CT
-
 “3D sketch” Your Ideas and Bring Them to Life, Instantly!
Professor Seok-Hyung Bae’s research team at the Department of Industrial Design developed a novel 3D sketching system that rapidly creates animated 3D concepts through simple user interactions like sketching on a piece of paper or playing a toy.
Foldable drones, transforming vehicles, and multi-legged robots from sci-fi movies are now becoming commonplace thanks to technological progress. However, designing them remains a difficult challenge even for skilled experts, because complex design decisions must be made regarding not only their form, but also the structure, poses, and motions, which are interdependent on one another.
Creating a 3D concept comprising of multiple moving parts connected by different types of joints using a traditional 3D CAD tool, which is more suited for processing precise and elaborate modeling, is a painstaking and time-consuming process. This presents a major bottleneck for the workflow during the early stage of design, in which it is preferred that as many ideas are tried and discarded out as quickly as possible in order to explore a wide range of possibilities in the shortest amount of time.
A research team led by Professor Bae has focused on designers’ freehand sketches drew up with a pen on a paper that serve as the starting point for virtually all design projects. This led them to develop their 3D sketching technology to generate desired 3D curves from the rough but expressive 2D strokes drawn with a digital stylus on a digital tablet.
Their latest research helps designers bring their 3D sketches to life almost instantly. Using the intuitive set of multi-touch gestures the team successfully designed and implemented, designers can handle the 3D sketches they are working on with their fingers as if they are playing with toys and put them into animation in no time.
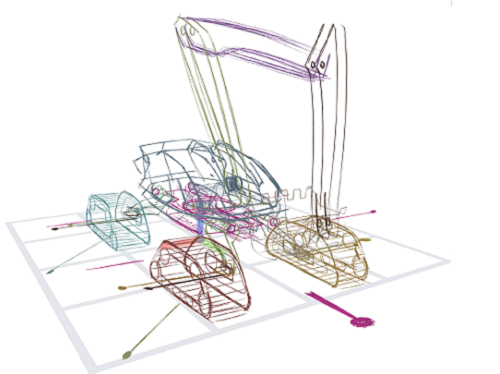
< Figure 1. A novel 3D sketching system for rapidly designing articulated 3D concepts with a small set of coherent pen and multi-touch gestures. (a) Sketching: A 3D sketch curve is created by marking a pen stroke that is projected onto a sketch plane widget. (b) Segmenting: Entire or partial sketch curves are added to separate parts that serve as links in the kinematic chain. (c) Rigging: Repeatedly demonstrating the desired motion of a part leaves behind a trail, from which the system infers a joint. (d) Posing: Desired poses can be achieved through actuating joints via forward or inverse kinematics. (e) Filming: A sequence of keyframes specifying desired poses and viewpoints is connected as a smooth motion. >
< Figure 2. (a) Concept drawing of an autonomous excavator. It features (b, c) four caterpillars that swivel for high maneuverability, (d) an extendable boom and a bucket connected by multiple links, and (e) a rotating platform. The concept’s designer, who had 8 years of work experience, estimated that it would take 1-2 weeks to express and communicate such a complex articulated object with existing tools. With the proposed system, it took only 2 hours and 52 minutes. >
The major findings of their work were published under the title “Rapid Design of Articulated Objects” in ACM Transactions on Graphics (impact factor: 7.403), the top international journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 (h5-index: 103), the world’s largest international academic conference in the field, which was held back in August in Vancouver, Canada with Joon Hyub Lee, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design as the first author.
The ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 conference was reportedly attended by over 10,000 participants including researchers, artists, and developers from world-renowned universities; film, animation, and game studies, such as Marvel, Pixar, and Blizzard; high-tech manufacturers, such as Lockheed Martin and Boston Dynamics; and metaverse platform companies, such as Meta and Roblox.
< Figure 3. The findings of Professor Bae’s research team were published in ACM Transactions on Graphics, the top international academic journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022, the largest international academic conference held in conjunction early August in Vancouver, Canada. The team’s live demo at the Emerging Technologies program was highly praised by numerous academics and industry officials and received an Honorable Mention. >
The team was also invited to present their technical paper as a demo and a special talk at the Emerging Technologies program at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 as one of the top-three impactful technologies. The live performance, in which Hanbit Kim, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST and a co-author, sketched and animated a sophisticated animal-shaped robot from scratch in a matter of a few minutes, wowed the audience and won the Honorable Mention Award from the jury.
Edwin Catmull, the co-founder of Pixar and a keynote speaker at the SIGGRAPH conference, praised the team’s research on 3D sketching as “really excellent work” and “a kind of tool that would be useful to Pixar's creative model designers.”
This technology, which became virally popular in Japan after featuring in an online IT media outlet and attracting more than 600K views, received a special award from the Digital Content Association of Japan (DCAJ) and was invited and exhibited for three days at Tokyo in November, as a part of Inter BEE 2022, the largest broadcasting and media expo in Japan.
“The more we come to understand how designers think and work, the more effective design tools can be built around that understanding,” said Professor Bae, explaining that “the key is to integrate different algorithms into a harmonious system as intuitive interactions.” He added that “this work wouldn’t have been possible if it weren’t for the convergent research environment cultivated by the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, in which all students see themselves not only as aspiring creative designers, but also as practical engineers.”
By enabling designers to produce highly expressive animated 3D concepts far more quickly and easily in comparison to using existing methods, this new tool is expected to revolutionize design practices and processes in the content creation, manufacturing, and metaverse-related industries.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
More info: https://sketch.kaist.ac.kr/publications/2022_siggraph_rapid_design
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rsBl0QvSDqI
< Figure 4. From left to right: Ph.D. students Hanbit Kim, and Joon Hyub Lee and Professor Bae of the Department of Industrial Design, KAIST >
2022.11.23 View 12787
“3D sketch” Your Ideas and Bring Them to Life, Instantly!
Professor Seok-Hyung Bae’s research team at the Department of Industrial Design developed a novel 3D sketching system that rapidly creates animated 3D concepts through simple user interactions like sketching on a piece of paper or playing a toy.
Foldable drones, transforming vehicles, and multi-legged robots from sci-fi movies are now becoming commonplace thanks to technological progress. However, designing them remains a difficult challenge even for skilled experts, because complex design decisions must be made regarding not only their form, but also the structure, poses, and motions, which are interdependent on one another.
Creating a 3D concept comprising of multiple moving parts connected by different types of joints using a traditional 3D CAD tool, which is more suited for processing precise and elaborate modeling, is a painstaking and time-consuming process. This presents a major bottleneck for the workflow during the early stage of design, in which it is preferred that as many ideas are tried and discarded out as quickly as possible in order to explore a wide range of possibilities in the shortest amount of time.
A research team led by Professor Bae has focused on designers’ freehand sketches drew up with a pen on a paper that serve as the starting point for virtually all design projects. This led them to develop their 3D sketching technology to generate desired 3D curves from the rough but expressive 2D strokes drawn with a digital stylus on a digital tablet.
Their latest research helps designers bring their 3D sketches to life almost instantly. Using the intuitive set of multi-touch gestures the team successfully designed and implemented, designers can handle the 3D sketches they are working on with their fingers as if they are playing with toys and put them into animation in no time.
< Figure 1. A novel 3D sketching system for rapidly designing articulated 3D concepts with a small set of coherent pen and multi-touch gestures. (a) Sketching: A 3D sketch curve is created by marking a pen stroke that is projected onto a sketch plane widget. (b) Segmenting: Entire or partial sketch curves are added to separate parts that serve as links in the kinematic chain. (c) Rigging: Repeatedly demonstrating the desired motion of a part leaves behind a trail, from which the system infers a joint. (d) Posing: Desired poses can be achieved through actuating joints via forward or inverse kinematics. (e) Filming: A sequence of keyframes specifying desired poses and viewpoints is connected as a smooth motion. >
< Figure 2. (a) Concept drawing of an autonomous excavator. It features (b, c) four caterpillars that swivel for high maneuverability, (d) an extendable boom and a bucket connected by multiple links, and (e) a rotating platform. The concept’s designer, who had 8 years of work experience, estimated that it would take 1-2 weeks to express and communicate such a complex articulated object with existing tools. With the proposed system, it took only 2 hours and 52 minutes. >
The major findings of their work were published under the title “Rapid Design of Articulated Objects” in ACM Transactions on Graphics (impact factor: 7.403), the top international journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 (h5-index: 103), the world’s largest international academic conference in the field, which was held back in August in Vancouver, Canada with Joon Hyub Lee, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design as the first author.
The ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 conference was reportedly attended by over 10,000 participants including researchers, artists, and developers from world-renowned universities; film, animation, and game studies, such as Marvel, Pixar, and Blizzard; high-tech manufacturers, such as Lockheed Martin and Boston Dynamics; and metaverse platform companies, such as Meta and Roblox.
< Figure 3. The findings of Professor Bae’s research team were published in ACM Transactions on Graphics, the top international academic journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022, the largest international academic conference held in conjunction early August in Vancouver, Canada. The team’s live demo at the Emerging Technologies program was highly praised by numerous academics and industry officials and received an Honorable Mention. >
The team was also invited to present their technical paper as a demo and a special talk at the Emerging Technologies program at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 as one of the top-three impactful technologies. The live performance, in which Hanbit Kim, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST and a co-author, sketched and animated a sophisticated animal-shaped robot from scratch in a matter of a few minutes, wowed the audience and won the Honorable Mention Award from the jury.
Edwin Catmull, the co-founder of Pixar and a keynote speaker at the SIGGRAPH conference, praised the team’s research on 3D sketching as “really excellent work” and “a kind of tool that would be useful to Pixar's creative model designers.”
This technology, which became virally popular in Japan after featuring in an online IT media outlet and attracting more than 600K views, received a special award from the Digital Content Association of Japan (DCAJ) and was invited and exhibited for three days at Tokyo in November, as a part of Inter BEE 2022, the largest broadcasting and media expo in Japan.
“The more we come to understand how designers think and work, the more effective design tools can be built around that understanding,” said Professor Bae, explaining that “the key is to integrate different algorithms into a harmonious system as intuitive interactions.” He added that “this work wouldn’t have been possible if it weren’t for the convergent research environment cultivated by the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, in which all students see themselves not only as aspiring creative designers, but also as practical engineers.”
By enabling designers to produce highly expressive animated 3D concepts far more quickly and easily in comparison to using existing methods, this new tool is expected to revolutionize design practices and processes in the content creation, manufacturing, and metaverse-related industries.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
More info: https://sketch.kaist.ac.kr/publications/2022_siggraph_rapid_design
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rsBl0QvSDqI
< Figure 4. From left to right: Ph.D. students Hanbit Kim, and Joon Hyub Lee and Professor Bae of the Department of Industrial Design, KAIST >
2022.11.23 View 12787 -
 Yuji Roh Awarded 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship
KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh of the School of Electrical Engineering (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) was selected as a recipient of the 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship.
< KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) >
The Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that recognizes outstanding graduate students for their exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. This year, 36 people from around the world received the fellowship, and Yuji Roh from KAIST EE is the only recipient from universities in Korea. Each selected fellow will receive a $10,000 scholarship and an opportunity to intern at Microsoft under the guidance of an experienced researcher.
