Intel
-
 KAIST Partners with WEF to Prepare for the 4th Industrial Revolution
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and the Head of the World Economic Forum Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Murat Sonmez, made a commitment to build cooperation in an active manner for addressing the ramifications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The two signed an MOU to cooperate in research in related fields on October 13 after holding a roundtable discussion titled “The Future of Jobs and Inclusive Growth in Korea”. It is the first partnership that the WEF has sealed with an academic institution.The roundtable discussion brought together distinguished guests from politics, non-profit civic organizations, academia, and enterprises including Daejeon Mayor Seon-Taek Kwon, Doosan Group Vice Chairman Lee Hyun-Soon, and Korean Venture Business Association President Ahn Keon-Joon.
During the news conference, President Shin said, “This event means a lot because it explores ways in which inclusive growth and job creation can be realized in Korea. To move forward in the new age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, every country needs to adopt appropriate new policies suitable for their specific market environments. KAIST will contribute to this process for Korea as well as for the global community.”
President Shin also said, “Korea has been a fast follower in previous industrial revolutions. Now, we have the momentum to seize the opportunities in the wake of this revolution. KAIST is dedicated to leading Korea into becoming a first mover in the Fourth Industrial Revolution by cooperating with the WEF.”
“Two decades later, we will live with considerable number of robots around us. It is possible that our societies in the future will consist of Homo sapiens and Robo sapiens. We need to create new jobs for Homo sapiens to prepare for a society that we will have to coexist with a new industrial tribe. Industries need continuing education to retrain workers for the ever evolving industrial landscape of the future,” President Shin emphasized.
Meanwhile, Sonmez pointed out that all stakeholders should participate in understanding the new industrial environment’s ramifications, saying “Societies, governments, public and private sectors, startups, and academia should co-design inclusive models through global efforts. Ethics and influences on the job market should also be taken into consideration.”
Sonmez said nine factors such as blockchains, internet of things, artificial intelligence, machine learning, cross-border data blow, drones, 3D printing, autonomous driving, the environment, and precision medicine will take center stage in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, In particular, he said that blockchains, which are a cybersecurity technology for online financial transactions, will bring even bigger changes than the ‘World Wide Web’ has done over the past three decades.
“To this end, we will have to work closely with major academic institutes. Through this partnership with KAIST, we will make the fruits of the new industrial environment benefit Koreans and Korean society,” Sonmez added.
2017.10.14 View 8893
KAIST Partners with WEF to Prepare for the 4th Industrial Revolution
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and the Head of the World Economic Forum Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Murat Sonmez, made a commitment to build cooperation in an active manner for addressing the ramifications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The two signed an MOU to cooperate in research in related fields on October 13 after holding a roundtable discussion titled “The Future of Jobs and Inclusive Growth in Korea”. It is the first partnership that the WEF has sealed with an academic institution.The roundtable discussion brought together distinguished guests from politics, non-profit civic organizations, academia, and enterprises including Daejeon Mayor Seon-Taek Kwon, Doosan Group Vice Chairman Lee Hyun-Soon, and Korean Venture Business Association President Ahn Keon-Joon.
During the news conference, President Shin said, “This event means a lot because it explores ways in which inclusive growth and job creation can be realized in Korea. To move forward in the new age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, every country needs to adopt appropriate new policies suitable for their specific market environments. KAIST will contribute to this process for Korea as well as for the global community.”
President Shin also said, “Korea has been a fast follower in previous industrial revolutions. Now, we have the momentum to seize the opportunities in the wake of this revolution. KAIST is dedicated to leading Korea into becoming a first mover in the Fourth Industrial Revolution by cooperating with the WEF.”
“Two decades later, we will live with considerable number of robots around us. It is possible that our societies in the future will consist of Homo sapiens and Robo sapiens. We need to create new jobs for Homo sapiens to prepare for a society that we will have to coexist with a new industrial tribe. Industries need continuing education to retrain workers for the ever evolving industrial landscape of the future,” President Shin emphasized.
Meanwhile, Sonmez pointed out that all stakeholders should participate in understanding the new industrial environment’s ramifications, saying “Societies, governments, public and private sectors, startups, and academia should co-design inclusive models through global efforts. Ethics and influences on the job market should also be taken into consideration.”
Sonmez said nine factors such as blockchains, internet of things, artificial intelligence, machine learning, cross-border data blow, drones, 3D printing, autonomous driving, the environment, and precision medicine will take center stage in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, In particular, he said that blockchains, which are a cybersecurity technology for online financial transactions, will bring even bigger changes than the ‘World Wide Web’ has done over the past three decades.
“To this end, we will have to work closely with major academic institutes. Through this partnership with KAIST, we will make the fruits of the new industrial environment benefit Koreans and Korean society,” Sonmez added.
2017.10.14 View 8893 -
 Postech-KAIST Rivalry Heats Up at the 16th Science War
The 16th Postech-KAIST Science War wrapped up its two-day rivals’ duel at the KAIST campus in Daejeon on September 23. The event was established in 2002 to build a close tie between the two renowned universities for science and technology, and to provide students with an opportunity to demonstrate their talents and abilities.
On September 21, a convoy of red Postech buses carrying more than 650 athletes, students, and supporters arrived at the KAIST campus in Daejeon. The two teams competed in eight events including both online and sports event.
The night before the actual games started, cheerleading teams from both Postech Cheero and KAIST ELKA kicked off the event.
1st Day (September 22)
The hacking tournament marked the beginning of the Science War. The event started at nine in the morning. Both teams had to solve four problems within 12 hours.
While the fierce hacking competition was underway, school music bands, including Twenties Dreams, opened up the event with beautiful voices.
The soccer game took place in the university stadium. The KAIST soccer team brought the first win to KAIST, and was their second straight victory in soccer.
At the outdoor theatre, the evening games, including Artificial Intelligence and E-sports (League of Legend) began. After the E-sports, both KAIST’s and Postech’s music and dance clubs showed amazing performances adding more excitement to the event.
Another fun aspect of the event was the ‘evening street food market’. Food trucks and food booths were lined up to satisfy students’ hunger. Talso here were various game booths such as can bowling, balloon darts, and lamp DIY.
2nd Day (September 23)
The baseball team marked the second day of the Science War in the Undergraduate Field. The KAIST team won the game by six runs.
Science quizzes sealed the Postech-KAIST Science War. Although the KAIST team led at the beginning, the Postech team overtook them by getting bonus point answers correct. This game decided Postech winning this year’s Science War.
As a spin-off, a badminton game was held in the Sports Complex and the KAIST team beat the Postech team with ease.
Last but not least, a basketball game was held in the Sports Complex. In the last game of the Science War, the KAIST team wiped away the stain of last year’s defeat.
At the closing ceremony, famous rappers and school music clubs celebrated the last moments of the Science War.
(Jiwon Hwang, Public Relations of the 16th Science War Committee)
(The 16th Science War Committee)
Cheers to the students committees, participants, and supporters who put every ounce of their effort into successfully running the 16th Postech-KAIST Science War.
Day
Category
Winner
Day 1
Hacking
Postech
Soccer
KAIST
Artificial Intelligence
Postech
E-Sports (LoL)
Postech
Day 2
Baseball
KAIST
Science Quizzes
Postech
Badminton (spin-off)
KAIST
Basketball
KAIST
(The final tally for KAIST in the Science Wars was eight wins and six losses)
2017.09.27 View 6314
Postech-KAIST Rivalry Heats Up at the 16th Science War
The 16th Postech-KAIST Science War wrapped up its two-day rivals’ duel at the KAIST campus in Daejeon on September 23. The event was established in 2002 to build a close tie between the two renowned universities for science and technology, and to provide students with an opportunity to demonstrate their talents and abilities.
On September 21, a convoy of red Postech buses carrying more than 650 athletes, students, and supporters arrived at the KAIST campus in Daejeon. The two teams competed in eight events including both online and sports event.
The night before the actual games started, cheerleading teams from both Postech Cheero and KAIST ELKA kicked off the event.
1st Day (September 22)
The hacking tournament marked the beginning of the Science War. The event started at nine in the morning. Both teams had to solve four problems within 12 hours.
While the fierce hacking competition was underway, school music bands, including Twenties Dreams, opened up the event with beautiful voices.
The soccer game took place in the university stadium. The KAIST soccer team brought the first win to KAIST, and was their second straight victory in soccer.
At the outdoor theatre, the evening games, including Artificial Intelligence and E-sports (League of Legend) began. After the E-sports, both KAIST’s and Postech’s music and dance clubs showed amazing performances adding more excitement to the event.
Another fun aspect of the event was the ‘evening street food market’. Food trucks and food booths were lined up to satisfy students’ hunger. Talso here were various game booths such as can bowling, balloon darts, and lamp DIY.
2nd Day (September 23)
The baseball team marked the second day of the Science War in the Undergraduate Field. The KAIST team won the game by six runs.
Science quizzes sealed the Postech-KAIST Science War. Although the KAIST team led at the beginning, the Postech team overtook them by getting bonus point answers correct. This game decided Postech winning this year’s Science War.
As a spin-off, a badminton game was held in the Sports Complex and the KAIST team beat the Postech team with ease.
Last but not least, a basketball game was held in the Sports Complex. In the last game of the Science War, the KAIST team wiped away the stain of last year’s defeat.
At the closing ceremony, famous rappers and school music clubs celebrated the last moments of the Science War.
(Jiwon Hwang, Public Relations of the 16th Science War Committee)
(The 16th Science War Committee)
Cheers to the students committees, participants, and supporters who put every ounce of their effort into successfully running the 16th Postech-KAIST Science War.
Day
Category
Winner
Day 1
Hacking
Postech
Soccer
KAIST
Artificial Intelligence
Postech
E-Sports (LoL)
Postech
Day 2
Baseball
KAIST
Science Quizzes
Postech
Badminton (spin-off)
KAIST
Basketball
KAIST
(The final tally for KAIST in the Science Wars was eight wins and six losses)
2017.09.27 View 6314 -
 Semiconductor Patterning of Seven Nanometers Technology Using a Camera Flash
A research team led by Professor Sang Ouk Kim in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed semiconductor manufacturing technology using a camera flash.
This technology can manufacture ultra-fine patterns over a large area by irradiating a single flash with a seven-nanometer patterning technique for semiconductors. It can facilitate the manufacturing of highly efficient, integrated semiconductor devices in the future.
