AR
-
 Scientists re-writes FDA-recommended equation to improve estimation of drug-drug interaction
Drugs absorbed into the body are metabolized and thus removed by enzymes from several organs like the liver. How fast a drug is cleared out of the system can be affected by other drugs that are taken together because added substance can increase the amount of enzyme secretion in the body. This dramatically decreases the concentration of a drug, reducing its efficacy, often leading to the failure of having any effect at all. Therefore, accurately predicting the clearance rate in the presence of drug-drug interaction* is critical in the process of drug prescription and development of a new drug in order to ensure its efficacy and/or to avoid unwanted side-effects.
*Drug-drug interaction: In terms of metabolism, drug-drug interaction is a phenomenon in which one drug changes the metabolism of another drug to promote or inhibit its excretion from the body when two or more drugs are taken together. As a result, it increases the toxicity of medicines or causes loss of efficacy.
Since it is practically impossible to evaluate all interactions between new drug candidates and all marketed drugs during the development process, the FDA recommends indirect evaluation of drug interactions using a formula suggested in their guidance, first published in 1997, revised in January of 2020, in order to evaluate drug interactions and minimize side effects of having to use more than one type of drugs at once.
The formula relies on the 110-year-old Michaelis-Menten (MM) model, which has a fundamental limit of making a very broad and groundless assumption on the part of the presence of the enzymes that metabolizes the drug. While MM equation has been one of the most widely known equations in biochemistry used in more than 220,000 published papers, the MM equation is accurate only when the concentration of the enzyme that metabolizes the drug is almost non-existent, causing the accuracy of the equation highly unsatisfactory – only 38 percent of the predictions had less than two-fold errors.
“To make up for the gap, researcher resorted to plugging in scientifically unjustified constants into the equation,” Professor Jung-woo Chae of Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy said. “This is comparable to having to have the epicyclic orbits introduced to explain the motion of the planets back in the days in order to explain the now-defunct Ptolemaic theory, because it was 'THE' theory back then.”
< (From left) Ph.D. student Yun Min Song (KAIST, co-first authors), Professor Sang Kyum Kim (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Jae Kyoung Kim, CI (KAIST, co-corresponding author), Professor Jung-woo Chae (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Ph.D. students Quyen Thi Tran and Ngoc-Anh Thi Vu (Chungnam National University, co-first authors) >
A joint research team composed of mathematicians from the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and pharmacological scientists from the Chungnam National University reported that they identified the major causes of the FDA-recommended equation’s inaccuracies and presented a solution.
When estimating the gut bioavailability (Fg), which is the key parameter of the equation, the fraction absorbed from the gut lumen (Fa) is usually assumed to be 1. However, many experiments have shown that Fa is less than 1, obviously since it can’t be expected that all of the orally taken drugs to be completely absorbed by the intestines. To solve this problem, the research team used an “estimated Fa” value based on factors such as the drug’s transit time, intestine radius, and permeability values and used it to re-calculate Fg.
Also, taking a different approach from the MM equation, the team used an alternative model they derived in a previous study back in 2020, which can more accurately predict the drug metabolism rate regardless of the enzyme concentration. Combining these changes, the modified equation with re-calculated Fg had a dramatically increased accuracy of the resulting estimate. The existing FDA formula predicted drug interactions within a 2-fold margin of error at the rate of 38%, whereas the accuracy rate of the revised formula reached 80%.
“Such drastic improvement in drug-drug interaction prediction accuracy is expected to make great contribution to increasing the success rate of new drug development and drug efficacy in clinical trials. As the results of this study were published in one of the top clinical pharmacology journal, it is expected that the FDA guidance will be revised according to the results of this study.” said Professor Sang Kyum Kim from Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy.
Furthermore, this study highlights the importance of collaborative research between research groups in vastly different disciplines, in a field that is as dynamic as drug interactions.
“Thanks to the collaborative research between mathematics and pharmacy, we were able to recify the formula that we have accepted to be the right answer for so long to finally grasp on the leads toward healthier life for mankind.,” said Professor Jae Kyung Kim. He continued, “I hope seeing a ‘K-formula’ entered into the US FDA guidance one day.”
The results of this study were published in the online edition of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (IF 7.051), an authoritative journal in the field of clinical pharmacology, on December 15, 2022 (Korean time).
Thesis Title: Beyond the Michaelis-Menten: Accurate Prediction of Drug Interactions through Cytochrome P450 3A4 Induction (doi: 10.1002/cpt.2824)
< Figure 1. The formula proposed by the FDA guidance for predicting drug-drug interactions (top) and the formula newly derived by the researchers (bottom). AUCR (the ratio of substrate area under the plasma concentration-time curve) represents the rate of change in drug concentration due to drug interactions. The research team more than doubled the accuracy of drug interaction prediction compared to the existing formula. >
< Figure 2. Existing FDA formulas tend to underestimate the extent of drug-drug interactions (gray dots) than the actual measured values. On the other hand, the newly derived equation (red dot) has a prediction rate that is within the error range of 2 times (0.5 to 2 times) of the measured value, and is more than twice as high as the existing equation. The solid line in the figure represents the predicted value that matches the measured value. The dotted line represents the predicted value with an error of 0.5 to 2 times. >
For further information or to request media assistance, please contact Jae Kyoung Kim at Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science (IBS) (jaekkim@ibs.re.kr) or William I. Suh at the IBS Communications Team (willisuh@ibs.re.kr).
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
IBS was founded in 2011 by the government of the Republic of Korea with the sole purpose of driving forward the development of basic science in South Korea. IBS has 4 research institutes and 33 research centers as of January 2023. There are eleven physics, three mathematics, five chemistry, nine life science, two earth science, and three interdisciplinary research centers.
2023.01.18 View 14723
Scientists re-writes FDA-recommended equation to improve estimation of drug-drug interaction
Drugs absorbed into the body are metabolized and thus removed by enzymes from several organs like the liver. How fast a drug is cleared out of the system can be affected by other drugs that are taken together because added substance can increase the amount of enzyme secretion in the body. This dramatically decreases the concentration of a drug, reducing its efficacy, often leading to the failure of having any effect at all. Therefore, accurately predicting the clearance rate in the presence of drug-drug interaction* is critical in the process of drug prescription and development of a new drug in order to ensure its efficacy and/or to avoid unwanted side-effects.
*Drug-drug interaction: In terms of metabolism, drug-drug interaction is a phenomenon in which one drug changes the metabolism of another drug to promote or inhibit its excretion from the body when two or more drugs are taken together. As a result, it increases the toxicity of medicines or causes loss of efficacy.
Since it is practically impossible to evaluate all interactions between new drug candidates and all marketed drugs during the development process, the FDA recommends indirect evaluation of drug interactions using a formula suggested in their guidance, first published in 1997, revised in January of 2020, in order to evaluate drug interactions and minimize side effects of having to use more than one type of drugs at once.
The formula relies on the 110-year-old Michaelis-Menten (MM) model, which has a fundamental limit of making a very broad and groundless assumption on the part of the presence of the enzymes that metabolizes the drug. While MM equation has been one of the most widely known equations in biochemistry used in more than 220,000 published papers, the MM equation is accurate only when the concentration of the enzyme that metabolizes the drug is almost non-existent, causing the accuracy of the equation highly unsatisfactory – only 38 percent of the predictions had less than two-fold errors.
“To make up for the gap, researcher resorted to plugging in scientifically unjustified constants into the equation,” Professor Jung-woo Chae of Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy said. “This is comparable to having to have the epicyclic orbits introduced to explain the motion of the planets back in the days in order to explain the now-defunct Ptolemaic theory, because it was 'THE' theory back then.”
< (From left) Ph.D. student Yun Min Song (KAIST, co-first authors), Professor Sang Kyum Kim (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Jae Kyoung Kim, CI (KAIST, co-corresponding author), Professor Jung-woo Chae (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Ph.D. students Quyen Thi Tran and Ngoc-Anh Thi Vu (Chungnam National University, co-first authors) >
A joint research team composed of mathematicians from the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and pharmacological scientists from the Chungnam National University reported that they identified the major causes of the FDA-recommended equation’s inaccuracies and presented a solution.
When estimating the gut bioavailability (Fg), which is the key parameter of the equation, the fraction absorbed from the gut lumen (Fa) is usually assumed to be 1. However, many experiments have shown that Fa is less than 1, obviously since it can’t be expected that all of the orally taken drugs to be completely absorbed by the intestines. To solve this problem, the research team used an “estimated Fa” value based on factors such as the drug’s transit time, intestine radius, and permeability values and used it to re-calculate Fg.
Also, taking a different approach from the MM equation, the team used an alternative model they derived in a previous study back in 2020, which can more accurately predict the drug metabolism rate regardless of the enzyme concentration. Combining these changes, the modified equation with re-calculated Fg had a dramatically increased accuracy of the resulting estimate. The existing FDA formula predicted drug interactions within a 2-fold margin of error at the rate of 38%, whereas the accuracy rate of the revised formula reached 80%.
“Such drastic improvement in drug-drug interaction prediction accuracy is expected to make great contribution to increasing the success rate of new drug development and drug efficacy in clinical trials. As the results of this study were published in one of the top clinical pharmacology journal, it is expected that the FDA guidance will be revised according to the results of this study.” said Professor Sang Kyum Kim from Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy.
Furthermore, this study highlights the importance of collaborative research between research groups in vastly different disciplines, in a field that is as dynamic as drug interactions.
“Thanks to the collaborative research between mathematics and pharmacy, we were able to recify the formula that we have accepted to be the right answer for so long to finally grasp on the leads toward healthier life for mankind.,” said Professor Jae Kyung Kim. He continued, “I hope seeing a ‘K-formula’ entered into the US FDA guidance one day.”
The results of this study were published in the online edition of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (IF 7.051), an authoritative journal in the field of clinical pharmacology, on December 15, 2022 (Korean time).
Thesis Title: Beyond the Michaelis-Menten: Accurate Prediction of Drug Interactions through Cytochrome P450 3A4 Induction (doi: 10.1002/cpt.2824)
< Figure 1. The formula proposed by the FDA guidance for predicting drug-drug interactions (top) and the formula newly derived by the researchers (bottom). AUCR (the ratio of substrate area under the plasma concentration-time curve) represents the rate of change in drug concentration due to drug interactions. The research team more than doubled the accuracy of drug interaction prediction compared to the existing formula. >
< Figure 2. Existing FDA formulas tend to underestimate the extent of drug-drug interactions (gray dots) than the actual measured values. On the other hand, the newly derived equation (red dot) has a prediction rate that is within the error range of 2 times (0.5 to 2 times) of the measured value, and is more than twice as high as the existing equation. The solid line in the figure represents the predicted value that matches the measured value. The dotted line represents the predicted value with an error of 0.5 to 2 times. >
For further information or to request media assistance, please contact Jae Kyoung Kim at Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science (IBS) (jaekkim@ibs.re.kr) or William I. Suh at the IBS Communications Team (willisuh@ibs.re.kr).