Yuji Roh was named a fellow in the field of “Machine Learning” for her outstanding achievements in Trustworthy AI. Her research highlights include designing a state-of-the-art fair training framework using batch selection and developing novel algorithms for both fair and robust training. Her works have been presented at the top machine learning conferences ICML, ICLR, and NeurIPS among others. She also co-presented a tutorial on Trustworthy AI at the top data mining conference ACM SIGKDD. She is currently interning at the NVIDIA Research AI Algorithms Group developing large-scale real-world fair AI frameworks.
The list of fellowship recipients and the interview videos are displayed on the Microsoft webpage and Youtube.
The list of recipients: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/academic-program/phd-fellowship/2022-recipients/
Interview (Global): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T4Q-XwOOoJc
Interview (Asia): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwq3R1XU8UE
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair batch selection framework]
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair and robust training framework]
2022.10.28 View 16343
Yuji Roh Awarded 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship
KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh of the School of Electrical Engineering (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) was selected as a recipient of the 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship.
< KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) >
The Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that recognizes outstanding graduate students for their exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. This year, 36 people from around the world received the fellowship, and Yuji Roh from KAIST EE is the only recipient from universities in Korea. Each selected fellow will receive a $10,000 scholarship and an opportunity to intern at Microsoft under the guidance of an experienced researcher.
Yuji Roh was named a fellow in the field of “Machine Learning” for her outstanding achievements in Trustworthy AI. Her research highlights include designing a state-of-the-art fair training framework using batch selection and developing novel algorithms for both fair and robust training. Her works have been presented at the top machine learning conferences ICML, ICLR, and NeurIPS among others. She also co-presented a tutorial on Trustworthy AI at the top data mining conference ACM SIGKDD. She is currently interning at the NVIDIA Research AI Algorithms Group developing large-scale real-world fair AI frameworks.
The list of fellowship recipients and the interview videos are displayed on the Microsoft webpage and Youtube.
The list of recipients: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/academic-program/phd-fellowship/2022-recipients/
Interview (Global): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T4Q-XwOOoJc
Interview (Asia): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwq3R1XU8UE
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair batch selection framework]
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair and robust training framework]
2022.10.28 View 16343 -
 KAIST develops biocompatible adhesive applicable to hair transplants
Aside from being used as a new medical adhesive, the new material can be applied to developing a new method of hair transplants, which cannot be repeated multiple times using current method of implanting the wholly intact follicles into the skin.
Medical adhesives are materials that can be applied to various uses such as wound healing, hemostasis, vascular anastomosis, and tissue engineering, and is expected to contribute greatly to the development of minimally invasive surgery and organ transplants. However, adhesives with high adhesion, low toxicity, and capable of decomposing in the body are rare. Adhesives based on natural proteins, such as fibrin and collagen, have high biocompatibility but insufficient adhesive strength. Synthetic polymer adhesives based on urethane or acrylic have greater adhesion but do not decompose well and may cause an inflammatory reaction in the body.
A joint research team led by Professor Myungeun Seo and Professor Haeshin Lee from the KAIST Department of Chemistry developed a bio-friendly adhesive from biocompatible polymers using tannic acid, the source of astringency in wine.
The research team focused on tannic acid, a natural polyphenolic product. Tannic acid is a polyphenol present in large amounts in fruit peels, nuts, and cacao. It has a high affinity and coating ability on other substances, and we sense the astringent taste in wine when tannic acid sticks to the surface of our tongue. When tannic acid is mixed with hydrophilic polymers, they form coacervates, or small droplets of jelly-like fluids that sink. If the polymers used are biocompatible, the mixture can be applied as a medical adhesive with low toxicity. However, coacervates are fundamentally fluid-like and cannot withstand large forces, which limits their adhesive capabilities. Thus, while research to utilize it as an adhesive has been actively discussed, a biodegradable material exhibiting strong adhesion due to its high shear strength has not yet been developed.
The research team figured out a way to enhance adhesion by mixing two biocompatible FDA-approved polymers, polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polylactic acid (PLA). While PEG, which is used widely in eyedrops and cream, is hydrophilic, PLA, a well-known bioplastic derived from lactic acid, is insoluble in water. The team combined the two into a block copolymer, which forms hydrophilic PLA aggregates in water with PEG blocks surrounding them. A coacervate created by mixing the micelles and tannic acid would behave like a solid due to the hard PLA components, and show an elastic modulus improved by a thousand times compared to PEG, enabling it to withstand much greater force as an adhesive.
Figure 1. (Above) Principle of biodegradable adhesive made by mixing poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) diblock copolymer and tannic acid in water. Yellow coacervate is precipitated through hydrogen bonding between the block copolymer micelles and tannic acid, and exhibits adhesion. After heat treatment, hydrogen bonds are rearranged to further improve adhesion. (Bottom) Adhesion comparison. Compared to using poly(ethylene glycol) polymer (d), it can support 10 times more weight when using block copolymer (e) and 60 times more weight after heat treatment (f). The indicated G' values represent the elastic modulus of the material.
Furthermore, the research team observed that the material’s mechanical properties can be improved by over a hundred times through a heating and cooling process that is used to heat-treat metals. They also discovered that this is due to the enforced interactions between micelle and tannic acid arrays.
The research team used the fact that the material shows minimal irritation to the skin and decomposes well in the body to demonstrate its possible application as an adhesive for hair transplantation through an animal experiment. Professor Haeshin Lee, who has pioneered various application fields including medical adhesives, hemostatic agents, and browning shampoo, focused on the adhesive capacities and low toxicity of polyphenols like tannic acid, and now looks forward to it improving the limitations of current hair transplant methods, which still involve follicle transfer and are difficult to be repeated multiple times.
Figure 2. (a) Overview of a hair transplantation method using a biodegradable adhesive (right) compared to a conventional hair transplantation method (left) that transplants hair containing hair follicles. After applying an adhesive to the tip of the hair, it is fixed to the skin by implanting it through a subcutaneous injection, and repeated treatment is possible. (b) Initial animal test results. One day after 15 hair transplantation, 12 strands of hair remain. If you pull the 3 strands of hair, you can see that the whole body is pulled up, indicating that it is firmly implanted into the skin. All strands of hair applied without the new adhesive material fell off, and in the case of adhesive without heat treatment, the efficiency was 1/7.
This research was conducted by first co-authors Dr. Jongmin Park (currently a senior researcher at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology) from Professor Myeongeun Seo’s team and Dr. Eunsook Park from Professor Haeshin Lee’s team in the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and through joint research with the teams led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The research was published online on August 22 in the international journal Au (JACS Au) under the title Biodegradable Block Copolymer-Tannic Acid Glue.
This study was funded by the Support Research Under Protection Project of the National Research Foundation (NRF), Leading Research Center Support Project (Research Center for Multiscale Chiral Structure), Biodegradable Plastics Commercialization and Demonstration Project by the Ministry of Trade and Industry, and institutional funding from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology.
2022.10.07 View 13719
KAIST develops biocompatible adhesive applicable to hair transplants
Aside from being used as a new medical adhesive, the new material can be applied to developing a new method of hair transplants, which cannot be repeated multiple times using current method of implanting the wholly intact follicles into the skin.
Medical adhesives are materials that can be applied to various uses such as wound healing, hemostasis, vascular anastomosis, and tissue engineering, and is expected to contribute greatly to the development of minimally invasive surgery and organ transplants. However, adhesives with high adhesion, low toxicity, and capable of decomposing in the body are rare. Adhesives based on natural proteins, such as fibrin and collagen, have high biocompatibility but insufficient adhesive strength. Synthetic polymer adhesives based on urethane or acrylic have greater adhesion but do not decompose well and may cause an inflammatory reaction in the body.
A joint research team led by Professor Myungeun Seo and Professor Haeshin Lee from the KAIST Department of Chemistry developed a bio-friendly adhesive from biocompatible polymers using tannic acid, the source of astringency in wine.
The research team focused on tannic acid, a natural polyphenolic product. Tannic acid is a polyphenol present in large amounts in fruit peels, nuts, and cacao. It has a high affinity and coating ability on other substances, and we sense the astringent taste in wine when tannic acid sticks to the surface of our tongue. When tannic acid is mixed with hydrophilic polymers, they form coacervates, or small droplets of jelly-like fluids that sink. If the polymers used are biocompatible, the mixture can be applied as a medical adhesive with low toxicity. However, coacervates are fundamentally fluid-like and cannot withstand large forces, which limits their adhesive capabilities. Thus, while research to utilize it as an adhesive has been actively discussed, a biodegradable material exhibiting strong adhesion due to its high shear strength has not yet been developed.
The research team figured out a way to enhance adhesion by mixing two biocompatible FDA-approved polymers, polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polylactic acid (PLA). While PEG, which is used widely in eyedrops and cream, is hydrophilic, PLA, a well-known bioplastic derived from lactic acid, is insoluble in water. The team combined the two into a block copolymer, which forms hydrophilic PLA aggregates in water with PEG blocks surrounding them. A coacervate created by mixing the micelles and tannic acid would behave like a solid due to the hard PLA components, and show an elastic modulus improved by a thousand times compared to PEG, enabling it to withstand much greater force as an adhesive.
Figure 1. (Above) Principle of biodegradable adhesive made by mixing poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) diblock copolymer and tannic acid in water. Yellow coacervate is precipitated through hydrogen bonding between the block copolymer micelles and tannic acid, and exhibits adhesion. After heat treatment, hydrogen bonds are rearranged to further improve adhesion. (Bottom) Adhesion comparison. Compared to using poly(ethylene glycol) polymer (d), it can support 10 times more weight when using block copolymer (e) and 60 times more weight after heat treatment (f). The indicated G' values represent the elastic modulus of the material.
Furthermore, the research team observed that the material’s mechanical properties can be improved by over a hundred times through a heating and cooling process that is used to heat-treat metals. They also discovered that this is due to the enforced interactions between micelle and tannic acid arrays.
The research team used the fact that the material shows minimal irritation to the skin and decomposes well in the body to demonstrate its possible application as an adhesive for hair transplantation through an animal experiment. Professor Haeshin Lee, who has pioneered various application fields including medical adhesives, hemostatic agents, and browning shampoo, focused on the adhesive capacities and low toxicity of polyphenols like tannic acid, and now looks forward to it improving the limitations of current hair transplant methods, which still involve follicle transfer and are difficult to be repeated multiple times.
Figure 2. (a) Overview of a hair transplantation method using a biodegradable adhesive (right) compared to a conventional hair transplantation method (left) that transplants hair containing hair follicles. After applying an adhesive to the tip of the hair, it is fixed to the skin by implanting it through a subcutaneous injection, and repeated treatment is possible. (b) Initial animal test results. One day after 15 hair transplantation, 12 strands of hair remain. If you pull the 3 strands of hair, you can see that the whole body is pulled up, indicating that it is firmly implanted into the skin. All strands of hair applied without the new adhesive material fell off, and in the case of adhesive without heat treatment, the efficiency was 1/7.
This research was conducted by first co-authors Dr. Jongmin Park (currently a senior researcher at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology) from Professor Myeongeun Seo’s team and Dr. Eunsook Park from Professor Haeshin Lee’s team in the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and through joint research with the teams led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The research was published online on August 22 in the international journal Au (JACS Au) under the title Biodegradable Block Copolymer-Tannic Acid Glue.