Technology for the Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoTs), and big data, which are the major keys for the fourth Industrial Revolution, require high-capacity, high-performance semiconductor devices. It is necessary to develop lithography technology to produce such next-generation, highly integrated semiconductor devices.
Although related industries have been using conventional photolithography for small patterns, this technique has limitations for forming a pattern of sub-10 nm patterns.
Molecular assembly patterning technology using polymers has been in the spotlight as the next generation technology to replace photolithography because it is inexpensive to produce and can easily form sub-10 nm patterns. However, since it generally takes a long time for heat treatment at high-temperature or toxic solvent vapor treatment, mass production is difficult and thus its commercialization has been limited.
The research team introduced a camera flash that instantly emits strong light to solve the issues of polymer molecular assembly patterning. Using a flash can possibly achieve a semiconductor patterning of seven nanometers within 15 milliseconds (1 millisecond = 1/1,000 second), which can generate a temperature of several hundred degrees Celsius in several tens of milliseconds.
The team has demonstrated that applying this technology to polymer molecular assembly allows a single flash of light to form molecular assembly patterns.
The team also identified its compatibility with polymer flexible substrates, which are impossible to process at high temperatures. Through these findings, the technology can be applied to the fabrication of next-generation, flexible semiconductors.
The researchers said the camera flash photo-thermal process will be introduced into molecular assembly technology and this highly-efficiency technology can accelerate the realization of molecular assembly semiconductor technology.
Professor Kim, who led the research, said, “Despite its potential, molecular assembly semiconductor technology has remained a big challenge in improving process efficiency.” “This technology will be a breakthrough for the practical use of molecular assembly-based semiconductors.”
The paper was published in the international journal, Advanced Materials on August 21 with first authors, researcher Hyeong Min Jin and PhD candidate Dae Yong Park.
The research, sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT, was co-led Professor by Keon Jae Lee in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, and Professor Kwang Ho Kim in the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Pusan National University.
(1. Formation of semiconductor patterns using a camera flash)
(Schematic diagram of molecular assembly pattern using a camera flash)
(Self-assembled patterns)
2017.09.18 View 11437
Semiconductor Patterning of Seven Nanometers Technology Using a Camera Flash
A research team led by Professor Sang Ouk Kim in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed semiconductor manufacturing technology using a camera flash.
This technology can manufacture ultra-fine patterns over a large area by irradiating a single flash with a seven-nanometer patterning technique for semiconductors. It can facilitate the manufacturing of highly efficient, integrated semiconductor devices in the future.
Technology for the Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoTs), and big data, which are the major keys for the fourth Industrial Revolution, require high-capacity, high-performance semiconductor devices. It is necessary to develop lithography technology to produce such next-generation, highly integrated semiconductor devices.
Although related industries have been using conventional photolithography for small patterns, this technique has limitations for forming a pattern of sub-10 nm patterns.
Molecular assembly patterning technology using polymers has been in the spotlight as the next generation technology to replace photolithography because it is inexpensive to produce and can easily form sub-10 nm patterns. However, since it generally takes a long time for heat treatment at high-temperature or toxic solvent vapor treatment, mass production is difficult and thus its commercialization has been limited.
The research team introduced a camera flash that instantly emits strong light to solve the issues of polymer molecular assembly patterning. Using a flash can possibly achieve a semiconductor patterning of seven nanometers within 15 milliseconds (1 millisecond = 1/1,000 second), which can generate a temperature of several hundred degrees Celsius in several tens of milliseconds.
The team has demonstrated that applying this technology to polymer molecular assembly allows a single flash of light to form molecular assembly patterns.
The team also identified its compatibility with polymer flexible substrates, which are impossible to process at high temperatures. Through these findings, the technology can be applied to the fabrication of next-generation, flexible semiconductors.
The researchers said the camera flash photo-thermal process will be introduced into molecular assembly technology and this highly-efficiency technology can accelerate the realization of molecular assembly semiconductor technology.
Professor Kim, who led the research, said, “Despite its potential, molecular assembly semiconductor technology has remained a big challenge in improving process efficiency.” “This technology will be a breakthrough for the practical use of molecular assembly-based semiconductors.”
The paper was published in the international journal, Advanced Materials on August 21 with first authors, researcher Hyeong Min Jin and PhD candidate Dae Yong Park.
The research, sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT, was co-led Professor by Keon Jae Lee in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, and Professor Kwang Ho Kim in the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Pusan National University.
(1. Formation of semiconductor patterns using a camera flash)
(Schematic diagram of molecular assembly pattern using a camera flash)
(Self-assembled patterns)
2017.09.18 View 11437 -
 KAIST AI Academy for LG CNS Employees
The Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering) at KAIST has collaborated with LG CNS to start a full-fledged KAIST AI Academy course after the two-week pilot course for employees of LG CNS, a Korean company specializing in IT services.
Approximately 100 employees participated in the first KAIST AI Academy course held over two weeks from August 24 to September 1. LG CNS is planning to enroll a total of 500 employees in this course by the end of the year.
Artificial intelligence is widely recognized as essential technology in various industries. In that sense, the KAIST AI Academy course was established to reinforce both the AI technology and the business ability of the company. In addition, it aims at leading employees to develop new business using novel technologies. The main contents of this course are as follows: i) discussing AI technology development and its influence on industries; ii) understanding AI technologies and acquiring the major technologies applicable to business; and iii) introducing cases of AI applications and deep learning.
During the course, seven professors with expertise in AI deep learning from the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering), including Jae-Gil Lee and Jinkyoo Park will be leading the class, including practical on-site educational programs.
Based on the accumulated business experience integrated with the latest AI technology, LG CNS has been making an effort to find new business opportunities to support companies that are hoping to make digital innovations.
The company aims to reinforce the AI capabilities of its employees and is planning to upgrade the course in a sustainable manner. It will also foster outside manpower by expanding the AI education to its clients who pursue manufacturing reinforcement and innovation in digital marketing.
Seong Wook Lee, the Director of the AI and Big Data Business Unit said, “As AI plays an important role in business services, LG CNS decided to open the KAIST AI Academy course to deliver better value to our clients by incorporating our AI-based business cases and KAIST’s up-to-date knowledge.”
2017.09.06 View 7543
KAIST AI Academy for LG CNS Employees
The Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering) at KAIST has collaborated with LG CNS to start a full-fledged KAIST AI Academy course after the two-week pilot course for employees of LG CNS, a Korean company specializing in IT services.
Approximately 100 employees participated in the first KAIST AI Academy course held over two weeks from August 24 to September 1. LG CNS is planning to enroll a total of 500 employees in this course by the end of the year.
Artificial intelligence is widely recognized as essential technology in various industries. In that sense, the KAIST AI Academy course was established to reinforce both the AI technology and the business ability of the company. In addition, it aims at leading employees to develop new business using novel technologies. The main contents of this course are as follows: i) discussing AI technology development and its influence on industries; ii) understanding AI technologies and acquiring the major technologies applicable to business; and iii) introducing cases of AI applications and deep learning.
During the course, seven professors with expertise in AI deep learning from the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering), including Jae-Gil Lee and Jinkyoo Park will be leading the class, including practical on-site educational programs.
Based on the accumulated business experience integrated with the latest AI technology, LG CNS has been making an effort to find new business opportunities to support companies that are hoping to make digital innovations.
The company aims to reinforce the AI capabilities of its employees and is planning to upgrade the course in a sustainable manner. It will also foster outside manpower by expanding the AI education to its clients who pursue manufacturing reinforcement and innovation in digital marketing.
Seong Wook Lee, the Director of the AI and Big Data Business Unit said, “As AI plays an important role in business services, LG CNS decided to open the KAIST AI Academy course to deliver better value to our clients by incorporating our AI-based business cases and KAIST’s up-to-date knowledge.”
2017.09.06 View 7543 -
 KAIST to Open the Meditation Research Center
KAIST announced that it will open its Meditation Research Center next June. The center will serve as a place for the wellness of KAIST community as well as for furthering the cognitive sciences and its relevant convergence studies.
For facilitating the center, KAIST signed an MOU with the Foundation Academia Platonica in Seoul, an academy working for enriching the humanities and insight meditation on Aug.31. The Venerable Misan, a Buddhist monk well-known for his ‘Heart Smile Meditation’ program, will head the center.
The center will also conduct convergence research on meditation, which will translate into brain imaging, cognitive behavior, and its psychological effects. Built upon the research, the center expects to publish textbooks on meditation and will distribute them to the public and schools in an effort to widely disseminate the benefits of meditation.
As mindful meditation has become mainstream and more extensively studied, growing evidence suggests multiple psychological and physical benefits of these mindfulness exercises as well as for similar practices. Mind-body practices like meditation have been shown to reduce the body’s stress response by strengthening the relaxation response and lowering stress hormones.
The Venerable Misan, a Ph.D in philosophy from Oxford University, also serves as the director of the Sangdo Meditation Center and a professor at Joong-Ang Sangha University, a higher educational institution for Buddhist monks.
Monk Misan said that meditation will play a crucial part in educating creative students with an empathetic mindset. He added, “Hi-tech companies in Silicon Valley such as Google and Intel have long introduced meditation programs for stress management. Such practices will enhance the wellness of employees as well as their working efficiency.”
President Sung-Chul Shin said of the opening of the center, “From long ago, many universities in foreign countries including Havard, Stanford, Oxfor universities and the Max Planck Institute in Germany have applied scientific approaches to meditation and installed meditation centers. I am pleased to open our own center next year and I believe that it will bring more diverse opportunities for advancing convergent studies in AI and cognitive sciences.
2017.08.31 View 6385
KAIST to Open the Meditation Research Center
KAIST announced that it will open its Meditation Research Center next June. The center will serve as a place for the wellness of KAIST community as well as for furthering the cognitive sciences and its relevant convergence studies.
For facilitating the center, KAIST signed an MOU with the Foundation Academia Platonica in Seoul, an academy working for enriching the humanities and insight meditation on Aug.31. The Venerable Misan, a Buddhist monk well-known for his ‘Heart Smile Meditation’ program, will head the center.
The center will also conduct convergence research on meditation, which will translate into brain imaging, cognitive behavior, and its psychological effects. Built upon the research, the center expects to publish textbooks on meditation and will distribute them to the public and schools in an effort to widely disseminate the benefits of meditation.
As mindful meditation has become mainstream and more extensively studied, growing evidence suggests multiple psychological and physical benefits of these mindfulness exercises as well as for similar practices. Mind-body practices like meditation have been shown to reduce the body’s stress response by strengthening the relaxation response and lowering stress hormones.
