a cell protection effect.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, “This research used systems biology, an integrated, convergence research of IT (information technology) and BT (biotechnology), to successfully identify the mechanism in deciding the fate of cardiomyocytes based on the β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway for the first time. I am hopeful that this research will enable the control of cardiomyocyte survival and death to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.”
Professor Cho’s team was the first to pioneer a new field of systems biology, especially concerning the complex signal transduction network involved in diseases. Their research is focused on modelling, analyzing simulations, and experimentally proving signal pathways. Professor Cho has published 140 articles in international journals including Cell, Science, and Nature.
* ERK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinases): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell survival
** ICER (Inducible cAMP early repressor): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell death
*** Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2): Key signal transduction molecule involved in promotion of cell survival
**** β-blocker: Drug that acts as β-adrenergic receptor inhibitor known to slow the progression of heart failure, hence used most commonly in medicine.
Picture: A schematic diagram for the β-AR signalling network
2015.01.05 View 13899
A Key Signal Transduction Pathway Switch in Cardiomyocyte Identified
A KAIST research team has identified the fundamental principle in deciding the fate of cardiomyocyte or heart muscle cells. They have determined that it depends on the degree of stimulus in β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway in the cardiomyocyte to control cells' survival or death. The findings, the team hopes, can be used to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.
The research was led by KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering Chair Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and conducted by Dr. Sung-Young Shin (lead author) and Ph.D. candidates Ho-Sung Lee and Joon-Hyuk Kang. The research was conducted jointly with GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology) Department of Biological Sciences Professor Do-Han Kim’s team. The research was supported by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The paper was published in Nature Communications on December 17, 2014 with the title, “The switching role of β-adrenergic receptor signalling in cell survival or death decision of cardiomyocytes.”
The β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway can promote cell survival (mediated by β2 receptors), but also can result in cell death by inducing toxin (mediated by β1 receptors) that leads to various heart diseases including heart failure. Past attempts to identify the fundamental principle in the fate determining process of cardiomyocyte based on β-adrenergic receptor signalling concluded without much success.
The β-adrenergic receptor is a type of protein on the cell membrane of cardiomyocyte (heart muscle cell) that when stimulated by neurohormones such as epinephrine or norepinephrine would transduce signals making the cardiomyocyte contract faster and stronger.
The research team used large-scale computer simulation analysis and systems biology to identify ERK* and ICER** signal transduction pathways mediated by a feed-forward circuit as a key molecular switch that decides between cell survival and death.
Weak β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ERK signal transduction pathway, increasing Bcl-2*** protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte survival. On the other hand, strong β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ICER signal transduction pathway, reducing Bcl-2 protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte death.
Researchers used a systems biology approach to identify the mechanism of B-blocker****, a common drug prescribed for heart failure. When cardiomyocyte is treated with β1 inhibitor, strong stimulation on β-adrenergic receptor increases Bcl-2 expression, improving the chance of cardiomyocyte survival, a cell protection effect.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, “This research used systems biology, an integrated, convergence research of IT (information technology) and BT (biotechnology), to successfully identify the mechanism in deciding the fate of cardiomyocytes based on the β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway for the first time. I am hopeful that this research will enable the control of cardiomyocyte survival and death to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.”
Professor Cho’s team was the first to pioneer a new field of systems biology, especially concerning the complex signal transduction network involved in diseases. Their research is focused on modelling, analyzing simulations, and experimentally proving signal pathways. Professor Cho has published 140 articles in international journals including Cell, Science, and Nature.
* ERK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinases): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell survival
** ICER (Inducible cAMP early repressor): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell death
*** Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2): Key signal transduction molecule involved in promotion of cell survival
**** β-blocker: Drug that acts as β-adrenergic receptor inhibitor known to slow the progression of heart failure, hence used most commonly in medicine.
