-
 The 4th Meeting of Korea and Denmark Alliance for Green Growth
President Steve Kang attended the “Fourth Meeting of Korea and Denmark Alliance for Green Growth” which took place on March 6, 2014 at the Shilla Hotel in Seoul. President Kang was a keynote speaker at the meeting and gave a lecture on sustainable energy.
KAIST and the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on the “Cooperation for Innovation and Entrepreneurship” at the meeting.
In the MOU, KAIST and DTU agreed to post the information on their websites regarding the patents acquired through the implementation of joint research programs. In addition, KAIST students will attend conferences and idea competitions organized by DTU, e.g., the Green Challenges. DTU students will participate in KAIST’s conferences and competitions including “Startup KAIST Global Idea Competition.”
2014.03.07 View 9393
The 4th Meeting of Korea and Denmark Alliance for Green Growth
President Steve Kang attended the “Fourth Meeting of Korea and Denmark Alliance for Green Growth” which took place on March 6, 2014 at the Shilla Hotel in Seoul. President Kang was a keynote speaker at the meeting and gave a lecture on sustainable energy.
KAIST and the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on the “Cooperation for Innovation and Entrepreneurship” at the meeting.
In the MOU, KAIST and DTU agreed to post the information on their websites regarding the patents acquired through the implementation of joint research programs. In addition, KAIST students will attend conferences and idea competitions organized by DTU, e.g., the Green Challenges. DTU students will participate in KAIST’s conferences and competitions including “Startup KAIST Global Idea Competition.”
2014.03.07 View 9393 -
 KAIST Holds Open Lecture For Daejeon Residents
Free of cost for any Korean citizen, the registration for the new course opens on the official website from 5th March KAIST’s Department of Humanities and Social Science is currently operating free humanities and liberal arts classes for Daejeon residents.
The theme of the course for this semester is “World and Politics,” which will begin on 13th March and run every Thursday for 6 weeks at KAIST’s International Seminar Room.
This course has been organized to introduce the general public to the current political situation with neighboring countries such as China, Japan and North Korea, as well as the characteristics of multinational companies.
Top experts in the related fields will give lectures. First, Professor Ha-Yong Jung from Kyunghee University will talk on “American liberalism and democracy”; Professor Gyeong-Mo An from Korea National Defense University on “Kim Jeong-Eun and the Future of North Korea--Is the Collapse of North Korea A Reality?” and Ja-Seon Koo, a visiting professor at Korea National Diplomatic Academy on “The Chinese Communist Party during the Xi Jinping Period.”
“With the era of globalization, the political situations in the neighboring countries have both direct and indirect effects on our lives,” said Professor Hyeon-Seok Park who has organized the courses. "These classes will be an opportunity for our citizens to understand and learn about the current affairs in the world.”
Anyone can attend the course, and registration is from March 5th to 9th at the official webpage of KAIST’s Humanities and Social Sciences Department (http://hss.kaist.ac.kr). All the courses are free of charge.
Contact: Department of Humanities and Social Science Research (Tel. 350-4687, E-mail: baobab@kaist.ac.kr)
2014.03.06 View 7609
KAIST Holds Open Lecture For Daejeon Residents
Free of cost for any Korean citizen, the registration for the new course opens on the official website from 5th March KAIST’s Department of Humanities and Social Science is currently operating free humanities and liberal arts classes for Daejeon residents.
The theme of the course for this semester is “World and Politics,” which will begin on 13th March and run every Thursday for 6 weeks at KAIST’s International Seminar Room.
This course has been organized to introduce the general public to the current political situation with neighboring countries such as China, Japan and North Korea, as well as the characteristics of multinational companies.
Top experts in the related fields will give lectures. First, Professor Ha-Yong Jung from Kyunghee University will talk on “American liberalism and democracy”; Professor Gyeong-Mo An from Korea National Defense University on “Kim Jeong-Eun and the Future of North Korea--Is the Collapse of North Korea A Reality?” and Ja-Seon Koo, a visiting professor at Korea National Diplomatic Academy on “The Chinese Communist Party during the Xi Jinping Period.”
“With the era of globalization, the political situations in the neighboring countries have both direct and indirect effects on our lives,” said Professor Hyeon-Seok Park who has organized the courses. "These classes will be an opportunity for our citizens to understand and learn about the current affairs in the world.”
Anyone can attend the course, and registration is from March 5th to 9th at the official webpage of KAIST’s Humanities and Social Sciences Department (http://hss.kaist.ac.kr). All the courses are free of charge.
Contact: Department of Humanities and Social Science Research (Tel. 350-4687, E-mail: baobab@kaist.ac.kr)
2014.03.06 View 7609 -
 Seo-Eun Lee, an undergaruate student receives the Best Paper Award from Optical Society of Korea
Seo-Eun Lee, a student studying at KAIST’s Department of Biological Sciences, has won the Best Paper Award from Bio-Photonics Division at the 2014 Optical Society of Korea Winter Conference, held on 19th February at Daejeon Convention Center.
Only one outstanding paper per division is given an award among the total of 270 papers, and it is very unusual for an undergraduate student to win the award in the field that is not her major.
Lee has studied cell imaging using holography technology since June 2013 under the supervision of Professor Yong-Geun Park from the Department of Physics.
The Optical Society of Korea was founded in 1989, and as the largest academy in the field of optics in Korea, it holds academic presentations, seminars and lectures every year.
2014.03.06 View 11770
Seo-Eun Lee, an undergaruate student receives the Best Paper Award from Optical Society of Korea
Seo-Eun Lee, a student studying at KAIST’s Department of Biological Sciences, has won the Best Paper Award from Bio-Photonics Division at the 2014 Optical Society of Korea Winter Conference, held on 19th February at Daejeon Convention Center.