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
IBS was founded in 2011 by the government of the Republic of Korea with the sole purpose of driving forward the development of basic science in South Korea. IBS has 4 research institutes and 33 research centers as of January 2023. There are eleven physics, three mathematics, five chemistry, nine life science, two earth science, and three interdisciplinary research centers.
2023.01.18 View 14723 -
 UAE Space Program Leaders named to be the 1st of the honorees of KAIST Alumni Association's special recognition for graduates of foreign nationality
The KAIST Alumni Association (Chairman, Chil-Hee Chung) announced on the 12th that the winners of the 2023 KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award and International Alumni Award has been selected.
The KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award, which produced the first recipient in 1992, is an award given to alumni who have contributed to the development of the nation and society, or who have glorified the honor of their alma mater with outstanding academic achievements and social and/or communal contributions.
On a special note, this year, there has been an addition to the honors, “the KAIST Distinguished International Alumni Award” to honor and encourage overseas alumni who are making their marks in the international community that will boost positive recognition of KAIST in the global setting and will later become a bridge that will expedite Korea's international efforts in the future.
As of 2022, the number of international students who succeeded in earning KAIST degrees has exceeded 1,700, and they are actively doing their part back in their home countries as leaders in various fields in which they belong, spanning from science and technology, to politics, industry and other corners of the society.
(From left) Omran Sharaf, the Assistant Minister of UAE Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation for Advanced Science and Technology, Amer Al Sayegh the Director General of Space Project at MBRSC, and Mohammed Al Harmi the Director General of Administration at MBRSC (Photos provided by the courtesy of MBRSC)
To celebrate and honor their outstanding achievements, the KAIST Alumni Association selected a team of three alumni of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) to receive the Distinguished International Alumni Award for the first time. The named honorees are Omran Sharaf, a master’s graduate from the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy, and Amer Al Sayegh and Mohammed Al Harmi, master’s graduates of the Department of Aerospace Engineering - all three of the class of 2013 in leading positions in the UAE space program to lead the advancement of the science and technology of the country.
Currently, the three alums are in directorship of the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) with Mr. Omran Sharaf, who has recently been appointed as the Assistant Minister in charge of Advanced Science and Technology at the UAE Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation, being the Project Director of the Emirates Mars Mission of MBRSC and Mr. Amer Al Sayegh in the Director General position in charge of Space Project and Mr. Mohammed Al Harmi, the Director General of Administration, at MBRSC.
They received technology transfer from “SatRec I”, Korea's first satellite system exporter and KAIST alumni company, for about 10 years from 2006, while carrying out their master’s studies at the same time.
Afterwards, they returned to UAE to lead the Emirates Mars Mission, which is already showing tangible progress including the successful launch of the Mars probe "Amal" (ال امل, meaning ‘Hope’ in Arabic), which was the first in the Arab world and the fifth in the world to successfully enter into orbit around Mars, and the UAE’s first independently developed Earth observation satellite "KhalifaSat".
An official from the KAIST Alumni Association said, "We selected the Distinguished International Alumni after evaluating their industrious leadership in promoting various space industry strategies, ranging from the development of Mars probes and Earth observation satellites, as well as lunar exploration, asteroid exploration, and Mars residence plans."
(From left) Joo-Sun Choi, President & CEO of Samsung Display Co. Ltd., Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), Kyunghyun Cho, Professor of New York University (NYU)
Also, four of the Korean graduates, Joo-Sun Choi, the CEO of Samsung Display, Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), and Kyunghyun Cho, a Professor of New York University (NYU), were selected as the winners of the “Distinguished Alumni Award”.
Mr. Joo-Sun Choi (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1989, Ph.D. in 1995), the CEO of Samsung Display, led the successful development and mass-production of the world's first ultra-high-definition QD-OLED Displays, and preemptively transformed the structure of business of the industry and has been leading the way in technological innovation.
Mr. Jung Goo Cho (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D. in 1992), the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., developed wireless power technology for the first time in Korea in the early 2000s and applied it to semiconductor/display lines and led the wireless power charging technology in various fields, such as developing KAIST On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEV) and commercializing the world's first wireless charger for 11kW electric vehicles.
Mr. Jong Seung Park (Mechanical Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D., in 1991), The President of ADD is an expert with abundant science and technology knowledge and organizational management capabilities. He is contributing greatly to national defense and security through science and technology.
Mr. Kyunghyun Cho (Computer Science, B.S., in 2009), the Professor of Computer Science and Data Science at NYU, is a world-renowned expert in Artificial Intelligence (AI), advancing the concept of 'Neural Machine Translation' in the field of natural language processing, to make great contributions to AI translation technology and related industries.
Chairman Chil-Hee Chung, the 26th Chair of KAIST Alumni Association “As each year goes by, I feel that the influence of KAIST alumni goes beyond science and technology to affect our society as a whole.” He went on to say, “This year, as it was more meaningful to extend the award to honor the international members of our Alums, we look forward to seeing more of our alumni continuing their social and academic endeavors to play an active role in the global stage in taking on the global challenges.”
The Ceremony for KAIST Distinguished Alumni and International Alumni Award Honorees will be conducted at the Annual New Year’s Event of KAIST Alumni Association for 2023 to be held on Friday, January 13th, at the Grand InterContinental Seoul Parnas.
2023.01.12 View 17031
UAE Space Program Leaders named to be the 1st of the honorees of KAIST Alumni Association's special recognition for graduates of foreign nationality
The KAIST Alumni Association (Chairman, Chil-Hee Chung) announced on the 12th that the winners of the 2023 KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award and International Alumni Award has been selected.
The KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award, which produced the first recipient in 1992, is an award given to alumni who have contributed to the development of the nation and society, or who have glorified the honor of their alma mater with outstanding academic achievements and social and/or communal contributions.
On a special note, this year, there has been an addition to the honors, “the KAIST Distinguished International Alumni Award” to honor and encourage overseas alumni who are making their marks in the international community that will boost positive recognition of KAIST in the global setting and will later become a bridge that will expedite Korea's international efforts in the future.
As of 2022, the number of international students who succeeded in earning KAIST degrees has exceeded 1,700, and they are actively doing their part back in their home countries as leaders in various fields in which they belong, spanning from science and technology, to politics, industry and other corners of the society.
(From left) Omran Sharaf, the Assistant Minister of UAE Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation for Advanced Science and Technology, Amer Al Sayegh the Director General of Space Project at MBRSC, and Mohammed Al Harmi the Director General of Administration at MBRSC (Photos provided by the courtesy of MBRSC)
To celebrate and honor their outstanding achievements, the KAIST Alumni Association selected a team of three alumni of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) to receive the Distinguished International Alumni Award for the first time. The named honorees are Omran Sharaf, a master’s graduate from the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy, and Amer Al Sayegh and Mohammed Al Harmi, master’s graduates of the Department of Aerospace Engineering - all three of the class of 2013 in leading positions in the UAE space program to lead the advancement of the science and technology of the country.
Currently, the three alums are in directorship of the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) with Mr. Omran Sharaf, who has recently been appointed as the Assistant Minister in charge of Advanced Science and Technology at the UAE Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation, being the Project Director of the Emirates Mars Mission of MBRSC and Mr. Amer Al Sayegh in the Director General position in charge of Space Project and Mr. Mohammed Al Harmi, the Director General of Administration, at MBRSC.
They received technology transfer from “SatRec I”, Korea's first satellite system exporter and KAIST alumni company, for about 10 years from 2006, while carrying out their master’s studies at the same time.
Afterwards, they returned to UAE to lead the Emirates Mars Mission, which is already showing tangible progress including the successful launch of the Mars probe "Amal" (ال امل, meaning ‘Hope’ in Arabic), which was the first in the Arab world and the fifth in the world to successfully enter into orbit around Mars, and the UAE’s first independently developed Earth observation satellite "KhalifaSat".
An official from the KAIST Alumni Association said, "We selected the Distinguished International Alumni after evaluating their industrious leadership in promoting various space industry strategies, ranging from the development of Mars probes and Earth observation satellites, as well as lunar exploration, asteroid exploration, and Mars residence plans."
(From left) Joo-Sun Choi, President & CEO of Samsung Display Co. Ltd., Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), Kyunghyun Cho, Professor of New York University (NYU)
Also, four of the Korean graduates, Joo-Sun Choi, the CEO of Samsung Display, Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), and Kyunghyun Cho, a Professor of New York University (NYU), were selected as the winners of the “Distinguished Alumni Award”.
Mr. Joo-Sun Choi (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1989, Ph.D. in 1995), the CEO of Samsung Display, led the successful development and mass-production of the world's first ultra-high-definition QD-OLED Displays, and preemptively transformed the structure of business of the industry and has been leading the way in technological innovation.
Mr. Jung Goo Cho (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D. in 1992), the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., developed wireless power technology for the first time in Korea in the early 2000s and applied it to semiconductor/display lines and led the wireless power charging technology in various fields, such as developing KAIST On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEV) and commercializing the world's first wireless charger for 11kW electric vehicles.
Mr. Jong Seung Park (Mechanical Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D., in 1991), The President of ADD is an expert with abundant science and technology knowledge and organizational management capabilities. He is contributing greatly to national defense and security through science and technology.
Mr. Kyunghyun Cho (Computer Science, B.S., in 2009), the Professor of Computer Science and Data Science at NYU, is a world-renowned expert in Artificial Intelligence (AI), advancing the concept of 'Neural Machine Translation' in the field of natural language processing, to make great contributions to AI translation technology and related industries.
Chairman Chil-Hee Chung, the 26th Chair of KAIST Alumni Association “As each year goes by, I feel that the influence of KAIST alumni goes beyond science and technology to affect our society as a whole.” He went on to say, “This year, as it was more meaningful to extend the award to honor the international members of our Alums, we look forward to seeing more of our alumni continuing their social and academic endeavors to play an active role in the global stage in taking on the global challenges.”
The Ceremony for KAIST Distinguished Alumni and International Alumni Award Honorees will be conducted at the Annual New Year’s Event of KAIST Alumni Association for 2023 to be held on Friday, January 13th, at the Grand InterContinental Seoul Parnas.
2023.01.12 View 17031 -
 KAIST to showcase a pack of KAIST Start-ups at CES 2023
- KAIST is to run an Exclusive Booth at the Venetian Expo (Hall G) in Eureka Park, at CES 2023, to be held in Las Vegas from Thursday, January 5th through Sunday, the 8th.
- Twelve businesses recently put together by KAIST faculty, alumni, and the start-ups given legal usage of KAIST technologies will be showcased.
- Out of the participating start-ups, the products by Fluiz and Hills Robotics were selected as the “CES Innovation Award 2023 Honoree”, scoring top in their respective categories.
On January 3, KAIST announced that there will be a KAIST booth at Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2023, the most influential tech event in the world, to be held in Las Vegas from January 3 to 8.
At this exclusive corner, KAIST will introduce the technologies of KAIST start-ups over the exhibition period.
KAIST first started holding its exclusive booth in CES 2019 with five start-up businesses, following up at CES 2020 with 12 start-ups and at CES 2022 with 10 start-ups. At CES 2023, which would be KAIST’s fourth conference, KAIST will be accompanying 12 businesses including start-ups by the faculty members, alumni, and technology transfer companies that just began their businesses with technologies from their research findings that stands a head above others.