Picture: A schematic diagram for the β-AR signalling network
2015.01.05 View 13899 -
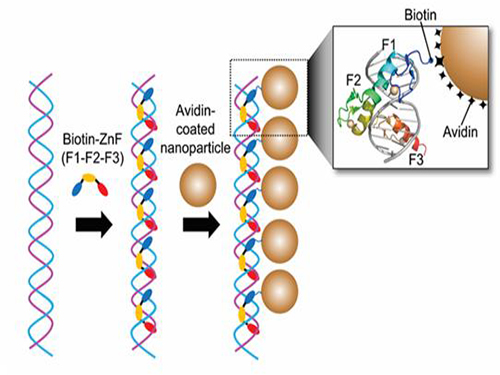 Nanoparticle Cluster Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Developed
Professor Hak-Sung Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Yiseul Ryu, a doctoral candidate, used the Zinc Finger protein that specifically binds to target DNA sequence to develop a new manufacturing technique for size-controllable magnetic Nanoparticle Clusters (NPCs). Their research results were published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition online on 25 November 2014.
NPCs are structures consisting of magnetic nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles, and quantum dots, each of which are smaller than 100 nm (10-9m). NPCs have a distinctive property of collectivity not seen in single nanoparticles.
Specifically NPCS differ in physical and optical properties such as Plasmon coupling absorbance, energy transfers between particles, electron transfers, and conductivity. Therefore, NPCs can be employed in biological and medical research as well as the development of nanoelectric and nanoplasmon devices.
To make use of these novel properties, the size and the composition of the cluster must be exquisitely controlled. However, previous techniques relied on chemical binding which required complex steps, making it difficult to control the size and composition of NPCs.
Professor Kim’s team used Zinc Finger, a DNA binding protein, to develop a NPCs manufacturing technique to create clusters of the desired size easily. The Zinc Finger protein contains a zinc ion and specifically recognizes DNA sequence upon binding, which allows the exquisite control of the size and the cluster composition. The technique is also bio-friendly.
Professor Kim’s team created linear structure of different sizes of NPCs using Zinc Finger proteins and three DNA sequences of different lengths. The NPCs they produced confirmed their ability to control the size and structure of the cluster by using different DNA lengths.
The NPCs showed tripled T2 relaxation rates compared to the existing MRI contrast media (Feridex) and effectively transported to targeted cells. The research findings show the potential use of NPCs in biological and medical fields such as MRI contrast media, fluorescence imaging, and drug transport.
The research used the specific binding property of protein and DNA to develop a new method to create an inorganic nanoparticle’s supramolecular assembly. The technique can be used and applied extensively in other nanoparticles for future research in diagnosis, imaging, and drug and gene delivery.
Figure 1. A Mimetic Diagram of NPCs Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Zinc Finger
Figure 2. Transmission Electron Microscopy Images showing different sizes of NPCs depending on the length of the DNA
2014.12.04 View 13330
Nanoparticle Cluster Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Developed
Professor Hak-Sung Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Yiseul Ryu, a doctoral candidate, used the Zinc Finger protein that specifically binds to target DNA sequence to develop a new manufacturing technique for size-controllable magnetic Nanoparticle Clusters (NPCs). Their research results were published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition online on 25 November 2014.
NPCs are structures consisting of magnetic nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles, and quantum dots, each of which are smaller than 100 nm (10-9m). NPCs have a distinctive property of collectivity not seen in single nanoparticles.
Specifically NPCS differ in physical and optical properties such as Plasmon coupling absorbance, energy transfers between particles, electron transfers, and conductivity. Therefore, NPCs can be employed in biological and medical research as well as the development of nanoelectric and nanoplasmon devices.
To make use of these novel properties, the size and the composition of the cluster must be exquisitely controlled. However, previous techniques relied on chemical binding which required complex steps, making it difficult to control the size and composition of NPCs.
Professor Kim’s team used Zinc Finger, a DNA binding protein, to develop a NPCs manufacturing technique to create clusters of the desired size easily. The Zinc Finger protein contains a zinc ion and specifically recognizes DNA sequence upon binding, which allows the exquisite control of the size and the cluster composition. The technique is also bio-friendly.
Professor Kim’s team created linear structure of different sizes of NPCs using Zinc Finger proteins and three DNA sequences of different lengths. The NPCs they produced confirmed their ability to control the size and structure of the cluster by using different DNA lengths.
The NPCs showed tripled T2 relaxation rates compared to the existing MRI contrast media (Feridex) and effectively transported to targeted cells. The research findings show the potential use of NPCs in biological and medical fields such as MRI contrast media, fluorescence imaging, and drug transport.
