system
-
 Book Announcement: Sound Visualization and Manipulation
The movie
Gravity
won seven Oscar awards this year, one of which was for its outstanding 3D sound mixing, immersing viewers in the full experience of the troubled space expedition.
3D audio effects are generated by manipulating the sound produced by speakers, speaker-arrays, or headphones to place a virtual sound source at a desired location in 3D space such as behind, above, or below the listener's head.
Two professors from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST have recently published a book that explains two important technologies related to 3D sound effects: sound visualization and manipulation.
Professor Yang-Hann Kim, an eminent scholar in sound engineering, and Professor Jung-Woo Choi collaborated to write Sound Visualization and Manipulation (Wily 2013), which uniquely addresses the two most important problems in the field in a unified way.
The book introduces general concepts and theories and describes a number of techniques in sound visualization and manipulation, offering an interrelated approach to two very different topics: sound field visualization techniques based on microphone arrays and controlled sound field generation techniques using loudspeaker arrays.
The authors also display a solid understanding of the associated physical and mathematical concepts applied to solve the visualization and manipulation problems and provide extensive examples demonstrating the benefits and drawbacks of various applications, including beamforming and acoustic holography technology.
The book will be an excellent reference for graduate students, researchers, and professionals in acoustic engineering, as well as in audio and noise control system development.
For detailed descriptions of the book:
http://as.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-1118368479.html
2014.03.10 View 14264
Book Announcement: Sound Visualization and Manipulation
The movie
Gravity
won seven Oscar awards this year, one of which was for its outstanding 3D sound mixing, immersing viewers in the full experience of the troubled space expedition.
3D audio effects are generated by manipulating the sound produced by speakers, speaker-arrays, or headphones to place a virtual sound source at a desired location in 3D space such as behind, above, or below the listener's head.
Two professors from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST have recently published a book that explains two important technologies related to 3D sound effects: sound visualization and manipulation.
Professor Yang-Hann Kim, an eminent scholar in sound engineering, and Professor Jung-Woo Choi collaborated to write Sound Visualization and Manipulation (Wily 2013), which uniquely addresses the two most important problems in the field in a unified way.
The book introduces general concepts and theories and describes a number of techniques in sound visualization and manipulation, offering an interrelated approach to two very different topics: sound field visualization techniques based on microphone arrays and controlled sound field generation techniques using loudspeaker arrays.
The authors also display a solid understanding of the associated physical and mathematical concepts applied to solve the visualization and manipulation problems and provide extensive examples demonstrating the benefits and drawbacks of various applications, including beamforming and acoustic holography technology.
The book will be an excellent reference for graduate students, researchers, and professionals in acoustic engineering, as well as in audio and noise control system development.
For detailed descriptions of the book:
http://as.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-1118368479.html
2014.03.10 View 14264 -
 Professor Dong-Soo Han received the Prime Minister's award for creative economy in 2013
The 2013 Korea Creative Economy Awards, presented to companies or individuals that contributed to the implementation of the Korean government’s economic growth initiative called “creative economy” with the development of new technology, was held on December 12th at the InterContinental Seoul Coex. Professor Dong-Soo Han from the Department of Computer Science at KAIST received the Prime Minister’s award.
Professor Han was recognized for his research accomplishments on the development of an indoor GPS system and an integrated indoor/outdoor navigation system, as well as for his publication of a book for beginners who are interested in patents. He has applied 50 patents and registered 30 patents in Korea and abroad for the indoor positioning technology and smartphone application services.
His research work was also introduced to the public at the exhibition held after the award ceremony during December 12th-15th at the Coex convention center in Seoul.
2014.01.05 View 8624
Professor Dong-Soo Han received the Prime Minister's award for creative economy in 2013
The 2013 Korea Creative Economy Awards, presented to companies or individuals that contributed to the implementation of the Korean government’s economic growth initiative called “creative economy” with the development of new technology, was held on December 12th at the InterContinental Seoul Coex. Professor Dong-Soo Han from the Department of Computer Science at KAIST received the Prime Minister’s award.
Professor Han was recognized for his research accomplishments on the development of an indoor GPS system and an integrated indoor/outdoor navigation system, as well as for his publication of a book for beginners who are interested in patents. He has applied 50 patents and registered 30 patents in Korea and abroad for the indoor positioning technology and smartphone application services.
His research work was also introduced to the public at the exhibition held after the award ceremony during December 12th-15th at the Coex convention center in Seoul.
2014.01.05 View 8624 -
 Professor Dong-Yol Yang received an award for scholar of the year 2013 from the Korean mechanical engineering community
Professor Dong-Yol Yang from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST was selected as “the scholar of the year 2013” at an annual event held by the Korean Federation of Mechanical Engineering Societies, the Korea Association of Machinery Industry, and other mechanical engineering research institutes in Korea. The event, the Day of the Machines, is the nation’s biggest gathering for engineers, scholars, and researchers in mechanical engineering, at which winners of the awards for the person of the year in academia, business, and engineering are announced.
