AT
-
 Center for Global Strategies and Planning Hosts Successful Virtual KAIST U.S. Alumni Connection Event
< Screen capture of the KAIST U.S. Alumni meeting held online on December 8 >
On December 8th, the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST, led by Vice President Man-Sung Yim of the International Office, conducted a virtual event to bring together KAIST alumni in the United States. The purpose of this event was to showcase KAIST's current initiatives in the U.S., facilitate information exchanges among U.S. alumni, and foster networking opportunities. Over 130 KAIST alumni based in the U.S. registered and attended the event.
The event began with a warm welcome from President Kwang-Hyung Lee, followed by a presentation from Vice President Man-Sung Yim on the current status and vision of KAIST's U.S. collaboration project as well as that of KAIST U.S. Foundation, Inc. Additionally, a distinguished KAIST alumnus, Seok-Hyun Yun, a professor from Harvard Medical School, delivered a keynote speech that highlighted the development of collaborative projects between KAIST and the United States. Alumni Hyun Gook Yoon, a manager at Ford Motor Company, and Eunkwang Joo, CEO of Wasder, also presented recent technological trends in the fields of batteries and blockchain, respectively.
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, "This event serves as a crucial opportunity to enhance exchanges between KAIST and the U.S., playing a pivotal role in expanding KAIST's global presence." The event also featured small group discussions and networking sessions focusing on revitalizing collaborative efforts between KAIST and the United States.
After the small group discussions, a KAIST alumna and the current president of the Boston KAIST Alumni Association, Jiyoung Lee, shared her belief that the event will provide a meaningful opportunity for KAIST alumni from across the U.S. to come together and build a strong alumni community. Vice President Man-Sung Yim said, "Because collaboration with KAIST alumni in the U.S. is essential for the development of KAIST and innovative science and technology at the global level, we are committed to sustainably organizing meaningful events."
This virtual event for KAIST U.S. alumni has set a new milestone for global networking, marking the beginning of future collaborations and development.
2023.12.08 View 6953
Center for Global Strategies and Planning Hosts Successful Virtual KAIST U.S. Alumni Connection Event
< Screen capture of the KAIST U.S. Alumni meeting held online on December 8 >
On December 8th, the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST, led by Vice President Man-Sung Yim of the International Office, conducted a virtual event to bring together KAIST alumni in the United States. The purpose of this event was to showcase KAIST's current initiatives in the U.S., facilitate information exchanges among U.S. alumni, and foster networking opportunities. Over 130 KAIST alumni based in the U.S. registered and attended the event.
The event began with a warm welcome from President Kwang-Hyung Lee, followed by a presentation from Vice President Man-Sung Yim on the current status and vision of KAIST's U.S. collaboration project as well as that of KAIST U.S. Foundation, Inc. Additionally, a distinguished KAIST alumnus, Seok-Hyun Yun, a professor from Harvard Medical School, delivered a keynote speech that highlighted the development of collaborative projects between KAIST and the United States. Alumni Hyun Gook Yoon, a manager at Ford Motor Company, and Eunkwang Joo, CEO of Wasder, also presented recent technological trends in the fields of batteries and blockchain, respectively.
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, "This event serves as a crucial opportunity to enhance exchanges between KAIST and the U.S., playing a pivotal role in expanding KAIST's global presence." The event also featured small group discussions and networking sessions focusing on revitalizing collaborative efforts between KAIST and the United States.
After the small group discussions, a KAIST alumna and the current president of the Boston KAIST Alumni Association, Jiyoung Lee, shared her belief that the event will provide a meaningful opportunity for KAIST alumni from across the U.S. to come together and build a strong alumni community. Vice President Man-Sung Yim said, "Because collaboration with KAIST alumni in the U.S. is essential for the development of KAIST and innovative science and technology at the global level, we are committed to sustainably organizing meaningful events."
This virtual event for KAIST U.S. alumni has set a new milestone for global networking, marking the beginning of future collaborations and development.
2023.12.08 View 6953 -
 North Korea and Beyond: AI-Powered Satellite Analysis Reveals the Unseen Economic Landscape of Underdeveloped Nations
- A joint research team in computer science, economics, and geography has developed an artificial intelligence (AI) technology to measure grid-level economic development within six-square-kilometer regions.
- This AI technology is applicable in regions with limited statistical data (e.g., North Korea), supporting international efforts to propose policies for economic growth and poverty reduction in underdeveloped countries.
- The research team plans to make this technology freely available for use to contribute to the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The United Nations reports that more than 700 million people are in extreme poverty, earning less than two dollars a day. However, an accurate assessment of poverty remains a global challenge. For example, 53 countries have not conducted agricultural surveys in the past 15 years, and 17 countries have not published a population census. To fill this data gap, new technologies are being explored to estimate poverty using alternative sources such as street views, aerial photos, and satellite images.
The paper published in Nature Communications demonstrates how artificial intelligence (AI) can help analyze economic conditions from daytime satellite imagery. This new technology can even apply to the least developed countries - such as North Korea - that do not have reliable statistical data for typical machine learning training.
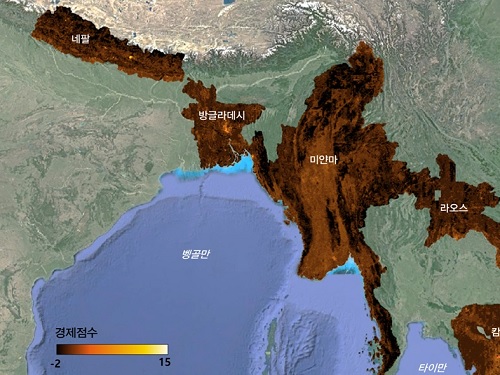
The researchers used Sentinel-2 satellite images from the European Space Agency (ESA) that are publicly available. They split these images into small six-square-kilometer grids. At this zoom level, visual information such as buildings, roads, and greenery can be used to quantify economic indicators. As a result, the team obtained the first ever fine-grained economic map of regions like North Korea. The same algorithm was applied to other underdeveloped countries in Asia: North Korea, Nepal, Laos, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Cambodia (see Image 1).
The key feature of their research model is the "human-machine collaborative approach," which lets researchers combine human input with AI predictions for areas with scarce data. In this research, ten human experts compared satellite images and judged the economic conditions in the area, with the AI learning from this human data and giving economic scores to each image. The results showed that the Human-AI collaborative approach outperformed machine-only learning algorithms.
< Image 1. Nightlight satellite images of North Korea (Top-left: Background photo provided by NASA's Earth Observatory). South Korea appears brightly lit compared to North Korea, which is mostly dark except for Pyongyang. In contrast, the model developed by the research team uses daytime satellite imagery to predict more detailed economic predictions for North Korea (top-right) and five Asian countries (Bottom: Background photo from Google Earth). >
The research was led by an interdisciplinary team of computer scientists, economists, and a geographer from KAIST & IBS (Donghyun Ahn, Meeyoung Cha, Jihee Kim), Sogang University (Hyunjoo Yang), HKUST (Sangyoon Park), and NUS (Jeasurk Yang). Dr Charles Axelsson, Associate Editor at Nature Communications, handled this paper during the peer review process at the journal.
The research team found that the scores showed a strong correlation with traditional socio-economic metrics such as population density, employment, and number of businesses. This demonstrates the wide applicability and scalability of the approach, particularly in data-scarce countries. Furthermore, the model's strength lies in its ability to detect annual changes in economic conditions at a more detailed geospatial level without using any survey data (see Image 2).
< Image 2. Differences in satellite imagery and economic scores in North Korea between 2016 and 2019. Significant development was found in the Wonsan Kalma area (top), one of the tourist development zones, but no changes were observed in the Wiwon Industrial Development Zone (bottom). (Background photo: Sentinel-2 satellite imagery provided by the European Space Agency (ESA)). >
This model would be especially valuable for rapidly monitoring the progress of Sustainable Development Goals such as reducing poverty and promoting more equitable and sustainable growth on an international scale. The model can also be adapted to measure various social and environmental indicators. For example, it can be trained to identify regions with high vulnerability to climate change and disasters to provide timely guidance on disaster relief efforts.
As an example, the researchers explored how North Korea changed before and after the United Nations sanctions against the country. By applying the model to satellite images of North Korea both in 2016 and in 2019, the researchers discovered three key trends in the country's economic development between 2016 and 2019. First, economic growth in North Korea became more concentrated in Pyongyang and major cities, exacerbating the urban-rural divide. Second, satellite imagery revealed significant changes in areas designated for tourism and economic development, such as new building construction and other meaningful alterations. Third, traditional industrial and export development zones showed relatively minor changes.
Meeyoung Cha, a data scientist in the team explained, "This is an important interdisciplinary effort to address global challenges like poverty. We plan to apply our AI algorithm to other international issues, such as monitoring carbon emissions, disaster damage detection, and the impact of climate change."
An economist on the research team, Jihee Kim, commented that this approach would enable detailed examinations of economic conditions in the developing world at a low cost, reducing data disparities between developed and developing nations. She further emphasized that this is most essential because many public policies require economic measurements to achieve their goals, whether they are for growth, equality, or sustainability.
The research team has made the source code publicly available via GitHub and plans to continue improving the technology, applying it to new satellite images updated annually. The results of this study, with Ph.D. candidate Donghyun Ahn at KAIST and Ph.D. candidate Jeasurk Yang at NUS as joint first authors, were published in Nature Communications under the title "A human-machine collaborative approach measures economic development using satellite imagery."
< Photos of the main authors. 1. Donghyun Ahn, PhD candidate at KAIST School of Computing 2. Jeasurk Yang, PhD candidate at the Department of Geography of National University of Singapore 3. Meeyoung Cha, Professor of KAIST School of Computing and CI at IBS 4. Jihee Kim, Professor of KAIST School of Business and Technology Management 5. Sangyoon Park, Professor of the Division of Social Science at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 6. Hyunjoo Yang, Professor of the Department of Economics at Sogang University >
2023.12.07 View 9027
North Korea and Beyond: AI-Powered Satellite Analysis Reveals the Unseen Economic Landscape of Underdeveloped Nations
- A joint research team in computer science, economics, and geography has developed an artificial intelligence (AI) technology to measure grid-level economic development within six-square-kilometer regions.
- This AI technology is applicable in regions with limited statistical data (e.g., North Korea), supporting international efforts to propose policies for economic growth and poverty reduction in underdeveloped countries.
- The research team plans to make this technology freely available for use to contribute to the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
The United Nations reports that more than 700 million people are in extreme poverty, earning less than two dollars a day. However, an accurate assessment of poverty remains a global challenge. For example, 53 countries have not conducted agricultural surveys in the past 15 years, and 17 countries have not published a population census. To fill this data gap, new technologies are being explored to estimate poverty using alternative sources such as street views, aerial photos, and satellite images.
The paper published in Nature Communications demonstrates how artificial intelligence (AI) can help analyze economic conditions from daytime satellite imagery. This new technology can even apply to the least developed countries - such as North Korea - that do not have reliable statistical data for typical machine learning training.
The researchers used Sentinel-2 satellite images from the European Space Agency (ESA) that are publicly available. They split these images into small six-square-kilometer grids. At this zoom level, visual information such as buildings, roads, and greenery can be used to quantify economic indicators. As a result, the team obtained the first ever fine-grained economic map of regions like North Korea. The same algorithm was applied to other underdeveloped countries in Asia: North Korea, Nepal, Laos, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Cambodia (see Image 1).