The Venerable Misan, a Ph.D in philosophy from Oxford University, also serves as the director of the Sangdo Meditation Center and a professor at Joong-Ang Sangha University, a higher educational institution for Buddhist monks.
Monk Misan said that meditation will play a crucial part in educating creative students with an empathetic mindset. He added, “Hi-tech companies in Silicon Valley such as Google and Intel have long introduced meditation programs for stress management. Such practices will enhance the wellness of employees as well as their working efficiency.”
President Sung-Chul Shin said of the opening of the center, “From long ago, many universities in foreign countries including Havard, Stanford, Oxfor universities and the Max Planck Institute in Germany have applied scientific approaches to meditation and installed meditation centers. I am pleased to open our own center next year and I believe that it will bring more diverse opportunities for advancing convergent studies in AI and cognitive sciences.
2017.08.31 View 6385 -
 2017 KAIST Tech Fair to Showcase Ten Cutting-Edge Technologies
KAIST will showcase the ten most cutting-edge technologies developed by KAIST faculty and researchers at the 2017 KAIST Tech Fair. The fair will be held on September 12 at the COEX in Seoul. The fair will bring companies, venture capitalists, and tech consultants from around the country to learn about the most commercially potential technology from KAIST.
The ten technologies, all already patented, will be highly relevant for the new industrial trends summed up by the Fourth Industrial Revolution. They include the fields of ICT, unmanned transportation, AI, robotics, IoT, nano, and big data.
The Technology Evaluation Committee, comprised of the heads of the departments at KAIST, patent lawyers, and venture capitalists, selected the ten technologies based on their applicability, innovativeness, and marketability. The selectees will be provided with various commercialization support and services including the manufacturing of prototypes, marketing consultation at home and abroad, as well as handling IPR issues, among others.
KAIST will hold an information session as well as consultations for successful technology commercialization as one of the innovative plans proposed by the KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin. This session will invite 200 entrepreneurs who are interested in the selected technologies.
Associate Vice President of University-Industry Cooperation Kyung Cheol Choi said, “Starting with the selection of 2017 top ten crucial technologies, KAIST will continue supporting technology marketing as well as its successful transfer. KAIST will make effort to carry out university-industry cooperation and find core patent technologies and project ideas in order to stimulate technology commercialization.”
The list of the ten critical patent technologies selected by KAIST is as follows:
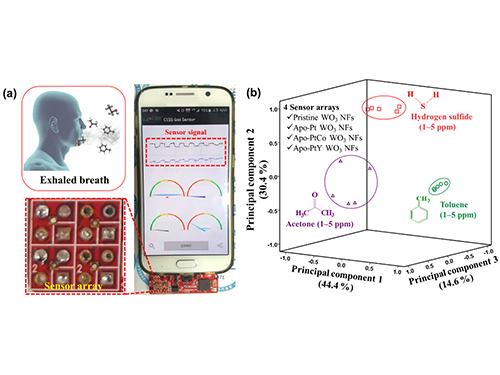
▶ Catalyst-Decorated Nanofiber Sensor for Health Monitoring
By Professor Il-Doo Kim (Department of Materials Science and Engineering)
Human breath carries diverse components of diseases such as asthma, lung cancer, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and halitosis. Thus, it is possible to analyze exhaled breath very rapidly with a simple analyzing process and it can detect trace changes in exhaled breath components, which trigger diseases.
The research team developed highly sensitive and selective chemical gas sensors that can detect specific disease, using protein-encapsulated nanocatalysts. They can diagnose certain diseases by analyzing human exhaled breath. This technology enables the early monitoring of various diseases through pattern recognition of biomarker gases associated with the diseases in human exhalation.
The established sensing libraries can detect biomarker species with high sensitivity and selectivity. The team hopes that the new and innovative breath gas analysis platform will be very helpful for reducing medical expenditures and the continuous monitoring of physical conditions.
# Detection of environmental toxic gases, monitoring of body health condition
Figure (a) Mobile device integrated with nanofiber based MEMS sensorsFigure (b) Exhaled breath pattern recognition: principle component analysis for the accurate detection of acetone, hydrogen sulfide, and toluene gases
▶ Technology for a Cancer Cure Using Big Data and Simulating Biological Network By Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering)
The complex and heterogeneous nature of cancer, which results in highly variable drug responses, is a major obstacle in curing cancer. Previous methods to predict drug responses mostly focus on the static analysis of genome-wide alternations, resulting in a limitation for the understanding of cancer heterogeneity and its variable responses.
The research team used a method to integrate cancer genomics data with the dynamics of biological networks for drug response prediction and to design of effective drug combination. It provides a computational framework for evaluating drug efficacies and synergistic effects by combining the attractor landscape analysis of a biological network with the genomic alteration profiles of cancer cells.
This technology can reduce the cost of drug development by predicting drug responses and help selecting more effective new drug targets in consideration of the overall cellular response landscape. It can also provide comprehensive insight into the mechanistic origin of variable drug responses. The patent technology can be applicable to designing more effective and cancer-specific combination therapies.
# Development of targeted anticancer drugs, genetic testing
Figure (a) The computational prediction of drug responses using attractor landscape analysis of network dynamics
▶ Highly Stretchable, Wearable Strain SensorBy Professor O Ok Park (Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
Conventional materials for strain sensor are metals or semiconductors, but these materials show a limited range of strain. To improve the stretchability of conventional materials, several projects have been done using novel materials with a high aspect ratio; nevertheless, these projects encountered problems, including complex and expensive processes, poor scalable features, and low controllability of the sensitivity in the manufacturing step.
The research team used a layer-by-layer assembly technique to control the sensitivity of the sensor in a facile and inexpensive method. By using stretchable yarn as a substrate, the graphene strain sensor gained more stretchability.
Through the newly-patented technology, the graphene strain sensor can be fabricated using an all-solution process; therefore, the sensitivity of the sensor can be easily controlled with a repetitive cycle of the coating process. The size of this sensor can be controlled as well, because it depends only on the size of coated substrate.
# Wearable strain sensor, planar strain sensor
Figure (a) Nylon-covered rubber yarn showing linear relationship between the applied strain load and its resistance change
Figure (b) Wool yarn showing an inverse relation of resistance with the applied strain load
▶ Chip & Flash Memory Data Security DeviceBy Professor Yang-Kyu Choi (School of Electrical Engineering)
Using software-based security methods can lead to having problems related to the backtracking of a security function through reverse engineering, the replication of an input value, and the forgery and modification of software. These problems should not be neglected, especially as people are increasingly recognizing the importance of personal information.
To meet the growing demands for new security methods for constructing a more perfect security system, the research team developed a hardware-based security device as well as methods for a higher level of security in the era of IoTs. The principles of the technologies are based on nanotechnology, such as mechanical deformation in a nanowire, electrical degradation in a field-effect transistor (FET), and thermal data erasing stored in the charge trap layer in flash memory. Hence, the security states are extremely safe, compared with software-based security methods and cannot be reverse-engineered by unauthorized users.
This patented technology can be used to improve the security level of logic circuits and flash memory against unauthorized users.
# Financial businesses, the defense industry, private electronics including smartphones, tablets and PCs, electronics for missions in extreme environments
Figure (a) Application for a high level of security in a logic circuit
▶ A Bio-Healthcare Device for Neuroimaging
By Professor Hyeonmin Bae (School of Electrical Engineering)There are no portable brain imaging devices and, as a result, brain diseases are often diagnosed after irreversible symptoms appeared. This can also be linked to an increase in social expenditures as a society ages.
A near-infrared spectroscopy neuroimaging device for functional brain imaging, NIRSIT, utilizes light to detect hemodynamic changes in cerebral blood flow and visualizes brain activation regions in the prefrontal area of the brain in real time.
Unlike any other existing brain imaging devices (i.e. fMRI and conventional fNIRS), NIRSIT has improved its spatial resolution while maintaining complete portability.
Furthermore, NIRSIT is probably the one and only portable and wireless NIRS device, designed to be used for brain research and clinical purposes. A software application allows the raw data extracted from the hemodynamic changes in the brain to be shown in real time on a tablet wirelessly connected to NIRSIT.
Thanks to its easy-to-use features and user-friendly design, both in hardware and in software, NIRSIT will surely set a new paradigm in the brain research and healthcare fields.
# Concussion analysis, wearable stroke monitoring, CPR monitoring, Alzheimer’s disease, neuro rehabilitation, determination of brain death
Figure (a) Image of NIRSIT, Figure (b) Neuroimaging using NIRSIT
▶ Technology for Virtual Creatures with Digitally-Emotional DNA of UsersBy Professor Jong-Hwan Kim (School of Electrical Engineering)
Currently, a large number of IT companies around the world are trying to develop a system that can offer active and emotional services and the interface method is one of the most important issues.
Although most of the existing software agents are equipped with virtual faces and voices, they do not possess a personality similar to humans. Having various personalities, like human beings, can be a charming point for users, which then leads them to have higher satisfaction with the product.
Dr. Kim’s research team developed Darwin C (Digital Agent Reconstruction with Intelligence and Natural Character), a digital agent software that provides an optimized emotional service based on personal big data, such as the user’s conversations, locations, photos, music, etc., collected from smart devices.
With this technology, the digital DNAs of a user (i.e. appearance, voice, and personality DNA) is extracted from personal data stored on various smart devices. Based on the extracted digital DNA, a 3-D software agent can be formed in a smartphone, which characterizes an individual that the user hopes to meet, such as parents, spouse, grandchild, or a celebrity.
The software agents will be expanded from Android devices to home appliances. The team expected that this technology can help customers who want to understand more about a friend or form and maintain interpersonal relations.
# Entertainment, hardware robots for education, healthcare curing depression and loneliness
Figure (a) Overview of the DarwinC technology, Figure (b) Structure of digital DNA
▶ Laser-Integrated Precision Metrological System Technology for Smart Factories By Professor Seung-woo Kim (Department of Mechanical Engineering)
In optical distance metrology, the time-of-flight method of using light pulses permits measuring distances over extensive ranges. However, the measurement precision reaches just a few tens of millimeters at most, mainly because the responsivity of the photodetectors available today is limited to the picosecond range. In addition, one device can measure only one target. For these reasons, a novel technology was devised to overcome the traditional limits of time-of-flight measurement.