Professor Yang was chosen for his lifetime achievement as a scholar in the field of three-dimensional shape precision processing by developing an innovative processing technology that contributes to the advancement of mechanical engineering and industry. He also introduced the three-dimensional fast processing to Korea from 1990 and developed world-class subminiature fast processing, the first of its kind in Korea.In 2013, Professor Yang identified geometric deformation elements in mechanical engineering for the first time in the world, an essential component for nano mobile system and received the best conference paper award at the 3M-Nano International Conference.
2014.01.05 View 10052
Professor Dong-Yol Yang received an award for scholar of the year 2013 from the Korean mechanical engineering community
Professor Dong-Yol Yang from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST was selected as “the scholar of the year 2013” at an annual event held by the Korean Federation of Mechanical Engineering Societies, the Korea Association of Machinery Industry, and other mechanical engineering research institutes in Korea. The event, the Day of the Machines, is the nation’s biggest gathering for engineers, scholars, and researchers in mechanical engineering, at which winners of the awards for the person of the year in academia, business, and engineering are announced.
Professor Yang was chosen for his lifetime achievement as a scholar in the field of three-dimensional shape precision processing by developing an innovative processing technology that contributes to the advancement of mechanical engineering and industry. He also introduced the three-dimensional fast processing to Korea from 1990 and developed world-class subminiature fast processing, the first of its kind in Korea.In 2013, Professor Yang identified geometric deformation elements in mechanical engineering for the first time in the world, an essential component for nano mobile system and received the best conference paper award at the 3M-Nano International Conference.
2014.01.05 View 10052 -
 Rechargeable Lithium Sulfur Battery for Greater Battery Capacity
Professor Do Kyung Kim from the Department of Material Science and Engineering and Professor Jang Wook Choi from the Graduate School of EEWS have been featured in the lead story of the renowned nanoscience journal Advanced Materials for their research on the lithium sulfur battery. This new type of battery developed by Professor Kim is expected to have a longer life battery life and [higher] energy density than currently commercial batteries.
With ample energy density up to 2100Wh/kg—almost 5.4 times that of lithium ion batteries—lithium sulfur batteries can withstand the sharp decrease in energy capacity resulting from charging and discharging—which has been considered the inherent limitation of the conventional batteries.
Professor Kim and his research team used one-dimensional, vertical alignment of 75nm tick, 15μm long sulfur nanowires to maximize electric conductivity. Then, to prevent loss of battery life, they carbon-coated each nanowire and prohibited direct contact between the sulfur and electrolyte.
The result was one of the most powerful batteries in terms of both energy performance and density. Compared to conventional batteries which suffer from continuous decrease in energy capacity after being discharged, the lithium sulfur battery maintained 99.2% of its initial capacity after being charged and discharged 300 times and up to 70% even after 1000 times.
Professor Kim claims that his new battery is an important step forward towards a high-performance rechargeable battery which is a vital technology for unmanned vehicles, electric automobiles and energy storage. He hopes that his research can solve the problems of battery-capacity loss and contribute to South Korea’s leading position in battery technology. Professor Kim’s research team has filed applications for one domestic and international patent for their research.
2013.12.11 View 13371
Rechargeable Lithium Sulfur Battery for Greater Battery Capacity
Professor Do Kyung Kim from the Department of Material Science and Engineering and Professor Jang Wook Choi from the Graduate School of EEWS have been featured in the lead story of the renowned nanoscience journal Advanced Materials for their research on the lithium sulfur battery. This new type of battery developed by Professor Kim is expected to have a longer life battery life and [higher] energy density than currently commercial batteries.
With ample energy density up to 2100Wh/kg—almost 5.4 times that of lithium ion batteries—lithium sulfur batteries can withstand the sharp decrease in energy capacity resulting from charging and discharging—which has been considered the inherent limitation of the conventional batteries.
Professor Kim and his research team used one-dimensional, vertical alignment of 75nm tick, 15μm long sulfur nanowires to maximize electric conductivity. Then, to prevent loss of battery life, they carbon-coated each nanowire and prohibited direct contact between the sulfur and electrolyte.
The result was one of the most powerful batteries in terms of both energy performance and density. Compared to conventional batteries which suffer from continuous decrease in energy capacity after being discharged, the lithium sulfur battery maintained 99.2% of its initial capacity after being charged and discharged 300 times and up to 70% even after 1000 times.
Professor Kim claims that his new battery is an important step forward towards a high-performance rechargeable battery which is a vital technology for unmanned vehicles, electric automobiles and energy storage. He hopes that his research can solve the problems of battery-capacity loss and contribute to South Korea’s leading position in battery technology. Professor Kim’s research team has filed applications for one domestic and international patent for their research.
