Technology
-
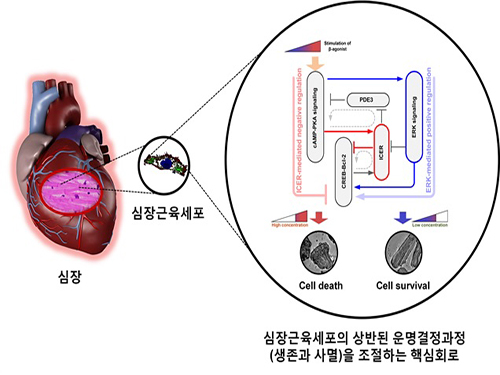 A Key Signal Transduction Pathway Switch in Cardiomyocyte Identified
A KAIST research team has identified the fundamental principle in deciding the fate of cardiomyocyte or heart muscle cells. They have determined that it depends on the degree of stimulus in β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway in the cardiomyocyte to control cells' survival or death. The findings, the team hopes, can be used to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.
The research was led by KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering Chair Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and conducted by Dr. Sung-Young Shin (lead author) and Ph.D. candidates Ho-Sung Lee and Joon-Hyuk Kang. The research was conducted jointly with GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology) Department of Biological Sciences Professor Do-Han Kim’s team. The research was supported by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The paper was published in Nature Communications on December 17, 2014 with the title, “The switching role of β-adrenergic receptor signalling in cell survival or death decision of cardiomyocytes.”
The β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway can promote cell survival (mediated by β2 receptors), but also can result in cell death by inducing toxin (mediated by β1 receptors) that leads to various heart diseases including heart failure. Past attempts to identify the fundamental principle in the fate determining process of cardiomyocyte based on β-adrenergic receptor signalling concluded without much success.
The β-adrenergic receptor is a type of protein on the cell membrane of cardiomyocyte (heart muscle cell) that when stimulated by neurohormones such as epinephrine or norepinephrine would transduce signals making the cardiomyocyte contract faster and stronger.
The research team used large-scale computer simulation analysis and systems biology to identify ERK* and ICER** signal transduction pathways mediated by a feed-forward circuit as a key molecular switch that decides between cell survival and death.
Weak β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ERK signal transduction pathway, increasing Bcl-2*** protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte survival. On the other hand, strong β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ICER signal transduction pathway, reducing Bcl-2 protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte death.
Researchers used a systems biology approach to identify the mechanism of B-blocker****, a common drug prescribed for heart failure. When cardiomyocyte is treated with β1 inhibitor, strong stimulation on β-adrenergic receptor increases Bcl-2 expression, improving the chance of cardiomyocyte survival, a cell protection effect.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, “This research used systems biology, an integrated, convergence research of IT (information technology) and BT (biotechnology), to successfully identify the mechanism in deciding the fate of cardiomyocytes based on the β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway for the first time. I am hopeful that this research will enable the control of cardiomyocyte survival and death to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.”
Professor Cho’s team was the first to pioneer a new field of systems biology, especially concerning the complex signal transduction network involved in diseases. Their research is focused on modelling, analyzing simulations, and experimentally proving signal pathways. Professor Cho has published 140 articles in international journals including Cell, Science, and Nature.
* ERK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinases): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell survival
** ICER (Inducible cAMP early repressor): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell death
*** Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2): Key signal transduction molecule involved in promotion of cell survival
**** β-blocker: Drug that acts as β-adrenergic receptor inhibitor known to slow the progression of heart failure, hence used most commonly in medicine.
Picture: A schematic diagram for the β-AR signalling network
2015.01.05 View 14135
A Key Signal Transduction Pathway Switch in Cardiomyocyte Identified
A KAIST research team has identified the fundamental principle in deciding the fate of cardiomyocyte or heart muscle cells. They have determined that it depends on the degree of stimulus in β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway in the cardiomyocyte to control cells' survival or death. The findings, the team hopes, can be used to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.
The research was led by KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering Chair Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and conducted by Dr. Sung-Young Shin (lead author) and Ph.D. candidates Ho-Sung Lee and Joon-Hyuk Kang. The research was conducted jointly with GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology) Department of Biological Sciences Professor Do-Han Kim’s team. The research was supported by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The paper was published in Nature Communications on December 17, 2014 with the title, “The switching role of β-adrenergic receptor signalling in cell survival or death decision of cardiomyocytes.”
The β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway can promote cell survival (mediated by β2 receptors), but also can result in cell death by inducing toxin (mediated by β1 receptors) that leads to various heart diseases including heart failure. Past attempts to identify the fundamental principle in the fate determining process of cardiomyocyte based on β-adrenergic receptor signalling concluded without much success.
The β-adrenergic receptor is a type of protein on the cell membrane of cardiomyocyte (heart muscle cell) that when stimulated by neurohormones such as epinephrine or norepinephrine would transduce signals making the cardiomyocyte contract faster and stronger.
The research team used large-scale computer simulation analysis and systems biology to identify ERK* and ICER** signal transduction pathways mediated by a feed-forward circuit as a key molecular switch that decides between cell survival and death.
Weak β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ERK signal transduction pathway, increasing Bcl-2*** protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte survival. On the other hand, strong β-adrenergic receptor stimulations activate ICER signal transduction pathway, reducing Bcl-2 protein expression to promote cardiomyocyte death.