This patented technology uses a highly precise, laser-integrated distance measurement system for diagnosing large machines and smart factories. This technology was devised to handle the status (e.g. position, 3-D coordinate, and thermal deformation) of multiple targets simultaneously. It is called the multi-target distance meter (MDM) and was constructed by combining a nonlinear optical crystal with a pair of femtosecond lasers.
This technology is able to measure the distances to multiple targets with a single piece of equipment, and it can easily extend the number of targets by just adding beam-splitting devices. Not only does the technology help by reducing cost and complexity, it also enables real-time quality control in the manufacturing industry.
# Real-time on-axis position inspection of a multiple-lens assembly, long-term thermal displacement monitoring of a large, precise machine, 3-D motion control of a mobile vehicle
Figure (a) Conceptual image of smart factory monitoring using laser-integrated precision metrological system technology
▶ SLAM Technology for Autonomous Robot Navigation in a Dynamic Indoor/Outdoor EnvironmentBy Professor Hyun Myung (Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering)
Dr. Myung’s research team developed SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) technology for autonomous robot navigation in dynamic indoor/outdoor environments. Two methods were applied to this technology: a hierarchical graph structure-based 3-D high resolution map building method using a low-cost 2D laser scanner and a magnetic field-based localization method for feature-poor environments.
Existing technology required expensive sensors for outdoor environment. The localization and mapping technique were also not very accurate, especially in dynamic environments. The team wanted to provide robust SLAM in low and high dynamic object environments using the fusion of low-cost sensors, such as magnetics, 2-D LiDAR, and camera sensors.
Through this technology, the accuracy of localization and mapping could be increased to within 10cm, using low-cost sensors. Also, it facilitates localization and mapping even in feature-poor environments.
# Autonomous robot navigation in warehouses, autonomous navigation of self-driving cars, autonomous navigation of AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) in smart factories
Figure (a) Built outdoor 3-D mappring using a mobile robot with tilted 2-D LiDAR sensor, Figure (b) Mobile robot system for GPS-less mappring
▶ Technology for Optimizing 5G Beamforming ICBy Songcheol Hong (School of Electrical Engineering)
Dr. Hong’s team introduced a new structure for low-power, subminiature, and highly-linear beamforming IC technology. The patent used in this technology reduced the chip size and the direct current (DC) power dissipations drastically, allowing it to make mmWave beamforming antennas.
Beam-forming technology has emerged as an important area in the field of 5G communications and radar systems. It facilitates communication and signal detection with very low RF power.
The patents can be applied to 5G communication beam-forming ICs and antenna modules in mobile terminals, base stations and terminals in the automotive field. Moreover, they can be used in various mmWave radar systems for automobiles, drones, human computer interfaces, and indoor positioning.
# 5G V2X, IoTs, virtual reality
Figure (a) Active phased array system
▶ Beam Division Multiple Access TechnologyBy Professor Dong Ho Cho (School of Electrical Engineering)
Using a 5G network, a communication infrastructure for supporting high-speed, real-time services requires new technologies that enable 4x4 MIMO transmissions within beam-based wireless systems in a new frequency band and improves spectral efficiency more than ten times compared to LTE in domestic and overseas mobile communication carriers and related industries.
P2BDMA, a pattern or polarization beam division multiple access technology, is a core technology for addressing this demand for 5G networks as it enables 4x4 MIMO transmissions in mmWave frequency bands by utilizing the pattern polarization characteristic of radio waves.
The research team upgraded BDMA technology in which the same frequency resource is reused in more than two spaces by using beamforming. This technology increases the degree of freedom (DOF) of wireless communication channels, and thereby improves the achievable data transmission rate by employing multiple pattern/polarization antennas in the conventional BDMA system. The P2BDMA technique has the advantage of eliminating the frequency shortage problem and increasing the transmission speed while using the wide frequency band in a more efficient manner.
The team expects that this technology will alleviate the frequency shortage problem and CAPEX/OPEX of domestic mobile telecommunication companies, support an increase in sales for related equipment makers to make it internationally competitive, and further play a central role in providing high-speed transmission rates to a large number of IoT devices in the future IoT era.
# Autonomous vehicle, communication infrastructure, mobile access system
Figure (a) Concept of P2BDMA technology
2017.08.30 View 15963
2017 KAIST Tech Fair to Showcase Ten Cutting-Edge Technologies
KAIST will showcase the ten most cutting-edge technologies developed by KAIST faculty and researchers at the 2017 KAIST Tech Fair. The fair will be held on September 12 at the COEX in Seoul. The fair will bring companies, venture capitalists, and tech consultants from around the country to learn about the most commercially potential technology from KAIST.
The ten technologies, all already patented, will be highly relevant for the new industrial trends summed up by the Fourth Industrial Revolution. They include the fields of ICT, unmanned transportation, AI, robotics, IoT, nano, and big data.
The Technology Evaluation Committee, comprised of the heads of the departments at KAIST, patent lawyers, and venture capitalists, selected the ten technologies based on their applicability, innovativeness, and marketability. The selectees will be provided with various commercialization support and services including the manufacturing of prototypes, marketing consultation at home and abroad, as well as handling IPR issues, among others.
KAIST will hold an information session as well as consultations for successful technology commercialization as one of the innovative plans proposed by the KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin. This session will invite 200 entrepreneurs who are interested in the selected technologies.
Associate Vice President of University-Industry Cooperation Kyung Cheol Choi said, “Starting with the selection of 2017 top ten crucial technologies, KAIST will continue supporting technology marketing as well as its successful transfer. KAIST will make effort to carry out university-industry cooperation and find core patent technologies and project ideas in order to stimulate technology commercialization.”
The list of the ten critical patent technologies selected by KAIST is as follows:
▶ Catalyst-Decorated Nanofiber Sensor for Health Monitoring
By Professor Il-Doo Kim (Department of Materials Science and Engineering)
Human breath carries diverse components of diseases such as asthma, lung cancer, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and halitosis. Thus, it is possible to analyze exhaled breath very rapidly with a simple analyzing process and it can detect trace changes in exhaled breath components, which trigger diseases.
The research team developed highly sensitive and selective chemical gas sensors that can detect specific disease, using protein-encapsulated nanocatalysts. They can diagnose certain diseases by analyzing human exhaled breath. This technology enables the early monitoring of various diseases through pattern recognition of biomarker gases associated with the diseases in human exhalation.
The established sensing libraries can detect biomarker species with high sensitivity and selectivity. The team hopes that the new and innovative breath gas analysis platform will be very helpful for reducing medical expenditures and the continuous monitoring of physical conditions.
# Detection of environmental toxic gases, monitoring of body health condition
Figure (a) Mobile device integrated with nanofiber based MEMS sensorsFigure (b) Exhaled breath pattern recognition: principle component analysis for the accurate detection of acetone, hydrogen sulfide, and toluene gases
▶ Technology for a Cancer Cure Using Big Data and Simulating Biological Network By Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering)
The complex and heterogeneous nature of cancer, which results in highly variable drug responses, is a major obstacle in curing cancer. Previous methods to predict drug responses mostly focus on the static analysis of genome-wide alternations, resulting in a limitation for the understanding of cancer heterogeneity and its variable responses.
The research team used a method to integrate cancer genomics data with the dynamics of biological networks for drug response prediction and to design of effective drug combination. It provides a computational framework for evaluating drug efficacies and synergistic effects by combining the attractor landscape analysis of a biological network with the genomic alteration profiles of cancer cells.
This technology can reduce the cost of drug development by predicting drug responses and help selecting more effective new drug targets in consideration of the overall cellular response landscape. It can also provide comprehensive insight into the mechanistic origin of variable drug responses. The patent technology can be applicable to designing more effective and cancer-specific combination therapies.
# Development of targeted anticancer drugs, genetic testing
Figure (a) The computational prediction of drug responses using attractor landscape analysis of network dynamics
▶ Highly Stretchable, Wearable Strain SensorBy Professor O Ok Park (Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
Conventional materials for strain sensor are metals or semiconductors, but these materials show a limited range of strain. To improve the stretchability of conventional materials, several projects have been done using novel materials with a high aspect ratio; nevertheless, these projects encountered problems, including complex and expensive processes, poor scalable features, and low controllability of the sensitivity in the manufacturing step.
The research team used a layer-by-layer assembly technique to control the sensitivity of the sensor in a facile and inexpensive method. By using stretchable yarn as a substrate, the graphene strain sensor gained more stretchability.
Through the newly-patented technology, the graphene strain sensor can be fabricated using an all-solution process; therefore, the sensitivity of the sensor can be easily controlled with a repetitive cycle of the coating process. The size of this sensor can be controlled as well, because it depends only on the size of coated substrate.
# Wearable strain sensor, planar strain sensor
Figure (a) Nylon-covered rubber yarn showing linear relationship between the applied strain load and its resistance change
Figure (b) Wool yarn showing an inverse relation of resistance with the applied strain load
▶ Chip & Flash Memory Data Security DeviceBy Professor Yang-Kyu Choi (School of Electrical Engineering)
Using software-based security methods can lead to having problems related to the backtracking of a security function through reverse engineering, the replication of an input value, and the forgery and modification of software. These problems should not be neglected, especially as people are increasingly recognizing the importance of personal information.
To meet the growing demands for new security methods for constructing a more perfect security system, the research team developed a hardware-based security device as well as methods for a higher level of security in the era of IoTs. The principles of the technologies are based on nanotechnology, such as mechanical deformation in a nanowire, electrical degradation in a field-effect transistor (FET), and thermal data erasing stored in the charge trap layer in flash memory. Hence, the security states are extremely safe, compared with software-based security methods and cannot be reverse-engineered by unauthorized users.
This patented technology can be used to improve the security level of logic circuits and flash memory against unauthorized users.
# Financial businesses, the defense industry, private electronics including smartphones, tablets and PCs, electronics for missions in extreme environments
Figure (a) Application for a high level of security in a logic circuit
▶ A Bio-Healthcare Device for Neuroimaging
By Professor Hyeonmin Bae (School of Electrical Engineering)There are no portable brain imaging devices and, as a result, brain diseases are often diagnosed after irreversible symptoms appeared. This can also be linked to an increase in social expenditures as a society ages.
A near-infrared spectroscopy neuroimaging device for functional brain imaging, NIRSIT, utilizes light to detect hemodynamic changes in cerebral blood flow and visualizes brain activation regions in the prefrontal area of the brain in real time.
Unlike any other existing brain imaging devices (i.e. fMRI and conventional fNIRS), NIRSIT has improved its spatial resolution while maintaining complete portability.
