THE
-
 President Shin Reaffirms Innovation Initiatives in New Year Speech
(President Shin and representatives of faculty, students, staff celebrate the New Year in a reception held on January 2 at the auditorium.)
The KAIST community gathered to celebrate a fresh start for the year 2018. At the ceremony, held in the auditorium on January 2, members of KAIST community reaffirmed their commitment to be the trailblazers of Korea and beyond through unwavering innovations.
President Sung-Chul Shin presented his new vision and plan in his New Year speech, which focused on innovation for enhancing institutional competitiveness and global visibility. He said that as you are the future of KAIST, KAIST is the future of Korea. KAIST’s vision for a better future will have a significant impact on national progress and beyond. He stressed that innovation in the five pillars of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future strategy will further advance the excellence of KAIST.
At the ceremony, President Shin also presented the award for ‘the KAISTian of the Year’ to Professor YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics. The annual award recognizes a distinguished professor whose academic accomplishments made the most significant impact.
In his New Year speech, President Shin said that the year 2018 will provide an opportunity to take a leap forward for becoming a ‘Global Value Creative, World-Leading University. The Vision 2031 Committee endorsed the five innovation initiatives to fulfill KAIST’s long-term vision and will open its recommendations to the public on March 20.
Educational innovation tops the initiatives. President Shin explained that the future of Korea is in the hands of talented individuals in science and technology, emphasizing the need to nurture creative, transdisciplinary talents with the capacity to enhance the social value of science and technology.
To this end, KAIST will establish a new undergraduate non-departmental program for transdisciplinary education. This plan will eventually provide students with more options in choosing their major, as well as help students build a strong foundation in basic science and engineering and encourage multidisciplinary approaches.
For creating an innovative institutional research infrastructure, KAIST plans to build a Network of Excellence for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (NExFire) for convergence research. The plan of ‘Cross-Generational Collaborative Labs,’ will bring out a new collaboration platform by pairing up senior and junior faculty. President Shin said it will be a stepping stone to extend the spectrum of knowledge without any cessation.
For technology commercialization, KAIST will maximize its intellectual property and economic value by stimulating technology-invested companies and startups. Close cooperation with venture capitalists at home and abroad will further accelerate the commercialization drive at KAIST.
Saying that the globalization is no long an option but a necessity, he stressed KAIST will strengthen its efforts to established a bilingual campus. “KAIST will make every effort to create a more welcoming and comfortable atmosphere for the international community and their families. We will expand benefits to our international community, such as access to the KAIST Child Care Center and collaboration with the Taejon Christian International School (TCIS),” he said. President Shin added he will further expand global networks and partnerships this year, participating in a diverse range of international events at home and abroad for increasing global visibility.
He also said that well-designed future strategies will complete innovation initiatives. The Future Strategy Research Center will serve as a think tank for identifying future agendas, establishing strategies and advocating for them.
In addition to the five innovation initiatives, President Shin emphasized a new organizational culture that embraces inclusiveness and mutual respect among all of the members of KAIST.
“So far, the ideal qualifications expected of KAISTians have included creativity and a challenging spirit. From now on, we will nurture talents with a focus on the 3Cs: Creativity, Challenge, and Caring. I would like to make a campus in which all members care for each other to help attain mutual growth with warmth and respect," he said.
For the full text, Click
2018.01.02 View 10723
President Shin Reaffirms Innovation Initiatives in New Year Speech
(President Shin and representatives of faculty, students, staff celebrate the New Year in a reception held on January 2 at the auditorium.)
The KAIST community gathered to celebrate a fresh start for the year 2018. At the ceremony, held in the auditorium on January 2, members of KAIST community reaffirmed their commitment to be the trailblazers of Korea and beyond through unwavering innovations.
President Sung-Chul Shin presented his new vision and plan in his New Year speech, which focused on innovation for enhancing institutional competitiveness and global visibility. He said that as you are the future of KAIST, KAIST is the future of Korea. KAIST’s vision for a better future will have a significant impact on national progress and beyond. He stressed that innovation in the five pillars of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future strategy will further advance the excellence of KAIST.
At the ceremony, President Shin also presented the award for ‘the KAISTian of the Year’ to Professor YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics. The annual award recognizes a distinguished professor whose academic accomplishments made the most significant impact.
In his New Year speech, President Shin said that the year 2018 will provide an opportunity to take a leap forward for becoming a ‘Global Value Creative, World-Leading University. The Vision 2031 Committee endorsed the five innovation initiatives to fulfill KAIST’s long-term vision and will open its recommendations to the public on March 20.
Educational innovation tops the initiatives. President Shin explained that the future of Korea is in the hands of talented individuals in science and technology, emphasizing the need to nurture creative, transdisciplinary talents with the capacity to enhance the social value of science and technology.
To this end, KAIST will establish a new undergraduate non-departmental program for transdisciplinary education. This plan will eventually provide students with more options in choosing their major, as well as help students build a strong foundation in basic science and engineering and encourage multidisciplinary approaches.
For creating an innovative institutional research infrastructure, KAIST plans to build a Network of Excellence for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (NExFire) for convergence research. The plan of ‘Cross-Generational Collaborative Labs,’ will bring out a new collaboration platform by pairing up senior and junior faculty. President Shin said it will be a stepping stone to extend the spectrum of knowledge without any cessation.
For technology commercialization, KAIST will maximize its intellectual property and economic value by stimulating technology-invested companies and startups. Close cooperation with venture capitalists at home and abroad will further accelerate the commercialization drive at KAIST.
Saying that the globalization is no long an option but a necessity, he stressed KAIST will strengthen its efforts to established a bilingual campus. “KAIST will make every effort to create a more welcoming and comfortable atmosphere for the international community and their families. We will expand benefits to our international community, such as access to the KAIST Child Care Center and collaboration with the Taejon Christian International School (TCIS),” he said. President Shin added he will further expand global networks and partnerships this year, participating in a diverse range of international events at home and abroad for increasing global visibility.
He also said that well-designed future strategies will complete innovation initiatives. The Future Strategy Research Center will serve as a think tank for identifying future agendas, establishing strategies and advocating for them.
In addition to the five innovation initiatives, President Shin emphasized a new organizational culture that embraces inclusiveness and mutual respect among all of the members of KAIST.