Researchers used a systems biology approach to identify the mechanism of B-blocker****, a common drug prescribed for heart failure. When cardiomyocyte is treated with β1 inhibitor, strong stimulation on β-adrenergic receptor increases Bcl-2 expression, improving the chance of cardiomyocyte survival, a cell protection effect.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, “This research used systems biology, an integrated, convergence research of IT (information technology) and BT (biotechnology), to successfully identify the mechanism in deciding the fate of cardiomyocytes based on the β-adrenergic receptor signal transduction pathway for the first time. I am hopeful that this research will enable the control of cardiomyocyte survival and death to treat various heart diseases including heart failure.”
Professor Cho’s team was the first to pioneer a new field of systems biology, especially concerning the complex signal transduction network involved in diseases. Their research is focused on modelling, analyzing simulations, and experimentally proving signal pathways. Professor Cho has published 140 articles in international journals including Cell, Science, and Nature.
* ERK (Extracellular signal-regulated kinases): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell survival
** ICER (Inducible cAMP early repressor): Signal transduction molecule involved in cell death
*** Bcl-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2): Key signal transduction molecule involved in promotion of cell survival
**** β-blocker: Drug that acts as β-adrenergic receptor inhibitor known to slow the progression of heart failure, hence used most commonly in medicine.
Picture: A schematic diagram for the β-AR signalling network
2015.01.05 View 14135 -
 The Bio-Synergy Research Center, KAIST, Hosts an Annual Meeting
The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of the Republic of Korea founded the Bio-Synergy Research Center (BSRC) at KAIST in 2013 to develop source technology and generate new knowledge by conducting convergence research projects in natural resources with information technology (IT) and biotechnology.
The BSRC hosted an annual meeting on November 21, 2014, at the KAIST campus and reviewed the progress it made this year with the participation of President Steve Kang of KAIST, Commissioner Young-min Kim of KIPO, and Director Doheon Lee of BSRC.
The Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPO) provided BSRC with its database in Korean traditional medicine that includes a vast amount of information about disease symptoms, native medicinal herbs and plant extracts, prescriptions, and chemical compounds used for medication. The database, “Compound Combination-Oriented Natural Product Database with Unified Terminology (COCUNUT),” holds approximately one million data sets in four major categories: prescriptions, medicinal resources, medicine components and functions, and diseases.
Based on COCUNUT, BSRC has been working on the standardization of Korean traditional medicine such as the development of data mapping and text mining technology and the analysis of big data in accordance with the said categories. Using IT and biotechnology, the center has also created a virtual human body to explain how traditional medicine works in human body, thereby contributing to the development of new natural materials for medicine.
2014.12.03 View 8306
The Bio-Synergy Research Center, KAIST, Hosts an Annual Meeting
The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of the Republic of Korea founded the Bio-Synergy Research Center (BSRC) at KAIST in 2013 to develop source technology and generate new knowledge by conducting convergence research projects in natural resources with information technology (IT) and biotechnology.
The BSRC hosted an annual meeting on November 21, 2014, at the KAIST campus and reviewed the progress it made this year with the participation of President Steve Kang of KAIST, Commissioner Young-min Kim of KIPO, and Director Doheon Lee of BSRC.
The Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPO) provided BSRC with its database in Korean traditional medicine that includes a vast amount of information about disease symptoms, native medicinal herbs and plant extracts, prescriptions, and chemical compounds used for medication. The database, “Compound Combination-Oriented Natural Product Database with Unified Terminology (COCUNUT),” holds approximately one million data sets in four major categories: prescriptions, medicinal resources, medicine components and functions, and diseases.
Based on COCUNUT, BSRC has been working on the standardization of Korean traditional medicine such as the development of data mapping and text mining technology and the analysis of big data in accordance with the said categories. Using IT and biotechnology, the center has also created a virtual human body to explain how traditional medicine works in human body, thereby contributing to the development of new natural materials for medicine.
2014.12.03 View 8306 -
 The 2014 Wearable Computer Competition Takes Place at KAIST
“This is a smart wig for patients who are reluctant to go outdoors because their hair is falling out from cancer treatment.”
A graduate student from Sungkyunkwan University, Jee-Hoon Lee enthusiastically explains his project at the KAIST KI Building where the 2014 Wearable Computer Competition was held. He said, “The sensor embedded inside the wig monitors the heart rate and the body temperature, and during an emergency, the device warns the patient about the situation. The product emphasizes two aspects; it notifies the patient in emergency situations, and it encourages patients to perform outdoor activities by enhancing their looks.”
The the tenth anniversary meeting of the 2014 Wearable Computer Competition took place at the KAIST campus on November 13-14, 2014.
A wearable computer is a mobile device designed to be put on the body or clothes so that a user can comfortably use it while walking. Recently, these devices that are able to support versatile internet-based services through smartphones are receiving a great deal of attention.
Wearable devices have been employed in two categorizes: health checks and information-entertainment. In this year’s competition, six healthcare products and nine information-entertainment products were exhibited.
Among these products, participants favored a smart helmet for motorcycle drivers. The driver can see through a rear camera with a navigation screen of the smartphone and text messages through the screen installed in the front glass of the helmet. Another product included a uniform that can control presentation slides by means of motion detection and voice recognition technology. Yet another popular device offered an insole to guide travelers to their destination with the help of motion sensors.
The chairman of the competition, Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST said, “Wearable devices such as smart watches, glasses, and clothes are gaining interest these days. Through this event, people will have a chance to look at the creativity of our students through the display of their wearable devices. In turn, these devices will advance computer technology.”