Furthermore, NIRSIT is probably the one and only portable and wireless NIRS device, designed to be used for brain research and clinical purposes. A software application allows the raw data extracted from the hemodynamic changes in the brain to be shown in real time on a tablet wirelessly connected to NIRSIT.
Thanks to its easy-to-use features and user-friendly design, both in hardware and in software, NIRSIT will surely set a new paradigm in the brain research and healthcare fields.
# Concussion analysis, wearable stroke monitoring, CPR monitoring, Alzheimer’s disease, neuro rehabilitation, determination of brain death
Figure (a) Image of NIRSIT, Figure (b) Neuroimaging using NIRSIT
▶ Technology for Virtual Creatures with Digitally-Emotional DNA of UsersBy Professor Jong-Hwan Kim (School of Electrical Engineering)
Currently, a large number of IT companies around the world are trying to develop a system that can offer active and emotional services and the interface method is one of the most important issues.
Although most of the existing software agents are equipped with virtual faces and voices, they do not possess a personality similar to humans. Having various personalities, like human beings, can be a charming point for users, which then leads them to have higher satisfaction with the product.
Dr. Kim’s research team developed Darwin C (Digital Agent Reconstruction with Intelligence and Natural Character), a digital agent software that provides an optimized emotional service based on personal big data, such as the user’s conversations, locations, photos, music, etc., collected from smart devices.
With this technology, the digital DNAs of a user (i.e. appearance, voice, and personality DNA) is extracted from personal data stored on various smart devices. Based on the extracted digital DNA, a 3-D software agent can be formed in a smartphone, which characterizes an individual that the user hopes to meet, such as parents, spouse, grandchild, or a celebrity.
The software agents will be expanded from Android devices to home appliances. The team expected that this technology can help customers who want to understand more about a friend or form and maintain interpersonal relations.
# Entertainment, hardware robots for education, healthcare curing depression and loneliness
Figure (a) Overview of the DarwinC technology, Figure (b) Structure of digital DNA
▶ Laser-Integrated Precision Metrological System Technology for Smart Factories By Professor Seung-woo Kim (Department of Mechanical Engineering)
In optical distance metrology, the time-of-flight method of using light pulses permits measuring distances over extensive ranges. However, the measurement precision reaches just a few tens of millimeters at most, mainly because the responsivity of the photodetectors available today is limited to the picosecond range. In addition, one device can measure only one target. For these reasons, a novel technology was devised to overcome the traditional limits of time-of-flight measurement.
This patented technology uses a highly precise, laser-integrated distance measurement system for diagnosing large machines and smart factories. This technology was devised to handle the status (e.g. position, 3-D coordinate, and thermal deformation) of multiple targets simultaneously. It is called the multi-target distance meter (MDM) and was constructed by combining a nonlinear optical crystal with a pair of femtosecond lasers.
This technology is able to measure the distances to multiple targets with a single piece of equipment, and it can easily extend the number of targets by just adding beam-splitting devices. Not only does the technology help by reducing cost and complexity, it also enables real-time quality control in the manufacturing industry.
# Real-time on-axis position inspection of a multiple-lens assembly, long-term thermal displacement monitoring of a large, precise machine, 3-D motion control of a mobile vehicle
Figure (a) Conceptual image of smart factory monitoring using laser-integrated precision metrological system technology
▶ SLAM Technology for Autonomous Robot Navigation in a Dynamic Indoor/Outdoor EnvironmentBy Professor Hyun Myung (Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering)
Dr. Myung’s research team developed SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) technology for autonomous robot navigation in dynamic indoor/outdoor environments. Two methods were applied to this technology: a hierarchical graph structure-based 3-D high resolution map building method using a low-cost 2D laser scanner and a magnetic field-based localization method for feature-poor environments.
Existing technology required expensive sensors for outdoor environment. The localization and mapping technique were also not very accurate, especially in dynamic environments. The team wanted to provide robust SLAM in low and high dynamic object environments using the fusion of low-cost sensors, such as magnetics, 2-D LiDAR, and camera sensors.
Through this technology, the accuracy of localization and mapping could be increased to within 10cm, using low-cost sensors. Also, it facilitates localization and mapping even in feature-poor environments.
# Autonomous robot navigation in warehouses, autonomous navigation of self-driving cars, autonomous navigation of AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) in smart factories
Figure (a) Built outdoor 3-D mappring using a mobile robot with tilted 2-D LiDAR sensor, Figure (b) Mobile robot system for GPS-less mappring
▶ Technology for Optimizing 5G Beamforming ICBy Songcheol Hong (School of Electrical Engineering)
Dr. Hong’s team introduced a new structure for low-power, subminiature, and highly-linear beamforming IC technology. The patent used in this technology reduced the chip size and the direct current (DC) power dissipations drastically, allowing it to make mmWave beamforming antennas.
Beam-forming technology has emerged as an important area in the field of 5G communications and radar systems. It facilitates communication and signal detection with very low RF power.
The patents can be applied to 5G communication beam-forming ICs and antenna modules in mobile terminals, base stations and terminals in the automotive field. Moreover, they can be used in various mmWave radar systems for automobiles, drones, human computer interfaces, and indoor positioning.
# 5G V2X, IoTs, virtual reality
Figure (a) Active phased array system
▶ Beam Division Multiple Access TechnologyBy Professor Dong Ho Cho (School of Electrical Engineering)
Using a 5G network, a communication infrastructure for supporting high-speed, real-time services requires new technologies that enable 4x4 MIMO transmissions within beam-based wireless systems in a new frequency band and improves spectral efficiency more than ten times compared to LTE in domestic and overseas mobile communication carriers and related industries.
P2BDMA, a pattern or polarization beam division multiple access technology, is a core technology for addressing this demand for 5G networks as it enables 4x4 MIMO transmissions in mmWave frequency bands by utilizing the pattern polarization characteristic of radio waves.
The research team upgraded BDMA technology in which the same frequency resource is reused in more than two spaces by using beamforming. This technology increases the degree of freedom (DOF) of wireless communication channels, and thereby improves the achievable data transmission rate by employing multiple pattern/polarization antennas in the conventional BDMA system. The P2BDMA technique has the advantage of eliminating the frequency shortage problem and increasing the transmission speed while using the wide frequency band in a more efficient manner.
The team expects that this technology will alleviate the frequency shortage problem and CAPEX/OPEX of domestic mobile telecommunication companies, support an increase in sales for related equipment makers to make it internationally competitive, and further play a central role in providing high-speed transmission rates to a large number of IoT devices in the future IoT era.
# Autonomous vehicle, communication infrastructure, mobile access system
Figure (a) Concept of P2BDMA technology
2017.08.30 View 15963 -
 KAIST to Host the 2017 AI World Cup in November
KAIST, the birthplace of the Robot World Cup in 1996, now presents a new technology matchup, the AI World Cup this November, which will be held at KAIST. The event is being organized by the Machine Intelligence and Robotics Multi-Sponsored Research and Education Platform (MIR-MSREP) of KAIST. The online, simulated AI soccer game, based on rolling updates, will be a draw for avid online gamers and tech-savvy university students from around the nation.
The tournament is comprised of three events: ▲A 5 on 5 AI soccer match to be played after self-learning using AI technology in an online simulation environment ▲Commentary in which online soccer videos are analyzed and commented on, and ▲Game reporters who will write articles on online soccer event results.
The participants will undergo a month-long online practice period in October and compete in preliminary matches from November 1 through 24. The top teams that scored the highest accumulated points will compete in the finals on December 1. In the finals, each team’s AI technology implementation method will be evaluated to select the final winning team. To ensure a successful event, KAIST will host a briefing session for participants on July 28.
Technological prowess and early exposure to AI accumulated at KAIST led to the launching of this tournament. Professor Jong-Hwan Kim, the chair of the Organizing Committee of the AI World Cup, hosted the first ever Robot World Cup back in 1996. His concept has now evolved into the emerging technology of AI and the members of the Organizing Committee encompass the professors from the various departments of electrical engineering, computing, industrial and systems engineering, aerospace engineering, civil and environmental engineering, and the graduate schools of Green Transportation, Cultural Technology, and Science and Technology Policy.
In particular, ongoing convergence research initiatives incorporating AI into a wide arrays of disciplines such as bio, nano, and IT, played a crucial role for making this AI World Cup happen. Professor Kim said, “The winner of this year’s competition will be awarded a certificate and a small gift. In 2018, we aim to expand the event to an international scale by allowing international teams.”
Any undergraduate or graduate student in Korea can apply to participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017’. KAIST will host a public trial event during the ‘Open KAIST’ event period to be held November 2-3 to help participating students understand the event better. ‘Open KAIST’ allows the general public to personally visit and experience what goes on in engineering departments and laboratories on the KAIST main campus. It is hosted by the College of Engineering every two years and is the largest event hosted by KAIST.
To participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017,’ teams consisting of Korean undergraduates or graduate students can fill out application forms and submit them by September 30 on http://mir.kaist.ac.kr .
2017.07.14 View 11671
KAIST to Host the 2017 AI World Cup in November
KAIST, the birthplace of the Robot World Cup in 1996, now presents a new technology matchup, the AI World Cup this November, which will be held at KAIST. The event is being organized by the Machine Intelligence and Robotics Multi-Sponsored Research and Education Platform (MIR-MSREP) of KAIST. The online, simulated AI soccer game, based on rolling updates, will be a draw for avid online gamers and tech-savvy university students from around the nation.
The tournament is comprised of three events: ▲A 5 on 5 AI soccer match to be played after self-learning using AI technology in an online simulation environment ▲Commentary in which online soccer videos are analyzed and commented on, and ▲Game reporters who will write articles on online soccer event results.
The participants will undergo a month-long online practice period in October and compete in preliminary matches from November 1 through 24. The top teams that scored the highest accumulated points will compete in the finals on December 1. In the finals, each team’s AI technology implementation method will be evaluated to select the final winning team. To ensure a successful event, KAIST will host a briefing session for participants on July 28.
Technological prowess and early exposure to AI accumulated at KAIST led to the launching of this tournament. Professor Jong-Hwan Kim, the chair of the Organizing Committee of the AI World Cup, hosted the first ever Robot World Cup back in 1996. His concept has now evolved into the emerging technology of AI and the members of the Organizing Committee encompass the professors from the various departments of electrical engineering, computing, industrial and systems engineering, aerospace engineering, civil and environmental engineering, and the graduate schools of Green Transportation, Cultural Technology, and Science and Technology Policy.