To maximize the publicity opportunity, KAIST will support each company’s marketing strategies through cooperation with the Korea International Trade Association (KITA), and provide an opportunity for the school and each startup to create global identity and exhibit the excellence of their technologies at the convention.
The following companies will be at the KAIST Booth in Eureka Park:
The twelve startups mentioned above aim to achieve global technology commecialization in their respective fields of expertise spanning from eXtended Reality (XR) and gaming, to AI and robotics, vehicle and transport, mobile platform, smart city, autonomous driving, healthcare, internet of thing (IoT), through joint research and development, technology transfer and investment attraction from world’s leading institutions and enterprises.
In particular, Fluiz and Hills Robotics won the CES Innovation Award as 2023 Honorees and is expected to attain greater achievements in the future.
A staff member from the KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation said, “The KAIST Showcase for CES 2023 has prepared a new pitching space for each of the companies for their own IR efforts, and we hope that KAIST startups will actively and effectively market their products and technologies while they are at the convention. We hope it will help them utilize their time here to establish their name in presence here which will eventually serve as a good foothold for them and their predecessors to further global commercialization goals.”
2023.01.04 View 17678
KAIST to showcase a pack of KAIST Start-ups at CES 2023
- KAIST is to run an Exclusive Booth at the Venetian Expo (Hall G) in Eureka Park, at CES 2023, to be held in Las Vegas from Thursday, January 5th through Sunday, the 8th.
- Twelve businesses recently put together by KAIST faculty, alumni, and the start-ups given legal usage of KAIST technologies will be showcased.
- Out of the participating start-ups, the products by Fluiz and Hills Robotics were selected as the “CES Innovation Award 2023 Honoree”, scoring top in their respective categories.
On January 3, KAIST announced that there will be a KAIST booth at Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2023, the most influential tech event in the world, to be held in Las Vegas from January 3 to 8.
At this exclusive corner, KAIST will introduce the technologies of KAIST start-ups over the exhibition period.
KAIST first started holding its exclusive booth in CES 2019 with five start-up businesses, following up at CES 2020 with 12 start-ups and at CES 2022 with 10 start-ups. At CES 2023, which would be KAIST’s fourth conference, KAIST will be accompanying 12 businesses including start-ups by the faculty members, alumni, and technology transfer companies that just began their businesses with technologies from their research findings that stands a head above others.
To maximize the publicity opportunity, KAIST will support each company’s marketing strategies through cooperation with the Korea International Trade Association (KITA), and provide an opportunity for the school and each startup to create global identity and exhibit the excellence of their technologies at the convention.
The following companies will be at the KAIST Booth in Eureka Park:
The twelve startups mentioned above aim to achieve global technology commecialization in their respective fields of expertise spanning from eXtended Reality (XR) and gaming, to AI and robotics, vehicle and transport, mobile platform, smart city, autonomous driving, healthcare, internet of thing (IoT), through joint research and development, technology transfer and investment attraction from world’s leading institutions and enterprises.
In particular, Fluiz and Hills Robotics won the CES Innovation Award as 2023 Honorees and is expected to attain greater achievements in the future.
A staff member from the KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation said, “The KAIST Showcase for CES 2023 has prepared a new pitching space for each of the companies for their own IR efforts, and we hope that KAIST startups will actively and effectively market their products and technologies while they are at the convention. We hope it will help them utilize their time here to establish their name in presence here which will eventually serve as a good foothold for them and their predecessors to further global commercialization goals.”
2023.01.04 View 17678 -
 A Quick but Clingy Creepy-Crawler that will MARVEL You
Engineered by KAIST Mechanics, a quadrupedal robot climbs steel walls and crawls across metal ceilings at the fastest speed that the world has ever seen.
< Photo 1. (From left) KAIST ME Prof. Hae-Won Park, Ph.D. Student Yong Um, Ph.D. Student Seungwoo Hong >
- Professor Hae-Won Park's team at the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal robot that can move at a high speed on ferrous walls and ceilings.
- It is expected to make a wide variety of contributions as it is to be used to conduct inspections and repairs of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, and transmission towers, offering an alternative to dangerous or risky activities required in hazardous environments while maintaining productivity and efficiency through automation and unmanning of such operations.
- The study was published as the cover paper of the December issue of Science Robotics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that a research team led by Professor Hae-Won Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal walking robot that can move at high speed on steel walls and ceilings named M.A.R.V.E.L. - rightly so as it is a Magnetically Adhesive Robot for Versatile and Expeditious Locomotion as described in their paper, “Agile and Versatile Climbing on Ferromagnetic Surfaces with a Quadrupedal Robot.” (DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.add1017)
To make this happen, Professor Park's research team developed a foot pad that can quickly turn the magnetic adhesive force on and off while retaining high adhesive force even on an uneven surface through the use of the Electro-Permanent Magnet (EPM), a device that can magnetize and demagnetize an electromagnet with little power, and the Magneto-Rheological Elastomer (MRE), an elastic material made by mixing a magnetic response factor, such as iron powder, with an elastic material, such as rubber, which they mounted on a small quadrupedal robot they made in-house, at their own laboratory. These walking robots are expected to be put into a wide variety of usage, including being programmed to perform inspections, repairs, and maintenance tasks on large structures made of steel, such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, large storage areas, and construction sites.
This study, in which Seungwoo Hong and Yong Um of the Department of Mechanical Engineering participated as co-first authors, was published as the cover paper in the December issue of Science Robotics.
< Image on the Cover of 2022 December issue of Science Robotics >
Existing wall-climbing robots use wheels or endless tracks, so their mobility is limited on surfaces with steps or irregularities. On the other hand, walking robots for climbing can expect improved mobility in obstacle terrain, but have disadvantages in that they have significantly slower moving speeds or cannot perform various movements.
In order to enable fast movement of the walking robot, the sole of the foot must have strong adhesion force and be able to control the adhesion to quickly switch from sticking to the surface or to be off of it. In addition, it is necessary to maintain the adhesion force even on a rough or uneven surface.
To solve this problem, the research team used the EPM and MRE for the first time in designing the soles of walking robots. An EPM is a magnet that can turn on and off the electromagnetic force with a short current pulse. Unlike general electromagnets, it has the advantage that it does not require energy to maintain the magnetic force. The research team proposed a new EPM with a rectangular structure arrangement, enabling faster switching while significantly lowering the voltage required for switching compared to existing electromagnets.
In addition, the research team was able to increase the frictional force without significantly reducing the magnetic force of the sole by covering the sole with an MRE. The proposed sole weighs only 169 g, but provides a vertical gripping force of about *535 Newtons (N) and a frictional force of 445 N, which is sufficient gripping force for a quadrupedal robot weighing 8 kg.
* 535 N converted to kg is 54.5 kg, and 445 N is 45.4 kg. In other words, even if an external force of up to 54.5 kg in the vertical direction and up to 45.4 kg in the horizontal direction is applied (or even if a corresponding weight is hung), the sole of the foot does not come off the steel plate.
MARVEL climbed up a vertical wall at high speed at a speed of 70 cm per second, and was able to walk while hanging upside down from the ceiling at a maximum speed of 50 cm per second. This is the world's fastest speed for a walking climbing robot. In addition, the research team demonstrated that the robot can climb at a speed of up to 35 cm even on a surface that is painted, dirty with dust and the rust-tainted surfaces of water tanks, proving the robot's performance in a real environment. It was experimentally demonstrated that the robot not only exhibited high speed, but also can switch from floor to wall and from wall to ceiling, and overcome 5-cm high obstacles protruding from walls without difficulty.
The new climbing quadrupedal robot is expected to be widely used for inspection, repair, and maintenance of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, oil pipelines, large storage areas, and construction sites. As the works required in these places involves risks such as falls, suffocation and other accidents that may result in serious injuries or casualties, the need for automation is of utmost urgency.
One of the first co-authors of the paper, a Ph.D. student, Yong Um of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, said, "By the use of the magnetic soles made up of the EPM and MRE and the non-linear model predictive controller suitable for climbing, the robot can speedily move through a variety of ferromagnetic surfaces including walls and ceilings, not just level grounds. We believe this would become a cornerstone that will expand the mobility and the places of pedal-mobile robots can venture into." He added, “These robots can be put into good use in executing dangerous and difficult tasks on steel structures in places like the shipbuilding yards.”
This research was carried out with support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers and Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering Co., Ltd..
< Figure 1. The quadrupedal robot (MARVEL) walking over various ferrous surfaces. (A) vertical wall (B) ceiling. (C) over obstacles on a vertical wall (D) making floor-to-wall and wall-to-ceiling transitions (E) moving over a storage tank (F) walking on a wall with a 2-kg weight and over a ceiling with a 3-kg load. >
< Figure 2. Description of the magnetic foot (A) Components of the magnet sole: ankle, Square Eletro-Permanent Magnet(S-EPM), MRE footpad. (B) Components of the S-EPM and MRE footpad. (C) Working principle of the S-EPM. When the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the left figure, magnetic flux comes out of the keeper and circulates through the steel plate, generating holding force (ON state). Conversely, if the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the figure on the right, the magnetic flux circulates inside the S-EPM and the holding force disappears (OFF state). >
Video Introduction: Agile and versatile climbing on ferromagnetic surfaces with a quadrupedal robot - YouTube
2022.12.30 View 18982
A Quick but Clingy Creepy-Crawler that will MARVEL You
Engineered by KAIST Mechanics, a quadrupedal robot climbs steel walls and crawls across metal ceilings at the fastest speed that the world has ever seen.
< Photo 1. (From left) KAIST ME Prof. Hae-Won Park, Ph.D. Student Yong Um, Ph.D. Student Seungwoo Hong >
- Professor Hae-Won Park's team at the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal robot that can move at a high speed on ferrous walls and ceilings.
- It is expected to make a wide variety of contributions as it is to be used to conduct inspections and repairs of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, and transmission towers, offering an alternative to dangerous or risky activities required in hazardous environments while maintaining productivity and efficiency through automation and unmanning of such operations.
- The study was published as the cover paper of the December issue of Science Robotics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that a research team led by Professor Hae-Won Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal walking robot that can move at high speed on steel walls and ceilings named M.A.R.V.E.L. - rightly so as it is a Magnetically Adhesive Robot for Versatile and Expeditious Locomotion as described in their paper, “Agile and Versatile Climbing on Ferromagnetic Surfaces with a Quadrupedal Robot.” (DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.add1017)
To make this happen, Professor Park's research team developed a foot pad that can quickly turn the magnetic adhesive force on and off while retaining high adhesive force even on an uneven surface through the use of the Electro-Permanent Magnet (EPM), a device that can magnetize and demagnetize an electromagnet with little power, and the Magneto-Rheological Elastomer (MRE), an elastic material made by mixing a magnetic response factor, such as iron powder, with an elastic material, such as rubber, which they mounted on a small quadrupedal robot they made in-house, at their own laboratory. These walking robots are expected to be put into a wide variety of usage, including being programmed to perform inspections, repairs, and maintenance tasks on large structures made of steel, such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, large storage areas, and construction sites.