The third annual wearable computer workshop on convergence technology of wearable computers followed the competition. In the workshop, experts from leading information technology companies such as Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, and KT Corporation addressed the convergence technology of wearable computers and trends in the field.
2014.11.19 View 10902
The 2014 Wearable Computer Competition Takes Place at KAIST
“This is a smart wig for patients who are reluctant to go outdoors because their hair is falling out from cancer treatment.”
A graduate student from Sungkyunkwan University, Jee-Hoon Lee enthusiastically explains his project at the KAIST KI Building where the 2014 Wearable Computer Competition was held. He said, “The sensor embedded inside the wig monitors the heart rate and the body temperature, and during an emergency, the device warns the patient about the situation. The product emphasizes two aspects; it notifies the patient in emergency situations, and it encourages patients to perform outdoor activities by enhancing their looks.”
The the tenth anniversary meeting of the 2014 Wearable Computer Competition took place at the KAIST campus on November 13-14, 2014.
A wearable computer is a mobile device designed to be put on the body or clothes so that a user can comfortably use it while walking. Recently, these devices that are able to support versatile internet-based services through smartphones are receiving a great deal of attention.
Wearable devices have been employed in two categorizes: health checks and information-entertainment. In this year’s competition, six healthcare products and nine information-entertainment products were exhibited.
Among these products, participants favored a smart helmet for motorcycle drivers. The driver can see through a rear camera with a navigation screen of the smartphone and text messages through the screen installed in the front glass of the helmet. Another product included a uniform that can control presentation slides by means of motion detection and voice recognition technology. Yet another popular device offered an insole to guide travelers to their destination with the help of motion sensors.
The chairman of the competition, Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST said, “Wearable devices such as smart watches, glasses, and clothes are gaining interest these days. Through this event, people will have a chance to look at the creativity of our students through the display of their wearable devices. In turn, these devices will advance computer technology.”
The third annual wearable computer workshop on convergence technology of wearable computers followed the competition. In the workshop, experts from leading information technology companies such as Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, and KT Corporation addressed the convergence technology of wearable computers and trends in the field.
2014.11.19 View 10902 -
 3D Printer Developed by KAIST Undergraduate Students
More than 100 Pre-orders Prior to Product Launch Made
KAIST undergraduate students received more than 100 pre-orders before the launch for 3D printers they developed and became a hot topic of interest.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations (Head Hong-Kyu Lee) had a launch party at Daejeon Riviera Hotel on 17 November 2014 for “Commercial Delta 3D Printer” developed by KAIST undergraduate students inviting around 50 businesses, buyers and representatives of 3D Printing Industry Association.
“3D Printer” uses blueprints of products such as toys, mug cups and chairs to make 3D objects and is thought to be revolutionary technology in manufacturing industry. The interest has grown as recent printers could print even fruits and cosmetics.
The printing structure of 3D printer can be divided roughly into horizontal Mendel method and Delta method. KAIST students focused on the Delta method to give a differentiated product from 90% of commercial products that use Mendel method.
First, the students focused on lowering the cost of unit price by using self-developed components. The carriage (transport machine) of the product is replaced by self-developed components instead of bearing to reduce the noise and the linking method was changed to beads from loop guide to increase the completeness of the printed product. Also, an auto-levelling is loaded to ensure the nozzle and the bed is parallel and hence increasing convenience for the users. Further, the printer, designed by a product designer in Germany, is linked to a smartphone application for blueprints.
A student in the development team, Seokhyeon Seo (Department of Computer Science, 3rd Year Undergraduate) said, “The biggest merits of the product are lowering the price to a 1/3 by using self-developed components and reducing the noise.” He continued, “By using a smartphone application, anyone can easily design the product. So it is applicable to use for education or at home”
In the exhibit, “3D Printing Korea 2014,” in Coex, Seoul the printer had a preview demonstration, and received more than 100 pre-orders from educational and business training institutions. Further, buyers from Canada and the US requested opening agencies in their countries.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations Head Hong-Kyu Lee said, “3D printing is an innovative technology that could bring the 3rd industrial revolution.” He continued, “It is still early days but the demand will increase exponentially.”
This project was a research project of KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations led by a development team consisting of 4 undergraduate students of KAIST, one student from University of Oxford and one German product designer.
Students in the picture below are Won-Hoi Kim (Department of Mechanical Engineering), Sung-Hyun Cho (Department of Mechanical Engineering), and Suk-Hyun Seo (Department of Computer Science) from left to right.
2014.11.19 View 11451
3D Printer Developed by KAIST Undergraduate Students
More than 100 Pre-orders Prior to Product Launch Made
KAIST undergraduate students received more than 100 pre-orders before the launch for 3D printers they developed and became a hot topic of interest.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations (Head Hong-Kyu Lee) had a launch party at Daejeon Riviera Hotel on 17 November 2014 for “Commercial Delta 3D Printer” developed by KAIST undergraduate students inviting around 50 businesses, buyers and representatives of 3D Printing Industry Association.
“3D Printer” uses blueprints of products such as toys, mug cups and chairs to make 3D objects and is thought to be revolutionary technology in manufacturing industry. The interest has grown as recent printers could print even fruits and cosmetics.
The printing structure of 3D printer can be divided roughly into horizontal Mendel method and Delta method. KAIST students focused on the Delta method to give a differentiated product from 90% of commercial products that use Mendel method.
