Graphene
-
 Mussel-Inspired Defect Engineering Enhances the Mechanical Strength of Graphene Fibers
Researchers demonstrated the mussel-inspired reinforcement of graphene fibers for the improvement of different material properties. A research group under Professor Sang Ouk Kim applied polydopamine as an effective infiltrate binder to achieve high mechanical and electrical properties for graphene-based liquid crystalline fibers.
This bio-inspired defect engineering is clearly distinguishable from previous attempts with insulating binders and proposes great potential for versatile applications of flexible and wearable devices as well as low-cost structural materials. The two-step defect engineering addresses the intrinsic limitation of graphene fibers arising from the folding and wrinkling of graphene layers during the fiber-spinning process.
Bio-inspired graphene-based fiber holds great promise for a wide range of applications, including flexible electronics, multifunctional textiles, and wearable sensors. In 2009, the research group discovered graphene oxide liquid crystals in aqueous media while introducing an effective purification process to remove ionic impurities. Graphene fibers, typically wet-spun from aqueous graphene oxide liquid crystal dispersion, are expected to demonstrate superior thermal and electrical conductivities as well as outstanding mechanical performance.
Nonetheless, owing to the inherent formation of defects and voids caused by bending and wrinkling the graphene oxide layer within graphene fibers, their mechanical strength and electrical/thermal conductivities are still far below the desired ideal values. Accordingly, finding an efficient method for constructing the densely packed graphene fibers with strong interlayer interaction is a principal challenge.
Professor Kim's team focused on the adhesion properties of dopamine, a polymer developed with the inspiration of the natural mussel, to solve the problem. This functional polymer, which is studied in various fields, can increase the adhesion between the graphene layers and prevent structural defects.
Professor Kim’s research group succeeded in fabricating high-strength graphene liquid crystalline fibers with controlled structural defects. They also fabricated fibers with improved electrical conductivity through the post-carbonization process of polydopamine.
Based on the theory that dopamine with subsequent high temperature annealing has a similar structure with that of graphene, the team optimized dopamine polymerization conditions and solved the inherent defect control problems of existing graphene fibers.
They also confirmed that the physical properties of dopamine are improved in terms of electrical conductivity due to the influence of nitrogen in dopamine molecules, without damaging the conductivity, which is the fundamental limit of conventional polymers.
Professor Kim, who led the research, said, "Despite its technological potential, carbon fiber using graphene liquid crystals still has limits in terms of its structural limitations." This technology will be applied to composite fiber fabrication and various wearable textile-based application devices." This work, in which Dr. In-Ho Kim participated as first author was selected as a front cover paper of Advanced Materials on October 4.
This research was supported by the National Creative Research Initiative (CRI) Center for Multi-Dimensional Directed Nanoscale Assembly and the Nanomaterial Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Cross-section SEM image of pure graphene fiber (left) and that of graphene fiber after two-stage defect control using polydopamine (middle and right).
2018.10.23 View 7158
Mussel-Inspired Defect Engineering Enhances the Mechanical Strength of Graphene Fibers
Researchers demonstrated the mussel-inspired reinforcement of graphene fibers for the improvement of different material properties. A research group under Professor Sang Ouk Kim applied polydopamine as an effective infiltrate binder to achieve high mechanical and electrical properties for graphene-based liquid crystalline fibers.
This bio-inspired defect engineering is clearly distinguishable from previous attempts with insulating binders and proposes great potential for versatile applications of flexible and wearable devices as well as low-cost structural materials. The two-step defect engineering addresses the intrinsic limitation of graphene fibers arising from the folding and wrinkling of graphene layers during the fiber-spinning process.
Bio-inspired graphene-based fiber holds great promise for a wide range of applications, including flexible electronics, multifunctional textiles, and wearable sensors. In 2009, the research group discovered graphene oxide liquid crystals in aqueous media while introducing an effective purification process to remove ionic impurities. Graphene fibers, typically wet-spun from aqueous graphene oxide liquid crystal dispersion, are expected to demonstrate superior thermal and electrical conductivities as well as outstanding mechanical performance.