Only one outstanding paper per division is given an award among the total of 270 papers, and it is very unusual for an undergraduate student to win the award in the field that is not her major.
Lee has studied cell imaging using holography technology since June 2013 under the supervision of Professor Yong-Geun Park from the Department of Physics.
The Optical Society of Korea was founded in 1989, and as the largest academy in the field of optics in Korea, it holds academic presentations, seminars and lectures every year.
2014.03.06 View 11770 -
 Welcoming the Class of 2014
“The four years from today will go quickly, and I urge you to make the most of your time in KAIST, a great educational and research institution where you will explore the frontiers of science and technology and take part in the creation of new knowledge,” President Kang told the freshmen at the convocation ceremony.
Freshmen Convocation for the Class of 2014 took place on March 3, 2014 at the auditorium on the main campus. Members of the KAIST community, along with hundreds of parents and guests, welcomed the incoming 800 freshmen, celebrating the beginning of their four-year college life.
Kwang-Joon Ahn, a graduate of the Korea Science Academy, and Ha-Rim Jin, a graduate of Daegu Il Science High School, were representatives of the incoming students, and they took the “Class of 2014 Pledge,” a commitment to uphold KAIST’s core values, which is "creativity and challenge (endeavoring spirit)," and to pursue intellectual passion and discovery.
President Steve Kang delivered congratulatory remarks, encouraging students to use their opportunities to the fullest while at KAIST to broaden their knowledge and experience. He also stressed the following four important principles they should cultivate to become the leaders of tomorrow: be grateful, excel in their field, keep open minds about what the globalized world would bring, and never give up on their dreams and belief.
President Kang said:
“Probably, many of you, the graduates of the best high schools in Korea, will find KAIST a tougher place to be in than you imagined. But challenges, particularly intellectual challenges, should be viewed as an opportunity to grow. It is ok to fail. In fact, without risking failures, there won’t be a meaningful growth because the real growth comes from overcoming challenges.”
“You can’t avoid failing in the course of your college life, but your perseverance to do it over will allow you to develop the skills and passion needed to become a leader who will contribute to the local community, as well as to the betterment of humanity.”
The KAIST Alumni Scholarship Foundation presented a scholarship of USD 3,700 to 24 freshmen.
The convocation ended with music performances by members of the student clubs at KAIST.
2014.03.04 View 9837
Welcoming the Class of 2014
“The four years from today will go quickly, and I urge you to make the most of your time in KAIST, a great educational and research institution where you will explore the frontiers of science and technology and take part in the creation of new knowledge,” President Kang told the freshmen at the convocation ceremony.
Freshmen Convocation for the Class of 2014 took place on March 3, 2014 at the auditorium on the main campus. Members of the KAIST community, along with hundreds of parents and guests, welcomed the incoming 800 freshmen, celebrating the beginning of their four-year college life.
Kwang-Joon Ahn, a graduate of the Korea Science Academy, and Ha-Rim Jin, a graduate of Daegu Il Science High School, were representatives of the incoming students, and they took the “Class of 2014 Pledge,” a commitment to uphold KAIST’s core values, which is "creativity and challenge (endeavoring spirit)," and to pursue intellectual passion and discovery.
President Steve Kang delivered congratulatory remarks, encouraging students to use their opportunities to the fullest while at KAIST to broaden their knowledge and experience. He also stressed the following four important principles they should cultivate to become the leaders of tomorrow: be grateful, excel in their field, keep open minds about what the globalized world would bring, and never give up on their dreams and belief.
President Kang said:
“Probably, many of you, the graduates of the best high schools in Korea, will find KAIST a tougher place to be in than you imagined. But challenges, particularly intellectual challenges, should be viewed as an opportunity to grow. It is ok to fail. In fact, without risking failures, there won’t be a meaningful growth because the real growth comes from overcoming challenges.”
“You can’t avoid failing in the course of your college life, but your perseverance to do it over will allow you to develop the skills and passion needed to become a leader who will contribute to the local community, as well as to the betterment of humanity.”
The KAIST Alumni Scholarship Foundation presented a scholarship of USD 3,700 to 24 freshmen.
The convocation ended with music performances by members of the student clubs at KAIST.
2014.03.04 View 9837 -
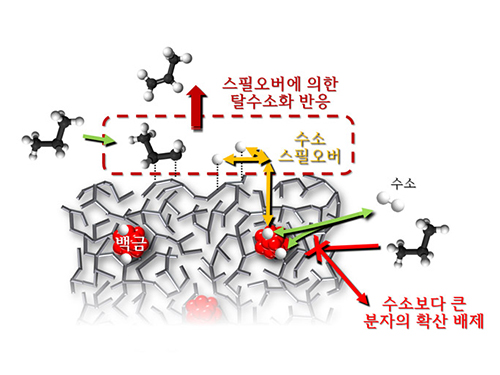 Spillover Phenomenon Identified Using Model Catalyst System
Researchers at KAIST have identified spillover phenomenon, which has remained controversial since its discovery in the early 1960s.
KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering’s Professor Min-Gi Choi and his team has explained the "spillover phenomenon," using their own model catalyst system where platinum is selectively located within the amorphous aluminosilicate.
The research results were published on the 25th February online edition of Nature Communications.
Spillover refers to a phenomenon that occurs when hydrogen atoms that have been activated on the surface of metals, such as platinum, move to the surface of the catalyst. It was predicted that this phenomenon can be used to design a catalyst with high activity and stability, and thus has been actively studied over the last 50 years.