This study, in which Seungwoo Hong and Yong Um of the Department of Mechanical Engineering participated as co-first authors, was published as the cover paper in the December issue of Science Robotics.
< Image on the Cover of 2022 December issue of Science Robotics >
Existing wall-climbing robots use wheels or endless tracks, so their mobility is limited on surfaces with steps or irregularities. On the other hand, walking robots for climbing can expect improved mobility in obstacle terrain, but have disadvantages in that they have significantly slower moving speeds or cannot perform various movements.
In order to enable fast movement of the walking robot, the sole of the foot must have strong adhesion force and be able to control the adhesion to quickly switch from sticking to the surface or to be off of it. In addition, it is necessary to maintain the adhesion force even on a rough or uneven surface.
To solve this problem, the research team used the EPM and MRE for the first time in designing the soles of walking robots. An EPM is a magnet that can turn on and off the electromagnetic force with a short current pulse. Unlike general electromagnets, it has the advantage that it does not require energy to maintain the magnetic force. The research team proposed a new EPM with a rectangular structure arrangement, enabling faster switching while significantly lowering the voltage required for switching compared to existing electromagnets.
In addition, the research team was able to increase the frictional force without significantly reducing the magnetic force of the sole by covering the sole with an MRE. The proposed sole weighs only 169 g, but provides a vertical gripping force of about *535 Newtons (N) and a frictional force of 445 N, which is sufficient gripping force for a quadrupedal robot weighing 8 kg.
* 535 N converted to kg is 54.5 kg, and 445 N is 45.4 kg. In other words, even if an external force of up to 54.5 kg in the vertical direction and up to 45.4 kg in the horizontal direction is applied (or even if a corresponding weight is hung), the sole of the foot does not come off the steel plate.
MARVEL climbed up a vertical wall at high speed at a speed of 70 cm per second, and was able to walk while hanging upside down from the ceiling at a maximum speed of 50 cm per second. This is the world's fastest speed for a walking climbing robot. In addition, the research team demonstrated that the robot can climb at a speed of up to 35 cm even on a surface that is painted, dirty with dust and the rust-tainted surfaces of water tanks, proving the robot's performance in a real environment. It was experimentally demonstrated that the robot not only exhibited high speed, but also can switch from floor to wall and from wall to ceiling, and overcome 5-cm high obstacles protruding from walls without difficulty.
The new climbing quadrupedal robot is expected to be widely used for inspection, repair, and maintenance of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, oil pipelines, large storage areas, and construction sites. As the works required in these places involves risks such as falls, suffocation and other accidents that may result in serious injuries or casualties, the need for automation is of utmost urgency.
One of the first co-authors of the paper, a Ph.D. student, Yong Um of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, said, "By the use of the magnetic soles made up of the EPM and MRE and the non-linear model predictive controller suitable for climbing, the robot can speedily move through a variety of ferromagnetic surfaces including walls and ceilings, not just level grounds. We believe this would become a cornerstone that will expand the mobility and the places of pedal-mobile robots can venture into." He added, “These robots can be put into good use in executing dangerous and difficult tasks on steel structures in places like the shipbuilding yards.”
This research was carried out with support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers and Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering Co., Ltd..
< Figure 1. The quadrupedal robot (MARVEL) walking over various ferrous surfaces. (A) vertical wall (B) ceiling. (C) over obstacles on a vertical wall (D) making floor-to-wall and wall-to-ceiling transitions (E) moving over a storage tank (F) walking on a wall with a 2-kg weight and over a ceiling with a 3-kg load. >
< Figure 2. Description of the magnetic foot (A) Components of the magnet sole: ankle, Square Eletro-Permanent Magnet(S-EPM), MRE footpad. (B) Components of the S-EPM and MRE footpad. (C) Working principle of the S-EPM. When the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the left figure, magnetic flux comes out of the keeper and circulates through the steel plate, generating holding force (ON state). Conversely, if the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the figure on the right, the magnetic flux circulates inside the S-EPM and the holding force disappears (OFF state). >
Video Introduction: Agile and versatile climbing on ferromagnetic surfaces with a quadrupedal robot - YouTube
2022.12.30 View 18982 -
 2022 Global Startup Internship Fair (GSIF)
From November 30 to December 1, 2022, the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST held the 2022 Global Startup Internship Fair (GSIF) on-line and off-line, as well.
Including the globally acknowledged unicorn companies such as PsiQuantum and Moloco, eleven startups — ImpriMed, Vessel AI, Genedit, Medic Life Sciences, Bringko, Brave Turtles, Neozips, Luckmon and CUPIX — joined the fair. Among the eleven invited companies, six were founded by KAIST Alumni representatives. The invited companies sought student interns in the field of AI, biotechnology, quantum, logistics, games, advertisement, real estate, and e-commerce. In response, about 100 KAIST students with various backgrounds have shown their interest in the event through pre-reservation.
Participating companies at this fair introduced their companies and conducted recruitment and career counseling with KAIST students. Sungwon Lim, the CEO of ImpriMed and a KAIST alumni, said, “It was very meaningful to introduce ImpriMed to junior students and share my experiences that I gained while pioneering and operating startups in the United States.” To share his journey as a global startup CEO, Lim has been invited as an off-line speaker during this event.
< ImpriMed CEO, Sungwon Lim >
In addition to the recruiting sessions, the fair held information sessions offering guidelines and useful tips on seeking opportunities overseas including information on obtaining a J1 visa, applying to U.S. internships, relocating to Silicon Valley, and writing CVs, cover letters, and business emails.
Professor Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President of the International Office at KAIST, stressed, “A growing number of students at KAIST want to become a global entrepreneur, and hands-on experience gained from U.S. startups is absolutely necessary to achieve their goals.” He added, “the 2022 GSIF was one of those opportunities for KAIST students to further their dream of becoming global leaders.”
2022.12.01 View 7726
2022 Global Startup Internship Fair (GSIF)
From November 30 to December 1, 2022, the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST held the 2022 Global Startup Internship Fair (GSIF) on-line and off-line, as well.
Including the globally acknowledged unicorn companies such as PsiQuantum and Moloco, eleven startups — ImpriMed, Vessel AI, Genedit, Medic Life Sciences, Bringko, Brave Turtles, Neozips, Luckmon and CUPIX — joined the fair. Among the eleven invited companies, six were founded by KAIST Alumni representatives. The invited companies sought student interns in the field of AI, biotechnology, quantum, logistics, games, advertisement, real estate, and e-commerce. In response, about 100 KAIST students with various backgrounds have shown their interest in the event through pre-reservation.
Participating companies at this fair introduced their companies and conducted recruitment and career counseling with KAIST students. Sungwon Lim, the CEO of ImpriMed and a KAIST alumni, said, “It was very meaningful to introduce ImpriMed to junior students and share my experiences that I gained while pioneering and operating startups in the United States.” To share his journey as a global startup CEO, Lim has been invited as an off-line speaker during this event.
< ImpriMed CEO, Sungwon Lim >
In addition to the recruiting sessions, the fair held information sessions offering guidelines and useful tips on seeking opportunities overseas including information on obtaining a J1 visa, applying to U.S. internships, relocating to Silicon Valley, and writing CVs, cover letters, and business emails.
Professor Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President of the International Office at KAIST, stressed, “A growing number of students at KAIST want to become a global entrepreneur, and hands-on experience gained from U.S. startups is absolutely necessary to achieve their goals.” He added, “the 2022 GSIF was one of those opportunities for KAIST students to further their dream of becoming global leaders.”
2022.12.01 View 7726 -
 “3D sketch” Your Ideas and Bring Them to Life, Instantly!
Professor Seok-Hyung Bae’s research team at the Department of Industrial Design developed a novel 3D sketching system that rapidly creates animated 3D concepts through simple user interactions like sketching on a piece of paper or playing a toy.
Foldable drones, transforming vehicles, and multi-legged robots from sci-fi movies are now becoming commonplace thanks to technological progress. However, designing them remains a difficult challenge even for skilled experts, because complex design decisions must be made regarding not only their form, but also the structure, poses, and motions, which are interdependent on one another.
Creating a 3D concept comprising of multiple moving parts connected by different types of joints using a traditional 3D CAD tool, which is more suited for processing precise and elaborate modeling, is a painstaking and time-consuming process. This presents a major bottleneck for the workflow during the early stage of design, in which it is preferred that as many ideas are tried and discarded out as quickly as possible in order to explore a wide range of possibilities in the shortest amount of time.
A research team led by Professor Bae has focused on designers’ freehand sketches drew up with a pen on a paper that serve as the starting point for virtually all design projects. This led them to develop their 3D sketching technology to generate desired 3D curves from the rough but expressive 2D strokes drawn with a digital stylus on a digital tablet.
Their latest research helps designers bring their 3D sketches to life almost instantly. Using the intuitive set of multi-touch gestures the team successfully designed and implemented, designers can handle the 3D sketches they are working on with their fingers as if they are playing with toys and put them into animation in no time.
< Figure 1. A novel 3D sketching system for rapidly designing articulated 3D concepts with a small set of coherent pen and multi-touch gestures. (a) Sketching: A 3D sketch curve is created by marking a pen stroke that is projected onto a sketch plane widget. (b) Segmenting: Entire or partial sketch curves are added to separate parts that serve as links in the kinematic chain. (c) Rigging: Repeatedly demonstrating the desired motion of a part leaves behind a trail, from which the system infers a joint. (d) Posing: Desired poses can be achieved through actuating joints via forward or inverse kinematics. (e) Filming: A sequence of keyframes specifying desired poses and viewpoints is connected as a smooth motion. >
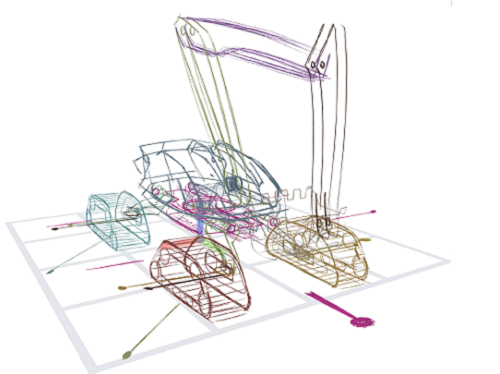
< Figure 2. (a) Concept drawing of an autonomous excavator. It features (b, c) four caterpillars that swivel for high maneuverability, (d) an extendable boom and a bucket connected by multiple links, and (e) a rotating platform. The concept’s designer, who had 8 years of work experience, estimated that it would take 1-2 weeks to express and communicate such a complex articulated object with existing tools. With the proposed system, it took only 2 hours and 52 minutes. >
The major findings of their work were published under the title “Rapid Design of Articulated Objects” in ACM Transactions on Graphics (impact factor: 7.403), the top international journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 (h5-index: 103), the world’s largest international academic conference in the field, which was held back in August in Vancouver, Canada with Joon Hyub Lee, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design as the first author.
The ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 conference was reportedly attended by over 10,000 participants including researchers, artists, and developers from world-renowned universities; film, animation, and game studies, such as Marvel, Pixar, and Blizzard; high-tech manufacturers, such as Lockheed Martin and Boston Dynamics; and metaverse platform companies, such as Meta and Roblox.
