Intracellular
-
 KAIST Develops CamBio - a New Biotemplating Method
- Professor Jae-Byum Chang and Professor Yeon Sik Jung’s joint research team of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a highly tunable bio-templating method “CamBio” that makes use of intracellular protein structures
- Substrate performance improvement of up to 230% demonstrated via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)
- Expected to have price competitiveness over bio-templating method as it expands the range of biological samples
- Expected to expand the range of application of nanostructure synthesis technology by utilizing various biological structures
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Yeon Sik Jung, Ph.D. candidate Dae-Hyeon Song, Professor Jae-Byum Chang, and (from top right) Dr. Chang Woo Song and Dr. Seunghee H. Cho of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering >
Biological structures have complex characteristics that are difficult to replicate artificially, but biotemplating methods* that directly utilize these biological structures have been used in various fields of application. The KAIST research team succeeded in utilizing previously unusable biological structures and expanding the areas in which biotemplate methods can be applied.
*Biotemplating: A method of using biotemplates as a mold to create functional structural materials, utilizing the functions of these biological structures, from viruses to the tissues and organs that make up our bodies
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th that a joint research team of Professors Jae-Byum Chang and Professor Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a biotemplating method that utilizes specific intracellular proteins in biological samples and has high tunability.
Existing biotemplate methods mainly utilize only the external surface of biological samples or have limitations in utilizing the structure-function correlation of various biological structures due to limited dimensions and sample sizes, making it difficult to create functional nanostructures.
To solve this problem, the research team studied a way to utilize various biological structures within the cells while retaining high tunability.
< Figure 1. CamBio utilizing microtubules, a intracellular protein structure. The silver nanoparticle chains synthesized along the microtubules that span the entire cell interior can be observed through an electron microscope, and it is shown that this can be used as a successful SERS substrate. >
As a result of the research, the team developed the “Conversion to advanced materials via labeled Biostructure”, shortened as “CamBio”, which enables the selective synthesis of nanostructures with various characteristics and sizes from specific protein structures composed of diverse proteins within biological specimens.
The CamBio method secures high tunability of functional nanostructures that can be manufactured from biological samples by merging various manufacturing and biological technologies.
Through the technology of repeatedly attaching antibodies, arranging cells in a certain shape, and thinly slicing tissue, the functional nanostructures made with CamBio showed improved performance on the surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)* substrate used for material detection.
*Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): A technology that can detect very small amounts of substances using light, based on the principle that specific substances react to light and amplifies signals on surfaces of metals such as gold or silver.
The research team found that the nanoparticle chains made using the intracellular protein structures through the process of repeated labeling with antibodies allowed easier control, and improved SERS performance by up to 230%.
In addition, the research team expanded from utilizing the structures inside cells to obtaining samples of muscle tissues inside meat using a cryostat and successfully producing a substrate with periodic bands made of metal particles by performing the CamBio process. This method of producing a substrate not only allows large-scale production using biological samples, but also shows that it is a cost-effective method.
< Figure 2. A method for securing tunability using CamBio at the cell level. Examples of controlling characteristics by integrating iterative labeling and cell pattering techniques with CamBio are shown. >
The CamBio developed by the research team is expected to be used as a way to solve problems faced by various research fields as it is to expand the range of bio-samples that can be produced for various usage.
The first author, Dae-Hyeon Song, a Ph.D. candidate of KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering said, “Through CamBio, we have comprehensively accumulated biotemplating methods that can utilize more diverse protein structures,” and “If combined with the state-of-the-art biological technologies such as gene editing and 3D bioprinting and new material synthesis technologies, biostructures can be utilized in various fields of application.”
< Figure 3. A method for securing tunability using CamBio at the tissue level. In order to utilize proteins inside muscle tissue, the frozen tissue sectioning technology is combined, and through this, a substrate with a periodic nanoparticle band pattern is successfully produced, and it is shown that large-area acquisition of samples and price competitiveness can be achieved. >
This study, in which the Ph.D. candidate Dae-Hyeon Song along with Dr. Chang Woo Song, and Dr. Seunghee H. Cho of the same department participated as the first authors, was published online in the international academic journal, Advanced Science, on November 13th, 2024.
