biology
-
 KAIST develops technology for selective RNA modification in living cells and animals
· A team led by Professor Won Do Heo from the Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, has developed a pioneering technology that selectively acetylates specific RNA molecules in living cells and tissues.
· The platform uses RNA-targeting CRISPR tools in combination with RNA-modifying enzymes to chemically modify only the intended RNA.
· The method opens new possibilities for gene therapy by enabling precise control of disease-related RNA without affecting the rest of the transcriptome.
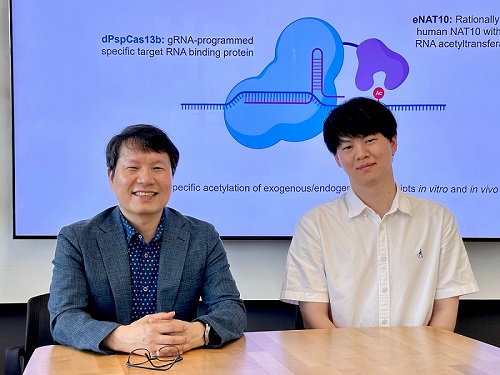
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Won Do Heo and Jihwan Yu, a Ph.D. Candidate of the Department of Biological Sciences >
CRISPR-Cas13, a powerful RNA-targeting technology is gaining increasing attention as a next-generation gene therapy platform due to its precision and reduced side effects. Utilizing this system, researchers at KAIST have now developed the world’s first technology capable of selectively acetylating (chemically modifying) specific RNA molecules among countless transcripts within living cells. This breakthrough enables precise, programmable control of RNA function and is expected to open new avenues in RNA-based therapeutic development.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professor Won Do Heo in the Department of Biological Sciences has recently developed a groundbreaking technology capable of selectively acetylating specific RNA molecules within the human body using the CRISPR-Cas13 system—an RNA-targeting platform gaining increasing attention in the fields of gene regulation and RNA-based therapeutics.
RNA molecules can undergo chemical modifications—the addition of specific chemical groups—which alter their function and behavior without changing the underlying nucleotide sequence. However, some of these modifications, a critical layer of post-transcriptional gene regulation, remain poorly understood. Among them, N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) has been particularly enigmatic, with ongoing debate about its existence and function in human messenger RNA (mRNA), the RNA that encodes proteins.
To address this gap, the KAIST research team developed a targeted RNA acetylation system, named dCas13-eNAT10. This platform combines a catalytically inactive Cas13 enzyme (dCas13) that guides the system to specific RNA targets, with a hyperactive variant of the NAT10 enzyme (eNAT10), which performs RNA acetylation. This approach enables precise acetylation of only the desired RNA molecules among the vast pool of transcripts within the cell.
< Figure 1. Development of hyperactive variant eNAT10 through NAT10 protein engineering. By engineering the NAT10 protein, which performs RNA acetylation in human cells, based on its domain and structure, eNAT10 was developed, showing approximately a 3-fold increase in RNA acetylation activity compared to the wild-type enzyme. >
Using this system, the researchers demonstrated that guide RNAs could direct the dCas13-eNAT10 complex to acetylate specific RNA targets, and acetylation significantly increased protein expression from the modified mRNA. Moreover, the study revealed, for the first time, that RNA acetylation plays a role in intracellular RNA localization, facilitating the export of RNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm—a critical step in gene expression regulation.
To validate its therapeutic potential, the team successfully delivered the targeted RNA acetylation system into the livers of live mice using adeno-associated virus (AAV), a commonly used gene therapy vector. This marks the first demonstration of in vivo RNA modification, extending the applicability of RNA chemical modification tools from cell culture models to living organisms.
< Figure 2. Acetylation of various RNA in cells using dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein. Utilizing the CRISPR-Cas13 system, which can precisely target specific RNA through guide RNA, a dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein was created, demonstrating its ability to specifically acetylate various endogenous RNA at different locations within cells. >
Professor Won Do Heo, who previously developed COVID-19 treatment technology using RNA gene scissors and technology to activate RNA gene scissors with light, stated, "Existing RNA chemical modification research faced difficulties in controlling specificity, temporality, and spatiality. However, this new technology allows selective acetylation of desired RNA, opening the door for accurate and detailed research into the functions of RNA acetylation." He added, "The RNA chemical modification technology developed in this study can be widely used as an RNA-based therapeutic agent and a tool for regulating RNA functions in living organisms in the future."
< Figure 3. In vivo delivery of targeted RNA acetylation system. The targeted RNA acetylation system was encoded in an AAV vector, commonly used in gene therapy, and delivered intravenously to adult mice, showing that target RNA in liver tissue was specifically acetylated according to the guide RNA. >
This research, with Ph.D. candidate Jihwan Yu from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST as the first author, was published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology on June 2, 2025. (Title: Programmable RNA acetylation with CRISPR-Cas13, Impact factor: 12.9, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-025-01922-3)
This research was supported by the Samsung Future Technology Foundation and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.06.10 View 1149
KAIST develops technology for selective RNA modification in living cells and animals
· A team led by Professor Won Do Heo from the Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, has developed a pioneering technology that selectively acetylates specific RNA molecules in living cells and tissues.
· The platform uses RNA-targeting CRISPR tools in combination with RNA-modifying enzymes to chemically modify only the intended RNA.
· The method opens new possibilities for gene therapy by enabling precise control of disease-related RNA without affecting the rest of the transcriptome.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Won Do Heo and Jihwan Yu, a Ph.D. Candidate of the Department of Biological Sciences >
CRISPR-Cas13, a powerful RNA-targeting technology is gaining increasing attention as a next-generation gene therapy platform due to its precision and reduced side effects. Utilizing this system, researchers at KAIST have now developed the world’s first technology capable of selectively acetylating (chemically modifying) specific RNA molecules among countless transcripts within living cells. This breakthrough enables precise, programmable control of RNA function and is expected to open new avenues in RNA-based therapeutic development.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professor Won Do Heo in the Department of Biological Sciences has recently developed a groundbreaking technology capable of selectively acetylating specific RNA molecules within the human body using the CRISPR-Cas13 system—an RNA-targeting platform gaining increasing attention in the fields of gene regulation and RNA-based therapeutics.
RNA molecules can undergo chemical modifications—the addition of specific chemical groups—which alter their function and behavior without changing the underlying nucleotide sequence. However, some of these modifications, a critical layer of post-transcriptional gene regulation, remain poorly understood. Among them, N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) has been particularly enigmatic, with ongoing debate about its existence and function in human messenger RNA (mRNA), the RNA that encodes proteins.
To address this gap, the KAIST research team developed a targeted RNA acetylation system, named dCas13-eNAT10. This platform combines a catalytically inactive Cas13 enzyme (dCas13) that guides the system to specific RNA targets, with a hyperactive variant of the NAT10 enzyme (eNAT10), which performs RNA acetylation. This approach enables precise acetylation of only the desired RNA molecules among the vast pool of transcripts within the cell.
< Figure 1. Development of hyperactive variant eNAT10 through NAT10 protein engineering. By engineering the NAT10 protein, which performs RNA acetylation in human cells, based on its domain and structure, eNAT10 was developed, showing approximately a 3-fold increase in RNA acetylation activity compared to the wild-type enzyme. >
Using this system, the researchers demonstrated that guide RNAs could direct the dCas13-eNAT10 complex to acetylate specific RNA targets, and acetylation significantly increased protein expression from the modified mRNA. Moreover, the study revealed, for the first time, that RNA acetylation plays a role in intracellular RNA localization, facilitating the export of RNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm—a critical step in gene expression regulation.
To validate its therapeutic potential, the team successfully delivered the targeted RNA acetylation system into the livers of live mice using adeno-associated virus (AAV), a commonly used gene therapy vector. This marks the first demonstration of in vivo RNA modification, extending the applicability of RNA chemical modification tools from cell culture models to living organisms.
< Figure 2. Acetylation of various RNA in cells using dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein. Utilizing the CRISPR-Cas13 system, which can precisely target specific RNA through guide RNA, a dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein was created, demonstrating its ability to specifically acetylate various endogenous RNA at different locations within cells. >
Professor Won Do Heo, who previously developed COVID-19 treatment technology using RNA gene scissors and technology to activate RNA gene scissors with light, stated, "Existing RNA chemical modification research faced difficulties in controlling specificity, temporality, and spatiality. However, this new technology allows selective acetylation of desired RNA, opening the door for accurate and detailed research into the functions of RNA acetylation." He added, "The RNA chemical modification technology developed in this study can be widely used as an RNA-based therapeutic agent and a tool for regulating RNA functions in living organisms in the future."
< Figure 3. In vivo delivery of targeted RNA acetylation system. The targeted RNA acetylation system was encoded in an AAV vector, commonly used in gene therapy, and delivered intravenously to adult mice, showing that target RNA in liver tissue was specifically acetylated according to the guide RNA. >
This research, with Ph.D. candidate Jihwan Yu from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST as the first author, was published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology on June 2, 2025. (Title: Programmable RNA acetylation with CRISPR-Cas13, Impact factor: 12.9, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-025-01922-3)
This research was supported by the Samsung Future Technology Foundation and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.06.10 View 1149 -
 KAIST Identifies Master Regulator Blocking Immunotherapy, Paving the Way for a New Lung Cancer Treatment
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, a class of immunotherapies that help immune cells attack cancer more effectively, have revolutionized cancer treatment. However, fewer than 20% of patients respond to these treatments, highlighting the urgent need for new strategies tailored to both responders and non-responders.
KAIST researchers have discovered that 'DEAD-box helicases 54 (DDX54)', a type of RNA-binding protein, is the master regulator that hinders the effectiveness of immunotherapy—opening a new path for lung cancer treatment. This breakthrough technology has been transferred to faculty startup BioRevert Inc., where it is currently being developed as a companion therapeutic and is expected to enter clinical trials by 2028.
< Photo 1. (From left) Researcher Jungeun Lee, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and Postdoctoral Researcher Jeong-Ryeol Gong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 8 that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering had identified DDX54 as a critical factor that determines the immune evasion capacity of lung cancer cells. They demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 enhances immune cell infiltration into tumors and significantly improves the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy using anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies is considered a powerful approach in cancer treatment. However, its low response rate limits the number of patients who actually benefit.
To identify likely responders, tumor mutational burden (TMB) has recently been approved by the FDA as a key biomarker for immunotherapy. Cancers with high mutation rates are thought to be more responsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, even tumors with high TMB can display an “immune-desert” phenotype—where immune cell infiltration is severely limited—resulting in poor treatment responses.
< Figure 1. DDX54 was identified as the master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy by orchestrating suppression of immune cell infiltration through cancer tissues as lung cancer cells become immune-evasive >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team compared transcriptome and genome data of lung cancer patients with immune evasion capabilities through gene regulatory network analysis (A) and discovered DDX54, a master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy (B-F).
This study is especially significant in that it successfully demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 in immune-desert lung tumors can overcome immunotherapy resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
The team used transcriptomic and genomic data from immune-evasive lung cancer patients and employed systems biology techniques to infer gene regulatory networks. Through this analysis, they identified DDX54 as a central regulator in the immune evasion of lung cancer cells.
In a syngeneic mouse model, the suppression of DDX54 led to significant increases in the infiltration of anti-cancer immune cells such as T cells and NK cells, and greatly improved the response to immunotherapy.
Single-cell transcriptomic and spatial transcriptomic analyses further showed that combination therapy targeting DDX54 promoted the differentiation of T cells and memory T cells that suppress tumors, while reducing the infiltration of regulatory T cells and exhausted T cells that support tumor growth.