First, the students focused on lowering the cost of unit price by using self-developed components. The carriage (transport machine) of the product is replaced by self-developed components instead of bearing to reduce the noise and the linking method was changed to beads from loop guide to increase the completeness of the printed product. Also, an auto-levelling is loaded to ensure the nozzle and the bed is parallel and hence increasing convenience for the users. Further, the printer, designed by a product designer in Germany, is linked to a smartphone application for blueprints.
A student in the development team, Seokhyeon Seo (Department of Computer Science, 3rd Year Undergraduate) said, “The biggest merits of the product are lowering the price to a 1/3 by using self-developed components and reducing the noise.” He continued, “By using a smartphone application, anyone can easily design the product. So it is applicable to use for education or at home”
In the exhibit, “3D Printing Korea 2014,” in Coex, Seoul the printer had a preview demonstration, and received more than 100 pre-orders from educational and business training institutions. Further, buyers from Canada and the US requested opening agencies in their countries.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations Head Hong-Kyu Lee said, “3D printing is an innovative technology that could bring the 3rd industrial revolution.” He continued, “It is still early days but the demand will increase exponentially.”
This project was a research project of KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations led by a development team consisting of 4 undergraduate students of KAIST, one student from University of Oxford and one German product designer.
Students in the picture below are Won-Hoi Kim (Department of Mechanical Engineering), Sung-Hyun Cho (Department of Mechanical Engineering), and Suk-Hyun Seo (Department of Computer Science) from left to right.
2014.11.19 View 11451 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Accepts an Honorary Professorship at Beijing University of Chemical Technology
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has been appointed an honorary professor at Beijing University of Chemical Technology (BUCT). Founded in 1958, BUCT is one of the outstanding universities in mainland China, especially in chemistry studies.
In addition to the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2012), Shanghai Jiao Tong University (2013), Wuhan University (2014), and Hebei University of Technology (2014), this is the fifth honorary professorship Professor Lee has received from higher education institutions in China.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving as the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
2014.11.13 View 12209
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Accepts an Honorary Professorship at Beijing University of Chemical Technology
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has been appointed an honorary professor at Beijing University of Chemical Technology (BUCT). Founded in 1958, BUCT is one of the outstanding universities in mainland China, especially in chemistry studies.
In addition to the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2012), Shanghai Jiao Tong University (2013), Wuhan University (2014), and Hebei University of Technology (2014), this is the fifth honorary professorship Professor Lee has received from higher education institutions in China.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving as the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
2014.11.13 View 12209 -
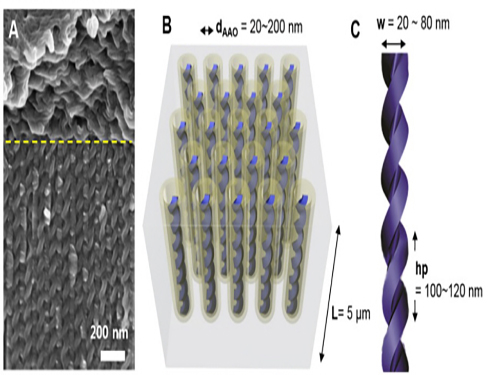 KAIST Develops Core Technology to Synthesize a Helical Nanostructure
Professor Dong-Ki Yoon’s research team of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology (GSNT) at KAIST has developed helical nanostructures using self-assembly processes. The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America(PNAS) on the October 7th.
This technology enables the synthesis of various helical structures on a relatively large confined area. Its synthesis is often considered the most arduous for three dimensional structures. Formed from liquid crystal, the structure holds a regular helical structure within the confined space of 20 to 300 nanometers. Also, the distance between each pattern increased as the diameter of the nanostructure increased.
Liquid crystals have a unique property of responding sensitively to the surrounding electromagnetic field. The technology, in combination with the electromagnetic property of liquid crystal, is expected to foster the development of highly efficient optoelectronic devices.
Using this technology, it is possible to develop three dimensional patterning technology beyond the current semiconductor manufacturing technology which uses two dimensional photolithography processes. Three-dimensional semiconductor devices are expected to store hundred times more data than current devices. They will also lower costs by simplifying manufacturing processes.
The essence of this research, “self-assembly in confined space,” refers to controlling complex nanostructures, which can be synthesized from materials such as macromolecules, liquid crystal molecules, and biomolecules in relation to surrounding environments including the temperature, concentration, and pH.
The research team produced a confined space with a length of tens of nanometers by using a porous anodized aluminum membrane induced from an electrochemical reaction. They successfully synthesized independently controlled helical nanostructures by forming the helical structures from liquid crystal molecules within that space.
Professor Yoon said, “This research examines the physicochemical principle of controlling helical nanostructures.” He highlighted the significance of the research and commented, “The technology enables the control of complex nanostructures from organic molecules by using confined space and surface reforming.”
He added that, “When grafted with nanotechnology or information technology, this technology will spur new growth to liquid crystal-related industries such as the LCD.”
The research was led by two Ph.D. candidates, Hanim Kim and Sunhee Lee, under the guidance of Professor Yoon. Dr. Tae-Joo Shin of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, Professor Sang-Bok Lee of the University of Maryland, and Professor Noel Clark of the University of Colorado also participated.
Picture 1. Electron Microscopy Pictures and Conceptual Diagrams of Helical Nanostructures
Picture 2. Electron Microscopy Pictures of Manufactured Helical Nanostructures
2014.10.29 View 9339
KAIST Develops Core Technology to Synthesize a Helical Nanostructure
Professor Dong-Ki Yoon’s research team of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology (GSNT) at KAIST has developed helical nanostructures using self-assembly processes. The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America(PNAS) on the October 7th.