The key feature of their research model is the "human-machine collaborative approach," which lets researchers combine human input with AI predictions for areas with scarce data. In this research, ten human experts compared satellite images and judged the economic conditions in the area, with the AI learning from this human data and giving economic scores to each image. The results showed that the Human-AI collaborative approach outperformed machine-only learning algorithms.
< Image 1. Nightlight satellite images of North Korea (Top-left: Background photo provided by NASA's Earth Observatory). South Korea appears brightly lit compared to North Korea, which is mostly dark except for Pyongyang. In contrast, the model developed by the research team uses daytime satellite imagery to predict more detailed economic predictions for North Korea (top-right) and five Asian countries (Bottom: Background photo from Google Earth). >
The research was led by an interdisciplinary team of computer scientists, economists, and a geographer from KAIST & IBS (Donghyun Ahn, Meeyoung Cha, Jihee Kim), Sogang University (Hyunjoo Yang), HKUST (Sangyoon Park), and NUS (Jeasurk Yang). Dr Charles Axelsson, Associate Editor at Nature Communications, handled this paper during the peer review process at the journal.
The research team found that the scores showed a strong correlation with traditional socio-economic metrics such as population density, employment, and number of businesses. This demonstrates the wide applicability and scalability of the approach, particularly in data-scarce countries. Furthermore, the model's strength lies in its ability to detect annual changes in economic conditions at a more detailed geospatial level without using any survey data (see Image 2).
< Image 2. Differences in satellite imagery and economic scores in North Korea between 2016 and 2019. Significant development was found in the Wonsan Kalma area (top), one of the tourist development zones, but no changes were observed in the Wiwon Industrial Development Zone (bottom). (Background photo: Sentinel-2 satellite imagery provided by the European Space Agency (ESA)). >
This model would be especially valuable for rapidly monitoring the progress of Sustainable Development Goals such as reducing poverty and promoting more equitable and sustainable growth on an international scale. The model can also be adapted to measure various social and environmental indicators. For example, it can be trained to identify regions with high vulnerability to climate change and disasters to provide timely guidance on disaster relief efforts.
As an example, the researchers explored how North Korea changed before and after the United Nations sanctions against the country. By applying the model to satellite images of North Korea both in 2016 and in 2019, the researchers discovered three key trends in the country's economic development between 2016 and 2019. First, economic growth in North Korea became more concentrated in Pyongyang and major cities, exacerbating the urban-rural divide. Second, satellite imagery revealed significant changes in areas designated for tourism and economic development, such as new building construction and other meaningful alterations. Third, traditional industrial and export development zones showed relatively minor changes.
Meeyoung Cha, a data scientist in the team explained, "This is an important interdisciplinary effort to address global challenges like poverty. We plan to apply our AI algorithm to other international issues, such as monitoring carbon emissions, disaster damage detection, and the impact of climate change."
An economist on the research team, Jihee Kim, commented that this approach would enable detailed examinations of economic conditions in the developing world at a low cost, reducing data disparities between developed and developing nations. She further emphasized that this is most essential because many public policies require economic measurements to achieve their goals, whether they are for growth, equality, or sustainability.
The research team has made the source code publicly available via GitHub and plans to continue improving the technology, applying it to new satellite images updated annually. The results of this study, with Ph.D. candidate Donghyun Ahn at KAIST and Ph.D. candidate Jeasurk Yang at NUS as joint first authors, were published in Nature Communications under the title "A human-machine collaborative approach measures economic development using satellite imagery."
< Photos of the main authors. 1. Donghyun Ahn, PhD candidate at KAIST School of Computing 2. Jeasurk Yang, PhD candidate at the Department of Geography of National University of Singapore 3. Meeyoung Cha, Professor of KAIST School of Computing and CI at IBS 4. Jihee Kim, Professor of KAIST School of Business and Technology Management 5. Sangyoon Park, Professor of the Division of Social Science at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 6. Hyunjoo Yang, Professor of the Department of Economics at Sogang University >
2023.12.07 View 9027 -
 The Relentless Rain: East Asia's Recent Floods and What Lies Beneath
In just a month's time, East Asia witnessed torrential downpours that would usually span an entire season. Japan, battered by three times its usual monthly rainfall, faced landslides and flooding that claimed over 200 lives. Meanwhile, South Korea grappled with its longest monsoon in seven years, leaving more than 40 individuals dead or missing. But these events, as harrowing as they sound, are more than just weather anomalies. They're telltale signs, symptoms of a larger malaise that has gripped our planet.
Diving deep into these rain-soaked mysteries, a recently published paper in the journal Science Advances offers a fresh perspective. Led by a research team at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Korea, the research unpacks the influence of human-induced climate changes on the East Asia Summer Monsoon frontal system.
Heavy summer rain has a significant impact on agriculture and industry, and can be said to be one of the greatest threats to human society by causing disasters such as floods and landslides, affecting the local ecosystem. It has been reported from all over the world that the intensity of summer heavy rain has changed over the past few decades. However, summer rain in East Asia is caused by various forms such as typhoons, extratropical cyclones, and fronts, and efforts to study heavy frontal rain, which account for more than 40% of summer rainfall, is still insufficient. In addition, because heavy rain is also influenced by natural fluctuations or coincidences in the climate system, it is not yet known to what extent warming due to human activities affects the intensity of heavy frontal precipitation.
An international joint research team consisting of eight institutions from Korea, the United States, and Japan, including KAIST, Tokyo University, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Chonnam National University, GIST, and Utah State University, confirmed the intensity of heavy rain caused by the weather fronts in East Asia using observation data for the past 60 years and found that the coast of southeastern China. It was found that the intensity of heavy rain increased by about 17% across the Korean Peninsula and Japan. To investigate the cause of these changes, the research team used the Earth Metaverse experiment, which simulated Earth with and without greenhouse gas emissions due to human activities, and found that heavy rain intensity was strengthened by about 6% due to greenhouse gas emissions, and the changes discovered were has succeeded for the first time in the world in showing that warming cannot be explained without the effects of human activities.
< Figure 1. (Left) Observed difference in frontal rainfall intensity (FRI) from the later (1991–2015) to the earlier periods (1958–1982) (Right) Visualization of the impact of anthropogenic warming on the intensity of heavy frontal rain analyzed using the Earth Metaverse experiment. >
"It's not just about connecting the dots," said Moon, the first author of the paper, "it's about seeing the larger pattern. Our data analysis reveals a clear and intensified trend in East Asia's frontal rainfall, one that's intertwined with human actions and increasingly harmful for lives and property."
One of the intriguing finds from the study is the mechanics behind this intensification. The team found increased moisture transport due to a warmer climate, which, when coupled with the strengthening of a gigantic weather system called the West North Pacific Subtropical High, results in enhanced frontal rainfall. It’s akin to the climate dialing up the volume on rain events. As the atmosphere warms, it holds more moisture, leading to heavier downpours when conditions are right.
Nobuyuki Utsumi, another voice from the team, makes the science accessible for all, saying, "Monsoon rain isn't just rain anymore. The frequency, the intensity, it's changing. And our actions, our carbon footprint, are casting a larger shadow than we anticipated."
While the devastating news of floods fills headlines, Professor Simon Wang of Utah State University, reminds us of the underlying importance of their study. "It's like reading a detective novel. To solve the mystery of these floods, one has to trace them back to their roots. This work hints at a future where such intense rain events aren't the exception but might become an everyday reality."
Hyungjun Kim, the principal investigator of the team throws in a note of caution, "Understanding this is just the first step. Predicting and preparing for these extremes is the real challenge. Every amplified rainfall event is a message from the future, urging us to adapt." So far, predicting rainfall intensity and locations remains a challenging task for even the most sophisticated weather models.
< Figure 2. Comparison of rates of change in Anthropocene fingerprints. The horizontal axis shows the long-term change slope of the Anthropocene fingerprint signal (1958 to 2015). Shows the probability distribution of slopes extracted from the non-warming experiment (blue) and the warming experiment (red). The vertical solid lines are the slope of the Anthropocene fingerprint signal extracted from observational data. >
The researchers say, “Facing climate change, the narrative of this new study is more than mere numbers and data. It's a story of our planet, our actions, and the rain-soaked repercussions we're beginning to face. As we mop up the aftermath of another flood, research like Moon's beckons us to look deeper, understand better, and act wiser.”
< Figure 3. Comparison of water vapor convergence and rate of change of the western North Pacific high pressure. Shows the gradient of change in water vapor convergence (horizontal axis) and the Northwestern Pacific-East Asia pressure gradient (vertical axis) extracted from warming (red) and non-warming (blue) experiments. Shows the distribution of slope changes of the two indices during the period 1958 to 1982 (P1) and 1991 to 2015 (P2). >
The results of this study were published on November 24 in Science Advances. (Paper title: Anthropogenic warming induced intensification of summer monsoon frontal precipitation over East Asia)
This research was conducted with support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Overseas Scientist Attraction Project (BP+) and the Anthropocene Research Center.
2023.12.05 View 6376
The Relentless Rain: East Asia's Recent Floods and What Lies Beneath
In just a month's time, East Asia witnessed torrential downpours that would usually span an entire season. Japan, battered by three times its usual monthly rainfall, faced landslides and flooding that claimed over 200 lives. Meanwhile, South Korea grappled with its longest monsoon in seven years, leaving more than 40 individuals dead or missing. But these events, as harrowing as they sound, are more than just weather anomalies. They're telltale signs, symptoms of a larger malaise that has gripped our planet.
Diving deep into these rain-soaked mysteries, a recently published paper in the journal Science Advances offers a fresh perspective. Led by a research team at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Korea, the research unpacks the influence of human-induced climate changes on the East Asia Summer Monsoon frontal system.
Heavy summer rain has a significant impact on agriculture and industry, and can be said to be one of the greatest threats to human society by causing disasters such as floods and landslides, affecting the local ecosystem. It has been reported from all over the world that the intensity of summer heavy rain has changed over the past few decades. However, summer rain in East Asia is caused by various forms such as typhoons, extratropical cyclones, and fronts, and efforts to study heavy frontal rain, which account for more than 40% of summer rainfall, is still insufficient. In addition, because heavy rain is also influenced by natural fluctuations or coincidences in the climate system, it is not yet known to what extent warming due to human activities affects the intensity of heavy frontal precipitation.
An international joint research team consisting of eight institutions from Korea, the United States, and Japan, including KAIST, Tokyo University, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Chonnam National University, GIST, and Utah State University, confirmed the intensity of heavy rain caused by the weather fronts in East Asia using observation data for the past 60 years and found that the coast of southeastern China. It was found that the intensity of heavy rain increased by about 17% across the Korean Peninsula and Japan. To investigate the cause of these changes, the research team used the Earth Metaverse experiment, which simulated Earth with and without greenhouse gas emissions due to human activities, and found that heavy rain intensity was strengthened by about 6% due to greenhouse gas emissions, and the changes discovered were has succeeded for the first time in the world in showing that warming cannot be explained without the effects of human activities.
< Figure 1. (Left) Observed difference in frontal rainfall intensity (FRI) from the later (1991–2015) to the earlier periods (1958–1982) (Right) Visualization of the impact of anthropogenic warming on the intensity of heavy frontal rain analyzed using the Earth Metaverse experiment. >
"It's not just about connecting the dots," said Moon, the first author of the paper, "it's about seeing the larger pattern. Our data analysis reveals a clear and intensified trend in East Asia's frontal rainfall, one that's intertwined with human actions and increasingly harmful for lives and property."
