OT
-
 Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu Receives IEEE ICRA 2020 Outstanding Reviewer Award
Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was selected as this year’s winner of the Outstanding Reviewer Award presented by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers International Conference on Robotics and Automation (IEEE ICRA). The award ceremony took place on June 5 during the conference that is being held online May 31 through August 31 for three months.
The IEEE ICRA Outstanding Reviewer Award is given every year to the top reviewers who have provided constructive and high-quality thesis reviews, and contributed to improving the quality of papers published as results of the conference.
Professor Ryu was one of the four winners of this year’s award. He was selected from 9,425 candidates, which was approximately three times bigger than the candidate pool in previous years. He was strongly recommended by the editorial committee of the conference.
(END)
2020.06.10 View 10674
Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu Receives IEEE ICRA 2020 Outstanding Reviewer Award
Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was selected as this year’s winner of the Outstanding Reviewer Award presented by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers International Conference on Robotics and Automation (IEEE ICRA). The award ceremony took place on June 5 during the conference that is being held online May 31 through August 31 for three months.
The IEEE ICRA Outstanding Reviewer Award is given every year to the top reviewers who have provided constructive and high-quality thesis reviews, and contributed to improving the quality of papers published as results of the conference.
Professor Ryu was one of the four winners of this year’s award. He was selected from 9,425 candidates, which was approximately three times bigger than the candidate pool in previous years. He was strongly recommended by the editorial committee of the conference.
(END)
2020.06.10 View 10674 -
 ‘Mole-bot’ Optimized for Underground and Space Exploration
Biomimetic drilling robot provides new insights into the development of efficient drilling technologies
Mole-bot, a drilling biomimetic robot designed by KAIST, boasts a stout scapula, a waist inclinable on all sides, and powerful forelimbs. Most of all, the powerful torque from the expandable drilling bit mimicking the chiseling ability of a mole’s front teeth highlights the best feature of the drilling robot.
The Mole-bot is expected to be used for space exploration and mining for underground resources such as coalbed methane and Rare Earth Elements (REE), which require highly advanced drilling technologies in complex environments.
The research team, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the School of Electrical Engineering, found inspiration for their drilling bot from two striking features of the African mole-rat and European mole.
“The crushing power of the African mole-rat’s teeth is so powerful that they can dig a hole with 48 times more power than their body weight. We used this characteristic for building the main excavation tool. And its expandable drill is designed not to collide with its forelimbs,” said Professor Myung.
The 25-cm wide and 84-cm long Mole-bot can excavate three times faster with six times higher directional accuracy than conventional models. The Mole-bot weighs 26 kg.
After digging, the robot removes the excavated soil and debris using its forelimbs. This embedded muscle feature, inspired by the European mole’s scapula, converts linear motion into a powerful rotational force. For directional drilling, the robot’s elongated waist changes its direction 360° like living mammals.
For exploring underground environments, the research team developed and applied new sensor systems and algorithms to identify the robot’s position and orientation using graph-based 3D Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) technology that matches the Earth’s magnetic field sequence, which enables 3D autonomous navigation underground.
According to Market & Market’s survey, the directional drilling market in 2016 is estimated to be 83.3 billion USD and is expected to grow to 103 billion USD in 2021. The growth of the drilling market, starting with the Shale Revolution, is likely to expand into the future development of space and polar resources. As initiated by Space X recently, more attention for planetary exploration will be on the rise and its related technology and equipment market will also increase.
The Mole-bot is a huge step forward for efficient underground drilling and exploration technologies. Unlike conventional drilling processes that use environmentally unfriendly mud compounds for cleaning debris, Mole-bot can mitigate environmental destruction. The researchers said their system saves on cost and labor and does not require additional pipelines or other ancillary equipment.
“We look forward to a more efficient resource exploration with this type of drilling robot. We also hope Mole-bot will have a very positive impact on the robotics market in terms of its extensive application spectra and economic feasibility,” said Professor Myung.
This research, made in collaboration with Professor Jung-Wuk Hong and Professor Tae-Hyuk Kwon’s team in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering for robot structure analysis and geotechnical experiments, was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy’s Industrial Technology Innovation Project.
Profile
Professor Hyun Myung
Urban Robotics Lab
http://urobot.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2020.06.05 View 12289
‘Mole-bot’ Optimized for Underground and Space Exploration
Biomimetic drilling robot provides new insights into the development of efficient drilling technologies
Mole-bot, a drilling biomimetic robot designed by KAIST, boasts a stout scapula, a waist inclinable on all sides, and powerful forelimbs. Most of all, the powerful torque from the expandable drilling bit mimicking the chiseling ability of a mole’s front teeth highlights the best feature of the drilling robot.
The Mole-bot is expected to be used for space exploration and mining for underground resources such as coalbed methane and Rare Earth Elements (REE), which require highly advanced drilling technologies in complex environments.
The research team, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the School of Electrical Engineering, found inspiration for their drilling bot from two striking features of the African mole-rat and European mole.
“The crushing power of the African mole-rat’s teeth is so powerful that they can dig a hole with 48 times more power than their body weight. We used this characteristic for building the main excavation tool. And its expandable drill is designed not to collide with its forelimbs,” said Professor Myung.
The 25-cm wide and 84-cm long Mole-bot can excavate three times faster with six times higher directional accuracy than conventional models. The Mole-bot weighs 26 kg.
After digging, the robot removes the excavated soil and debris using its forelimbs. This embedded muscle feature, inspired by the European mole’s scapula, converts linear motion into a powerful rotational force. For directional drilling, the robot’s elongated waist changes its direction 360° like living mammals.
For exploring underground environments, the research team developed and applied new sensor systems and algorithms to identify the robot’s position and orientation using graph-based 3D Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) technology that matches the Earth’s magnetic field sequence, which enables 3D autonomous navigation underground.
According to Market & Market’s survey, the directional drilling market in 2016 is estimated to be 83.3 billion USD and is expected to grow to 103 billion USD in 2021. The growth of the drilling market, starting with the Shale Revolution, is likely to expand into the future development of space and polar resources. As initiated by Space X recently, more attention for planetary exploration will be on the rise and its related technology and equipment market will also increase.
The Mole-bot is a huge step forward for efficient underground drilling and exploration technologies. Unlike conventional drilling processes that use environmentally unfriendly mud compounds for cleaning debris, Mole-bot can mitigate environmental destruction. The researchers said their system saves on cost and labor and does not require additional pipelines or other ancillary equipment.
“We look forward to a more efficient resource exploration with this type of drilling robot. We also hope Mole-bot will have a very positive impact on the robotics market in terms of its extensive application spectra and economic feasibility,” said Professor Myung.
This research, made in collaboration with Professor Jung-Wuk Hong and Professor Tae-Hyuk Kwon’s team in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering for robot structure analysis and geotechnical experiments, was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy’s Industrial Technology Innovation Project.
Profile
Professor Hyun Myung
Urban Robotics Lab
http://urobot.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2020.06.05 View 12289 -
 Hubo Debuts as a News Anchor
HUBO, a humanoid robot developed by Professor Jun-Ho Oh’s team, made its debut as a co-anchor during the TJB prime time news 8 on May 14.
“Un-contact" became the new normal after Covid-19 and many business solutions are being transformed using robotics. HUBO made two news reports on contactless services using robots in medical, manufacturing, and logistics industries. HUBO 2, the second generation of HUBO, appeared as a special anchor on the local broadcasting network’s special program in celebration of its 25th anniversary.
HUBO is the champion of the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge held in the USA. Its FX-2 riding robot also participated in the Olympic torch relay during the 2018 PyeongChang Winter Olympics.
Click here to watch a full video of HUBO anchoring the news.
(END)
2020.05.14 View 13728
Hubo Debuts as a News Anchor
HUBO, a humanoid robot developed by Professor Jun-Ho Oh’s team, made its debut as a co-anchor during the TJB prime time news 8 on May 14.
“Un-contact" became the new normal after Covid-19 and many business solutions are being transformed using robotics. HUBO made two news reports on contactless services using robots in medical, manufacturing, and logistics industries. HUBO 2, the second generation of HUBO, appeared as a special anchor on the local broadcasting network’s special program in celebration of its 25th anniversary.