This technology enables the synthesis of various helical structures on a relatively large confined area. Its synthesis is often considered the most arduous for three dimensional structures. Formed from liquid crystal, the structure holds a regular helical structure within the confined space of 20 to 300 nanometers. Also, the distance between each pattern increased as the diameter of the nanostructure increased.
Liquid crystals have a unique property of responding sensitively to the surrounding electromagnetic field. The technology, in combination with the electromagnetic property of liquid crystal, is expected to foster the development of highly efficient optoelectronic devices.
Using this technology, it is possible to develop three dimensional patterning technology beyond the current semiconductor manufacturing technology which uses two dimensional photolithography processes. Three-dimensional semiconductor devices are expected to store hundred times more data than current devices. They will also lower costs by simplifying manufacturing processes.
The essence of this research, “self-assembly in confined space,” refers to controlling complex nanostructures, which can be synthesized from materials such as macromolecules, liquid crystal molecules, and biomolecules in relation to surrounding environments including the temperature, concentration, and pH.
The research team produced a confined space with a length of tens of nanometers by using a porous anodized aluminum membrane induced from an electrochemical reaction. They successfully synthesized independently controlled helical nanostructures by forming the helical structures from liquid crystal molecules within that space.
Professor Yoon said, “This research examines the physicochemical principle of controlling helical nanostructures.” He highlighted the significance of the research and commented, “The technology enables the control of complex nanostructures from organic molecules by using confined space and surface reforming.”
He added that, “When grafted with nanotechnology or information technology, this technology will spur new growth to liquid crystal-related industries such as the LCD.”
The research was led by two Ph.D. candidates, Hanim Kim and Sunhee Lee, under the guidance of Professor Yoon. Dr. Tae-Joo Shin of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, Professor Sang-Bok Lee of the University of Maryland, and Professor Noel Clark of the University of Colorado also participated.
Picture 1. Electron Microscopy Pictures and Conceptual Diagrams of Helical Nanostructures
Picture 2. Electron Microscopy Pictures of Manufactured Helical Nanostructures
2014.10.29 View 9339 -
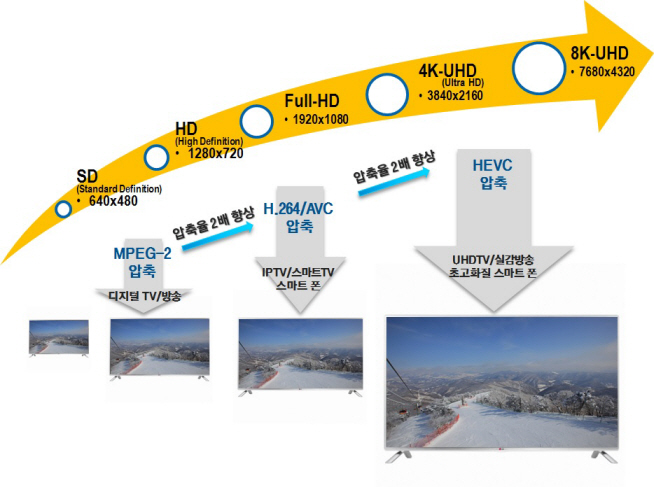 KAIST Registers an Internationally Recognized Standard Patent
A video compression technology, jointly developed by Professor Mun-Chul Kim of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), and the Korean Broadcasting System (KBS), is registered internationally as the standard patent in the next-generation High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC).
HEVC (H.265) is an international technology standard that compresses large image data for Ultra High Definition (UHD) televisions and smartphones. It has the twice the compression efficiency as that of H.264/AVC which is most commonly used for processing full HD sources. This means that it is able to compress a video file to half the size while maintaining the same image quality.
Although the related market is at a nascent stage, HEVC technology has already been applied to the latest version of televisions and smartphones. Experts predict that the market will grow to USD 200 billion by 2016, and KAIST is expected to receive a royalty payment of USD 9.3 million from this patent.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO/IEC) established the HEVC standard in January 2013. Also, an international patent pool licensing corporation, MPEG LA announced the HEVC standard patent pool on September 29, 2014.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae, Dean of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) of KAIST, said, “This is an unprecedented case for Korea whereby a core technology developed by a university became an international standard, which has a vast impact on the market.”
President of KAIST, Steve Kang commented, “With its advanced technology, KAIST joined the HEVC standard patent pool as one of the 23 founding members along with Apple, Siemens, and NEC. This is a remarkable achievement.”
Picture 1: Improvements in video compression technology
Picture 2: Comparison of different screen resolutions
2014.10.09 View 13297
KAIST Registers an Internationally Recognized Standard Patent
A video compression technology, jointly developed by Professor Mun-Chul Kim of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), and the Korean Broadcasting System (KBS), is registered internationally as the standard patent in the next-generation High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC).
HEVC (H.265) is an international technology standard that compresses large image data for Ultra High Definition (UHD) televisions and smartphones. It has the twice the compression efficiency as that of H.264/AVC which is most commonly used for processing full HD sources. This means that it is able to compress a video file to half the size while maintaining the same image quality.