(Paper title: Highly Tunable, Nanomaterial-Functionalized Structural Templating of Intracellular Protein Structures Within Biological Species) https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202406492
This study was conducted with a combination of support from various programs including the National Convergence Research of Scientific Challenges (National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) 2024), Engineering Reseach Center (ERC) (Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center, NRF 2023), ERC (Global Bio-integrated Materials Center, NRF 2024), and the National Advanced Program for Biological Research Resources (Bioimaging Data Curation Center, NRF 2024) funded by Ministry of Science and ICT.
2025.01.10 View 6206
KAIST Develops CamBio - a New Biotemplating Method
- Professor Jae-Byum Chang and Professor Yeon Sik Jung’s joint research team of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a highly tunable bio-templating method “CamBio” that makes use of intracellular protein structures
- Substrate performance improvement of up to 230% demonstrated via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)
- Expected to have price competitiveness over bio-templating method as it expands the range of biological samples
- Expected to expand the range of application of nanostructure synthesis technology by utilizing various biological structures
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Yeon Sik Jung, Ph.D. candidate Dae-Hyeon Song, Professor Jae-Byum Chang, and (from top right) Dr. Chang Woo Song and Dr. Seunghee H. Cho of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering >
Biological structures have complex characteristics that are difficult to replicate artificially, but biotemplating methods* that directly utilize these biological structures have been used in various fields of application. The KAIST research team succeeded in utilizing previously unusable biological structures and expanding the areas in which biotemplate methods can be applied.
*Biotemplating: A method of using biotemplates as a mold to create functional structural materials, utilizing the functions of these biological structures, from viruses to the tissues and organs that make up our bodies
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th that a joint research team of Professors Jae-Byum Chang and Professor Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a biotemplating method that utilizes specific intracellular proteins in biological samples and has high tunability.
Existing biotemplate methods mainly utilize only the external surface of biological samples or have limitations in utilizing the structure-function correlation of various biological structures due to limited dimensions and sample sizes, making it difficult to create functional nanostructures.
To solve this problem, the research team studied a way to utilize various biological structures within the cells while retaining high tunability.
< Figure 1. CamBio utilizing microtubules, a intracellular protein structure. The silver nanoparticle chains synthesized along the microtubules that span the entire cell interior can be observed through an electron microscope, and it is shown that this can be used as a successful SERS substrate. >
As a result of the research, the team developed the “Conversion to advanced materials via labeled Biostructure”, shortened as “CamBio”, which enables the selective synthesis of nanostructures with various characteristics and sizes from specific protein structures composed of diverse proteins within biological specimens.
The CamBio method secures high tunability of functional nanostructures that can be manufactured from biological samples by merging various manufacturing and biological technologies.
Through the technology of repeatedly attaching antibodies, arranging cells in a certain shape, and thinly slicing tissue, the functional nanostructures made with CamBio showed improved performance on the surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)* substrate used for material detection.
*Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): A technology that can detect very small amounts of substances using light, based on the principle that specific substances react to light and amplifies signals on surfaces of metals such as gold or silver.
The research team found that the nanoparticle chains made using the intracellular protein structures through the process of repeated labeling with antibodies allowed easier control, and improved SERS performance by up to 230%.
In addition, the research team expanded from utilizing the structures inside cells to obtaining samples of muscle tissues inside meat using a cryostat and successfully producing a substrate with periodic bands made of metal particles by performing the CamBio process. This method of producing a substrate not only allows large-scale production using biological samples, but also shows that it is a cost-effective method.
< Figure 2. A method for securing tunability using CamBio at the cell level. Examples of controlling characteristics by integrating iterative labeling and cell pattering techniques with CamBio are shown. >
The CamBio developed by the research team is expected to be used as a way to solve problems faced by various research fields as it is to expand the range of bio-samples that can be produced for various usage.
The first author, Dae-Hyeon Song, a Ph.D. candidate of KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering said, “Through CamBio, we have comprehensively accumulated biotemplating methods that can utilize more diverse protein structures,” and “If combined with the state-of-the-art biological technologies such as gene editing and 3D bioprinting and new material synthesis technologies, biostructures can be utilized in various fields of application.”
< Figure 3. A method for securing tunability using CamBio at the tissue level. In order to utilize proteins inside muscle tissue, the frozen tissue sectioning technology is combined, and through this, a substrate with a periodic nanoparticle band pattern is successfully produced, and it is shown that large-area acquisition of samples and price competitiveness can be achieved. >
This study, in which the Ph.D. candidate Dae-Hyeon Song along with Dr. Chang Woo Song, and Dr. Seunghee H. Cho of the same department participated as the first authors, was published online in the international academic journal, Advanced Science, on November 13th, 2024.