< Figure 2. In the syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells, it was confirmed that inhibiting DDX54 reversed the immune-evasion ability of cancer cells and enhanced the sensitivity to anti-PD-1 therapy >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells exhibiting immunotherapy resistance, the treatment applied after DDX54 inhibition resulted in statistically significant inhibition of lung cancer growth (B-D) and a significant increase in immune cell infiltration into the tumor tissue (E, F).
The mechanism is believed to involve DDX54 suppression inactivating signaling pathways such as JAK-STAT, MYC, and NF-κB, thereby downregulating immune-evasive proteins CD38 and CD47. This also reduced the infiltration of circulating monocytes—which promote tumor development—and promoted the differentiation of M1 macrophages that play anti-tumor roles.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho stated, “We have, for the first time, identified a master regulatory factor that enables immune evasion in lung cancer cells. By targeting this factor, we developed a new therapeutic strategy that can induce responsiveness to immunotherapy in previously resistant cancers.”
He added, “The discovery of DDX54—hidden within the complex molecular networks of cancer cells—was made possible through the systematic integration of systems biology, combining IT and BT.”
The study, led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on April 2, 2025, with Jeong-Ryeol Gong being the first author, Jungeun Lee, a co-first author, and Younghyun Han, a co-author of the article.
< Figure 3. Single-cell transcriptome and spatial transcriptome analysis confirmed that knockdown of DDX54 increased immune cell infiltration into cancer tissues >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells that underwent immunotherapy in combination with DDX54 inhibition, single-cell transcriptome (H-L) and spatial transcriptome (A-G) analysis of immune cells infiltrating inside cancer tissues were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that anticancer immune cells such as T cells, B cells, and NK cells actively infiltrated the core of lung cancer tissues when DDX54 inhibition and immunotherapy were concurrently administered.
(Paper title: “DDX54 downregulation enhances anti-PD1 therapy in immune-desert lung tumors with high tumor mutational burden,” DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2412310122)
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Research Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program.
< Figure 4. The identified master regulator DDX54 was confirmed to induce CD38 and CD47 expression through Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB activation. >
DDX54 activates the Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB pathways in lung cancer cells to increase CD38 and CD47 expression (A-G). This creates a cancer microenvironment that contributes to cancer development (H) and ultimately induces immune anticancer treatment resistance.
< Figure 5. It was confirmed that an immune-inflamed environment can be created by combining DDX54 inhibition and immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. >
When DDX54 inhibition and ICI therapy are simultaneously administered, the cancer cell characteristics change, the immune evasion ability is restored, and the environment is transformed into an ‘immune-activated’ environment in which immune cells easily infiltrate cancer tissues. This strengthens the anticancer immune response, thereby increasing the sensitivity of immunotherapy even in lung cancer tissues that previously had low responsiveness to immunotherapy.
2025.04.08 View 5084
KAIST Identifies Master Regulator Blocking Immunotherapy, Paving the Way for a New Lung Cancer Treatment
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, a class of immunotherapies that help immune cells attack cancer more effectively, have revolutionized cancer treatment. However, fewer than 20% of patients respond to these treatments, highlighting the urgent need for new strategies tailored to both responders and non-responders.
KAIST researchers have discovered that 'DEAD-box helicases 54 (DDX54)', a type of RNA-binding protein, is the master regulator that hinders the effectiveness of immunotherapy—opening a new path for lung cancer treatment. This breakthrough technology has been transferred to faculty startup BioRevert Inc., where it is currently being developed as a companion therapeutic and is expected to enter clinical trials by 2028.
< Photo 1. (From left) Researcher Jungeun Lee, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and Postdoctoral Researcher Jeong-Ryeol Gong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 8 that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering had identified DDX54 as a critical factor that determines the immune evasion capacity of lung cancer cells. They demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 enhances immune cell infiltration into tumors and significantly improves the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy using anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies is considered a powerful approach in cancer treatment. However, its low response rate limits the number of patients who actually benefit.
To identify likely responders, tumor mutational burden (TMB) has recently been approved by the FDA as a key biomarker for immunotherapy. Cancers with high mutation rates are thought to be more responsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, even tumors with high TMB can display an “immune-desert” phenotype—where immune cell infiltration is severely limited—resulting in poor treatment responses.
< Figure 1. DDX54 was identified as the master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy by orchestrating suppression of immune cell infiltration through cancer tissues as lung cancer cells become immune-evasive >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team compared transcriptome and genome data of lung cancer patients with immune evasion capabilities through gene regulatory network analysis (A) and discovered DDX54, a master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy (B-F).
This study is especially significant in that it successfully demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 in immune-desert lung tumors can overcome immunotherapy resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
The team used transcriptomic and genomic data from immune-evasive lung cancer patients and employed systems biology techniques to infer gene regulatory networks. Through this analysis, they identified DDX54 as a central regulator in the immune evasion of lung cancer cells.
In a syngeneic mouse model, the suppression of DDX54 led to significant increases in the infiltration of anti-cancer immune cells such as T cells and NK cells, and greatly improved the response to immunotherapy.
Single-cell transcriptomic and spatial transcriptomic analyses further showed that combination therapy targeting DDX54 promoted the differentiation of T cells and memory T cells that suppress tumors, while reducing the infiltration of regulatory T cells and exhausted T cells that support tumor growth.
< Figure 2. In the syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells, it was confirmed that inhibiting DDX54 reversed the immune-evasion ability of cancer cells and enhanced the sensitivity to anti-PD-1 therapy >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells exhibiting immunotherapy resistance, the treatment applied after DDX54 inhibition resulted in statistically significant inhibition of lung cancer growth (B-D) and a significant increase in immune cell infiltration into the tumor tissue (E, F).
The mechanism is believed to involve DDX54 suppression inactivating signaling pathways such as JAK-STAT, MYC, and NF-κB, thereby downregulating immune-evasive proteins CD38 and CD47. This also reduced the infiltration of circulating monocytes—which promote tumor development—and promoted the differentiation of M1 macrophages that play anti-tumor roles.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho stated, “We have, for the first time, identified a master regulatory factor that enables immune evasion in lung cancer cells. By targeting this factor, we developed a new therapeutic strategy that can induce responsiveness to immunotherapy in previously resistant cancers.”
He added, “The discovery of DDX54—hidden within the complex molecular networks of cancer cells—was made possible through the systematic integration of systems biology, combining IT and BT.”
The study, led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on April 2, 2025, with Jeong-Ryeol Gong being the first author, Jungeun Lee, a co-first author, and Younghyun Han, a co-author of the article.
< Figure 3. Single-cell transcriptome and spatial transcriptome analysis confirmed that knockdown of DDX54 increased immune cell infiltration into cancer tissues >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells that underwent immunotherapy in combination with DDX54 inhibition, single-cell transcriptome (H-L) and spatial transcriptome (A-G) analysis of immune cells infiltrating inside cancer tissues were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that anticancer immune cells such as T cells, B cells, and NK cells actively infiltrated the core of lung cancer tissues when DDX54 inhibition and immunotherapy were concurrently administered.
(Paper title: “DDX54 downregulation enhances anti-PD1 therapy in immune-desert lung tumors with high tumor mutational burden,” DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2412310122)
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Research Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program.
< Figure 4. The identified master regulator DDX54 was confirmed to induce CD38 and CD47 expression through Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB activation. >
DDX54 activates the Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB pathways in lung cancer cells to increase CD38 and CD47 expression (A-G). This creates a cancer microenvironment that contributes to cancer development (H) and ultimately induces immune anticancer treatment resistance.
< Figure 5. It was confirmed that an immune-inflamed environment can be created by combining DDX54 inhibition and immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. >
When DDX54 inhibition and ICI therapy are simultaneously administered, the cancer cell characteristics change, the immune evasion ability is restored, and the environment is transformed into an ‘immune-activated’ environment in which immune cells easily infiltrate cancer tissues. This strengthens the anticancer immune response, thereby increasing the sensitivity of immunotherapy even in lung cancer tissues that previously had low responsiveness to immunotherapy.
2025.04.08 View 5084 -
 KAIST provides a comprehensive resource on microbial cell factories for sustainable chemical production
In silico analysis of five industrial microorganisms identifies optimal strains and metabolic engineering strategies for producing 235 valuable chemicals
Climate change and the depletion of fossil fuels have raised the global need for sustainable chemical production. In response to these environmental challenges, microbial cell factories are gaining attention as eco-friendly platforms for producing chemicals using renewable resources, while metabolic engineering technologies to enhance these cell factories are becoming crucial tools for maximizing production efficiency. However, difficulties in selecting suitable microbial strains and optimizing complex metabolic pathways continue to pose significant obstacles to practical industrial applications.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on 27th of March that Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering comprehensively evaluated the production capabilities of various industrial microbial cell factories using in silico simulations and, based on these findings, identified the most suitable microbial strains for producing specific chemicals as well as optimal metabolic engineering strategies.
Previously, researchers attempted to determine the best strains and efficient metabolic engineering strategies among numerous microbial candidates through extensive biological experiments and meticulous verification processes. However, this approach required substantial time and costs. Recently, the introduction of genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs), which reconstruct the metabolic networks within an organism based on its entire genome information, has enabled systematic analysis of metabolic fluxes via computer simulations. This development offers a new way to overcome limitations of conventional experimental approaches, revolutionizing both strain selection and metabolic pathway design.
Accordingly, Professor Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, evaluated the production capabilities of five representative industrial microorganisms—Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis, Corynebacterium glutamicum, and Pseudomonas putida—for 235 bio-based chemicals. Using GEMs, the researchers calculated both the maximum theoretical yields and the maximum achievable yields under industrial conditions for each chemical, thereby establishing criteria to identify the most suitable strains for each target compound.
< Figure 1. Outline of the strategy for improving microbial cell factories using a genome-scale metabolic model (GEM) >
The team specifically proposed strategies such as introducing heterologous enzyme reactions derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors used by microbes to expand metabolic pathways. These strategies were shown to increase yields beyond the innate metabolic capacities of the microorganisms, resulting in higher production of industrially important chemicals such as mevalonic acid, propanol, fatty acids, and isoprenoids.
Moreover, by applying a computational approach to analyze metabolic fluxes in silico, the researchers suggested strategies for improving microbial strains to maximize the production of various chemicals. They quantitatively identified the relationships between specific enzyme reactions and target chemical production, as well as the relationships between enzymes and metabolites, determining which enzyme reactions should be up- or down-regulated. Through this, the team presented strategies not only to achieve high theoretical yields but also to maximize actual production capacities.