However, many cases of the known catalysts involved competing reactions on the exposed metal surface, which made it impossible to directly identify the presence and formation mechanism of spillover.
The catalysts developed by the researchers at KAIST used platinum nanoparticles covered with aluminosilicate. This only allowed the hydrogen molecules to pass through and has effectively blocked the competing reactions, enabling the research team to study the spillover phenomenon.
Through various catalyst structure and reactivity analysis, as well as computer modeling, the team has discovered that Brönsted acid sites present on the aluminosilicate plays a crucial role in spillover phenomenon.
In addition, the spillover-based hydrogenation catalyst proposed by the research team showed very high hydrogenation and dehydrogenation activity. The ability of the catalyst to significantly inhibit unwanted hydrogenolysis reaction during the petrochemical processes also suggested a large industrial potential.
Professor Min-Gi Choi said, “This particular catalyst, which can trigger the reaction only by spillover phenomenon, can be properly designed to exceed the capacity of the conventional metal catalysts. The future goal is to make a catalyst with much higher activity and selectivity.”
The research was conducted through funds subsidized by SK Innovation and Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
The senior research fellow of SK Innovation Seung-Hun Oh said, “SK Innovation will continue to develop a new commercial catalyst based on the technology from this research.”
Juh-Wan Lim and Hye-Yeong Shin led the research as joint first authors under supervision of Professor Min-Gi Choi and computer modeling works were conducted by KAIST EEWS (environment, energy, water, and sustainability) graduate school’s Professor Hyeong-Jun Kim.
2014.03.03 View 11961
Spillover Phenomenon Identified Using Model Catalyst System
Researchers at KAIST have identified spillover phenomenon, which has remained controversial since its discovery in the early 1960s.
KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering’s Professor Min-Gi Choi and his team has explained the "spillover phenomenon," using their own model catalyst system where platinum is selectively located within the amorphous aluminosilicate.
The research results were published on the 25th February online edition of Nature Communications.
Spillover refers to a phenomenon that occurs when hydrogen atoms that have been activated on the surface of metals, such as platinum, move to the surface of the catalyst. It was predicted that this phenomenon can be used to design a catalyst with high activity and stability, and thus has been actively studied over the last 50 years.
However, many cases of the known catalysts involved competing reactions on the exposed metal surface, which made it impossible to directly identify the presence and formation mechanism of spillover.
The catalysts developed by the researchers at KAIST used platinum nanoparticles covered with aluminosilicate. This only allowed the hydrogen molecules to pass through and has effectively blocked the competing reactions, enabling the research team to study the spillover phenomenon.
Through various catalyst structure and reactivity analysis, as well as computer modeling, the team has discovered that Brönsted acid sites present on the aluminosilicate plays a crucial role in spillover phenomenon.
In addition, the spillover-based hydrogenation catalyst proposed by the research team showed very high hydrogenation and dehydrogenation activity. The ability of the catalyst to significantly inhibit unwanted hydrogenolysis reaction during the petrochemical processes also suggested a large industrial potential.
Professor Min-Gi Choi said, “This particular catalyst, which can trigger the reaction only by spillover phenomenon, can be properly designed to exceed the capacity of the conventional metal catalysts. The future goal is to make a catalyst with much higher activity and selectivity.”
The research was conducted through funds subsidized by SK Innovation and Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
The senior research fellow of SK Innovation Seung-Hun Oh said, “SK Innovation will continue to develop a new commercial catalyst based on the technology from this research.”
Juh-Wan Lim and Hye-Yeong Shin led the research as joint first authors under supervision of Professor Min-Gi Choi and computer modeling works were conducted by KAIST EEWS (environment, energy, water, and sustainability) graduate school’s Professor Hyeong-Jun Kim.
2014.03.03 View 11961 -
 Seung-Han Lee, a doctoral student in electrical engineering, receives the best paper award from ISQED 2014
Seung-Han
Lee, a doctoral candidate in the department of electrical engineering at KAIST,
received a Best Paper Award from the International Symposium on Quality
Electronic Design (ISQED), a high-profile international conference started in 2000 to promote innovation and quality in electronic and
engineering designs through inter- and multidisciplinary approaches. The
award ceremony will take place at the 2014 ISQED on March 3-5, 2014 at the Convention
Center in Santa Clara, CA, USA.
Professor
Chong-Min Kyung, an advisor to Seung-Han, expressed his excitement about his student's achievement.
“This is
the first time a Korean has ever received the best paper award at this academic
conference. It’s great news to our student as well as to KAIST.”
The topic
of Lee’s research paper was dynamic cache data management for minimizing the
energy consumption of three-dimensional multi-processor semiconductor chips.
2014.03.03 View 12834
Seung-Han Lee, a doctoral student in electrical engineering, receives the best paper award from ISQED 2014
Seung-Han
Lee, a doctoral candidate in the department of electrical engineering at KAIST,
received a Best Paper Award from the International Symposium on Quality
Electronic Design (ISQED), a high-profile international conference started in 2000 to promote innovation and quality in electronic and
engineering designs through inter- and multidisciplinary approaches. The
award ceremony will take place at the 2014 ISQED on March 3-5, 2014 at the Convention
Center in Santa Clara, CA, USA.
Professor
Chong-Min Kyung, an advisor to Seung-Han, expressed his excitement about his student's achievement.
“This is
the first time a Korean has ever received the best paper award at this academic
conference. It’s great news to our student as well as to KAIST.”
The topic
of Lee’s research paper was dynamic cache data management for minimizing the
energy consumption of three-dimensional multi-processor semiconductor chips.