“So far, the ideal qualifications expected of KAISTians have included creativity and a challenging spirit. From now on, we will nurture talents with a focus on the 3Cs: Creativity, Challenge, and Caring. I would like to make a campus in which all members care for each other to help attain mutual growth with warmth and respect," he said.
For the full text, Click
2018.01.02 View 10723 -
 Expanding Gas Storage Capacity of Nanoporous Materials
A KAIST research team led by Professor Jihan Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has successfully proposed a rational defect engineering methodology that can greatly enhance the gas storage capacity of nanoporous materials. The team conducted a high-throughput computational screening of a large experimental metal-organic framework database to identify 13 candidate materials that could experience significant methane uptake enhancement with only a small proportion of linker vacancy defects.
This research was published online on November 16 in Nature Communications, with M.S. candidate Sanggyu Chong from KAIST as the first author and post-doctorate researcher Günther Thiele from the Department of Chemistry at UC Berkeley as a contributing author.
Metal-organic frameworks, hereinafter MOF, are crystalline nanoporous materials that are comprised of metal clusters and organic linkers continuously bound together by coordination bonds. Due to their ultrahigh surface areas and pore volumes, they have been widely studied for various energy and environment applications.
Similar to other crystalline materials, MOFs are never perfectly crystalline and are likely to contain several different types of defects within their crystalline structures. Among these defects, linker vacancy defects, or the random absence of linker vacancies in their designated bonding positions, are known to be controllable by practicing careful control over the synthesis conditions.
The research team combined the concepts of rational defect engineering over the linker vacancy defects and the potential presence of inaccessible pores within MOFs to propose a methodology where controlled the introduction of linker vacancy defects could lead to a dramatic enhancement in gas adsorption and storage capacities.
The study utilized a Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) code developed by Professor Kim in a high-throughput computational screening of 12,000 experimentally synthesized MOFs to identify the structures with significant amounts of pores that were inaccessible for methane. In determining the presence of inaccessible pores, a flood-fill algorithm was performed over the energy-low regions of the structure, which is the same algorithm used for filling an area with color in Microsoft Paint.
For the MOFs with significant amounts of inaccessible pores, as determined from the screening, the research team emulated linker vacancy defects in their crystalline structures so that the previously inaccessible pores would be newly merged into the main adsorption channel with the introduction of defects for additional surface area and pore volume available for adsorption. The research team successfully identified 13 structures that would experience up to a 55.56% increase in their methane uptake with less than 8.33% of the linker vacancy defects.
The research team believes that this rational defect engineering scheme can be further utilized for many other applications in areas such as selective adsorption of an adsorbate from a gas mixture and the semi-permanent capture of gas molecules.
This research was conducted with the support of the Mid-career Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure1. A diagram for flood fill algorithm and example of identification of inaccessible regions within the MOFs, using the flood fill algorithm
Figure2. Methane energy contours before and after detect introduction
2017.12.04 View 8692
Expanding Gas Storage Capacity of Nanoporous Materials
A KAIST research team led by Professor Jihan Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has successfully proposed a rational defect engineering methodology that can greatly enhance the gas storage capacity of nanoporous materials. The team conducted a high-throughput computational screening of a large experimental metal-organic framework database to identify 13 candidate materials that could experience significant methane uptake enhancement with only a small proportion of linker vacancy defects.
This research was published online on November 16 in Nature Communications, with M.S. candidate Sanggyu Chong from KAIST as the first author and post-doctorate researcher Günther Thiele from the Department of Chemistry at UC Berkeley as a contributing author.
Metal-organic frameworks, hereinafter MOF, are crystalline nanoporous materials that are comprised of metal clusters and organic linkers continuously bound together by coordination bonds. Due to their ultrahigh surface areas and pore volumes, they have been widely studied for various energy and environment applications.
Similar to other crystalline materials, MOFs are never perfectly crystalline and are likely to contain several different types of defects within their crystalline structures. Among these defects, linker vacancy defects, or the random absence of linker vacancies in their designated bonding positions, are known to be controllable by practicing careful control over the synthesis conditions.
The research team combined the concepts of rational defect engineering over the linker vacancy defects and the potential presence of inaccessible pores within MOFs to propose a methodology where controlled the introduction of linker vacancy defects could lead to a dramatic enhancement in gas adsorption and storage capacities.
The study utilized a Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) code developed by Professor Kim in a high-throughput computational screening of 12,000 experimentally synthesized MOFs to identify the structures with significant amounts of pores that were inaccessible for methane. In determining the presence of inaccessible pores, a flood-fill algorithm was performed over the energy-low regions of the structure, which is the same algorithm used for filling an area with color in Microsoft Paint.
For the MOFs with significant amounts of inaccessible pores, as determined from the screening, the research team emulated linker vacancy defects in their crystalline structures so that the previously inaccessible pores would be newly merged into the main adsorption channel with the introduction of defects for additional surface area and pore volume available for adsorption. The research team successfully identified 13 structures that would experience up to a 55.56% increase in their methane uptake with less than 8.33% of the linker vacancy defects.
The research team believes that this rational defect engineering scheme can be further utilized for many other applications in areas such as selective adsorption of an adsorbate from a gas mixture and the semi-permanent capture of gas molecules.
This research was conducted with the support of the Mid-career Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure1. A diagram for flood fill algorithm and example of identification of inaccessible regions within the MOFs, using the flood fill algorithm
Figure2. Methane energy contours before and after detect introduction
2017.12.04 View 8692 -
 Professor Je-Kyun Park, Awarded by The Korean BioChip Society
On November 9, Je-Kyun Park from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST received an award from the 2017 Fall Meeting of The Korean BioChip Society held in Paradise Hotel Busan, Korea. This year’s meeting recognized Professor Park for developing lab-on-a-chip and microfluidic analytical technologies.
The Korean BioChip Society is a corporation of biochip professional established in 2006 for the development of biochip technology. Every year, the Society selects a recipient based on the nominees’ academic achievements and contributions to bio-fusion industry.
Professor Park served on the international editorial boards of renowned international journals in related fields, including Biosensors and Bioelectronics and Lab on a Chip. He was also the Committee Chairman of MicroTas in 2015.
2017.11.22 View 9672
Professor Je-Kyun Park, Awarded by The Korean BioChip Society
On November 9, Je-Kyun Park from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST received an award from the 2017 Fall Meeting of The Korean BioChip Society held in Paradise Hotel Busan, Korea. This year’s meeting recognized Professor Park for developing lab-on-a-chip and microfluidic analytical technologies.