The research used the specific binding property of protein and DNA to develop a new method to create an inorganic nanoparticle’s supramolecular assembly. The technique can be used and applied extensively in other nanoparticles for future research in diagnosis, imaging, and drug and gene delivery.
Figure 1. A Mimetic Diagram of NPCs Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Zinc Finger
Figure 2. Transmission Electron Microscopy Images showing different sizes of NPCs depending on the length of the DNA
2014.12.04 View 13330 -
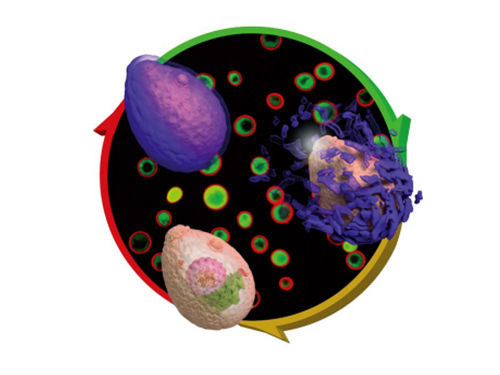 Eggshell-like Cell Encapsulation and Degradation Technology Developed
Some bacteria form endospores on cell walls to protect their DNA in case of nutrient deficiency. When an endospore meets a suitable environment for survival, the cell can revert to the original state from which it can reproduce.
The technique that can artificially control such phenomenon was developed by an international team of researchers. At first, a cell is wrapped and preserved like an egg. When the cell is needed, the technique allows the endospore to decompose while it is alive. Future applications for this technique include cell-based biosensor, cell therapy, and biocatalyst processes.
Professors Insung Choi and Younghoon Lee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST as well as and Professor Frank Caruso from the University of Melbourne developed this technique which permits a cell to stay alive by coating it with film on a nanometer scale and then to be decomposed while it is alive.
The research finding was published in the November 10th issue of Angewandte Chemie International Edition as the lead article.
Cell encapsulation allows researchers to capture a cell in a tight capsule while it is alive. It is highly recognized in cell-based applications where the control of cell stability and cell-division is the biggest issue.
Traditional cell encapsulation methods utilized organic film or inorganic capsules that are made of organic film moldings. Although these films tightly closed around the cell, because they were not easily decomposable, it was difficult to apply the method.
The research team succeeded in encapsulating each cell in a metal-polyphenol film by mixing tannic acid and iron ion solution with yeast cells.
Usually extracted from oak barks or grape peels, tannic acid is a natural substance. It forms a metal-polyphenol film within ten seconds when it meets iron ions due to its high affinity with cells. Cells encapsulated with this film presented high survival rates. Since the film forms quickly in a simple manner, it was possible to obtain large amount of encapsulated cells.
The research team also found that the metal-polyphenol film was stable in neutral pH, but is easily degradable under a weak acidic condition. Using this property, they were able to control cell division by restoring the cell to its pre-encapsulated state at a desired moment.
Protecting the cell from the external environment like an egg shell, the metal-polyphenol film protected the cell against foreign conditions such as lytic enzymes, extended exposure to UV radiation, and silver nanoparticles. The research indicated that the encapsulated cells had a high survival rate even under extreme environments.
Professor Lee said that “not only the cells remain alive during the encapsulation stage, but also they can be protected under extreme environment.” He added, “This is an advanced cell encapsulation technology that allows controlling cell-division of those cells through responsive shell degradation on-demand.”
Professor Choi commented, “Although the cell encapsulation technology is still in its infancy, as the technology matures the application of cell-manipulation technology will be actualized.” He highlighted that “it will serve as a breakthrough to problems faced by cell-based applications.”
Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research was led by two Master’s candidates, Ji Hun Park and Kyung Hwan Kim, under the joint guidance of research professors from KAIST and the University of Melbourne.
Figure 1: Lead article of Angewandte Chemie
Background: Shows a live native yeast (in green) encapsulated in a metal-polyphenol film (in red) illustrating the vitality of the yeast
Front: A native yeast at each encapsulation stage
Pictured on the bottom left is a cell prior to encapsulation. Following the red arrow, the native yeast is in purple to show metal-polyphenol film formed around the cell. The cell after the green arrow is a visualization of the degradation of the film in weak acidic condition.