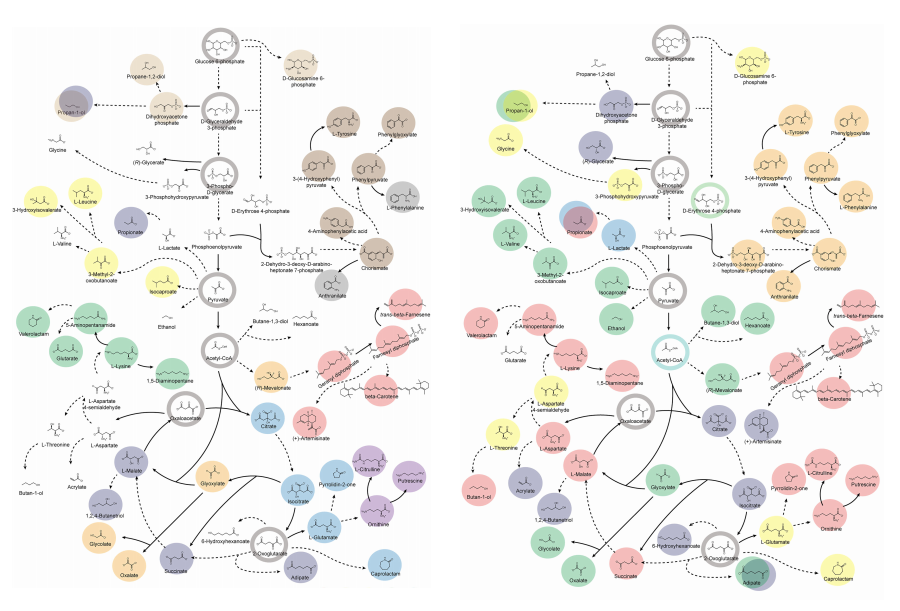
< Figure 2. Comparison of production routes and maximum yields of useful chemicals using representative industrial microorganisms >
Dr. Gi Bae Kim, the first author of this paper from the KAIST BioProcess Engineering Research Center, explained, “By introducing metabolic pathways derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors, it is possible to design new microbial cell factories that surpass existing limitations. The strategies presented in this study will play a pivotal role in making microbial-based production processes more economical and efficient.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted, “This research serves as a key resource in the field of systems metabolic engineering, reducing difficulties in strain selection and pathway design, and enabling more efficient development of microbial cell factories. We expect it to greatly contribute to the future development of technologies for producing various eco-friendly chemicals, such as biofuels, bioplastics, and functional food materials.”
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project and Development of advanced synthetic biology source technologies for leading the biomanufacturing industry project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) from National Research Foundation supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2025.03.27 View 3710
KAIST provides a comprehensive resource on microbial cell factories for sustainable chemical production
In silico analysis of five industrial microorganisms identifies optimal strains and metabolic engineering strategies for producing 235 valuable chemicals
Climate change and the depletion of fossil fuels have raised the global need for sustainable chemical production. In response to these environmental challenges, microbial cell factories are gaining attention as eco-friendly platforms for producing chemicals using renewable resources, while metabolic engineering technologies to enhance these cell factories are becoming crucial tools for maximizing production efficiency. However, difficulties in selecting suitable microbial strains and optimizing complex metabolic pathways continue to pose significant obstacles to practical industrial applications.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on 27th of March that Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering comprehensively evaluated the production capabilities of various industrial microbial cell factories using in silico simulations and, based on these findings, identified the most suitable microbial strains for producing specific chemicals as well as optimal metabolic engineering strategies.
Previously, researchers attempted to determine the best strains and efficient metabolic engineering strategies among numerous microbial candidates through extensive biological experiments and meticulous verification processes. However, this approach required substantial time and costs. Recently, the introduction of genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs), which reconstruct the metabolic networks within an organism based on its entire genome information, has enabled systematic analysis of metabolic fluxes via computer simulations. This development offers a new way to overcome limitations of conventional experimental approaches, revolutionizing both strain selection and metabolic pathway design.
Accordingly, Professor Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, evaluated the production capabilities of five representative industrial microorganisms—Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis, Corynebacterium glutamicum, and Pseudomonas putida—for 235 bio-based chemicals. Using GEMs, the researchers calculated both the maximum theoretical yields and the maximum achievable yields under industrial conditions for each chemical, thereby establishing criteria to identify the most suitable strains for each target compound.
< Figure 1. Outline of the strategy for improving microbial cell factories using a genome-scale metabolic model (GEM) >
The team specifically proposed strategies such as introducing heterologous enzyme reactions derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors used by microbes to expand metabolic pathways. These strategies were shown to increase yields beyond the innate metabolic capacities of the microorganisms, resulting in higher production of industrially important chemicals such as mevalonic acid, propanol, fatty acids, and isoprenoids.
Moreover, by applying a computational approach to analyze metabolic fluxes in silico, the researchers suggested strategies for improving microbial strains to maximize the production of various chemicals. They quantitatively identified the relationships between specific enzyme reactions and target chemical production, as well as the relationships between enzymes and metabolites, determining which enzyme reactions should be up- or down-regulated. Through this, the team presented strategies not only to achieve high theoretical yields but also to maximize actual production capacities.
< Figure 2. Comparison of production routes and maximum yields of useful chemicals using representative industrial microorganisms >
Dr. Gi Bae Kim, the first author of this paper from the KAIST BioProcess Engineering Research Center, explained, “By introducing metabolic pathways derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors, it is possible to design new microbial cell factories that surpass existing limitations. The strategies presented in this study will play a pivotal role in making microbial-based production processes more economical and efficient.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted, “This research serves as a key resource in the field of systems metabolic engineering, reducing difficulties in strain selection and pathway design, and enabling more efficient development of microbial cell factories. We expect it to greatly contribute to the future development of technologies for producing various eco-friendly chemicals, such as biofuels, bioplastics, and functional food materials.”
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project and Development of advanced synthetic biology source technologies for leading the biomanufacturing industry project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) from National Research Foundation supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2025.03.27 View 3710 -
 KAIST Develops Eco-Friendly, Nylon-Like Plastic Using Microorganisms
Poly(ester amide) amide is a next-generation material that combines the advantages of PET (polyester) and nylon (polyamide), two widely used plastics. However, it could only be produced from fossil fuels, which posed environmental concerns. Using microorganisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a new bio-based plastic to replace conventional plastic.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed microbial strains through systems metabolic engineering to produce various eco-friendly, bio-based poly(ester amide)s. The team collaborated with researchers from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT, President Young-Kook Lee) to analyze and confirm the properties of the resulting plastic.
Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team designed new metabolic pathways that do not naturally exist in microorganisms, and developed a platform microbial strain capable of producing nine different types of poly(ester amide)s, including poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-3-aminopropionate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-4-aminobutyrate).
Using glucose derived from abundant biomass sources such as waste wood and weeds, the team successfully produced poly(ester amide)s in an eco-friendly manner. The researchers also confirmed the potential for industrial-scale production by demonstrating high production efficiency (54.57 g/L) using fed-batch fermentation of the engineered strain.
In collaboration with researchers Haemin Jeong and Jihoon Shin from KRICT, the KAIST team analyzed the properties of the bio-based plastic and found that it exhibited characteristics similar to high-density polyethylene (HDPE). This means the new plastic is not only eco-friendly but also strong and durable enough to replace conventional plastics.
The engineered strains and strategies developed in this study are expected to be useful not only for producing various poly(ester amide)s but also for constructing metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of other types of polymers.
Professor Sang Yup Lee stated, “This study is the first to demonstrate the possibility of producing poly(ester amide)s (plastics) through a renewable bio-based chemical process rather than relying on the petroleum-based chemical industry. We plan to further enhance the production yield and efficiency through continued research.”
The study was published online on March 17 in the international journal Nature Chemical Biology.
·Title: Biosynthesis of poly(ester amide)s in engineered Escherichia coli
·DOI: 10.1038/s41589-025-01842-2
·Authors: A total of seven authors including Tong Un Chae (KAIST, first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, second author), Da-Hee Ahn (KAIST, third author), Woo Dae Jang (KAIST, fourth author), Haemin Jeong (KRICT, fifth author), Jihoon Shin (KRICT, sixth author), and Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author).
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) under the Eco-Friendly Chemical Technology Development Project as part of the "Next-Generation Biorefinery Technology Development to Lead the Bio-Chemical Industry" initiative (project led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST).
2025.03.24 View 4904
KAIST Develops Eco-Friendly, Nylon-Like Plastic Using Microorganisms
Poly(ester amide) amide is a next-generation material that combines the advantages of PET (polyester) and nylon (polyamide), two widely used plastics. However, it could only be produced from fossil fuels, which posed environmental concerns. Using microorganisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a new bio-based plastic to replace conventional plastic.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed microbial strains through systems metabolic engineering to produce various eco-friendly, bio-based poly(ester amide)s. The team collaborated with researchers from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT, President Young-Kook Lee) to analyze and confirm the properties of the resulting plastic.
Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team designed new metabolic pathways that do not naturally exist in microorganisms, and developed a platform microbial strain capable of producing nine different types of poly(ester amide)s, including poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-3-aminopropionate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-4-aminobutyrate).
Using glucose derived from abundant biomass sources such as waste wood and weeds, the team successfully produced poly(ester amide)s in an eco-friendly manner. The researchers also confirmed the potential for industrial-scale production by demonstrating high production efficiency (54.57 g/L) using fed-batch fermentation of the engineered strain.
In collaboration with researchers Haemin Jeong and Jihoon Shin from KRICT, the KAIST team analyzed the properties of the bio-based plastic and found that it exhibited characteristics similar to high-density polyethylene (HDPE). This means the new plastic is not only eco-friendly but also strong and durable enough to replace conventional plastics.
The engineered strains and strategies developed in this study are expected to be useful not only for producing various poly(ester amide)s but also for constructing metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of other types of polymers.
Professor Sang Yup Lee stated, “This study is the first to demonstrate the possibility of producing poly(ester amide)s (plastics) through a renewable bio-based chemical process rather than relying on the petroleum-based chemical industry. We plan to further enhance the production yield and efficiency through continued research.”
The study was published online on March 17 in the international journal Nature Chemical Biology.
·Title: Biosynthesis of poly(ester amide)s in engineered Escherichia coli
·DOI: 10.1038/s41589-025-01842-2
·Authors: A total of seven authors including Tong Un Chae (KAIST, first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, second author), Da-Hee Ahn (KAIST, third author), Woo Dae Jang (KAIST, fourth author), Haemin Jeong (KRICT, fifth author), Jihoon Shin (KRICT, sixth author), and Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author).
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) under the Eco-Friendly Chemical Technology Development Project as part of the "Next-Generation Biorefinery Technology Development to Lead the Bio-Chemical Industry" initiative (project led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST).
2025.03.24 View 4904 -
 KAIST Discovers Molecular Switch that Reverses Cancerous Transformation at the Critical Moment of Transition
< (From left) PhD student Seoyoon D. Jeong, (bottom) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, (top) Dr. Dongkwan Shin, Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho’s research team has recently been highlighted for their work on developing an original technology for cancer reversal treatment that does not kill cancer cells but only changes their characteristics to reverse them to a state similar to normal cells. This time, they have succeeded in revealing for the first time that a molecular switch that can induce cancer reversal at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells is hidden in the genetic network.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of February that Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has succeeded in developing a fundamental technology to capture the critical transition phenomenon at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells and analyze it to discover a molecular switch that can revert cancer cells back into normal cells.
A critical transition is a phenomenon in which a sudden change in state occurs at a specific point in time, like water changing into steam at 100℃. This critical transition phenomenon also occurs in the process in which normal cells change into cancer cells at a specific point in time due to the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic changes.
The research team discovered that normal cells can enter an unstable critical transition state where normal cells and cancer cells coexist just before they change into cancer cells during tumorigenesis, the production or development of tumors, and analyzed this critical transition state using a systems biology method to develop a cancer reversal molecular switch identification technology that can reverse the cancerization process. They then applied this to colon cancer cells and confirmed through molecular cell experiments that cancer cells can recover the characteristics of normal cells.
This is an original technology that automatically infers a computer model of the genetic network that controls the critical transition of cancer development from single-cell RNA sequencing data, and systematically finds molecular switches for cancer reversion by simulation analysis. It is expected that this technology will be applied to the development of reversion therapies for other cancers in the future.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "We have discovered a molecular switch that can revert the fate of cancer cells back to a normal state by capturing the moment of critical transition right before normal cells are changed into an irreversible cancerous state."