2014.03.03 View 12834 -
 Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) World University Rankings by Subject 2014
The QS
World University Rankings are annual university rankings published by
Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) which provides the overall rankings of top global
universities as well as the rankings for individual subjects. The 2014 QS World
University Rankings by Subject is a comprehensive guide to the world’s best universities
in 30 popular subjects of 5 academic disciplines: arts & humanities,
engineering & technology, life sciences & medicine, natural sciences,
and social sciences.
According
to the 2014 subject rankings, released on February 26, KAIST made the list of top
50 universities in 9 subjects: physics & astronomy; materials sciences;
chemistry; chemical engineering; mechanical, aeronautical & manufacturing
engineering; electrical & electronic engineering; civil & structural engineering;
computer science & information systems; and biological sciences.
Among
them, KAIST was ranked number one in Korea for 5 subjects: materials sciences
(16th); mechanical, aeronautical & manufacturing engineering (21st);
civil & structural engineering (32nd); computer science &
information systems (36th), and biological sciences (43rd).
For basic sciences, KAIST has made good progress as well. For example, in
mathematics, KAIST took first place in Korea and was ranked in the 51st-100th
of the world’s top universities. Another notable result was that its business college
in Seoul campus, a relatively new addition to KAIST, made the rankings list of
51st-100th in accounting & finance.
The 2014
QS subject rankings used the following criteria for its evaluation of
university performance: a survey of academic and employer reputation, citations
per paper, inclusion of specialists, and the h-index, known as the Hirsch index or Hirsch number, which was
suggested by Jorge E. Hirsch, a physicist at the University of California in
San Diego, as a tool for determining theoretical physicists’ relative quality.
Today, the h-index is used to measure
both the productivity and impact of the published work of a scientist or
scholar.
2014.02.28 View 12292
Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) World University Rankings by Subject 2014
The QS
World University Rankings are annual university rankings published by
Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) which provides the overall rankings of top global
universities as well as the rankings for individual subjects. The 2014 QS World
University Rankings by Subject is a comprehensive guide to the world’s best universities
in 30 popular subjects of 5 academic disciplines: arts & humanities,
engineering & technology, life sciences & medicine, natural sciences,
and social sciences.
According
to the 2014 subject rankings, released on February 26, KAIST made the list of top
50 universities in 9 subjects: physics & astronomy; materials sciences;
chemistry; chemical engineering; mechanical, aeronautical & manufacturing
engineering; electrical & electronic engineering; civil & structural engineering;
computer science & information systems; and biological sciences.
Among
them, KAIST was ranked number one in Korea for 5 subjects: materials sciences
(16th); mechanical, aeronautical & manufacturing engineering (21st);
civil & structural engineering (32nd); computer science &
information systems (36th), and biological sciences (43rd).
For basic sciences, KAIST has made good progress as well. For example, in
mathematics, KAIST took first place in Korea and was ranked in the 51st-100th
of the world’s top universities. Another notable result was that its business college
in Seoul campus, a relatively new addition to KAIST, made the rankings list of
51st-100th in accounting & finance.
The 2014
QS subject rankings used the following criteria for its evaluation of
university performance: a survey of academic and employer reputation, citations
per paper, inclusion of specialists, and the h-index, known as the Hirsch index or Hirsch number, which was
suggested by Jorge E. Hirsch, a physicist at the University of California in
San Diego, as a tool for determining theoretical physicists’ relative quality.
Today, the h-index is used to measure
both the productivity and impact of the published work of a scientist or
scholar.
2014.02.28 View 12292 -
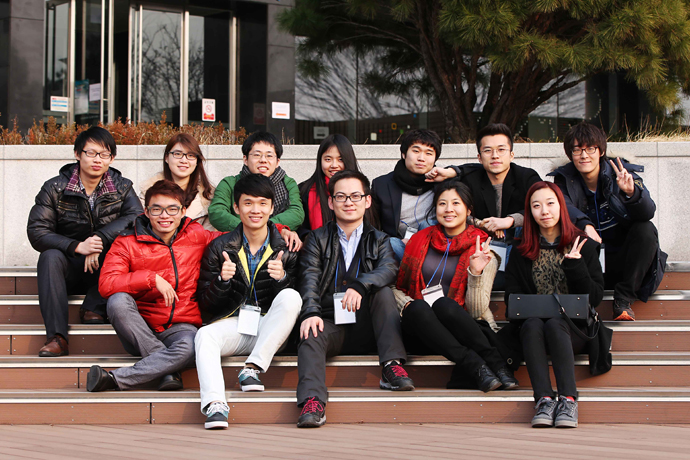 Festival Featuring Asia's Best Science Students to be Held
The first Electronic Olympics, which will host students from five top Asian research-centered universities, will be held in August at KAIST. Students will take part in competitive events and explore cultural diversity. Student representatives of HKUST, NTU, TITECH, Tsinghua University, and KAIST gathered on February 20 to begin planning the tentatively named “ASPIRE E-Olympics.”
The key words of this Olympics are "Harmony" and "Competition." The events will be composed of an AI programming contest, SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope) picture contest, and the other technology-based contests. Cultural events, where each university’s students can interact, will also be prepared.
ASPIRE (Asian Science and Technology Pioneering Institutes of Research and Education) events have been held from 2009. Previously, the ASPIRE forum has been an exchange event for groups of vice presidents and graduate school students from the five schools to exchange achievements in education and research. This year, it has been extended to undergraduates.
Yoseop Kim, KAIST’s student body vice president, said that he wants to make a MOU with some of Asia’s best research-centered universities and develop it into something similar to the Davos Forum. His intention is to support the E-Olympics in the hope that ASPIRE will become a top university consortium.