HUBO is the champion of the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge held in the USA. Its FX-2 riding robot also participated in the Olympic torch relay during the 2018 PyeongChang Winter Olympics.
Click here to watch a full video of HUBO anchoring the news.
(END)
2020.05.14 View 13728 -
 Highly Efficient and Stable Double Layer Solar Cell Developed
Solar cells convert light into energy, but they can be inefficient and vulnerable to the environment, degrading with, ironically, too much light or other factors, including moisture and low temperature. An international research team has developed a new type of solar cell that can both withstand environmental hazards and is 26.7% efficient in power conversion.
They published their results on March 26 in Science.
The researchers, led by Byungha Shin, a professor from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, focused on developing a new class of light-absorbing material, called a wide bandgap perovskite. The material has a highly effective crystal structure that can process the power needs, but it can become problematic when exposed to environmental hazards, such as moisture. Researchers have made some progress increasing the efficiency of solar cells based on perovskite, but the material has greater potential than what was previously achieved.
To achieve better performance, Shin and his team built a double layer solar cell, called tandem, in which two or more light absorbers are stacked together to better utilize solar energy. To use perovskite in these tandem devices, the scientists modified the material’s optical property, which allows it to absorb a wider range of solar energy. Without the adjustment, the material is not as useful in achieving high performing tandem solar cells. The modification of the optical property of perovskite, however, comes with a penalty — the material becomes hugely vulnerable to the environment, in particular, to light.
To counteract the wide bandgap perovskite’s delicate nature, the researchers engineered combinations of molecules composing a two-dimensional layer in the perovskite, stabilizing the solar cells.
“We developed a high-quality wide bandgap perovskite material and, in combination with silicon solar cells, achieved world-class perovskite-silicon tandem cells,” Shin said.
The development was only possible due to the engineering method, in which the mixing ratio of the molecules building the two-dimensional layer are carefully controlled. In this case, the perovskite material not only improved efficiency of the resulting solar cell but also gained durability, retaining 80% of its initial power conversion capability even after 1,000 hours of continuous illumination. This is the first time such a high efficiency has been achieved with a wide bandgap perovskite single layer alone, according to Shin.
“Such high-efficiency wide bandgap perovskite is an essential technology for achieving ultra-high efficiency of perovskite-silicon tandem (double layer) solar cells,” Shin said. “The results also show the importance of bandgap matching of upper and lower cells in these tandem solar cells.”
The researchers, having stabilized the wide bandgap perovskite material, are now focused on developing even more efficient tandem solar cells that are expected to have more than 30% of power conversion efficiency, something that no one has achieved yet,
“Our ultimate goal is to develop ultra-high-efficiency tandem solar cells that contribute to the increase of shared solar energy among all energy sources,” Shin said. “We want to contribute to making the planet healthier.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning, the Ministry of Trade Industry and Energy of Korea, and the U.S. Department of Energy.
Other contributors include Daehan Kim, Jekyung Kim, Passarut Boonmongkolras, Seong Ryul Pae and Minkyu Kim, all of whom affiliated with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST. Other authors include Byron W. Larson, Sean P. Dunfield, Chuanxiao Xiao, Jinhui Tong, Fei Zhang, Joseph J. Berry, Kai Zhu and Dong Hoe Kim, all of who are affiliated with the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in Colorado. Dunfield is also affiliated with the Materials Science and Engineering Program at the University of Colorado; Berry is also affiliated with the Department of Physics and the Renewable and Sustainable Energy Institute at the University of Colorado Boulder; and Kim is also affiliated with the Department of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials Engineering at Sejong University. Hee Joon Jung and Vinayak Dravid of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Northwestern University; Ik Jae Park, Su Geun Ji and Jin Young Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Seoul National University; and Seok Beom Kang of the Department of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials Engineering of Sejong University also contributed.
Image credit: Professor Byungha Shin, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication: Kim et al. (2020) “Efficient, stable silicon tandem cells enabled by anion-engineered wide band gap perovskites”. Science. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba3433
Profile:
Byungha Shin
Professor
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Daehan Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
zxzx4592@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.27 View 22868
Highly Efficient and Stable Double Layer Solar Cell Developed
Solar cells convert light into energy, but they can be inefficient and vulnerable to the environment, degrading with, ironically, too much light or other factors, including moisture and low temperature. An international research team has developed a new type of solar cell that can both withstand environmental hazards and is 26.7% efficient in power conversion.
They published their results on March 26 in Science.
The researchers, led by Byungha Shin, a professor from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, focused on developing a new class of light-absorbing material, called a wide bandgap perovskite. The material has a highly effective crystal structure that can process the power needs, but it can become problematic when exposed to environmental hazards, such as moisture. Researchers have made some progress increasing the efficiency of solar cells based on perovskite, but the material has greater potential than what was previously achieved.
To achieve better performance, Shin and his team built a double layer solar cell, called tandem, in which two or more light absorbers are stacked together to better utilize solar energy. To use perovskite in these tandem devices, the scientists modified the material’s optical property, which allows it to absorb a wider range of solar energy. Without the adjustment, the material is not as useful in achieving high performing tandem solar cells. The modification of the optical property of perovskite, however, comes with a penalty — the material becomes hugely vulnerable to the environment, in particular, to light.
To counteract the wide bandgap perovskite’s delicate nature, the researchers engineered combinations of molecules composing a two-dimensional layer in the perovskite, stabilizing the solar cells.
“We developed a high-quality wide bandgap perovskite material and, in combination with silicon solar cells, achieved world-class perovskite-silicon tandem cells,” Shin said.
The development was only possible due to the engineering method, in which the mixing ratio of the molecules building the two-dimensional layer are carefully controlled. In this case, the perovskite material not only improved efficiency of the resulting solar cell but also gained durability, retaining 80% of its initial power conversion capability even after 1,000 hours of continuous illumination. This is the first time such a high efficiency has been achieved with a wide bandgap perovskite single layer alone, according to Shin.
“Such high-efficiency wide bandgap perovskite is an essential technology for achieving ultra-high efficiency of perovskite-silicon tandem (double layer) solar cells,” Shin said. “The results also show the importance of bandgap matching of upper and lower cells in these tandem solar cells.”
The researchers, having stabilized the wide bandgap perovskite material, are now focused on developing even more efficient tandem solar cells that are expected to have more than 30% of power conversion efficiency, something that no one has achieved yet,
“Our ultimate goal is to develop ultra-high-efficiency tandem solar cells that contribute to the increase of shared solar energy among all energy sources,” Shin said. “We want to contribute to making the planet healthier.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning, the Ministry of Trade Industry and Energy of Korea, and the U.S. Department of Energy.
Other contributors include Daehan Kim, Jekyung Kim, Passarut Boonmongkolras, Seong Ryul Pae and Minkyu Kim, all of whom affiliated with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST. Other authors include Byron W. Larson, Sean P. Dunfield, Chuanxiao Xiao, Jinhui Tong, Fei Zhang, Joseph J. Berry, Kai Zhu and Dong Hoe Kim, all of who are affiliated with the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in Colorado. Dunfield is also affiliated with the Materials Science and Engineering Program at the University of Colorado; Berry is also affiliated with the Department of Physics and the Renewable and Sustainable Energy Institute at the University of Colorado Boulder; and Kim is also affiliated with the Department of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials Engineering at Sejong University. Hee Joon Jung and Vinayak Dravid of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Northwestern University; Ik Jae Park, Su Geun Ji and Jin Young Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Seoul National University; and Seok Beom Kang of the Department of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials Engineering of Sejong University also contributed.