One of the intriguing finds from the study is the mechanics behind this intensification. The team found increased moisture transport due to a warmer climate, which, when coupled with the strengthening of a gigantic weather system called the West North Pacific Subtropical High, results in enhanced frontal rainfall. It’s akin to the climate dialing up the volume on rain events. As the atmosphere warms, it holds more moisture, leading to heavier downpours when conditions are right.
Nobuyuki Utsumi, another voice from the team, makes the science accessible for all, saying, "Monsoon rain isn't just rain anymore. The frequency, the intensity, it's changing. And our actions, our carbon footprint, are casting a larger shadow than we anticipated."
While the devastating news of floods fills headlines, Professor Simon Wang of Utah State University, reminds us of the underlying importance of their study. "It's like reading a detective novel. To solve the mystery of these floods, one has to trace them back to their roots. This work hints at a future where such intense rain events aren't the exception but might become an everyday reality."
Hyungjun Kim, the principal investigator of the team throws in a note of caution, "Understanding this is just the first step. Predicting and preparing for these extremes is the real challenge. Every amplified rainfall event is a message from the future, urging us to adapt." So far, predicting rainfall intensity and locations remains a challenging task for even the most sophisticated weather models.
< Figure 2. Comparison of rates of change in Anthropocene fingerprints. The horizontal axis shows the long-term change slope of the Anthropocene fingerprint signal (1958 to 2015). Shows the probability distribution of slopes extracted from the non-warming experiment (blue) and the warming experiment (red). The vertical solid lines are the slope of the Anthropocene fingerprint signal extracted from observational data. >
The researchers say, “Facing climate change, the narrative of this new study is more than mere numbers and data. It's a story of our planet, our actions, and the rain-soaked repercussions we're beginning to face. As we mop up the aftermath of another flood, research like Moon's beckons us to look deeper, understand better, and act wiser.”
< Figure 3. Comparison of water vapor convergence and rate of change of the western North Pacific high pressure. Shows the gradient of change in water vapor convergence (horizontal axis) and the Northwestern Pacific-East Asia pressure gradient (vertical axis) extracted from warming (red) and non-warming (blue) experiments. Shows the distribution of slope changes of the two indices during the period 1958 to 1982 (P1) and 1991 to 2015 (P2). >
The results of this study were published on November 24 in Science Advances. (Paper title: Anthropogenic warming induced intensification of summer monsoon frontal precipitation over East Asia)
This research was conducted with support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Overseas Scientist Attraction Project (BP+) and the Anthropocene Research Center.
2023.12.05 View 6376 -
 2023 Global Startup Internship Seminar (GSIS)
The Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST hosted the 2023 Global Startup Internship Seminar (GSIS) both online and offline from November 29th to December 1st.
Following the success of the 2022 Global Startup Internship Fair (GSIF), the 2023 KAIST GSIS was organized in an enhanced format. This event provided students with the opportunity to explore internship opportunities with U.S. startups. Six startups in the fields of AI, bio, digital healthcare, drones, and e-commerce, Imprimed, Soundable Health, Vessl AI, B Garage, UNEEKOR, and Bringko, all founded by KAIST alumni, were invited. More than 80 KAIST students registered in advance to participate in the event.
The participating companies in this seminar shared who they and what they do and provided career mentoring for KAIST students. Catherine Song, the CEO of Soundable Health and a KAIST alumna, said, "It is very meaningful to introduce our company to KAIST students and provide them with the opportunity to take part in global internships."
In addition to startup company information and mentoring sessions, the seminar included sessions on preparing CVs, cover letters, and business emails for U.S. internships, and how to settle in Silicon Valley. Internship experiences were also shared by current KAIST students. Finally, a J-1 visa information session was conducted, providing useful tips for students preparing for U.S. internships.
Man-Sung Yim, the Vice President of the International Office at KAIST, said, "We hope that KAIST students, who have nurtured a global entrepreneurial spirit through this event, will grow into aspiring entrepreneurs with confidence on the global stage." He also mentioned plans to leverage the success of this event by connecting it with other KAIST global entrepreneurship programs.
2023.12.05 View 7112
2023 Global Startup Internship Seminar (GSIS)
The Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST hosted the 2023 Global Startup Internship Seminar (GSIS) both online and offline from November 29th to December 1st.
Following the success of the 2022 Global Startup Internship Fair (GSIF), the 2023 KAIST GSIS was organized in an enhanced format. This event provided students with the opportunity to explore internship opportunities with U.S. startups. Six startups in the fields of AI, bio, digital healthcare, drones, and e-commerce, Imprimed, Soundable Health, Vessl AI, B Garage, UNEEKOR, and Bringko, all founded by KAIST alumni, were invited. More than 80 KAIST students registered in advance to participate in the event.
The participating companies in this seminar shared who they and what they do and provided career mentoring for KAIST students. Catherine Song, the CEO of Soundable Health and a KAIST alumna, said, "It is very meaningful to introduce our company to KAIST students and provide them with the opportunity to take part in global internships."
In addition to startup company information and mentoring sessions, the seminar included sessions on preparing CVs, cover letters, and business emails for U.S. internships, and how to settle in Silicon Valley. Internship experiences were also shared by current KAIST students. Finally, a J-1 visa information session was conducted, providing useful tips for students preparing for U.S. internships.
Man-Sung Yim, the Vice President of the International Office at KAIST, said, "We hope that KAIST students, who have nurtured a global entrepreneurial spirit through this event, will grow into aspiring entrepreneurs with confidence on the global stage." He also mentioned plans to leverage the success of this event by connecting it with other KAIST global entrepreneurship programs.
2023.12.05 View 7112 -
 An intravenous needle that irreversibly softens via body temperature on insertion
- A joint research team at KAIST developed an intravenous (IV) needle that softens upon insertion, minimizing risk of damage to blood vessels and tissues.
- Once used, it remains soft even at room temperature, preventing accidental needle stick injuries and unethical multiple use of needle.
- A thin-film temperature sensor can be embedded with this needle, enabling real-time monitoring of the patient's core body temperature, or detection of unintended fluid leakage, during IV medication.
Intravenous (IV) injection is a method commonly used in patient’s treatment worldwide as it induces rapid effects and allows treatment through continuous administration of medication by directly injecting drugs into the blood vessel. However, medical IV needles, made of hard materials such as stainless steel or plastic which do not mechanically match the soft biological tissues of the body, can cause critical problems in healthcare settings, starting from minor tissue damages in the injection sites to serious inflammations.
The structure and dexterity of rigid medical IV devices also enable unethical reuse of needles for reduction of injection costs, leading to transmission of deadly blood-borne disease infections such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis B/C viruses. Furthermore, unintended needlestick injuries are frequently occurring in medical settings worldwide, that are viable sources of such infections, with IV needles having the greatest susceptibility of being the medium of transmissible diseases. For these reasons, the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2015 launched a policy on safe injection practices to encourage the development and use of “smart” syringes that have features to prevent re-use, after a tremendous increase in the number of deadly infectious disease worldwide due to medical-sharps related issues.
KAIST announced on the 13th that Professor Jae-Woong Jeong and his research team of its School of Electrical Engineering succeeded in developing the Phase-Convertible, Adapting and non-REusable (P-CARE) needle with variable stiffness that can improve patient health and ensure the safety of medical staff through convergent joint research with another team led by Professor Won-Il Jeong of the Graduate School of Medical Sciences.
The new technology is expected to allow patients to move without worrying about pain at the injection site as it reduces the risk of damage to the wall of the blood vessel as patients receive IV medication. This is possible with the needle’s stiffness-tunable characteristics which will make it soft and flexible upon insertion into the body due to increased temperature, adapting to the movement of thin-walled vein. It is also expected to prevent blood-borne disease infections caused by accidental needlestick injuries or unethical re-using of syringes as the deformed needle remains perpetually soft even after it is retracted from the injection site.
The results of this research, in which Karen-Christian Agno, a doctoral researcher of the School of Electrical Engineering at and Dr. Keungmo Yang of the Graduate School of Medical Sciences participated as co-first authors, was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering on October 30. (Paper title: A temperature-responsive intravenous needle that irreversibly softens on insertion)
< Figure 1. Disposable variable stiffness intravenous needle. (a) Conceptual illustration of the key features of the P-CARE needle whose mechanical properties can be changed by body temperature, (b) Photograph of commonly used IV access devices and the P-CARE needle, (c) Performance of common IV access devices and the P-CARE needle >
“We’ve developed this special needle using advanced materials and micro/nano engineering techniques, and it can solve many global problems related to conventional medical needles used in healthcare worldwide”, said Jae-Woong Jeong, Ph.D., an associate professor of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and a lead senior author of the study.
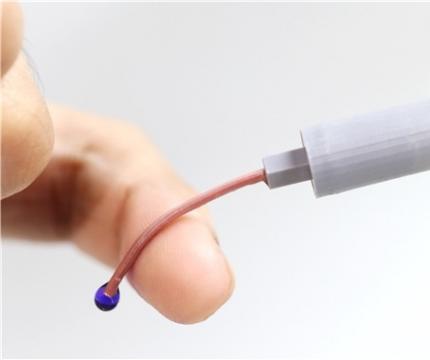
The softening IV needle created by the research team is made up of liquid metal gallium that forms the hollow, mechanical needle frame encapsulated within an ultra-soft silicone material. In its solid state, gallium has sufficient hardness that enables puncturing of soft biological tissues. However, gallium melts when it is exposed to body temperature upon insertion, and changes it into a soft state like the surrounding tissue, enabling stable delivery of the drug without damaging blood vessels. Once used, a needle remains soft even at room temperature due to the supercooling phenomenon of gallium, fundamentally preventing needlestick accidents and reuse problems.
Biocompatibility of the softening IV needle was validated through in vivo studies in mice. The studies showed that implanted needles caused significantly less inflammation relative to the standard IV access devices of similar size made of metal needles or plastic catheters. The study also confirmed the new needle was able to deliver medications as reliably as commercial injection needles.
< Photo 1. Photo of the P-CARE needle that softens with body temperature. >
Researchers also showed possibility of integrating a customized ultra-thin temperature sensor with the softening IV needle to measure the on-site temperature which can further enhance patient’s well-being. The single assembly of sensor-needle device can be used to monitor the core body temperature, or even detect if there is a fluid leakage on-site during indwelling use, eliminating the need for additional medical tools or procedures to provide the patients with better health care services.
The researchers believe that this transformative IV needle can open new opportunities for wide range of applications particularly in clinical setups, in terms of redesigning other medical needles and sharp medical tools to reduce muscle tissue injury during indwelling use. The softening IV needle may become even more valuable in the present times as there is an estimated 16 billion medical injections administered annually in a global scale, yet not all needles are disposed of properly, based on a 2018 WHO report.
< Figure 2. Biocompatibility test for P-CARE needle: Images of H&E stained histology (the area inside the dashed box on the left is provided in an expanded view in the right), TUNEL staining (green), DAPI staining of nuclei (blue) and co-staining (TUNEL and DAPI) of muscle tissue from different organs. >
< Figure 3. Conceptual images of potential utilization for temperature monitoring function of P-CARE needle integrated with a temperature sensor. >
(a) Schematic diagram of injecting a drug through intravenous injection into the abdomen of a laboratory mouse (b) Change of body temperature upon injection of drug (c) Conceptual illustration of normal intravenous drug injection (top) and fluid leakage (bottom) (d) Comparison of body temperature during normal drug injection and fluid leakage: when the fluid leak occur due to incorrect insertion, a sudden drop of temperature is detected.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.11.13 View 9638
An intravenous needle that irreversibly softens via body temperature on insertion
- A joint research team at KAIST developed an intravenous (IV) needle that softens upon insertion, minimizing risk of damage to blood vessels and tissues.