Nonetheless, owing to the inherent formation of defects and voids caused by bending and wrinkling the graphene oxide layer within graphene fibers, their mechanical strength and electrical/thermal conductivities are still far below the desired ideal values. Accordingly, finding an efficient method for constructing the densely packed graphene fibers with strong interlayer interaction is a principal challenge.
Professor Kim's team focused on the adhesion properties of dopamine, a polymer developed with the inspiration of the natural mussel, to solve the problem. This functional polymer, which is studied in various fields, can increase the adhesion between the graphene layers and prevent structural defects.
Professor Kim’s research group succeeded in fabricating high-strength graphene liquid crystalline fibers with controlled structural defects. They also fabricated fibers with improved electrical conductivity through the post-carbonization process of polydopamine.
Based on the theory that dopamine with subsequent high temperature annealing has a similar structure with that of graphene, the team optimized dopamine polymerization conditions and solved the inherent defect control problems of existing graphene fibers.
They also confirmed that the physical properties of dopamine are improved in terms of electrical conductivity due to the influence of nitrogen in dopamine molecules, without damaging the conductivity, which is the fundamental limit of conventional polymers.
Professor Kim, who led the research, said, "Despite its technological potential, carbon fiber using graphene liquid crystals still has limits in terms of its structural limitations." This technology will be applied to composite fiber fabrication and various wearable textile-based application devices." This work, in which Dr. In-Ho Kim participated as first author was selected as a front cover paper of Advanced Materials on October 4.
This research was supported by the National Creative Research Initiative (CRI) Center for Multi-Dimensional Directed Nanoscale Assembly and the Nanomaterial Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Cross-section SEM image of pure graphene fiber (left) and that of graphene fiber after two-stage defect control using polydopamine (middle and right).
2018.10.23 View 7158 -
 Making Graphene Using Laser-induced Phase Separation
IBS & KAIST researchers clarify how laser annealing technology can lead to the production of ultrathin nanomaterials
All our smart phones have shiny flat AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays. Behind each single pixel of these displays hides at least two silicon transistors which are mass-manufactured using laser annealing technology. While the traditional methods to make the transistors use temperature above 1,000°C, the laser technique reaches the same results at low temperatures even on plastic substrates (melting temperature below 300°C). Interestingly, a similar procedure can be used to generate crystals of graphene. Graphene is a strong and thin nano-material made of carbon, its electric and heat-conductive properties have attracted the attention of scientists worldwide.
Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and his research group at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), as well as Professor Sung-Yool Choi of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team discovered graphene synthesis mechanism using laser-induced solid-state phase separation of single-crystal silicon carbide (SiC). This study, available in Nature Communications, clarifies how this laser technology can separate a complex compound (SiC) into its ultrathin elements of carbon and silicon.
Although several fundamental studies presented the effect of excimer lasers in transforming elemental materials like silicon, the laser interaction with more complex compounds like SiC has rarely been studied due to the complexity of compound phase transition and ultra-short processing time.
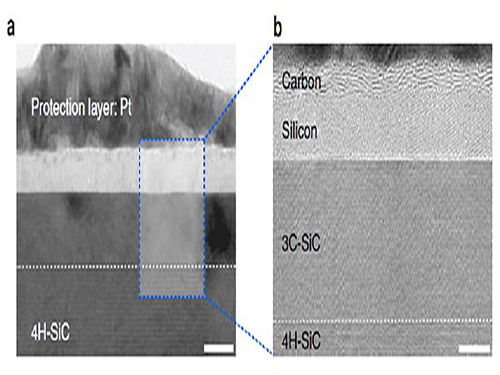
With high resolution microscope images and molecular dynamic simulations, scientists found that a single-pulse irradiation of xenon chloride excimer laser of 30 nanoseconds melts SiC, leading to the separation of a liquid SiC layer, a disordered carbon layer with graphitic domains (about 2.5 nm thick) on top surface and a polycrystalline silicon layer (about 5 nm) below carbon layer. Giving additional pulses causes the sublimation of the separated silicon, while the disordered carbon layer is transformed into a multilayer graphene.