< Figure 3. The findings of Professor Bae’s research team were published in ACM Transactions on Graphics, the top international academic journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022, the largest international academic conference held in conjunction early August in Vancouver, Canada. The team’s live demo at the Emerging Technologies program was highly praised by numerous academics and industry officials and received an Honorable Mention. >
The team was also invited to present their technical paper as a demo and a special talk at the Emerging Technologies program at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 as one of the top-three impactful technologies. The live performance, in which Hanbit Kim, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST and a co-author, sketched and animated a sophisticated animal-shaped robot from scratch in a matter of a few minutes, wowed the audience and won the Honorable Mention Award from the jury.
Edwin Catmull, the co-founder of Pixar and a keynote speaker at the SIGGRAPH conference, praised the team’s research on 3D sketching as “really excellent work” and “a kind of tool that would be useful to Pixar's creative model designers.”
This technology, which became virally popular in Japan after featuring in an online IT media outlet and attracting more than 600K views, received a special award from the Digital Content Association of Japan (DCAJ) and was invited and exhibited for three days at Tokyo in November, as a part of Inter BEE 2022, the largest broadcasting and media expo in Japan.
“The more we come to understand how designers think and work, the more effective design tools can be built around that understanding,” said Professor Bae, explaining that “the key is to integrate different algorithms into a harmonious system as intuitive interactions.” He added that “this work wouldn’t have been possible if it weren’t for the convergent research environment cultivated by the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, in which all students see themselves not only as aspiring creative designers, but also as practical engineers.”
By enabling designers to produce highly expressive animated 3D concepts far more quickly and easily in comparison to using existing methods, this new tool is expected to revolutionize design practices and processes in the content creation, manufacturing, and metaverse-related industries.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
More info: https://sketch.kaist.ac.kr/publications/2022_siggraph_rapid_design
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rsBl0QvSDqI
< Figure 4. From left to right: Ph.D. students Hanbit Kim, and Joon Hyub Lee and Professor Bae of the Department of Industrial Design, KAIST >
2022.11.23 View 11895
“3D sketch” Your Ideas and Bring Them to Life, Instantly!
Professor Seok-Hyung Bae’s research team at the Department of Industrial Design developed a novel 3D sketching system that rapidly creates animated 3D concepts through simple user interactions like sketching on a piece of paper or playing a toy.
Foldable drones, transforming vehicles, and multi-legged robots from sci-fi movies are now becoming commonplace thanks to technological progress. However, designing them remains a difficult challenge even for skilled experts, because complex design decisions must be made regarding not only their form, but also the structure, poses, and motions, which are interdependent on one another.
Creating a 3D concept comprising of multiple moving parts connected by different types of joints using a traditional 3D CAD tool, which is more suited for processing precise and elaborate modeling, is a painstaking and time-consuming process. This presents a major bottleneck for the workflow during the early stage of design, in which it is preferred that as many ideas are tried and discarded out as quickly as possible in order to explore a wide range of possibilities in the shortest amount of time.
A research team led by Professor Bae has focused on designers’ freehand sketches drew up with a pen on a paper that serve as the starting point for virtually all design projects. This led them to develop their 3D sketching technology to generate desired 3D curves from the rough but expressive 2D strokes drawn with a digital stylus on a digital tablet.
Their latest research helps designers bring their 3D sketches to life almost instantly. Using the intuitive set of multi-touch gestures the team successfully designed and implemented, designers can handle the 3D sketches they are working on with their fingers as if they are playing with toys and put them into animation in no time.
< Figure 1. A novel 3D sketching system for rapidly designing articulated 3D concepts with a small set of coherent pen and multi-touch gestures. (a) Sketching: A 3D sketch curve is created by marking a pen stroke that is projected onto a sketch plane widget. (b) Segmenting: Entire or partial sketch curves are added to separate parts that serve as links in the kinematic chain. (c) Rigging: Repeatedly demonstrating the desired motion of a part leaves behind a trail, from which the system infers a joint. (d) Posing: Desired poses can be achieved through actuating joints via forward or inverse kinematics. (e) Filming: A sequence of keyframes specifying desired poses and viewpoints is connected as a smooth motion. >
< Figure 2. (a) Concept drawing of an autonomous excavator. It features (b, c) four caterpillars that swivel for high maneuverability, (d) an extendable boom and a bucket connected by multiple links, and (e) a rotating platform. The concept’s designer, who had 8 years of work experience, estimated that it would take 1-2 weeks to express and communicate such a complex articulated object with existing tools. With the proposed system, it took only 2 hours and 52 minutes. >
The major findings of their work were published under the title “Rapid Design of Articulated Objects” in ACM Transactions on Graphics (impact factor: 7.403), the top international journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 (h5-index: 103), the world’s largest international academic conference in the field, which was held back in August in Vancouver, Canada with Joon Hyub Lee, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design as the first author.
The ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 conference was reportedly attended by over 10,000 participants including researchers, artists, and developers from world-renowned universities; film, animation, and game studies, such as Marvel, Pixar, and Blizzard; high-tech manufacturers, such as Lockheed Martin and Boston Dynamics; and metaverse platform companies, such as Meta and Roblox.
< Figure 3. The findings of Professor Bae’s research team were published in ACM Transactions on Graphics, the top international academic journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022, the largest international academic conference held in conjunction early August in Vancouver, Canada. The team’s live demo at the Emerging Technologies program was highly praised by numerous academics and industry officials and received an Honorable Mention. >
The team was also invited to present their technical paper as a demo and a special talk at the Emerging Technologies program at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 as one of the top-three impactful technologies. The live performance, in which Hanbit Kim, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST and a co-author, sketched and animated a sophisticated animal-shaped robot from scratch in a matter of a few minutes, wowed the audience and won the Honorable Mention Award from the jury.
Edwin Catmull, the co-founder of Pixar and a keynote speaker at the SIGGRAPH conference, praised the team’s research on 3D sketching as “really excellent work” and “a kind of tool that would be useful to Pixar's creative model designers.”
This technology, which became virally popular in Japan after featuring in an online IT media outlet and attracting more than 600K views, received a special award from the Digital Content Association of Japan (DCAJ) and was invited and exhibited for three days at Tokyo in November, as a part of Inter BEE 2022, the largest broadcasting and media expo in Japan.
“The more we come to understand how designers think and work, the more effective design tools can be built around that understanding,” said Professor Bae, explaining that “the key is to integrate different algorithms into a harmonious system as intuitive interactions.” He added that “this work wouldn’t have been possible if it weren’t for the convergent research environment cultivated by the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, in which all students see themselves not only as aspiring creative designers, but also as practical engineers.”
By enabling designers to produce highly expressive animated 3D concepts far more quickly and easily in comparison to using existing methods, this new tool is expected to revolutionize design practices and processes in the content creation, manufacturing, and metaverse-related industries.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
More info: https://sketch.kaist.ac.kr/publications/2022_siggraph_rapid_design
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rsBl0QvSDqI
< Figure 4. From left to right: Ph.D. students Hanbit Kim, and Joon Hyub Lee and Professor Bae of the Department of Industrial Design, KAIST >
2022.11.23 View 11895 -
 KAIST Team Develops Surface-Lighting MicroLED Patch with Significant Melanogenesis Inhibition Effect
A KAIST research team led by Ph.d candidate Jae Hee Lee and Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a surface-lighting microLED patch for UV-induced melanogenesis inhibition.
Melanin is brown or dark pigments existing in the skin, which can be abnormally synthesized by external UV or stress. Since the excessive melanin leads to skin diseases such as spots and freckles, proper treatment is required to return normal skin condition.
Recently, LED-based photo-stimulators have been released for skin care, however, their therapeutic effect is still controversial. Since conventional LED stimulators cannot conformally attach to the human skin, distance-induced side effects are caused by light loss and high heat transfer. To achieve effective phototreatment, the LED stimulator needs to be irradiated in contact with the human skin surface, enabling proper and uniform light deliver to the dermis with minimal optical loss.
In this work, the research team fabricated skin-attachable surface-lighting microLED (SµLED, 4 × 4 cm2) patch by utilizing a thousand of microLED chips and silica-embedded light diffusion layer. 100 µm-sized LED chips are vertically-interconnected for high flexibility and low heat generation, allowing its long-term operation on the human skin.
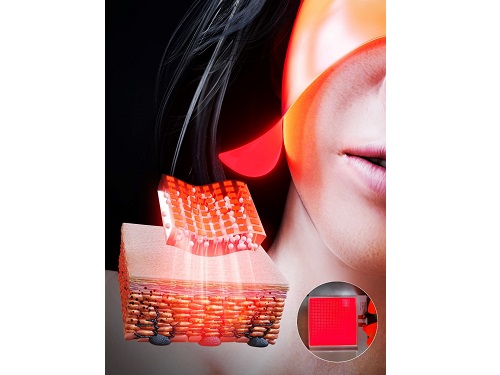
< Image 1. The overall concept of SµLED patch. a) SµLED patch operated on the human skin. b) Schematic illustration of SµLED patch structure. c) 4 × 4 cm2-sized SµLED patch. d) Schematic illustration of the advantages of SµLED patch such as efficient light delivery, low heat generation, and surface-lighting irradiation. >
The research team confirmed melanogenesis inhibition by irradiating the SµLED patch and the conventional LED (CLED) on the artificial human skin and mice dorsal skin. The SµLED-treated groups of human cells and mouse tissues showed minimal epidermal photo-toxicity and consistently effective reduction in synthesized melanin, compared to CLED-treated groups. In addition, significant suppression of proteins/catalysts expression involved in melanin synthesis such as MITF (microphthalmia-associated transcription factor), Melan-A and tyrosinase was verified.
< Image 2. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on 3D human skin cells. a). Different irradiation conditions for a-MSH (major factor to stimulate melanin synthesis) treated cells. b) The ratio of pigmented area to total epidermis area. c) Relative variance of melanin level in 1 cm2-sized skin cells. A low variance means that melanin is evenly distributed, and a high variance means that the melanin is irregularly distributed. d) Optical images after in vitro experiments for 12 days. Scale bar, 1cm. e) Histological analysis of 3D skin, showing the greatest reduction in melanin after SµLED irradiation. Scale bar, 20 µm. >
< Image 3. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on mouse dorsal skin. a) Optical images of mice dorsal skin after photo-treatment for 20 days. b) Histological analysis of mice dorsal skin. Less brown color means less expression of protein/catalysis involved in melanin synthesis. Scale bar, 50 µm. >
Prof. Keon Jae Lee said, “Our inorganic-based SµLED patch has outstanding characteristics in light efficiency, reliability, and durability. The SµLED patch is expected to give a great impact on the cosmetic field by reducing side effects and maximizing phototherapeutic effects.” The core technology of cosmetic SµLED has been transferred to Fronics co., Ltd, founded by Prof. Lee. Fronics is building foundry and equipment for mass production of SµLED masks for whole face cover and plans to release the products in March next year.