In particular, ongoing convergence research initiatives incorporating AI into a wide arrays of disciplines such as bio, nano, and IT, played a crucial role for making this AI World Cup happen. Professor Kim said, “The winner of this year’s competition will be awarded a certificate and a small gift. In 2018, we aim to expand the event to an international scale by allowing international teams.”
Any undergraduate or graduate student in Korea can apply to participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017’. KAIST will host a public trial event during the ‘Open KAIST’ event period to be held November 2-3 to help participating students understand the event better. ‘Open KAIST’ allows the general public to personally visit and experience what goes on in engineering departments and laboratories on the KAIST main campus. It is hosted by the College of Engineering every two years and is the largest event hosted by KAIST.
To participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017,’ teams consisting of Korean undergraduates or graduate students can fill out application forms and submit them by September 30 on http://mir.kaist.ac.kr .
2017.07.14 View 11671 -
 Reform of Universities Key in the Wake of the 4th Industrial Revolution
(President Shin makes a keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4.)
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed that innovations in education, research, and technology commercialization of universities are critical for responding to the transformations that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about.
In his keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4, he cited connectivity, superintelligence, and convergence in science and technology as three components the Fourth Industrial Revolution will pierce, saying the speed and breadth of the transformation will be beyond our imagination. He also presented megatrends in science and technology in the years to come and how KAIST is addressing the challenges and opportunities.
“It is imperative to foster creative young talents fluent in convergence, collaboration, and communication skills in the new era. To this end, we need to focus on whole brain education by enhancing basic education in science and engineering plus humanities and social studies,” he stressed. He also presented a Non-Departmental Education Track, which KAIST plans to implement from next semester. The track, designed to prepare students for the new industrial era, will focus on whole brain education including entrepreneurship and leadership education during the undergraduate period.
He also emphasized an effective new teaching methodology. “We need to develop various new teaching methods. The paradigm should shift from lecturer-centered to student-centered. KAIST is revising our curriculum to facilitate team-based, project-based learning and flipped learning,” he explained.
President Shin also pointed out that the educational goals for the next generation should be to sustain the value of people’s own thoughtfulness, wisdom, emotion, and caring against the advent of a new tribe of AI, dubbed Robo Sapiens. “Those traits add undeniable educational value that we should continue to pursue even in the era of Robo Sapiens,” he added.
As for research innovation, he emphasized inter- and multi-disciplinary collaborative research. “Especially, in addressing pressing global issues and big science, international collaboration will be very effective and crucial,” he said.
At the summit, convergence research projects currently underway at KAIST using emerging technologies such as the smart mobile healthcare project, Dr, M; the humanoid robot, HUBO; and AI drone swarms drew lots of attention from the participants, even receiving proposals to join the projects as collaborators.
In the new era, according to Shin, technology commercialization at universities will emerge as a hub of R&DB. Citing that KAIST has long been a draw for startups, he noted that KAIST has also set a high value on entrepreneurship education including social entrepreneurship and startups.
He continued, “The Korean government is making every effort to harness the challenges and opportunities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution by creating a new economic growth engine. For the success of the government initiative, universities should also respond to make innovations commensurate with the changing needs and challenges. KAIST will take the lead in this new initiative for making a new future.”
2017.07.06 View 7596
Reform of Universities Key in the Wake of the 4th Industrial Revolution
(President Shin makes a keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4.)
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed that innovations in education, research, and technology commercialization of universities are critical for responding to the transformations that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about.
In his keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4, he cited connectivity, superintelligence, and convergence in science and technology as three components the Fourth Industrial Revolution will pierce, saying the speed and breadth of the transformation will be beyond our imagination. He also presented megatrends in science and technology in the years to come and how KAIST is addressing the challenges and opportunities.
“It is imperative to foster creative young talents fluent in convergence, collaboration, and communication skills in the new era. To this end, we need to focus on whole brain education by enhancing basic education in science and engineering plus humanities and social studies,” he stressed. He also presented a Non-Departmental Education Track, which KAIST plans to implement from next semester. The track, designed to prepare students for the new industrial era, will focus on whole brain education including entrepreneurship and leadership education during the undergraduate period.
He also emphasized an effective new teaching methodology. “We need to develop various new teaching methods. The paradigm should shift from lecturer-centered to student-centered. KAIST is revising our curriculum to facilitate team-based, project-based learning and flipped learning,” he explained.
President Shin also pointed out that the educational goals for the next generation should be to sustain the value of people’s own thoughtfulness, wisdom, emotion, and caring against the advent of a new tribe of AI, dubbed Robo Sapiens. “Those traits add undeniable educational value that we should continue to pursue even in the era of Robo Sapiens,” he added.
As for research innovation, he emphasized inter- and multi-disciplinary collaborative research. “Especially, in addressing pressing global issues and big science, international collaboration will be very effective and crucial,” he said.
At the summit, convergence research projects currently underway at KAIST using emerging technologies such as the smart mobile healthcare project, Dr, M; the humanoid robot, HUBO; and AI drone swarms drew lots of attention from the participants, even receiving proposals to join the projects as collaborators.
In the new era, according to Shin, technology commercialization at universities will emerge as a hub of R&DB. Citing that KAIST has long been a draw for startups, he noted that KAIST has also set a high value on entrepreneurship education including social entrepreneurship and startups.
He continued, “The Korean government is making every effort to harness the challenges and opportunities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution by creating a new economic growth engine. For the success of the government initiative, universities should also respond to make innovations commensurate with the changing needs and challenges. KAIST will take the lead in this new initiative for making a new future.”
2017.07.06 View 7596 -
 Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2017
The World Economic Forum’s Expert Network and Global Future Councils in collaboration with Scientific American and its Board of Advisors announced the top 10 emerging technologies of 2017 on June 26 in Dalian, China where the 2017 Summer Davos Forum is being held. Each technology was chosen for its potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet.
The KAIST delegation, headed by President Sung-Chul Shin, is participating in the forum’s diverse activities including IdeasLab and GULF (Global University Leaders Forum). KAIST is the only Korean representative participating in the IdeasLab. KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, director of KAIST Institute, has served as a committee member of the Global Agenda Council on Emerging Technologies since 2012 and Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He also chairs the Global Future Council on Biotechnologies.
Professor Lee said, “Very diverse technological breakthroughs were proposed for the final list of candidates. We made the final selections through very in-depth discussion with experts in each field.
We focused on the technologies which have a level of maturity that will enable them to be adopted widely within three to five years."
The top 10 emerging technologies are
(courtesy from https://
www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/06/these-are-the-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2017):
2017 10대 기술.
1. Liquid biopsies
Liquid biopsies mark a step forward in the fight against cancer. First, they are an alternative where traditional tissue-based biopsies are not possible. Second, they provide a full spectrum of information compared to tissue samples, which only reflect the information available in the sample. Lastly, by homing in on circulating-tumor DNA (ctDNA), genetic material that routinely finds its way from cancer cells into the bloodstream, disease progression or resistance to treatment can be spotted much faster than otherwise relying on symptoms or imaging.
2. Harvesting clean water from air
The ability to extract clean water from air is not new, however existing techniques require high moisture levels and a lot of electricity. This is changing. A team from MIT and University of California, Berkeley has successfully tested a process using porous crystals that convert the water using no energy at all.
3. Deep learning for visual tasks
Computers are beginning to recognize images better than humans. Thanks to deep learning, an emerging field of artificial intelligence, computer-vision technologies are increasingly being used in applications as diverse as driving autonomous vehicles, medical diagnostics, damage assessment for insurance claims, and monitoring water levels and crop yield.
4. Liquid fuels from sunshine
Can we mimic the humble leaf to create artificial photosynthesis to generate and store energy? The prospects are looking increasingly positive. The answer lies in using sunlight-activated catalysts to split water molecules into water and hydrogen, and then using the same hydrogen to convert CO2 into hydrocarbons.
5. The Human Cell Atlas
An international collaboration aimed at deciphering the human body, called the Human Cell Atlas, was launched in October 2016. The project aims to identify every cell type in every tissue; learn exactly which genes, proteins, and other molecules are active in each type, and the processes which control that activity.
6. Precision farming
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is providing farmers with a new set of tools to boost crop yield and quality while reducing water and chemical use. Sensors, robots, GPS, mapping tools, and data-analytics software are all being used to customize the care that plants need.
7. Affordable catalysts for green vehicles
Progress is being made on a promising zero-emission technology, the hydrogen-fed fuel cell. Progress to date has been stymied by the high price of catalysts which contain platinum. However, much progress has been made in reducing reliance on this rare and expensive metal, and the latest developments involve catalysts that include no platinum, or in some cases no metal at all.
8. Genomic vaccines
Vaccines based on genes are superior to more conventional ones in a number of ways. They are faster to manufacture, which is crucial during violent outbreaks. Compared to manufacturing proteins in cell cultures or eggs, producing genetic material should also be simpler and less expensive.
9. Sustainable design of communities
Applying green construction to multiple buildings at once has the potential to revolutionize the amount of energy and water we consume. Sending locally-generated solar power to a smart microgrid could reduce electricity consumption by half and reduce carbon emissions to zero if a project currently under development at the University of California at Berkeley goes according to plan.
10. Quantum computing
Quantum computers’ almost limitless potential has only ever been matched by the difficulty and cost of their construction. This explains why today the small ones that have been built have not yet managed to exceed the power of supercomputers. But progress is being made and in 2016 the technology firm IBM provided public access to the first quantum computer in the cloud.
2017.06.28 View 13042
Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2017
The World Economic Forum’s Expert Network and Global Future Councils in collaboration with Scientific American and its Board of Advisors announced the top 10 emerging technologies of 2017 on June 26 in Dalian, China where the 2017 Summer Davos Forum is being held. Each technology was chosen for its potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet.
The KAIST delegation, headed by President Sung-Chul Shin, is participating in the forum’s diverse activities including IdeasLab and GULF (Global University Leaders Forum). KAIST is the only Korean representative participating in the IdeasLab. KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, director of KAIST Institute, has served as a committee member of the Global Agenda Council on Emerging Technologies since 2012 and Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He also chairs the Global Future Council on Biotechnologies.
Professor Lee said, “Very diverse technological breakthroughs were proposed for the final list of candidates. We made the final selections through very in-depth discussion with experts in each field.
We focused on the technologies which have a level of maturity that will enable them to be adopted widely within three to five years."
The top 10 emerging technologies are
(courtesy from https://
www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/06/these-are-the-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2017):
2017 10대 기술.