The Korean BioChip Society is a corporation of biochip professional established in 2006 for the development of biochip technology. Every year, the Society selects a recipient based on the nominees’ academic achievements and contributions to bio-fusion industry.
Professor Park served on the international editorial boards of renowned international journals in related fields, including Biosensors and Bioelectronics and Lab on a Chip. He was also the Committee Chairman of MicroTas in 2015.
2017.11.22 View 9672 -
 WEF-KAIST to Host a Forum Next April in Korea
(President Shin poses with Chairman Schwab at the meeting in Dubai)
President Sung-Chul Shin and Executive Chairman Klaus Schwab of the World Economic Forum agreed to co-host the Fourth Industrial Revolution Forum next April in Seoul during a meeting at the WEF Global Future Councils 2017 held in Dubai November 11-12.
Next April’s forum will be a follow-up event of the roundtable discussion KAIST and the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution co-hosted in October in Seoul. The two hosted the roundtable discussion titled “Mastering the Fourth Industrial Revolution: The Future of Jobs and Inclusive Growth in Korea.”
During the annual meeting in Dubai, Chairman Schwab expressed his deep appreciation to President Shin for hosting the roundtable discussion and proposed a full-fledged forum in partnership with KAIST once again, which Chairman Schwab will be scheduled to attend.
Chairman Schwab emphasized once again that Korea, who has the world’s top high-end technologies such as 5G telecommunications and semiconductor memory, will be the best fit to realize the Fourth Industrial Revolution most rapidly. He also expressed his great interest in the city of Daejeon in which is being considered to become the Special City for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The Global Future Council of the WEF is the interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking on the future. The annual council convenes in Dubai the most relevant and knowledgeable thought leaders from academia, government, business, and civil society to challenge conventional thinking and develop new insights and perspectives on key global systems, as well as the impact and governance of key emerging technologies. This year, more than 850 world-leading experts from 74 countries participated.
Under the theme of ‘Vision 2030,’ participants explored systematic changes in key areas such as energy, mobility, and infrastructure while reflecting on the impact of technological breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and other areas related to the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
2017.11.13 View 10489
WEF-KAIST to Host a Forum Next April in Korea
(President Shin poses with Chairman Schwab at the meeting in Dubai)
President Sung-Chul Shin and Executive Chairman Klaus Schwab of the World Economic Forum agreed to co-host the Fourth Industrial Revolution Forum next April in Seoul during a meeting at the WEF Global Future Councils 2017 held in Dubai November 11-12.
Next April’s forum will be a follow-up event of the roundtable discussion KAIST and the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution co-hosted in October in Seoul. The two hosted the roundtable discussion titled “Mastering the Fourth Industrial Revolution: The Future of Jobs and Inclusive Growth in Korea.”
During the annual meeting in Dubai, Chairman Schwab expressed his deep appreciation to President Shin for hosting the roundtable discussion and proposed a full-fledged forum in partnership with KAIST once again, which Chairman Schwab will be scheduled to attend.
Chairman Schwab emphasized once again that Korea, who has the world’s top high-end technologies such as 5G telecommunications and semiconductor memory, will be the best fit to realize the Fourth Industrial Revolution most rapidly. He also expressed his great interest in the city of Daejeon in which is being considered to become the Special City for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The Global Future Council of the WEF is the interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking on the future. The annual council convenes in Dubai the most relevant and knowledgeable thought leaders from academia, government, business, and civil society to challenge conventional thinking and develop new insights and perspectives on key global systems, as well as the impact and governance of key emerging technologies. This year, more than 850 world-leading experts from 74 countries participated.
Under the theme of ‘Vision 2030,’ participants explored systematic changes in key areas such as energy, mobility, and infrastructure while reflecting on the impact of technological breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and other areas related to the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
2017.11.13 View 10489 -
 LG's Woo Jong Lee Named the Alumnus of College of Engineering
The College of Engineering at KAIST selected Woo Jong Lee, President and Head of the VC Business Division at LG Electronics Inc., as the 2017 Alumnus of the Year for the College of Engineering.
‘Alumnus of the Year’ is an award given to a distinguished alumnus who has contributed to the development of industrial technology or made outstanding academic achievements.
Lee graduated from KAIST with the master’s degrees in Industrial Engineering. He also worked at Daewoo Motors as an executive member in the development division. He has been a crucial human resource for LG since he joined the company in 2000.
While leading the VC business Division, which was established in 2013, Lee is recognized as a creative engineer as well as a leader in the automotive industry. Focusing on autonomous driving and eco-friendliness, he has been engaged in the production of major projects from the beginning to the end.
Since 2014, outstanding alumni whose achievements have represented KAIST at the highest level have received the award. The first recipient was Tae-Kyung Yoo, an executive at Lumens Co., Ltd., and the second recipient was Jung-Ju Kim, the founder of NXC. In 2016, the award was not given because an appropriate candidate could not be identified.
The award was held in the Industrial Engineering & Management Building (E2) on November 8. Faculty members including the dean of the College of Engineering Jong-Hwan Kim, the vice dean Hyochoong Bang, the head of Industrial & Systems Engineering Taesik Lee, and the dean of the KAIST Academy Tae-Eog Lee attended the ceremony.
After the ceremony, Lee delivered a lecture on ‘Auto-components Business of LG Electronics’ to KAIST students.
2017.11.09 View 9768
LG's Woo Jong Lee Named the Alumnus of College of Engineering
The College of Engineering at KAIST selected Woo Jong Lee, President and Head of the VC Business Division at LG Electronics Inc., as the 2017 Alumnus of the Year for the College of Engineering.
‘Alumnus of the Year’ is an award given to a distinguished alumnus who has contributed to the development of industrial technology or made outstanding academic achievements.
Lee graduated from KAIST with the master’s degrees in Industrial Engineering. He also worked at Daewoo Motors as an executive member in the development division. He has been a crucial human resource for LG since he joined the company in 2000.
While leading the VC business Division, which was established in 2013, Lee is recognized as a creative engineer as well as a leader in the automotive industry. Focusing on autonomous driving and eco-friendliness, he has been engaged in the production of major projects from the beginning to the end.