- Once used, it remains soft even at room temperature, preventing accidental needle stick injuries and unethical multiple use of needle.
- A thin-film temperature sensor can be embedded with this needle, enabling real-time monitoring of the patient's core body temperature, or detection of unintended fluid leakage, during IV medication.
Intravenous (IV) injection is a method commonly used in patient’s treatment worldwide as it induces rapid effects and allows treatment through continuous administration of medication by directly injecting drugs into the blood vessel. However, medical IV needles, made of hard materials such as stainless steel or plastic which do not mechanically match the soft biological tissues of the body, can cause critical problems in healthcare settings, starting from minor tissue damages in the injection sites to serious inflammations.
The structure and dexterity of rigid medical IV devices also enable unethical reuse of needles for reduction of injection costs, leading to transmission of deadly blood-borne disease infections such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis B/C viruses. Furthermore, unintended needlestick injuries are frequently occurring in medical settings worldwide, that are viable sources of such infections, with IV needles having the greatest susceptibility of being the medium of transmissible diseases. For these reasons, the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2015 launched a policy on safe injection practices to encourage the development and use of “smart” syringes that have features to prevent re-use, after a tremendous increase in the number of deadly infectious disease worldwide due to medical-sharps related issues.
KAIST announced on the 13th that Professor Jae-Woong Jeong and his research team of its School of Electrical Engineering succeeded in developing the Phase-Convertible, Adapting and non-REusable (P-CARE) needle with variable stiffness that can improve patient health and ensure the safety of medical staff through convergent joint research with another team led by Professor Won-Il Jeong of the Graduate School of Medical Sciences.
The new technology is expected to allow patients to move without worrying about pain at the injection site as it reduces the risk of damage to the wall of the blood vessel as patients receive IV medication. This is possible with the needle’s stiffness-tunable characteristics which will make it soft and flexible upon insertion into the body due to increased temperature, adapting to the movement of thin-walled vein. It is also expected to prevent blood-borne disease infections caused by accidental needlestick injuries or unethical re-using of syringes as the deformed needle remains perpetually soft even after it is retracted from the injection site.
The results of this research, in which Karen-Christian Agno, a doctoral researcher of the School of Electrical Engineering at and Dr. Keungmo Yang of the Graduate School of Medical Sciences participated as co-first authors, was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering on October 30. (Paper title: A temperature-responsive intravenous needle that irreversibly softens on insertion)
< Figure 1. Disposable variable stiffness intravenous needle. (a) Conceptual illustration of the key features of the P-CARE needle whose mechanical properties can be changed by body temperature, (b) Photograph of commonly used IV access devices and the P-CARE needle, (c) Performance of common IV access devices and the P-CARE needle >
“We’ve developed this special needle using advanced materials and micro/nano engineering techniques, and it can solve many global problems related to conventional medical needles used in healthcare worldwide”, said Jae-Woong Jeong, Ph.D., an associate professor of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and a lead senior author of the study.
The softening IV needle created by the research team is made up of liquid metal gallium that forms the hollow, mechanical needle frame encapsulated within an ultra-soft silicone material. In its solid state, gallium has sufficient hardness that enables puncturing of soft biological tissues. However, gallium melts when it is exposed to body temperature upon insertion, and changes it into a soft state like the surrounding tissue, enabling stable delivery of the drug without damaging blood vessels. Once used, a needle remains soft even at room temperature due to the supercooling phenomenon of gallium, fundamentally preventing needlestick accidents and reuse problems.
Biocompatibility of the softening IV needle was validated through in vivo studies in mice. The studies showed that implanted needles caused significantly less inflammation relative to the standard IV access devices of similar size made of metal needles or plastic catheters. The study also confirmed the new needle was able to deliver medications as reliably as commercial injection needles.
< Photo 1. Photo of the P-CARE needle that softens with body temperature. >
Researchers also showed possibility of integrating a customized ultra-thin temperature sensor with the softening IV needle to measure the on-site temperature which can further enhance patient’s well-being. The single assembly of sensor-needle device can be used to monitor the core body temperature, or even detect if there is a fluid leakage on-site during indwelling use, eliminating the need for additional medical tools or procedures to provide the patients with better health care services.
The researchers believe that this transformative IV needle can open new opportunities for wide range of applications particularly in clinical setups, in terms of redesigning other medical needles and sharp medical tools to reduce muscle tissue injury during indwelling use. The softening IV needle may become even more valuable in the present times as there is an estimated 16 billion medical injections administered annually in a global scale, yet not all needles are disposed of properly, based on a 2018 WHO report.
< Figure 2. Biocompatibility test for P-CARE needle: Images of H&E stained histology (the area inside the dashed box on the left is provided in an expanded view in the right), TUNEL staining (green), DAPI staining of nuclei (blue) and co-staining (TUNEL and DAPI) of muscle tissue from different organs. >
< Figure 3. Conceptual images of potential utilization for temperature monitoring function of P-CARE needle integrated with a temperature sensor. >
(a) Schematic diagram of injecting a drug through intravenous injection into the abdomen of a laboratory mouse (b) Change of body temperature upon injection of drug (c) Conceptual illustration of normal intravenous drug injection (top) and fluid leakage (bottom) (d) Comparison of body temperature during normal drug injection and fluid leakage: when the fluid leak occur due to incorrect insertion, a sudden drop of temperature is detected.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.11.13 View 9638 -
 KAIST proposes alternatives to chemical factories through “iBridge”
- A computer simulation program “iBridge” was developed at KAIST that can put together microbial cell factories quickly and efficiently to produce cosmetics and food additives, and raw materials for nylons
- Eco-friendly and sustainable fermentation process to establish an alternative to chemical plants
As climate change and environmental concerns intensify, sustainable microbial cell factories garner significant attention as candidates to replace chemical plants. To develop microorganisms to be used in the microbial cell factories, it is crucial to modify their metabolic processes to induce efficient target chemical production by modulating its gene expressions. Yet, the challenge persists in determining which gene expressions to amplify and suppress, and the experimental verification of these modification targets is a time- and resource-intensive process even for experts. The challenges were addressed by a team of researchers at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
It was announced on the 9th by the school that a method for building a microbial factory at low cost, quickly and efficiently, was presented by a novel computer simulation program developed by the team under Professor Lee’s guidance, which is named “iBridge”. This innovative system is designed to predict gene targets to either overexpress or downregulate in the goal of producing a desired compound to enable the cost-effective and efficient construction of microbial cell factories specifically tailored for producing the chemical compound in demand from renewable biomass.
Systems metabolic engineering is a field of research and engineering pioneered by KAIST’s Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee that seeks to produce valuable compounds in industrial demands using microorganisms that are re-configured by a combination of methods including, but not limited to, metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, systems biology, and fermentation engineering.
In order to improve microorganisms’ capability to produce useful compounds, it is essential to delete, suppress, or overexpress microbial genes. However, it is difficult even for the experts to identify the gene targets to modify without experimental confirmations for each of them, which can take up immeasurable amount of time and resources.
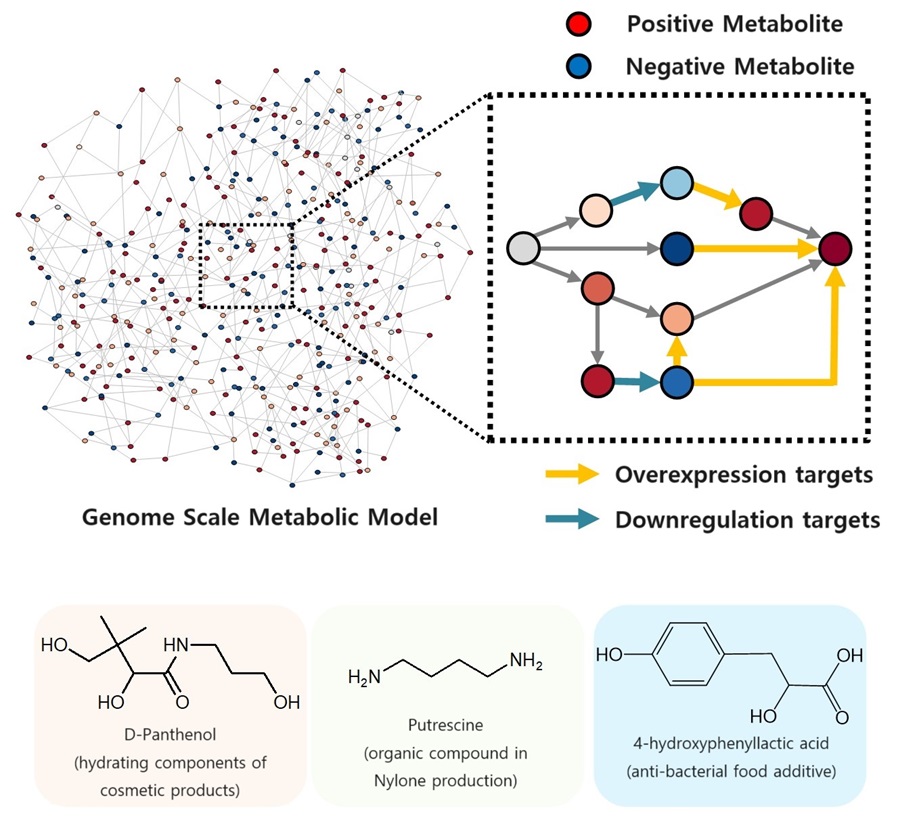
The newly developed iBridge identifies positive and negative metabolites within cells, which exert positive and/or negative impact on formation of the products, by calculating the sum of covariances of their outgoing (consuming) reaction fluxes for a target chemical. Subsequently, it pinpoints "bridge" reactions responsible for converting negative metabolites into positive ones as candidates for overexpression, while identifying the opposites as targets for downregulation.
The research team successfully utilized the iBridge simulation to establish E. coli microbial cell factories each capable of producing three of the compounds that are in high demands at a production capacity that has not been reported around the world. They developed E. coli strains that can each produce panthenol, a moisturizing agent found in many cosmetics, putrescine, which is one of the key components in nylon production, and 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid, an anti-bacterial food additive. In addition to these three compounds, the study presents predictions for overexpression and suppression genes to construct microbial factories for 298 other industrially valuable compounds.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, emphasized the accelerated construction of various microbial factories the newly developed simulation enabled. He stated, "With the use of this simulation, multiple microbial cell factories have been established significantly faster than it would have been using the conventional methods. Microbial cell factories producing a wider range of valuable compounds can now be constructed quickly using this technology."
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "Systems metabolic engineering is a crucial technology for addressing the current climate change issues." He added, "This simulation could significantly expedite the transition from resorting to conventional chemical factories to utilizing environmentally friendly microbial factories."
< Figure. Conceptual diagram of the flow of iBridge simulation >
The team’s work on iBridge is described in a paper titled "Genome-Wide Identification of Overexpression and Downregulation Gene Targets Based on the Sum of Covariances of the Outgoing Reaction Fluxes" written by Dr. Won Jun Kim, and Dr. Youngjoon Lee of the Bioprocess Research Center and Professors Hyun Uk Kim and Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST. The paper was published via peer-review on the 6th of November on “Cell Systems” by Cell Press.