This study was funded by the Support Research Under Protection Project of the National Research Foundation (NRF), Leading Research Center Support Project (Research Center for Multiscale Chiral Structure), Biodegradable Plastics Commercialization and Demonstration Project by the Ministry of Trade and Industry, and institutional funding from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology.
2022.10.07 View 13719 -
 NYC-KAIST Cooperation Agreement Signed in New York for KAIST NYU Joint Campus
A ceremony was held to celebrate the signing of the Cooperative Agreement between NYC and KAIST and the presentation of the signage for KAIST NYU Joint Campus at NYU’s Kimmel Center in Manhattan.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYU President Andrew Hamilton (right)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) signed a cooperative agreement with the City of New York and had an official showing of the signage for the Joint Campus of KAIST and New York University (NYU) on September 21 at 4:00 pm (Eastern Standard Time) at NYU’s Kimmel Center in New York City with the NYC Mayor Eric Adams, the Korean Minister of Science and ICT Dr. Lee Jong-ho, NYU Chairman William Berkley, NYU President Andrew Hamilton, and other distinguished guests in attendance.
KAIST and NYU signed a Memorandum of Understanding in June about building a joint campus in an effort to educate global talent. As a follow-up measure, NYU has provided KAIST with space to begin joint research programs and held a ceremony to present the signage designed for the future KAIST NYU Campus. In line with these efforts, KAIST has also signed an agreement with New York City, the administrative authority in charge of the establishment of the campus, for mutual cooperation.
NYU is a prestigious university headquartered in Manhattan, New York. It has nurtured outstanding talents in the humanities, art, and basic sciences, including 38 Nobel Prize winners, 5 Fields Prize winners, 26 Pulitzer Prize winners, and 38 Academy Award winners to be deserving of the evaluation.
The proposed joint campus is to be centered on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) by combining NYU's excellent basic sciences and convergence research capabilities with KAIST's globally renowned science and technology capabilities. The joint initiative is expected to launch in 2023; its programs will focus on areas such as AI Basic Science, AI Convergence Brain Science, AI-Applied Cyber Security, Cyber Security, and Sustainable High-Tech Smart City/Climate Change in order to lead the Digital Era and to solve the problems that surfaced following the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, in order to prepare for the Post-AI Era, it was decided to create the “New Engineering” program for undergraduate program that employs a hyper-convergence learning model that combines project-based, problem-solving learning (PBL, PSL) pedagogy.
▲ Biomedical Engineering- Research and development of technology to respond to the entire cycle (prevention-treatment-diagnosis-prediction) for a new infectious disease (Disease X) by converging new technologies such as IT and NT with biomedical technologies
▲ AI Convergence Neuroscience- Research on brain-machine interaction and brain-based machine learning through AI technology convergence
▲ AI Science- Algorithm development and in-depth research in preparation for the post AI era
▲ Sustainability and Climate Change- R&DB for advanced smart cities, sustainability for the global environment and carbon zero
▲ Next-generation Wireless Communications- From ICT to AIT: Research on 6G/7G related technologies, new communications theories, and etc.
▲ Cyber Security- Advanced research on protection of digital information and information safety/reliability
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYC Mayor Eric Adams (right)
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus has started enlisting professors and researchers from both institutions to participate in the collaboration. The campus will also function as the headquarter that will oversee the operation of the joint research program. At Daejeon, KAIST is also setting up a location for NYU on its main campus to provide space for NYU researchers upon their visit to KAIST.
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus, which has begun to take basic shape with the space for collaboration rendered this time, is to be upgraded to “KAIST New York Campus” in the future to function also as an industry-academic cooperation campus in which that promotes strategic cooperation with industries and expands start-up opportunities. To this end, the related procedures from the detailing of the establishment plans through a preliminary feasibility studies, to deliberation and decision on whether to proceed with the establishment by the KAIST Board of Trustees, will be taken.
The KAIST NYU Campus is expected to serve as a stepping stone for the outstanding talents of KAIST to pursue their dreams in the global market and research environment while seizing the attention of the world-class talents drawn to New York at the same time. In addition, by combining NYU's strong basic academic capabilities with KAIST’s strengths, it is expected to contribute to achieving 'global innovation' by creating synergies in various fields such as education, research, and entrepreneurship. The future KAIST-NYU Campus is also expected to encompass an industry-academic cooperation campus with industrial partners and startups.
Meanwhile, KAIST is planning to expand its excellent scientific and technological capabilities to the global stage through the cooperative agreement with New York City, and to prepare a pathway for KAIST students, faculty, and startups to enter their respective fields in the global markets. In the future, KAIST plans to explore areas of cooperation in different fields, such as education, economy, society, and culture, to prepare and implement detailed cooperation plans.
< KAIST-New York City Cooperation Items (Example) >
▲ Education: Joint degree program with a university in New York City, training of key talents in the field of artificial intelligence, etc.
▲ Economy: A hub for technology startups, job creation in the tech sector, etc.
▲ Society: Economics, finance, media-related engineering research, etc.
▲ Culture: Diversity-based culture and art-tech research, etc.▲ Etc: Joint research in the field of artificial intelligence healthcare, etc.
As a global mecca for startups, education, and investment, New York has a well-developed global network for cultural diversity and successful career development, and has great power to attract various resources including funds and talented individuals. Based on this, it has established itself as a mecca of global tech companies and global top media groups, and is building the reputation as 'Silicon Alley' in addition to its legends of the ‘Wall Street'.
Dr. Andrew Hamilton, the president of NYU, said, “We’re delighted by our newly established partnership with KAIST. We see great potential in the opportunities to collaborate on development of courses, research, cutting edge technologies, university-level courses, degrees, entrepreneurship initiatives and industrial partnerships, and exchanges. We believe this partnership is very much in line with NYU’s commitment to global engagement and will make important contributions to New York’s tech sector. It’s exciting to think how much NYU and KAIST have much to learn from one another, and how much we may accomplish together.”
New York City Mayor Eric Adams said, “We’re proud to have helped facilitate this partnership between KAIST and New York University, which will be a real win for students and help drive continued innovation in our city.” He added, “From the time that senior members of our administration learned about this opportunity during a recent trip to South Korea, we have worked closely with KAIST to develop strategies for increasing their presence and investments in New York. This is the start of a relationship that I am confident will bring even more academic, business, and technological opportunities to the five boroughs.”
Dr. Kwang Hyung Lee, the president of KAIST, urged, “Based on the KAIST-NYU partnership, we must create an interdisciplinary hyper-convergence model of collaboration and use cutting-edge tools to create an innovative model for new type of problem-solving engineering education to prepare to solve the challenges facing the world.” He went on to stress, “The new fusion engineering degree program will leverage the unique strengths of the two institutions to provide a uniquely colored education not found anywhere else.” In addition, he added, “KAIST will utilize the advantages that are unique to the global city of New York to contribute to advancing the science and technology research in New York City and creating jobs in the tech sector to lead the renaissance of Silicon Alley.”
2022.09.27 View 15174
NYC-KAIST Cooperation Agreement Signed in New York for KAIST NYU Joint Campus
A ceremony was held to celebrate the signing of the Cooperative Agreement between NYC and KAIST and the presentation of the signage for KAIST NYU Joint Campus at NYU’s Kimmel Center in Manhattan.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYU President Andrew Hamilton (right)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) signed a cooperative agreement with the City of New York and had an official showing of the signage for the Joint Campus of KAIST and New York University (NYU) on September 21 at 4:00 pm (Eastern Standard Time) at NYU’s Kimmel Center in New York City with the NYC Mayor Eric Adams, the Korean Minister of Science and ICT Dr. Lee Jong-ho, NYU Chairman William Berkley, NYU President Andrew Hamilton, and other distinguished guests in attendance.
KAIST and NYU signed a Memorandum of Understanding in June about building a joint campus in an effort to educate global talent. As a follow-up measure, NYU has provided KAIST with space to begin joint research programs and held a ceremony to present the signage designed for the future KAIST NYU Campus. In line with these efforts, KAIST has also signed an agreement with New York City, the administrative authority in charge of the establishment of the campus, for mutual cooperation.
NYU is a prestigious university headquartered in Manhattan, New York. It has nurtured outstanding talents in the humanities, art, and basic sciences, including 38 Nobel Prize winners, 5 Fields Prize winners, 26 Pulitzer Prize winners, and 38 Academy Award winners to be deserving of the evaluation.
The proposed joint campus is to be centered on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) by combining NYU's excellent basic sciences and convergence research capabilities with KAIST's globally renowned science and technology capabilities. The joint initiative is expected to launch in 2023; its programs will focus on areas such as AI Basic Science, AI Convergence Brain Science, AI-Applied Cyber Security, Cyber Security, and Sustainable High-Tech Smart City/Climate Change in order to lead the Digital Era and to solve the problems that surfaced following the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, in order to prepare for the Post-AI Era, it was decided to create the “New Engineering” program for undergraduate program that employs a hyper-convergence learning model that combines project-based, problem-solving learning (PBL, PSL) pedagogy.
▲ Biomedical Engineering- Research and development of technology to respond to the entire cycle (prevention-treatment-diagnosis-prediction) for a new infectious disease (Disease X) by converging new technologies such as IT and NT with biomedical technologies
▲ AI Convergence Neuroscience- Research on brain-machine interaction and brain-based machine learning through AI technology convergence
▲ AI Science- Algorithm development and in-depth research in preparation for the post AI era
▲ Sustainability and Climate Change- R&DB for advanced smart cities, sustainability for the global environment and carbon zero
▲ Next-generation Wireless Communications- From ICT to AIT: Research on 6G/7G related technologies, new communications theories, and etc.
▲ Cyber Security- Advanced research on protection of digital information and information safety/reliability
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYC Mayor Eric Adams (right)
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus has started enlisting professors and researchers from both institutions to participate in the collaboration. The campus will also function as the headquarter that will oversee the operation of the joint research program. At Daejeon, KAIST is also setting up a location for NYU on its main campus to provide space for NYU researchers upon their visit to KAIST.
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus, which has begun to take basic shape with the space for collaboration rendered this time, is to be upgraded to “KAIST New York Campus” in the future to function also as an industry-academic cooperation campus in which that promotes strategic cooperation with industries and expands start-up opportunities. To this end, the related procedures from the detailing of the establishment plans through a preliminary feasibility studies, to deliberation and decision on whether to proceed with the establishment by the KAIST Board of Trustees, will be taken.
The KAIST NYU Campus is expected to serve as a stepping stone for the outstanding talents of KAIST to pursue their dreams in the global market and research environment while seizing the attention of the world-class talents drawn to New York at the same time. In addition, by combining NYU's strong basic academic capabilities with KAIST’s strengths, it is expected to contribute to achieving 'global innovation' by creating synergies in various fields such as education, research, and entrepreneurship. The future KAIST-NYU Campus is also expected to encompass an industry-academic cooperation campus with industrial partners and startups.
Meanwhile, KAIST is planning to expand its excellent scientific and technological capabilities to the global stage through the cooperative agreement with New York City, and to prepare a pathway for KAIST students, faculty, and startups to enter their respective fields in the global markets. In the future, KAIST plans to explore areas of cooperation in different fields, such as education, economy, society, and culture, to prepare and implement detailed cooperation plans.
