the+World+Economic+Forum
-
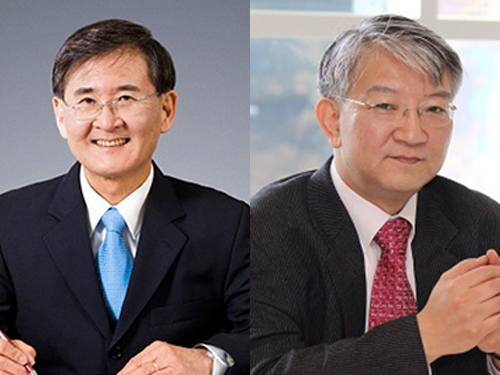 KAIST Participates in the 2014 Davos Forum on January 22-25 in Switzerland
Through the sessions of the Global University Leaders Forum, IdeasLab, and Global Agenda Councils on Biotechnology, KAIST participants will actively engage with global leaders in the discussion of issues on education innovation and technological breakthroughs.
The 2014 Annual Meeting of the World Economic Forum (WEF), known as the Davos Forum, will kick off on January 22-25 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland, under the theme of "The Reshaping of the World: Consequences for Society, Politics, and Business." Each year, the Forum attracts about 2,500 distinguished leaders from all around the world and provides an open platform to identify the current and emerging challenges facing the global community and to develop ideas and actions necessary to respond to such challenges.
President Sung-Mo Steve Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, will attend the Forum and engage in a series of dialogues on such issues as Massive Open Online Courses, new paradigms for universities and researchers, the transformation of higher education, the role and value of scientific discoveries, and the impact of biotechnology on the future of society and business.
At the session entitled "New Paradigms for Universities of the Future" hosted by the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF), President Kang will introduce KAIST"s ongoing online education program, Education 3.0. GULF was created in 2006 by WEF, which is a small community of the presidents and senior representatives of the top universities in the world.
Implemented in 2012, Education 3.0 incorporates advanced information and communications technology (ICT) to offer students and teachers a learner-based, team-oriented learning and teaching environment. Under Education 3.0, students study online and meet in groups with a professor for in-depth discussions, collaboration, and problem-solving. KAIST plans to expand the program to embrace the global community in earnest by establishing Education 3.0 Global in order to have interactive real-time classes for students and researchers across regions and cultures.
President Kang will also present a paper entitled "Toward Socially Responsible Technology: KAIST"s Approach to Integrating Social and Behavioral Perspectives into Technology Development" at another session of GULF called "Seeking New Approaches to Critical Global Challenges." In the paper, President Kang points out that notwithstanding the many benefits we enjoy from the increasingly interconnected world, digital media may pose a threat to become a new outlet for social problems, for example, Internet or digital addiction.
Experts say that early exposure to digital devices harms the healthy development of cognitive functions, emotions, and social behavior. President Kang will introduce KAIST"s recent endeavor to develop a non-intrusive technology to help prevent digital addiction, which will ultimately be embedded in the form of a virtual coach or mentor that helps and guides people under risk to make constructive use of digital devices. President Kang stresses the fundamental shift in the science and technology development paradigm from research and development (R&D) to a research and solution development (R&SD), taking serious consideration of societal needs, quality of life, and social impacts when conducting research.
Professor Sang Yup Lee will moderate the IdeasLab session at the Davos Forum entitled "From Lab to Life with the California Institute of Technology (Caltech)." Together with scientists from Caltech, he will discuss scientific breakthroughs that transform institutions, industries, and individuals in the near future, such as the development of damage-tolerant lightweight materials with nanotechnology, the ability to read and write genomes, and wireless lab-in-the-body monitors. In addition, he will meet global business leaders at the session of "Sustainability, Innovation, and Growth" and speak about how emerging technologies, biotechnology in particular, will transform future societies, business, and industries.
As a current special adviser of the World Economic Forum"s (WEF) Chemicals Industry Community, Professor Lee will meet global chairs and chief executive officers of chemical companies and discuss ways to advance the industry to become more bio-based and environmentally friendly. He served as a founding chairman of WEF"s Global Agenda Councils on Biotechnology in 2013.
President Sung-Mo Steve Kang Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
2014.01.17 View 11410
KAIST Participates in the 2014 Davos Forum on January 22-25 in Switzerland
Through the sessions of the Global University Leaders Forum, IdeasLab, and Global Agenda Councils on Biotechnology, KAIST participants will actively engage with global leaders in the discussion of issues on education innovation and technological breakthroughs.
The 2014 Annual Meeting of the World Economic Forum (WEF), known as the Davos Forum, will kick off on January 22-25 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland, under the theme of "The Reshaping of the World: Consequences for Society, Politics, and Business." Each year, the Forum attracts about 2,500 distinguished leaders from all around the world and provides an open platform to identify the current and emerging challenges facing the global community and to develop ideas and actions necessary to respond to such challenges.
President Sung-Mo Steve Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, will attend the Forum and engage in a series of dialogues on such issues as Massive Open Online Courses, new paradigms for universities and researchers, the transformation of higher education, the role and value of scientific discoveries, and the impact of biotechnology on the future of society and business.
At the session entitled "New Paradigms for Universities of the Future" hosted by the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF), President Kang will introduce KAIST"s ongoing online education program, Education 3.0. GULF was created in 2006 by WEF, which is a small community of the presidents and senior representatives of the top universities in the world.