Image credit: Professor Byungha Shin, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication: Kim et al. (2020) “Efficient, stable silicon tandem cells enabled by anion-engineered wide band gap perovskites”. Science. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba3433
Profile:
Byungha Shin
Professor
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Daehan Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
zxzx4592@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.27 View 22868 -
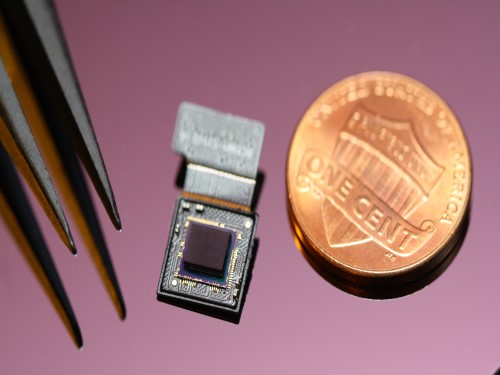 Ultrathin but Fully Packaged High-Resolution Camera
- Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera captures super-resolution images. -
The unique structures of biological vision systems in nature inspired scientists to design ultracompact imaging systems. A research group led by Professor Ki-Hun Jeong have made an ultracompact camera that captures high-contrast and high-resolution images. Fully packaged with micro-optical elements such as inverted micro-lenses, multilayered pinhole arrays, and gap spacers on the image sensor, the camera boasts a total track length of 740 μm and a field of view of 73°.
Inspired by the eye structures of the paper wasp species Xenos peckii, the research team completely suppressed optical noise between micro-lenses while reducing camera thickness. The camera has successfully demonstrated high-contrast clear array images acquired from tiny micro lenses. To further enhance the image quality of the captured image, the team combined the arrayed images into one image through super-resolution imaging.
An insect’s compound eye has superior visual characteristics, such as a wide viewing angle, high motion sensitivity, and a large depth of field while maintaining a small volume of visual structure with a small focal length. Among them, the eyes of Xenos peckii and an endoparasite found on paper wasps have hundreds of photoreceptors in a single lens unlike conventional compound eyes. In particular, the eye structures of an adult Xenos peckii exhibit hundreds of photoreceptors on an individual eyelet and offer engineering inspiration for ultrathin cameras or imaging applications because they have higher visual acuity than other compound eyes.
For instance, Xenos peckii’s eye-inspired cameras provide a 50 times higher spatial resolution than those based on arthropod eyes. In addition, the effective image resolution of the Xenos peckii’s eye can be further improved using the image overlaps between neighboring eyelets. This unique structure offers higher visual resolution than other insect eyes.
The team achieved high-contrast and super-resolution imaging through a novel arrayed design of micro-optical elements comprising multilayered aperture arrays and inverted micro-lens arrays directly stacked over an image sensor. This optical component was integrated with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor.
This is first demonstration of super-resolution imaging which acquires a single integrated image with high contrast and high resolving power reconstructed from high-contrast array images. It is expected that this ultrathin arrayed camera can be applied for further developing mobile devices, advanced surveillance vehicles, and endoscopes.
Professor Jeong said, “This research has led to technological advances in imaging technology. We will continue to strive to make significant impacts on multidisciplinary research projects in the fields of microtechnology and nanotechnology, seeking inspiration from natural photonic structures.”
This work was featured in Light Science & Applications last month and was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of and the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kisoo Kim, Kyung-Won Jang, Jae-Kwan Ryu, and Ki-Hun Jeong. (2020) “Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera for high-contrast and high-resolution imaging”. Light Science & Applications. Volume 9. Article 28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0261-8
Profile:
Ki-Hun Jeong
Professor
kjeong@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Kisoo Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
kisoo.kim1@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.23 View 20522
Ultrathin but Fully Packaged High-Resolution Camera
- Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera captures super-resolution images. -
The unique structures of biological vision systems in nature inspired scientists to design ultracompact imaging systems. A research group led by Professor Ki-Hun Jeong have made an ultracompact camera that captures high-contrast and high-resolution images. Fully packaged with micro-optical elements such as inverted micro-lenses, multilayered pinhole arrays, and gap spacers on the image sensor, the camera boasts a total track length of 740 μm and a field of view of 73°.
Inspired by the eye structures of the paper wasp species Xenos peckii, the research team completely suppressed optical noise between micro-lenses while reducing camera thickness. The camera has successfully demonstrated high-contrast clear array images acquired from tiny micro lenses. To further enhance the image quality of the captured image, the team combined the arrayed images into one image through super-resolution imaging.
An insect’s compound eye has superior visual characteristics, such as a wide viewing angle, high motion sensitivity, and a large depth of field while maintaining a small volume of visual structure with a small focal length. Among them, the eyes of Xenos peckii and an endoparasite found on paper wasps have hundreds of photoreceptors in a single lens unlike conventional compound eyes. In particular, the eye structures of an adult Xenos peckii exhibit hundreds of photoreceptors on an individual eyelet and offer engineering inspiration for ultrathin cameras or imaging applications because they have higher visual acuity than other compound eyes.
For instance, Xenos peckii’s eye-inspired cameras provide a 50 times higher spatial resolution than those based on arthropod eyes. In addition, the effective image resolution of the Xenos peckii’s eye can be further improved using the image overlaps between neighboring eyelets. This unique structure offers higher visual resolution than other insect eyes.
The team achieved high-contrast and super-resolution imaging through a novel arrayed design of micro-optical elements comprising multilayered aperture arrays and inverted micro-lens arrays directly stacked over an image sensor. This optical component was integrated with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor.
This is first demonstration of super-resolution imaging which acquires a single integrated image with high contrast and high resolving power reconstructed from high-contrast array images. It is expected that this ultrathin arrayed camera can be applied for further developing mobile devices, advanced surveillance vehicles, and endoscopes.
Professor Jeong said, “This research has led to technological advances in imaging technology. We will continue to strive to make significant impacts on multidisciplinary research projects in the fields of microtechnology and nanotechnology, seeking inspiration from natural photonic structures.”
This work was featured in Light Science & Applications last month and was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of and the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kisoo Kim, Kyung-Won Jang, Jae-Kwan Ryu, and Ki-Hun Jeong. (2020) “Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera for high-contrast and high-resolution imaging”. Light Science & Applications. Volume 9. Article 28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0261-8
Profile:
Ki-Hun Jeong
Professor
kjeong@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Kisoo Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
kisoo.kim1@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.23 View 20522 -
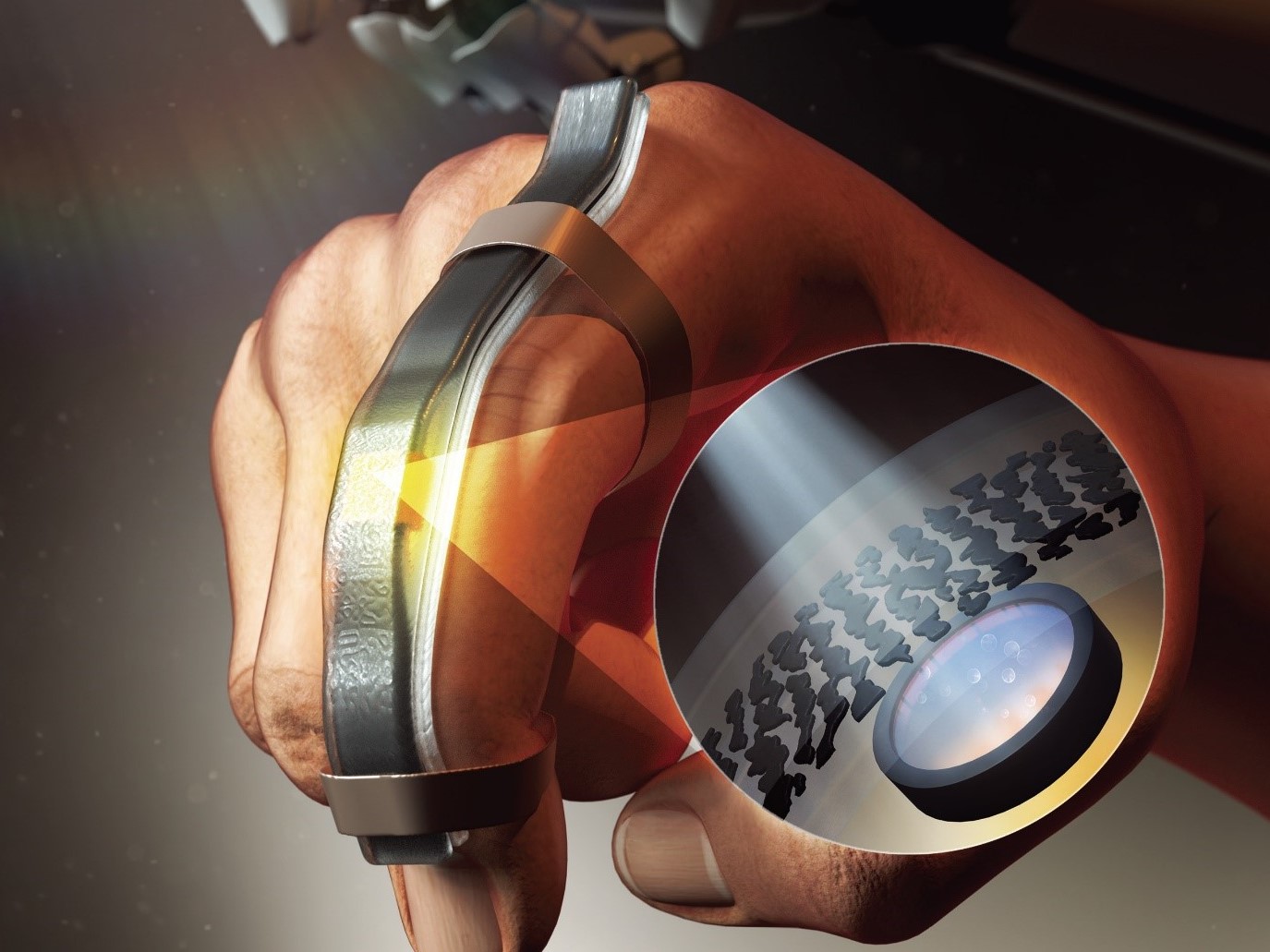 Wearable Strain Sensor Using Light Transmittance Helps Measure Physical Signals Better
KAIST researchers have developed a novel wearable strain sensor based on the modulation of optical transmittance of a carbon nanotube (CNT)-embedded elastomer. The sensor is capable of sensitive, stable, and continuous measurement of physical signals. This technology, featured in the March 4th issue of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces as a front cover article, shows great potential for the detection of subtle human motions and the real-time monitoring of body postures for healthcare applications.