This paper entitled “Wearable Surface-Lighting Micro-Light-Emitting Diode Patch for Melanogenesis Inhibition” was published in the November 2022 issue of Advanced Healthcare Materials.
2022.11.22 View 13347
KAIST Team Develops Surface-Lighting MicroLED Patch with Significant Melanogenesis Inhibition Effect
A KAIST research team led by Ph.d candidate Jae Hee Lee and Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a surface-lighting microLED patch for UV-induced melanogenesis inhibition.
Melanin is brown or dark pigments existing in the skin, which can be abnormally synthesized by external UV or stress. Since the excessive melanin leads to skin diseases such as spots and freckles, proper treatment is required to return normal skin condition.
Recently, LED-based photo-stimulators have been released for skin care, however, their therapeutic effect is still controversial. Since conventional LED stimulators cannot conformally attach to the human skin, distance-induced side effects are caused by light loss and high heat transfer. To achieve effective phototreatment, the LED stimulator needs to be irradiated in contact with the human skin surface, enabling proper and uniform light deliver to the dermis with minimal optical loss.
In this work, the research team fabricated skin-attachable surface-lighting microLED (SµLED, 4 × 4 cm2) patch by utilizing a thousand of microLED chips and silica-embedded light diffusion layer. 100 µm-sized LED chips are vertically-interconnected for high flexibility and low heat generation, allowing its long-term operation on the human skin.
< Image 1. The overall concept of SµLED patch. a) SµLED patch operated on the human skin. b) Schematic illustration of SµLED patch structure. c) 4 × 4 cm2-sized SµLED patch. d) Schematic illustration of the advantages of SµLED patch such as efficient light delivery, low heat generation, and surface-lighting irradiation. >
The research team confirmed melanogenesis inhibition by irradiating the SµLED patch and the conventional LED (CLED) on the artificial human skin and mice dorsal skin. The SµLED-treated groups of human cells and mouse tissues showed minimal epidermal photo-toxicity and consistently effective reduction in synthesized melanin, compared to CLED-treated groups. In addition, significant suppression of proteins/catalysts expression involved in melanin synthesis such as MITF (microphthalmia-associated transcription factor), Melan-A and tyrosinase was verified.
< Image 2. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on 3D human skin cells. a). Different irradiation conditions for a-MSH (major factor to stimulate melanin synthesis) treated cells. b) The ratio of pigmented area to total epidermis area. c) Relative variance of melanin level in 1 cm2-sized skin cells. A low variance means that melanin is evenly distributed, and a high variance means that the melanin is irregularly distributed. d) Optical images after in vitro experiments for 12 days. Scale bar, 1cm. e) Histological analysis of 3D skin, showing the greatest reduction in melanin after SµLED irradiation. Scale bar, 20 µm. >
< Image 3. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on mouse dorsal skin. a) Optical images of mice dorsal skin after photo-treatment for 20 days. b) Histological analysis of mice dorsal skin. Less brown color means less expression of protein/catalysis involved in melanin synthesis. Scale bar, 50 µm. >
Prof. Keon Jae Lee said, “Our inorganic-based SµLED patch has outstanding characteristics in light efficiency, reliability, and durability. The SµLED patch is expected to give a great impact on the cosmetic field by reducing side effects and maximizing phototherapeutic effects.” The core technology of cosmetic SµLED has been transferred to Fronics co., Ltd, founded by Prof. Lee. Fronics is building foundry and equipment for mass production of SµLED masks for whole face cover and plans to release the products in March next year.
This paper entitled “Wearable Surface-Lighting Micro-Light-Emitting Diode Patch for Melanogenesis Inhibition” was published in the November 2022 issue of Advanced Healthcare Materials.
2022.11.22 View 13347 -
 Professor Shinhyun Choi’s team, selected for Nature Communications Editors’ highlight
[ From left, Ph.D. candidates See-On Park and Hakcheon Jeong, along with Master's student Jong-Yong Park and Professor Shinhyun Choi ]
See-On Park, Hakcheon Jeong, Jong-Yong Park - a team of researchers under the leadership of Professor Shinhyun Choi of the School of Electrical Engineering, developed a highly reliable variable resistor (memristor) array that simulates the behavior of neurons using a metal oxide layer with an oxygen concentration gradient, and published their work in Nature Communications. The study was selected as the Nature Communications' Editor's highlight, and as the featured article posted on the main page of the journal's website.
Link : https://www.nature.com/ncomms/
[ Figure 1. The featured image on the main page of the Nature Communications' website introducing the research by Professor Choi's team on the memristor for artificial neurons ]
Thesis title: Experimental demonstration of highly reliable dynamic memristor for artificial neuron and neuromorphic computing.
( https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30539-6 )
At KAIST, their research was introduced on the 2022 Fall issue of Breakthroughs, the biannual newsletter published by KAIST College of Engineering.
This research was conducted with the support from the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
2022.11.01 View 10339
Professor Shinhyun Choi’s team, selected for Nature Communications Editors’ highlight
[ From left, Ph.D. candidates See-On Park and Hakcheon Jeong, along with Master's student Jong-Yong Park and Professor Shinhyun Choi ]
See-On Park, Hakcheon Jeong, Jong-Yong Park - a team of researchers under the leadership of Professor Shinhyun Choi of the School of Electrical Engineering, developed a highly reliable variable resistor (memristor) array that simulates the behavior of neurons using a metal oxide layer with an oxygen concentration gradient, and published their work in Nature Communications. The study was selected as the Nature Communications' Editor's highlight, and as the featured article posted on the main page of the journal's website.
Link : https://www.nature.com/ncomms/
[ Figure 1. The featured image on the main page of the Nature Communications' website introducing the research by Professor Choi's team on the memristor for artificial neurons ]
Thesis title: Experimental demonstration of highly reliable dynamic memristor for artificial neuron and neuromorphic computing.
( https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30539-6 )
At KAIST, their research was introduced on the 2022 Fall issue of Breakthroughs, the biannual newsletter published by KAIST College of Engineering.
This research was conducted with the support from the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
2022.11.01 View 10339 -
 Yuji Roh Awarded 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship
KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh of the School of Electrical Engineering (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) was selected as a recipient of the 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship.
< KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) >
The Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that recognizes outstanding graduate students for their exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. This year, 36 people from around the world received the fellowship, and Yuji Roh from KAIST EE is the only recipient from universities in Korea. Each selected fellow will receive a $10,000 scholarship and an opportunity to intern at Microsoft under the guidance of an experienced researcher.
Yuji Roh was named a fellow in the field of “Machine Learning” for her outstanding achievements in Trustworthy AI. Her research highlights include designing a state-of-the-art fair training framework using batch selection and developing novel algorithms for both fair and robust training. Her works have been presented at the top machine learning conferences ICML, ICLR, and NeurIPS among others. She also co-presented a tutorial on Trustworthy AI at the top data mining conference ACM SIGKDD. She is currently interning at the NVIDIA Research AI Algorithms Group developing large-scale real-world fair AI frameworks.
The list of fellowship recipients and the interview videos are displayed on the Microsoft webpage and Youtube.
The list of recipients: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/academic-program/phd-fellowship/2022-recipients/
Interview (Global): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T4Q-XwOOoJc
Interview (Asia): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwq3R1XU8UE
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair batch selection framework]
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair and robust training framework]
2022.10.28 View 15300
Yuji Roh Awarded 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship
KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh of the School of Electrical Engineering (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) was selected as a recipient of the 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship.
< KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) >
The Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that recognizes outstanding graduate students for their exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. This year, 36 people from around the world received the fellowship, and Yuji Roh from KAIST EE is the only recipient from universities in Korea. Each selected fellow will receive a $10,000 scholarship and an opportunity to intern at Microsoft under the guidance of an experienced researcher.
Yuji Roh was named a fellow in the field of “Machine Learning” for her outstanding achievements in Trustworthy AI. Her research highlights include designing a state-of-the-art fair training framework using batch selection and developing novel algorithms for both fair and robust training. Her works have been presented at the top machine learning conferences ICML, ICLR, and NeurIPS among others. She also co-presented a tutorial on Trustworthy AI at the top data mining conference ACM SIGKDD. She is currently interning at the NVIDIA Research AI Algorithms Group developing large-scale real-world fair AI frameworks.
The list of fellowship recipients and the interview videos are displayed on the Microsoft webpage and Youtube.
The list of recipients: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/academic-program/phd-fellowship/2022-recipients/
Interview (Global): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T4Q-XwOOoJc
Interview (Asia): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwq3R1XU8UE
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair batch selection framework]
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair and robust training framework]
2022.10.28 View 15300 -
 See-through exhibitions using smartphones: KAIST develops the AR magic lens, WonderScope
WonderScope shows what’s underneath the surface of an object through an augmented reality technology.
< Photo 1. Demonstration at ACM SIGGRAPH >
- A KAIST research team led by Professor Woohun Lee from the Department of Industrial Design and Professor Geehyuk Lee from the School of Computing have developed a smartphone “appcessory” called WonderScope that can easily add an augmented reality (AR) perspective to the surface of exhibits
- The research won an Honorable Mention for Emerging Technologies Best in Show at ACM SIGGRAPH, one of the largest international conferences on computer graphics and interactions
- The technology was improved and validated through real-life applications in three special exhibitions including one at the Geological Museum at the Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM) held in 2020, and two at the National Science Museum each in 2021 and 2022
- The technology is expected to be used for public science exhibitions and museums as well as for interactive teaching materials to stimulate children’s curiosity
A KAIST research team led by Professor Woohun Lee from the Department of Industrial Design and Professor Geehyuk Lee from the School of Computing developed a novel augmented reality (AR) device, WonderScope, which displays the insides of an object directly from its surface. By installing and connecting WonderScope to a mobile device through Bluetooth, users can see through exhibits as if looking through a magic lens.
Many science museums nowadays have incorporated the use of AR apps for mobile devices. Such apps add digital information to the exhibition, providing a unique experience. However, visitors must watch the screen from a certain distance away from the exhibited items, often causing them to focus more on the digital contents rather than the exhibits themselves. In other words, the distance and distractions that exist between the exhibit and the mobile device may actually cause the visitors to feel detached from the exhibition. To solve this problem, museums needed a magic AR lens that could be used directly from the surface of the item.
To accomplish this, smartphones must know exactly where on the surface of an object it is placed. Generally, this would require an additional recognition device either on the inside or on the surface of the item, or a special pattern printed on its surface. Realistically speaking, these are impractical solutions, as exhibits would either appear overly complex or face spatial restrictions.
WonderScope, on the other hand, uses a much more practical method to identify the location of a smartphone on the surface of an exhibit. First, it reads a small RFID tag attached to the surface of an object, and calculates the location of the moving smartphone by adding its relative movements based on the readings from an optical displacement sensor and an acceleration sensor. The research team also took into consideration the height of the smartphone, and the characteristics of the surface profile in order to calculate the device’s position more accurately. By attaching or embedding RFID tags on exhibits, visitors can easily experience the effects of a magic AR lens through their smartphones.