(Paper title: Highly Tunable, Nanomaterial-Functionalized Structural Templating of Intracellular Protein Structures Within Biological Species) https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202406492
This study was conducted with a combination of support from various programs including the National Convergence Research of Scientific Challenges (National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) 2024), Engineering Reseach Center (ERC) (Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center, NRF 2023), ERC (Global Bio-integrated Materials Center, NRF 2024), and the National Advanced Program for Biological Research Resources (Bioimaging Data Curation Center, NRF 2024) funded by Ministry of Science and ICT.
2025.01.10 View 6206 -
 Researchers Describe a Mechanism Inducing Self-Killing of Cancer Cells
(Professor Kim (left) and lead author Lee)
Researchers have described a new mechanism which induces the self-killing of cancer cells by perturbing ion homeostasis. A research team from the Department of Biochemical Engineering has developed helical polypeptide potassium ionophores that lead to the onset of programmed cell death. The ionophores increase the active oxygen concentration to stress endoplasmic reticulum to the point of cellular death.
The electrochemical gradient between extracellular and intracellular conditions plays an important role in cell growth and metabolism. When a cell’s ion homeostasis is disturbed, critical functions accelerating the activation of apoptosis are inhibited in the cell.
Although ionophores have been intensively used as an ion homeostasis disturber, the mechanisms of cell death have been unclear and the bio-applicability has been limited. In the study featured at Advanced Science, the team presented an alpha helical peptide-based anticancer agent that is capable of transporting potassium ions with water solubility. The cationic, hydrophilic, and potassium ionic groups were combined at the end of the peptide side chain to provide both ion transport and hydrophilic properties.
These peptide-based ionophores reduce the intracellular potassium concentration and at the same time increase the intracellular calcium concentration. Increased intracellular calcium concentrations produce intracellular reactive oxygen species, causing endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ultimately leading to apoptosis.
Anticancer effects were evaluated using tumor-bearing mice to confirm the therapeutic effect, even in animal models. It was found that tumor growth was strongly inhibited by endoplasmic stress-mediated apoptosis.
Lead author Dr. Dae-Yong Lee said, “A peptide-based ionophore is more effective than conventional chemotherapeutic agents because it induces apoptosis via elevated reactive oxygen species levels. Professor Yeu-Chun Kim said he expects this new mechanism to be widely used as a new chemotherapeutic strategy. This research was funded by the National Research Foundation.
2019.08.28 View 22790
Researchers Describe a Mechanism Inducing Self-Killing of Cancer Cells
(Professor Kim (left) and lead author Lee)
Researchers have described a new mechanism which induces the self-killing of cancer cells by perturbing ion homeostasis. A research team from the Department of Biochemical Engineering has developed helical polypeptide potassium ionophores that lead to the onset of programmed cell death. The ionophores increase the active oxygen concentration to stress endoplasmic reticulum to the point of cellular death.
The electrochemical gradient between extracellular and intracellular conditions plays an important role in cell growth and metabolism. When a cell’s ion homeostasis is disturbed, critical functions accelerating the activation of apoptosis are inhibited in the cell.
Although ionophores have been intensively used as an ion homeostasis disturber, the mechanisms of cell death have been unclear and the bio-applicability has been limited. In the study featured at Advanced Science, the team presented an alpha helical peptide-based anticancer agent that is capable of transporting potassium ions with water solubility. The cationic, hydrophilic, and potassium ionic groups were combined at the end of the peptide side chain to provide both ion transport and hydrophilic properties.
These peptide-based ionophores reduce the intracellular potassium concentration and at the same time increase the intracellular calcium concentration. Increased intracellular calcium concentrations produce intracellular reactive oxygen species, causing endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ultimately leading to apoptosis.
Anticancer effects were evaluated using tumor-bearing mice to confirm the therapeutic effect, even in animal models. It was found that tumor growth was strongly inhibited by endoplasmic stress-mediated apoptosis.