Although the related market is at a nascent stage, HEVC technology has already been applied to the latest version of televisions and smartphones. Experts predict that the market will grow to USD 200 billion by 2016, and KAIST is expected to receive a royalty payment of USD 9.3 million from this patent.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO/IEC) established the HEVC standard in January 2013. Also, an international patent pool licensing corporation, MPEG LA announced the HEVC standard patent pool on September 29, 2014.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae, Dean of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) of KAIST, said, “This is an unprecedented case for Korea whereby a core technology developed by a university became an international standard, which has a vast impact on the market.”
President of KAIST, Steve Kang commented, “With its advanced technology, KAIST joined the HEVC standard patent pool as one of the 23 founding members along with Apple, Siemens, and NEC. This is a remarkable achievement.”
Picture 1: Improvements in video compression technology
Picture 2: Comparison of different screen resolutions
2014.10.09 View 13297 -
 KAIST Ranks 26th in Engineering & Technology and 52nd overall in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2014-2015
The 2014-2015 Times Higher Education (THE) World University Rankings were released on October 1, 2014. KAIST took 52nd place in the overall rankings and 26th in the field of engineering and technology.
THE used 13 performance indicators to evaluate universities, grouping them into five areas of teaching, research, citations, industry income, and international outlook.
In recent years, KAIST has seen steady improvements in areas of research, citations, and international outlook. In addition to KAIST, two Korean universities, Seoul National University (50th) and Pohang University of Science and Technology (66th), were included within the top 100 universities.
For details, please visit:
http://www.timeshighereducation.co.uk/world-university-rankings/2014-15/world-ranking.
2014.10.03 View 8945
KAIST Ranks 26th in Engineering & Technology and 52nd overall in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2014-2015
The 2014-2015 Times Higher Education (THE) World University Rankings were released on October 1, 2014. KAIST took 52nd place in the overall rankings and 26th in the field of engineering and technology.
THE used 13 performance indicators to evaluate universities, grouping them into five areas of teaching, research, citations, industry income, and international outlook.
In recent years, KAIST has seen steady improvements in areas of research, citations, and international outlook. In addition to KAIST, two Korean universities, Seoul National University (50th) and Pohang University of Science and Technology (66th), were included within the top 100 universities.
For details, please visit:
http://www.timeshighereducation.co.uk/world-university-rankings/2014-15/world-ranking.
2014.10.03 View 8945 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Participates in the 2014 Summer Davos Forum
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, was invited to lead four sessions at the Annual Meeting 2014, the World Economic Forum, also known as the Summer Davos Forum, which was held in Tianjin, China, from September 10th to 12th.
Two of the four sessions Professor Lee participated in were held on September 10th. At the first session entitled “Biotechnology Ecosystem,” he examined with other panelists the future of bioengineering in depth and discussed major policies and industry trends that will be necessary for the development of future biotechnologies.
Professor Lee later attended the “Strategic Shifts in Healthcare” session as a moderator. Issues related to transforming the health industry such as the next-generation genomics, mobile health and telemedicine, and wearable devices and predictive analytics were addressed.
On September 12, Professor Lee joined the “IdeasLab with KAIST” and gave a presentation on nanotechnology. There was a total of ten IdeasLab sessions held at the Summer Davos Forum, and KAIST was the only Korean university ever invited to host this session. In addition to Professor Lee’s presentation, three more presentations were made by KAIST professors on such topics as “Sustainable Energy and Materials” and “Next-generation Semiconductors.”
Lastly, Professor Lee participated in the “Global Promising Technology” session with the World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council members. At this session, he explained the selection of the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” and “Bio Sector’s Top 10 Technologies” and led discussions about the “2015 Top 10 Technologies” with the council members.
The Davos Forum has been announcing the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” since 2012, and Professor Lee has played a key role in the selection while working as the Chairman of Global Agenda Council. The selection results are presented at the Davos Forum every year and have attracted a lot of attention from around the world.
2014.09.15 View 12536
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Participates in the 2014 Summer Davos Forum
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, was invited to lead four sessions at the Annual Meeting 2014, the World Economic Forum, also known as the Summer Davos Forum, which was held in Tianjin, China, from September 10th to 12th.
Two of the four sessions Professor Lee participated in were held on September 10th. At the first session entitled “Biotechnology Ecosystem,” he examined with other panelists the future of bioengineering in depth and discussed major policies and industry trends that will be necessary for the development of future biotechnologies.
Professor Lee later attended the “Strategic Shifts in Healthcare” session as a moderator. Issues related to transforming the health industry such as the next-generation genomics, mobile health and telemedicine, and wearable devices and predictive analytics were addressed.
On September 12, Professor Lee joined the “IdeasLab with KAIST” and gave a presentation on nanotechnology. There was a total of ten IdeasLab sessions held at the Summer Davos Forum, and KAIST was the only Korean university ever invited to host this session. In addition to Professor Lee’s presentation, three more presentations were made by KAIST professors on such topics as “Sustainable Energy and Materials” and “Next-generation Semiconductors.”
Lastly, Professor Lee participated in the “Global Promising Technology” session with the World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council members. At this session, he explained the selection of the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” and “Bio Sector’s Top 10 Technologies” and led discussions about the “2015 Top 10 Technologies” with the council members.
The Davos Forum has been announcing the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” since 2012, and Professor Lee has played a key role in the selection while working as the Chairman of Global Agenda Council. The selection results are presented at the Davos Forum every year and have attracted a lot of attention from around the world.