A wearable strain sensor must have high sensitivity, flexibility, and stretchability, as well as low cost. Those used especially for health monitoring should also be tied to long-term solid performance, and be environmentally stable. Various stretchable strain sensors based on piezo-resistive and capacitive principles have been developed to meet all these requirements.
Conventional piezo-resistive strain sensors using functional nanomaterials, including CNTs as the most common example, have shown high sensitivity and great sensing performance. However, they suffer from poor long-term stability and linearity, as well as considerable signal hysteresis. As an alternative, piezo-capacitive strain sensors with better stability, lower hysteresis, and higher stretchability have been suggested. But due to the fact that piezo-capacitive strain sensors exhibit limited sensitivity and strong electromagnetic interference caused by the conductive objects in the surrounding environment, these conventional stretchable strain sensors are still facing limitations that are yet to be resolved.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering suggested that an optical-type stretchable strain sensor can be a good alternative to resolve the limitations of conventional piezo-resistive and piezo-capacitive strain sensors, because they have high stability and are less affected by environmental disturbances. The team then introduced an optical wearable strain sensor based on the light transmittance changes of a CNT-embedded elastomer, which further addresses the low sensitivity problem of conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
In order to achieve a large dynamic range for the sensor, Professor Park and his researchers chose Ecoflex as an elastomeric substrate with good mechanical durability, flexibility, and attachability on human skin, and the new optical wearable strain sensor developed by the research group actually shows a wide dynamic range of 0 to 400%.
In addition, the researchers propagated the microcracks under tensile strain within the film of multi-walled CNTs embedded in the Ecoflex substrate, changing the optical transmittance of the film. By doing so, it was possible for them to develop a wearable strain sensor having a sensitivity 10 times higher than conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
The proposed sensor has also passed the durability test with excellent results. The sensor’s response after 13,000 sets of cyclic loading was stable without any noticeable drift. This suggests that the sensor response can be used without degradation, even if the sensor is repeatedly used for a long time and in various environmental conditions.
Using the developed sensor, the research team could measure the finger bending motion and used it for robot control. They also developed a three-axes sensor array for body posture monitoring. The sensor was able to monitor human motions with small strains such as a pulse near the carotid artery and muscle movement around the mouth during pronunciation.
Professor Park said, “In this study, our group developed a new wearable strain sensor platform that overcomes many limitations of previously developed resistive, capacitive, and optical-type stretchable strain sensors. Our sensor could be widely used in a variety of fields including soft robotics, wearable electronics, electronic skin, healthcare, and even entertainment.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Jimin Gu, Donguk Kwon, Junseong Ahn, and Inkyu Park. (2020) “Wearable Strain sensors Using Light Transmittance Change of Carbon Nanotube-Embedded Elastomers with Microcracks” ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. Volume 12. Issue 9. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b18069
Profile:
Inkyu Park
Professor
inkyu@kaist.ac.kr
http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr
Micro/Nano Transducers Laboratory (MINT Lab)
Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME)Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Profile:
Jimin Gu
Ph.D. Candidate
mint9411@kaist.ac.kr
http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr
MINT Lab
KAIST ME
(END)
2020.03.20 View 21364
Wearable Strain Sensor Using Light Transmittance Helps Measure Physical Signals Better
KAIST researchers have developed a novel wearable strain sensor based on the modulation of optical transmittance of a carbon nanotube (CNT)-embedded elastomer. The sensor is capable of sensitive, stable, and continuous measurement of physical signals. This technology, featured in the March 4th issue of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces as a front cover article, shows great potential for the detection of subtle human motions and the real-time monitoring of body postures for healthcare applications.
A wearable strain sensor must have high sensitivity, flexibility, and stretchability, as well as low cost. Those used especially for health monitoring should also be tied to long-term solid performance, and be environmentally stable. Various stretchable strain sensors based on piezo-resistive and capacitive principles have been developed to meet all these requirements.
Conventional piezo-resistive strain sensors using functional nanomaterials, including CNTs as the most common example, have shown high sensitivity and great sensing performance. However, they suffer from poor long-term stability and linearity, as well as considerable signal hysteresis. As an alternative, piezo-capacitive strain sensors with better stability, lower hysteresis, and higher stretchability have been suggested. But due to the fact that piezo-capacitive strain sensors exhibit limited sensitivity and strong electromagnetic interference caused by the conductive objects in the surrounding environment, these conventional stretchable strain sensors are still facing limitations that are yet to be resolved.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering suggested that an optical-type stretchable strain sensor can be a good alternative to resolve the limitations of conventional piezo-resistive and piezo-capacitive strain sensors, because they have high stability and are less affected by environmental disturbances. The team then introduced an optical wearable strain sensor based on the light transmittance changes of a CNT-embedded elastomer, which further addresses the low sensitivity problem of conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
In order to achieve a large dynamic range for the sensor, Professor Park and his researchers chose Ecoflex as an elastomeric substrate with good mechanical durability, flexibility, and attachability on human skin, and the new optical wearable strain sensor developed by the research group actually shows a wide dynamic range of 0 to 400%.
In addition, the researchers propagated the microcracks under tensile strain within the film of multi-walled CNTs embedded in the Ecoflex substrate, changing the optical transmittance of the film. By doing so, it was possible for them to develop a wearable strain sensor having a sensitivity 10 times higher than conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
The proposed sensor has also passed the durability test with excellent results. The sensor’s response after 13,000 sets of cyclic loading was stable without any noticeable drift. This suggests that the sensor response can be used without degradation, even if the sensor is repeatedly used for a long time and in various environmental conditions.
Using the developed sensor, the research team could measure the finger bending motion and used it for robot control. They also developed a three-axes sensor array for body posture monitoring. The sensor was able to monitor human motions with small strains such as a pulse near the carotid artery and muscle movement around the mouth during pronunciation.