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic using Microbial Cell Factories Project (Project Leader: Research Professor So Young Choi, KAIST) of the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.11.09 View 8684
KAIST proposes alternatives to chemical factories through “iBridge”
- A computer simulation program “iBridge” was developed at KAIST that can put together microbial cell factories quickly and efficiently to produce cosmetics and food additives, and raw materials for nylons
- Eco-friendly and sustainable fermentation process to establish an alternative to chemical plants
As climate change and environmental concerns intensify, sustainable microbial cell factories garner significant attention as candidates to replace chemical plants. To develop microorganisms to be used in the microbial cell factories, it is crucial to modify their metabolic processes to induce efficient target chemical production by modulating its gene expressions. Yet, the challenge persists in determining which gene expressions to amplify and suppress, and the experimental verification of these modification targets is a time- and resource-intensive process even for experts. The challenges were addressed by a team of researchers at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
It was announced on the 9th by the school that a method for building a microbial factory at low cost, quickly and efficiently, was presented by a novel computer simulation program developed by the team under Professor Lee’s guidance, which is named “iBridge”. This innovative system is designed to predict gene targets to either overexpress or downregulate in the goal of producing a desired compound to enable the cost-effective and efficient construction of microbial cell factories specifically tailored for producing the chemical compound in demand from renewable biomass.
Systems metabolic engineering is a field of research and engineering pioneered by KAIST’s Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee that seeks to produce valuable compounds in industrial demands using microorganisms that are re-configured by a combination of methods including, but not limited to, metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, systems biology, and fermentation engineering.
In order to improve microorganisms’ capability to produce useful compounds, it is essential to delete, suppress, or overexpress microbial genes. However, it is difficult even for the experts to identify the gene targets to modify without experimental confirmations for each of them, which can take up immeasurable amount of time and resources.
The newly developed iBridge identifies positive and negative metabolites within cells, which exert positive and/or negative impact on formation of the products, by calculating the sum of covariances of their outgoing (consuming) reaction fluxes for a target chemical. Subsequently, it pinpoints "bridge" reactions responsible for converting negative metabolites into positive ones as candidates for overexpression, while identifying the opposites as targets for downregulation.
The research team successfully utilized the iBridge simulation to establish E. coli microbial cell factories each capable of producing three of the compounds that are in high demands at a production capacity that has not been reported around the world. They developed E. coli strains that can each produce panthenol, a moisturizing agent found in many cosmetics, putrescine, which is one of the key components in nylon production, and 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid, an anti-bacterial food additive. In addition to these three compounds, the study presents predictions for overexpression and suppression genes to construct microbial factories for 298 other industrially valuable compounds.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, emphasized the accelerated construction of various microbial factories the newly developed simulation enabled. He stated, "With the use of this simulation, multiple microbial cell factories have been established significantly faster than it would have been using the conventional methods. Microbial cell factories producing a wider range of valuable compounds can now be constructed quickly using this technology."
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "Systems metabolic engineering is a crucial technology for addressing the current climate change issues." He added, "This simulation could significantly expedite the transition from resorting to conventional chemical factories to utilizing environmentally friendly microbial factories."
< Figure. Conceptual diagram of the flow of iBridge simulation >
The team’s work on iBridge is described in a paper titled "Genome-Wide Identification of Overexpression and Downregulation Gene Targets Based on the Sum of Covariances of the Outgoing Reaction Fluxes" written by Dr. Won Jun Kim, and Dr. Youngjoon Lee of the Bioprocess Research Center and Professors Hyun Uk Kim and Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST. The paper was published via peer-review on the 6th of November on “Cell Systems” by Cell Press.
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic using Microbial Cell Factories Project (Project Leader: Research Professor So Young Choi, KAIST) of the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.11.09 View 8684 -
 NYU-KAIST Global AI & Digital Governance Conference Held
< Photo 1. Opening of NYU-KAIST Global AI & Digital Governance Conference >
In attendance of the Minister of Science and ICT Jong-ho Lee, NYU President Linda G. Mills, and KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, KAIST co-hosted the NYU-KAIST Global AI & Digital Governance Conference at the Paulson Center of New York University (NYU) in New York City, USA on September 21st, 9:30 pm.
At the conference, KAIST and NYU discussed the direction and policies for ‘global AI and digital governance’ with participants of upto 300 people which includes scholars, professors, and students involved in the academic field of AI and digitalization from both Korea and the United States and other international backgrounds. This conference was a forum of an international discussion that sought new directions for AI and digital technology take in the future and gathered consensus on regulations.
Following a welcoming address by KAIST President, Kwang Hyung Lee and a congratulatory message from the Minister of Science and ICT, Jong-ho Lee, a panel discussion was held, moderated by Professor Matthew Liao, a graduate of Princeton and Oxford University, currently serving as a professor at NYU and the director at the Center for Bioethics of the NYU School of Global Public Health.
Six prominent scholars took part in the panel discussion. Prof. Kyung-hyun Cho of NYU Applied Mathematics and Data Science Center, a KAIST graduate who has joined the ranks of the world-class in AI language models and Professor Jong Chul Ye, the Director of Promotion Council for Digital Health at KAIST, who is leading innovative research in the field of medical AI working in collaboration with major hospitals at home and abroad was on the panel. Additionally, Professor Luciano Floridi, a founding member of the Yale University Center for Digital Ethics, Professor Shannon Vallor, the Baillie Gifford Professor in the Ethics of Data and Artificial Intelligence at the University of Edinburgh of the UK, Professor Stefaan Verhulst, a Co-Founder and the DIrector of GovLab‘s Data Program at NYU’s Tandon School of Engineering, and Professor Urs Gasser, who is in charge of public policy, governance and innovative technology at the Technical University of Munich, also participated.
Professor Matthew Liao from NYU led the discussion on various topics such as the ways to to regulate AI and digital technologies; the concerns about how deep learning technology being developed in medicinal purposes could be used in warfare; the scope of responsibilities Al scientists' responsibility should carry in ensuring the usage of AI are limited to benign purposes only; the effects of external regulation on the AI model developers and the research they pursue; and on the lessons that can be learned from the regulations in other fields.
During the panel discussion, there was an exchange of ideas about a system of standards that could harmonize digital development and regulatory and social ethics in today’s situation in which digital transformation accelerates technological development at a global level, there is a looming concern that while such advancements are bringing economic vitality it may create digital divides and probles like manipulation of public opinion. Professor Jong-cheol Ye of KAIST (Director of the Promotion Council for Digital Health), in particular, emphasized that it is important to find a point of balance that does not hinder the advancements rather than opting to enforcing strict regulations.
< Photo 2. Panel Discussion in Session at NYU-KAIST Global AI & Digital Governance Conference >
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee explained, “At the Digital Governance Forum we had last October, we focused on exploring new governance to solve digital challenges in the time of global digital transition, and this year’s main focus was on regulations.”
“This conference served as an opportunity of immense value as we came to understand that appropriate regulations can be a motivation to spur further developments rather than a hurdle when it comes to technological advancements, and that it is important for us to clearly understand artificial intelligence and consider what should and can be regulated when we are to set regulations on artificial intelligence,” he continued.
Earlier, KAIST signed a cooperation agreement with NYU to build a joint campus, June last year and held a plaque presentation ceremony for the KAIST NYU Joint Campus last September to promote joint research between the two universities. KAIST is currently conducting joint research with NYU in nine fields, including AI and digital research. The KAIST-NYU Joint Campus was conceived with the goal of building an innovative sandbox campus centering aroung science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) combining NYU's excellent humanities and arts as well as basic science and convergence research capabilities with KAIST's science and technology.
KAIST has contributed to the development of Korea's industry and economy through technological innovation aiding in the nation’s transformation into an innovative nation with scientific and technological prowess. KAIST will now pursue an anchor/base strategy to raise KAIST's awareness in New York through the NYU Joint Campus by establishing a KAIST campus within the campus of NYU, the heart of New York.
2023.09.22 View 11744
NYU-KAIST Global AI & Digital Governance Conference Held
< Photo 1. Opening of NYU-KAIST Global AI & Digital Governance Conference >
In attendance of the Minister of Science and ICT Jong-ho Lee, NYU President Linda G. Mills, and KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, KAIST co-hosted the NYU-KAIST Global AI & Digital Governance Conference at the Paulson Center of New York University (NYU) in New York City, USA on September 21st, 9:30 pm.
At the conference, KAIST and NYU discussed the direction and policies for ‘global AI and digital governance’ with participants of upto 300 people which includes scholars, professors, and students involved in the academic field of AI and digitalization from both Korea and the United States and other international backgrounds. This conference was a forum of an international discussion that sought new directions for AI and digital technology take in the future and gathered consensus on regulations.
Following a welcoming address by KAIST President, Kwang Hyung Lee and a congratulatory message from the Minister of Science and ICT, Jong-ho Lee, a panel discussion was held, moderated by Professor Matthew Liao, a graduate of Princeton and Oxford University, currently serving as a professor at NYU and the director at the Center for Bioethics of the NYU School of Global Public Health.
Six prominent scholars took part in the panel discussion. Prof. Kyung-hyun Cho of NYU Applied Mathematics and Data Science Center, a KAIST graduate who has joined the ranks of the world-class in AI language models and Professor Jong Chul Ye, the Director of Promotion Council for Digital Health at KAIST, who is leading innovative research in the field of medical AI working in collaboration with major hospitals at home and abroad was on the panel. Additionally, Professor Luciano Floridi, a founding member of the Yale University Center for Digital Ethics, Professor Shannon Vallor, the Baillie Gifford Professor in the Ethics of Data and Artificial Intelligence at the University of Edinburgh of the UK, Professor Stefaan Verhulst, a Co-Founder and the DIrector of GovLab‘s Data Program at NYU’s Tandon School of Engineering, and Professor Urs Gasser, who is in charge of public policy, governance and innovative technology at the Technical University of Munich, also participated.
Professor Matthew Liao from NYU led the discussion on various topics such as the ways to to regulate AI and digital technologies; the concerns about how deep learning technology being developed in medicinal purposes could be used in warfare; the scope of responsibilities Al scientists' responsibility should carry in ensuring the usage of AI are limited to benign purposes only; the effects of external regulation on the AI model developers and the research they pursue; and on the lessons that can be learned from the regulations in other fields.
During the panel discussion, there was an exchange of ideas about a system of standards that could harmonize digital development and regulatory and social ethics in today’s situation in which digital transformation accelerates technological development at a global level, there is a looming concern that while such advancements are bringing economic vitality it may create digital divides and probles like manipulation of public opinion. Professor Jong-cheol Ye of KAIST (Director of the Promotion Council for Digital Health), in particular, emphasized that it is important to find a point of balance that does not hinder the advancements rather than opting to enforcing strict regulations.
< Photo 2. Panel Discussion in Session at NYU-KAIST Global AI & Digital Governance Conference >
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee explained, “At the Digital Governance Forum we had last October, we focused on exploring new governance to solve digital challenges in the time of global digital transition, and this year’s main focus was on regulations.”
“This conference served as an opportunity of immense value as we came to understand that appropriate regulations can be a motivation to spur further developments rather than a hurdle when it comes to technological advancements, and that it is important for us to clearly understand artificial intelligence and consider what should and can be regulated when we are to set regulations on artificial intelligence,” he continued.
Earlier, KAIST signed a cooperation agreement with NYU to build a joint campus, June last year and held a plaque presentation ceremony for the KAIST NYU Joint Campus last September to promote joint research between the two universities. KAIST is currently conducting joint research with NYU in nine fields, including AI and digital research. The KAIST-NYU Joint Campus was conceived with the goal of building an innovative sandbox campus centering aroung science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) combining NYU's excellent humanities and arts as well as basic science and convergence research capabilities with KAIST's science and technology.