2013.12.11 View 13371 -
 Professor Ji-Yun Lee, Received FAA Recognition Award
Professor Ji-Yun Lee, from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, received the US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Recognition Award for her Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS) and her contribution to the development of satellite navigation technology.
GBAS contributes to the safety of aircraft navigation by providing flawless information with real-time location accuracy within one meter.
Professor Lee developed the monitoring software to improve the safety of GBAS users in her paper published in the International Journal of Radio Science in July of 2012.
The software will be distributed and used by many organizations including Eurocontrol following verification from the FAA technical center. It is expected to be standardized after discussions among international organizations.Professor Lee said, “As satellite navigation is applied to the infrastructure of air, marine, and ground transportation, as well as information & communications and finance, ensuring the performance and safety of the system is the most important factor. GBAS will be further developed and applied as a part of a global service system through international collaboration.”
2013.11.15 View 11957
Professor Ji-Yun Lee, Received FAA Recognition Award
Professor Ji-Yun Lee, from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, received the US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Recognition Award for her Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS) and her contribution to the development of satellite navigation technology.
GBAS contributes to the safety of aircraft navigation by providing flawless information with real-time location accuracy within one meter.
Professor Lee developed the monitoring software to improve the safety of GBAS users in her paper published in the International Journal of Radio Science in July of 2012.
The software will be distributed and used by many organizations including Eurocontrol following verification from the FAA technical center. It is expected to be standardized after discussions among international organizations.Professor Lee said, “As satellite navigation is applied to the infrastructure of air, marine, and ground transportation, as well as information & communications and finance, ensuring the performance and safety of the system is the most important factor. GBAS will be further developed and applied as a part of a global service system through international collaboration.”
2013.11.15 View 11957 -
 2013 International Forum on Eco-Friendly Vehicle and System
Leaders in transportation technology gathered at KAIST to discuss commercialization & standardization and to encourage the exchange of research progress, strategy, and future initiatives in transportation technology.
The Graduate School for Green Transportation at KAIST hosted the 2013 International Forum on Eco-friendly Vehicles and Systems (IFEV) in Fusion Hall of the KAIST Institute Building from October 21 to 22.
About 50 leaders in the field of future transportation from academic institutes and industries including Dr. Soon-Man Hong, President of Korea Railroad Research Institute (KRRI), Dr. Kwang-Hee Nam, Professor at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), and Mr. Mike Schagrin, the Intelligent Transportation Systems Program Manager of the US Department of Transportation (retired) participated in the 4th annual IFEV.
The commercialization & standardization session and a technical session were followed by the plenary meeting of the forum.
Dr. Hong, the keynote speaker, introduced the High Capacity Double Deck High Speed Train, Near Surface Subway System, and Urban Railway System with Wireless Power Transfer Technology under the title “Korea’s Policy and Technology Initiative for Enhancing Green Transport Systems.”
Dr. Kwang-Hee Nam presented “Electric Vehicle Trends & the POSTECH E-Car Research Center Power Train Design,” followed by Mr. Mike Schagrin who spoke about “Going Green with Connected Automation.”
Dr. Omer C. Onar from the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) shared recent research on “ORNL Development in Stationary and Dynamic Wireless Charging.”
In the commercialization session, Faical Turki of Vahle, Germany, presented “Wireless Inductive Battery Chargers,” and Professor Kazuyuki Ouchi from Tokyo University presented “Wind Challenger, the Next Generation Hybrid Vessels.”
In the technical session, presentations and discussions were performed on future ground vehicles and railroad technology, intelligent transportation systems and strategy, and policy on eco-friendly vehicle technology, including Professor In-Soo Suh of the Graduate School for Green Transportation at KAIST who presented on “Armadillo-T: 4WD Micro Electric EV with a Foldable Body Concept.”
On the second day of IFEV 2013, representatives of the European Union’s Safe and Green Road Vehicles (SAGE) consortium discussed connectivity in road transportation as a means of improving safety, efficiency and convenience in future safe and green vehicles with collaboration from Korean transportation organizations such as the Korea Transport Institute and Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute.
Professor Suh, who organized the forum, said, “This forum will serve as an excellent opportunity to discuss and share R&BD progress in the green transportation field. “Details can be found at http://gt.kaist.ac.kr/ifev2013/.
2013.11.15 View 13260
2013 International Forum on Eco-Friendly Vehicle and System
Leaders in transportation technology gathered at KAIST to discuss commercialization & standardization and to encourage the exchange of research progress, strategy, and future initiatives in transportation technology.
The Graduate School for Green Transportation at KAIST hosted the 2013 International Forum on Eco-friendly Vehicles and Systems (IFEV) in Fusion Hall of the KAIST Institute Building from October 21 to 22.