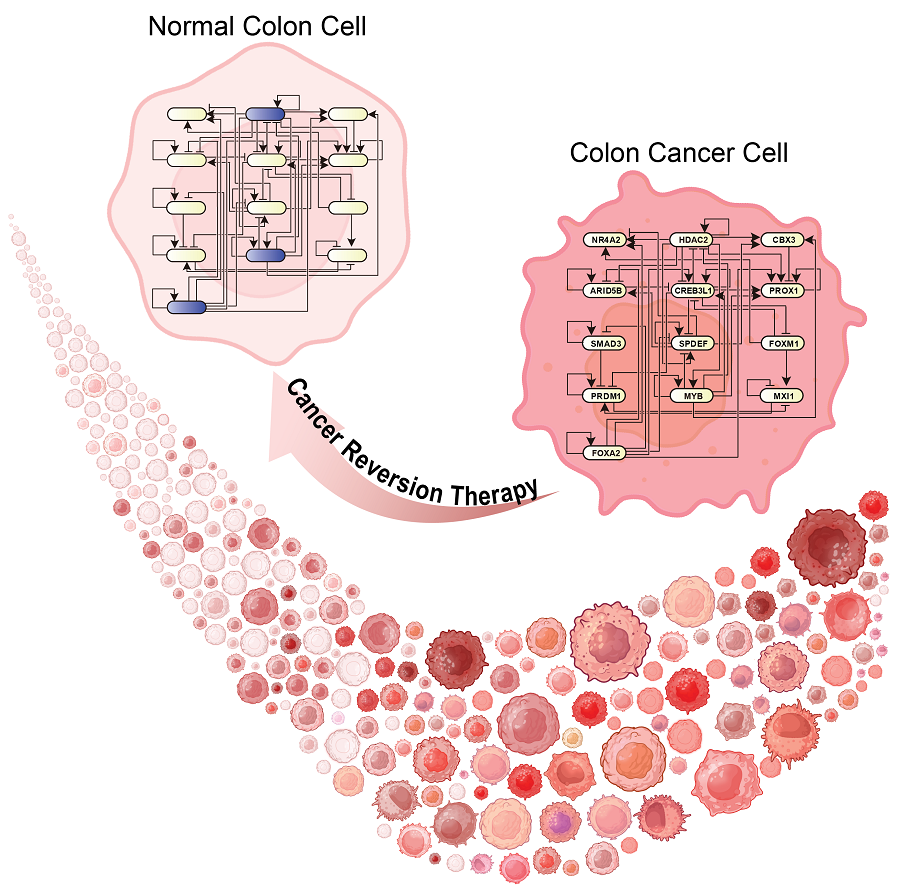
< Figure 1. Overall conceptual framework of the technology that automatically constructs a molecular regulatory network from single-cell RNA sequencing data of colon cancer cells to discover molecular switches for cancer reversion through computer simulation analysis. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a fundamental technology for automatic construction of a computer model of a core gene network by analyzing the entire process of tumorigenesis of colon cells turning into cancer cells, and developed an original technology for discovering the molecular switches that can induce cancer cell reversal through attractor landscape analysis. >
He continued, "In particular, this study has revealed in detail, at the genetic network level, what changes occur within cells behind the process of cancer development, which has been considered a mystery until now." He emphasized, "This is the first study to reveal that an important clue that can revert the fate of tumorigenesis is hidden at this very critical moment of change."
< Figure 2. Identification of tumor transition state using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer. Using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer patient-derived organoids for normal and cancerous tissues, a critical transition was identified in which normal and cancerous cells coexist and instability increases (a-d). The critical transition was confirmed to show intermediate levels of major phenotypic features related to cancer or normal tissues that are indicative of the states between the normal and cancerous cells (e). >
The results of this study, conducted by KAIST Dr. Dongkwan Shin (currently at the National Cancer Center), Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong, and doctoral student Seoyoon D. Jeong jointly with a research team at Seoul National University that provided the organoids (in vitro cultured tissues) from colon cancer patient, were published as an online paper in the international journal ‘Advanced Science’ published by Wiley on January 22nd.
(Paper title: Attractor landscape analysis reveals a reversion switch in the transition of colorectal tumorigenesis) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202412503)
< Figure 3. Reconstruction of a dynamic network model for the transition state of colorectal cancer.
A new technology was established to build a gene network computer model that can simulate the dynamic changes between genes by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing data and existing experimental results on gene-to-gene interactions in the critical transition of cancer. (a). Using this technology, a gene network computer model for the critical transition of colorectal cancer was constructed, and the distribution of attractors representing normal and cancer cell phenotypes was investigated through attractor landscape analysis (b-e). >
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program and the Disease-Centered Translational Research Project of the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) of the Ministry of Health and Welfare.
< Figure 4. Quantification of attractor landscapes and discovery of transcription factors for cancer reversibility through perturbation simulation analysis. A methodology for implementing discontinuous attractor landscapes continuously from a computer model of gene networks and quantifying them as cancer scores was introduced (a), and attractor landscapes for the critical transition of colorectal cancer were secured (b-d). By tracking the change patterns of normal and cancer cell attractors through perturbation simulation analysis for each gene, the optimal combination of transcription factors for cancer reversion was discovered (e-h). This was confirmed in various parameter combinations as well (i). >
< Figure 5. Identification and experimental validation of the optimal target gene for cancer reversion. Among the common target genes of the discovered transcription factor combinations, we identified cancer reversing molecular switches that are predicted to suppress cancer cell proliferation and restore the characteristics of normal colon cells (a-d). When inhibitors for the molecular switches were treated to organoids derived from colon cancer patients, it was confirmed that cancer cell proliferation was suppressed and the expression of key genes related to cancer development was inhibited (e-h), and a group of genes related to normal colon epithelium was activated and transformed into a state similar to normal colon cells (i-j). >
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed an original technology to systematically discover key molecular switches that can induce reversion of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach using an attractor landscape analysis of a genetic network model for the critical transition at the moment of transformation from normal cells to cancer cells, and verified the reversing effect of actual colon cancer through cellular experiments. >
2025.02.05 View 26622
KAIST Discovers Molecular Switch that Reverses Cancerous Transformation at the Critical Moment of Transition
< (From left) PhD student Seoyoon D. Jeong, (bottom) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, (top) Dr. Dongkwan Shin, Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho’s research team has recently been highlighted for their work on developing an original technology for cancer reversal treatment that does not kill cancer cells but only changes their characteristics to reverse them to a state similar to normal cells. This time, they have succeeded in revealing for the first time that a molecular switch that can induce cancer reversal at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells is hidden in the genetic network.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of February that Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has succeeded in developing a fundamental technology to capture the critical transition phenomenon at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells and analyze it to discover a molecular switch that can revert cancer cells back into normal cells.
A critical transition is a phenomenon in which a sudden change in state occurs at a specific point in time, like water changing into steam at 100℃. This critical transition phenomenon also occurs in the process in which normal cells change into cancer cells at a specific point in time due to the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic changes.
The research team discovered that normal cells can enter an unstable critical transition state where normal cells and cancer cells coexist just before they change into cancer cells during tumorigenesis, the production or development of tumors, and analyzed this critical transition state using a systems biology method to develop a cancer reversal molecular switch identification technology that can reverse the cancerization process. They then applied this to colon cancer cells and confirmed through molecular cell experiments that cancer cells can recover the characteristics of normal cells.
This is an original technology that automatically infers a computer model of the genetic network that controls the critical transition of cancer development from single-cell RNA sequencing data, and systematically finds molecular switches for cancer reversion by simulation analysis. It is expected that this technology will be applied to the development of reversion therapies for other cancers in the future.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "We have discovered a molecular switch that can revert the fate of cancer cells back to a normal state by capturing the moment of critical transition right before normal cells are changed into an irreversible cancerous state."
< Figure 1. Overall conceptual framework of the technology that automatically constructs a molecular regulatory network from single-cell RNA sequencing data of colon cancer cells to discover molecular switches for cancer reversion through computer simulation analysis. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a fundamental technology for automatic construction of a computer model of a core gene network by analyzing the entire process of tumorigenesis of colon cells turning into cancer cells, and developed an original technology for discovering the molecular switches that can induce cancer cell reversal through attractor landscape analysis. >
He continued, "In particular, this study has revealed in detail, at the genetic network level, what changes occur within cells behind the process of cancer development, which has been considered a mystery until now." He emphasized, "This is the first study to reveal that an important clue that can revert the fate of tumorigenesis is hidden at this very critical moment of change."
< Figure 2. Identification of tumor transition state using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer. Using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer patient-derived organoids for normal and cancerous tissues, a critical transition was identified in which normal and cancerous cells coexist and instability increases (a-d). The critical transition was confirmed to show intermediate levels of major phenotypic features related to cancer or normal tissues that are indicative of the states between the normal and cancerous cells (e). >
The results of this study, conducted by KAIST Dr. Dongkwan Shin (currently at the National Cancer Center), Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong, and doctoral student Seoyoon D. Jeong jointly with a research team at Seoul National University that provided the organoids (in vitro cultured tissues) from colon cancer patient, were published as an online paper in the international journal ‘Advanced Science’ published by Wiley on January 22nd.
(Paper title: Attractor landscape analysis reveals a reversion switch in the transition of colorectal tumorigenesis) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202412503)
< Figure 3. Reconstruction of a dynamic network model for the transition state of colorectal cancer.
A new technology was established to build a gene network computer model that can simulate the dynamic changes between genes by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing data and existing experimental results on gene-to-gene interactions in the critical transition of cancer. (a). Using this technology, a gene network computer model for the critical transition of colorectal cancer was constructed, and the distribution of attractors representing normal and cancer cell phenotypes was investigated through attractor landscape analysis (b-e). >
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program and the Disease-Centered Translational Research Project of the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) of the Ministry of Health and Welfare.
< Figure 4. Quantification of attractor landscapes and discovery of transcription factors for cancer reversibility through perturbation simulation analysis. A methodology for implementing discontinuous attractor landscapes continuously from a computer model of gene networks and quantifying them as cancer scores was introduced (a), and attractor landscapes for the critical transition of colorectal cancer were secured (b-d). By tracking the change patterns of normal and cancer cell attractors through perturbation simulation analysis for each gene, the optimal combination of transcription factors for cancer reversion was discovered (e-h). This was confirmed in various parameter combinations as well (i). >
< Figure 5. Identification and experimental validation of the optimal target gene for cancer reversion. Among the common target genes of the discovered transcription factor combinations, we identified cancer reversing molecular switches that are predicted to suppress cancer cell proliferation and restore the characteristics of normal colon cells (a-d). When inhibitors for the molecular switches were treated to organoids derived from colon cancer patients, it was confirmed that cancer cell proliferation was suppressed and the expression of key genes related to cancer development was inhibited (e-h), and a group of genes related to normal colon epithelium was activated and transformed into a state similar to normal colon cells (i-j). >
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed an original technology to systematically discover key molecular switches that can induce reversion of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach using an attractor landscape analysis of a genetic network model for the critical transition at the moment of transformation from normal cells to cancer cells, and verified the reversing effect of actual colon cancer through cellular experiments. >
2025.02.05 View 26622 -
 KAIST Develops Foundational Technology to Revert Cancer Cells to Normal Cells
Despite the development of numerous cancer treatment technologies, the common goal of current cancer therapies is to eliminate cancer cells. This approach, however, faces fundamental limitations, including cancer cells developing resistance and returning, as well as severe side effects from the destruction of healthy cells.
< (From top left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD candidates Juhee Kim, Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, and Hoon-Min Kim posed for a group photo with Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of December that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has developed a groundbreaking technology that can treat colon cancer by converting cancer cells into a state resembling normal colon cells without killing them, thus avoiding side effects.
The research team focused on the observation that during the oncogenesis process, normal cells regress along their differentiation trajectory. Building on this insight, they developed a technology to create a digital twin of the gene network associated with the differentiation trajectory of normal cells.