Since 2014, outstanding alumni whose achievements have represented KAIST at the highest level have received the award. The first recipient was Tae-Kyung Yoo, an executive at Lumens Co., Ltd., and the second recipient was Jung-Ju Kim, the founder of NXC. In 2016, the award was not given because an appropriate candidate could not be identified.
The award was held in the Industrial Engineering & Management Building (E2) on November 8. Faculty members including the dean of the College of Engineering Jong-Hwan Kim, the vice dean Hyochoong Bang, the head of Industrial & Systems Engineering Taesik Lee, and the dean of the KAIST Academy Tae-Eog Lee attended the ceremony.
After the ceremony, Lee delivered a lecture on ‘Auto-components Business of LG Electronics’ to KAIST students.
2017.11.09 View 9768 -
 College of Business Honored with the WRDS-SSNR Innovation Award
(Professor Inmoo Lee (far left), Robert Zarazowski (WRDS), Gregg Gordon (SSRN) and Professor Jae Kyu Lee)
The KAIST College of Business received the WRDS (Wharton Research Data Services)-SSNR Innovation Award for the Asia-Pacific region on October 31 during the AACSB Asia-Pacific Conference in Seoul.
The WRDS-SSRN Innovation Award is intended to elevate the visibility of pioneering research across a broad range of financial and economic topics. Three winners are selected annually from across North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific based on their ability to demonstrate innovation and research excellence.
The award was created through collaboration with SSRN, the world’s leading early-stage research platform and Elsevier, a global information analytics company specializing in science and health. It honors top business schools that produce exceptional data-driven research. A part of the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania, WRDS provides global corporations, universities, and regulatory agencies with the thought leadership, data access, and analytics needed to enable impactful research.
The Dean of the College of Business Youngbae Kim, said that KAIST has been taking the lead in responding to global trends, offering many innovative programs such as an MBA for Social Entrepreneurship and the Master Course for Green Growth Management. KAIST already has been selected as the Most Innovative University in the Asia-Pacific Region by Thomson Reuters for the last two years.
Robert Zarazowski, managing director of WRDS said they recognize and support the outstanding achievement taking place at KAIST as well as its commitment to growth and innovation in business education.
2017.11.03 View 7965
College of Business Honored with the WRDS-SSNR Innovation Award
(Professor Inmoo Lee (far left), Robert Zarazowski (WRDS), Gregg Gordon (SSRN) and Professor Jae Kyu Lee)
The KAIST College of Business received the WRDS (Wharton Research Data Services)-SSNR Innovation Award for the Asia-Pacific region on October 31 during the AACSB Asia-Pacific Conference in Seoul.
The WRDS-SSRN Innovation Award is intended to elevate the visibility of pioneering research across a broad range of financial and economic topics. Three winners are selected annually from across North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific based on their ability to demonstrate innovation and research excellence.
The award was created through collaboration with SSRN, the world’s leading early-stage research platform and Elsevier, a global information analytics company specializing in science and health. It honors top business schools that produce exceptional data-driven research. A part of the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania, WRDS provides global corporations, universities, and regulatory agencies with the thought leadership, data access, and analytics needed to enable impactful research.
The Dean of the College of Business Youngbae Kim, said that KAIST has been taking the lead in responding to global trends, offering many innovative programs such as an MBA for Social Entrepreneurship and the Master Course for Green Growth Management. KAIST already has been selected as the Most Innovative University in the Asia-Pacific Region by Thomson Reuters for the last two years.
Robert Zarazowski, managing director of WRDS said they recognize and support the outstanding achievement taking place at KAIST as well as its commitment to growth and innovation in business education.
2017.11.03 View 7965 -
 Scientist of November, Professor Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Hyung Jin Sung from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST received a ‘Science and Technology Award of the Month’ given by the Ministry of ICT and Science and the National Research Foundation of Korea for November 2017. He developed technology that can exquisitely control a micrometer-scaled liquid drop on a dime-sized lab-on-a-chip. With his work, he was recognized for reinforcing research capability on microfluidics.
Lab-on-a-chip is an emerging experiment and diagnostic technology in the form of a bio-microchip that facilitates complex and various experiments with only a minimal sample size required. This technology draws a lot of attention not only from medical and pharmaceutical areas, but also the health and environmental field. The biggest problem was that technology for the temperature control of a fluid sample, which is one of the core technologies in microfluidics, has low accuracy. This limit had to be overcome in order to use the lab-on-a-chip more widely.
Professor Sung developed an acoustic and thermal method which controls the temperature of a droplet quickly and meticulously by using sound and energy. This is a thermal method that uses heat generated during the absorption of an acoustic wave into viscoelastic substances. It facilitates a rapid heating rate and spatial-temporal temperature control, allowing heating in desired areas. In addition, Professor Sung applied his technology to polymerase chain reactions, which are used to amplify DNA.
Through this experiment, he successfully shortened the reaction time from 1-2 hours to only three minutes, making this a groundbreaking achievement.
Professor Sung said, “My research is significant for enhancing the applicability of microfluidics. I expect that it will lead to technological innovations in healthcare fields including biochemistry, medical checkups, and new medicine development.”
2017.11.03 View 11477
Scientist of November, Professor Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Hyung Jin Sung from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST received a ‘Science and Technology Award of the Month’ given by the Ministry of ICT and Science and the National Research Foundation of Korea for November 2017. He developed technology that can exquisitely control a micrometer-scaled liquid drop on a dime-sized lab-on-a-chip. With his work, he was recognized for reinforcing research capability on microfluidics.
Lab-on-a-chip is an emerging experiment and diagnostic technology in the form of a bio-microchip that facilitates complex and various experiments with only a minimal sample size required. This technology draws a lot of attention not only from medical and pharmaceutical areas, but also the health and environmental field. The biggest problem was that technology for the temperature control of a fluid sample, which is one of the core technologies in microfluidics, has low accuracy. This limit had to be overcome in order to use the lab-on-a-chip more widely.
Professor Sung developed an acoustic and thermal method which controls the temperature of a droplet quickly and meticulously by using sound and energy. This is a thermal method that uses heat generated during the absorption of an acoustic wave into viscoelastic substances. It facilitates a rapid heating rate and spatial-temporal temperature control, allowing heating in desired areas. In addition, Professor Sung applied his technology to polymerase chain reactions, which are used to amplify DNA.
Through this experiment, he successfully shortened the reaction time from 1-2 hours to only three minutes, making this a groundbreaking achievement.