About 50 leaders in the field of future transportation from academic institutes and industries including Dr. Soon-Man Hong, President of Korea Railroad Research Institute (KRRI), Dr. Kwang-Hee Nam, Professor at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), and Mr. Mike Schagrin, the Intelligent Transportation Systems Program Manager of the US Department of Transportation (retired) participated in the 4th annual IFEV.
The commercialization & standardization session and a technical session were followed by the plenary meeting of the forum.
Dr. Hong, the keynote speaker, introduced the High Capacity Double Deck High Speed Train, Near Surface Subway System, and Urban Railway System with Wireless Power Transfer Technology under the title “Korea’s Policy and Technology Initiative for Enhancing Green Transport Systems.”
Dr. Kwang-Hee Nam presented “Electric Vehicle Trends & the POSTECH E-Car Research Center Power Train Design,” followed by Mr. Mike Schagrin who spoke about “Going Green with Connected Automation.”
Dr. Omer C. Onar from the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) shared recent research on “ORNL Development in Stationary and Dynamic Wireless Charging.”
In the commercialization session, Faical Turki of Vahle, Germany, presented “Wireless Inductive Battery Chargers,” and Professor Kazuyuki Ouchi from Tokyo University presented “Wind Challenger, the Next Generation Hybrid Vessels.”
In the technical session, presentations and discussions were performed on future ground vehicles and railroad technology, intelligent transportation systems and strategy, and policy on eco-friendly vehicle technology, including Professor In-Soo Suh of the Graduate School for Green Transportation at KAIST who presented on “Armadillo-T: 4WD Micro Electric EV with a Foldable Body Concept.”
On the second day of IFEV 2013, representatives of the European Union’s Safe and Green Road Vehicles (SAGE) consortium discussed connectivity in road transportation as a means of improving safety, efficiency and convenience in future safe and green vehicles with collaboration from Korean transportation organizations such as the Korea Transport Institute and Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute.
Professor Suh, who organized the forum, said, “This forum will serve as an excellent opportunity to discuss and share R&BD progress in the green transportation field. “Details can be found at http://gt.kaist.ac.kr/ifev2013/.
2013.11.15 View 13260 -
 Prof. Jiyun Lee receives the U.S. FAA Achievement Award
- Ensures the safe operation of aircraft by monitoring ionospheric changes caused by solar storms.
KAIST’s Aerospace Engineering Department’s Professor Jiyun Lee has received an award from the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), in recognition of her work for developing a Global Positioning System (GPS) reinforcing system and improving Satellite Navigation technology.
A GPS reinforcing system provides real-time GPS location and integrity information within 1m ranges to enable the accurate and safe navigation of aircraft. However, when the sun reaches Solar Max, the amount of total electron increases rapidly in the ionosphere. This also increases the possibility of the position error of navigation using the GPS reinforcing system. In order to solve this problem, Professor Lee built an Ionosphere Danger model that monitors the changes in the ionosphere due to solar storm. The model has been implemented into original monitoring software that secures the safety of the GPS reinforcing system user. The research results were published in July 2012 in Radio Science, one of the most prestigious international journals in the field of geophysical studies.
The FAA Technical Center successfully verified Professor Lee’s software and the software is currently being distributed and used by major institutions around the globe, including Eurocontrol. It is expected that the software will be standardized after consultations with international organizations in the recent future.
Professor Lee said, “Satellite navigation is the core of future navigation technology. Since its utilization has been extended to aviation, marine, transportation, telecommunications, finance and other major national infrastructures, it is crucial to ensure the performance and reliability of the system … In the future, cooperation between nations will help to develop the worldwide service of the GPS reinforcing system.”
2013.10.12 View 9798
Prof. Jiyun Lee receives the U.S. FAA Achievement Award
- Ensures the safe operation of aircraft by monitoring ionospheric changes caused by solar storms.
KAIST’s Aerospace Engineering Department’s Professor Jiyun Lee has received an award from the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), in recognition of her work for developing a Global Positioning System (GPS) reinforcing system and improving Satellite Navigation technology.
A GPS reinforcing system provides real-time GPS location and integrity information within 1m ranges to enable the accurate and safe navigation of aircraft. However, when the sun reaches Solar Max, the amount of total electron increases rapidly in the ionosphere. This also increases the possibility of the position error of navigation using the GPS reinforcing system. In order to solve this problem, Professor Lee built an Ionosphere Danger model that monitors the changes in the ionosphere due to solar storm. The model has been implemented into original monitoring software that secures the safety of the GPS reinforcing system user. The research results were published in July 2012 in Radio Science, one of the most prestigious international journals in the field of geophysical studies.
The FAA Technical Center successfully verified Professor Lee’s software and the software is currently being distributed and used by major institutions around the globe, including Eurocontrol. It is expected that the software will be standardized after consultations with international organizations in the recent future.
Professor Lee said, “Satellite navigation is the core of future navigation technology. Since its utilization has been extended to aviation, marine, transportation, telecommunications, finance and other major national infrastructures, it is crucial to ensure the performance and reliability of the system … In the future, cooperation between nations will help to develop the worldwide service of the GPS reinforcing system.”