< Figure 1. Technology for creating a digital twin of a gene network from single-cell transcriptome data of a normal cell differentiation trajectory. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a digital twin creation technology that precisely observes the dynamics of gene regulatory relationships during the process of normal cells differentiating along a differentiation trajectory and analyzes the relationships among key genes to build a mathematical model that can be simulated (A-F). In addition, they developed a technology to discover key regulatory factors that control the differentiation trajectory of normal cells by simulating and analyzing this digital twin. >
< Figure 2. Digital twin simulation simulating the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells. The dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data for the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells were analyzed (A) and a digital twin of the gene network was developed representing the regulatory relationships of key genes in this differentiation trajectory (B). The simulation results of the digital twin confirm that it readily reproduces the dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data (C, D). >
Through simulation analysis, the team systematically identified master molecular switches that induce normal cell differentiation. When these switches were applied to colon cancer cells, the cancer cells reverted to a normal-like state, a result confirmed through molecular and cellular experiments as well as animal studies.
< Figure 3. Discovery of top-level key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells. By applying control factor discovery technology to the digital twin model, three genes, HDAC2, FOXA2, and MYB, were discovered as key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells (A, B). The results of simulation analysis of the regulatory effects of the discovered control factors through the digital twin confirmed that they could induce complete differentiation of colon cells (C). >
< Figure 4. Verification of the effect of the key control factors discovered using colon cancer cells and animal experiments on the reversibility of colon cancer. The key control factors of the normal colon cell differentiation trajectory discovered through digital twin simulation analysis were applied to actual colon cancer cells and colon cancer mouse animal models to experimentally verify the effect of cancer reversibility. The key control factors significantly reduced the proliferation of three colon cancer cell lines (A), and this was confirmed in the same way in animal models (B-D). >
This research demonstrates that cancer cell reversion can be systematically achieved by analyzing and utilizing the digital twin of the cancer cell gene network, rather than relying on serendipitous discoveries. The findings hold significant promise for developing reversible cancer therapies that can be applied to various types of cancer.
< Figure 5. The change in overall gene expression was confirmed through the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors, which converted the state of colon cancer cells to that of normal colon cells. The transcriptomes of colon cancer tissues and normal colon tissues from more than 400 colon cancer patients were compared with the transcriptomes of colon cancer cell lines and reversible colon cancer cell lines, respectively. The comparison results confirmed that the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors converted all three colon cancer cell lines to a state similar to the transcriptome expression of normal colon tissues. >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho remarked, "The fact that cancer cells can be converted back to normal cells is an astonishing phenomenon. This study proves that such reversion can be systematically induced."
He further emphasized, "This research introduces the novel concept of reversible cancer therapy by reverting cancer cells to normal cells. It also develops foundational technology for identifying targets for cancer reversion through the systematic analysis of normal cell differentiation trajectories."
This research included contributions from Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, Hoon-Min Kim, Juhee Kim, and Jaeog Jeon, and was published in the online edition of the international journal Advanced Science by Wiley on December 11. (Title: “Control of Cellular Differentiation Trajectories for Cancer Reversion”) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202402132
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a source technology to systematically discover key control factors that can induce reversibility of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach and a digital twin simulation analysis of the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells, and verified the effects of reversion on actual colon cancer through molecular cell experiments and animal experiments. >
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program. The research findings have been transferred to BioRevert Inc., where they will be used for the development of practical cancer reversion therapies.
2024.12.23 View 101777
KAIST Develops Foundational Technology to Revert Cancer Cells to Normal Cells
Despite the development of numerous cancer treatment technologies, the common goal of current cancer therapies is to eliminate cancer cells. This approach, however, faces fundamental limitations, including cancer cells developing resistance and returning, as well as severe side effects from the destruction of healthy cells.
< (From top left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD candidates Juhee Kim, Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, and Hoon-Min Kim posed for a group photo with Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of December that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has developed a groundbreaking technology that can treat colon cancer by converting cancer cells into a state resembling normal colon cells without killing them, thus avoiding side effects.
The research team focused on the observation that during the oncogenesis process, normal cells regress along their differentiation trajectory. Building on this insight, they developed a technology to create a digital twin of the gene network associated with the differentiation trajectory of normal cells.
< Figure 1. Technology for creating a digital twin of a gene network from single-cell transcriptome data of a normal cell differentiation trajectory. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a digital twin creation technology that precisely observes the dynamics of gene regulatory relationships during the process of normal cells differentiating along a differentiation trajectory and analyzes the relationships among key genes to build a mathematical model that can be simulated (A-F). In addition, they developed a technology to discover key regulatory factors that control the differentiation trajectory of normal cells by simulating and analyzing this digital twin. >
< Figure 2. Digital twin simulation simulating the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells. The dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data for the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells were analyzed (A) and a digital twin of the gene network was developed representing the regulatory relationships of key genes in this differentiation trajectory (B). The simulation results of the digital twin confirm that it readily reproduces the dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data (C, D). >
Through simulation analysis, the team systematically identified master molecular switches that induce normal cell differentiation. When these switches were applied to colon cancer cells, the cancer cells reverted to a normal-like state, a result confirmed through molecular and cellular experiments as well as animal studies.
< Figure 3. Discovery of top-level key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells. By applying control factor discovery technology to the digital twin model, three genes, HDAC2, FOXA2, and MYB, were discovered as key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells (A, B). The results of simulation analysis of the regulatory effects of the discovered control factors through the digital twin confirmed that they could induce complete differentiation of colon cells (C). >
< Figure 4. Verification of the effect of the key control factors discovered using colon cancer cells and animal experiments on the reversibility of colon cancer. The key control factors of the normal colon cell differentiation trajectory discovered through digital twin simulation analysis were applied to actual colon cancer cells and colon cancer mouse animal models to experimentally verify the effect of cancer reversibility. The key control factors significantly reduced the proliferation of three colon cancer cell lines (A), and this was confirmed in the same way in animal models (B-D). >
This research demonstrates that cancer cell reversion can be systematically achieved by analyzing and utilizing the digital twin of the cancer cell gene network, rather than relying on serendipitous discoveries. The findings hold significant promise for developing reversible cancer therapies that can be applied to various types of cancer.
< Figure 5. The change in overall gene expression was confirmed through the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors, which converted the state of colon cancer cells to that of normal colon cells. The transcriptomes of colon cancer tissues and normal colon tissues from more than 400 colon cancer patients were compared with the transcriptomes of colon cancer cell lines and reversible colon cancer cell lines, respectively. The comparison results confirmed that the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors converted all three colon cancer cell lines to a state similar to the transcriptome expression of normal colon tissues. >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho remarked, "The fact that cancer cells can be converted back to normal cells is an astonishing phenomenon. This study proves that such reversion can be systematically induced."
He further emphasized, "This research introduces the novel concept of reversible cancer therapy by reverting cancer cells to normal cells. It also develops foundational technology for identifying targets for cancer reversion through the systematic analysis of normal cell differentiation trajectories."
This research included contributions from Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, Hoon-Min Kim, Juhee Kim, and Jaeog Jeon, and was published in the online edition of the international journal Advanced Science by Wiley on December 11. (Title: “Control of Cellular Differentiation Trajectories for Cancer Reversion”) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202402132
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a source technology to systematically discover key control factors that can induce reversibility of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach and a digital twin simulation analysis of the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells, and verified the effects of reversion on actual colon cancer through molecular cell experiments and animal experiments. >
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program. The research findings have been transferred to BioRevert Inc., where they will be used for the development of practical cancer reversion therapies.
2024.12.23 View 101777 -
 KAIST introduces microbial food as a strategy food production of the future
The global food crisis is increasing due to rapid population growth and declining food productivity to climate change. Moreover, today's food production and supply system emit a huge amount of carbon dioxide, reaching 30% of the total amount emitted by humanity, aggravating climate change. Sustainable and nutritious microbial food is attracting attention as a key to overcoming this impasse.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi of the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper that proposes a direction of research on ‘microbial food production from sustainable raw materials.’
Microbial food refers to various foods and food ingredients produced using microorganisms. Microbial biomass contains a large amount of protein per unit in dry mass, comparable to that of meat, and emits the smallest amount of carbon dioxide and is required to produce a unit mass compared to various livestock, fish, shellfish, and crops. Since the amount of water and space requirement is small, it can be an eco-friendly, sustainable and highly nutritious food resource.
Fermented foods are the most readily available microbial foods around us. Although the proportion of microbial biomass in fermented foods is small, compounds with relatively low nutritional value, such as carbohydrates, are consumed during the fermentation process, and as microorganisms proliferate, the content of nutrients with higher nutritional value, such as proteins and vitamins, increases.
Various food compounds isolated and purified from biomass or culture media obtained through microbial culture are also a branch of microbial food. Examples that can be found around us include various amino acids, including monosodium glutamate, food proteins, enzymes, flavoring compounds, food colorings, and bioactive substances.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram portraying various microbial biomass production strategies utlizing sustainable feedstocks >
Lastly, the most ultimate and fundamental form of microbial food can be said to be microbial biomass or extracts produced through microbial culture and foods cooked using them. A representative example is single-cell protein, which collectively refers to microbial biomass or microbial proteins extracted from it.
In this paper, the researchers comprehensively covered various non-edible raw materials and strategies for using them that can be used to produce microbial food in a more sustainable way. Furthermore, it covers various microbial foods that are actually produced in the industry using the relevant raw materials and their characteristics, as well as prospects for the production and generalization of sustainable microbial foods.
Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “Microbial foods produced from various sustainable raw materials will soon be commonly encountered at our tables.” Second author Seok Yeong Jung, a doctoral student, also said, “Microbial foods of the future will not be limited foods consumed only out of a sense of obligation to the environment, but will be complete foods that are consumed by choice because of their nutritional value and taste.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is time for the industry and academia, as well as the public and private sectors, to cooperate more closely so that more diverse microbial foods can be developed and supplied in order to create a sustainable society for ourselves and our descendants.”
< Figure 2. Compositions and environmental footprints of animal, plant and microbial biomass. >
This paper was published online on April 9 in ‘Nature Microbiology’ published by Nature.
※ Paper title: From sustainable feedstocks to microbial foods
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Seok Yeong Jung (second author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was conducted under the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (project leader KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project leader KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) of the Agricultural Microbiology Project Group (Director, Professor Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration.
2024.04.12 View 7998
KAIST introduces microbial food as a strategy food production of the future
The global food crisis is increasing due to rapid population growth and declining food productivity to climate change. Moreover, today's food production and supply system emit a huge amount of carbon dioxide, reaching 30% of the total amount emitted by humanity, aggravating climate change. Sustainable and nutritious microbial food is attracting attention as a key to overcoming this impasse.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi of the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper that proposes a direction of research on ‘microbial food production from sustainable raw materials.’
Microbial food refers to various foods and food ingredients produced using microorganisms. Microbial biomass contains a large amount of protein per unit in dry mass, comparable to that of meat, and emits the smallest amount of carbon dioxide and is required to produce a unit mass compared to various livestock, fish, shellfish, and crops. Since the amount of water and space requirement is small, it can be an eco-friendly, sustainable and highly nutritious food resource.
Fermented foods are the most readily available microbial foods around us. Although the proportion of microbial biomass in fermented foods is small, compounds with relatively low nutritional value, such as carbohydrates, are consumed during the fermentation process, and as microorganisms proliferate, the content of nutrients with higher nutritional value, such as proteins and vitamins, increases.