KAIST has contributed to the development of Korea's industry and economy through technological innovation aiding in the nation’s transformation into an innovative nation with scientific and technological prowess. KAIST will now pursue an anchor/base strategy to raise KAIST's awareness in New York through the NYU Joint Campus by establishing a KAIST campus within the campus of NYU, the heart of New York.
2023.09.22 View 11744 -
 KAIST holds its first ‘KAIST Tech Fair’ in New York, USA
< Photo 1. 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 11th that it will hold the ‘2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York’ at the Kimmel Center at New York University in Manhattan, USA, on the 22nd of this month. It is an event designed to be the starting point for KAIST to expand its startup ecosystem into the global stage, and it is to attract investments and secure global customers in New York by demonstrating the technological value of KAIST startup companies directly at location.
< Photo 2. President Kwang Hyung Lee at the 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York >
KAIST has been holding briefing sessions for technology transfer in Korea every year since 2018, and this year is the first time to hold a tech fair overseas for global companies.
KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation (Director Sung-Yool Choi) has prepared for this event over the past six months with the Korea International Trade Association (hereinafter KITA, CEO Christopher Koo) to survey customer base and investment companies to conduct market analysis.
Among the companies founded with the technologies developed by the faculty and students of KAIST and their partners, 7 companies were selected to be matched with companies overseas that expressed interests in these technologies. Global multinational companies in the fields of IT, artificial intelligence, environment, logistics, distribution, and retail are participating as demand agencies and are testing the marketability of the start-up's technology as of September.
Daim Research, founded by Professor Young Jae Jang of the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, is a company specializing in smart factory automation solutions and is knocking on the door of the global market with a platform technology optimized for automated logistics systems.
< Photo 3. Presentation by Professor Young Jae Jang for DAIM Research >
It is a ‘collaborative intelligence’ solution that maximizes work productivity by having a number of robots used in industrial settings collaborate with one another. The strength of their solution is that logistics robots equipped with AI reinforced learning technology can respond to processes and environmental changes on their own, minimizing maintenance costs and the system can achieve excellent performance even with a small amount of data when it is combined with the digital twin technology the company has developed on its own.
A student startup, ‘Aniai’, is entering the US market, the home of hamburgers, with hamburger patty automation equipments and solutions. This is a robot kitchen startup founded by its CEO Gunpil Hwang, a graduate of KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering which gathered together the experts in the fields of robot control, design, and artificial intelligence and cognitive technology to develop technology to automatically cook hamburger patties.
At the touch of a button, both sides of the patty are cooked simultaneously for consistent taste and quality according to the set condition. Since it can cook about 200 dishes in an hour, it is attracting attention as a technology that can not only solve manpower shortages but also accelerate the digital transformation of the restaurant industry.
Also, at the tech fair to be held at the Kimmel Center of New York University on the 22nd, the following startups who are currently under market verification in the U.S. will be participating: ▴'TheWaveTalk', which developed a water quality management system that can measure external substances and metal ions by transferring original technology from KAIST; ▴‘VIRNECT’, which helps workers improve their skills by remotely managing industrial sites using XR*; ▴‘Datumo’, a solution that helps process and analyze artificial intelligence big data, ▴‘VESSL AI’, the provider of a solution to eliminate the overhead** of machine learning systems; and ▴ ‘DolbomDream’, which developed an inflatable vest that helps the psychological stability of people with developmental disabilities.
* XR (eXtended Reality): Ultra-realistic technology that enhances immersion by utilizing augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality technologies
** Overhead: Additional time required for stable processing of the program
In addition, two companies (Plasmapp and NotaAI) that are participating in the D-Unicorn program with the support of the Daejeon City and two companies (Enget and ILIAS Biologics) that are receiving support from the Scale Up Tips of the Ministry of SMEs and Startups, three companies (WiPowerOne, IDK Lab, and Artificial Photosynthesis Lab) that are continuing to realize the sustainable development goals for a total of 14 KAIST startups, will hold a corporate information session with about 100 invited guests from global companies and venture capital.
< Photo 4. Presentation for AP Lab >
Prior to this event, participating startups will be visiting the New York Economic Development Corporation and large law firms to receive advice on U.S. government support programs and on their attemps to enter the U.S. market. In addition, the participating companies plan to visit a startup support investment institution pursuing sustainable development goals and the Leslie eLab, New York University's one-stop startup support space, to lay the foundation for KAIST's leap forward in global technology commercialization.
< Photo 5. Sung-Yool Choi, the Director of KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation (left) at the 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York with the key participants >
Sung-Yool Choi, the Director of KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation, said, “KAIST prepared this event to realize its vision of being a leading university in creating global value.” He added, “We hope that our startups founded with KAIST technology would successfully completed market verification to be successful in securing global demands and in attracting investments for their endeavors.”
2023.09.11 View 18557
KAIST holds its first ‘KAIST Tech Fair’ in New York, USA
< Photo 1. 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 11th that it will hold the ‘2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York’ at the Kimmel Center at New York University in Manhattan, USA, on the 22nd of this month. It is an event designed to be the starting point for KAIST to expand its startup ecosystem into the global stage, and it is to attract investments and secure global customers in New York by demonstrating the technological value of KAIST startup companies directly at location.
< Photo 2. President Kwang Hyung Lee at the 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York >
KAIST has been holding briefing sessions for technology transfer in Korea every year since 2018, and this year is the first time to hold a tech fair overseas for global companies.
KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation (Director Sung-Yool Choi) has prepared for this event over the past six months with the Korea International Trade Association (hereinafter KITA, CEO Christopher Koo) to survey customer base and investment companies to conduct market analysis.
Among the companies founded with the technologies developed by the faculty and students of KAIST and their partners, 7 companies were selected to be matched with companies overseas that expressed interests in these technologies. Global multinational companies in the fields of IT, artificial intelligence, environment, logistics, distribution, and retail are participating as demand agencies and are testing the marketability of the start-up's technology as of September.
Daim Research, founded by Professor Young Jae Jang of the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, is a company specializing in smart factory automation solutions and is knocking on the door of the global market with a platform technology optimized for automated logistics systems.
< Photo 3. Presentation by Professor Young Jae Jang for DAIM Research >
It is a ‘collaborative intelligence’ solution that maximizes work productivity by having a number of robots used in industrial settings collaborate with one another. The strength of their solution is that logistics robots equipped with AI reinforced learning technology can respond to processes and environmental changes on their own, minimizing maintenance costs and the system can achieve excellent performance even with a small amount of data when it is combined with the digital twin technology the company has developed on its own.
A student startup, ‘Aniai’, is entering the US market, the home of hamburgers, with hamburger patty automation equipments and solutions. This is a robot kitchen startup founded by its CEO Gunpil Hwang, a graduate of KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering which gathered together the experts in the fields of robot control, design, and artificial intelligence and cognitive technology to develop technology to automatically cook hamburger patties.
At the touch of a button, both sides of the patty are cooked simultaneously for consistent taste and quality according to the set condition. Since it can cook about 200 dishes in an hour, it is attracting attention as a technology that can not only solve manpower shortages but also accelerate the digital transformation of the restaurant industry.
Also, at the tech fair to be held at the Kimmel Center of New York University on the 22nd, the following startups who are currently under market verification in the U.S. will be participating: ▴'TheWaveTalk', which developed a water quality management system that can measure external substances and metal ions by transferring original technology from KAIST; ▴‘VIRNECT’, which helps workers improve their skills by remotely managing industrial sites using XR*; ▴‘Datumo’, a solution that helps process and analyze artificial intelligence big data, ▴‘VESSL AI’, the provider of a solution to eliminate the overhead** of machine learning systems; and ▴ ‘DolbomDream’, which developed an inflatable vest that helps the psychological stability of people with developmental disabilities.
* XR (eXtended Reality): Ultra-realistic technology that enhances immersion by utilizing augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality technologies
** Overhead: Additional time required for stable processing of the program
In addition, two companies (Plasmapp and NotaAI) that are participating in the D-Unicorn program with the support of the Daejeon City and two companies (Enget and ILIAS Biologics) that are receiving support from the Scale Up Tips of the Ministry of SMEs and Startups, three companies (WiPowerOne, IDK Lab, and Artificial Photosynthesis Lab) that are continuing to realize the sustainable development goals for a total of 14 KAIST startups, will hold a corporate information session with about 100 invited guests from global companies and venture capital.
< Photo 4. Presentation for AP Lab >
Prior to this event, participating startups will be visiting the New York Economic Development Corporation and large law firms to receive advice on U.S. government support programs and on their attemps to enter the U.S. market. In addition, the participating companies plan to visit a startup support investment institution pursuing sustainable development goals and the Leslie eLab, New York University's one-stop startup support space, to lay the foundation for KAIST's leap forward in global technology commercialization.
< Photo 5. Sung-Yool Choi, the Director of KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation (left) at the 2023 KAIST Tech Fair in New York with the key participants >
Sung-Yool Choi, the Director of KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation, said, “KAIST prepared this event to realize its vision of being a leading university in creating global value.” He added, “We hope that our startups founded with KAIST technology would successfully completed market verification to be successful in securing global demands and in attracting investments for their endeavors.”
2023.09.11 View 18557 -
 KAIST builds a high-resolution 3D holographic sensor using a single mask
Holographic cameras can provide more realistic images than ordinary cameras thanks to their ability to acquire 3D information about objects. However, existing holographic cameras use interferometers that measure the wavelength and refraction of light through the interference of light waves, which makes them complex and sensitive to their surrounding environment.
On August 23, a KAIST research team led by Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics announced a new leap forward in 3D holographic imaging sensor technology.
The team proposed an innovative holographic camera technology that does not use complex interferometry. Instead, it uses a mask to precisely measure the phase information of light and reconstruct the 3D information of an object with higher accuracy.
< Figure 1. Structure and principle of the proposed holographic camera. The amplitude and phase information of light scattered from a holographic camera can be measured. >
The team used a mask that fulfills certain mathematical conditions and incorporated it into an ordinary camera, and the light scattered from a laser is measured through the mask and analyzed using a computer. This does not require a complex interferometer and allows the phase information of light to be collected through a simplified optical system. With this technique, the mask that is placed between the two lenses and behind an object plays an important role. The mask selectively filters specific parts of light,, and the intensity of the light passing through the lens can be measured using an ordinary commercial camera. This technique combines the image data received from the camera with the unique pattern received from the mask and reconstructs an object’s precise 3D information using an algorithm.
This method allows a high-resolution 3D image of an object to be captured in any position. In practical situations, one can construct a laser-based holographic 3D image sensor by adding a mask with a simple design to a general image sensor. This makes the design and construction of the optical system much easier. In particular, this novel technology can capture high-resolution holographic images of objects moving at high speeds, which widens its potential field of application.
< Figure 2. A moving doll captured by a conventional camera and the proposed holographic camera. When taking a picture without focusing on the object, only a blurred image of the doll can be obtained from a general camera, but the proposed holographic camera can restore the blurred image of the doll into a clear image. >
The results of this study, conducted by Dr. Jeonghun Oh from the KAIST Department of Physics as the first author, were published in Nature Communications on August 12 under the title, "Non-interferometric stand-alone single-shot holographic camera using reciprocal diffractive imaging".