2013.10.12 View 9798 -
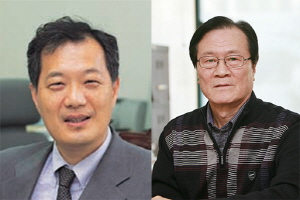 KAIST to establish Ombudsperson system
KAIST has recently undergone a massive reorganization to achieve a streamlined system and highly efficient administration; and it will now implement the new “Ombudsperson” system to hear the opinions of the members of the university.
On September 9th, President Sungmo Kang held a ceremony to appoint Professors Sang-Young Shin and Hong-Gu Shim as the new “Ombudspersons”.
The previous Shinmungo system raised complaints and recommendations for improvements by members of the university, but this is the first time that KAIST has assigned a direct department for handling such matters.
The newly appointed Ombudspersons will review for the possibility of any unjust, irrational systems, violations of research ethics and such. It is their role to take a neutral stance and advise on the correction and improvement.
The merit of the Ombudsperson system is that diverse opinions can be reflected on the policy. The Ombudsperson guarantees the security of the contents of discussion so that anyone can share his or her opinion without fear of being recorded in documents.
It is expected that the Ombudsperson system will protect the interests of the individuals and thus contribute to making a “happy campus”.
President [Sungmo] Kang has said that the reason establishing the office of the Ombudsperson is “In order for KAIST to take a new leap toward the world, it is crucial to bring the minds of the members together…. Even the smallest voices must be heard to present solutions to make the university where everyone’s happy.”
In 1809, the Swedish Parliament appointed the first “Ombudsperson” to investigate and resolve civil complaints. Now, it is widely used in public institutions, corporations and universities to improve the communication and work efficiency of the members.
The new Ombudsmen: Prof. Sang-Young Shin (left) and Prof. Hong-Gu Shim (right)
2013.09.27 View 11973
KAIST to establish Ombudsperson system
KAIST has recently undergone a massive reorganization to achieve a streamlined system and highly efficient administration; and it will now implement the new “Ombudsperson” system to hear the opinions of the members of the university.
On September 9th, President Sungmo Kang held a ceremony to appoint Professors Sang-Young Shin and Hong-Gu Shim as the new “Ombudspersons”.
The previous Shinmungo system raised complaints and recommendations for improvements by members of the university, but this is the first time that KAIST has assigned a direct department for handling such matters.
The newly appointed Ombudspersons will review for the possibility of any unjust, irrational systems, violations of research ethics and such. It is their role to take a neutral stance and advise on the correction and improvement.
The merit of the Ombudsperson system is that diverse opinions can be reflected on the policy. The Ombudsperson guarantees the security of the contents of discussion so that anyone can share his or her opinion without fear of being recorded in documents.
It is expected that the Ombudsperson system will protect the interests of the individuals and thus contribute to making a “happy campus”.
President [Sungmo] Kang has said that the reason establishing the office of the Ombudsperson is “In order for KAIST to take a new leap toward the world, it is crucial to bring the minds of the members together…. Even the smallest voices must be heard to present solutions to make the university where everyone’s happy.”
In 1809, the Swedish Parliament appointed the first “Ombudsperson” to investigate and resolve civil complaints. Now, it is widely used in public institutions, corporations and universities to improve the communication and work efficiency of the members.
The new Ombudsmen: Prof. Sang-Young Shin (left) and Prof. Hong-Gu Shim (right)
2013.09.27 View 11973 -
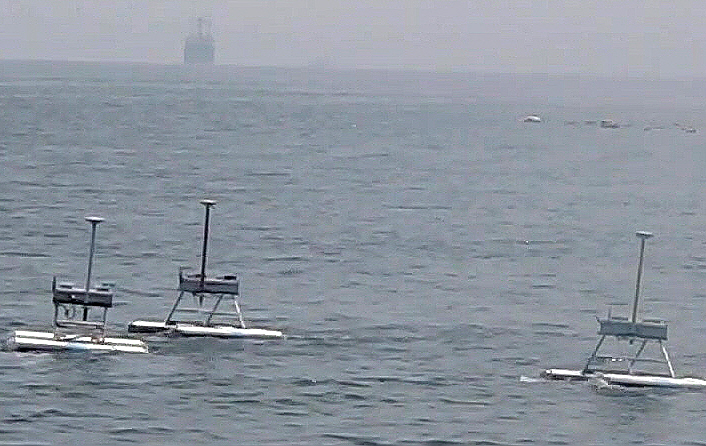 Jellyfish Exterminator Robot Developed
Formation Control demonstrated by JEROS
- Trial performance successfully completed with three assembly robots -
A team led by KAIST Civil and Environmental Engineering Department’s Professor Hyeon Myeong has just finished testing the cooperative assembly robot for jellyfish population control, named JEROS, in the field.