From left, HKUST, KAIST, NTU, TITECH, Tsinghua University Logos
Student representative group photo of Top Asian Research-Centered Universities
Electronic Olympics for students from five top Asian science and engineering universities to be held in August
2014.02.27 View 9936
Festival Featuring Asia's Best Science Students to be Held
The first Electronic Olympics, which will host students from five top Asian research-centered universities, will be held in August at KAIST. Students will take part in competitive events and explore cultural diversity. Student representatives of HKUST, NTU, TITECH, Tsinghua University, and KAIST gathered on February 20 to begin planning the tentatively named “ASPIRE E-Olympics.”
The key words of this Olympics are "Harmony" and "Competition." The events will be composed of an AI programming contest, SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope) picture contest, and the other technology-based contests. Cultural events, where each university’s students can interact, will also be prepared.
ASPIRE (Asian Science and Technology Pioneering Institutes of Research and Education) events have been held from 2009. Previously, the ASPIRE forum has been an exchange event for groups of vice presidents and graduate school students from the five schools to exchange achievements in education and research. This year, it has been extended to undergraduates.
Yoseop Kim, KAIST’s student body vice president, said that he wants to make a MOU with some of Asia’s best research-centered universities and develop it into something similar to the Davos Forum. His intention is to support the E-Olympics in the hope that ASPIRE will become a top university consortium.
From left, HKUST, KAIST, NTU, TITECH, Tsinghua University Logos
Student representative group photo of Top Asian Research-Centered Universities
Electronic Olympics for students from five top Asian science and engineering universities to be held in August
2014.02.27 View 9936 -
 A game enthusiast received a Ph.D. at the 2014 commencement
A high school student, who was addicted to video gaming and had barely managed to gain entrance to KAIST, became a star of its 2014 commencement ceremony.
The student was Tae-Woo Park who received his Ph.D. in games at 32 years of age.
Park entered KAIST in 2002 as an undergraduate student. However, owning to bad grades, he was not accepted to the graduate school of KAIST until 2006. He began playing games at the age of 7, which distracted him from his studies at an early age. Nevertheless, he was able to complete master’s degree after two and a half years, which normally takes two years for average students.
Professor Joon-Hwa Song saw a possibility from his student’s experience of producing and commercializing a mobile puzzle game while Park was working as a president of the game club, HAJE, at KAIST. Professor Song advised him to take the advantage of his interests and try developing game platforms and contents. Park decided to develop a game that could help others and would change people’s negative views of games. He created a whole new generation of games.
In order to find ideas for games that can be easily enjoyed in daily lives, Park went to numerous gyms, swimming pools, daycare centers, and parks to analyze people’s behaviors and discussed with his colleagues who were also interested in games. During this process, the experience of organizing creative ideas through cooperation and discussions became a great foundation for his future research.
He observed some people quitting midway during a workout on treadmills because they were bored with working out alone. From this, Park embarked on developing a new style of game that allowed people to exercise together.
Park used the system on a treadmill, which recognizes the speed of the person running to automatically adjust the machine’s speed, to develop an interactive game platform for Swan Boat. The Swan Boat game is a race exercise game that adjusts the direction according to speed difference between two players. The game utilizes the difference of running speed between two people on treadmills to change the direction of the boat.
With the Swan Boat game, people can now play games and exercise at the same time. The technology also allows online access anywhere in the world, which means checking friends’ rankings at nearby gyms or homes, or even a World Gym Running Contest.
In addition, Park helped develop various next generation exercise games and life-based services, including the sparrow chirp application, which finds children that go astray, or an avatar game that utilizes the user’s daily life patterns. These results and papers attracted attention from international societies and have also won a number of awards.
Professor Song said, “There has been no precedent of receiving a Ph.D. at KAIST for developing games, however, Park’s case has given courage to many people that if you can create what is really required in everyday life, you can indeed receive a doctor’s degree.”
Park remarked, “I’d like to express my gratitude to my advisor, Professor Song, for giving me courage. I want to continue to make games that can help people’s lives in the future.”
Park will continue his work at the NASA Ames Research Center this June.
2014.02.27 View 12300
A game enthusiast received a Ph.D. at the 2014 commencement
A high school student, who was addicted to video gaming and had barely managed to gain entrance to KAIST, became a star of its 2014 commencement ceremony.
The student was Tae-Woo Park who received his Ph.D. in games at 32 years of age.
Park entered KAIST in 2002 as an undergraduate student. However, owning to bad grades, he was not accepted to the graduate school of KAIST until 2006. He began playing games at the age of 7, which distracted him from his studies at an early age. Nevertheless, he was able to complete master’s degree after two and a half years, which normally takes two years for average students.
Professor Joon-Hwa Song saw a possibility from his student’s experience of producing and commercializing a mobile puzzle game while Park was working as a president of the game club, HAJE, at KAIST. Professor Song advised him to take the advantage of his interests and try developing game platforms and contents. Park decided to develop a game that could help others and would change people’s negative views of games. He created a whole new generation of games.
In order to find ideas for games that can be easily enjoyed in daily lives, Park went to numerous gyms, swimming pools, daycare centers, and parks to analyze people’s behaviors and discussed with his colleagues who were also interested in games. During this process, the experience of organizing creative ideas through cooperation and discussions became a great foundation for his future research.
He observed some people quitting midway during a workout on treadmills because they were bored with working out alone. From this, Park embarked on developing a new style of game that allowed people to exercise together.
Park used the system on a treadmill, which recognizes the speed of the person running to automatically adjust the machine’s speed, to develop an interactive game platform for Swan Boat. The Swan Boat game is a race exercise game that adjusts the direction according to speed difference between two players. The game utilizes the difference of running speed between two people on treadmills to change the direction of the boat.