< KAIST-New York City Cooperation Items (Example) >
▲ Education: Joint degree program with a university in New York City, training of key talents in the field of artificial intelligence, etc.
▲ Economy: A hub for technology startups, job creation in the tech sector, etc.
▲ Society: Economics, finance, media-related engineering research, etc.
▲ Culture: Diversity-based culture and art-tech research, etc.▲ Etc: Joint research in the field of artificial intelligence healthcare, etc.
As a global mecca for startups, education, and investment, New York has a well-developed global network for cultural diversity and successful career development, and has great power to attract various resources including funds and talented individuals. Based on this, it has established itself as a mecca of global tech companies and global top media groups, and is building the reputation as 'Silicon Alley' in addition to its legends of the ‘Wall Street'.
Dr. Andrew Hamilton, the president of NYU, said, “We’re delighted by our newly established partnership with KAIST. We see great potential in the opportunities to collaborate on development of courses, research, cutting edge technologies, university-level courses, degrees, entrepreneurship initiatives and industrial partnerships, and exchanges. We believe this partnership is very much in line with NYU’s commitment to global engagement and will make important contributions to New York’s tech sector. It’s exciting to think how much NYU and KAIST have much to learn from one another, and how much we may accomplish together.”
New York City Mayor Eric Adams said, “We’re proud to have helped facilitate this partnership between KAIST and New York University, which will be a real win for students and help drive continued innovation in our city.” He added, “From the time that senior members of our administration learned about this opportunity during a recent trip to South Korea, we have worked closely with KAIST to develop strategies for increasing their presence and investments in New York. This is the start of a relationship that I am confident will bring even more academic, business, and technological opportunities to the five boroughs.”
Dr. Kwang Hyung Lee, the president of KAIST, urged, “Based on the KAIST-NYU partnership, we must create an interdisciplinary hyper-convergence model of collaboration and use cutting-edge tools to create an innovative model for new type of problem-solving engineering education to prepare to solve the challenges facing the world.” He went on to stress, “The new fusion engineering degree program will leverage the unique strengths of the two institutions to provide a uniquely colored education not found anywhere else.” In addition, he added, “KAIST will utilize the advantages that are unique to the global city of New York to contribute to advancing the science and technology research in New York City and creating jobs in the tech sector to lead the renaissance of Silicon Alley.”
2022.09.27 View 15174 -
 A KAIST Research Team Develops Diesel Reforming Catalyst Enabling Hydrogen Production for Future Mobile Fuel Cells
This catalyst capability allowing stable hydrogen production from commercial diesel is expected to be applied in mobile fuel cell systems in the future hydrogen economy
On August 16, a joint research team led by Professors Joongmyeon Bae and Kang Taek Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) announced the successful development of a highly active and durable reforming catalyst allowing hydrogen production from commercial diesel.
Fuel reforming is a hydrogen production technique that extracts hydrogen from hydrocarbons through catalytic reactions. Diesel, being a liquid fuel, has a high storage density for hydrogen and is easy to transport and store. There have therefore been continuous research efforts to apply hydrogel supply systems using diesel reformation in mobile fuel cells, such as for auxiliary power in heavy trucks or air-independent propulsion (AIP) systems in submarines.
However, diesel is a mixture of high hydrocarbons including long-chained paraffin, double-bonded olefin, and aromatic hydrocarbons with benzene groups, and it requires a highly active catalyst to effectively break them down. In addition, the catalyst must be extremely durable against caulking and sintering, as they are often the main causes of catalyst degradation. Such challenges have limited the use of diesel reformation technologies to date.
The joint research team successfully developed a highly active and durable diesel reforming catalyst through elution (a heat treatment method used to uniformly grow active metals retained in an oxide support as ions in the form of metal nanoparticles), forming alloy nanoparticles. The design was based on the fact that eluted nanoparticles strongly interact with the support, allowing a high degree of dispersion at high temperatures, and that producing an alloy from dissimilar metals can increase the performance of catalysts through a synergistic effect.
The research team introduced a solution combustion synthesis method to produce a multi-component catalyst with a trace amount of platinum (Pt) and ruthenium (Ru) penetrated into a ceria (CeO2) lattice, which is a structure commonly used as a support for catalysts in redox reactions. When exposed to a diesel reforming reaction environment, the catalyst induces Pt-Ru alloy nanoparticle formation upon Pt and Ru elution onto the support surface.
In addition to the catalyst analysis, the research team also succeeded in characterizing the behaviour of active metal elution and alloy formation from an energetic perspective using a density functional theory-based calculation. In a performance comparison test between the Pt-Ru alloy catalyst against existing single-metal catalysts, the reforming activity was shown to have improved, as it showed a 100% fuel conversion rate even at a low temperature (600oC, compared to the original 800oC). In a long-term durability test (800oC, 200 hours), the catalyst showed commercial stability by successfully producing hydrogen from commercial diesel without performance degradation.
The study was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jaemyung Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering as the first author. Ph.D. candidate Changho Yeon of KIER, Dr. Jiwoo Oh of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Gwangwoo Han of KIER, Ph.D. candidate Jeong Do Yoo of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Dr. Hyung Joong Yun of the Korea Basic Science Institute contributed as co-authors. Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of KIER and Professors Kang Taek Lee and Joongmyeon Bae of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering contributed as corresponding authors. The research was published in the online version of Applied Catalysis B: Environmental (IF 24.319, JCR 0.93%) on June 17, under the title “Highly Active and Stable Catalyst with Exsolved PtRu Alloy Nanoparticles for Hydrogen Production via Commercial Diesel Reforming”.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae said, “The fact that hydrogen can be stably produced from commercial diesel makes this a very meaningful achievement, and we look forward to this technology contributing to the active introduction of mobile fuel cell systems in the early hydrogen economy.” He added, “Our approach to catalyst design may be applied not only to reforming reactions, but also in various other fields.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through funding from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
Figure. Schematic diagram of high-performance diesel reforming catalyst with eluted platinum-ruthenium alloy nanoparticles and long-term durability verification experiment results for commercial diesel reforming reaction
2022.09.07 View 16727
A KAIST Research Team Develops Diesel Reforming Catalyst Enabling Hydrogen Production for Future Mobile Fuel Cells
This catalyst capability allowing stable hydrogen production from commercial diesel is expected to be applied in mobile fuel cell systems in the future hydrogen economy
On August 16, a joint research team led by Professors Joongmyeon Bae and Kang Taek Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) announced the successful development of a highly active and durable reforming catalyst allowing hydrogen production from commercial diesel.
Fuel reforming is a hydrogen production technique that extracts hydrogen from hydrocarbons through catalytic reactions. Diesel, being a liquid fuel, has a high storage density for hydrogen and is easy to transport and store. There have therefore been continuous research efforts to apply hydrogel supply systems using diesel reformation in mobile fuel cells, such as for auxiliary power in heavy trucks or air-independent propulsion (AIP) systems in submarines.
However, diesel is a mixture of high hydrocarbons including long-chained paraffin, double-bonded olefin, and aromatic hydrocarbons with benzene groups, and it requires a highly active catalyst to effectively break them down. In addition, the catalyst must be extremely durable against caulking and sintering, as they are often the main causes of catalyst degradation. Such challenges have limited the use of diesel reformation technologies to date.
The joint research team successfully developed a highly active and durable diesel reforming catalyst through elution (a heat treatment method used to uniformly grow active metals retained in an oxide support as ions in the form of metal nanoparticles), forming alloy nanoparticles. The design was based on the fact that eluted nanoparticles strongly interact with the support, allowing a high degree of dispersion at high temperatures, and that producing an alloy from dissimilar metals can increase the performance of catalysts through a synergistic effect.
The research team introduced a solution combustion synthesis method to produce a multi-component catalyst with a trace amount of platinum (Pt) and ruthenium (Ru) penetrated into a ceria (CeO2) lattice, which is a structure commonly used as a support for catalysts in redox reactions. When exposed to a diesel reforming reaction environment, the catalyst induces Pt-Ru alloy nanoparticle formation upon Pt and Ru elution onto the support surface.
In addition to the catalyst analysis, the research team also succeeded in characterizing the behaviour of active metal elution and alloy formation from an energetic perspective using a density functional theory-based calculation. In a performance comparison test between the Pt-Ru alloy catalyst against existing single-metal catalysts, the reforming activity was shown to have improved, as it showed a 100% fuel conversion rate even at a low temperature (600oC, compared to the original 800oC). In a long-term durability test (800oC, 200 hours), the catalyst showed commercial stability by successfully producing hydrogen from commercial diesel without performance degradation.
The study was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jaemyung Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering as the first author. Ph.D. candidate Changho Yeon of KIER, Dr. Jiwoo Oh of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Gwangwoo Han of KIER, Ph.D. candidate Jeong Do Yoo of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Dr. Hyung Joong Yun of the Korea Basic Science Institute contributed as co-authors. Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of KIER and Professors Kang Taek Lee and Joongmyeon Bae of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering contributed as corresponding authors. The research was published in the online version of Applied Catalysis B: Environmental (IF 24.319, JCR 0.93%) on June 17, under the title “Highly Active and Stable Catalyst with Exsolved PtRu Alloy Nanoparticles for Hydrogen Production via Commercial Diesel Reforming”.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae said, “The fact that hydrogen can be stably produced from commercial diesel makes this a very meaningful achievement, and we look forward to this technology contributing to the active introduction of mobile fuel cell systems in the early hydrogen economy.” He added, “Our approach to catalyst design may be applied not only to reforming reactions, but also in various other fields.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through funding from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
Figure. Schematic diagram of high-performance diesel reforming catalyst with eluted platinum-ruthenium alloy nanoparticles and long-term durability verification experiment results for commercial diesel reforming reaction
2022.09.07 View 16727 -
 Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 16706
Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 16706 -
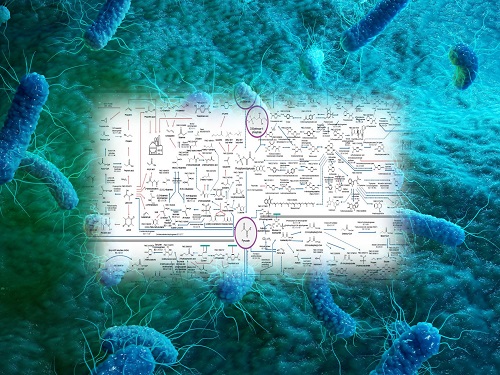 Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 18147
Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 18147 -
 Shaping the AI Semiconductor Ecosystem
- As the marriage of AI and semiconductor being highlighted as the strategic technology of national enthusiasm, KAIST's achievements in the related fields accumulated through top-class education and research capabilities that surpass that of peer universities around the world are standing far apart from the rest of the pack.
As Artificial Intelligence Semiconductor, or a system of semiconductors designed for specifically for highly complicated computation need for AI to conduct its learning and deducing calculations, (hereafter AI semiconductors) stand out as a national strategic technology, the related achievements of KAIST, headed by President Kwang Hyung Lee, are also attracting attention. The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIT) of Korea initiated a program to support the advancement of AI semiconductor last year with the goal of occupying 20% of the global AI semiconductor market by 2030. This year, through industry-university-research discussions, the Ministry expanded to the program with the addition of 1.2 trillion won of investment over five years through 'Support Plan for AI Semiconductor Industry Promotion'. Accordingly, major universities began putting together programs devised to train students to develop expertise in AI semiconductors.