"This research shows that the laser material interaction technology can be a powerful tool for the next generation of two dimensional nanomaterials," said Professor Lee.
Professor Choi added: "Using laser-induced phase separation of complex compounds, new types of two dimensional materials can be synthesized in the future."
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy shows that after just one laser pulse of 30 nanoseconds, the silicon carbide (SiC) substrate is melted and separates into a carbon and a silicon layer. More pulses cause the carbon layer to organize into graphene and the silicon to leave as gas.
Molecular dynamics simulates the graphene formation mechanism. The carbon layer on the top forms because the laser-induced liquid SiC (SiC (l)) is unstable.
(Press Release by Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS))
2016.12.01 View 12676
Making Graphene Using Laser-induced Phase Separation
IBS & KAIST researchers clarify how laser annealing technology can lead to the production of ultrathin nanomaterials
All our smart phones have shiny flat AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays. Behind each single pixel of these displays hides at least two silicon transistors which are mass-manufactured using laser annealing technology. While the traditional methods to make the transistors use temperature above 1,000°C, the laser technique reaches the same results at low temperatures even on plastic substrates (melting temperature below 300°C). Interestingly, a similar procedure can be used to generate crystals of graphene. Graphene is a strong and thin nano-material made of carbon, its electric and heat-conductive properties have attracted the attention of scientists worldwide.
Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and his research group at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), as well as Professor Sung-Yool Choi of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team discovered graphene synthesis mechanism using laser-induced solid-state phase separation of single-crystal silicon carbide (SiC). This study, available in Nature Communications, clarifies how this laser technology can separate a complex compound (SiC) into its ultrathin elements of carbon and silicon.
Although several fundamental studies presented the effect of excimer lasers in transforming elemental materials like silicon, the laser interaction with more complex compounds like SiC has rarely been studied due to the complexity of compound phase transition and ultra-short processing time.
With high resolution microscope images and molecular dynamic simulations, scientists found that a single-pulse irradiation of xenon chloride excimer laser of 30 nanoseconds melts SiC, leading to the separation of a liquid SiC layer, a disordered carbon layer with graphitic domains (about 2.5 nm thick) on top surface and a polycrystalline silicon layer (about 5 nm) below carbon layer. Giving additional pulses causes the sublimation of the separated silicon, while the disordered carbon layer is transformed into a multilayer graphene.
"This research shows that the laser material interaction technology can be a powerful tool for the next generation of two dimensional nanomaterials," said Professor Lee.
Professor Choi added: "Using laser-induced phase separation of complex compounds, new types of two dimensional materials can be synthesized in the future."
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy shows that after just one laser pulse of 30 nanoseconds, the silicon carbide (SiC) substrate is melted and separates into a carbon and a silicon layer. More pulses cause the carbon layer to organize into graphene and the silicon to leave as gas.
Molecular dynamics simulates the graphene formation mechanism. The carbon layer on the top forms because the laser-induced liquid SiC (SiC (l)) is unstable.
(Press Release by Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS))
2016.12.01 View 12676 -
 KAIST Team Develops Technology to Enable Unzipping of the Graphene Plane
Professor Sang-Wook Kim’s research team of the Material Science and Engineering Department has developed a technique, which enables unzipping of the graphene plane without uncontrollable damage. The research findings were published online on the January 22 issue of Nature Communications.
Graphene is a form of carbon in which its atoms form a honey-comb structure through chemical bonding. If this structure can be cut to a desired form, other carbon materials with nanostructure can be created. Many researchers have tried to obtain the accurate unzipping of graphene structures, but faced challenges doing so.