For its wider use, WonderScope must be able to locate itself from various types of exhibit surfaces. To this end, WoderScope uses readings from an optical displacement sensor and an acceleration sensor with complementary characteristics, allowing stable locating capacities on various textures including paper, stone, wood, plastic, acrylic, and glass, as well as surfaces with physical patterns or irregularities. As a result, WonderScope can identify its location from a distance as close as 4 centimeters from an object, also enabling simple three-dimensional interactions near the surface of the exhibits.
The research team developed various case project templates and WonderScope support tools to allow the facile production of smartphone apps that use general-purpose virtual reality (VR) and the game engine Unity. WonderScope is also compatible with various types of devices that run on the Android operating system, including smartwatches, smartphones, and tablets, allowing it to be applied to exhibitions in many forms.
< Photo 2. Human body model showing demonstration >
< Photo 3. Demonstration of the underground mineral exploration game >
< Photo 4. Demonstration of Apollo 11 moon exploration experience >
The research team developed WonderScope with funding from the science and culture exhibition enhancement support project by the Ministry of Science and ICT. Between October 27, 2020 and February 28, 2021, WonderScope was used to observe underground volcanic activity and the insides of volcanic rocks at “There Once was a Volcano”, a special exhibition held at the Geological Museum in the Korea institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM). From September 28 to October 3, 2021, it was used to observe the surface of Jung-moon-kyung (a bronze mirror with fine linear design) at the special exhibition “A Bronze Mirror Shines on Science” at the National Science Museum. And from August 2 to October 3, 2022 it was applied to a moon landing simulation at “The Special Exhibition on Moon Exploration”, also at the National Science Museum. Through various field demonstrations over the years, the research team has improved the performance and usability of WonderScope.
< Photo 5. Observation of surface corrosion of the main gate >
The research team demonstrated WonderScope at the Emerging Technologies forum during ACM SIGGRAPH 2022, a computer graphics and interaction technology conference that was held in Vancouver, Canada between August 8 and 11 this year. At this conference, where the latest interactive technologies are introduced, the team won an Honorable Mention for Best in Show. The judges commented that “WonderScope will be a new technology that provides the audience with a unique joy of participation during their visits to exhibitions and museums.”
< Photo 6. Cover of Digital Creativity >
WonderScope is a cylindrical “appcessory” module, 5cm in diameter and 4.5cm in height. It is small enough to be easily attached to a smartphone and embedded on most exhibits. Professor Woohun Lee from the KAIST Department of Industrial Design, who supervised the research, said, “WonderScope can be applied to various applications including not only educational, but also industrial exhibitions, in many ways.” He added, “We also expect for it to be used as an interactive teaching tool that stimulates children’s curiosity.”
Introductory video of WonderScope: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X2MyAXRt7h4&t=7s
2022.10.24 View 11389
See-through exhibitions using smartphones: KAIST develops the AR magic lens, WonderScope
WonderScope shows what’s underneath the surface of an object through an augmented reality technology.
< Photo 1. Demonstration at ACM SIGGRAPH >
- A KAIST research team led by Professor Woohun Lee from the Department of Industrial Design and Professor Geehyuk Lee from the School of Computing have developed a smartphone “appcessory” called WonderScope that can easily add an augmented reality (AR) perspective to the surface of exhibits
- The research won an Honorable Mention for Emerging Technologies Best in Show at ACM SIGGRAPH, one of the largest international conferences on computer graphics and interactions
- The technology was improved and validated through real-life applications in three special exhibitions including one at the Geological Museum at the Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM) held in 2020, and two at the National Science Museum each in 2021 and 2022
- The technology is expected to be used for public science exhibitions and museums as well as for interactive teaching materials to stimulate children’s curiosity
A KAIST research team led by Professor Woohun Lee from the Department of Industrial Design and Professor Geehyuk Lee from the School of Computing developed a novel augmented reality (AR) device, WonderScope, which displays the insides of an object directly from its surface. By installing and connecting WonderScope to a mobile device through Bluetooth, users can see through exhibits as if looking through a magic lens.
Many science museums nowadays have incorporated the use of AR apps for mobile devices. Such apps add digital information to the exhibition, providing a unique experience. However, visitors must watch the screen from a certain distance away from the exhibited items, often causing them to focus more on the digital contents rather than the exhibits themselves. In other words, the distance and distractions that exist between the exhibit and the mobile device may actually cause the visitors to feel detached from the exhibition. To solve this problem, museums needed a magic AR lens that could be used directly from the surface of the item.
To accomplish this, smartphones must know exactly where on the surface of an object it is placed. Generally, this would require an additional recognition device either on the inside or on the surface of the item, or a special pattern printed on its surface. Realistically speaking, these are impractical solutions, as exhibits would either appear overly complex or face spatial restrictions.
WonderScope, on the other hand, uses a much more practical method to identify the location of a smartphone on the surface of an exhibit. First, it reads a small RFID tag attached to the surface of an object, and calculates the location of the moving smartphone by adding its relative movements based on the readings from an optical displacement sensor and an acceleration sensor. The research team also took into consideration the height of the smartphone, and the characteristics of the surface profile in order to calculate the device’s position more accurately. By attaching or embedding RFID tags on exhibits, visitors can easily experience the effects of a magic AR lens through their smartphones.
For its wider use, WonderScope must be able to locate itself from various types of exhibit surfaces. To this end, WoderScope uses readings from an optical displacement sensor and an acceleration sensor with complementary characteristics, allowing stable locating capacities on various textures including paper, stone, wood, plastic, acrylic, and glass, as well as surfaces with physical patterns or irregularities. As a result, WonderScope can identify its location from a distance as close as 4 centimeters from an object, also enabling simple three-dimensional interactions near the surface of the exhibits.
The research team developed various case project templates and WonderScope support tools to allow the facile production of smartphone apps that use general-purpose virtual reality (VR) and the game engine Unity. WonderScope is also compatible with various types of devices that run on the Android operating system, including smartwatches, smartphones, and tablets, allowing it to be applied to exhibitions in many forms.
< Photo 2. Human body model showing demonstration >
< Photo 3. Demonstration of the underground mineral exploration game >
< Photo 4. Demonstration of Apollo 11 moon exploration experience >
The research team developed WonderScope with funding from the science and culture exhibition enhancement support project by the Ministry of Science and ICT. Between October 27, 2020 and February 28, 2021, WonderScope was used to observe underground volcanic activity and the insides of volcanic rocks at “There Once was a Volcano”, a special exhibition held at the Geological Museum in the Korea institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM). From September 28 to October 3, 2021, it was used to observe the surface of Jung-moon-kyung (a bronze mirror with fine linear design) at the special exhibition “A Bronze Mirror Shines on Science” at the National Science Museum. And from August 2 to October 3, 2022 it was applied to a moon landing simulation at “The Special Exhibition on Moon Exploration”, also at the National Science Museum. Through various field demonstrations over the years, the research team has improved the performance and usability of WonderScope.
< Photo 5. Observation of surface corrosion of the main gate >
The research team demonstrated WonderScope at the Emerging Technologies forum during ACM SIGGRAPH 2022, a computer graphics and interaction technology conference that was held in Vancouver, Canada between August 8 and 11 this year. At this conference, where the latest interactive technologies are introduced, the team won an Honorable Mention for Best in Show. The judges commented that “WonderScope will be a new technology that provides the audience with a unique joy of participation during their visits to exhibitions and museums.”
< Photo 6. Cover of Digital Creativity >
WonderScope is a cylindrical “appcessory” module, 5cm in diameter and 4.5cm in height. It is small enough to be easily attached to a smartphone and embedded on most exhibits. Professor Woohun Lee from the KAIST Department of Industrial Design, who supervised the research, said, “WonderScope can be applied to various applications including not only educational, but also industrial exhibitions, in many ways.” He added, “We also expect for it to be used as an interactive teaching tool that stimulates children’s curiosity.”
Introductory video of WonderScope: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X2MyAXRt7h4&t=7s
2022.10.24 View 11389 -
 Globally renowned stained-glass artist Fr. En Joon Kim appointed as a distinguished invited professor in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design
World-renowned master of stained-glass Father En Joong Kim was appointed to a two-year distinguished invited professorship in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design starting August 1, 2022
- Fr. Kim will share his life, spirit, and artistic capabilities with the members of KAIST through special lectures for undergraduate and graduate students, and through a stained-glass piece he will work on and donate to the KAIST Academic and Cultural Complex
- The 53-piece work of art will provide KAIST with fresh inspiration and add to its dynamic atmosphere
KAIST appointed the world-renowned stained-glass artist and priest Fr. En Joong Kim of the Dominican Order as a distinguished invited professor in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design. His term starts from August 1 of this year and ends on July 31, 2024.
The appointment aims to share the life, spirit, and artistic capabilities of Fr. Kim, who is internationally recognized for his creative work. The purpose of the appointment is not only to provide professional advice on lighting color and space, which are core contents of industrial design courses, but also to bring new inspiration to KAIST community.
Fr. Kim, who studied in the College of Fine Arts at Seoul National University, won the Korean Art Award in 1965, and later studied at the University of Fribourg in Switzerland and the Catholic University of Paris. Joining the Dominican Order in France in 1974, he started his career as both a priest and an artist, and continued his artistic activities via 200 exhibitions around the world and by working on the stained-glass windows of 50 European churches.
In recognition of the artistic merit of combining colorful tones with the beauty of blank spaces, a distinctive characteristic of Asian art, and Fr. Kim’s contributions to establishing such combinations, Passage Kim En Joong, an art gallery, was founded in Ambert, France in 2019, and for his artwork installed all over France, he was presented with the insignia of Officer in the Order of Arts and Letters by the French government in 2010.
Following the appointment, the KAIST Department of Industrial Design is preparing a special seminar lecture by Fr. Kim under the title “Search the Future”. Fr. Kim will share his experience and philosophy for pursuing aesthetic values and efforts. In addition, the department plans to set up a special studio for Fr. Kim to both work and interact with students, encouraging them to naturally communicate and share ideas together.
One of Fr. Kim's art piece being installed at the main administration building at KAIST.
In a studio at the KAIST Academic Cultural Complex (ACC), Fr. Kim is currently working on his 53-piece stained-glass project that, when finished, will be added to the ACC. KAISTians will be able to enjoy a master’s art on a daily basis as the 53 sheets of glasses combine to form one magnificent piece.
Fr. Kim said, “I am very happy to be a distinguished invited professor at KAIST, where excellent scientists are at work. It is my wish and prayer that my presence here may comfort the students’ hearts with artwork and art philosophy that carries sensitivity and sincerity, and that they may garner richer experiences.”
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said, “The purpose of research and art are similar in that they pioneer through endless contemplations and attempts. The art piece to be installed at ACC, which will combine 53 pieces of stained glass, resembles our school, where our members each with their own distinctive colors and textures come together create a harmonious new form known as KAIST.”
He added, “I hope that the artistic spirit of Fr. Kim, a world-class master, will be a beacon that would bring a new type of stimulation and ease here at KAIST”
KAIST also appointed world-renowned soprano Sumi Jo as a distinguished invited professor in the Graduate School of Culture Technology in October 2021, and SM Entertainment’s executive producer Soo-man Lee as a distinguished invited professor in the School of Computing in March 2022. KAIST continues to expand and incorporate science and technology into the fields of art and culture, and to establish itself as a place for joint research and creative endeavors.