1. Liquid biopsies
Liquid biopsies mark a step forward in the fight against cancer. First, they are an alternative where traditional tissue-based biopsies are not possible. Second, they provide a full spectrum of information compared to tissue samples, which only reflect the information available in the sample. Lastly, by homing in on circulating-tumor DNA (ctDNA), genetic material that routinely finds its way from cancer cells into the bloodstream, disease progression or resistance to treatment can be spotted much faster than otherwise relying on symptoms or imaging.
2. Harvesting clean water from air
The ability to extract clean water from air is not new, however existing techniques require high moisture levels and a lot of electricity. This is changing. A team from MIT and University of California, Berkeley has successfully tested a process using porous crystals that convert the water using no energy at all.
3. Deep learning for visual tasks
Computers are beginning to recognize images better than humans. Thanks to deep learning, an emerging field of artificial intelligence, computer-vision technologies are increasingly being used in applications as diverse as driving autonomous vehicles, medical diagnostics, damage assessment for insurance claims, and monitoring water levels and crop yield.
4. Liquid fuels from sunshine
Can we mimic the humble leaf to create artificial photosynthesis to generate and store energy? The prospects are looking increasingly positive. The answer lies in using sunlight-activated catalysts to split water molecules into water and hydrogen, and then using the same hydrogen to convert CO2 into hydrocarbons.
5. The Human Cell Atlas
An international collaboration aimed at deciphering the human body, called the Human Cell Atlas, was launched in October 2016. The project aims to identify every cell type in every tissue; learn exactly which genes, proteins, and other molecules are active in each type, and the processes which control that activity.
6. Precision farming
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is providing farmers with a new set of tools to boost crop yield and quality while reducing water and chemical use. Sensors, robots, GPS, mapping tools, and data-analytics software are all being used to customize the care that plants need.
7. Affordable catalysts for green vehicles
Progress is being made on a promising zero-emission technology, the hydrogen-fed fuel cell. Progress to date has been stymied by the high price of catalysts which contain platinum. However, much progress has been made in reducing reliance on this rare and expensive metal, and the latest developments involve catalysts that include no platinum, or in some cases no metal at all.
8. Genomic vaccines
Vaccines based on genes are superior to more conventional ones in a number of ways. They are faster to manufacture, which is crucial during violent outbreaks. Compared to manufacturing proteins in cell cultures or eggs, producing genetic material should also be simpler and less expensive.
9. Sustainable design of communities
Applying green construction to multiple buildings at once has the potential to revolutionize the amount of energy and water we consume. Sending locally-generated solar power to a smart microgrid could reduce electricity consumption by half and reduce carbon emissions to zero if a project currently under development at the University of California at Berkeley goes according to plan.
10. Quantum computing
Quantum computers’ almost limitless potential has only ever been matched by the difficulty and cost of their construction. This explains why today the small ones that have been built have not yet managed to exceed the power of supercomputers. But progress is being made and in 2016 the technology firm IBM provided public access to the first quantum computer in the cloud.
2017.06.28 View 13042 -
 Face Recognition System 'K-Eye' Presented by KAIST
Artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the key emerging technologies. Global IT companies are competitively launching the newest technologies and competition is heating up more than ever. However, most AI technologies focus on software and their operating speeds are low, making them a poor fit for mobile devices. Therefore, many big companies are investing to develop semiconductor chips for running AI programs with low power requirements but at high speeds.
A research team led by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering has developed a semiconductor chip, CNNP (CNN Processor), that runs AI algorithms with ultra-low power, and K-Eye, a face recognition system using CNNP. The system was made in collaboration with a start-up company, UX Factory Co.
The K-Eye series consists of two types: a wearable type and a dongle type. The wearable type device can be used with a smartphone via Bluetooth, and it can operate for more than 24 hours with its internal battery. Users hanging K-Eye around their necks can conveniently check information about people by using their smartphone or smart watch, which connects K-Eye and allows users to access a database via their smart devices. A smartphone with K-EyeQ, the dongle type device, can recognize and share information about users at any time.
When recognizing that an authorized user is looking at its screen, the smartphone automatically turns on without a passcode, fingerprint, or iris authentication. Since it can distinguish whether an input face is coming from a saved photograph versus a real person, the smartphone cannot be tricked by the user’s photograph.
The K-Eye series carries other distinct features. It can detect a face at first and then recognize it, and it is possible to maintain “Always-on” status with low power consumption of less than 1mW. To accomplish this, the research team proposed two key technologies: an image sensor with “Always-on” face detection and the CNNP face recognition chip.
The first key technology, the “Always-on” image sensor, can determine if there is a face in its camera range. Then, it can capture frames and set the device to operate only when a face exists, reducing the standby power significantly. The face detection sensor combines analog and digital processing to reduce power consumption. With this approach, the analog processor, combined with the CMOS Image Sensor array, distinguishes the background area from the area likely to include a face, and the digital processor then detects the face only in the selected area. Hence, it becomes effective in terms of frame capture, face detection processing, and memory usage.
The second key technology, CNNP, achieved incredibly low power consumption by optimizing a convolutional neural network (CNN) in the areas of circuitry, architecture, and algorithms. First, the on-chip memory integrated in CNNP is specially designed to enable data to be read in a vertical direction as well as in a horizontal direction. Second, it has immense computational power with 1024 multipliers and accumulators operating in parallel and is capable of directly transferring the temporal results to each other without accessing to the external memory or on-chip communication network. Third, convolution calculations with a two-dimensional filter in the CNN algorithm are approximated into two sequential calculations of one-dimensional filters to achieve higher speeds and lower power consumption.
With these new technologies, CNNP achieved 97% high accuracy but consumed only 1/5000 power of the GPU. Face recognition can be performed with only 0.62mW of power consumption, and the chip can show higher performance than the GPU by using more power.
These chips were developed by Kyeongryeol Bong, a Ph. D. student under Professor Yoo and presented at the International Solid-State Circuit Conference (ISSCC) held in San Francisco in February. CNNP, which has the lowest reported power consumption in the world, has achieved a great deal of attention and has led to the development of the present K-Eye series for face recognition.
Professor Yoo said “AI - processors will lead the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. With the development of this AI chip, we expect Korea to take the lead in global AI technology.”
The research team and UX Factory Co. are preparing to commercialize the K-Eye series by the end of this year. According to a market researcher IDC, the market scale of the AI industry will grow from $127 billion last year to $165 billion in this year.
(Photo caption: Schematic diagram of K-Eye system)
2017.06.14 View 16963
Face Recognition System 'K-Eye' Presented by KAIST
Artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the key emerging technologies. Global IT companies are competitively launching the newest technologies and competition is heating up more than ever. However, most AI technologies focus on software and their operating speeds are low, making them a poor fit for mobile devices. Therefore, many big companies are investing to develop semiconductor chips for running AI programs with low power requirements but at high speeds.
A research team led by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering has developed a semiconductor chip, CNNP (CNN Processor), that runs AI algorithms with ultra-low power, and K-Eye, a face recognition system using CNNP. The system was made in collaboration with a start-up company, UX Factory Co.
The K-Eye series consists of two types: a wearable type and a dongle type. The wearable type device can be used with a smartphone via Bluetooth, and it can operate for more than 24 hours with its internal battery. Users hanging K-Eye around their necks can conveniently check information about people by using their smartphone or smart watch, which connects K-Eye and allows users to access a database via their smart devices. A smartphone with K-EyeQ, the dongle type device, can recognize and share information about users at any time.
When recognizing that an authorized user is looking at its screen, the smartphone automatically turns on without a passcode, fingerprint, or iris authentication. Since it can distinguish whether an input face is coming from a saved photograph versus a real person, the smartphone cannot be tricked by the user’s photograph.
The K-Eye series carries other distinct features. It can detect a face at first and then recognize it, and it is possible to maintain “Always-on” status with low power consumption of less than 1mW. To accomplish this, the research team proposed two key technologies: an image sensor with “Always-on” face detection and the CNNP face recognition chip.
The first key technology, the “Always-on” image sensor, can determine if there is a face in its camera range. Then, it can capture frames and set the device to operate only when a face exists, reducing the standby power significantly. The face detection sensor combines analog and digital processing to reduce power consumption. With this approach, the analog processor, combined with the CMOS Image Sensor array, distinguishes the background area from the area likely to include a face, and the digital processor then detects the face only in the selected area. Hence, it becomes effective in terms of frame capture, face detection processing, and memory usage.
The second key technology, CNNP, achieved incredibly low power consumption by optimizing a convolutional neural network (CNN) in the areas of circuitry, architecture, and algorithms. First, the on-chip memory integrated in CNNP is specially designed to enable data to be read in a vertical direction as well as in a horizontal direction. Second, it has immense computational power with 1024 multipliers and accumulators operating in parallel and is capable of directly transferring the temporal results to each other without accessing to the external memory or on-chip communication network. Third, convolution calculations with a two-dimensional filter in the CNN algorithm are approximated into two sequential calculations of one-dimensional filters to achieve higher speeds and lower power consumption.
With these new technologies, CNNP achieved 97% high accuracy but consumed only 1/5000 power of the GPU. Face recognition can be performed with only 0.62mW of power consumption, and the chip can show higher performance than the GPU by using more power.
These chips were developed by Kyeongryeol Bong, a Ph. D. student under Professor Yoo and presented at the International Solid-State Circuit Conference (ISSCC) held in San Francisco in February. CNNP, which has the lowest reported power consumption in the world, has achieved a great deal of attention and has led to the development of the present K-Eye series for face recognition.
Professor Yoo said “AI - processors will lead the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. With the development of this AI chip, we expect Korea to take the lead in global AI technology.”
The research team and UX Factory Co. are preparing to commercialize the K-Eye series by the end of this year. According to a market researcher IDC, the market scale of the AI industry will grow from $127 billion last year to $165 billion in this year.
(Photo caption: Schematic diagram of K-Eye system)
2017.06.14 View 16963 -
 Bio-based p-Xylene Oxidation into Terephthalic Acid by Engineered E.coli
KAIST researchers have established an efficient biocatalytic system to produce terephthalic acid (TPA) from p-xylene (pX). It will allow this industrially important bulk chemical to be made available in a more environmentally-friendly manner.
The research team developed metabolically engineered Escherichia coli (E.coli) to biologically transform pX into TPA, a chemical necessary in the manufacturing of polyethylene terephthalate (PET). This biocatalysis system represents a greener and more efficient alternative to the traditional chemical methods for TPA production. This research, headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, was published in Nature Communications on May 31.