To break a very strong bond between carbon atoms, an equivalently strong chemical reaction must be induced. But the chemical reaction not only cuts out the desirable borders, but also damages the surrounding ones. Conventional techniques, which cut out graphene at once, damaged the chemical properties of the graphene structure after unzipping. This is similar to wearing out paper while manipulating it.
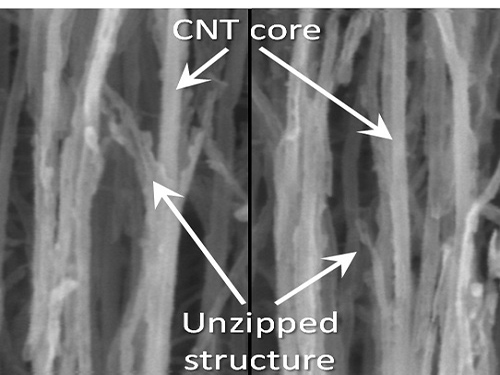
To solve this problem, the research team adopted “heteroatom doping.” The idea is similar to a sheet of paper being split following a groove drawn on the sheet. After making some regions of the structure unstable by doping other atoms such as nitrogen on a carbon plane, the regions are electrochemically stimulated to split the parts. Nitrogen or other atoms act as the groove on the grapheme plane.
The researchers finely controlled the amount of unzipping graphene by adjusting the amount of heteroatom dopants, from which they were able to create a quality nano graphene without any damage in its 2-dimensional crystalline structure. Using this technique, the researchers were able to obtain a capacitor with state-of-the-art energy transfer speed. The nano graphene can be combined with polymer, metal, and semiconductor nano molecules to form carbon composites.
Professor Kim said, “In order to commercialize this technique, heteroatom doping should be researched further. We plan to develop fabric-like carbon materials with excellent mechanical and electrical properties using this technique.”
Picture 1: Unzipped Carbon Nano Tube
Picture 2: Development of Nano Graphene from Carbon Nano Tube Using Heteroatom Dopants
Korean descriptions translated into English:
Unzipping Process of Graphene
Carbon Nano Tube → Nano Graphen
Heteroatom
This process is similar to a paper being split in two from a tiny hole punched therein.
2016.03.22 View 9718
KAIST Team Develops Technology to Enable Unzipping of the Graphene Plane
Professor Sang-Wook Kim’s research team of the Material Science and Engineering Department has developed a technique, which enables unzipping of the graphene plane without uncontrollable damage. The research findings were published online on the January 22 issue of Nature Communications.
Graphene is a form of carbon in which its atoms form a honey-comb structure through chemical bonding. If this structure can be cut to a desired form, other carbon materials with nanostructure can be created. Many researchers have tried to obtain the accurate unzipping of graphene structures, but faced challenges doing so.
To break a very strong bond between carbon atoms, an equivalently strong chemical reaction must be induced. But the chemical reaction not only cuts out the desirable borders, but also damages the surrounding ones. Conventional techniques, which cut out graphene at once, damaged the chemical properties of the graphene structure after unzipping. This is similar to wearing out paper while manipulating it.
To solve this problem, the research team adopted “heteroatom doping.” The idea is similar to a sheet of paper being split following a groove drawn on the sheet. After making some regions of the structure unstable by doping other atoms such as nitrogen on a carbon plane, the regions are electrochemically stimulated to split the parts. Nitrogen or other atoms act as the groove on the grapheme plane.
The researchers finely controlled the amount of unzipping graphene by adjusting the amount of heteroatom dopants, from which they were able to create a quality nano graphene without any damage in its 2-dimensional crystalline structure. Using this technique, the researchers were able to obtain a capacitor with state-of-the-art energy transfer speed. The nano graphene can be combined with polymer, metal, and semiconductor nano molecules to form carbon composites.
Professor Kim said, “In order to commercialize this technique, heteroatom doping should be researched further. We plan to develop fabric-like carbon materials with excellent mechanical and electrical properties using this technique.”