Professor Park said, “In this study, our group developed a new wearable strain sensor platform that overcomes many limitations of previously developed resistive, capacitive, and optical-type stretchable strain sensors. Our sensor could be widely used in a variety of fields including soft robotics, wearable electronics, electronic skin, healthcare, and even entertainment.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Jimin Gu, Donguk Kwon, Junseong Ahn, and Inkyu Park. (2020) “Wearable Strain sensors Using Light Transmittance Change of Carbon Nanotube-Embedded Elastomers with Microcracks” ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. Volume 12. Issue 9. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b18069
Profile:
Inkyu Park
Professor
inkyu@kaist.ac.kr
http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr
Micro/Nano Transducers Laboratory (MINT Lab)
Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME)Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Profile:
Jimin Gu
Ph.D. Candidate
mint9411@kaist.ac.kr
http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr
MINT Lab
KAIST ME
(END)
2020.03.20 View 21364 -
 Scientists Observe the Elusive Kondo Screening Cloud
Scientists ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon
An international research group of Professor Heung-Sun Sim has ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon known as a Kondo screening cloud. This research, published in Nature on March 11, opens a novel way to engineer spin screening and entanglement. According to the research, the cloud can mediate interactions between distant spins confined in quantum dots, which is a necessary protocol for semiconductor spin-based quantum information processing. This spin-spin interaction mediated by the Kondo cloud is unique since both its strength and sign (two spins favor either parallel or anti-parallel configuration) are electrically tunable, while conventional schemes cannot reverse the sign.
This phenomenon, which is important for many physical phenomena such as dilute magnetic impurities and spin glasses, is essentially a cloud that masks magnetic impurities in a material. It was known to exist but its spatial extension had never been observed, creating controversy over whether such an extension actually existed.
Magnetism arises from a property of electrons known as spin, meaning that they have angular momentum aligned in one of either two directions, conventionally known as up and down. However, due to a phenomenon known as the Kondo effect, the spins of conduction electrons—the electrons that flow freely in a material—become entangled with a localized magnetic impurity, and effectively screen it. The strength of this spin coupling, calibrated as a temperature, is known as the Kondo temperature.
The size of the cloud is another important parameter for a material containing multiple magnetic impurities because the spins in the cloud couple with one another and mediate the coupling between magnetic impurities when the clouds overlap. This happens in various materials such as Kondo lattices, spin glasses, and high temperature superconductors.
Although the Kondo effect for a single magnetic impurity is now a text-book subject in many-body physics, detection of its key object, the Kondo cloud and its length, has remained elusive despite many attempts during the past five decades. Experiments using nuclear magnetic resonance or scanning tunneling microscopy, two common methods for understanding the structure of matter, have either shown no signature of the cloud, or demonstrated a signature only at a very short distance, less than 1 nanometer, so much shorter than the predicted cloud size, which was in the micron range.
In the present study, the authors observed a Kondo screening cloud formed by an impurity defined as a localized electron spin in a quantum dot—a type of “artificial atom”—coupled to quasi-one-dimensional conduction electrons, and then used an interferometer to measure changes in the Kondo temperature, allowing them to investigate the presence of a cloud at the interferometer end.
Essentially, they slightly perturbed the conduction electrons at a location away from the quantum dot using an electrostatic gate. The wave of conducting electrons scattered by this perturbation returned back to the quantum dot and interfered with itself. This is similar to how a wave on a water surface being scattered by a wall forms a stripe pattern. The Kondo cloud is a quantum mechanical object which acts to preserve the wave nature of electrons inside the cloud.
Even though there is no direct electrostatic influence of the perturbation on the quantum dot, this interference modifies the Kondo signature measured by electron conductance through the quantum dot if the perturbation is present inside the cloud. In the study, the researchers found that the length as well as the shape of the cloud is universally scaled by the inverse of the Kondo temperature, and that the cloud’s size and shape were in good agreement with theoretical calculations.
Professor Sim at the Department of Physics proposed the method for detecting the Kondo cloud in the co-research with the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science, the City University of Hong Kong, the University of Tokyo, and Ruhr University Bochum in Germany.
Professor Sim said, “The observed spin cloud is a micrometer-size object that has quantum mechanical wave nature and entanglement. This is why the spin cloud has not been observed despite a long search. It is remarkable in a fundamental and technical point of view that such a large quantum object can now be created, controlled, and detected.
Dr. Michihisa Yamamoto of the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science also said, “It is very satisfying to have been able to obtain real space image of the Kondo cloud, as it is a real breakthrough for understanding various systems containing multiple magnetic impurities. The size of the Kondo cloud in semiconductors was found to be much larger than the typical size of semiconductor devices.”
Publication:
Borzenets et al. (2020) Observation of the Kondo screening cloud. Nature, 579. pp.210-213. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2058-6
Profile:
Heung-Sun Sim, PhD
Professor
hssim@kaist.ac.kr
https://qet.kaist.ac.kr/
Quantum Electron Correlation & Transport Theory Group (QECT Lab)
https://qc.kaist.ac.kr/index.php/group1/
Center for Quantum Coherence In COndensed Matter
Department of Physics
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2020.03.13 View 17700
Scientists Observe the Elusive Kondo Screening Cloud
Scientists ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon
An international research group of Professor Heung-Sun Sim has ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon known as a Kondo screening cloud. This research, published in Nature on March 11, opens a novel way to engineer spin screening and entanglement. According to the research, the cloud can mediate interactions between distant spins confined in quantum dots, which is a necessary protocol for semiconductor spin-based quantum information processing. This spin-spin interaction mediated by the Kondo cloud is unique since both its strength and sign (two spins favor either parallel or anti-parallel configuration) are electrically tunable, while conventional schemes cannot reverse the sign.
This phenomenon, which is important for many physical phenomena such as dilute magnetic impurities and spin glasses, is essentially a cloud that masks magnetic impurities in a material. It was known to exist but its spatial extension had never been observed, creating controversy over whether such an extension actually existed.
Magnetism arises from a property of electrons known as spin, meaning that they have angular momentum aligned in one of either two directions, conventionally known as up and down. However, due to a phenomenon known as the Kondo effect, the spins of conduction electrons—the electrons that flow freely in a material—become entangled with a localized magnetic impurity, and effectively screen it. The strength of this spin coupling, calibrated as a temperature, is known as the Kondo temperature.
The size of the cloud is another important parameter for a material containing multiple magnetic impurities because the spins in the cloud couple with one another and mediate the coupling between magnetic impurities when the clouds overlap. This happens in various materials such as Kondo lattices, spin glasses, and high temperature superconductors.
Although the Kondo effect for a single magnetic impurity is now a text-book subject in many-body physics, detection of its key object, the Kondo cloud and its length, has remained elusive despite many attempts during the past five decades. Experiments using nuclear magnetic resonance or scanning tunneling microscopy, two common methods for understanding the structure of matter, have either shown no signature of the cloud, or demonstrated a signature only at a very short distance, less than 1 nanometer, so much shorter than the predicted cloud size, which was in the micron range.
In the present study, the authors observed a Kondo screening cloud formed by an impurity defined as a localized electron spin in a quantum dot—a type of “artificial atom”—coupled to quasi-one-dimensional conduction electrons, and then used an interferometer to measure changes in the Kondo temperature, allowing them to investigate the presence of a cloud at the interferometer end.
Essentially, they slightly perturbed the conduction electrons at a location away from the quantum dot using an electrostatic gate. The wave of conducting electrons scattered by this perturbation returned back to the quantum dot and interfered with itself. This is similar to how a wave on a water surface being scattered by a wall forms a stripe pattern. The Kondo cloud is a quantum mechanical object which acts to preserve the wave nature of electrons inside the cloud.
Even though there is no direct electrostatic influence of the perturbation on the quantum dot, this interference modifies the Kondo signature measured by electron conductance through the quantum dot if the perturbation is present inside the cloud. In the study, the researchers found that the length as well as the shape of the cloud is universally scaled by the inverse of the Kondo temperature, and that the cloud’s size and shape were in good agreement with theoretical calculations.
Professor Sim at the Department of Physics proposed the method for detecting the Kondo cloud in the co-research with the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science, the City University of Hong Kong, the University of Tokyo, and Ruhr University Bochum in Germany.