Professor Sung said, “My research is significant for enhancing the applicability of microfluidics. I expect that it will lead to technological innovations in healthcare fields including biochemistry, medical checkups, and new medicine development.”
2017.11.03 View 11477 -
 In Jin Cho Earned the Best Poster Prize at ME Summit 2017
In Jin Cho, a Ph.D. student in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST received the best poster prize at the International Metabolic Engineering Summit 2017 held on October 24 in Beijing, China.
The International Metabolic Engineering Summit is a global conference where scientists and corporate researchers in the field of metabolic engineering present their latest research outcomes and build networks.
At this year’s summit, about 500 researchers from around the world participated in active academic exchanges, including giving keynote speeches and presenting posters.
During the poster session, the summit selects one person for the KeAi-synthetic and Systems Biotechnology Poster Award, two for Microbial Cell Factories Poster Awards, and three for Biotechnology Journal Poster Awards among the posters presented by graduate students, post-doctoral fellows and researchers. Cho received the KeAi-synthetic and Systems Biotechnology Poster Award. Her winning poster is on the biotransformation of p-xylene to terephthalic acid using engineered Escherichia coli.
Terephthalic acid is generally produced by p-xylene oxidation; however, this process requires a high temperature and pressure as well as a toxic catalyst during the reaction process.
Cho and Ziwei Luo, a Ph.D. student at KAIST, co-conducted the research and developed a successful biological conversion process. Compared to the existing chemical process, it does not require a high temperature and pressure; and it is environmentally friendly with a relatively high conversion rate of approximately 97%.
Cho’s advisor, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Further research on glucose-derived terephthalic acid will enable us to produce biomass-based eco-friendly terephthalic acid through engineered Escherichia coli.”
2017.10.31 View 11480
In Jin Cho Earned the Best Poster Prize at ME Summit 2017
In Jin Cho, a Ph.D. student in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST received the best poster prize at the International Metabolic Engineering Summit 2017 held on October 24 in Beijing, China.
The International Metabolic Engineering Summit is a global conference where scientists and corporate researchers in the field of metabolic engineering present their latest research outcomes and build networks.
At this year’s summit, about 500 researchers from around the world participated in active academic exchanges, including giving keynote speeches and presenting posters.
During the poster session, the summit selects one person for the KeAi-synthetic and Systems Biotechnology Poster Award, two for Microbial Cell Factories Poster Awards, and three for Biotechnology Journal Poster Awards among the posters presented by graduate students, post-doctoral fellows and researchers. Cho received the KeAi-synthetic and Systems Biotechnology Poster Award. Her winning poster is on the biotransformation of p-xylene to terephthalic acid using engineered Escherichia coli.
Terephthalic acid is generally produced by p-xylene oxidation; however, this process requires a high temperature and pressure as well as a toxic catalyst during the reaction process.
Cho and Ziwei Luo, a Ph.D. student at KAIST, co-conducted the research and developed a successful biological conversion process. Compared to the existing chemical process, it does not require a high temperature and pressure; and it is environmentally friendly with a relatively high conversion rate of approximately 97%.
Cho’s advisor, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Further research on glucose-derived terephthalic acid will enable us to produce biomass-based eco-friendly terephthalic acid through engineered Escherichia coli.”
2017.10.31 View 11480 -
 KAIST and KOICA Invited Dominican Republic Officials for Workshop
KAIST will host a two-week workshop for Dominican Republic officials and scholars in collaboration with KOICA (Korea International Cooperation Agency) beginning October 23 at KAIST.
The workshop aims to encourage academia-industry cooperation as one of the Projects for Human Resource Development for Science and Technology at KOICA. Dominican participants including the assistant minister of the Ministry of Higher Education, Science and Technology (MESCYT) and deans of engineering colleges at major universities will enjoy lectures from experts and visit enterprises known for excellent academia-industry collaboration.
According to the Center for Overseas Development, at which Professor WonJoon Kim in the School of Business and Technology Management at KAIST holds the position of director, the workshop is designed to develop human resources in the science and technology (S&T) area, share knowledge on research and development in the field of academia-industry cooperation, and help the participants acquire know-how for managing partnerships between related organizations and industries.
During the workshop, KAIST plans to transfer know-how and share knowledge on its academia-industry cooperation R&D system, in hopes that the workshop will help the Dominican Republic foster its manpower in higher education. The workshop organizers hope that the officers and scholars will be able to apply what they will learn for establishing and carrying out detailed action plans for academia-industry cooperation policies in an effective manner.
“This workshop provides an opportunity to learn about the development of S&T in Korea, academia-industry cooperation R&D, and fostering manpower in advanced S&T. Through the knowledge sharing, we can have a better understanding of academia-industry cooperation as well as education on advanced manpower,” said Pedro Antonio Eduardo, the assistant minister of MESCYT.
He added, “I hope that this workshop will further detailed cooperation between the two countries for Korean high-tech enterprises’ overseas expansion and advanced manpower education. The development model in Korea has many essential elements, so learning its engine for growth and polytechnic manpower education will help develop my country’s industry sector.”
The Project for Human Resource Development for Science and Technology is one of the official development assistance projects running from last year until 2019. It promotes R&D activities for S&T in the Dominican Republic, encouraging academia-industry cooperation by improving trainers in charge of advanced manpower education.
2017.10.30 View 9115
KAIST and KOICA Invited Dominican Republic Officials for Workshop
KAIST will host a two-week workshop for Dominican Republic officials and scholars in collaboration with KOICA (Korea International Cooperation Agency) beginning October 23 at KAIST.
The workshop aims to encourage academia-industry cooperation as one of the Projects for Human Resource Development for Science and Technology at KOICA. Dominican participants including the assistant minister of the Ministry of Higher Education, Science and Technology (MESCYT) and deans of engineering colleges at major universities will enjoy lectures from experts and visit enterprises known for excellent academia-industry collaboration.
According to the Center for Overseas Development, at which Professor WonJoon Kim in the School of Business and Technology Management at KAIST holds the position of director, the workshop is designed to develop human resources in the science and technology (S&T) area, share knowledge on research and development in the field of academia-industry cooperation, and help the participants acquire know-how for managing partnerships between related organizations and industries.