Various food compounds isolated and purified from biomass or culture media obtained through microbial culture are also a branch of microbial food. Examples that can be found around us include various amino acids, including monosodium glutamate, food proteins, enzymes, flavoring compounds, food colorings, and bioactive substances.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram portraying various microbial biomass production strategies utlizing sustainable feedstocks >
Lastly, the most ultimate and fundamental form of microbial food can be said to be microbial biomass or extracts produced through microbial culture and foods cooked using them. A representative example is single-cell protein, which collectively refers to microbial biomass or microbial proteins extracted from it.
In this paper, the researchers comprehensively covered various non-edible raw materials and strategies for using them that can be used to produce microbial food in a more sustainable way. Furthermore, it covers various microbial foods that are actually produced in the industry using the relevant raw materials and their characteristics, as well as prospects for the production and generalization of sustainable microbial foods.
Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “Microbial foods produced from various sustainable raw materials will soon be commonly encountered at our tables.” Second author Seok Yeong Jung, a doctoral student, also said, “Microbial foods of the future will not be limited foods consumed only out of a sense of obligation to the environment, but will be complete foods that are consumed by choice because of their nutritional value and taste.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is time for the industry and academia, as well as the public and private sectors, to cooperate more closely so that more diverse microbial foods can be developed and supplied in order to create a sustainable society for ourselves and our descendants.”
< Figure 2. Compositions and environmental footprints of animal, plant and microbial biomass. >
This paper was published online on April 9 in ‘Nature Microbiology’ published by Nature.
※ Paper title: From sustainable feedstocks to microbial foods
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Seok Yeong Jung (second author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was conducted under the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (project leader KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project leader KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) of the Agricultural Microbiology Project Group (Director, Professor Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration.
2024.04.12 View 7998 -
 KAIST introduces eco-friendly technologies for plastic production and biodegradation
- A research team under Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper in Nature Microbiology on the overview and trends of plastic production and degradation technology using microorganisms.
- Eco-friendly and sustainable plastic production and degradation technology using microorganisms as a core technology to achieve a plastic circular economy was presented.
Plastic is one of the important materials in modern society, with approximately 460 million tons produced annually and with expected production reaching approximately 1.23 billion tons in 2060. However, since 1950, plastic waste totaling more than 6.3 billion tons has been generated, and it is believed that more than 140 million tons of plastic waste has accumulated in the aquatic environment. Recently, the seriousness of microplastic pollution has emerged, not only posing a risk to the marine ecosystem and human health, but also worsening global warming by inhibiting the activity of marine plankton, which play an important role in lowering the Earth's carbon dioxide concentration.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee announced on December 11 that a research team under Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering had published a paper titled 'Sustainable production and degradation of plastics using microbes', which covers the latest technologies for producing plastics and processing waste plastics in an eco-friendly manner using microorganisms.
As the international community moves to solve this plastic problem, various efforts are being made, including 175 countries participating to conclude a legally binding agreement with the goal of ending plastic pollution by 2024. Various technologies are being developed for sustainable plastic production and processing, and among them, biotechnology using microorganisms is attracting attention.
Microorganisms have the ability to naturally produce or decompose certain compounds, and this ability is maximized through biotechnologies such as metabolic engineering and enzyme engineering to produce plastics from renewable biomass resources instead of fossil raw materials and to decompose waste plastics.
Accordingly, the research team comprehensively analyzed the latest microorganism-based technologies for the sustainable production and decomposition of plastics and presented how they actually contribute to solving the plastic problem. Based on this, they presented limitations, prospects, and research directions of the technologies for achieving a circular economy for plastics.
Microorganism-based technologies for various plastics range from widely used synthetic plastics such as polyethylene (PE) to promising bioplastics such as natural polymers derived from microorganisms (polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)) that are completely biodegradable in the natural environment and do not pose a risk of microplastic generation. Commercialization statuses and latest technologies were also discussed. In addition, the technology to decompose these plastics using microorganisms and their enzymes and the upcycling technology to convert them into other useful compounds after decomposition were introduced, highlighting the competitiveness and potential of technology using microorganisms.
First author So Young Choi, a research assistant professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, said, “In the future, we will be able to easily find eco-friendly plastics made using microorganisms all around us,” and corresponding author Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Plastic can be made more sustainable. It is important to use plastics responsibly to protect the environment and simultaneously achieve economic and social development through the new plastics industry, and we look forward to the improved performance of microbial metabolic engineering technology.”
This paper was published on November 30th in the online edition of Nature Microbiology.
※ Paper Title : Sustainable production and degradation of plastics using microbes
Authors: So Young Choi, Youngjoon Lee, Hye Eun Yu, In Jin Cho, Minju Kang & Sang Yup Lee
2023.12.11 View 7359
KAIST introduces eco-friendly technologies for plastic production and biodegradation
- A research team under Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper in Nature Microbiology on the overview and trends of plastic production and degradation technology using microorganisms.
- Eco-friendly and sustainable plastic production and degradation technology using microorganisms as a core technology to achieve a plastic circular economy was presented.
Plastic is one of the important materials in modern society, with approximately 460 million tons produced annually and with expected production reaching approximately 1.23 billion tons in 2060. However, since 1950, plastic waste totaling more than 6.3 billion tons has been generated, and it is believed that more than 140 million tons of plastic waste has accumulated in the aquatic environment. Recently, the seriousness of microplastic pollution has emerged, not only posing a risk to the marine ecosystem and human health, but also worsening global warming by inhibiting the activity of marine plankton, which play an important role in lowering the Earth's carbon dioxide concentration.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee announced on December 11 that a research team under Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering had published a paper titled 'Sustainable production and degradation of plastics using microbes', which covers the latest technologies for producing plastics and processing waste plastics in an eco-friendly manner using microorganisms.
As the international community moves to solve this plastic problem, various efforts are being made, including 175 countries participating to conclude a legally binding agreement with the goal of ending plastic pollution by 2024. Various technologies are being developed for sustainable plastic production and processing, and among them, biotechnology using microorganisms is attracting attention.
Microorganisms have the ability to naturally produce or decompose certain compounds, and this ability is maximized through biotechnologies such as metabolic engineering and enzyme engineering to produce plastics from renewable biomass resources instead of fossil raw materials and to decompose waste plastics.
Accordingly, the research team comprehensively analyzed the latest microorganism-based technologies for the sustainable production and decomposition of plastics and presented how they actually contribute to solving the plastic problem. Based on this, they presented limitations, prospects, and research directions of the technologies for achieving a circular economy for plastics.
Microorganism-based technologies for various plastics range from widely used synthetic plastics such as polyethylene (PE) to promising bioplastics such as natural polymers derived from microorganisms (polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)) that are completely biodegradable in the natural environment and do not pose a risk of microplastic generation. Commercialization statuses and latest technologies were also discussed. In addition, the technology to decompose these plastics using microorganisms and their enzymes and the upcycling technology to convert them into other useful compounds after decomposition were introduced, highlighting the competitiveness and potential of technology using microorganisms.
First author So Young Choi, a research assistant professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, said, “In the future, we will be able to easily find eco-friendly plastics made using microorganisms all around us,” and corresponding author Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Plastic can be made more sustainable. It is important to use plastics responsibly to protect the environment and simultaneously achieve economic and social development through the new plastics industry, and we look forward to the improved performance of microbial metabolic engineering technology.”
This paper was published on November 30th in the online edition of Nature Microbiology.
※ Paper Title : Sustainable production and degradation of plastics using microbes
Authors: So Young Choi, Youngjoon Lee, Hye Eun Yu, In Jin Cho, Minju Kang & Sang Yup Lee
2023.12.11 View 7359 -
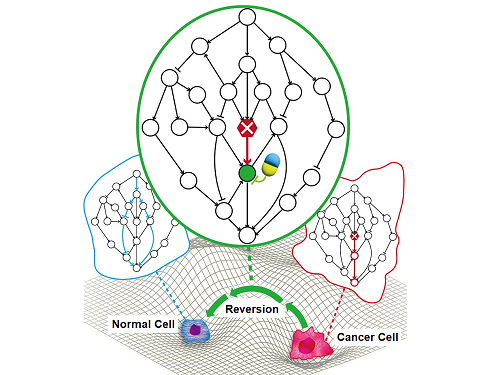 A KAIST Research Team Identifies a Cancer Reversion Mechanism
Despite decades of intensive cancer research by numerous biomedical scientists, cancer still holds its place as the number one cause of death in Korea. The fundamental reason behind the limitations of current cancer treatment methods is the fact that they all aim to completely destroy cancer cells, which eventually allows the cancer cells to acquire immunity. In other words, recurrences and side-effects caused by the destruction of healthy cells are inevitable. To this end, some have suggested anticancer treatment methods based on cancer reversion, which can revert cancer cells back to normal or near-normal cells under certain conditions. However, the practical development of this idea has not yet been attempted.
On June 8, a KAIST research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering reported to have successfully identified the fundamental principle of a process that can revert cancer cells back to normal cells without killing the cells.
Professor Cho’s team focused on the fact that unlike normal cells, which react according to external stimuli, cancer cells tend to ignore such stimuli and only undergo uncontrolled cell division. Through computer simulation analysis, the team discovered that the input-output (I/O) relationships that were distorted by genetic mutations could be reverted back to normal I/O relationships under certain conditions. The team then demonstrated through molecular cell experiments that such I/O relationship recovery also occurred in real cancer cells.
The results of this study, written by Dr. Jae Il Joo and Dr. Hwa-Jeong Park, were published in Wiley’s Advanced Science online on June 2 under the title, "Normalizing input-output relationships of cancer networks for reversion therapy."
< Image 1. Input-output (I/O) relationships in gene regulatory networks >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team classified genes into four types by simulation-analyzing the effect of gene mutations on the I/O relationship of gene regulatory networks. (Figure A-J) In addition, by analyzing 18 genes of the cancer-related gene regulatory network, it was confirmed that when mutations occur in more than half of the genes constituting each network, reversibility is possible through appropriate control. (Figure K)
Professor Cho’s team uncovered that the reason the distorted I/O relationships of cancer cells could be reverted back to normal ones was the robustness and redundancy of intracellular gene control networks that developed over the course of evolution. In addition, they found that some genes were more promising as targets for cancer reversion than others, and showed through molecular cell experiments that controlling such genes could revert the distorted I/O relationships of cancer cells back to normal ones.
< Image 2. Simulation results of restoration of bladder cancer gene regulation network and I/O relationship of bladder cancer cells. >
The research team classified the effects of gene mutations on the I/O relationship in the bladder cancer gene regulation network by simulation analysis and classified them into 4 types. (Figure A) Through this, it was found that the distorted input-output relationship between bladder cancer cell lines KU-1919 and HCT-1197 could be restored to normal. (Figure B)
< Image 3. Analysis of survival of bladder cancer patients according to reversible gene mutation and I/O recovery experiment of bladder cancer cells. >
As predicted through network simulation analysis, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team confirmed through molecular cell experiments that the response to TGF-b was normally restored when AKT and MAP3K1 were inhibited in the bladder cancer cell line KU-1919. (Figure A-G) In addition, it was confirmed that there is a difference in the survival rate of bladder cancer patients depending on the presence or absence of a reversible gene mutation. (Figure H)
The results of this research show that the reversion of real cancer cells does not happen by chance, and that it is possible to systematically explore targets that can induce this phenomenon, thereby creating the potential for the development of innovative anticancer drugs that can control such target genes.
< Image 4. Cancer cell reversibility principle >
The research team analyzed the reversibility, redundancy, and robustness of various networks and found that there was a positive correlation between them. From this, it was found that reversibility was additionally inherent in the process of evolution in which the gene regulatory network acquired redundancy and consistency.
Professor Cho said, “By uncovering the fundamental principles of a new cancer reversion treatment strategy that may overcome the unresolved limitations of existing chemotherapy, we have increased the possibility of developing new and innovative drugs that can improve both the prognosis and quality of life of cancer patients.”