KAIST has accumulated top-notch educational and research capabilities in the two core fields of AI semiconductor - Semiconductor and Artificial Intelligence. Notably, in the field of semiconductors, the International Solid-State Circuit Conference (ISSCC) is the world's most prestigious conference about designing of semiconductor integrated circuit. Established in 1954, with more than 60% of the participants coming from companies including Samsung, Qualcomm, TSMC, and Intel, the conference naturally focuses on practical value of the studies from the industrial point-of-view, earning the nickname the ‘Semiconductor Design Olympics’. At such conference of legacy and influence, KAIST kept its presence widely visible over other participating universities, leading in terms of the number of accepted papers over world-class schools such as Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Stanford for the past 17 years.
Number of papers published at the InternationalSolid-State Circuit Conference (ISSCC) in 2022 sorted by nations and by institutions
Number of papers by universities presented at the International Solid-State Circuit Conference (ISCCC) in 2006~2022
In terms of the number of papers accepted at the ISSCC, KAIST ranked among top two universities each year since 2006. Looking at the average number of accepted papers over the past 17 years, KAIST stands out as an unparalleled leader. The average number of KAIST papers adopted during the period of 17 years from 2006 through 2022, was 8.4, which is almost double of that of competitors like MIT (4.6) and UCLA (3.6). In Korea, it maintains the second place overall after Samsung, the undisputed number one in the semiconductor design field. Also, this year, KAIST was ranked first among universities participating at the Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits, an academic conference in the field of integrated circuits that rivals the ISSCC.
Number of papers adopted by the Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits in 2022 submitted from the universities
With KAIST researchers working and presenting new technologies at the frontiers of all key areas of the semiconductor industry, the quality of KAIST research is also maintained at the highest level. Professor Myoungsoo Jung's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering is actively working to develop heterogeneous computing environment with high energy efficiency in response to the industry's demand for high performance at low power. In the field of materials, a research team led by Professor Byong-Guk Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed the Spin Orbit Torque (SOT)-based Magnetic RAM (MRAM) memory that operates at least 10 times faster than conventional memories to suggest a way to overcome the limitations of the existing 'von Neumann structure'.
As such, while providing solutions to major challenges in the current semiconductor industry, the development of new technologies necessary to preoccupy new fields in the semiconductor industry are also very actively pursued. In the field of Quantum Computing, which is attracting attention as next-generation computing technology needed in order to take the lead in the fields of cryptography and nonlinear computation, Professor Sanghyeon Kim's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering presented the world's first 3D integrated quantum computing system at 2021 VLSI Symposium. In Neuromorphic Computing, which is expected to bring remarkable advancements in the field of artificial intelligence by utilizing the principles of the neurology, the research team of Professor Shinhyun Choi of School of Electrical Engineering is developing a next-generation memristor that mimics neurons.
The number of papers by the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) and the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), two of the world’s most prestigious academic societies in the field of artificial intelligence (KAIST 6th in the world, 1st in Asia, in 2020)
The field of artificial intelligence has also grown rapidly. Based on the number of papers from the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) and the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), two of the world's most prestigious conferences in the field of artificial intelligence, KAIST ranked 6th in the world in 2020 and 1st in Asia. Since 2012, KAIST's ranking steadily inclined from 37th to 6th, climbing 31 steps over the period of eight years. In 2021, 129 papers, or about 40%, of Korean papers published at 11 top artificial intelligence conferences were presented by KAIST. Thanks to KAIST's efforts, in 2021, Korea ranked sixth after the United States, China, United Kingdom, Canada, and Germany in terms of the number of papers published by global AI academic societies.
Number of papers from Korea (and by KAIST) published at 11 top conferences in the field of artificial intelligence in 2021
In terms of content, KAIST's AI research is also at the forefront. Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering compensated for the shortcomings of the “edge networks” by implementing artificial intelligence real-time learning networks on mobile devices. In order to materialize artificial intelligence, data accumulation and a huge amount of computation is required. For this, a high-performance server takes care of massive computation, and for the user terminals, the “edge network” that collects data and performs simple computations are used. Professor Yoo's research greatly increased AI’s processing speed and performance by allotting the learning task to the user terminal as well.
In June, a research team led by Professor Min-Soo Kim of the School of Computing presented a solution that is essential for processing super-scale artificial intelligence models. The super-scale machine learning system developed by the research team is expected to achieve speeds up to 8.8 times faster than Google's Tensorflow or IBM's System DS, which are mainly used in the industry.
KAIST is also making remarkable achievements in the field of AI semiconductors. In 2020, Professor Minsoo Rhu's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering succeeded in developing the world's first AI semiconductor optimized for AI recommendation systems. Due to the nature of the AI recommendation system having to handle vast amounts of contents and user information, it quickly meets its limitation because of the information bottleneck when the process is operated through a general-purpose artificial intelligence system. Professor Minsoo Rhu's team developed a semiconductor that can achieve a speed that is 21 times faster than existing systems using the 'Processing-In-Memory (PIM)' technology. PIM is a technology that improves efficiency by performing the calculations in 'RAM', or random-access memory, which is usually only used to store data temporarily just before they are processed. When PIM technology is put out on the market, it is expected that fortify competitiveness of Korean companies in the AI semiconductor market drastically, as they already hold great strength in the memory area.
KAIST does not plan to be complacent with its achievements, but is making various plans to further the distance from the competitors catching on in the fields of artificial intelligence, semiconductors, and AI semiconductors. Following the establishment of the first artificial intelligence research center in Korea in 1990, the Kim Jaechul AI Graduate School was opened in 2019 to sustain the supply chain of the experts in the field. In 2020, Artificial Intelligence Semiconductor System Research Center was launched to conduct convergent research on AI and semiconductors, which was followed by the establishment of the AI Institutes to promote “AI+X” research efforts.
Based on the internal capabilities accumulated through these efforts, KAIST is also making efforts to train human resources needed in these areas. KAIST established joint research centers with companies such as Naver, while collaborating with local governments such as Hwaseong City to simultaneously nurture professional manpower. Back in 2021, KAIST signed an agreement to establish the Semiconductor System Engineering Department with Samsung Electronics and are preparing a new semiconductor specialist training program. The newly established Department of Semiconductor System Engineering will select around 100 new students every year from 2023 and provide special scholarships to all students so that they can develop their professional skills. In addition, through close cooperation with the industry, they will receive special support which includes field trips and internships at Samsung Electronics, and joint workshops and on-site training.
KAIST has made a significant contribution to the growth of the Korean semiconductor industry ecosystem, producing 25% of doctoral workers in the domestic semiconductor field and 20% of CEOs of mid-sized and venture companies with doctoral degrees. With the dawn coming up on the AI semiconductor ecosystem, whether KAIST will reprise the pivotal role seems to be the crucial point of business.
2022.08.05 View 14239
Shaping the AI Semiconductor Ecosystem
- As the marriage of AI and semiconductor being highlighted as the strategic technology of national enthusiasm, KAIST's achievements in the related fields accumulated through top-class education and research capabilities that surpass that of peer universities around the world are standing far apart from the rest of the pack.
As Artificial Intelligence Semiconductor, or a system of semiconductors designed for specifically for highly complicated computation need for AI to conduct its learning and deducing calculations, (hereafter AI semiconductors) stand out as a national strategic technology, the related achievements of KAIST, headed by President Kwang Hyung Lee, are also attracting attention. The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIT) of Korea initiated a program to support the advancement of AI semiconductor last year with the goal of occupying 20% of the global AI semiconductor market by 2030. This year, through industry-university-research discussions, the Ministry expanded to the program with the addition of 1.2 trillion won of investment over five years through 'Support Plan for AI Semiconductor Industry Promotion'. Accordingly, major universities began putting together programs devised to train students to develop expertise in AI semiconductors.
KAIST has accumulated top-notch educational and research capabilities in the two core fields of AI semiconductor - Semiconductor and Artificial Intelligence. Notably, in the field of semiconductors, the International Solid-State Circuit Conference (ISSCC) is the world's most prestigious conference about designing of semiconductor integrated circuit. Established in 1954, with more than 60% of the participants coming from companies including Samsung, Qualcomm, TSMC, and Intel, the conference naturally focuses on practical value of the studies from the industrial point-of-view, earning the nickname the ‘Semiconductor Design Olympics’. At such conference of legacy and influence, KAIST kept its presence widely visible over other participating universities, leading in terms of the number of accepted papers over world-class schools such as Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Stanford for the past 17 years.
Number of papers published at the InternationalSolid-State Circuit Conference (ISSCC) in 2022 sorted by nations and by institutions
Number of papers by universities presented at the International Solid-State Circuit Conference (ISCCC) in 2006~2022
In terms of the number of papers accepted at the ISSCC, KAIST ranked among top two universities each year since 2006. Looking at the average number of accepted papers over the past 17 years, KAIST stands out as an unparalleled leader. The average number of KAIST papers adopted during the period of 17 years from 2006 through 2022, was 8.4, which is almost double of that of competitors like MIT (4.6) and UCLA (3.6). In Korea, it maintains the second place overall after Samsung, the undisputed number one in the semiconductor design field. Also, this year, KAIST was ranked first among universities participating at the Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits, an academic conference in the field of integrated circuits that rivals the ISSCC.
Number of papers adopted by the Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits in 2022 submitted from the universities
With KAIST researchers working and presenting new technologies at the frontiers of all key areas of the semiconductor industry, the quality of KAIST research is also maintained at the highest level. Professor Myoungsoo Jung's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering is actively working to develop heterogeneous computing environment with high energy efficiency in response to the industry's demand for high performance at low power. In the field of materials, a research team led by Professor Byong-Guk Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed the Spin Orbit Torque (SOT)-based Magnetic RAM (MRAM) memory that operates at least 10 times faster than conventional memories to suggest a way to overcome the limitations of the existing 'von Neumann structure'.
As such, while providing solutions to major challenges in the current semiconductor industry, the development of new technologies necessary to preoccupy new fields in the semiconductor industry are also very actively pursued. In the field of Quantum Computing, which is attracting attention as next-generation computing technology needed in order to take the lead in the fields of cryptography and nonlinear computation, Professor Sanghyeon Kim's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering presented the world's first 3D integrated quantum computing system at 2021 VLSI Symposium. In Neuromorphic Computing, which is expected to bring remarkable advancements in the field of artificial intelligence by utilizing the principles of the neurology, the research team of Professor Shinhyun Choi of School of Electrical Engineering is developing a next-generation memristor that mimics neurons.
The number of papers by the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) and the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), two of the world’s most prestigious academic societies in the field of artificial intelligence (KAIST 6th in the world, 1st in Asia, in 2020)
The field of artificial intelligence has also grown rapidly. Based on the number of papers from the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) and the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), two of the world's most prestigious conferences in the field of artificial intelligence, KAIST ranked 6th in the world in 2020 and 1st in Asia. Since 2012, KAIST's ranking steadily inclined from 37th to 6th, climbing 31 steps over the period of eight years. In 2021, 129 papers, or about 40%, of Korean papers published at 11 top artificial intelligence conferences were presented by KAIST. Thanks to KAIST's efforts, in 2021, Korea ranked sixth after the United States, China, United Kingdom, Canada, and Germany in terms of the number of papers published by global AI academic societies.