The rising number of accidents and financial losses by fishing industry, estimated at 300 billion won per year, caused by the recent swarm of jellyfish in coastal waters has been a major problem for many years. The research team led by Prof. Hyeon Myeong began developing an unmanned automated system capable of eradicating jellyfishin in 2009, and has since completed field-tests last year with success.
This year, JEROS’s performance and speed has been improved with the ability to work in formation as a cooperative group to efficiently exterminate jellyfish.
An unmanned aquatic robot JEROS with a mountable grinding part is buoyed by two cylindrical bodies that utilizes propulsion motors to move forward and reverse, as well as rotate 360 degrees. Furthermore, GIS (geographic information system)-based map data is used to specify the region for jellyfish extermination, which automatically calculates the path for the task. JEROS then navigates autonomously using a GPS (Global Positioning System) receiver and an INS(inertial navigation system).
The assembly robots maintain a set formation pattern, while calculating its course to perform jellyfish extermination. The advantage of this method is that there is no need for individual control of the robots. Only the leader robot requires the calculated path, and the other robots can simply follow in a formation by exchanging their location information via wireless communication (ZigBee method).
JEROS uses its propulsion speed to capture jellyfish into the grinding part on the bottom, which then suctions the jellyfish toward the propeller to be exterminated.
The field test results show that three assembly robots operating at 4 knots (7.2km/h) disposes jellyfish at the rate of about 900kg/h.
The research team has currently completed testing JEROS at Gyeongnam Masan Bay and is expected to further experiment and improve the performance at various environment and conditions.
JEROS may also be utilized for other purposes including marine patrols, prevention of oil spills and waste removal in the sea.
JEROS research has been funded by Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
2013.09.27 View 17552
Jellyfish Exterminator Robot Developed
Formation Control demonstrated by JEROS
- Trial performance successfully completed with three assembly robots -
A team led by KAIST Civil and Environmental Engineering Department’s Professor Hyeon Myeong has just finished testing the cooperative assembly robot for jellyfish population control, named JEROS, in the field.
The rising number of accidents and financial losses by fishing industry, estimated at 300 billion won per year, caused by the recent swarm of jellyfish in coastal waters has been a major problem for many years. The research team led by Prof. Hyeon Myeong began developing an unmanned automated system capable of eradicating jellyfishin in 2009, and has since completed field-tests last year with success.
This year, JEROS’s performance and speed has been improved with the ability to work in formation as a cooperative group to efficiently exterminate jellyfish.
An unmanned aquatic robot JEROS with a mountable grinding part is buoyed by two cylindrical bodies that utilizes propulsion motors to move forward and reverse, as well as rotate 360 degrees. Furthermore, GIS (geographic information system)-based map data is used to specify the region for jellyfish extermination, which automatically calculates the path for the task. JEROS then navigates autonomously using a GPS (Global Positioning System) receiver and an INS(inertial navigation system).
The assembly robots maintain a set formation pattern, while calculating its course to perform jellyfish extermination. The advantage of this method is that there is no need for individual control of the robots. Only the leader robot requires the calculated path, and the other robots can simply follow in a formation by exchanging their location information via wireless communication (ZigBee method).
JEROS uses its propulsion speed to capture jellyfish into the grinding part on the bottom, which then suctions the jellyfish toward the propeller to be exterminated.
The field test results show that three assembly robots operating at 4 knots (7.2km/h) disposes jellyfish at the rate of about 900kg/h.
The research team has currently completed testing JEROS at Gyeongnam Masan Bay and is expected to further experiment and improve the performance at various environment and conditions.
JEROS may also be utilized for other purposes including marine patrols, prevention of oil spills and waste removal in the sea.
JEROS research has been funded by Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
2013.09.27 View 17552 -
 Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho publishes Encyclopaedia of Systems Biology
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho
KAIST Biological and Brain Engineering Department’s Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho edited the Encyclopaedia of Systems Biology with three scholars, all experts of Systems Biology in England, Germany and the United States. It is rare that a Korean scientist edits a world renowned academic science encyclopaedia.
The Encyclopaedia, published by the New York office of Springer Verlag, was a grand international project five years in the making by 28 editors and 391 scientists with expertise in Systems Biology from around the world. The Encyclopaedia compiles various research areas of Systems Biology, the new academic paradigm of the 21st century through the integration of IT and BT, comprehensively on 3,000 pages in 4 four volumes.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, who led this international project, majored in electrical engineering and pioneered the field of Systems Biology, the integrated study of biological sciences and engineering, as a new integrated field of IT since the 1990s. The professor has achieved various innovative research results since then. Recently he has investigated “kernel,” an evolutionary core structure in complex biological networks and developed a new cancer treatment through the state space analysis of the molecular network of cancer cells. His work was published in Science Signalling, a sister journal of Science, as a cover story several times, and contributed to foundational research as well as commercialisation of the integrated fields of IT and BT.