The research team utilized a metabolic engineering and synthetic biology approach to develop a recombinant microorganism that can oxidize pX into TPA using microbial fermentation. TPA is a globally important chemical commodity for manufacturing PET. It can be applied to manufacture plastic bottles, clothing fibers, films, and many other products. Currently, TPA is produced from pX oxidation through an industrially well-known chemical process (with a typical TPA yield of over 95 mol%), which shows, however, such drawbacks as intensive energy requirements at high temperatures and pressure, usage of heavy metal catalysts, and the unavoidable byproduct formation of 4-carboxybenzaldehyde.
The research team designed and constructed a synthetic metabolic pathway by incorporating the upper xylene degradation pathway of Pseudomonas putida F1 and the lower p-toluene sulfonate pathway of Comamonas testosteroni T-2, which successfully produced TPA from pX in small-scale cultures, with the formation of p-toluate (pTA) as the major byproduct. The team further optimized the pathway gene expression levels by using a synthetic biology toolkit, which gave the final engineered E. coli strain showing increased TPA production and the complete elimination of the byproduct.
Using this best-performing strain, the team designed an elegant two-phase (aqueous/organic) fermentation system for TPA production on a larger scale, where pX was supplied in the organic phase. Through a number of optimization steps, the team ultimately achieved production of 13.3 g TPA from 8.8 g pX, which represented an extraordinary yield of 97 mol%.
The team has developed a microbial biotechnology application which is reportedly the first successful example of the bio-based production of TPA from pX by the microbial fermentation of engineered E. coli. This bio-based TPA technology presents several advantages such as ambient reaction temperature and pressure, no use of heavy metals or other toxic chemicals, the removable of byproduct formation, and it is 100% environmentally compatible.
Professor Lee said, “We presented promising biotechnology for producing large amounts of the commodity chemical TPA, which is used for PET manufacturing, through metabolically engineered gut bacterium. Our research is meaningful in that it demonstrates the feasibility of the biotechnological production of bulk chemicals, and if reproducible when up-scaled, it will represent a breakthrough in hydrocarbon bioconversions.”
Ph.D. candidate Zi Wei Luo is the first author of this research (DOI:10.1038/ncomms15689).The research was supported by the Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center through the Global Frontier Project (2011-0031963) of the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure: Biotransformation of pX into TPA by engineered E. coli.
This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of how metabolically engineered E. coli produced TPA from pX. The engineered E. coli was developed through reconstituting a synthetic metabolic pathway for pX conversion to TPA and optimized for increased TPA yield and byproduct elimination. Two-phase partitioning fermentation system was developed for demonstrating the feasibility of large-scale production of TPA from pX using the engineered E. coli strains, where pX was supplied in the organic phase and TPA was produced in the aqueous phase.
2017.06.05 View 11855
Bio-based p-Xylene Oxidation into Terephthalic Acid by Engineered E.coli
KAIST researchers have established an efficient biocatalytic system to produce terephthalic acid (TPA) from p-xylene (pX). It will allow this industrially important bulk chemical to be made available in a more environmentally-friendly manner.
The research team developed metabolically engineered Escherichia coli (E.coli) to biologically transform pX into TPA, a chemical necessary in the manufacturing of polyethylene terephthalate (PET). This biocatalysis system represents a greener and more efficient alternative to the traditional chemical methods for TPA production. This research, headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, was published in Nature Communications on May 31.
The research team utilized a metabolic engineering and synthetic biology approach to develop a recombinant microorganism that can oxidize pX into TPA using microbial fermentation. TPA is a globally important chemical commodity for manufacturing PET. It can be applied to manufacture plastic bottles, clothing fibers, films, and many other products. Currently, TPA is produced from pX oxidation through an industrially well-known chemical process (with a typical TPA yield of over 95 mol%), which shows, however, such drawbacks as intensive energy requirements at high temperatures and pressure, usage of heavy metal catalysts, and the unavoidable byproduct formation of 4-carboxybenzaldehyde.
The research team designed and constructed a synthetic metabolic pathway by incorporating the upper xylene degradation pathway of Pseudomonas putida F1 and the lower p-toluene sulfonate pathway of Comamonas testosteroni T-2, which successfully produced TPA from pX in small-scale cultures, with the formation of p-toluate (pTA) as the major byproduct. The team further optimized the pathway gene expression levels by using a synthetic biology toolkit, which gave the final engineered E. coli strain showing increased TPA production and the complete elimination of the byproduct.
Using this best-performing strain, the team designed an elegant two-phase (aqueous/organic) fermentation system for TPA production on a larger scale, where pX was supplied in the organic phase. Through a number of optimization steps, the team ultimately achieved production of 13.3 g TPA from 8.8 g pX, which represented an extraordinary yield of 97 mol%.
The team has developed a microbial biotechnology application which is reportedly the first successful example of the bio-based production of TPA from pX by the microbial fermentation of engineered E. coli. This bio-based TPA technology presents several advantages such as ambient reaction temperature and pressure, no use of heavy metals or other toxic chemicals, the removable of byproduct formation, and it is 100% environmentally compatible.
Professor Lee said, “We presented promising biotechnology for producing large amounts of the commodity chemical TPA, which is used for PET manufacturing, through metabolically engineered gut bacterium. Our research is meaningful in that it demonstrates the feasibility of the biotechnological production of bulk chemicals, and if reproducible when up-scaled, it will represent a breakthrough in hydrocarbon bioconversions.”
Ph.D. candidate Zi Wei Luo is the first author of this research (DOI:10.1038/ncomms15689).The research was supported by the Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center through the Global Frontier Project (2011-0031963) of the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure: Biotransformation of pX into TPA by engineered E. coli.
This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of how metabolically engineered E. coli produced TPA from pX. The engineered E. coli was developed through reconstituting a synthetic metabolic pathway for pX conversion to TPA and optimized for increased TPA yield and byproduct elimination. Two-phase partitioning fermentation system was developed for demonstrating the feasibility of large-scale production of TPA from pX using the engineered E. coli strains, where pX was supplied in the organic phase and TPA was produced in the aqueous phase.
2017.06.05 View 11855 -
 Policy Debate Series for Industry 4.0
(Photo caption: President Shin takes the podium as the first speaker of a year-long monthly policy dabate series on Industry 4.0 on May 11.)
KAIST will kick off a monthly policy debate series on Industry 4.0 every Thursday from May 11 at the Startup KAIST building. The year-long series, featuring professors from key technology fields associated with Industry 4.0, is designed to help policy makers from government, industry, and research institutes respond better to the ramifications that Industry 4.0 brings about in each sector.
The series will help them establish the vision and strategy that will work for the new industrial environment to take the lead in the new industrial era.
Twelve professors, including President Sung-Chul Shin, from departments that are researching emerging technologies will speak on the megatrend of new technology, while facilitating debates and Q& A sessions with participants.
The participants will include officials from the government complexes in Sejong and Daejeon cities, government-funded research institutes in Daejeon, and businessmen, among others. For registration, please go to https://startup.kaist.ac.kr/register.
Schedule
Speaker
Theme
May 11
President Sung-Chul Shin
Challenges and Innovations of KAIST in the Era of Industry 4.0
June 8
Professor Jonghwan Kim
Machine Intelligence and Deep Learning
July 6
Professor Jun Ho Oh
Robot Technology and the Future
Aug. 3
Professor Hyunchul Shim
Unmanned Vehicle Technology and Industry 4.0
Sept. 7
Professor Hawoong Jeong
Complex Systems and Data Science
Oct. 12
Professor Yongdae Kim
Technology, Policy, and the Fostering of Talents: Industry 4.0 and Information Protection
Nov. 9
Professor Sang Yup Lee
The Role of Biotechnology in Industry 4.0
Dec. 7
Professor Meeyoung Cha
AI-Based Research for Fake News Detection
2018 Jan. 4
Professor Joungho Kim
Innovation for the Korean Semiconductor Industry: Kim’s Law
Feb. 8
Professor Jaekyun Moon
Education for Industry 4.0
March 8
Professor Sang Kil Cha
Artificial Intelligence Cyber Warfare: Its Present and Future
April 5
Professor Jaeseung Jeong
The Future of Brain Engineering and Artificial Intelligence
2017.05.08 View 10459
Policy Debate Series for Industry 4.0
(Photo caption: President Shin takes the podium as the first speaker of a year-long monthly policy dabate series on Industry 4.0 on May 11.)
KAIST will kick off a monthly policy debate series on Industry 4.0 every Thursday from May 11 at the Startup KAIST building. The year-long series, featuring professors from key technology fields associated with Industry 4.0, is designed to help policy makers from government, industry, and research institutes respond better to the ramifications that Industry 4.0 brings about in each sector.
The series will help them establish the vision and strategy that will work for the new industrial environment to take the lead in the new industrial era.
Twelve professors, including President Sung-Chul Shin, from departments that are researching emerging technologies will speak on the megatrend of new technology, while facilitating debates and Q& A sessions with participants.
The participants will include officials from the government complexes in Sejong and Daejeon cities, government-funded research institutes in Daejeon, and businessmen, among others. For registration, please go to https://startup.kaist.ac.kr/register.
Schedule
Speaker
Theme
May 11
President Sung-Chul Shin
Challenges and Innovations of KAIST in the Era of Industry 4.0
June 8
Professor Jonghwan Kim
Machine Intelligence and Deep Learning
July 6
Professor Jun Ho Oh
Robot Technology and the Future
Aug. 3
Professor Hyunchul Shim
Unmanned Vehicle Technology and Industry 4.0
Sept. 7
Professor Hawoong Jeong
Complex Systems and Data Science
Oct. 12
Professor Yongdae Kim
Technology, Policy, and the Fostering of Talents: Industry 4.0 and Information Protection
Nov. 9
Professor Sang Yup Lee
The Role of Biotechnology in Industry 4.0
Dec. 7
Professor Meeyoung Cha
AI-Based Research for Fake News Detection
2018 Jan. 4
Professor Joungho Kim
Innovation for the Korean Semiconductor Industry: Kim’s Law
Feb. 8
Professor Jaekyun Moon
Education for Industry 4.0
March 8
Professor Sang Kil Cha
Artificial Intelligence Cyber Warfare: Its Present and Future
April 5
Professor Jaeseung Jeong
The Future of Brain Engineering and Artificial Intelligence
2017.05.08 View 10459