Number of papers from Korea (and by KAIST) published at 11 top conferences in the field of artificial intelligence in 2021
In terms of content, KAIST's AI research is also at the forefront. Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering compensated for the shortcomings of the “edge networks” by implementing artificial intelligence real-time learning networks on mobile devices. In order to materialize artificial intelligence, data accumulation and a huge amount of computation is required. For this, a high-performance server takes care of massive computation, and for the user terminals, the “edge network” that collects data and performs simple computations are used. Professor Yoo's research greatly increased AI’s processing speed and performance by allotting the learning task to the user terminal as well.
In June, a research team led by Professor Min-Soo Kim of the School of Computing presented a solution that is essential for processing super-scale artificial intelligence models. The super-scale machine learning system developed by the research team is expected to achieve speeds up to 8.8 times faster than Google's Tensorflow or IBM's System DS, which are mainly used in the industry.
KAIST is also making remarkable achievements in the field of AI semiconductors. In 2020, Professor Minsoo Rhu's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering succeeded in developing the world's first AI semiconductor optimized for AI recommendation systems. Due to the nature of the AI recommendation system having to handle vast amounts of contents and user information, it quickly meets its limitation because of the information bottleneck when the process is operated through a general-purpose artificial intelligence system. Professor Minsoo Rhu's team developed a semiconductor that can achieve a speed that is 21 times faster than existing systems using the 'Processing-In-Memory (PIM)' technology. PIM is a technology that improves efficiency by performing the calculations in 'RAM', or random-access memory, which is usually only used to store data temporarily just before they are processed. When PIM technology is put out on the market, it is expected that fortify competitiveness of Korean companies in the AI semiconductor market drastically, as they already hold great strength in the memory area.
KAIST does not plan to be complacent with its achievements, but is making various plans to further the distance from the competitors catching on in the fields of artificial intelligence, semiconductors, and AI semiconductors. Following the establishment of the first artificial intelligence research center in Korea in 1990, the Kim Jaechul AI Graduate School was opened in 2019 to sustain the supply chain of the experts in the field. In 2020, Artificial Intelligence Semiconductor System Research Center was launched to conduct convergent research on AI and semiconductors, which was followed by the establishment of the AI Institutes to promote “AI+X” research efforts.
Based on the internal capabilities accumulated through these efforts, KAIST is also making efforts to train human resources needed in these areas. KAIST established joint research centers with companies such as Naver, while collaborating with local governments such as Hwaseong City to simultaneously nurture professional manpower. Back in 2021, KAIST signed an agreement to establish the Semiconductor System Engineering Department with Samsung Electronics and are preparing a new semiconductor specialist training program. The newly established Department of Semiconductor System Engineering will select around 100 new students every year from 2023 and provide special scholarships to all students so that they can develop their professional skills. In addition, through close cooperation with the industry, they will receive special support which includes field trips and internships at Samsung Electronics, and joint workshops and on-site training.
KAIST has made a significant contribution to the growth of the Korean semiconductor industry ecosystem, producing 25% of doctoral workers in the domestic semiconductor field and 20% of CEOs of mid-sized and venture companies with doctoral degrees. With the dawn coming up on the AI semiconductor ecosystem, whether KAIST will reprise the pivotal role seems to be the crucial point of business.
2022.08.05 View 14239 -
 Metabolically Engineered Bacterium Produces Lutein
A research group at KAIST has engineered a bacterial strain capable of producing lutein. The research team applied systems metabolic engineering strategies, including substrate channeling and electron channeling, to enhance the production of lutein in an engineered Escherichia coli strain. The strategies will be also useful for the efficient production of other industrially important natural products used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Figure: Systems metabolic engineering was employed to construct and optimize the metabolic pathways for lutein production, and substrate channeling and electron channeling strategies were additionally employed to increase the production of the lutein with high productivity.
Lutein is classified as a xanthophyll chemical that is abundant in egg yolk, fruits, and vegetables. It protects the eye from oxidative damage from radiation and reduces the risk of eye diseases including macular degeneration and cataracts. Commercialized products featuring lutein are derived from the extracts of the marigold flower, which is known to harbor abundant amounts of lutein. However, the drawback of lutein production from nature is that it takes a long time to grow and harvest marigold flowers. Furthermore, it requires additional physical and chemical-based extractions with a low yield, which makes it economically unfeasible in terms of productivity. The high cost and low yield of these bioprocesses has made it difficult to readily meet the demand for lutein.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineers at KAIST, including researchers Dr. Seon Young Park, Ph.D. Candidate Hyunmin Eun, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The team’s study entitled “Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli with electron channeling for the production of natural products” was published in Nature Catalysis on August 5, 2022.
This research details the ability to produce lutein from E. coli with a high yield using a cheap carbon source, glycerol, via systems metabolic engineering. The research group focused on solving the bottlenecks of the biosynthetic pathway for lutein production constructed within an individual cell. First, using systems metabolic engineering, which is an integrated technology to engineer the metabolism of a microorganism, lutein was produced when the lutein biosynthesis pathway was introduced, albeit in very small amounts.
To improve the productivity of lutein production, the bottleneck enzymes within the metabolic pathway were first identified. It turned out that metabolic reactions that involve a promiscuous enzyme, an enzyme that is involved in two or more metabolic reactions, and electron-requiring cytochrome P450 enzymes are the main bottleneck steps of the pathway inhibiting lutein biosynthesis.
To overcome these challenges, substrate channeling, a strategy to artificially recruit enzymes in physical proximity within the cell in order to increase the local concentrations of substrates that can be converted into products, was employed to channel more metabolic flux towards the target chemical while reducing the formation of unwanted byproducts.
Furthermore, electron channeling, a strategy similar to substrate channeling but differing in terms of increasing the local concentrations of electrons required for oxidoreduction reactions mediated by P450 and its reductase partners, was applied to further streamline the metabolic flux towards lutein biosynthesis, which led to the highest titer of lutein production achieved in a bacterial host ever reported. The same electron channeling strategy was successfully applied for the production of other natural products including nootkatone and apigenin in E. coli, showcasing the general applicability of the strategy in the research field.
“It is expected that this microbial cell factory-based production of lutein will be able to replace the current plant extraction-based process,” said Dr. Seon Young Park, the first author of the paper. She explained that another important point of the research is that integrated metabolic engineering strategies developed from this study can be generally applicable for the efficient production of other natural products useful as pharmaceuticals or nutraceuticals.
“As maintaining good health in an aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” explained Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development funded by the Rural Development Administration of Korea, with further support from the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and by the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project of the National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea.
2022.08.05 View 12082
Metabolically Engineered Bacterium Produces Lutein
A research group at KAIST has engineered a bacterial strain capable of producing lutein. The research team applied systems metabolic engineering strategies, including substrate channeling and electron channeling, to enhance the production of lutein in an engineered Escherichia coli strain. The strategies will be also useful for the efficient production of other industrially important natural products used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Figure: Systems metabolic engineering was employed to construct and optimize the metabolic pathways for lutein production, and substrate channeling and electron channeling strategies were additionally employed to increase the production of the lutein with high productivity.
Lutein is classified as a xanthophyll chemical that is abundant in egg yolk, fruits, and vegetables. It protects the eye from oxidative damage from radiation and reduces the risk of eye diseases including macular degeneration and cataracts. Commercialized products featuring lutein are derived from the extracts of the marigold flower, which is known to harbor abundant amounts of lutein. However, the drawback of lutein production from nature is that it takes a long time to grow and harvest marigold flowers. Furthermore, it requires additional physical and chemical-based extractions with a low yield, which makes it economically unfeasible in terms of productivity. The high cost and low yield of these bioprocesses has made it difficult to readily meet the demand for lutein.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineers at KAIST, including researchers Dr. Seon Young Park, Ph.D. Candidate Hyunmin Eun, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The team’s study entitled “Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli with electron channeling for the production of natural products” was published in Nature Catalysis on August 5, 2022.
This research details the ability to produce lutein from E. coli with a high yield using a cheap carbon source, glycerol, via systems metabolic engineering. The research group focused on solving the bottlenecks of the biosynthetic pathway for lutein production constructed within an individual cell. First, using systems metabolic engineering, which is an integrated technology to engineer the metabolism of a microorganism, lutein was produced when the lutein biosynthesis pathway was introduced, albeit in very small amounts.
To improve the productivity of lutein production, the bottleneck enzymes within the metabolic pathway were first identified. It turned out that metabolic reactions that involve a promiscuous enzyme, an enzyme that is involved in two or more metabolic reactions, and electron-requiring cytochrome P450 enzymes are the main bottleneck steps of the pathway inhibiting lutein biosynthesis.
To overcome these challenges, substrate channeling, a strategy to artificially recruit enzymes in physical proximity within the cell in order to increase the local concentrations of substrates that can be converted into products, was employed to channel more metabolic flux towards the target chemical while reducing the formation of unwanted byproducts.
Furthermore, electron channeling, a strategy similar to substrate channeling but differing in terms of increasing the local concentrations of electrons required for oxidoreduction reactions mediated by P450 and its reductase partners, was applied to further streamline the metabolic flux towards lutein biosynthesis, which led to the highest titer of lutein production achieved in a bacterial host ever reported. The same electron channeling strategy was successfully applied for the production of other natural products including nootkatone and apigenin in E. coli, showcasing the general applicability of the strategy in the research field.
“It is expected that this microbial cell factory-based production of lutein will be able to replace the current plant extraction-based process,” said Dr. Seon Young Park, the first author of the paper. She explained that another important point of the research is that integrated metabolic engineering strategies developed from this study can be generally applicable for the efficient production of other natural products useful as pharmaceuticals or nutraceuticals.
“As maintaining good health in an aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” explained Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development funded by the Rural Development Administration of Korea, with further support from the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and by the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project of the National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea.
2022.08.05 View 12082 -
 A System for Stable Simultaneous Communication among Thousands of IoT Devices
A mmWave Backscatter System, developed by a team led by Professor Song Min Kim is exciting news for the IoT market as it will be able to provide fast and stable connectivity even for a massive network, which could finally allow IoT devices to reach their full potential.
A research team led by Professor Song Min Kim of the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering developed a system that can support concurrent communications for tens of millions of IoT devices using backscattering millimeter-level waves (mmWave).
With their mmWave backscatter method, the research team built a design enabling simultaneous signal demodulation in a complex environment for communication where tens of thousands of IoT devices are arranged indoors. The wide frequency range of mmWave exceeds 10GHz, which provides great scalability. In addition, backscattering reflects radiated signals instead of wirelessly creating its own, which allows operation at ultralow power. Therefore, the mmWave backscatter system offers internet connectivity on a mass scale to IoT devices at a low installation cost.
This research by Kangmin Bae et al. was presented at ACM MobiSys 2022. At this world-renowned conference for mobile systems, the research won the Best Paper Award under the title “OmniScatter: Sensitivity mmWave Backscattering Using Commodity FMCW Radar”. It is meaningful that members of the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering have won the Best Paper Award at ACM MobiSys for two consecutive years, as last year was the first time the award was presented to an institute from Asia.