2013.08.27 View 10276
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho publishes Encyclopaedia of Systems Biology
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho
KAIST Biological and Brain Engineering Department’s Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho edited the Encyclopaedia of Systems Biology with three scholars, all experts of Systems Biology in England, Germany and the United States. It is rare that a Korean scientist edits a world renowned academic science encyclopaedia.
The Encyclopaedia, published by the New York office of Springer Verlag, was a grand international project five years in the making by 28 editors and 391 scientists with expertise in Systems Biology from around the world. The Encyclopaedia compiles various research areas of Systems Biology, the new academic paradigm of the 21st century through the integration of IT and BT, comprehensively on 3,000 pages in 4 four volumes.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, who led this international project, majored in electrical engineering and pioneered the field of Systems Biology, the integrated study of biological sciences and engineering, as a new integrated field of IT since the 1990s. The professor has achieved various innovative research results since then. Recently he has investigated “kernel,” an evolutionary core structure in complex biological networks and developed a new cancer treatment through the state space analysis of the molecular network of cancer cells. His work was published in Science Signalling, a sister journal of Science, as a cover story several times, and contributed to foundational research as well as commercialisation of the integrated fields of IT and BT.
2013.08.27 View 10276 -
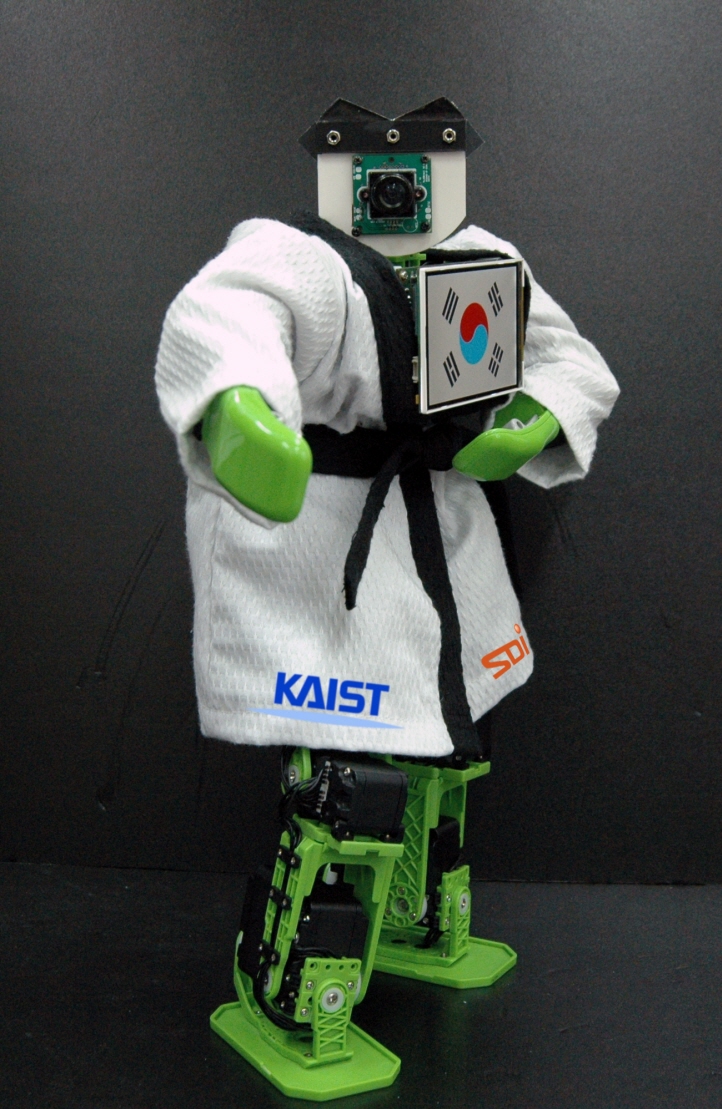 KAIST Holds Robot Taekwondo Competition Recognized by the World Taekwondo Federation
KAIST will host the 12th Intelligent System-on-Chip (SoC) Robot War in October 2013, a robot competition. The event will have two entries: robot Taekwondo contest and HURO competition.
The World Taekwondo Federation has decided to offer an honorary Taekwondo degree to the winner of SoC Taekwondo Robot competition.
The Intelligent SoC Robot War was created in 2002 by KAIST’s Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo in the Department of Electrical Engineering.
For SoC Taekwondo Robot event, two robots compete in the form of Taekwondo, traditional Korean martial arts. The robots competing in this event have a camera and semiconductor chips on board, and therefore they have the brain-like functions to identify an object and control movements on their own. The robots have 21 joints with humanoid robot technology on their body for the techniques needed to compete in a typical Taekwondo match. They employ moves such as front kicks, side kicks, and upper punches.