During the workshop, KAIST plans to transfer know-how and share knowledge on its academia-industry cooperation R&D system, in hopes that the workshop will help the Dominican Republic foster its manpower in higher education. The workshop organizers hope that the officers and scholars will be able to apply what they will learn for establishing and carrying out detailed action plans for academia-industry cooperation policies in an effective manner.
“This workshop provides an opportunity to learn about the development of S&T in Korea, academia-industry cooperation R&D, and fostering manpower in advanced S&T. Through the knowledge sharing, we can have a better understanding of academia-industry cooperation as well as education on advanced manpower,” said Pedro Antonio Eduardo, the assistant minister of MESCYT.
He added, “I hope that this workshop will further detailed cooperation between the two countries for Korean high-tech enterprises’ overseas expansion and advanced manpower education. The development model in Korea has many essential elements, so learning its engine for growth and polytechnic manpower education will help develop my country’s industry sector.”
The Project for Human Resource Development for Science and Technology is one of the official development assistance projects running from last year until 2019. It promotes R&D activities for S&T in the Dominican Republic, encouraging academia-industry cooperation by improving trainers in charge of advanced manpower education.
2017.10.30 View 9115 -
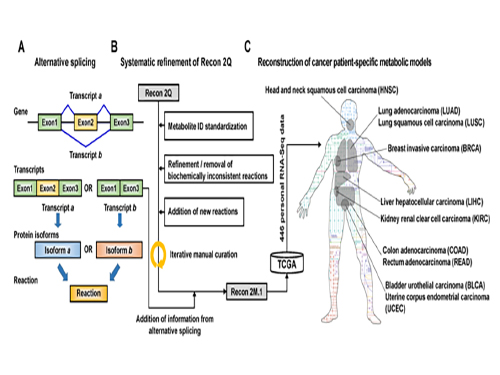 Development of a Highly-Accurate Computational Model of Human Metabolism
A research team from KAIST developed a computational framework that enables the reconstruction of a comprehensive computational model of human metabolism, which allows for an accurate prediction of personal metabolic features (or phenotypes).
Understanding personal metabolic phenotypes allows us to design effective therapeutic strategies for various chronic and infectious diseases. A human computational model called the genome-scale metabolic model (GEM) contains information on thousands of metabolic genes and their corresponding reactions and metabolites, and has played an important role in predicting metabolic phenotypes. Although several versions of human GEMs have been released, they had room for further development, especially as to incorporating biological information coming from a human genetics mechanism called “alternative splicing.” Alternative splicing is a genetic mechanism that allows a gene to give rise to multiple reactions, and is strongly associated with pathology.
To tackle this problem, Jae Yong Ryu (a Ph.D. student), Dr. Hyun Uk Kim (Research Fellow), and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, all from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, developed a computational framework that systematically generates metabolic reactions, and adds them to the human GEM. The resulting human GEM was demonstrated to accurately predict metabolic phenotypes under varied environmental conditions. The research results were published online in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) on October 24, 2017, under the title “Framework and resource for more than 11,000 gene-transcript-protein-reaction associations in human metabolism.”
The research team first updated the biological contents of a previous version of the human GEM. The updated biological contents include metabolic genes and their corresponding metabolites and reactions. In particular, metabolic reactions catalyzed by already-known protein isoforms were additionally incorporated into the human GEM; protein isoforms are multiple variants of proteins generated from individual genes through the alternative splicing process. Each protein isoform is often responsible for the operation of a metabolic reaction. Although multiple protein isoforms generated from one gene can play different functions by having different sets of protein domains and/or subcellular localizations, such information was not properly considered in previous versions of human GEMs.
Upon the initial update of the human GEM, named Recon 2M.1, the research team subsequently implemented a computational framework that systematically generates information on Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA) in order to identify protein isoforms that were previously not identified. This framework was developed in this study. As a result of the implementation of the framework for GeTPRA, more than 11,000 GeTPRA were automatically predicted, and thoroughly validated. Additional metabolic reactions were then added to Recon 2M.1 based on the predicted GeTPRA for the previously uncharacterized protein isoforms; Recon 2M.1 was renamed Recon 2M.2 from this upgrade.
Finally, Recon 2M.2 was integrated with 446 sets of personal biological data (RNA-Seq data) in order to build patient-specific cancer models. These patient-specific cancer models were used to predict cancer metabolism activities and anticancer targets.
The development of a new version of human GEMs along with the computational framework for GeTPRA is expected to boost studies in fundamental human genetics and medicine. Model files of the human GEMs Recon 2M.1 and 2M.2, a full list of the GeTPRA and the source code for the computational framework to predict the GeTPRA are all available as part of the publication of this study.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “The predicted GeTPRA from the computational framework is expected to serve as a guideline for future experiments on human genetics and biochemistry, whereas the resulting Recon 2M.2 can be used to predict drug targets for various human diseases.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
(Figure 1:A scheme of Recon 2M.1 development and its use in reconstructing personal genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs). (A) A concept of alternative splicing of human genes and its use in Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA) of Recon 2M.1. (B) A procedure of systematic refinement of the Recon 2Q. Recon 2Q is one of the previously released human GEMs. Biochemically inconsistent reactions include unbalanced, artificial, blocked, and/or redundant reactions. Iterative manual curation was conducted while validating the Recon 2M.1. (C) Reconstruction of cancer patient-specific GEMs using Recon 2M.1 for further simulation studies. In this study, personal biological data (RNA-Seq data) were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA; https://cancergenome.nih.gov/ ) across the ten cancer types.
(Figure 2: Computational framework for the systematic generation of Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA; red box in the flowchart). Peptide sequences of metabolic genes defined in Recon 2M.1 were retrieved from a database called Ensembl. EC numbers and subcellular localizations of all the protein isoforms of metabolic genes in Recon 2M.1 were predicted using software programs EFICAz2.5 and Wolf PSort, respectively. Information on the newly predicted GeTPRA was systematically incorporated into the Recon 2M.1, thereby resulting in Recon 2M.2.)
2017.10.25 View 10907
Development of a Highly-Accurate Computational Model of Human Metabolism
A research team from KAIST developed a computational framework that enables the reconstruction of a comprehensive computational model of human metabolism, which allows for an accurate prediction of personal metabolic features (or phenotypes).