IoT, as a core component of 5G/6G network, is showing exponential growth, and is expected to be part of a trillion devices by 2035. To support the connection of IoT devices on a mass scale, 5G and 6G each aim to support ten times and 100 times the network density of 4G, respectively. As a result, the importance of practical systems for large-scale communication has been raised.
The mmWave is a next-generation communication technology that can be incorporated in 5G/6G standards, as it utilizes carrier waves at frequencies between 30 to 300GHz. However, due to signal reduction at high frequencies and reflection loss, the current mmWave backscatter system enables communication in limited environments. In other words, it cannot operate in complex environments where various obstacles and reflectors are present. As a result, it is limited to the large-scale connection of IoT devices that require a relatively free arrangement.
The research team found the solution in the high coding gain of an FMCW radar. The team developed a signal processing method that can fundamentally separate backscatter signals from ambient noise while maintaining the coding gain of the radar. They achieved a receiver sensitivity of over 100 thousand times that of previously reported FMCW radars, which can support communication in practical environments. Additionally, given the radar’s property where the frequency of the demodulated signal changes depending on the physical location of the tag, the team designed a system that passively assigns them channels. This lets the ultralow-power backscatter communication system to take full advantage of the frequency range at 10 GHz or higher.
The developed system can use the radar of existing commercial products as gateway, making it easily compatible. In addition, since the backscatter system works at ultralow power levels of 10uW or below, it can operate for over 40 years with a single button cell and drastically reduce installation and maintenance costs.
The research team confirmed that mmWave backscatter devices arranged randomly in an office with various obstacles and reflectors could communicate effectively. The team then took things one step further and conducted a successful trace-driven evaluation where they simultaneously received information sent by 1,100 devices.
Their research presents connectivity that greatly exceeds network density required by next-generation communication like 5G and 6G. The system is expected to become a stepping stone for the hyper-connected future to come.
Professor Kim said, “mmWave backscatter is the technology we’ve dreamt of. The mass scalability and ultralow power at which it can operate IoT devices is unmatched by any existing technology”. He added, “We look forward to this system being actively utilized to enable the wide availability of IoT in the hyper-connected generation to come”.
To demonstrate the massive connectivity of the system, a trace-driven evaluation of 1,100 concurrent tag transmissions are made. Figure shows the demodulation result of each and every 1,100 tags as red triangles, where they successfully communicate without collision.
This work was supported by Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics and by the ITRC (Information Technology Research Center) support program supervised by the IITP (Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation).
Profile: Song Min Kim, Ph.D.Professorsongmin@kaist.ac.krhttps://smile.kaist.ac.kr
SMILE Lab.School of Electrical Engineering
2022.07.28 View 12108
A System for Stable Simultaneous Communication among Thousands of IoT Devices
A mmWave Backscatter System, developed by a team led by Professor Song Min Kim is exciting news for the IoT market as it will be able to provide fast and stable connectivity even for a massive network, which could finally allow IoT devices to reach their full potential.
A research team led by Professor Song Min Kim of the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering developed a system that can support concurrent communications for tens of millions of IoT devices using backscattering millimeter-level waves (mmWave).
With their mmWave backscatter method, the research team built a design enabling simultaneous signal demodulation in a complex environment for communication where tens of thousands of IoT devices are arranged indoors. The wide frequency range of mmWave exceeds 10GHz, which provides great scalability. In addition, backscattering reflects radiated signals instead of wirelessly creating its own, which allows operation at ultralow power. Therefore, the mmWave backscatter system offers internet connectivity on a mass scale to IoT devices at a low installation cost.
This research by Kangmin Bae et al. was presented at ACM MobiSys 2022. At this world-renowned conference for mobile systems, the research won the Best Paper Award under the title “OmniScatter: Sensitivity mmWave Backscattering Using Commodity FMCW Radar”. It is meaningful that members of the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering have won the Best Paper Award at ACM MobiSys for two consecutive years, as last year was the first time the award was presented to an institute from Asia.
IoT, as a core component of 5G/6G network, is showing exponential growth, and is expected to be part of a trillion devices by 2035. To support the connection of IoT devices on a mass scale, 5G and 6G each aim to support ten times and 100 times the network density of 4G, respectively. As a result, the importance of practical systems for large-scale communication has been raised.
The mmWave is a next-generation communication technology that can be incorporated in 5G/6G standards, as it utilizes carrier waves at frequencies between 30 to 300GHz. However, due to signal reduction at high frequencies and reflection loss, the current mmWave backscatter system enables communication in limited environments. In other words, it cannot operate in complex environments where various obstacles and reflectors are present. As a result, it is limited to the large-scale connection of IoT devices that require a relatively free arrangement.
The research team found the solution in the high coding gain of an FMCW radar. The team developed a signal processing method that can fundamentally separate backscatter signals from ambient noise while maintaining the coding gain of the radar. They achieved a receiver sensitivity of over 100 thousand times that of previously reported FMCW radars, which can support communication in practical environments. Additionally, given the radar’s property where the frequency of the demodulated signal changes depending on the physical location of the tag, the team designed a system that passively assigns them channels. This lets the ultralow-power backscatter communication system to take full advantage of the frequency range at 10 GHz or higher.
The developed system can use the radar of existing commercial products as gateway, making it easily compatible. In addition, since the backscatter system works at ultralow power levels of 10uW or below, it can operate for over 40 years with a single button cell and drastically reduce installation and maintenance costs.
The research team confirmed that mmWave backscatter devices arranged randomly in an office with various obstacles and reflectors could communicate effectively. The team then took things one step further and conducted a successful trace-driven evaluation where they simultaneously received information sent by 1,100 devices.
Their research presents connectivity that greatly exceeds network density required by next-generation communication like 5G and 6G. The system is expected to become a stepping stone for the hyper-connected future to come.
Professor Kim said, “mmWave backscatter is the technology we’ve dreamt of. The mass scalability and ultralow power at which it can operate IoT devices is unmatched by any existing technology”. He added, “We look forward to this system being actively utilized to enable the wide availability of IoT in the hyper-connected generation to come”.
To demonstrate the massive connectivity of the system, a trace-driven evaluation of 1,100 concurrent tag transmissions are made. Figure shows the demodulation result of each and every 1,100 tags as red triangles, where they successfully communicate without collision.
This work was supported by Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics and by the ITRC (Information Technology Research Center) support program supervised by the IITP (Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation).
Profile: Song Min Kim, Ph.D.Professorsongmin@kaist.ac.krhttps://smile.kaist.ac.kr
SMILE Lab.School of Electrical Engineering
2022.07.28 View 12108 -
 Atomically-Smooth Gold Crystals Help to Compress Light for Nanophotonic Applications
Highly compressed mid-infrared optical waves in a thin dielectric crystal on monocrystalline gold substrate investigated for the first time using a high-resolution scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope.
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new platform for guiding the compressed light waves in very thin van der Waals crystals. Their method to guide the mid-infrared light with minimal loss will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of ultra-thin dielectric crystals in next-generation optoelectronic devices based on strong light-matter interactions at the nanoscale.
Phonon-polaritons are collective oscillations of ions in polar dielectrics coupled to electromagnetic waves of light, whose electromagnetic field is much more compressed compared to the light wavelength. Recently, it was demonstrated that the phonon-polaritons in thin van der Waals crystals can be compressed even further when the material is placed on top of a highly conductive metal. In such a configuration, charges in the polaritonic crystal are “reflected” in the metal, and their coupling with light results in a new type of polariton waves called the image phonon-polaritons. Highly compressed image modes provide strong light-matter interactions, but are very sensitive to the substrate roughness, which hinders their practical application.
Challenged by these limitations, four research groups combined their efforts to develop a unique experimental platform using advanced fabrication and measurement methods. Their findings were published in Science Advances on July 13.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering used a highly sensitive scanning near-field optical microscope (SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of the hyperbolic image phonon-polaritons (HIP) propagating in a 63 nm-thick slab of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) on a monocrystalline gold substrate, showing the mid-infrared light waves in dielectric crystal compressed by a hundred times.
Professor Jang and a research professor in his group, Sergey Menabde, successfully obtained direct images of HIP waves propagating for many wavelengths, and detected a signal from the ultra-compressed high-order HIP in a regular h-BN crystals for the first time. They showed that the phonon-polaritons in van der Waals crystals can be significantly more compressed without sacrificing their lifetime.
This became possible due to the atomically-smooth surfaces of the home-grown gold crystals used as a substrate for the h-BN. Practically zero surface scattering and extremely small ohmic loss in gold at mid-infrared frequencies provide a low-loss environment for the HIP propagation. The HIP mode probed by the researchers was 2.4 times more compressed and yet exhibited a similar lifetime compared to the phonon-polaritons with a low-loss dielectric substrate, resulting in a twice higher figure of merit in terms of the normalized propagation length.
The ultra-smooth monocrystalline gold flakes used in the experiment were chemically grown by the team of Professor N. Asger Mortensen from the Center for Nano Optics at the University of Southern Denmark.
Mid-infrared spectrum is particularly important for sensing applications since many important organic molecules have absorption lines in the mid-infrared. However, a large number of molecules is required by the conventional detection methods for successful operation, whereas the ultra-compressed phonon-polariton fields can provide strong light-matter interactions at the microscopic level, thus significantly improving the detection limit down to a single molecule. The long lifetime of the HIP on monocrystalline gold will further improve the detection performance.
Furthermore, the study conducted by Professor Jang and the team demonstrated the striking similarity between the HIP and the image graphene plasmons. Both image modes possess significantly more confined electromagnetic field, yet their lifetime remains unaffected by the shorter polariton wavelength. This observation provides a broader perspective on image polaritons in general, and highlights their superiority in terms of the nanolight waveguiding compared to the conventional low-dimensional polaritons in van der Waals crystals on a dielectric substrate.
Professor Jang said, “Our research demonstrated the advantages of image polaritons, and especially the image phonon-polaritons. These optical modes can be used in the future optoelectronic devices where both the low-loss propagation and the strong light-matter interaction are necessary. I hope that our results will pave the way for the realization of more efficient nanophotonic devices such as metasurfaces, optical switches, sensors, and other applications operating at infrared frequencies.”
This research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and The Villum Foundation, Denmark, also supported the work.
Figure. Nano-tip is used for the ultra-high-resolution imaging of the image phonon-polaritons in hBN launched by the gold crystal edge.
Publication:
Menabde, S. G., et al. (2022) Near-field probing of image phonon-polaritons in hexagonal boron nitride on gold crystals. Science Advances 8, Article ID: eabn0627. Available online at https://science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abn0627.
Profile:
Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
Associate Professor
jang.minseok@kaist.ac.kr
http://janglab.org/
Min Seok Jang Research Group
School of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 16521
Atomically-Smooth Gold Crystals Help to Compress Light for Nanophotonic Applications
Highly compressed mid-infrared optical waves in a thin dielectric crystal on monocrystalline gold substrate investigated for the first time using a high-resolution scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope.
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new platform for guiding the compressed light waves in very thin van der Waals crystals. Their method to guide the mid-infrared light with minimal loss will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of ultra-thin dielectric crystals in next-generation optoelectronic devices based on strong light-matter interactions at the nanoscale.