Figure 2: A mimetic diagram of cell encapsulation with a metal-polyphenol film
Top: A native yeast before encapsulation
Middle: A native yeast encapsulated with Tannic Acid-Fe (III) Nanoshell – cell-division of the encapsulated cell is controlled by pH and the shell is protected against silver nanoparticle, lytic enzyme, and UV-C
Bottom: Shell degradation on-demand depending on pH
2014.11.18 View 10623
Eggshell-like Cell Encapsulation and Degradation Technology Developed
Some bacteria form endospores on cell walls to protect their DNA in case of nutrient deficiency. When an endospore meets a suitable environment for survival, the cell can revert to the original state from which it can reproduce.
The technique that can artificially control such phenomenon was developed by an international team of researchers. At first, a cell is wrapped and preserved like an egg. When the cell is needed, the technique allows the endospore to decompose while it is alive. Future applications for this technique include cell-based biosensor, cell therapy, and biocatalyst processes.
Professors Insung Choi and Younghoon Lee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST as well as and Professor Frank Caruso from the University of Melbourne developed this technique which permits a cell to stay alive by coating it with film on a nanometer scale and then to be decomposed while it is alive.
The research finding was published in the November 10th issue of Angewandte Chemie International Edition as the lead article.
Cell encapsulation allows researchers to capture a cell in a tight capsule while it is alive. It is highly recognized in cell-based applications where the control of cell stability and cell-division is the biggest issue.
Traditional cell encapsulation methods utilized organic film or inorganic capsules that are made of organic film moldings. Although these films tightly closed around the cell, because they were not easily decomposable, it was difficult to apply the method.
The research team succeeded in encapsulating each cell in a metal-polyphenol film by mixing tannic acid and iron ion solution with yeast cells.
Usually extracted from oak barks or grape peels, tannic acid is a natural substance. It forms a metal-polyphenol film within ten seconds when it meets iron ions due to its high affinity with cells. Cells encapsulated with this film presented high survival rates. Since the film forms quickly in a simple manner, it was possible to obtain large amount of encapsulated cells.
The research team also found that the metal-polyphenol film was stable in neutral pH, but is easily degradable under a weak acidic condition. Using this property, they were able to control cell division by restoring the cell to its pre-encapsulated state at a desired moment.
Protecting the cell from the external environment like an egg shell, the metal-polyphenol film protected the cell against foreign conditions such as lytic enzymes, extended exposure to UV radiation, and silver nanoparticles. The research indicated that the encapsulated cells had a high survival rate even under extreme environments.
Professor Lee said that “not only the cells remain alive during the encapsulation stage, but also they can be protected under extreme environment.” He added, “This is an advanced cell encapsulation technology that allows controlling cell-division of those cells through responsive shell degradation on-demand.”
Professor Choi commented, “Although the cell encapsulation technology is still in its infancy, as the technology matures the application of cell-manipulation technology will be actualized.” He highlighted that “it will serve as a breakthrough to problems faced by cell-based applications.”
Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research was led by two Master’s candidates, Ji Hun Park and Kyung Hwan Kim, under the joint guidance of research professors from KAIST and the University of Melbourne.
Figure 1: Lead article of Angewandte Chemie
Background: Shows a live native yeast (in green) encapsulated in a metal-polyphenol film (in red) illustrating the vitality of the yeast
Front: A native yeast at each encapsulation stage
Pictured on the bottom left is a cell prior to encapsulation. Following the red arrow, the native yeast is in purple to show metal-polyphenol film formed around the cell. The cell after the green arrow is a visualization of the degradation of the film in weak acidic condition.
Figure 2: A mimetic diagram of cell encapsulation with a metal-polyphenol film
Top: A native yeast before encapsulation
Middle: A native yeast encapsulated with Tannic Acid-Fe (III) Nanoshell – cell-division of the encapsulated cell is controlled by pH and the shell is protected against silver nanoparticle, lytic enzyme, and UV-C
Bottom: Shell degradation on-demand depending on pH
2014.11.18 View 10623