Understanding personal metabolic phenotypes allows us to design effective therapeutic strategies for various chronic and infectious diseases. A human computational model called the genome-scale metabolic model (GEM) contains information on thousands of metabolic genes and their corresponding reactions and metabolites, and has played an important role in predicting metabolic phenotypes. Although several versions of human GEMs have been released, they had room for further development, especially as to incorporating biological information coming from a human genetics mechanism called “alternative splicing.” Alternative splicing is a genetic mechanism that allows a gene to give rise to multiple reactions, and is strongly associated with pathology.
To tackle this problem, Jae Yong Ryu (a Ph.D. student), Dr. Hyun Uk Kim (Research Fellow), and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, all from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, developed a computational framework that systematically generates metabolic reactions, and adds them to the human GEM. The resulting human GEM was demonstrated to accurately predict metabolic phenotypes under varied environmental conditions. The research results were published online in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) on October 24, 2017, under the title “Framework and resource for more than 11,000 gene-transcript-protein-reaction associations in human metabolism.”
The research team first updated the biological contents of a previous version of the human GEM. The updated biological contents include metabolic genes and their corresponding metabolites and reactions. In particular, metabolic reactions catalyzed by already-known protein isoforms were additionally incorporated into the human GEM; protein isoforms are multiple variants of proteins generated from individual genes through the alternative splicing process. Each protein isoform is often responsible for the operation of a metabolic reaction. Although multiple protein isoforms generated from one gene can play different functions by having different sets of protein domains and/or subcellular localizations, such information was not properly considered in previous versions of human GEMs.
Upon the initial update of the human GEM, named Recon 2M.1, the research team subsequently implemented a computational framework that systematically generates information on Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA) in order to identify protein isoforms that were previously not identified. This framework was developed in this study. As a result of the implementation of the framework for GeTPRA, more than 11,000 GeTPRA were automatically predicted, and thoroughly validated. Additional metabolic reactions were then added to Recon 2M.1 based on the predicted GeTPRA for the previously uncharacterized protein isoforms; Recon 2M.1 was renamed Recon 2M.2 from this upgrade.
Finally, Recon 2M.2 was integrated with 446 sets of personal biological data (RNA-Seq data) in order to build patient-specific cancer models. These patient-specific cancer models were used to predict cancer metabolism activities and anticancer targets.
The development of a new version of human GEMs along with the computational framework for GeTPRA is expected to boost studies in fundamental human genetics and medicine. Model files of the human GEMs Recon 2M.1 and 2M.2, a full list of the GeTPRA and the source code for the computational framework to predict the GeTPRA are all available as part of the publication of this study.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “The predicted GeTPRA from the computational framework is expected to serve as a guideline for future experiments on human genetics and biochemistry, whereas the resulting Recon 2M.2 can be used to predict drug targets for various human diseases.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
(Figure 1:A scheme of Recon 2M.1 development and its use in reconstructing personal genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs). (A) A concept of alternative splicing of human genes and its use in Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA) of Recon 2M.1. (B) A procedure of systematic refinement of the Recon 2Q. Recon 2Q is one of the previously released human GEMs. Biochemically inconsistent reactions include unbalanced, artificial, blocked, and/or redundant reactions. Iterative manual curation was conducted while validating the Recon 2M.1. (C) Reconstruction of cancer patient-specific GEMs using Recon 2M.1 for further simulation studies. In this study, personal biological data (RNA-Seq data) were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA; https://cancergenome.nih.gov/ ) across the ten cancer types.
(Figure 2: Computational framework for the systematic generation of Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA; red box in the flowchart). Peptide sequences of metabolic genes defined in Recon 2M.1 were retrieved from a database called Ensembl. EC numbers and subcellular localizations of all the protein isoforms of metabolic genes in Recon 2M.1 were predicted using software programs EFICAz2.5 and Wolf PSort, respectively. Information on the newly predicted GeTPRA was systematically incorporated into the Recon 2M.1, thereby resulting in Recon 2M.2.)
2017.10.25 View 10907 -
 KAIST Partners with WEF to Prepare for the 4th Industrial Revolution
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and the Head of the World Economic Forum Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Murat Sonmez, made a commitment to build cooperation in an active manner for addressing the ramifications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The two signed an MOU to cooperate in research in related fields on October 13 after holding a roundtable discussion titled “The Future of Jobs and Inclusive Growth in Korea”. It is the first partnership that the WEF has sealed with an academic institution.The roundtable discussion brought together distinguished guests from politics, non-profit civic organizations, academia, and enterprises including Daejeon Mayor Seon-Taek Kwon, Doosan Group Vice Chairman Lee Hyun-Soon, and Korean Venture Business Association President Ahn Keon-Joon.
During the news conference, President Shin said, “This event means a lot because it explores ways in which inclusive growth and job creation can be realized in Korea. To move forward in the new age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, every country needs to adopt appropriate new policies suitable for their specific market environments. KAIST will contribute to this process for Korea as well as for the global community.”
President Shin also said, “Korea has been a fast follower in previous industrial revolutions. Now, we have the momentum to seize the opportunities in the wake of this revolution. KAIST is dedicated to leading Korea into becoming a first mover in the Fourth Industrial Revolution by cooperating with the WEF.”
“Two decades later, we will live with considerable number of robots around us. It is possible that our societies in the future will consist of Homo sapiens and Robo sapiens. We need to create new jobs for Homo sapiens to prepare for a society that we will have to coexist with a new industrial tribe. Industries need continuing education to retrain workers for the ever evolving industrial landscape of the future,” President Shin emphasized.
Meanwhile, Sonmez pointed out that all stakeholders should participate in understanding the new industrial environment’s ramifications, saying “Societies, governments, public and private sectors, startups, and academia should co-design inclusive models through global efforts. Ethics and influences on the job market should also be taken into consideration.”
Sonmez said nine factors such as blockchains, internet of things, artificial intelligence, machine learning, cross-border data blow, drones, 3D printing, autonomous driving, the environment, and precision medicine will take center stage in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, In particular, he said that blockchains, which are a cybersecurity technology for online financial transactions, will bring even bigger changes than the ‘World Wide Web’ has done over the past three decades.
“To this end, we will have to work closely with major academic institutes. Through this partnership with KAIST, we will make the fruits of the new industrial environment benefit Koreans and Korean society,” Sonmez added.