Professor Sim said, “The observed spin cloud is a micrometer-size object that has quantum mechanical wave nature and entanglement. This is why the spin cloud has not been observed despite a long search. It is remarkable in a fundamental and technical point of view that such a large quantum object can now be created, controlled, and detected.
Dr. Michihisa Yamamoto of the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science also said, “It is very satisfying to have been able to obtain real space image of the Kondo cloud, as it is a real breakthrough for understanding various systems containing multiple magnetic impurities. The size of the Kondo cloud in semiconductors was found to be much larger than the typical size of semiconductor devices.”
Publication:
Borzenets et al. (2020) Observation of the Kondo screening cloud. Nature, 579. pp.210-213. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2058-6
Profile:
Heung-Sun Sim, PhD
Professor
hssim@kaist.ac.kr
https://qet.kaist.ac.kr/
Quantum Electron Correlation & Transport Theory Group (QECT Lab)
https://qc.kaist.ac.kr/index.php/group1/
Center for Quantum Coherence In COndensed Matter
Department of Physics
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2020.03.13 View 17700 -
 Professor Hojong Chang’s Research Team Wins ISIITA 2020 Best Paper Award
The paper written by Professor Hojong Chang’s research team from KAIST Institute for IT Convergence won the best paper award from the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology Application (ISIITA) 2020, held this month at Ton Duc Thang University in Vietnam.
ISIITA is a networking symposium where leading researchers from various fields including information and communications, biotechnology, and computer systems come together and share on the convergence of technology.
Professor Chang’s team won the best paper award at this year’s symposium with its paper, “A Study of Single Photon Counting System for Quantitative Analysis of Luminescence”. The awarded paper discusses the realization of a signal processing system for silicon photomultipliers.
The silicon photomultiplier is the core of a urinalysis technique that tests for sodium and potassium in the body using simple chemical reactions. If our bodily sodium and potassium levels exceed a certain amount, it can lead to high blood pressure, cardiovascular problems, and kidney damage.
Through this research, the team has developed a core technique that quantifies the sodium and potassium discharged in the urine. When the reagent is injected into the urine, a very small amount of light is emitted as a result of the chemical reaction. However, if there is a large amount of sodium and potassium, they interrupt the reaction and reduce the emission. The key to this measurement technique is digitizing the strength of this very fine emission of light. Professor Chang’s team developed a system that uses a photomultiplier to measure the chemiluminescence.
Professor Chang said, “I look forward for this signal processing system greatly helping to prevent diseases caused by the excessive consumption of sodium and potassium through quick and easy detection.”
Researcher Byunghun Han who carried out the central research for the system design added, “We are planning to focus on miniaturizing the developed technique, so that anyone can carry our device around like a cellphone.”
The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(END)
2020.02.27 View 11820
Professor Hojong Chang’s Research Team Wins ISIITA 2020 Best Paper Award
The paper written by Professor Hojong Chang’s research team from KAIST Institute for IT Convergence won the best paper award from the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology Application (ISIITA) 2020, held this month at Ton Duc Thang University in Vietnam.
ISIITA is a networking symposium where leading researchers from various fields including information and communications, biotechnology, and computer systems come together and share on the convergence of technology.
Professor Chang’s team won the best paper award at this year’s symposium with its paper, “A Study of Single Photon Counting System for Quantitative Analysis of Luminescence”. The awarded paper discusses the realization of a signal processing system for silicon photomultipliers.
The silicon photomultiplier is the core of a urinalysis technique that tests for sodium and potassium in the body using simple chemical reactions. If our bodily sodium and potassium levels exceed a certain amount, it can lead to high blood pressure, cardiovascular problems, and kidney damage.
Through this research, the team has developed a core technique that quantifies the sodium and potassium discharged in the urine. When the reagent is injected into the urine, a very small amount of light is emitted as a result of the chemical reaction. However, if there is a large amount of sodium and potassium, they interrupt the reaction and reduce the emission. The key to this measurement technique is digitizing the strength of this very fine emission of light. Professor Chang’s team developed a system that uses a photomultiplier to measure the chemiluminescence.
Professor Chang said, “I look forward for this signal processing system greatly helping to prevent diseases caused by the excessive consumption of sodium and potassium through quick and easy detection.”
Researcher Byunghun Han who carried out the central research for the system design added, “We are planning to focus on miniaturizing the developed technique, so that anyone can carry our device around like a cellphone.”
The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(END)
2020.02.27 View 11820 -
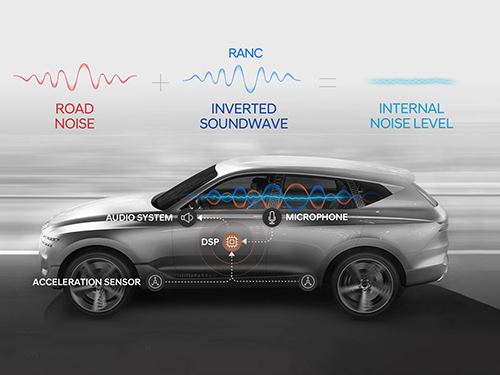 A System Controlling Road Active Noise to Hit the Road
The research team led by Professor Youngjin Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a road noise active noise control (RANC) system to be commercialized in partnership with Hyundai Motor Group.
On December 11, Hyundai Motor Group announced the successful development of the RANC system, which significantly reduces the road noise flowing into cars. The carmaker has completed the domestic and American patent applications for the location of sensors and the signal selection method, the core technology of RANC.
RANC is a technology for reducing road noise during driving. This system consists of an acceleration sensor, digital signal processor (the control computer to analyze sound signals), microphone, amplifier, and audio system. To make the system as simple as possible, the audio system utilizes the original audio system embedded in the car instead of a separate system.
The acceleration sensor first calculates the vibration from the road into the car. The location of the sensor is important for accurately identifying the vibration path. The research team was able to find the optimal sensor location through a number of tests.
The System Dynamics and Applied Control Laboratory of Professor Park researched ways to significantly reduce road noise with Hyundai Motor Group for four years from 1993 as a G7 national project and published the results in international journals. In 2002, the researchers published an article titled “Noise Quietens Driving” in Nature, where they announced the first success in reducing road noise in actual cars. The achievement did not lead to commercialization, however, due to the lack of auxiliary technologies at the time, digital amplifiers and DSP for cars for example, and pricing issues.
Since 2013, Professor Park’s research team has participated in one technology transfer and eight university-industry projects. Based on these efforts, the team was able to successfully develop the RANC system with domestic technology in partnership with Hyundai’s NVH Research Lab (Research Fellow, Dr. Gangdeok Lee; Ph.D. in aviation engineering, 1996), Optomech (Founder, Professor Gyeongsu Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1999), ARE (CEO Hyeonseok Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1998), WeAcom, and BurnYoung.
Professor Park’s team led the project by performing theory-based research during the commercialization stage in collaboration with Hyundai Motor Group.
For the commercialization of the RANC system, Hyundai Motor Group is planning to collaborate with the global car audio company Harman to increase the degree of completion and apply the RANC system to the GV 80, the first SUV model of the Genesis brand.
“I am very delighted as an engineer to see the research I worked on from my early days at KAIST be commercialized after 20 years,” noted Professor Park. “I am thrilled to make a contribution to such commercialization with my students in my lab.”
2019.12.27 View 13167
A System Controlling Road Active Noise to Hit the Road
The research team led by Professor Youngjin Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a road noise active noise control (RANC) system to be commercialized in partnership with Hyundai Motor Group.
On December 11, Hyundai Motor Group announced the successful development of the RANC system, which significantly reduces the road noise flowing into cars. The carmaker has completed the domestic and American patent applications for the location of sensors and the signal selection method, the core technology of RANC.
RANC is a technology for reducing road noise during driving. This system consists of an acceleration sensor, digital signal processor (the control computer to analyze sound signals), microphone, amplifier, and audio system. To make the system as simple as possible, the audio system utilizes the original audio system embedded in the car instead of a separate system.
The acceleration sensor first calculates the vibration from the road into the car. The location of the sensor is important for accurately identifying the vibration path. The research team was able to find the optimal sensor location through a number of tests.