With the Swan Boat game, people can now play games and exercise at the same time. The technology also allows online access anywhere in the world, which means checking friends’ rankings at nearby gyms or homes, or even a World Gym Running Contest.
In addition, Park helped develop various next generation exercise games and life-based services, including the sparrow chirp application, which finds children that go astray, or an avatar game that utilizes the user’s daily life patterns. These results and papers attracted attention from international societies and have also won a number of awards.
Professor Song said, “There has been no precedent of receiving a Ph.D. at KAIST for developing games, however, Park’s case has given courage to many people that if you can create what is really required in everyday life, you can indeed receive a doctor’s degree.”
Park remarked, “I’d like to express my gratitude to my advisor, Professor Song, for giving me courage. I want to continue to make games that can help people’s lives in the future.”
Park will continue his work at the NASA Ames Research Center this June.
2014.02.27 View 12300 -
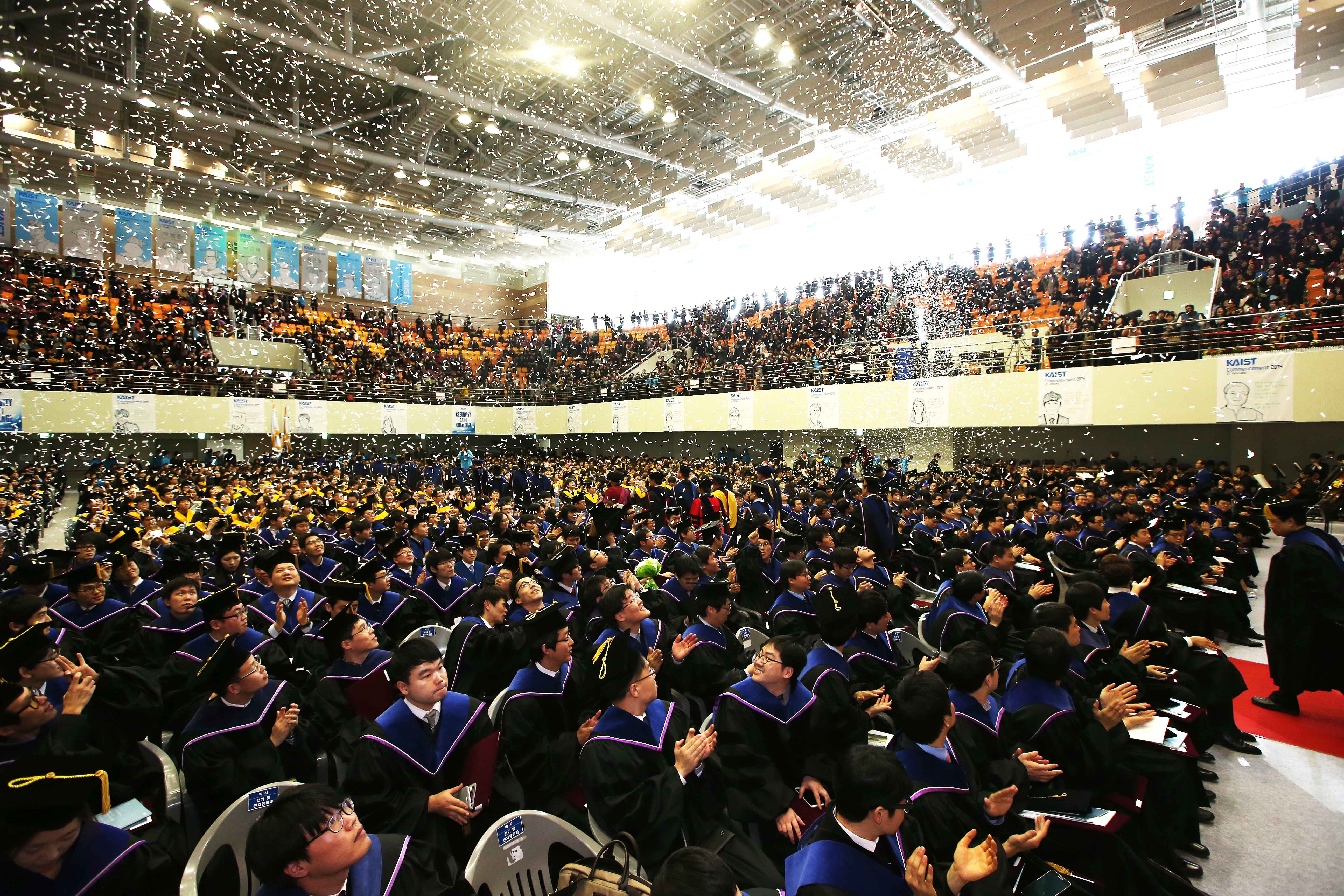 KAIST held its 2014 Commencement Ceremony
The KAIST Commencement Ceremony for 2014 was held on Friday, 21st February, at Sports Complex, KAIST.
On this day, a total of 2,619 students
received their degrees. This included 499 doctorates, 1,220 masters, and 900 students with bachelor’s degrees. Since its establishment in 1971,
KAIST has produced 9,881 Ph.D., 25,161 MA and 13,693 BA,
which amounts to 48,735 scientific and engineering personnel.
The former Minister for Science and Technology
of the Republic of Korea, Dr. KunMo Chung, received an honorary doctorate for his effort in establishing the Korea Advanced Institute of Science (KAIS) to foster talented scientists and engineers, thus contributing to the significant growth
of Korea that has led it to stand as a scientifically advanced nation today.
The student graduating with summa cum laude was Jang-Geun
Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences. Mr. Kim received the Minister of Science, ICT and
Future Planning Award.