Lead author Dr. Dae-Yong Lee said, “A peptide-based ionophore is more effective than conventional chemotherapeutic agents because it induces apoptosis via elevated reactive oxygen species levels. Professor Yeu-Chun Kim said he expects this new mechanism to be widely used as a new chemotherapeutic strategy. This research was funded by the National Research Foundation.
2019.08.28 View 22790 -
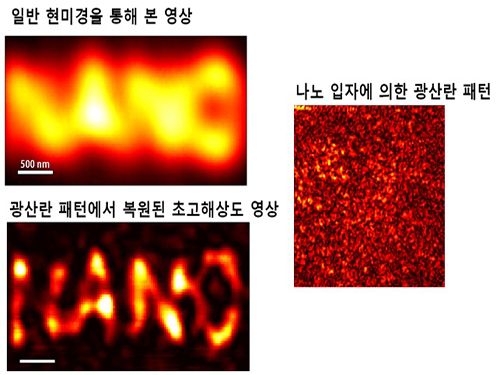 Ultra-high Resolution 2-dimentional Real-time Image Capture with Super Lens
Ultra-high Resolution 2-dimentional Real-time Image Capture with Super Lens
Applications to high-precision semiconductor processing or intracellular structures observation are possible.
A joint research team led by Professors Yongkeun Park and Yong-Hoon Cho from the Department of Physics, KAIST, has succeeded in capturing real-time 2D images at a resolution of 100 nm (nanometers), which was impossible with optical lens due to the diffraction limit of light until now. Its future application includes high-precision semiconductor manufacturing process or observation of intracellular structures.
This research follows the past research of the super-lens developed by Professor Park last April, using paint spray to observe images that have three times higher resolution than those discovered by conventional optical lens.
Since optical lens utilize the refraction of light, the diffraction limit, which prevents achieving focus smaller than the wavelength of light, has always been a barrier for acquiring high-resolution images. In the past, it was impossible to observe objects less than the size of 200 to 300 nm in the visible light spectrum.
In order to solve the problem of near-field extinction due to scattering of light, the research team used spray paint consisting of nano-particles massed with dense scattering materials to obtain high-resolution information.
Then, by calculating and restoring the first scattering shape of light using the time reversibility of light, the researchers were able to overcome the diffraction limit. The original position of an object to be observed is obtained by deriving the complex trajectory of the light, and reversing the time to locate the particular position of the object.
Professor Park said, “This new technology can be used as the core technology in all fields which require optical measurement and control. The existing electron microscopy cannot observe cells without destroying them, but the new technology allows us to visualize at ultra-high resolution without destruction.”
The research results were published online in the 9th edition of Physical Review Letters, a prestigious international journal in the field of physics.
2014.09.23 View 11758
Ultra-high Resolution 2-dimentional Real-time Image Capture with Super Lens
Ultra-high Resolution 2-dimentional Real-time Image Capture with Super Lens
Applications to high-precision semiconductor processing or intracellular structures observation are possible.
A joint research team led by Professors Yongkeun Park and Yong-Hoon Cho from the Department of Physics, KAIST, has succeeded in capturing real-time 2D images at a resolution of 100 nm (nanometers), which was impossible with optical lens due to the diffraction limit of light until now. Its future application includes high-precision semiconductor manufacturing process or observation of intracellular structures.
This research follows the past research of the super-lens developed by Professor Park last April, using paint spray to observe images that have three times higher resolution than those discovered by conventional optical lens.
Since optical lens utilize the refraction of light, the diffraction limit, which prevents achieving focus smaller than the wavelength of light, has always been a barrier for acquiring high-resolution images. In the past, it was impossible to observe objects less than the size of 200 to 300 nm in the visible light spectrum.
In order to solve the problem of near-field extinction due to scattering of light, the research team used spray paint consisting of nano-particles massed with dense scattering materials to obtain high-resolution information.
Then, by calculating and restoring the first scattering shape of light using the time reversibility of light, the researchers were able to overcome the diffraction limit. The original position of an object to be observed is obtained by deriving the complex trajectory of the light, and reversing the time to locate the particular position of the object.
Professor Park said, “This new technology can be used as the core technology in all fields which require optical measurement and control. The existing electron microscopy cannot observe cells without destroying them, but the new technology allows us to visualize at ultra-high resolution without destruction.”
The research results were published online in the 9th edition of Physical Review Letters, a prestigious international journal in the field of physics.
2014.09.23 View 11758