Phonon-polaritons are collective oscillations of ions in polar dielectrics coupled to electromagnetic waves of light, whose electromagnetic field is much more compressed compared to the light wavelength. Recently, it was demonstrated that the phonon-polaritons in thin van der Waals crystals can be compressed even further when the material is placed on top of a highly conductive metal. In such a configuration, charges in the polaritonic crystal are “reflected” in the metal, and their coupling with light results in a new type of polariton waves called the image phonon-polaritons. Highly compressed image modes provide strong light-matter interactions, but are very sensitive to the substrate roughness, which hinders their practical application.
Challenged by these limitations, four research groups combined their efforts to develop a unique experimental platform using advanced fabrication and measurement methods. Their findings were published in Science Advances on July 13.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering used a highly sensitive scanning near-field optical microscope (SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of the hyperbolic image phonon-polaritons (HIP) propagating in a 63 nm-thick slab of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) on a monocrystalline gold substrate, showing the mid-infrared light waves in dielectric crystal compressed by a hundred times.
Professor Jang and a research professor in his group, Sergey Menabde, successfully obtained direct images of HIP waves propagating for many wavelengths, and detected a signal from the ultra-compressed high-order HIP in a regular h-BN crystals for the first time. They showed that the phonon-polaritons in van der Waals crystals can be significantly more compressed without sacrificing their lifetime.
This became possible due to the atomically-smooth surfaces of the home-grown gold crystals used as a substrate for the h-BN. Practically zero surface scattering and extremely small ohmic loss in gold at mid-infrared frequencies provide a low-loss environment for the HIP propagation. The HIP mode probed by the researchers was 2.4 times more compressed and yet exhibited a similar lifetime compared to the phonon-polaritons with a low-loss dielectric substrate, resulting in a twice higher figure of merit in terms of the normalized propagation length.
The ultra-smooth monocrystalline gold flakes used in the experiment were chemically grown by the team of Professor N. Asger Mortensen from the Center for Nano Optics at the University of Southern Denmark.
Mid-infrared spectrum is particularly important for sensing applications since many important organic molecules have absorption lines in the mid-infrared. However, a large number of molecules is required by the conventional detection methods for successful operation, whereas the ultra-compressed phonon-polariton fields can provide strong light-matter interactions at the microscopic level, thus significantly improving the detection limit down to a single molecule. The long lifetime of the HIP on monocrystalline gold will further improve the detection performance.
Furthermore, the study conducted by Professor Jang and the team demonstrated the striking similarity between the HIP and the image graphene plasmons. Both image modes possess significantly more confined electromagnetic field, yet their lifetime remains unaffected by the shorter polariton wavelength. This observation provides a broader perspective on image polaritons in general, and highlights their superiority in terms of the nanolight waveguiding compared to the conventional low-dimensional polaritons in van der Waals crystals on a dielectric substrate.
Professor Jang said, “Our research demonstrated the advantages of image polaritons, and especially the image phonon-polaritons. These optical modes can be used in the future optoelectronic devices where both the low-loss propagation and the strong light-matter interaction are necessary. I hope that our results will pave the way for the realization of more efficient nanophotonic devices such as metasurfaces, optical switches, sensors, and other applications operating at infrared frequencies.”
This research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and The Villum Foundation, Denmark, also supported the work.
Figure. Nano-tip is used for the ultra-high-resolution imaging of the image phonon-polaritons in hBN launched by the gold crystal edge.
Publication:
Menabde, S. G., et al. (2022) Near-field probing of image phonon-polaritons in hexagonal boron nitride on gold crystals. Science Advances 8, Article ID: eabn0627. Available online at https://science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abn0627.
Profile:
Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
Associate Professor
jang.minseok@kaist.ac.kr
http://janglab.org/
Min Seok Jang Research Group
School of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 16521 -
 Professor Juho Kim’s Team Wins Best Paper Award at ACM CHI 2022
The research team led by Professor Juho Kim from the KAIST School of Computing won a Best Paper Award and an Honorable Mention Award at the Association for Computing Machinery Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (ACM CHI) held between April 30 and May 6.
ACM CHI is the world’s most recognized conference in the field of human computer interactions (HCI), and is ranked number one out of all HCI-related journals and conferences based on Google Scholar’s h-5 index. Best paper awards are given to works that rank in the top one percent, and honorable mention awards are given to the top five percent of the papers accepted by the conference.
Professor Juho Kim presented a total of seven papers at ACM CHI 2022, and tied for the largest number of papers. A total of 19 papers were affiliated with KAIST, putting it fifth out of all participating institutes and thereby proving KAIST’s competence in research.
One of Professor Kim’s research teams composed of Jeongyeon Kim (first author, MS graduate) from the School of Computing, MS candidate Yubin Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering, and Dr. Meng Xia (post-doctoral associate in the School of Computing, currently a post-doctoral associate at Carnegie Mellon University) received a best paper award for their paper, “Mobile-Friendly Content Design for MOOCs: Challenges, Requirements, and Design Opportunities”.
The study analyzed the difficulties experienced by learners watching video-based educational content in a mobile environment and suggests guidelines for solutions. The research team analyzed 134 survey responses and 21 interviews, and revealed that texts that are too small or overcrowded are what mainly brings down the legibility of video contents. Additionally, lighting, noise, and surrounding environments that change frequently are also important factors that may disturb a learning experience.
Based on these findings, the team analyzed the aptness of 41,722 frames from 101 video lectures for mobile environments, and confirmed that they generally show low levels of adequacy. For instance, in the case of text sizes, only 24.5% of the frames were shown to be adequate for learning in mobile environments. To overcome this issue, the research team suggested a guideline that may improve the legibility of video contents and help overcome the difficulties arising from mobile learning environments.
The importance of and dependency on video-based learning continue to rise, especially in the wake of the pandemic, and it is meaningful that this research suggested a means to analyze and tackle the difficulties of users that learn from the small screens of mobile devices. Furthermore, the paper also suggested technology that can solve problems related to video-based learning through human-AI collaborations, enhancing existing video lectures and improving learning experiences. This technology can be applied to various video-based platforms and content creation.
Meanwhile, a research team composed of Ph.D. candidate Tae Soo Kim (first author), MS candidate DaEun Choi, and Ph.D. candidate Yoonseo Choi from the School of Computing received an honorable mention award for their paper, “Stylette: styling the Web with Natural Language”.
The research team developed a novel interface technology that allows nonexperts who are unfamiliar with technical jargon to edit website features through speech. People often find it difficult to use or find the information they need from various websites due to accessibility issues, device-related constraints, inconvenient design, style preferences, etc. However, it is not easy for laymen to edit website features without expertise in programming or design, and most end up just putting up with the inconveniences. But what if the system could read the intentions of its users from their everyday language like “emphasize this part a little more”, or “I want a more modern design”, and edit the features automatically?
Based on this question, Professor Kim’s research team developed ‘Stylette’, a system in which AI analyses its users’ speech expressed in their natural language and automatically recommends a new style that best fits their intentions. The research team created a new system by putting together language AI, visual AI, and user interface technologies. On the linguistic side, a large-scale language model AI converts the intentions of the users expressed through their everyday language into adequate style elements. On the visual side, computer vision AI compares 1.7 million existing web design features and recommends a style adequate for the current website. In an experiment where 40 nonexperts were asked to edit a website design, the subjects that used this system showed double the success rate in a time span that was 35% shorter compared to the control group.
It is meaningful that this research proposed a practical case in which AI technology constructs intuitive interactions with users. The developed technology can be applied to existing design applications and web browsers in a plug-in format, and can be utilized to improve websites or for advertisements by collecting the natural intention data of users on a large scale.
2022.06.13 View 10514
Professor Juho Kim’s Team Wins Best Paper Award at ACM CHI 2022
The research team led by Professor Juho Kim from the KAIST School of Computing won a Best Paper Award and an Honorable Mention Award at the Association for Computing Machinery Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (ACM CHI) held between April 30 and May 6.
ACM CHI is the world’s most recognized conference in the field of human computer interactions (HCI), and is ranked number one out of all HCI-related journals and conferences based on Google Scholar’s h-5 index. Best paper awards are given to works that rank in the top one percent, and honorable mention awards are given to the top five percent of the papers accepted by the conference.
Professor Juho Kim presented a total of seven papers at ACM CHI 2022, and tied for the largest number of papers. A total of 19 papers were affiliated with KAIST, putting it fifth out of all participating institutes and thereby proving KAIST’s competence in research.
One of Professor Kim’s research teams composed of Jeongyeon Kim (first author, MS graduate) from the School of Computing, MS candidate Yubin Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering, and Dr. Meng Xia (post-doctoral associate in the School of Computing, currently a post-doctoral associate at Carnegie Mellon University) received a best paper award for their paper, “Mobile-Friendly Content Design for MOOCs: Challenges, Requirements, and Design Opportunities”.
The study analyzed the difficulties experienced by learners watching video-based educational content in a mobile environment and suggests guidelines for solutions. The research team analyzed 134 survey responses and 21 interviews, and revealed that texts that are too small or overcrowded are what mainly brings down the legibility of video contents. Additionally, lighting, noise, and surrounding environments that change frequently are also important factors that may disturb a learning experience.
Based on these findings, the team analyzed the aptness of 41,722 frames from 101 video lectures for mobile environments, and confirmed that they generally show low levels of adequacy. For instance, in the case of text sizes, only 24.5% of the frames were shown to be adequate for learning in mobile environments. To overcome this issue, the research team suggested a guideline that may improve the legibility of video contents and help overcome the difficulties arising from mobile learning environments.
The importance of and dependency on video-based learning continue to rise, especially in the wake of the pandemic, and it is meaningful that this research suggested a means to analyze and tackle the difficulties of users that learn from the small screens of mobile devices. Furthermore, the paper also suggested technology that can solve problems related to video-based learning through human-AI collaborations, enhancing existing video lectures and improving learning experiences. This technology can be applied to various video-based platforms and content creation.
Meanwhile, a research team composed of Ph.D. candidate Tae Soo Kim (first author), MS candidate DaEun Choi, and Ph.D. candidate Yoonseo Choi from the School of Computing received an honorable mention award for their paper, “Stylette: styling the Web with Natural Language”.
The research team developed a novel interface technology that allows nonexperts who are unfamiliar with technical jargon to edit website features through speech. People often find it difficult to use or find the information they need from various websites due to accessibility issues, device-related constraints, inconvenient design, style preferences, etc. However, it is not easy for laymen to edit website features without expertise in programming or design, and most end up just putting up with the inconveniences. But what if the system could read the intentions of its users from their everyday language like “emphasize this part a little more”, or “I want a more modern design”, and edit the features automatically?
Based on this question, Professor Kim’s research team developed ‘Stylette’, a system in which AI analyses its users’ speech expressed in their natural language and automatically recommends a new style that best fits their intentions. The research team created a new system by putting together language AI, visual AI, and user interface technologies. On the linguistic side, a large-scale language model AI converts the intentions of the users expressed through their everyday language into adequate style elements. On the visual side, computer vision AI compares 1.7 million existing web design features and recommends a style adequate for the current website. In an experiment where 40 nonexperts were asked to edit a website design, the subjects that used this system showed double the success rate in a time span that was 35% shorter compared to the control group.
It is meaningful that this research proposed a practical case in which AI technology constructs intuitive interactions with users. The developed technology can be applied to existing design applications and web browsers in a plug-in format, and can be utilized to improve websites or for advertisements by collecting the natural intention data of users on a large scale.
2022.06.13 View 10514