Mr. Kim said, “I am honored to receive the
award from the minister. I hope a lot of talented students will go onto science and
engineering field, so that Korea can earn a place among the technologically
elite countries.” Jang-Geun Kim will continue his
study of genomic medicine at KAIST graduate school.
President Steve Kang spoke
to the graduates:
“The whole nation has given their wholehearted support to KAIST so that students can study in a good environment. Please have
great aspirations and hopes, and continue to
broaden your knowledge and solve the challenges that humanity is facing today,
so our country and the world can advance.”
2014.02.27 View 10379
KAIST held its 2014 Commencement Ceremony
The KAIST Commencement Ceremony for 2014 was held on Friday, 21st February, at Sports Complex, KAIST.
On this day, a total of 2,619 students
received their degrees. This included 499 doctorates, 1,220 masters, and 900 students with bachelor’s degrees. Since its establishment in 1971,
KAIST has produced 9,881 Ph.D., 25,161 MA and 13,693 BA,
which amounts to 48,735 scientific and engineering personnel.
The former Minister for Science and Technology
of the Republic of Korea, Dr. KunMo Chung, received an honorary doctorate for his effort in establishing the Korea Advanced Institute of Science (KAIS) to foster talented scientists and engineers, thus contributing to the significant growth
of Korea that has led it to stand as a scientifically advanced nation today.
The student graduating with summa cum laude was Jang-Geun
Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences. Mr. Kim received the Minister of Science, ICT and
Future Planning Award.
Mr. Kim said, “I am honored to receive the
award from the minister. I hope a lot of talented students will go onto science and
engineering field, so that Korea can earn a place among the technologically
elite countries.” Jang-Geun Kim will continue his
study of genomic medicine at KAIST graduate school.
President Steve Kang spoke
to the graduates:
“The whole nation has given their wholehearted support to KAIST so that students can study in a good environment. Please have
great aspirations and hopes, and continue to
broaden your knowledge and solve the challenges that humanity is facing today,
so our country and the world can advance.”
2014.02.27 View 10379 -
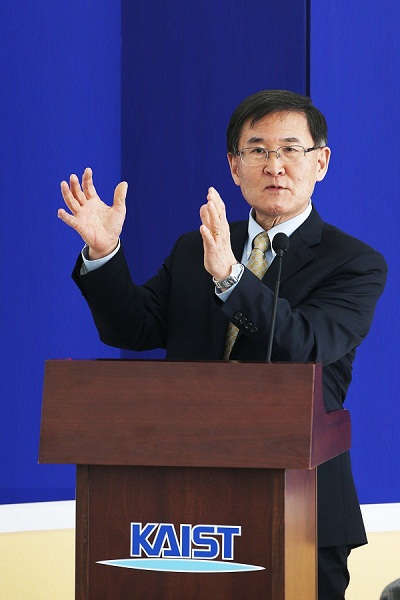 KAIST President Held One-year Anniversary Press Conference
President Steve Kang had a press conference
on February 25, 2014 at the Faculty Club on campus, commemorating the first
year of his presidency. About 30 different media representatives nationwide
attended the meeting.
At his first press conference on the anniversary of his tenure, President Kang
described what he has achieved in the past year, which were: 1) rebuilding the
campus culture to start a campaign for mutual respect, trust, and open
communication by holding meetings with the members of the KAIST community more
than 60 times, 2) establishing core values, creativity and challenge, to
enhance the fabric of the community, 3) restructuring of the university
administration, and 4) the announcement of the mid- and long-term development
plan.
He also mentioned that “2014 will be another exciting year for KAIST to make
more progress” and laid out a few major projects to be implemented this year:
launching of the “Committee for Engineering Education Innovation,” “Startup
KAIST” (an entrepreneurship program), “Greater Collaboration in Technology
Translation and Management with Seoul National University,” and “KAIST End Run”
(a global business incubation program).Explanation of 2014 Major Endeavors by President KangFor
the past decade, domestic engineering schools weighed SCI dissertation
publication more heavily in university evaluations, yielding a world-class
research level. However, such an approach resulted in placing less importance
on entrepreneurship, commercialization, or creating economic values.As a
result, engineering Professors have been evaluated as being too focused on theoretical
SCI dissertation research rather than practical research that could yield
economic benefits through commercialization of developed technology. In
addition, some have criticized that engineering universities have not educated
creative researchers demanded by the industry.KAIST
has begun responding to these criticisms and has made a few suggestions to strengthen
engineering education, promote entrepreneurship in engineers, and globalize Korean
venture companies.As
part of such efforts, KAIST established the KAIST Education and Research
Innovation Committee, composed of various individuals from the industry,
research institutes, alumni, faculty members, and others, to discuss ways to reinforce
engineering education.
A
course to encourage entrepreneurship will be implemented.Startup
KAIST will develop and commercialize innovative ideas from members of KAIST, and
the End Run project will enable students and faculty to establish a global,
venture company. KAIST hopes that a new entrepreneurial culture will be created
on campus, thereby the research success of KAIST members will lead to commercialization
and startups.KAIST
plans on releasing free internet lectures as part of its knowledge contribution
and sponsoring programs which will level the playing field in eduation.KAIST
will establish the KAIST Open Online Course (KOOC). An entrepreneurship
curriculum will be developed for KOOC. KAIST will start trials for KOOC from
2015, gradually expanding to include more courses.
2014.02.27 View 10844
KAIST President Held One-year Anniversary Press Conference
President Steve Kang had a press conference
on February 25, 2014 at the Faculty Club on campus, commemorating the first
year of his presidency. About 30 different media representatives nationwide
attended the meeting.