2014.09.15 View 12536 -
 President Steve Kang of KAIST Attends the 2014 Summer Davos Forum in Tianjin, China
President Steve Kang of KAIST will attend the 2014 Annual Meeting of the New Champions, the World Economic Forum (WEF), to be held on September 10-12, 2014 in Tianjin, China.
KAIST holds its own IdeasLab session on nanotechnology on September 12, 2014.
On September 10, 2014, President Steve Kang will participate in a private session hosted by the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) community at WEF as a panelist.
In addition to President Kang, eight presidents from top global universities such as the National University of Singapore, Peking University, ETH Zurich (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology), University of Tokyo, and Carnegie Mellon University will join the panel discussion under the topic, “Increasing the Translational Impact of University Research.” Specifically, the presidents will address issues related to the importance of university-led technology transfer in Asia, key strategies and goals for technology transfer, and implementation approaches taken by each university to promote technology transfer from university to industry.
President Kang was invited to this GULF session, the only attendant from Korean universities, in recognition of his long time experience and expertise in education and research.
In 2006, WEF created the GULF, a small community of the presidents of top universities in the world, aiming to offer an open platform for high-level dialogues on issues of higher education and research with other sectors, as well as to foster collaboration between universities in areas of significance for global policy.
As of 2014, a total of 25 globally leading universities, including Harvard University, University of Cambridge, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology, are GULF members. KAIST, which joined the club this year, is the only Korean university.
The 2014 Annual Meeting of the New Champions, also known as the Summer Davos Forum, hosts numerous sessions under the theme of “Creating Value through Innovation.” At the Forum, a total of ten IdeasLab sessions will be hosted. KAIST was invited to run its own IdeasLab on nanotechnology on September 12, 2014.
Together with President Kang, Professors Sang Ouk Kim and Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science Engineering, KAIST, and Professors Sang Yup Lee and Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, will present their own speeches on the topic entitled “From diagnostics to materials, how is nanotechnology changing lives?”
President Kang will give the opening speech at the KAIST IdeasLab.
He said that an invitation from WEF to join the IdeasLab spoke well for KAIST:
“KAIST is the first and the only Korean university ever invited to run its own IdeasLab at the World Economic Forum. The IdeasLab is an expert group meeting, conducted only by the world’s most prestigious universities and research institutes. At the IdeasLab sessions, global leaders from different sectors identify major issues facing higher education and humanity and explore solutions through science and technology innovation. Holding our own IdeasLab on one of our strongest fields, nanotechnology, is indeed an excellent opportunity for KAIST to show its strength in academic and research excellence on the global stage.”
2014.09.08 View 14827
President Steve Kang of KAIST Attends the 2014 Summer Davos Forum in Tianjin, China
President Steve Kang of KAIST will attend the 2014 Annual Meeting of the New Champions, the World Economic Forum (WEF), to be held on September 10-12, 2014 in Tianjin, China.
KAIST holds its own IdeasLab session on nanotechnology on September 12, 2014.
On September 10, 2014, President Steve Kang will participate in a private session hosted by the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) community at WEF as a panelist.
In addition to President Kang, eight presidents from top global universities such as the National University of Singapore, Peking University, ETH Zurich (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology), University of Tokyo, and Carnegie Mellon University will join the panel discussion under the topic, “Increasing the Translational Impact of University Research.” Specifically, the presidents will address issues related to the importance of university-led technology transfer in Asia, key strategies and goals for technology transfer, and implementation approaches taken by each university to promote technology transfer from university to industry.
President Kang was invited to this GULF session, the only attendant from Korean universities, in recognition of his long time experience and expertise in education and research.
In 2006, WEF created the GULF, a small community of the presidents of top universities in the world, aiming to offer an open platform for high-level dialogues on issues of higher education and research with other sectors, as well as to foster collaboration between universities in areas of significance for global policy.
As of 2014, a total of 25 globally leading universities, including Harvard University, University of Cambridge, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology, are GULF members. KAIST, which joined the club this year, is the only Korean university.
The 2014 Annual Meeting of the New Champions, also known as the Summer Davos Forum, hosts numerous sessions under the theme of “Creating Value through Innovation.” At the Forum, a total of ten IdeasLab sessions will be hosted. KAIST was invited to run its own IdeasLab on nanotechnology on September 12, 2014.
Together with President Kang, Professors Sang Ouk Kim and Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science Engineering, KAIST, and Professors Sang Yup Lee and Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, will present their own speeches on the topic entitled “From diagnostics to materials, how is nanotechnology changing lives?”
President Kang will give the opening speech at the KAIST IdeasLab.
He said that an invitation from WEF to join the IdeasLab spoke well for KAIST:
“KAIST is the first and the only Korean university ever invited to run its own IdeasLab at the World Economic Forum. The IdeasLab is an expert group meeting, conducted only by the world’s most prestigious universities and research institutes. At the IdeasLab sessions, global leaders from different sectors identify major issues facing higher education and humanity and explore solutions through science and technology innovation. Holding our own IdeasLab on one of our strongest fields, nanotechnology, is indeed an excellent opportunity for KAIST to show its strength in academic and research excellence on the global stage.”
2014.09.08 View 14827 -
 Kiseok Song, a Ph.D. candidate in the Electrical Engineering Department, receives the 2014 Marconi Society Young Scholar Award
Established
in 1974 to commemorate the eminent Italian inventor and electrical engineer,
Guglielmo Marconi, the Marconi Society has recognized significant contributions
in science and technology by awarding the Marconi Prize, with an annual USD
100,000 grant, to a living scientist who has made great advancements in
communications technology.