2017.10.14 View 9895
KAIST Partners with WEF to Prepare for the 4th Industrial Revolution
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and the Head of the World Economic Forum Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Murat Sonmez, made a commitment to build cooperation in an active manner for addressing the ramifications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The two signed an MOU to cooperate in research in related fields on October 13 after holding a roundtable discussion titled “The Future of Jobs and Inclusive Growth in Korea”. It is the first partnership that the WEF has sealed with an academic institution.The roundtable discussion brought together distinguished guests from politics, non-profit civic organizations, academia, and enterprises including Daejeon Mayor Seon-Taek Kwon, Doosan Group Vice Chairman Lee Hyun-Soon, and Korean Venture Business Association President Ahn Keon-Joon.
During the news conference, President Shin said, “This event means a lot because it explores ways in which inclusive growth and job creation can be realized in Korea. To move forward in the new age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, every country needs to adopt appropriate new policies suitable for their specific market environments. KAIST will contribute to this process for Korea as well as for the global community.”
President Shin also said, “Korea has been a fast follower in previous industrial revolutions. Now, we have the momentum to seize the opportunities in the wake of this revolution. KAIST is dedicated to leading Korea into becoming a first mover in the Fourth Industrial Revolution by cooperating with the WEF.”
“Two decades later, we will live with considerable number of robots around us. It is possible that our societies in the future will consist of Homo sapiens and Robo sapiens. We need to create new jobs for Homo sapiens to prepare for a society that we will have to coexist with a new industrial tribe. Industries need continuing education to retrain workers for the ever evolving industrial landscape of the future,” President Shin emphasized.
Meanwhile, Sonmez pointed out that all stakeholders should participate in understanding the new industrial environment’s ramifications, saying “Societies, governments, public and private sectors, startups, and academia should co-design inclusive models through global efforts. Ethics and influences on the job market should also be taken into consideration.”
Sonmez said nine factors such as blockchains, internet of things, artificial intelligence, machine learning, cross-border data blow, drones, 3D printing, autonomous driving, the environment, and precision medicine will take center stage in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, In particular, he said that blockchains, which are a cybersecurity technology for online financial transactions, will bring even bigger changes than the ‘World Wide Web’ has done over the past three decades.
“To this end, we will have to work closely with major academic institutes. Through this partnership with KAIST, we will make the fruits of the new industrial environment benefit Koreans and Korean society,” Sonmez added.
2017.10.14 View 9895 -
 KAIST-WEF Roundtable on Inclusive Growth and Job Creation
The World Economic Forum (WEF) will join KAIST in an effort to address sweeping global problems in the wake of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The two will co-host a roundtable on ‘Shaping Korea’s Priorities for Inclusive Growth and Job Creation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution’ on October 13 at Lotte Hotel in Seoul.
The roundtable will bring together leaders from government, industry, universities, and non-profit civic organizations to have an in-depth discussion on a thought-provoking agenda of inclusive growth and job creation which scientific and technological changes will bring about. The event will provide a platform to explore practical collaboration and innovative strategies for better job creation and innovation ecosystems.
The two will also sign an MOU for collaboration between the Fourth Industrial Revolution Information Center (FIRIC) of KAIST and the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR).
President Sung-Chul Shin of KAIST and the Head of the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Murat Sonmez, will lead the panel discussion titled ‘Inclusive Growth and the Fourth Industrial Revolution’ which will be attended by leaders from government, industry, and non-profit civic organizations.
At the breakout sessions, the topics will be “Future Jobs” and the “Creation of Innovation Ecosystems”. Additionally, a discussion on the “SME 4.0 Initiative”, which is a program pushed forward by KAIST in collaboration with local governments, will talk about job creation through innovation in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The WEF will introduce their two-year activities and research on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, which have great potential and a high possibility of successfully undergoing the revolution, to Korea.
Since WEF Executive Chairman Klaus Schwab brought up the topic of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the WEF has been leading agenda topics and discussions on high-profile matters, including ‘technology-driven but human-centered inclusive growth’ in predicting the future of jobs.
The WEF is a nonprofit organization committed to addressing the world’s weightiest problems. It is best known for its annual meetings in Davos, Switzerland, which attracts leaders from around the world. KAIST has been participating in this summit since 2009. President Shin will also attend the upcoming Davos summit next January. Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee who heads the KAIST Institute and the FIRIC is the co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the WEF.
Moreover, President Shin and Mr. Sonmez will explain the background of the roundtable and share the results of the sessions at a joint news conference.
2017.09.28 View 11257
KAIST-WEF Roundtable on Inclusive Growth and Job Creation
The World Economic Forum (WEF) will join KAIST in an effort to address sweeping global problems in the wake of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The two will co-host a roundtable on ‘Shaping Korea’s Priorities for Inclusive Growth and Job Creation in the Fourth Industrial Revolution’ on October 13 at Lotte Hotel in Seoul.
The roundtable will bring together leaders from government, industry, universities, and non-profit civic organizations to have an in-depth discussion on a thought-provoking agenda of inclusive growth and job creation which scientific and technological changes will bring about. The event will provide a platform to explore practical collaboration and innovative strategies for better job creation and innovation ecosystems.
The two will also sign an MOU for collaboration between the Fourth Industrial Revolution Information Center (FIRIC) of KAIST and the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR).
President Sung-Chul Shin of KAIST and the Head of the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Murat Sonmez, will lead the panel discussion titled ‘Inclusive Growth and the Fourth Industrial Revolution’ which will be attended by leaders from government, industry, and non-profit civic organizations.
At the breakout sessions, the topics will be “Future Jobs” and the “Creation of Innovation Ecosystems”. Additionally, a discussion on the “SME 4.0 Initiative”, which is a program pushed forward by KAIST in collaboration with local governments, will talk about job creation through innovation in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The WEF will introduce their two-year activities and research on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, which have great potential and a high possibility of successfully undergoing the revolution, to Korea.
Since WEF Executive Chairman Klaus Schwab brought up the topic of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the WEF has been leading agenda topics and discussions on high-profile matters, including ‘technology-driven but human-centered inclusive growth’ in predicting the future of jobs.
The WEF is a nonprofit organization committed to addressing the world’s weightiest problems. It is best known for its annual meetings in Davos, Switzerland, which attracts leaders from around the world. KAIST has been participating in this summit since 2009. President Shin will also attend the upcoming Davos summit next January. Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee who heads the KAIST Institute and the FIRIC is the co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the WEF.
Moreover, President Shin and Mr. Sonmez will explain the background of the roundtable and share the results of the sessions at a joint news conference.
2017.09.28 View 11257