2022.09.08 View 10840
Globally renowned stained-glass artist Fr. En Joon Kim appointed as a distinguished invited professor in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design
World-renowned master of stained-glass Father En Joong Kim was appointed to a two-year distinguished invited professorship in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design starting August 1, 2022
- Fr. Kim will share his life, spirit, and artistic capabilities with the members of KAIST through special lectures for undergraduate and graduate students, and through a stained-glass piece he will work on and donate to the KAIST Academic and Cultural Complex
- The 53-piece work of art will provide KAIST with fresh inspiration and add to its dynamic atmosphere
KAIST appointed the world-renowned stained-glass artist and priest Fr. En Joong Kim of the Dominican Order as a distinguished invited professor in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design. His term starts from August 1 of this year and ends on July 31, 2024.
The appointment aims to share the life, spirit, and artistic capabilities of Fr. Kim, who is internationally recognized for his creative work. The purpose of the appointment is not only to provide professional advice on lighting color and space, which are core contents of industrial design courses, but also to bring new inspiration to KAIST community.
Fr. Kim, who studied in the College of Fine Arts at Seoul National University, won the Korean Art Award in 1965, and later studied at the University of Fribourg in Switzerland and the Catholic University of Paris. Joining the Dominican Order in France in 1974, he started his career as both a priest and an artist, and continued his artistic activities via 200 exhibitions around the world and by working on the stained-glass windows of 50 European churches.
In recognition of the artistic merit of combining colorful tones with the beauty of blank spaces, a distinctive characteristic of Asian art, and Fr. Kim’s contributions to establishing such combinations, Passage Kim En Joong, an art gallery, was founded in Ambert, France in 2019, and for his artwork installed all over France, he was presented with the insignia of Officer in the Order of Arts and Letters by the French government in 2010.
Following the appointment, the KAIST Department of Industrial Design is preparing a special seminar lecture by Fr. Kim under the title “Search the Future”. Fr. Kim will share his experience and philosophy for pursuing aesthetic values and efforts. In addition, the department plans to set up a special studio for Fr. Kim to both work and interact with students, encouraging them to naturally communicate and share ideas together.
One of Fr. Kim's art piece being installed at the main administration building at KAIST.
In a studio at the KAIST Academic Cultural Complex (ACC), Fr. Kim is currently working on his 53-piece stained-glass project that, when finished, will be added to the ACC. KAISTians will be able to enjoy a master’s art on a daily basis as the 53 sheets of glasses combine to form one magnificent piece.
Fr. Kim said, “I am very happy to be a distinguished invited professor at KAIST, where excellent scientists are at work. It is my wish and prayer that my presence here may comfort the students’ hearts with artwork and art philosophy that carries sensitivity and sincerity, and that they may garner richer experiences.”
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said, “The purpose of research and art are similar in that they pioneer through endless contemplations and attempts. The art piece to be installed at ACC, which will combine 53 pieces of stained glass, resembles our school, where our members each with their own distinctive colors and textures come together create a harmonious new form known as KAIST.”
He added, “I hope that the artistic spirit of Fr. Kim, a world-class master, will be a beacon that would bring a new type of stimulation and ease here at KAIST”
KAIST also appointed world-renowned soprano Sumi Jo as a distinguished invited professor in the Graduate School of Culture Technology in October 2021, and SM Entertainment’s executive producer Soo-man Lee as a distinguished invited professor in the School of Computing in March 2022. KAIST continues to expand and incorporate science and technology into the fields of art and culture, and to establish itself as a place for joint research and creative endeavors.
2022.09.08 View 10840 -
 A KAIST Research Team Develops Diesel Reforming Catalyst Enabling Hydrogen Production for Future Mobile Fuel Cells
This catalyst capability allowing stable hydrogen production from commercial diesel is expected to be applied in mobile fuel cell systems in the future hydrogen economy
On August 16, a joint research team led by Professors Joongmyeon Bae and Kang Taek Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) announced the successful development of a highly active and durable reforming catalyst allowing hydrogen production from commercial diesel.
Fuel reforming is a hydrogen production technique that extracts hydrogen from hydrocarbons through catalytic reactions. Diesel, being a liquid fuel, has a high storage density for hydrogen and is easy to transport and store. There have therefore been continuous research efforts to apply hydrogel supply systems using diesel reformation in mobile fuel cells, such as for auxiliary power in heavy trucks or air-independent propulsion (AIP) systems in submarines.
However, diesel is a mixture of high hydrocarbons including long-chained paraffin, double-bonded olefin, and aromatic hydrocarbons with benzene groups, and it requires a highly active catalyst to effectively break them down. In addition, the catalyst must be extremely durable against caulking and sintering, as they are often the main causes of catalyst degradation. Such challenges have limited the use of diesel reformation technologies to date.
The joint research team successfully developed a highly active and durable diesel reforming catalyst through elution (a heat treatment method used to uniformly grow active metals retained in an oxide support as ions in the form of metal nanoparticles), forming alloy nanoparticles. The design was based on the fact that eluted nanoparticles strongly interact with the support, allowing a high degree of dispersion at high temperatures, and that producing an alloy from dissimilar metals can increase the performance of catalysts through a synergistic effect.
The research team introduced a solution combustion synthesis method to produce a multi-component catalyst with a trace amount of platinum (Pt) and ruthenium (Ru) penetrated into a ceria (CeO2) lattice, which is a structure commonly used as a support for catalysts in redox reactions. When exposed to a diesel reforming reaction environment, the catalyst induces Pt-Ru alloy nanoparticle formation upon Pt and Ru elution onto the support surface.
In addition to the catalyst analysis, the research team also succeeded in characterizing the behaviour of active metal elution and alloy formation from an energetic perspective using a density functional theory-based calculation. In a performance comparison test between the Pt-Ru alloy catalyst against existing single-metal catalysts, the reforming activity was shown to have improved, as it showed a 100% fuel conversion rate even at a low temperature (600oC, compared to the original 800oC). In a long-term durability test (800oC, 200 hours), the catalyst showed commercial stability by successfully producing hydrogen from commercial diesel without performance degradation.
The study was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jaemyung Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering as the first author. Ph.D. candidate Changho Yeon of KIER, Dr. Jiwoo Oh of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Gwangwoo Han of KIER, Ph.D. candidate Jeong Do Yoo of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Dr. Hyung Joong Yun of the Korea Basic Science Institute contributed as co-authors. Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of KIER and Professors Kang Taek Lee and Joongmyeon Bae of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering contributed as corresponding authors. The research was published in the online version of Applied Catalysis B: Environmental (IF 24.319, JCR 0.93%) on June 17, under the title “Highly Active and Stable Catalyst with Exsolved PtRu Alloy Nanoparticles for Hydrogen Production via Commercial Diesel Reforming”.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae said, “The fact that hydrogen can be stably produced from commercial diesel makes this a very meaningful achievement, and we look forward to this technology contributing to the active introduction of mobile fuel cell systems in the early hydrogen economy.” He added, “Our approach to catalyst design may be applied not only to reforming reactions, but also in various other fields.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through funding from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
Figure. Schematic diagram of high-performance diesel reforming catalyst with eluted platinum-ruthenium alloy nanoparticles and long-term durability verification experiment results for commercial diesel reforming reaction
2022.09.07 View 15552
A KAIST Research Team Develops Diesel Reforming Catalyst Enabling Hydrogen Production for Future Mobile Fuel Cells
This catalyst capability allowing stable hydrogen production from commercial diesel is expected to be applied in mobile fuel cell systems in the future hydrogen economy
On August 16, a joint research team led by Professors Joongmyeon Bae and Kang Taek Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) announced the successful development of a highly active and durable reforming catalyst allowing hydrogen production from commercial diesel.
Fuel reforming is a hydrogen production technique that extracts hydrogen from hydrocarbons through catalytic reactions. Diesel, being a liquid fuel, has a high storage density for hydrogen and is easy to transport and store. There have therefore been continuous research efforts to apply hydrogel supply systems using diesel reformation in mobile fuel cells, such as for auxiliary power in heavy trucks or air-independent propulsion (AIP) systems in submarines.
However, diesel is a mixture of high hydrocarbons including long-chained paraffin, double-bonded olefin, and aromatic hydrocarbons with benzene groups, and it requires a highly active catalyst to effectively break them down. In addition, the catalyst must be extremely durable against caulking and sintering, as they are often the main causes of catalyst degradation. Such challenges have limited the use of diesel reformation technologies to date.
The joint research team successfully developed a highly active and durable diesel reforming catalyst through elution (a heat treatment method used to uniformly grow active metals retained in an oxide support as ions in the form of metal nanoparticles), forming alloy nanoparticles. The design was based on the fact that eluted nanoparticles strongly interact with the support, allowing a high degree of dispersion at high temperatures, and that producing an alloy from dissimilar metals can increase the performance of catalysts through a synergistic effect.
The research team introduced a solution combustion synthesis method to produce a multi-component catalyst with a trace amount of platinum (Pt) and ruthenium (Ru) penetrated into a ceria (CeO2) lattice, which is a structure commonly used as a support for catalysts in redox reactions. When exposed to a diesel reforming reaction environment, the catalyst induces Pt-Ru alloy nanoparticle formation upon Pt and Ru elution onto the support surface.
In addition to the catalyst analysis, the research team also succeeded in characterizing the behaviour of active metal elution and alloy formation from an energetic perspective using a density functional theory-based calculation. In a performance comparison test between the Pt-Ru alloy catalyst against existing single-metal catalysts, the reforming activity was shown to have improved, as it showed a 100% fuel conversion rate even at a low temperature (600oC, compared to the original 800oC). In a long-term durability test (800oC, 200 hours), the catalyst showed commercial stability by successfully producing hydrogen from commercial diesel without performance degradation.
The study was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jaemyung Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering as the first author. Ph.D. candidate Changho Yeon of KIER, Dr. Jiwoo Oh of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Gwangwoo Han of KIER, Ph.D. candidate Jeong Do Yoo of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Dr. Hyung Joong Yun of the Korea Basic Science Institute contributed as co-authors. Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of KIER and Professors Kang Taek Lee and Joongmyeon Bae of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering contributed as corresponding authors. The research was published in the online version of Applied Catalysis B: Environmental (IF 24.319, JCR 0.93%) on June 17, under the title “Highly Active and Stable Catalyst with Exsolved PtRu Alloy Nanoparticles for Hydrogen Production via Commercial Diesel Reforming”.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae said, “The fact that hydrogen can be stably produced from commercial diesel makes this a very meaningful achievement, and we look forward to this technology contributing to the active introduction of mobile fuel cell systems in the early hydrogen economy.” He added, “Our approach to catalyst design may be applied not only to reforming reactions, but also in various other fields.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through funding from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
Figure. Schematic diagram of high-performance diesel reforming catalyst with eluted platinum-ruthenium alloy nanoparticles and long-term durability verification experiment results for commercial diesel reforming reaction
2022.09.07 View 15552