Along
with the Marconi Prize, the Society has been presenting the Young Scholars
Awards over the past six years to reward young and emerging scientists’ brilliant
academic and research achievements as well as their entrepreneurship. For this
year’s seventh Young Scholar Awards, a KAIST doctoral student was selected as
one of the two recipients.
Kiseok
Song, a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Electrical Engineering, KAIST, has
been named as a 2014 Marconi Society Paul Baran Young Scholar. The Marconi Society said that Song was being recognized for "his
academic achievements and leadership in the field of communications and
information science,” according to a press release distributed by the Society on August 28, 2014.
Studying
under the advice of Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Department of Electrical
Engineering at KAIST, Song has developed bio-medical System on a Chip (SoC)
such as smart wireless bio-medical systems combined with optimized SoCs,
compact bio-medical patch systems connected to smart phones, smart electro-acupuncture
and transdermal drug delivery, and multi-modal non-invasive glucose monitors.
The
press release quoted Professor Yoo’s comment on the meaning of Song’s research:
“All
of these bio-medical systems open a new healthcare paradigm to improve people’s
quality of life in combination with the current mobile smart phones.”
In
addition to Song, Himanshu Asnani, a Stanford Ph.D. candidate and system engineer
at Ericsson Silicon Valley, received the other award. The award
ceremony will be held at the Marconi Society’s annual award gala at the
National Academies of Science Building in Washington D.C., on October 2, 2014.
For
details, please read the following press release:
The
Marconi Society, Press Release, August 28, 2014
“Kiseok
Song Receives the 2014 Marconi Society Young Scholar Award”
http://www.marconisociety.org/press/2014Song.html
2014.09.08 View 9217
Kiseok Song, a Ph.D. candidate in the Electrical Engineering Department, receives the 2014 Marconi Society Young Scholar Award
Established
in 1974 to commemorate the eminent Italian inventor and electrical engineer,
Guglielmo Marconi, the Marconi Society has recognized significant contributions
in science and technology by awarding the Marconi Prize, with an annual USD
100,000 grant, to a living scientist who has made great advancements in
communications technology.
Along
with the Marconi Prize, the Society has been presenting the Young Scholars
Awards over the past six years to reward young and emerging scientists’ brilliant
academic and research achievements as well as their entrepreneurship. For this
year’s seventh Young Scholar Awards, a KAIST doctoral student was selected as
one of the two recipients.
Kiseok
Song, a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Electrical Engineering, KAIST, has
been named as a 2014 Marconi Society Paul Baran Young Scholar. The Marconi Society said that Song was being recognized for "his
academic achievements and leadership in the field of communications and
information science,” according to a press release distributed by the Society on August 28, 2014.
Studying
under the advice of Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Department of Electrical
Engineering at KAIST, Song has developed bio-medical System on a Chip (SoC)
such as smart wireless bio-medical systems combined with optimized SoCs,
compact bio-medical patch systems connected to smart phones, smart electro-acupuncture
and transdermal drug delivery, and multi-modal non-invasive glucose monitors.
The
press release quoted Professor Yoo’s comment on the meaning of Song’s research:
“All
of these bio-medical systems open a new healthcare paradigm to improve people’s
quality of life in combination with the current mobile smart phones.”
In
addition to Song, Himanshu Asnani, a Stanford Ph.D. candidate and system engineer
at Ericsson Silicon Valley, received the other award. The award
ceremony will be held at the Marconi Society’s annual award gala at the
National Academies of Science Building in Washington D.C., on October 2, 2014.
For
details, please read the following press release:
The
Marconi Society, Press Release, August 28, 2014
“Kiseok
Song Receives the 2014 Marconi Society Young Scholar Award”
http://www.marconisociety.org/press/2014Song.html
2014.09.08 View 9217 -
 Professor Ilkwon Oh Receives the Energy Technology Innovation Award
Professor Ilkwon Oh from the Division of Ocean Systems Engineering at the School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, KAIST, received the Energy Technology Innovation Award at the Energy Tech Insight 2014 Conference, which was held on August 28, 2014 at COEX in Seoul. The conference was co-hosted by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, Republic of Korea, and the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Oh has been recognized for his distinguished research on a synthetic technology to develop 3-dimensional carbon nanostructures based on defect engineering and for his efforts to apply this technology to produce cathode materials for high performance, high density lithium-ion secondary batteries.
In 2010, the Ministry of Education, the Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea included Professor Oh's research in the 100 Best Research in Basic Sciences of the Year, and the 50 Best Research in Basic Sciences in 2012 and 2014, respectively.
2014.09.07 View 9241
Professor Ilkwon Oh Receives the Energy Technology Innovation Award
Professor Ilkwon Oh from the Division of Ocean Systems Engineering at the School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, KAIST, received the Energy Technology Innovation Award at the Energy Tech Insight 2014 Conference, which was held on August 28, 2014 at COEX in Seoul. The conference was co-hosted by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, Republic of Korea, and the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Oh has been recognized for his distinguished research on a synthetic technology to develop 3-dimensional carbon nanostructures based on defect engineering and for his efforts to apply this technology to produce cathode materials for high performance, high density lithium-ion secondary batteries.
In 2010, the Ministry of Education, the Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea included Professor Oh's research in the 100 Best Research in Basic Sciences of the Year, and the 50 Best Research in Basic Sciences in 2012 and 2014, respectively.
2014.09.07 View 9241