Brain+stimulation
-
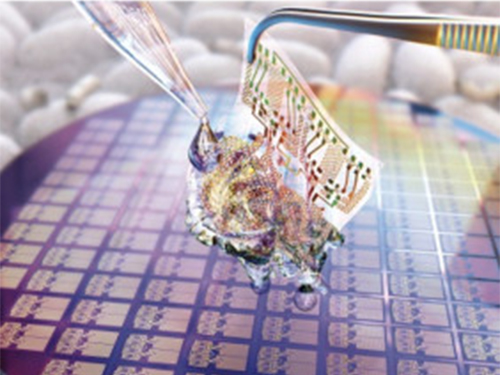 Wafer-Scale Multilayer Fabrication of Silk Fibroin-Based Microelectronics
A KAIST research team developed a novel fabrication method for the multilayer processing of silk-based microelectronics. This technology for creating a biodegradable silk fibroin film allows microfabrication with polymer or metal structures manufactured from photolithography. It can be a key technology in the implementation of silk fibroin-based biodegradable electronic devices or localized drug delivery through silk fibroin patterns.
Silk fibroins are biocompatible, biodegradable, transparent, and flexible, which makes them excellent candidates for implantable biomedical devices, and they have also been used as biodegradable films and functional microstructures in biomedical applications. However, conventional microfabrication processes require strong etching solutions and solvents to modify the structure of silk fibroins.
To prevent the silk fibroin from being damaged during the process, Professor Hyunjoo J. Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering and her team came up with a novel process, named aluminum hard mask on silk fibroin (AMoS), which is capable of micropatterning multiple layers composed of both fibroin and inorganic materials, such as metal and dielectrics with high-precision microscale alignment. The AMoS process can make silk fibroin patterns on devices, or make patterns on silk fibroin thin films with other materials by using photolithography, which is a core technology in the current microfabrication process.
The team successfully cultured primary neurons on the processed silk fibroin micro-patterns, and confirmed that silk fibroin has excellent biocompatibility before and after the fabrication process and that it also can be applied to implanted biological devices.
Through this technology, the team realized the multilayer micropatterning of fibroin films on a silk fibroin substrate and fabricated a biodegradable microelectric circuit consisting of resistors and silk fibroin dielectric capacitors in a silicon wafer with large areas.
They also used this technology to position the micro-pattern of the silk fibroin thin film closer to the flexible polymer-based brain electrode, and confirmed the dye molecules mounted on the silk fibroin were transferred successfully from the micropatterns.
Professor Lee said, “This technology facilitates wafer-scale, large-area processing of sensitive materials. We expect it to be applied to a wide range of biomedical devices in the future. Using the silk fibroin with micro-patterned brain electrodes can open up many new possibilities in research on brain circuits by mounting drugs that restrict or promote brain cell activities.”
This research, in collaboration with Dr. Nakwon Choi from KIST and led by PhD candidate Geon Kook, was published in ACS AMI (10.1021/acsami.8b13170) on January 16, 2019.
Figure 1. The cover page of ACS AMI
Figure 2. Fibroin microstructures and metal patterns on a fibroin produced by using the AMoS mask.
Figure 3. Biocompatibility assessment of the AMoS Process. Top: Schematics image of a) fibroin-coated silicon b) fibroin-pattered silicon and c) gold-patterned fibroin. Bottom: Representative confocal microscopy images of live (green) and dead (red) primary cortical neurons cultured on the substrates.
2019.03.15 View 23356
Wafer-Scale Multilayer Fabrication of Silk Fibroin-Based Microelectronics
A KAIST research team developed a novel fabrication method for the multilayer processing of silk-based microelectronics. This technology for creating a biodegradable silk fibroin film allows microfabrication with polymer or metal structures manufactured from photolithography. It can be a key technology in the implementation of silk fibroin-based biodegradable electronic devices or localized drug delivery through silk fibroin patterns.
Silk fibroins are biocompatible, biodegradable, transparent, and flexible, which makes them excellent candidates for implantable biomedical devices, and they have also been used as biodegradable films and functional microstructures in biomedical applications. However, conventional microfabrication processes require strong etching solutions and solvents to modify the structure of silk fibroins.