Picture 1: Unzipped Carbon Nano Tube
Picture 2: Development of Nano Graphene from Carbon Nano Tube Using Heteroatom Dopants
Korean descriptions translated into English:
Unzipping Process of Graphene
Carbon Nano Tube → Nano Graphen
Heteroatom
This process is similar to a paper being split in two from a tiny hole punched therein.
2016.03.22 View 9718 -
 KAIST Develops a Method to Transfer Graphene by Stamping
Professor Sung-Yool Choi’s research team from KAIST's Department of Electrical Engineering has developed a technique that can produce a single-layer graphene from a metal etching. Through this, transferring a graphene layer onto a circuit board can be done as easily as stamping a seal on paper.
The research findings were published in the January 14th issue of Small as the lead article.
This technology will allow different types of wafer transfer methods such as transfer onto a surface of a device or a curved surface, and large surface transfer onto a 4 inch wafer. It will be applied in the field of wearable smart gadgets through commercialization of graphene electronic devices.
The traditional method used to transfer graphene onto a circuit board is a wet transfer. However, it has some drawbacks as the graphene layer can be damaged or contaminated during the transfer process from residue from the metal etching. This may affect the electrical properties of the transferred graphene.
After a graphene growth substrate formed on a catalytic metal substrate is pretreated in an aqueous poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) solution, a PVA film forms on the pretreated substrate. The substrate and the graphene layers bond strongly. The graphene is lifted from the growth substrate by means of an elastomeric stamp.
The delaminated graphene layer is isolated state from the elastomeric stamp and thus can be freely transferred onto a circuit board. As the catalytic metal substrate can be reused and does not contain harmful chemical substances, such transfer method is very eco-friendly.
Professor Choi said, “As the new graphene transfer method has a wide range of applications and allows a large surface transfer, it will contribute to the commercialization of graphene electronic devices.” He added that “because this technique has a high degree of freedom in transfer process, it has a variety of usages for graphene and 2 dimensional nano-devices.”
This research was sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, the Republic of Korea.
Figure 1. Cover photo of the journal Small which illustrates the research findings
Figure 2. Above view of Graphene layer transferred through the new method
Figure 3. Large surface transfer of Graphene
2015.01.23 View 12383
KAIST Develops a Method to Transfer Graphene by Stamping
Professor Sung-Yool Choi’s research team from KAIST's Department of Electrical Engineering has developed a technique that can produce a single-layer graphene from a metal etching. Through this, transferring a graphene layer onto a circuit board can be done as easily as stamping a seal on paper.
The research findings were published in the January 14th issue of Small as the lead article.
This technology will allow different types of wafer transfer methods such as transfer onto a surface of a device or a curved surface, and large surface transfer onto a 4 inch wafer. It will be applied in the field of wearable smart gadgets through commercialization of graphene electronic devices.
The traditional method used to transfer graphene onto a circuit board is a wet transfer. However, it has some drawbacks as the graphene layer can be damaged or contaminated during the transfer process from residue from the metal etching. This may affect the electrical properties of the transferred graphene.
After a graphene growth substrate formed on a catalytic metal substrate is pretreated in an aqueous poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) solution, a PVA film forms on the pretreated substrate. The substrate and the graphene layers bond strongly. The graphene is lifted from the growth substrate by means of an elastomeric stamp.
The delaminated graphene layer is isolated state from the elastomeric stamp and thus can be freely transferred onto a circuit board. As the catalytic metal substrate can be reused and does not contain harmful chemical substances, such transfer method is very eco-friendly.
Professor Choi said, “As the new graphene transfer method has a wide range of applications and allows a large surface transfer, it will contribute to the commercialization of graphene electronic devices.” He added that “because this technique has a high degree of freedom in transfer process, it has a variety of usages for graphene and 2 dimensional nano-devices.”
This research was sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, the Republic of Korea.
Figure 1. Cover photo of the journal Small which illustrates the research findings
Figure 2. Above view of Graphene layer transferred through the new method
Figure 3. Large surface transfer of Graphene
2015.01.23 View 12383