< Image 5. Conceptual diagram of research results >
The research team identified the fundamental control principle of cancer cell reversibility through systems biology research. When the I/O relationship of the intracellular gene regulatory network is distorted by mutation, the distorted I/O relationship can be restored to a normal state by identifying and adjusting the reversible gene target based on the redundancy of the molecular circuit inherent in the complex network.
After Professor Cho’s team first suggested the concept of reversion treatment, they published their results for reverting colorectal cancer in January 2020, and in January 2022 they successfully re-programmed malignant breast cancer cells back into hormone-treatable ones. In January 2023, the team successfully removed the metastasis ability from lung cancer cells and reverted them back to a state that allowed improved drug reactivity. However, these results were case studies of specific types of cancer and did not reveal what common principle allowed cancer reversion across all cancer types, making this the first revelation of the general principle of cancer reversion and its evolutionary origins.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2023.06.20 View 12002
A KAIST Research Team Identifies a Cancer Reversion Mechanism
Despite decades of intensive cancer research by numerous biomedical scientists, cancer still holds its place as the number one cause of death in Korea. The fundamental reason behind the limitations of current cancer treatment methods is the fact that they all aim to completely destroy cancer cells, which eventually allows the cancer cells to acquire immunity. In other words, recurrences and side-effects caused by the destruction of healthy cells are inevitable. To this end, some have suggested anticancer treatment methods based on cancer reversion, which can revert cancer cells back to normal or near-normal cells under certain conditions. However, the practical development of this idea has not yet been attempted.
On June 8, a KAIST research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering reported to have successfully identified the fundamental principle of a process that can revert cancer cells back to normal cells without killing the cells.
Professor Cho’s team focused on the fact that unlike normal cells, which react according to external stimuli, cancer cells tend to ignore such stimuli and only undergo uncontrolled cell division. Through computer simulation analysis, the team discovered that the input-output (I/O) relationships that were distorted by genetic mutations could be reverted back to normal I/O relationships under certain conditions. The team then demonstrated through molecular cell experiments that such I/O relationship recovery also occurred in real cancer cells.
The results of this study, written by Dr. Jae Il Joo and Dr. Hwa-Jeong Park, were published in Wiley’s Advanced Science online on June 2 under the title, "Normalizing input-output relationships of cancer networks for reversion therapy."
< Image 1. Input-output (I/O) relationships in gene regulatory networks >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team classified genes into four types by simulation-analyzing the effect of gene mutations on the I/O relationship of gene regulatory networks. (Figure A-J) In addition, by analyzing 18 genes of the cancer-related gene regulatory network, it was confirmed that when mutations occur in more than half of the genes constituting each network, reversibility is possible through appropriate control. (Figure K)
Professor Cho’s team uncovered that the reason the distorted I/O relationships of cancer cells could be reverted back to normal ones was the robustness and redundancy of intracellular gene control networks that developed over the course of evolution. In addition, they found that some genes were more promising as targets for cancer reversion than others, and showed through molecular cell experiments that controlling such genes could revert the distorted I/O relationships of cancer cells back to normal ones.
< Image 2. Simulation results of restoration of bladder cancer gene regulation network and I/O relationship of bladder cancer cells. >
The research team classified the effects of gene mutations on the I/O relationship in the bladder cancer gene regulation network by simulation analysis and classified them into 4 types. (Figure A) Through this, it was found that the distorted input-output relationship between bladder cancer cell lines KU-1919 and HCT-1197 could be restored to normal. (Figure B)
< Image 3. Analysis of survival of bladder cancer patients according to reversible gene mutation and I/O recovery experiment of bladder cancer cells. >
As predicted through network simulation analysis, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team confirmed through molecular cell experiments that the response to TGF-b was normally restored when AKT and MAP3K1 were inhibited in the bladder cancer cell line KU-1919. (Figure A-G) In addition, it was confirmed that there is a difference in the survival rate of bladder cancer patients depending on the presence or absence of a reversible gene mutation. (Figure H)
The results of this research show that the reversion of real cancer cells does not happen by chance, and that it is possible to systematically explore targets that can induce this phenomenon, thereby creating the potential for the development of innovative anticancer drugs that can control such target genes.
< Image 4. Cancer cell reversibility principle >
The research team analyzed the reversibility, redundancy, and robustness of various networks and found that there was a positive correlation between them. From this, it was found that reversibility was additionally inherent in the process of evolution in which the gene regulatory network acquired redundancy and consistency.
Professor Cho said, “By uncovering the fundamental principles of a new cancer reversion treatment strategy that may overcome the unresolved limitations of existing chemotherapy, we have increased the possibility of developing new and innovative drugs that can improve both the prognosis and quality of life of cancer patients.”
< Image 5. Conceptual diagram of research results >
The research team identified the fundamental control principle of cancer cell reversibility through systems biology research. When the I/O relationship of the intracellular gene regulatory network is distorted by mutation, the distorted I/O relationship can be restored to a normal state by identifying and adjusting the reversible gene target based on the redundancy of the molecular circuit inherent in the complex network.
After Professor Cho’s team first suggested the concept of reversion treatment, they published their results for reverting colorectal cancer in January 2020, and in January 2022 they successfully re-programmed malignant breast cancer cells back into hormone-treatable ones. In January 2023, the team successfully removed the metastasis ability from lung cancer cells and reverted them back to a state that allowed improved drug reactivity. However, these results were case studies of specific types of cancer and did not reveal what common principle allowed cancer reversion across all cancer types, making this the first revelation of the general principle of cancer reversion and its evolutionary origins.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2023.06.20 View 12002 -
 VP Sang Yup Lee Receives Honorary Doctorate from DTU
Vice President for Research, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, was awarded an honorary doctorate from the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) during the DTU Commemoration Day 2022 on April 29. The event drew distinguished guests, students, and faculty including HRH The Crown Prince Frederik Andre Henrik Christian and DTU President Anders Bjarklev.
Professor Lee was recognized for his exceptional scholarship in the field of systems metabolic engineering, which led to the development of microcell factories capable of producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds, many for the first time.
Professor Lee said in his acceptance speech that KAIST’s continued partnership with DTU in the field of biotechnology will lead to significant contributions in the global efforts to respond to climate change and promote green growth.
DTU CPO and CSO Dina Petronovic Nielson, who heads DTU Biosustain, also lauded Professor Lee saying, “It is not only a great honor for Professor Lee to be induced at DTU but also great honor for DTU to have him.”
Professor Lee also gave commemorative lectures at DTU Biosustain in Lingby and the Bio Innovation Research Institute at the Novo Nordisk Foundation in Copenhagen while in Denmark.
DTU, one of the leading science and technology universities in Europe, has been awarding honorary doctorates since 1921, including to Nobel laureate in chemistry Professor Frances Arnold at Caltech. Professor Lee is the first Korean to receive an honorary doctorate from DTU.
2022.05.03 View 11857
VP Sang Yup Lee Receives Honorary Doctorate from DTU
Vice President for Research, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, was awarded an honorary doctorate from the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) during the DTU Commemoration Day 2022 on April 29. The event drew distinguished guests, students, and faculty including HRH The Crown Prince Frederik Andre Henrik Christian and DTU President Anders Bjarklev.
Professor Lee was recognized for his exceptional scholarship in the field of systems metabolic engineering, which led to the development of microcell factories capable of producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds, many for the first time.
Professor Lee said in his acceptance speech that KAIST’s continued partnership with DTU in the field of biotechnology will lead to significant contributions in the global efforts to respond to climate change and promote green growth.
DTU CPO and CSO Dina Petronovic Nielson, who heads DTU Biosustain, also lauded Professor Lee saying, “It is not only a great honor for Professor Lee to be induced at DTU but also great honor for DTU to have him.”
Professor Lee also gave commemorative lectures at DTU Biosustain in Lingby and the Bio Innovation Research Institute at the Novo Nordisk Foundation in Copenhagen while in Denmark.
DTU, one of the leading science and technology universities in Europe, has been awarding honorary doctorates since 1921, including to Nobel laureate in chemistry Professor Frances Arnold at Caltech. Professor Lee is the first Korean to receive an honorary doctorate from DTU.
2022.05.03 View 11857 -
 Scientist Discover How Circadian Rhythm Can Be Both Strong and Flexible
Study reveals that master and slave oscillators function via different molecular mechanisms
From tiny fruit flies to human beings, all animals on Earth maintain their daily rhythms based on their internal circadian clock. The circadian clock enables organisms to undergo rhythmic changes in behavior and physiology based on a 24-hour circadian cycle. For example, our own biological clock tells our brain to release melatonin, a sleep-inducing hormone, at night time.
The discovery of the molecular mechanism of the circadian clock was bestowed the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2017. From what we know, no one centralized clock is responsible for our circadian cycles. Instead, it operates in a hierarchical network where there are “master pacemaker” and “slave oscillator”.
The master pacemaker receives various input signals from the environment such as light. The master then drives the slave oscillator that regulates various outputs such as sleep, feeding, and metabolism. Despite the different roles of the pacemaker neurons, they are known to share common molecular mechanisms that are well conserved in all lifeforms. For example, interlocked systems of multiple transcriptional-translational feedback loops (TTFLs) composed of core clock proteins have been deeply studied in fruit flies.
However, there is still much that we need to learn about our own biological clock. The hierarchically-organized nature of master and slave clock neurons leads to a prevailing belief that they share an identical molecular clockwork. At the same time, the different roles they serve in regulating bodily rhythms also raise the question of whether they might function under different molecular clockworks.
Research team led by Professor Kim Jae Kyoung from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, a chief investigator at the Biomedical Mathematics Group at the Institute for Basic Science, used a combination of mathematical and experimental approaches using fruit flies to answer this question. The team found that the master clock and the slave clock operate via different molecular mechanisms.
In both master and slave neurons of fruit flies, a circadian rhythm-related protein called PER is produced and degraded at different rates depending on the time of the day. Previously, the team found that the master clock neuron (sLNvs) and the slave clock neuron (DN1ps) have different profiles of PER in wild-type and Clk-Δ mutant Drosophila. This hinted that there might be a potential difference in molecular clockworks between the master and slave clock neurons.
However, due to the complexity of the molecular clockwork, it was challenging to identify the source of such differences. Thus, the team developed a mathematical model describing the molecular clockworks of the master and slave clocks. Then, all possible molecular differences between the master and slave clock neurons were systematically investigated by using computer simulations. The model predicted that PER is more efficiently produced and then rapidly degraded in the master clock compared to the slave clock neurons. This prediction was then confirmed by the follow-up experiments using animal.
Then, why do the master clock neurons have such different molecular properties from the slave clock neurons? To answer this question, the research team again used the combination of mathematical model simulation and experiments. It was found that the faster rate of synthesis of PER in the master clock neurons allows them to generate synchronized rhythms with a high level of amplitude. Generation of such a strong rhythm with high amplitude is critical to delivering clear signals to slave clock neurons.
However, such strong rhythms would typically be unfavorable when it comes to adapting to environmental changes. These include natural causes such as different daylight hours across summer and winter seasons, up to more extreme artificial cases such as jet lag that occurs after international travel. Thanks to the distinct property of the master clock neurons, it is able to undergo phase dispersion when the standard light-dark cycle is disrupted, drastically reducing the level of PER. The master clock neurons can then easily adapt to the new diurnal cycle. Our master pacemaker’s plasticity explains how we can quickly adjust to the new time zones after international flights after just a brief period of jet lag.