To prevent the silk fibroin from being damaged during the process, Professor Hyunjoo J. Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering and her team came up with a novel process, named aluminum hard mask on silk fibroin (AMoS), which is capable of micropatterning multiple layers composed of both fibroin and inorganic materials, such as metal and dielectrics with high-precision microscale alignment. The AMoS process can make silk fibroin patterns on devices, or make patterns on silk fibroin thin films with other materials by using photolithography, which is a core technology in the current microfabrication process.
The team successfully cultured primary neurons on the processed silk fibroin micro-patterns, and confirmed that silk fibroin has excellent biocompatibility before and after the fabrication process and that it also can be applied to implanted biological devices.
Through this technology, the team realized the multilayer micropatterning of fibroin films on a silk fibroin substrate and fabricated a biodegradable microelectric circuit consisting of resistors and silk fibroin dielectric capacitors in a silicon wafer with large areas.
They also used this technology to position the micro-pattern of the silk fibroin thin film closer to the flexible polymer-based brain electrode, and confirmed the dye molecules mounted on the silk fibroin were transferred successfully from the micropatterns.
Professor Lee said, “This technology facilitates wafer-scale, large-area processing of sensitive materials. We expect it to be applied to a wide range of biomedical devices in the future. Using the silk fibroin with micro-patterned brain electrodes can open up many new possibilities in research on brain circuits by mounting drugs that restrict or promote brain cell activities.”
This research, in collaboration with Dr. Nakwon Choi from KIST and led by PhD candidate Geon Kook, was published in ACS AMI (10.1021/acsami.8b13170) on January 16, 2019.
Figure 1. The cover page of ACS AMI
Figure 2. Fibroin microstructures and metal patterns on a fibroin produced by using the AMoS mask.
Figure 3. Biocompatibility assessment of the AMoS Process. Top: Schematics image of a) fibroin-coated silicon b) fibroin-pattered silicon and c) gold-patterned fibroin. Bottom: Representative confocal microscopy images of live (green) and dead (red) primary cortical neurons cultured on the substrates.
2019.03.15 View 23356 -
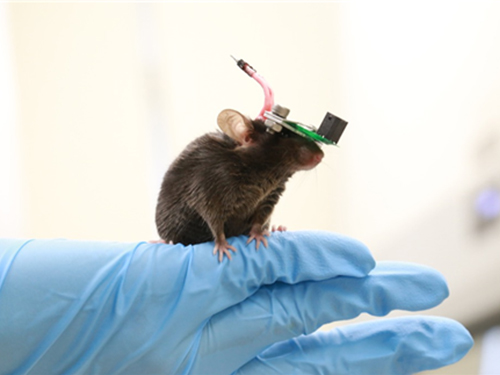 1g-Ultrasound System for the Brain Stimulation of a Freely-moving Mouse
A KAIST research team developed a light-weight capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer (CMUT) and succeeded in the ultrasound brain stimulation of a freely-moving mouse. With this lightweight and compact system, researchers can conduct a versatile set of in vivo experiments.
Conventional methods for stimulating a specific brain region, such as deep brain stimulation (DBS) and optogenetics technology, are highly invasive because they have to insert probes into a target brain, which makes them difficult to use for clinical application. While transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and transcranial electrical stimulation (TES) are noninvasive, they have a wide range of stimulation and problems with in-depth stimulation, which makes them problematic for target-specific treatment.
Therefore, noninvasive and focused ultrasound stimulation technology is gaining a great deal of attention as a next-generation brain stimulation alternative. Since it is delivered noninvasively, it can be applied safely in humans as well as animal experiments. Focused ultrasound stimulation is more advantageous than conventional methods in terms of providing both local and deep stimulation.
Animal behavior experiments are essential for brain stimulation research; however, ultrasonic brain stimulation technology is currently in the early stages of development. So far, only research outcomes with fixed anesthetized mice have been studied because of the heavy ultrasonic device.
Professor Hyunjoo J. Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering and her team reported a technology that can provide ultrasound stimulation to the brain of a freely-moving mouse through a microminiaturized ultrasound device.