At his first press conference on the anniversary of his tenure, President Kang
described what he has achieved in the past year, which were: 1) rebuilding the
campus culture to start a campaign for mutual respect, trust, and open
communication by holding meetings with the members of the KAIST community more
than 60 times, 2) establishing core values, creativity and challenge, to
enhance the fabric of the community, 3) restructuring of the university
administration, and 4) the announcement of the mid- and long-term development
plan.
He also mentioned that “2014 will be another exciting year for KAIST to make
more progress” and laid out a few major projects to be implemented this year:
launching of the “Committee for Engineering Education Innovation,” “Startup
KAIST” (an entrepreneurship program), “Greater Collaboration in Technology
Translation and Management with Seoul National University,” and “KAIST End Run”
(a global business incubation program).Explanation of 2014 Major Endeavors by President KangFor
the past decade, domestic engineering schools weighed SCI dissertation
publication more heavily in university evaluations, yielding a world-class
research level. However, such an approach resulted in placing less importance
on entrepreneurship, commercialization, or creating economic values.As a
result, engineering Professors have been evaluated as being too focused on theoretical
SCI dissertation research rather than practical research that could yield
economic benefits through commercialization of developed technology. In
addition, some have criticized that engineering universities have not educated
creative researchers demanded by the industry.KAIST
has begun responding to these criticisms and has made a few suggestions to strengthen
engineering education, promote entrepreneurship in engineers, and globalize Korean
venture companies.As
part of such efforts, KAIST established the KAIST Education and Research
Innovation Committee, composed of various individuals from the industry,
research institutes, alumni, faculty members, and others, to discuss ways to reinforce
engineering education.
A
course to encourage entrepreneurship will be implemented.Startup
KAIST will develop and commercialize innovative ideas from members of KAIST, and
the End Run project will enable students and faculty to establish a global,
venture company. KAIST hopes that a new entrepreneurial culture will be created
on campus, thereby the research success of KAIST members will lead to commercialization
and startups.KAIST
plans on releasing free internet lectures as part of its knowledge contribution
and sponsoring programs which will level the playing field in eduation.KAIST
will establish the KAIST Open Online Course (KOOC). An entrepreneurship
curriculum will be developed for KOOC. KAIST will start trials for KOOC from
2015, gradually expanding to include more courses.
2014.02.27 View 10844 -
 Professor Yong-Tak Im of Mechanical Engineering Appointed as President of Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials
Yong-Tak Im, Professor of the Department of
Mechanical Engineering at KAIST, was sworn in on February 25, 2014 as
the 16th president of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials
(KIMM), a leading government-funded research institution in Korea. KIMM was
established in 1976 to contribute to the development of
Korea through the invention of source technology and technology transfer in
mechanical engineering.
President Im graduated from Seoul National
University, obtaining degrees of Bachelor of Science and Master’s in mechanical
engineering. He later studied at the University of California in Berkeley and
received a doctoral degree in mechanical engineering.
After working as an assistant professor of
the Industrial and Systems Engineering at the Ohio State University,
President Im joined KAIST as a professor of mechanical engineering in 1989.
President Im took many important posts at
KAIST, including Dean of Planning Office, Dean of External Affairs and Public
Relations Office, and Associate Vice President of Special Projects and
Institutional Relations, making a great addition to the university’s endeavors for
globalization.
Among the awards President Im received was the
William Johnson Award in 2007 presented by the Advances in Materials and
Processing Technologies, the Research Achievement Award in 2010 by the Global
Congress on Manufacturing and Management, and the Presidential Award in 2012 by
the Republic of Korea. He was also elected as the vice president of the Korean
Society of Mechanical Engineers, the largest association of professionals in
the mechanical engineering field in Korea.
President Im is currently a professor at
POSCO, an internationally known Korean steel company, and a member of the
Korean Academy of Science and Technology and the National Academy of
Engineering of Korea, respectively.
President Im will serve KIMM for three
years until February 24, 2017.
2014.02.25 View 13275
Professor Yong-Tak Im of Mechanical Engineering Appointed as President of Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials
Yong-Tak Im, Professor of the Department of
Mechanical Engineering at KAIST, was sworn in on February 25, 2014 as
the 16th president of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials
(KIMM), a leading government-funded research institution in Korea. KIMM was
established in 1976 to contribute to the development of
Korea through the invention of source technology and technology transfer in
mechanical engineering.
President Im graduated from Seoul National
University, obtaining degrees of Bachelor of Science and Master’s in mechanical
engineering. He later studied at the University of California in Berkeley and
received a doctoral degree in mechanical engineering.
After working as an assistant professor of
the Industrial and Systems Engineering at the Ohio State University,
President Im joined KAIST as a professor of mechanical engineering in 1989.
President Im took many important posts at
KAIST, including Dean of Planning Office, Dean of External Affairs and Public
Relations Office, and Associate Vice President of Special Projects and
Institutional Relations, making a great addition to the university’s endeavors for
globalization.
Among the awards President Im received was the
William Johnson Award in 2007 presented by the Advances in Materials and
Processing Technologies, the Research Achievement Award in 2010 by the Global
Congress on Manufacturing and Management, and the Presidential Award in 2012 by
the Republic of Korea. He was also elected as the vice president of the Korean
Society of Mechanical Engineers, the largest association of professionals in
the mechanical engineering field in Korea.
President Im is currently a professor at
POSCO, an internationally known Korean steel company, and a member of the
Korean Academy of Science and Technology and the National Academy of
Engineering of Korea, respectively.
President Im will serve KIMM for three
years until February 24, 2017.
2014.02.25 View 13275