Dr. Oh said, “The holographic camera module we are suggesting can be built by adding a filter to an ordinary camera, which would allow even non-experts to handle it easily in everyday life if it were to be commercialized.” He added, “In particular, it is a promising candidate with the potential to replace existing remote sensing technologies.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation’s Leader Research Project, the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT’s Core Hologram Technology Support Project, and the Nano and Material Technology Development Project.
2023.09.05 View 8903
KAIST builds a high-resolution 3D holographic sensor using a single mask
Holographic cameras can provide more realistic images than ordinary cameras thanks to their ability to acquire 3D information about objects. However, existing holographic cameras use interferometers that measure the wavelength and refraction of light through the interference of light waves, which makes them complex and sensitive to their surrounding environment.
On August 23, a KAIST research team led by Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics announced a new leap forward in 3D holographic imaging sensor technology.
The team proposed an innovative holographic camera technology that does not use complex interferometry. Instead, it uses a mask to precisely measure the phase information of light and reconstruct the 3D information of an object with higher accuracy.
< Figure 1. Structure and principle of the proposed holographic camera. The amplitude and phase information of light scattered from a holographic camera can be measured. >
The team used a mask that fulfills certain mathematical conditions and incorporated it into an ordinary camera, and the light scattered from a laser is measured through the mask and analyzed using a computer. This does not require a complex interferometer and allows the phase information of light to be collected through a simplified optical system. With this technique, the mask that is placed between the two lenses and behind an object plays an important role. The mask selectively filters specific parts of light,, and the intensity of the light passing through the lens can be measured using an ordinary commercial camera. This technique combines the image data received from the camera with the unique pattern received from the mask and reconstructs an object’s precise 3D information using an algorithm.
This method allows a high-resolution 3D image of an object to be captured in any position. In practical situations, one can construct a laser-based holographic 3D image sensor by adding a mask with a simple design to a general image sensor. This makes the design and construction of the optical system much easier. In particular, this novel technology can capture high-resolution holographic images of objects moving at high speeds, which widens its potential field of application.
< Figure 2. A moving doll captured by a conventional camera and the proposed holographic camera. When taking a picture without focusing on the object, only a blurred image of the doll can be obtained from a general camera, but the proposed holographic camera can restore the blurred image of the doll into a clear image. >
The results of this study, conducted by Dr. Jeonghun Oh from the KAIST Department of Physics as the first author, were published in Nature Communications on August 12 under the title, "Non-interferometric stand-alone single-shot holographic camera using reciprocal diffractive imaging".
Dr. Oh said, “The holographic camera module we are suggesting can be built by adding a filter to an ordinary camera, which would allow even non-experts to handle it easily in everyday life if it were to be commercialized.” He added, “In particular, it is a promising candidate with the potential to replace existing remote sensing technologies.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation’s Leader Research Project, the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT’s Core Hologram Technology Support Project, and the Nano and Material Technology Development Project.
2023.09.05 View 8903 -
 A KAIST Research Team Develops a Smart Color-Changing Flexible Battery with Ultra-high Efficiency
With the rapid growth of the smart and wearable electronic devices market, smart next-generation energy storage systems that have energy storage functions as well as additional color-changing properties are receiving a great deal of attention. However, existing electrochromic devices have low electrical conductivity, leading to low efficiency in electron and ion mobility, and low storage capacities. Such batteries have therefore been limited to use in flexible and wearable devices.
On August 21, a joint research team led by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering (DMSE) and Professor Tae Gwang Yun from the Myongji University Department of Materials Science and Engineering announced the development of a smart electrochromic Zn-ion battery that can visually represent its charging and discharging processes using an electrochromic polymer anode incorporated with a “π-bridge spacer”, which increases electron and ion mobility efficiency.
Batteries topped with electrochromic properties are groundbreaking inventions that can visually represent their charged and discharged states using colors, and can be used as display devices that cut down energy consumption for indoor cooling by controlling solar absorbance. The research team successfully built a flexible and electrochromic smart Zn-ion battery that can maintain its excellent electrochromic and electrochemical properties, even under long-term exposure to the atmosphere and mechanical deformations.
< Figure 1. Electrochromic zinc ion battery whose anode is made of a polymer that turns dark blue when charged and transparent when discharged. >
To maximize the efficiency of electron and ion mobility, the team modelled and synthesized the first π-bridge spacer-incorporated polymer anode in the world. π-bonds can improve the mobility of electrons within a structure to speed up ion movement and maximize ion adsorption efficiency, which improves its energy storage capacity.
In anode-based batteries with a π-bridge spacer, the spacer provides room for quicker ion movement. This allows fast charging, an improved zinc-ion discharging capacity of 110 mAh/g, which is 40% greater than previously reported, and a 30% increase in electrochromic function that switches from dark blue to transparent when the device is charged/discharged. In addition, should the transparent flexible battery technology be applied to smart windows, they would display darker colors during the day while they absorb solar energy, and function as a futuristic energy storage technique that can block out UV radiation and replace curtains.
< Figure 2. A schematic diagram of the structure of the electrochromic polymer with π-π spacer and the operation of a smart flexible battery using this cathode material. >
< Figure 3. (A) Density Functional Theory (DFT) theory-based atomic and electronic structure analysis. (B) Comparison of rate characteristics for polymers with and without π-bridge spacers. (C) Electrochemical performance comparison graph with previously reported zinc ion batteries. The anode material, which has an electron donor-acceptor structure with a built-in π-bridge spacer, shows better electrochemical performance and electrochromic properties than existing zinc ion batteries and electrochromic devices. >
Professor Il-Doo Kim said, “We have developed a polymer incorporated with a π-bridge spacer and successfully built a smart Zn-ion battery with excellent electrochromic efficiency and high energy storage capacity.” He added, “This technique goes beyond the existing concept of batteries that are used simply as energy storage devices, and we expect this technology to be used as a futuristic energy storage system that accelerates innovation in smart batteries and wearable technologies.”
This research, co-first authored by the alums of KAIST Departments of Material Sciences of Engineering, Professor Tae Gwang Yun of Myongji University, Dr. Jiyoung Lee, a post-doctoral associate at Northwestern University, and Professor Han Seul Kim at Chungbuk National University, was published as an inside cover article for Advanced Materials on August 3 under the title, “A π-Bridge Spacer Embedded Electron Donor-Acceptor Polymer for Flexible Electrochromic Zn-Ion Batteries”.
< Figure 4. Advanced Materials Inside Cover (August Issue) >
This research was supported by the Nanomaterial Technology Development Project under the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT, the Nano and Material Technology Development Project under the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Successive Academic Generation Development Project under the Korean Ministry of Education, and the Alchemist Project under the Korean Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy.
2023.09.01 View 8898
A KAIST Research Team Develops a Smart Color-Changing Flexible Battery with Ultra-high Efficiency
With the rapid growth of the smart and wearable electronic devices market, smart next-generation energy storage systems that have energy storage functions as well as additional color-changing properties are receiving a great deal of attention. However, existing electrochromic devices have low electrical conductivity, leading to low efficiency in electron and ion mobility, and low storage capacities. Such batteries have therefore been limited to use in flexible and wearable devices.
On August 21, a joint research team led by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering (DMSE) and Professor Tae Gwang Yun from the Myongji University Department of Materials Science and Engineering announced the development of a smart electrochromic Zn-ion battery that can visually represent its charging and discharging processes using an electrochromic polymer anode incorporated with a “π-bridge spacer”, which increases electron and ion mobility efficiency.
Batteries topped with electrochromic properties are groundbreaking inventions that can visually represent their charged and discharged states using colors, and can be used as display devices that cut down energy consumption for indoor cooling by controlling solar absorbance. The research team successfully built a flexible and electrochromic smart Zn-ion battery that can maintain its excellent electrochromic and electrochemical properties, even under long-term exposure to the atmosphere and mechanical deformations.
< Figure 1. Electrochromic zinc ion battery whose anode is made of a polymer that turns dark blue when charged and transparent when discharged. >
To maximize the efficiency of electron and ion mobility, the team modelled and synthesized the first π-bridge spacer-incorporated polymer anode in the world. π-bonds can improve the mobility of electrons within a structure to speed up ion movement and maximize ion adsorption efficiency, which improves its energy storage capacity.
In anode-based batteries with a π-bridge spacer, the spacer provides room for quicker ion movement. This allows fast charging, an improved zinc-ion discharging capacity of 110 mAh/g, which is 40% greater than previously reported, and a 30% increase in electrochromic function that switches from dark blue to transparent when the device is charged/discharged. In addition, should the transparent flexible battery technology be applied to smart windows, they would display darker colors during the day while they absorb solar energy, and function as a futuristic energy storage technique that can block out UV radiation and replace curtains.
< Figure 2. A schematic diagram of the structure of the electrochromic polymer with π-π spacer and the operation of a smart flexible battery using this cathode material. >
< Figure 3. (A) Density Functional Theory (DFT) theory-based atomic and electronic structure analysis. (B) Comparison of rate characteristics for polymers with and without π-bridge spacers. (C) Electrochemical performance comparison graph with previously reported zinc ion batteries. The anode material, which has an electron donor-acceptor structure with a built-in π-bridge spacer, shows better electrochemical performance and electrochromic properties than existing zinc ion batteries and electrochromic devices. >
Professor Il-Doo Kim said, “We have developed a polymer incorporated with a π-bridge spacer and successfully built a smart Zn-ion battery with excellent electrochromic efficiency and high energy storage capacity.” He added, “This technique goes beyond the existing concept of batteries that are used simply as energy storage devices, and we expect this technology to be used as a futuristic energy storage system that accelerates innovation in smart batteries and wearable technologies.”
This research, co-first authored by the alums of KAIST Departments of Material Sciences of Engineering, Professor Tae Gwang Yun of Myongji University, Dr. Jiyoung Lee, a post-doctoral associate at Northwestern University, and Professor Han Seul Kim at Chungbuk National University, was published as an inside cover article for Advanced Materials on August 3 under the title, “A π-Bridge Spacer Embedded Electron Donor-Acceptor Polymer for Flexible Electrochromic Zn-Ion Batteries”.
< Figure 4. Advanced Materials Inside Cover (August Issue) >
This research was supported by the Nanomaterial Technology Development Project under the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT, the Nano and Material Technology Development Project under the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Successive Academic Generation Development Project under the Korean Ministry of Education, and the Alchemist Project under the Korean Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy.
2023.09.01 View 8898 -
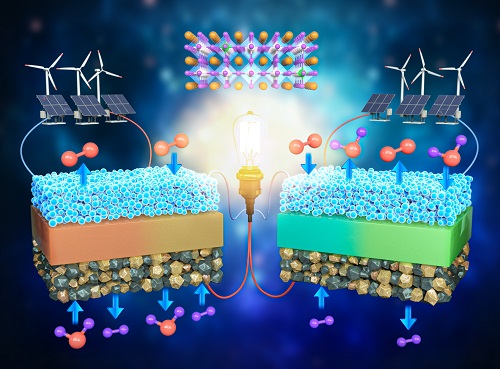 A KAIST Research Team Develops an Ultra-High Performing “Universal Electrode” for Next-Generation Fuel Cells
Fuel cells are devices that generate electricity with high efficiency using hydrogen, a clean energy source, and are expected to play an important part in the upcoming hydrogen society. The recent development of an excellent universal electrode material that is applicable to all next-generation fuel cells and can withstand 700 hours of operation has therefore garnered a great deal of attention.