The team studied miniaturization and ultra-lightweight CMUTs through microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology and designed a device suitable for behavior experiments. The device weighing less than 1g (around 0.05% of the mouse’s weight) has the center frequency, size, focal length, and ultrasonic intensity to fit a mouse’s dimensions.
To evaluate the performance of the ultrasonic device, the team stimulated the motor cortex of the mouse brain and observed the movement reaction of its forefoot. They also measured the electromyography (EMG) of the trapezius.
As a result, the team confirmed that their ultrasonic device can deliver ultrasound to a depth of 3-4mm in the mouse brain and stimulate an area of the mouse brain that represents 25% of its total size.
Based on this research, the team is investigating the effects of ultrasound on sleep by stimulating the brain of sleeping mice.
Professor Lee said, “Going beyond experimenting on fixed anesthetized mice, this research succeeded in the brain stimulation of a freely-moving mouse. We are planning to study mice with diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, dementia, depression, and epilepsy. I believe that this basic research can contribute to treating human brain-related diseases through ultrasound brain stimulation.
This research, led by Masters candidates Hyunggug Kim and Seongyeon Kim, was published in Brain Stimulation (10.1016/j.brs.2018.11.007) on November 17, 2018.
Figure 1. The miniature transducer for the transcranial ultrasound of a freely-moving mouse
Figure 2. Its structure and simulated 2D beam profile in the axial ad radial directions
2019.03.13 View 10028
1g-Ultrasound System for the Brain Stimulation of a Freely-moving Mouse
A KAIST research team developed a light-weight capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer (CMUT) and succeeded in the ultrasound brain stimulation of a freely-moving mouse. With this lightweight and compact system, researchers can conduct a versatile set of in vivo experiments.
Conventional methods for stimulating a specific brain region, such as deep brain stimulation (DBS) and optogenetics technology, are highly invasive because they have to insert probes into a target brain, which makes them difficult to use for clinical application. While transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and transcranial electrical stimulation (TES) are noninvasive, they have a wide range of stimulation and problems with in-depth stimulation, which makes them problematic for target-specific treatment.
Therefore, noninvasive and focused ultrasound stimulation technology is gaining a great deal of attention as a next-generation brain stimulation alternative. Since it is delivered noninvasively, it can be applied safely in humans as well as animal experiments. Focused ultrasound stimulation is more advantageous than conventional methods in terms of providing both local and deep stimulation.
Animal behavior experiments are essential for brain stimulation research; however, ultrasonic brain stimulation technology is currently in the early stages of development. So far, only research outcomes with fixed anesthetized mice have been studied because of the heavy ultrasonic device.
Professor Hyunjoo J. Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering and her team reported a technology that can provide ultrasound stimulation to the brain of a freely-moving mouse through a microminiaturized ultrasound device.
The team studied miniaturization and ultra-lightweight CMUTs through microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) technology and designed a device suitable for behavior experiments. The device weighing less than 1g (around 0.05% of the mouse’s weight) has the center frequency, size, focal length, and ultrasonic intensity to fit a mouse’s dimensions.
To evaluate the performance of the ultrasonic device, the team stimulated the motor cortex of the mouse brain and observed the movement reaction of its forefoot. They also measured the electromyography (EMG) of the trapezius.
As a result, the team confirmed that their ultrasonic device can deliver ultrasound to a depth of 3-4mm in the mouse brain and stimulate an area of the mouse brain that represents 25% of its total size.
Based on this research, the team is investigating the effects of ultrasound on sleep by stimulating the brain of sleeping mice.
Professor Lee said, “Going beyond experimenting on fixed anesthetized mice, this research succeeded in the brain stimulation of a freely-moving mouse. We are planning to study mice with diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, dementia, depression, and epilepsy. I believe that this basic research can contribute to treating human brain-related diseases through ultrasound brain stimulation.
This research, led by Masters candidates Hyunggug Kim and Seongyeon Kim, was published in Brain Stimulation (10.1016/j.brs.2018.11.007) on November 17, 2018.
Figure 1. The miniature transducer for the transcranial ultrasound of a freely-moving mouse
Figure 2. Its structure and simulated 2D beam profile in the axial ad radial directions
2019.03.13 View 10028