The System Dynamics and Applied Control Laboratory of Professor Park researched ways to significantly reduce road noise with Hyundai Motor Group for four years from 1993 as a G7 national project and published the results in international journals. In 2002, the researchers published an article titled “Noise Quietens Driving” in Nature, where they announced the first success in reducing road noise in actual cars. The achievement did not lead to commercialization, however, due to the lack of auxiliary technologies at the time, digital amplifiers and DSP for cars for example, and pricing issues.
Since 2013, Professor Park’s research team has participated in one technology transfer and eight university-industry projects. Based on these efforts, the team was able to successfully develop the RANC system with domestic technology in partnership with Hyundai’s NVH Research Lab (Research Fellow, Dr. Gangdeok Lee; Ph.D. in aviation engineering, 1996), Optomech (Founder, Professor Gyeongsu Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1999), ARE (CEO Hyeonseok Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1998), WeAcom, and BurnYoung.
Professor Park’s team led the project by performing theory-based research during the commercialization stage in collaboration with Hyundai Motor Group.
For the commercialization of the RANC system, Hyundai Motor Group is planning to collaborate with the global car audio company Harman to increase the degree of completion and apply the RANC system to the GV 80, the first SUV model of the Genesis brand.
“I am very delighted as an engineer to see the research I worked on from my early days at KAIST be commercialized after 20 years,” noted Professor Park. “I am thrilled to make a contribution to such commercialization with my students in my lab.”
2019.12.27 View 13167 -
 Two Professors Receive Awards from the Korea Robotics Society
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu and Professor Ayoung Kim >
The Korea Robotics Society (KROS) conferred awards onto two KAIST professors from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in recognition of their achievements and contributions to the development of the robotics industry in 2019. Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu has been actively engaged in researching the field of teleoperation, and this led him to win the KROS Robotics Innovation (KRI) Award. The KRI Award was newly established in 2019 by the KROS, in order to encourage researchers who have made innovative achievements in robotics. Professor Ryu shared the honor of being the first winner of this award with Professor Jaeheung Park of Seoul National University. Professor Ayoung Kim, from the same department, received the Young Investigator Award presented to emerging robitics researchers under 40 years of age. (END)
2019.12.19 View 12225
Two Professors Receive Awards from the Korea Robotics Society
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu and Professor Ayoung Kim >
The Korea Robotics Society (KROS) conferred awards onto two KAIST professors from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in recognition of their achievements and contributions to the development of the robotics industry in 2019. Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu has been actively engaged in researching the field of teleoperation, and this led him to win the KROS Robotics Innovation (KRI) Award. The KRI Award was newly established in 2019 by the KROS, in order to encourage researchers who have made innovative achievements in robotics. Professor Ryu shared the honor of being the first winner of this award with Professor Jaeheung Park of Seoul National University. Professor Ayoung Kim, from the same department, received the Young Investigator Award presented to emerging robitics researchers under 40 years of age. (END)
2019.12.19 View 12225 -
 ‘Carrier-Resolved Photo-Hall’ to Push Semiconductor Advances
(Professor Shin and Dr. Gunawan (left))
An IBM-KAIST research team described a breakthrough in a 140-year-old mystery in physics. The research reported in Nature last month unlocks the physical characteristics of semiconductors in much greater detail and aids in the development of new and improved semiconductor materials.
Research team under Professor Byungha Shin at the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering and Dr. Oki Gunawan at IBM discovered a new formula and technique that enables the simultaneous extraction of both majority and minority carrier information such as their density and mobility, as well as gain additional insights about carrier lifetimes, diffusion lengths, and the recombination process. This new discovery and technology will help push semiconductor advances in both existing and emerging technologies.
Semiconductors are the basic building blocks of today’s digital electronics age, providing us with a multitude of devices that benefit our modern life. To truly appreciate the physics of semiconductors, it is very important to understand the fundamental properties of the charge carriers inside the materials, whether those particles are positive or negative, their speed under an applied electric field, and how densely they are packed into the material.
Physicist Edwin Hall found a way to determine those properties in 1879, when he discovered that a magnetic field will deflect the movement of electronic charges inside a conductor and that the amount of deflection can be measured as a voltage perpendicular to the flow of the charge. Decades after Hall’s discovery, researchers also recognized that they can measure the Hall effect with light via “photo-Hall experiments”. During such experiments, the light generates multiple carriers or electron–hole pairs in the semiconductors.
Unfortunately, the basic Hall effect only provided insights into the dominant charge carrier (or majority carrier). Researchers were unable to extract the properties of both carriers (the majority and minority carriers) simultaneously. The property information of both carriers is crucial for many applications that involve light such as solar cells and other optoelectronic devices.
In the photo-Hall experiment by the KAIST-IBM team, both carriers contribute to changes in conductivity and the Hall coefficient. The key insight comes from measuring the conductivity and Hall coefficient as a function of light intensity. Hidden in the trajectory of the conductivity, the Hall coefficient curve reveals crucial new information: the difference in the mobility of both carriers. As discussed in the paper, this relationship can be expressed elegantly as: Δµ = d (σ²H)/dσ
The research team solved for both majority and minority carrier mobility and density as a function of light intensity, naming the new technique Carrier-Resolved Photo Hall (CRPH) measurement. With known light illumination intensity, the carrier lifetime can be established in a similar way.
Beyond advances in theoretical understanding, advances in experimental techniques were also critical for enabling this breakthrough. The technique requires a clean Hall signal measurement, which can be challenging for materials where the Hall signal is weak due to low mobility or when extra unwanted signals are present, such as under strong light illumination.
The newly developed photo-Hall technique allows the extraction of an astonishing amount of information from semiconductors. In contrast to only three parameters obtained in the classic Hall measurements, this new technique yields up to seven parameters at every tested level of light intensity. These include the mobility of both the electron and hole; their carrier density under light; the recombination lifetime; and the diffusion lengths for electrons, holes, and ambipolar types. All of these can be repeated N times (i.e. the number of light intensity settings used in the experiment).
Professor Shin said, “This novel technology sheds new light on understanding the physical characteristics of semiconductor materials in great detail.” Dr. Gunawan added, “This will will help accelerate the development of next-generation semiconductor technology such as better solar cells, better optoelectronics devices, and new materials and devices for artificial intelligence technology.”
Profile:
Professor Byungha Shin
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
2019.11.18 View 15681
‘Carrier-Resolved Photo-Hall’ to Push Semiconductor Advances
(Professor Shin and Dr. Gunawan (left))
An IBM-KAIST research team described a breakthrough in a 140-year-old mystery in physics. The research reported in Nature last month unlocks the physical characteristics of semiconductors in much greater detail and aids in the development of new and improved semiconductor materials.
Research team under Professor Byungha Shin at the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering and Dr. Oki Gunawan at IBM discovered a new formula and technique that enables the simultaneous extraction of both majority and minority carrier information such as their density and mobility, as well as gain additional insights about carrier lifetimes, diffusion lengths, and the recombination process. This new discovery and technology will help push semiconductor advances in both existing and emerging technologies.
Semiconductors are the basic building blocks of today’s digital electronics age, providing us with a multitude of devices that benefit our modern life. To truly appreciate the physics of semiconductors, it is very important to understand the fundamental properties of the charge carriers inside the materials, whether those particles are positive or negative, their speed under an applied electric field, and how densely they are packed into the material.
Physicist Edwin Hall found a way to determine those properties in 1879, when he discovered that a magnetic field will deflect the movement of electronic charges inside a conductor and that the amount of deflection can be measured as a voltage perpendicular to the flow of the charge. Decades after Hall’s discovery, researchers also recognized that they can measure the Hall effect with light via “photo-Hall experiments”. During such experiments, the light generates multiple carriers or electron–hole pairs in the semiconductors.
Unfortunately, the basic Hall effect only provided insights into the dominant charge carrier (or majority carrier). Researchers were unable to extract the properties of both carriers (the majority and minority carriers) simultaneously. The property information of both carriers is crucial for many applications that involve light such as solar cells and other optoelectronic devices.
