research

(Professor Han (far right) and his research team)
A KAIST research team observed a new quantum mechanical magnetic state ‘Jeff = 3/2.’ This first observation of ‘Jeff=3/2’ could be the foundation for future research on superconductivity and quantum magnetism.
In quantum mechanics, total angular momentum is defined as the sum of spin and orbital angular momenta and is denoted with the ‘J.’ The newly identified magnetic moment can be described as a kind of angular momentum that occurs when specific conditions are met and has been denoted ‘Jeff’ with the meaning ‘effective angular momentum’ in the field. Jeff=3/2 has been a topic of discussion but was yet to be observed.
The research was co-led by Professor Myung Joon Han of the Department of Physics at Chung-Ang University in Korea, RIKEN in Japan, and the Argonne National Laboratory in the US. This research was published in Nature Communications on October 14, 2017.
In academia, spin-orbital coupling was known to lead to a unique quantum state and has been an active area of recent research. In contrast to magnetic moment by electron spin and orbital, the effective magnetic moment Jeff, formed from the coupling of the two, shows a unique ground state and interaction patterns, which could lead to new phenomena and properties.
Most studies in the last decade focused on ‘Jeff=1/2’, but there has not been any observation of ‘Jeff=3/2’, which led to slow progress. In 2014, the research team led by Prof. Han theoretically predicted the possibility of the ‘Jeff=3/2’ state in a certain type of materials based on molecular orbital, instead of atomic orbital. In the current study, the team applied the Selection Rule of quantum mechanics for the ‘Jeff=3/2’ state, which differs to the general spin moment, in order to experimentally detect this moment.
When electrons near the atomic nucleus are excited by X-rays, the excited electrons can be absorbed or re-emitted through interactions with other electrons. Here, the Selection Rule is applied to electrons. According to quantum mechanics, this rule is very unique in the ‘Jeff=3/2’ state and ‘Jeff=3/2’ is predicted to be distinguishable from general spin states. The prediction that was made using this idea was verified through the experiment using electrons extracted from tantalum at two different energy levels. In this material, the unique quantum mechanical interference by the ‘Jeff=3/2’ moment can be taken as direct evidence for its existence.
The new quantum state is very unique from any of the previously known magnetic states and this study could be the starting point for future research on the ‘Jeff=3/2’ moment. Further, this finding could contribute to future research on various properties of the magnetic states and its interactions.
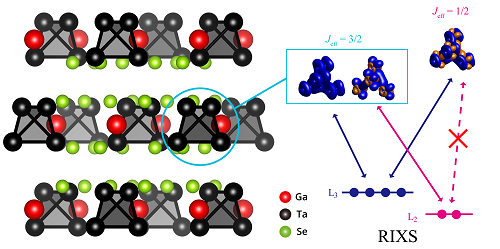
(Figure 1: Crystal structure, MO levels, and RIXS process in GaTa4Se8.)

(Figure 2: Cluster model calculations of the L3 and L2 RIXS spectra)
-
research KAIST Develops AI to Easily Find Promising Materials That Capture Only CO₂
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Jihan Kim, Ph.D. candidate Yunsung Lim and Dr. Hyunsoo Park of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering > In order to help prevent the climate crisis, actively reducing already-emitted CO₂ is essential. Accordingly, direct air capture (DAC) — a technology that directly extracts only CO₂ from the air — is gaining attention. However, effectively capturing pure CO₂ is not easy due to water vapor (H₂O) present in the air. KAIST r
2025-06-29 -
people KAIST Invites World-Renowned Scholars, Elevating Global Competitiveness
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor John Rogers, Professor Gregg Rothermel, Dr. Sang H. Choi > KAIST announced on June 27th that it has appointed three world-renowned scholars, including Professor John A. Rogers of Northwestern University, USA, as Invited Distinguished Professors in key departments such as Materials Science and Engineering. Professor John A. Rogers (Northwestern University, USA) will be working with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering from July 2025 to J
2025-06-27 -
research New and Highly Efficient Recycling Technology to Turn Used Tires into Raw Materials for Rubber and Nylon
< (From left) Kyungmin Choi (MS-Ph.D. integrated course, Department of Chemistry), Dr. Beomsoon Park, Professor Soon Hyeok Hong, Dr. Kyoungil Cho > Approximately 1.5 billions of tires are discarded globally every year, and this is identified as one of the major causes of serious environmental pollution. The research team at the Department of Chemistry at KAIST has achieved a breakthrough by selectively converting waste tires into high-purity cyclic alkenes, valuable chemical buildin
2025-06-26 -
research Military Combatants Usher in an Era of Personalized Training with New Materials
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Steve Park of Materials Science and Engineering, Kyusoon Pak, Ph.D. Candidate (Army Major) > Traditional military training often relies on standardized methods, which has limited the provision of optimized training tailored to individual combatants' characteristics or specific combat situations. To address this, our research team developed an e-textile platform, securing core technology that can reflect the unique traits of individual combatants and
2025-06-25 -
research KAIST's Li-Fi - Achieves 100 Times Faster Speed and Enhanced Security of Wi-Fi
- KAIST-KRISS Develop 'On-Device Encryption Optical Transmitter' Based on Eco-Friendly Quantum Dots - New Li-Fi Platform Technology Achieves High Performance with 17.4% Device Efficiency and 29,000 nit Brightness, Simultaneously Improving Transmission Speed and Security - Presents New Methodology for High-Speed and Encrypted Communication Through Single-Device-Based Dual-Channel Optical Modulation < Photo 1. (Front row from left) Seungmin Shin, First Author; Professor Himchan Cho; (Bac
2025-06-24