In particular, KAIST’s System Design Innovation & Application Research Center, the organizer of this competition, has operated a team to demonstrate robot Taekwondo since last year with the purpose of displaying the basic movements of Taekwondo.
“Robots received attention as the source of growth in the near future. We have been developing robotics technology, and as part of our endeavor, preparing the Taekwondo demonstration team since 2012 to exhibit Korea’s robot technology and introduce our traditional martial arts,” said Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo. “We will continue to develop various capabilities for Taekwondo robots in cooperation with the World Taekwondo Federation.”
In HURO-Competition, robots compete for crossing the finishing line first by completing various missions, such as putting in a golf ball or overcoming obstacles while avoiding unexpected accidents. The winning team is awarded with a Presidential Award of Korea.
The 12th Intelligent SoC Robot War Competition is open to all graduate or undergraduate students. For details, visit the homepage at http://www.socrobotwar.org/.
2013.05.06 View 11259
KAIST Holds Robot Taekwondo Competition Recognized by the World Taekwondo Federation
KAIST will host the 12th Intelligent System-on-Chip (SoC) Robot War in October 2013, a robot competition. The event will have two entries: robot Taekwondo contest and HURO competition.
The World Taekwondo Federation has decided to offer an honorary Taekwondo degree to the winner of SoC Taekwondo Robot competition.
The Intelligent SoC Robot War was created in 2002 by KAIST’s Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo in the Department of Electrical Engineering.
For SoC Taekwondo Robot event, two robots compete in the form of Taekwondo, traditional Korean martial arts. The robots competing in this event have a camera and semiconductor chips on board, and therefore they have the brain-like functions to identify an object and control movements on their own. The robots have 21 joints with humanoid robot technology on their body for the techniques needed to compete in a typical Taekwondo match. They employ moves such as front kicks, side kicks, and upper punches.
In particular, KAIST’s System Design Innovation & Application Research Center, the organizer of this competition, has operated a team to demonstrate robot Taekwondo since last year with the purpose of displaying the basic movements of Taekwondo.
“Robots received attention as the source of growth in the near future. We have been developing robotics technology, and as part of our endeavor, preparing the Taekwondo demonstration team since 2012 to exhibit Korea’s robot technology and introduce our traditional martial arts,” said Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo. “We will continue to develop various capabilities for Taekwondo robots in cooperation with the World Taekwondo Federation.”
In HURO-Competition, robots compete for crossing the finishing line first by completing various missions, such as putting in a golf ball or overcoming obstacles while avoiding unexpected accidents. The winning team is awarded with a Presidential Award of Korea.
The 12th Intelligent SoC Robot War Competition is open to all graduate or undergraduate students. For details, visit the homepage at http://www.socrobotwar.org/.
2013.05.06 View 11259 -
 Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yeop Appointed as Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers
Professor Lee Sang Yeop (Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences) has become the first Korea Scientist to be appointed as the Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
The American Institute of Chemical Engineers was founded in 1908 and boasts a 100 year history. It is composed of 43,000 members over 90 countries and is the largest international Academic Institute in the field of Chemical Engineering.
The Institute appoints Fellows after a rigorous procedure of recommendation and evaluation and Professor Lee is the first Korean to become a Fellow.
Professor Lee’s expertise is the field of Metabolic Engineering and successfully applied the system design method and optimization strategy of chemical engineering to biological systems thereby developing numerous core technologies for the biology based chemical industries.
Professor Lee is the founder of the System Metabolic Engineering and enabled the medical application of microorganisms by manipulating the metabolic pathways on a systems level in addition to making great progress in synthesizing various oil originated chemical materials using biology based, environmentally friends methods.
Professor Lee received the Marvin J. Johnson Award, Charles Thom Award, and has been appointed by the first Chairman of the Biotech Global Agenda Counsel of the World Economic Forum.
2012.09.22 View 9888
Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yeop Appointed as Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers
Professor Lee Sang Yeop (Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences) has become the first Korea Scientist to be appointed as the Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
The American Institute of Chemical Engineers was founded in 1908 and boasts a 100 year history. It is composed of 43,000 members over 90 countries and is the largest international Academic Institute in the field of Chemical Engineering.
The Institute appoints Fellows after a rigorous procedure of recommendation and evaluation and Professor Lee is the first Korean to become a Fellow.
Professor Lee’s expertise is the field of Metabolic Engineering and successfully applied the system design method and optimization strategy of chemical engineering to biological systems thereby developing numerous core technologies for the biology based chemical industries.
Professor Lee is the founder of the System Metabolic Engineering and enabled the medical application of microorganisms by manipulating the metabolic pathways on a systems level in addition to making great progress in synthesizing various oil originated chemical materials using biology based, environmentally friends methods.
Professor Lee received the Marvin J. Johnson Award, Charles Thom Award, and has been appointed by the first Chairman of the Biotech Global Agenda Counsel of the World Economic Forum.
2012.09.22 View 9888