It is hoped that the findings of this study can have future clinical implications when it comes to treating various disorders that affect our circadian rhythm. Professor Kim notes, “When the circadian clock loses its robustness and flexibility, the circadian rhythms sleep disorders can occur. As this study identifies the molecular mechanism that generates robustness and flexibility of the circadian clock, it can facilitate the identification of the cause of and treatment strategy for the circadian rhythm sleep disorders.” This work was supported by the Human Frontier Science Program.
-PublicationEui Min Jeong, Miri Kwon, Eunjoo Cho, Sang Hyuk Lee, Hyun Kim, Eun Young Kim, and Jae Kyoung Kim, “Systematic modeling-driven experiments identify distinct molecularclockworks underlying hierarchically organized pacemaker neurons,” February 22, 2022, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyoung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.02.23 View 11463
Scientist Discover How Circadian Rhythm Can Be Both Strong and Flexible
Study reveals that master and slave oscillators function via different molecular mechanisms
From tiny fruit flies to human beings, all animals on Earth maintain their daily rhythms based on their internal circadian clock. The circadian clock enables organisms to undergo rhythmic changes in behavior and physiology based on a 24-hour circadian cycle. For example, our own biological clock tells our brain to release melatonin, a sleep-inducing hormone, at night time.
The discovery of the molecular mechanism of the circadian clock was bestowed the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2017. From what we know, no one centralized clock is responsible for our circadian cycles. Instead, it operates in a hierarchical network where there are “master pacemaker” and “slave oscillator”.
The master pacemaker receives various input signals from the environment such as light. The master then drives the slave oscillator that regulates various outputs such as sleep, feeding, and metabolism. Despite the different roles of the pacemaker neurons, they are known to share common molecular mechanisms that are well conserved in all lifeforms. For example, interlocked systems of multiple transcriptional-translational feedback loops (TTFLs) composed of core clock proteins have been deeply studied in fruit flies.
However, there is still much that we need to learn about our own biological clock. The hierarchically-organized nature of master and slave clock neurons leads to a prevailing belief that they share an identical molecular clockwork. At the same time, the different roles they serve in regulating bodily rhythms also raise the question of whether they might function under different molecular clockworks.
Research team led by Professor Kim Jae Kyoung from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, a chief investigator at the Biomedical Mathematics Group at the Institute for Basic Science, used a combination of mathematical and experimental approaches using fruit flies to answer this question. The team found that the master clock and the slave clock operate via different molecular mechanisms.
In both master and slave neurons of fruit flies, a circadian rhythm-related protein called PER is produced and degraded at different rates depending on the time of the day. Previously, the team found that the master clock neuron (sLNvs) and the slave clock neuron (DN1ps) have different profiles of PER in wild-type and Clk-Δ mutant Drosophila. This hinted that there might be a potential difference in molecular clockworks between the master and slave clock neurons.
However, due to the complexity of the molecular clockwork, it was challenging to identify the source of such differences. Thus, the team developed a mathematical model describing the molecular clockworks of the master and slave clocks. Then, all possible molecular differences between the master and slave clock neurons were systematically investigated by using computer simulations. The model predicted that PER is more efficiently produced and then rapidly degraded in the master clock compared to the slave clock neurons. This prediction was then confirmed by the follow-up experiments using animal.
Then, why do the master clock neurons have such different molecular properties from the slave clock neurons? To answer this question, the research team again used the combination of mathematical model simulation and experiments. It was found that the faster rate of synthesis of PER in the master clock neurons allows them to generate synchronized rhythms with a high level of amplitude. Generation of such a strong rhythm with high amplitude is critical to delivering clear signals to slave clock neurons.
However, such strong rhythms would typically be unfavorable when it comes to adapting to environmental changes. These include natural causes such as different daylight hours across summer and winter seasons, up to more extreme artificial cases such as jet lag that occurs after international travel. Thanks to the distinct property of the master clock neurons, it is able to undergo phase dispersion when the standard light-dark cycle is disrupted, drastically reducing the level of PER. The master clock neurons can then easily adapt to the new diurnal cycle. Our master pacemaker’s plasticity explains how we can quickly adjust to the new time zones after international flights after just a brief period of jet lag.
It is hoped that the findings of this study can have future clinical implications when it comes to treating various disorders that affect our circadian rhythm. Professor Kim notes, “When the circadian clock loses its robustness and flexibility, the circadian rhythms sleep disorders can occur. As this study identifies the molecular mechanism that generates robustness and flexibility of the circadian clock, it can facilitate the identification of the cause of and treatment strategy for the circadian rhythm sleep disorders.” This work was supported by the Human Frontier Science Program.
-PublicationEui Min Jeong, Miri Kwon, Eunjoo Cho, Sang Hyuk Lee, Hyun Kim, Eun Young Kim, and Jae Kyoung Kim, “Systematic modeling-driven experiments identify distinct molecularclockworks underlying hierarchically organized pacemaker neurons,” February 22, 2022, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyoung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.02.23 View 11463 -
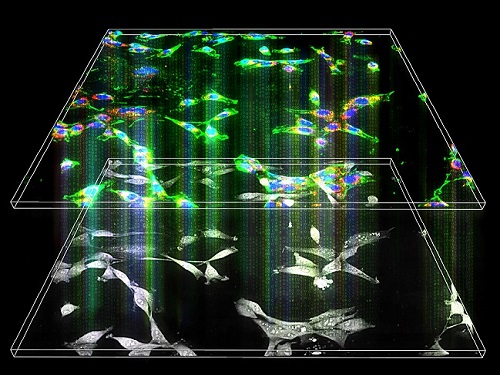 Label-Free Multiplexed Microtomography of Endogenous Subcellular Dynamics Using Deep Learning
AI-based holographic microscopy allows molecular imaging without introducing exogenous labeling agents
A research team upgraded the 3D microtomography observing dynamics of label-free live cells in multiplexed fluorescence imaging. The AI-powered 3D holotomographic microscopy extracts various molecular information from live unlabeled biological cells in real time without exogenous labeling or staining agents.
Professor YongKeum Park’s team and the startup Tomocube encoded 3D refractive index tomograms using the refractive index as a means of measurement. Then they decoded the information with a deep learning-based model that infers multiple 3D fluorescence tomograms from the refractive index measurements of the corresponding subcellular targets, thereby achieving multiplexed micro tomography. This study was reported in Nature Cell Biology online on December 7, 2021.
Fluorescence microscopy is the most widely used optical microscopy technique due to its high biochemical specificity. However, it needs to genetically manipulate or to stain cells with fluorescent labels in order to express fluorescent proteins. These labeling processes inevitably affect the intrinsic physiology of cells. It also has challenges in long-term measuring due to photobleaching and phototoxicity. The overlapped spectra of multiplexed fluorescence signals also hinder the viewing of various structures at the same time. More critically, it took several hours to observe the cells after preparing them.
3D holographic microscopy, also known as holotomography, is providing new ways to quantitatively image live cells without pretreatments such as staining. Holotomography can accurately and quickly measure the morphological and structural information of cells, but only provides limited biochemical and molecular information.
The 'AI microscope' created in this process takes advantage of the features of both holographic microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. That is, a specific image from a fluorescence microscope can be obtained without a fluorescent label. Therefore, the microscope can observe many types of cellular structures in their natural state in 3D and at the same time as fast as one millisecond, and long-term measurements over several days are also possible.
The Tomocube-KAIST team showed that fluorescence images can be directly and precisely predicted from holotomographic images in various cells and conditions. Using the quantitative relationship between the spatial distribution of the refractive index found by AI and the major structures in cells, it was possible to decipher the spatial distribution of the refractive index. And surprisingly, it confirmed that this relationship is constant regardless of cell type.
Professor Park said, “We were able to develop a new concept microscope that combines the advantages of several microscopes with the multidisciplinary research of AI, optics, and biology. It will be immediately applicable for new types of cells not included in the existing data and is expected to be widely applicable for various biological and medical research.”
When comparing the molecular image information extracted by AI with the molecular image information physically obtained by fluorescence staining in 3D space, it showed a 97% or more conformity, which is a level that is difficult to distinguish with the naked eye.
“Compared to the sub-60% accuracy of the fluorescence information extracted from the model developed by the Google AI team, it showed significantly higher performance,” Professor Park added.
This work was supported by the KAIST Up program, the BK21+ program, Tomocube, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Health & Welfare.
-Publication
Hyun-seok Min, Won-Do Heo, YongKeun Park, et al. “Label-free multiplexed microtomography of endogenous subcellular dynamics using generalizable deep learning,” Nature Cell Biology (doi.org/10.1038/s41556-021-00802-x) published online December 07 2021.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
Department of Physics
KAIST
2022.02.09 View 12559
Label-Free Multiplexed Microtomography of Endogenous Subcellular Dynamics Using Deep Learning
AI-based holographic microscopy allows molecular imaging without introducing exogenous labeling agents
A research team upgraded the 3D microtomography observing dynamics of label-free live cells in multiplexed fluorescence imaging. The AI-powered 3D holotomographic microscopy extracts various molecular information from live unlabeled biological cells in real time without exogenous labeling or staining agents.
Professor YongKeum Park’s team and the startup Tomocube encoded 3D refractive index tomograms using the refractive index as a means of measurement. Then they decoded the information with a deep learning-based model that infers multiple 3D fluorescence tomograms from the refractive index measurements of the corresponding subcellular targets, thereby achieving multiplexed micro tomography. This study was reported in Nature Cell Biology online on December 7, 2021.
Fluorescence microscopy is the most widely used optical microscopy technique due to its high biochemical specificity. However, it needs to genetically manipulate or to stain cells with fluorescent labels in order to express fluorescent proteins. These labeling processes inevitably affect the intrinsic physiology of cells. It also has challenges in long-term measuring due to photobleaching and phototoxicity. The overlapped spectra of multiplexed fluorescence signals also hinder the viewing of various structures at the same time. More critically, it took several hours to observe the cells after preparing them.
3D holographic microscopy, also known as holotomography, is providing new ways to quantitatively image live cells without pretreatments such as staining. Holotomography can accurately and quickly measure the morphological and structural information of cells, but only provides limited biochemical and molecular information.
The 'AI microscope' created in this process takes advantage of the features of both holographic microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. That is, a specific image from a fluorescence microscope can be obtained without a fluorescent label. Therefore, the microscope can observe many types of cellular structures in their natural state in 3D and at the same time as fast as one millisecond, and long-term measurements over several days are also possible.
The Tomocube-KAIST team showed that fluorescence images can be directly and precisely predicted from holotomographic images in various cells and conditions. Using the quantitative relationship between the spatial distribution of the refractive index found by AI and the major structures in cells, it was possible to decipher the spatial distribution of the refractive index. And surprisingly, it confirmed that this relationship is constant regardless of cell type.
Professor Park said, “We were able to develop a new concept microscope that combines the advantages of several microscopes with the multidisciplinary research of AI, optics, and biology. It will be immediately applicable for new types of cells not included in the existing data and is expected to be widely applicable for various biological and medical research.”
When comparing the molecular image information extracted by AI with the molecular image information physically obtained by fluorescence staining in 3D space, it showed a 97% or more conformity, which is a level that is difficult to distinguish with the naked eye.
“Compared to the sub-60% accuracy of the fluorescence information extracted from the model developed by the Google AI team, it showed significantly higher performance,” Professor Park added.
This work was supported by the KAIST Up program, the BK21+ program, Tomocube, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Health & Welfare.
-Publication
Hyun-seok Min, Won-Do Heo, YongKeun Park, et al. “Label-free multiplexed microtomography of endogenous subcellular dynamics using generalizable deep learning,” Nature Cell Biology (doi.org/10.1038/s41556-021-00802-x) published online December 07 2021.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
Department of Physics
KAIST
2022.02.09 View 12559