In the photo-Hall experiment by the KAIST-IBM team, both carriers contribute to changes in conductivity and the Hall coefficient. The key insight comes from measuring the conductivity and Hall coefficient as a function of light intensity. Hidden in the trajectory of the conductivity, the Hall coefficient curve reveals crucial new information: the difference in the mobility of both carriers. As discussed in the paper, this relationship can be expressed elegantly as: Δµ = d (σ²H)/dσ
The research team solved for both majority and minority carrier mobility and density as a function of light intensity, naming the new technique Carrier-Resolved Photo Hall (CRPH) measurement. With known light illumination intensity, the carrier lifetime can be established in a similar way.
Beyond advances in theoretical understanding, advances in experimental techniques were also critical for enabling this breakthrough. The technique requires a clean Hall signal measurement, which can be challenging for materials where the Hall signal is weak due to low mobility or when extra unwanted signals are present, such as under strong light illumination.
The newly developed photo-Hall technique allows the extraction of an astonishing amount of information from semiconductors. In contrast to only three parameters obtained in the classic Hall measurements, this new technique yields up to seven parameters at every tested level of light intensity. These include the mobility of both the electron and hole; their carrier density under light; the recombination lifetime; and the diffusion lengths for electrons, holes, and ambipolar types. All of these can be repeated N times (i.e. the number of light intensity settings used in the experiment).
Professor Shin said, “This novel technology sheds new light on understanding the physical characteristics of semiconductor materials in great detail.” Dr. Gunawan added, “This will will help accelerate the development of next-generation semiconductor technology such as better solar cells, better optoelectronics devices, and new materials and devices for artificial intelligence technology.”
Profile:
Professor Byungha Shin
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
2019.11.18 View 15681 -
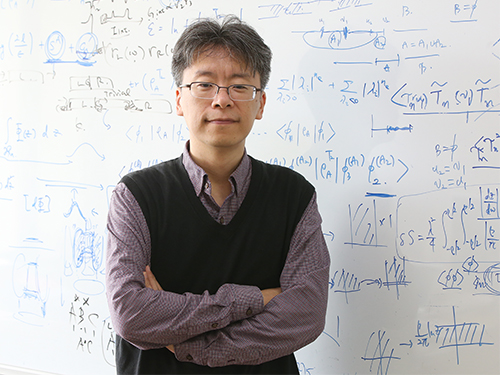 Ultrafast Quantum Motion in a Nanoscale Trap Detected
< Professor Heung-Sun Sim (left) and Co-author Dr. Sungguen Ryu (right) >
KAIST researchers have reported the detection of a picosecond electron motion in a silicon transistor. This study has presented a new protocol for measuring ultrafast electronic dynamics in an effective time-resolved fashion of picosecond resolution. The detection was made in collaboration with Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corp. (NTT) in Japan and National Physical Laboratory (NPL) in the UK and is the first report to the best of our knowledge.
When an electron is captured in a nanoscale trap in solids, its quantum mechanical wave function can exhibit spatial oscillation at sub-terahertz frequencies. Time-resolved detection of such picosecond dynamics of quantum waves is important, as the detection provides a way of understanding the quantum behavior of electrons in nano-electronics. It also applies to quantum information technologies such as the ultrafast quantum-bit operation of quantum computing and high-sensitivity electromagnetic-field sensing. However, detecting picosecond dynamics has been a challenge since the sub-terahertz scale is far beyond the latest bandwidth measurement tools.
A KAIST team led by Professor Heung-Sun Sim developed a theory of ultrafast electron dynamics in a nanoscale trap, and proposed a scheme for detecting the dynamics, which utilizes a quantum-mechanical resonant state formed beside the trap. The coupling between the electron dynamics and the resonant state is switched on and off at a picosecond so that information on the dynamics is read out on the electric current being generated when the coupling is switched on.
NTT realized, together with NPL, the detection scheme and applied it to electron motions in a nanoscale trap formed in a silicon transistor. A single electron was captured in the trap by controlling electrostatic gates, and a resonant state was formed in the potential barrier of the trap.
The switching on and off of the coupling between the electron and the resonant state was achieved by aligning the resonance energy with the energy of the electron within a picosecond. An electric current from the trap through the resonant state to an electrode was measured at only a few Kelvin degrees, unveiling the spatial quantum-coherent oscillation of the electron with 250 GHz frequency inside the trap.
Professor Sim said, “This work suggests a scheme of detecting picosecond electron motions in submicron scales by utilizing quantum resonance. It will be useful in dynamical control of quantum mechanical electron waves for various purposes in nano-electronics, quantum sensing, and quantum information”.
This work was published online at Nature Nanotechnology on November 4. It was partly supported by the Korea National Research Foundation through the SRC Center for Quantum Coherence in Condensed Matter. For more on the NTT news release this article, please visit https://www.ntt.co.jp/news2019/1911e/191105a.html
-ProfileProfessor Heung-Sun Sim
Department of PhysicsDirector, SRC Center for Quantum Coherence in Condensed Matterhttps://qet.kaist.ac.kr KAIST
-Publication:Gento Yamahata, Sungguen Ryu, Nathan Johnson, H.-S. Sim, Akira Fujiwara, and Masaya Kataoka. 2019. Picosecond coherent electron motion in a silicon single-electron source. Nature Nanotechnology (Online Publication). 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0563-2
2019.11.05 View 19680
Ultrafast Quantum Motion in a Nanoscale Trap Detected
< Professor Heung-Sun Sim (left) and Co-author Dr. Sungguen Ryu (right) >
KAIST researchers have reported the detection of a picosecond electron motion in a silicon transistor. This study has presented a new protocol for measuring ultrafast electronic dynamics in an effective time-resolved fashion of picosecond resolution. The detection was made in collaboration with Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corp. (NTT) in Japan and National Physical Laboratory (NPL) in the UK and is the first report to the best of our knowledge.
When an electron is captured in a nanoscale trap in solids, its quantum mechanical wave function can exhibit spatial oscillation at sub-terahertz frequencies. Time-resolved detection of such picosecond dynamics of quantum waves is important, as the detection provides a way of understanding the quantum behavior of electrons in nano-electronics. It also applies to quantum information technologies such as the ultrafast quantum-bit operation of quantum computing and high-sensitivity electromagnetic-field sensing. However, detecting picosecond dynamics has been a challenge since the sub-terahertz scale is far beyond the latest bandwidth measurement tools.
A KAIST team led by Professor Heung-Sun Sim developed a theory of ultrafast electron dynamics in a nanoscale trap, and proposed a scheme for detecting the dynamics, which utilizes a quantum-mechanical resonant state formed beside the trap. The coupling between the electron dynamics and the resonant state is switched on and off at a picosecond so that information on the dynamics is read out on the electric current being generated when the coupling is switched on.
NTT realized, together with NPL, the detection scheme and applied it to electron motions in a nanoscale trap formed in a silicon transistor. A single electron was captured in the trap by controlling electrostatic gates, and a resonant state was formed in the potential barrier of the trap.
The switching on and off of the coupling between the electron and the resonant state was achieved by aligning the resonance energy with the energy of the electron within a picosecond. An electric current from the trap through the resonant state to an electrode was measured at only a few Kelvin degrees, unveiling the spatial quantum-coherent oscillation of the electron with 250 GHz frequency inside the trap.
Professor Sim said, “This work suggests a scheme of detecting picosecond electron motions in submicron scales by utilizing quantum resonance. It will be useful in dynamical control of quantum mechanical electron waves for various purposes in nano-electronics, quantum sensing, and quantum information”.
This work was published online at Nature Nanotechnology on November 4. It was partly supported by the Korea National Research Foundation through the SRC Center for Quantum Coherence in Condensed Matter. For more on the NTT news release this article, please visit https://www.ntt.co.jp/news2019/1911e/191105a.html
-ProfileProfessor Heung-Sun Sim
Department of PhysicsDirector, SRC Center for Quantum Coherence in Condensed Matterhttps://qet.kaist.ac.kr KAIST
-Publication:Gento Yamahata, Sungguen Ryu, Nathan Johnson, H.-S. Sim, Akira Fujiwara, and Masaya Kataoka. 2019. Picosecond coherent electron motion in a silicon single-electron source. Nature Nanotechnology (Online Publication). 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0563-2
2019.11.05 View 19680