On August 9, a joint research team led by Prof. WooChul Jung from the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Prof. Kang Taek Lee from the KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Prof. Jun Hyuk Kim from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Hongik University announced the development of an electrode material that is applicable to both oxygen- and proton-conducting solid oxide cells.
Depending on the type of ion conducted by the electrolyte, ceramic fuel cells are categorized into either solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) or protonic ceramic fuel cells (PCFC). As they can both convert between electricity and hydrogen production, fuel cells can be categorized into a total of four device types. These devices are applicable in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, hydrogen charging stations, and power generation systems, and are henceforth emerging as core next-generation technologies for a carbon-neutral society.
However, these devices have a chronic problem where the speed of their slowest reaction would decrease with a drop of driving temperature, which greatly reduces device efficiency. Various studies have been conducted to solve this, but most reported that electrode materials have low catalytic activity and their applications are limited to specific devices, which limits them from being used as SOFCs that require reversible power conversion and hydrogen production.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of high-performance oxygen ion conductive solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) and proton conductive ceramic fuel cell (PCFC) operates with the new universal electrodes >
To solve this issue, the research team doped a perovskite oxide material with Ta5+, a high valence ion that did not receive much attention in the field. Through this, the team successfully stabilized what is usually a highly unstable crystal structure, and confirmed that catalytic activity improved by 100 times.
The electrode material developed by the team was applied to all four of the mentioned device types. Furthermore, their efficiencies were greater than any of the devices reported thus far, and showed excellent performance by stably running for much longer (700 hours) compared to existing materials that deteriorated within the first 100 hours of operation.
< Figure 2. (a) Power conversion and hydrogen production performance chart for the protonic ceramic fuel cell (PCFC) with the new universal electrodes (b) and performance comparison with other reported devices >
This research, in which KAIST’s Ph.D. candidates Dongyeon Kim and Sejong Ahn, and Professor Jun Hyuk Kim from Hongik University contributed as co-first authors, was published in the internationally renowned Energy & Environmental Science under the title, "Oxygen-Electrode for Reversible Solid Oxide Electrochemical Cells at Reduced Temperatures".
Prof. WooChul Jung said, “We broke free from the idea that we must develop a completely new material to solve an existing problem, and instead suggested a way to control the crystal structure of a lesser-known material to develop a high-efficiency fuel cell, and that’s what makes these results more significant.”
Prof. Kang Taek Lee added, “Unlike previously reported materials that could only be applied to one device type at a time, our material has the flexibility of being applicable to all four. We therefore look forward to its contribution in the commercialization of eco-friendly energy technology including fuel cells and water-splitting equipment for hydrogen production.”
This research was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.08.22 View 8676
A KAIST Research Team Develops an Ultra-High Performing “Universal Electrode” for Next-Generation Fuel Cells
Fuel cells are devices that generate electricity with high efficiency using hydrogen, a clean energy source, and are expected to play an important part in the upcoming hydrogen society. The recent development of an excellent universal electrode material that is applicable to all next-generation fuel cells and can withstand 700 hours of operation has therefore garnered a great deal of attention.
On August 9, a joint research team led by Prof. WooChul Jung from the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Prof. Kang Taek Lee from the KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Prof. Jun Hyuk Kim from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Hongik University announced the development of an electrode material that is applicable to both oxygen- and proton-conducting solid oxide cells.
Depending on the type of ion conducted by the electrolyte, ceramic fuel cells are categorized into either solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC) or protonic ceramic fuel cells (PCFC). As they can both convert between electricity and hydrogen production, fuel cells can be categorized into a total of four device types. These devices are applicable in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, hydrogen charging stations, and power generation systems, and are henceforth emerging as core next-generation technologies for a carbon-neutral society.
However, these devices have a chronic problem where the speed of their slowest reaction would decrease with a drop of driving temperature, which greatly reduces device efficiency. Various studies have been conducted to solve this, but most reported that electrode materials have low catalytic activity and their applications are limited to specific devices, which limits them from being used as SOFCs that require reversible power conversion and hydrogen production.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of high-performance oxygen ion conductive solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) and proton conductive ceramic fuel cell (PCFC) operates with the new universal electrodes >
To solve this issue, the research team doped a perovskite oxide material with Ta5+, a high valence ion that did not receive much attention in the field. Through this, the team successfully stabilized what is usually a highly unstable crystal structure, and confirmed that catalytic activity improved by 100 times.
The electrode material developed by the team was applied to all four of the mentioned device types. Furthermore, their efficiencies were greater than any of the devices reported thus far, and showed excellent performance by stably running for much longer (700 hours) compared to existing materials that deteriorated within the first 100 hours of operation.
< Figure 2. (a) Power conversion and hydrogen production performance chart for the protonic ceramic fuel cell (PCFC) with the new universal electrodes (b) and performance comparison with other reported devices >
This research, in which KAIST’s Ph.D. candidates Dongyeon Kim and Sejong Ahn, and Professor Jun Hyuk Kim from Hongik University contributed as co-first authors, was published in the internationally renowned Energy & Environmental Science under the title, "Oxygen-Electrode for Reversible Solid Oxide Electrochemical Cells at Reduced Temperatures".
Prof. WooChul Jung said, “We broke free from the idea that we must develop a completely new material to solve an existing problem, and instead suggested a way to control the crystal structure of a lesser-known material to develop a high-efficiency fuel cell, and that’s what makes these results more significant.”
Prof. Kang Taek Lee added, “Unlike previously reported materials that could only be applied to one device type at a time, our material has the flexibility of being applicable to all four. We therefore look forward to its contribution in the commercialization of eco-friendly energy technology including fuel cells and water-splitting equipment for hydrogen production.”
This research was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.08.22 View 8676 -
 KAIST Research Team Develops World’s First Humanoid Pilot, PIBOT
In the Spring of last year, the legendary, fictional pilot “Maverick” flew his plane in the film “Top Gun: Maverick” that drew crowds to theatres around the world. This year, the appearance of a humanoid pilot, PIBOT, has stolen the spotlight at KAIST.
< Photo 1. Humanoid pilot robot, PIBOT >
A KAIST research team has developed a humanoid robot that can understand manuals written in natural language and fly a plane on its own. The team also announced their plans to commercialize the humanoid pilot.
< Photo 2. PIBOT on flight simulator (view from above) >
The project was led by KAIST Professor David Hyunchul Shim, and was conducted as a joint research project with Professors Jaegul Choo, Kuk-Jin Yoon, and Min Jun Kim. The study was supported by Future Challenge Funding under the project title, “Development of Human-like Pilot Robot based on Natural Language Processing”. The team utilized AI and robotics technologies, and demonstrated that the humanoid could sit itself in a real cockpit and operate the various pieces of equipment without modifying any part of the aircraft. This is a fundamental difference that distinguishes this technology from existing autopilot functions or unmanned aircrafts.
< Photo 3. PIBOT operating a flight simulator (side) >
The KAIST team’s humanoid pilot is still under development but it can already remember Jeppeson charts from all around the world, which is impossible for human pilots to do, and fly without error. In particular, it can make use of recent ChatGPT technology to remember the full Quick Reference Handbook (QRF) and respond immediately to various situations, as well as calculate safe routes in real time based on the flight status of the aircraft, with emergency response times quicker than human pilots.
Furthermore, while existing robots usually carry out repeated motions in a fixed position, PIBOT can analyze the state of the cockpit as well as the situation outside the aircraft using an embedded camera. PIBOT can accurately control the various switches in the cockpit and, using high-precision control technology, it can accurately control its robotic arms and hands even during harsh turbulence.
< Photo 4. PIBOT on-board KLA-100, Korea’s first light aircraft >
The humanoid pilot is currently capable of carrying out all operations from starting the aircraft to taxiing, takeoff and landing, cruising, and cycling using a flight control simulator. The research team plans to use the humanoid pilot to fly a real-life light aircraft to verify its abilities. Prof. Shim explained, “Humanoid pilot robots do not require the modification of existing aircrafts and can be applied immediately to automated flights. They are therefore highly applicable and practical. We expect them to be applied into various other vehicles like cars and military trucks since they can control a wide range of equipment. They will particularly be particularly helpful in situations where military resources are severely depleted.”
This research was supported by Future Challenge Funding (total: 5.7 bn KRW) from the Agency for Defense Development. The project started in 2022 as a joint research project by Prof. David Hyunchul Shim (chief of research) from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering (EE), Prof. Jaegul Choo from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST, Prof. Kuk-Jin Yoon from the KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Prof. Min Jun Kim from the KAIST School of EE. The project is to be completed by 2026 and the involved researchers are also considering commercialization strategies for both military and civil use.
2023.08.03 View 15596
KAIST Research Team Develops World’s First Humanoid Pilot, PIBOT
In the Spring of last year, the legendary, fictional pilot “Maverick” flew his plane in the film “Top Gun: Maverick” that drew crowds to theatres around the world. This year, the appearance of a humanoid pilot, PIBOT, has stolen the spotlight at KAIST.
< Photo 1. Humanoid pilot robot, PIBOT >
A KAIST research team has developed a humanoid robot that can understand manuals written in natural language and fly a plane on its own. The team also announced their plans to commercialize the humanoid pilot.
< Photo 2. PIBOT on flight simulator (view from above) >
The project was led by KAIST Professor David Hyunchul Shim, and was conducted as a joint research project with Professors Jaegul Choo, Kuk-Jin Yoon, and Min Jun Kim. The study was supported by Future Challenge Funding under the project title, “Development of Human-like Pilot Robot based on Natural Language Processing”. The team utilized AI and robotics technologies, and demonstrated that the humanoid could sit itself in a real cockpit and operate the various pieces of equipment without modifying any part of the aircraft. This is a fundamental difference that distinguishes this technology from existing autopilot functions or unmanned aircrafts.
< Photo 3. PIBOT operating a flight simulator (side) >
The KAIST team’s humanoid pilot is still under development but it can already remember Jeppeson charts from all around the world, which is impossible for human pilots to do, and fly without error. In particular, it can make use of recent ChatGPT technology to remember the full Quick Reference Handbook (QRF) and respond immediately to various situations, as well as calculate safe routes in real time based on the flight status of the aircraft, with emergency response times quicker than human pilots.
Furthermore, while existing robots usually carry out repeated motions in a fixed position, PIBOT can analyze the state of the cockpit as well as the situation outside the aircraft using an embedded camera. PIBOT can accurately control the various switches in the cockpit and, using high-precision control technology, it can accurately control its robotic arms and hands even during harsh turbulence.
< Photo 4. PIBOT on-board KLA-100, Korea’s first light aircraft >
The humanoid pilot is currently capable of carrying out all operations from starting the aircraft to taxiing, takeoff and landing, cruising, and cycling using a flight control simulator. The research team plans to use the humanoid pilot to fly a real-life light aircraft to verify its abilities. Prof. Shim explained, “Humanoid pilot robots do not require the modification of existing aircrafts and can be applied immediately to automated flights. They are therefore highly applicable and practical. We expect them to be applied into various other vehicles like cars and military trucks since they can control a wide range of equipment. They will particularly be particularly helpful in situations where military resources are severely depleted.”
This research was supported by Future Challenge Funding (total: 5.7 bn KRW) from the Agency for Defense Development. The project started in 2022 as a joint research project by Prof. David Hyunchul Shim (chief of research) from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering (EE), Prof. Jaegul Choo from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST, Prof. Kuk-Jin Yoon from the KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Prof. Min Jun Kim from the KAIST School of EE. The project is to be completed by 2026 and the involved researchers are also considering commercialization strategies for both military and civil use.
2023.08.03 View 15596