Implemented in 2012, Education 3.0 incorporates advanced information and communications technology (ICT) to offer students and teachers a learner-based, team-oriented learning and teaching environment. Under Education 3.0, students study online and meet in groups with a professor for in-depth discussions, collaboration, and problem-solving. KAIST plans to expand the program to embrace the global community in earnest by establishing Education 3.0 Global in order to have interactive real-time classes for students and researchers across regions and cultures.
President Kang will also present a paper entitled "Toward Socially Responsible Technology: KAIST"s Approach to Integrating Social and Behavioral Perspectives into Technology Development" at another session of GULF called "Seeking New Approaches to Critical Global Challenges." In the paper, President Kang points out that notwithstanding the many benefits we enjoy from the increasingly interconnected world, digital media may pose a threat to become a new outlet for social problems, for example, Internet or digital addiction.
Experts say that early exposure to digital devices harms the healthy development of cognitive functions, emotions, and social behavior. President Kang will introduce KAIST"s recent endeavor to develop a non-intrusive technology to help prevent digital addiction, which will ultimately be embedded in the form of a virtual coach or mentor that helps and guides people under risk to make constructive use of digital devices. President Kang stresses the fundamental shift in the science and technology development paradigm from research and development (R&D) to a research and solution development (R&SD), taking serious consideration of societal needs, quality of life, and social impacts when conducting research.
Professor Sang Yup Lee will moderate the IdeasLab session at the Davos Forum entitled "From Lab to Life with the California Institute of Technology (Caltech)." Together with scientists from Caltech, he will discuss scientific breakthroughs that transform institutions, industries, and individuals in the near future, such as the development of damage-tolerant lightweight materials with nanotechnology, the ability to read and write genomes, and wireless lab-in-the-body monitors. In addition, he will meet global business leaders at the session of "Sustainability, Innovation, and Growth" and speak about how emerging technologies, biotechnology in particular, will transform future societies, business, and industries.
As a current special adviser of the World Economic Forum"s (WEF) Chemicals Industry Community, Professor Lee will meet global chairs and chief executive officers of chemical companies and discuss ways to advance the industry to become more bio-based and environmentally friendly. He served as a founding chairman of WEF"s Global Agenda Councils on Biotechnology in 2013.
President Sung-Mo Steve Kang Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
2014.01.17 View 11410 -
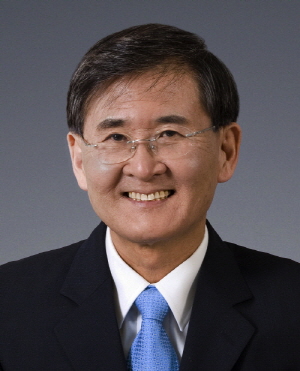 The World Economic Forum Invites KAIST to 2014 Davos Forum
President Steve Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee have been invited by the World Economic Forum (WEF) to attend its annual meeting slated for January 22-25, 2014 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland.
The president will also join the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) to be held during the annual meeting. The GULF consists of leading research universities throughout the world, at which President Kang will address agenda related to higher education and research.
From September 11th to 13th, KAIST was invited to the WEF’s 2013 Summer Davos Forum held in Dalian, China. The Summer Davos Forum is recognized as a barometer of the world economy, and KAIST hosted three sessions there.
In a session titled “Smart Regulations,” Professor Sang Yup Lee hosted presentations and discussions under the topic of “How regulation models can strengthen technical innovation and expansion.” President Steve Kang, Peter Sands, CEO of Standard Chartered Bank Group, Mark Weinberger, CEO of Ernest & Young, and Peter Terium, CEO of RWE, participated in the discussions.
The KAIST delegates also presented and participated in a session titled “From Trade Center to Innovative Hub” to discuss how to lead innovations in Asia, as well as “Marine Resources: Finding New Frontier” to address issues of how to develop and manage oceanic resources for potential growth.
President Kang said, “The World Economic Forum allows us to introduce the results of our innovative and creative research to global leaders and to demonstrate that our global position continues to grow.”
The WEF has been hosting Summer Davos Forum in China since 2007. About 1,500 participants from over 90 countries joined in this year’s summer forum under the theme of “Innovation: Inevitable Mainstream.” New strategies for innovations and solutions for global threats were suggested through presentations and discussions in 125 sessions.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an independent, international, and non-profit organization based in Geneva, Switzerland. It is committed to improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and government leaders to shape global, regional and industry agenda.
Among the meetings and forums organized by the WEF, its annual meeting held each January in Davos, a.k.a. the Davos Forum, has been the best known gathering. The Davos Forum brings together some 2,500 top business leaders, international political leaders, selected intellectuals and journalists to discuss the most pressing issues facing the world including health and environment.
2013.11.07 View 11562
The World Economic Forum Invites KAIST to 2014 Davos Forum
President Steve Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee have been invited by the World Economic Forum (WEF) to attend its annual meeting slated for January 22-25, 2014 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland.
The president will also join the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) to be held during the annual meeting. The GULF consists of leading research universities throughout the world, at which President Kang will address agenda related to higher education and research.
From September 11th to 13th, KAIST was invited to the WEF’s 2013 Summer Davos Forum held in Dalian, China. The Summer Davos Forum is recognized as a barometer of the world economy, and KAIST hosted three sessions there.
In a session titled “Smart Regulations,” Professor Sang Yup Lee hosted presentations and discussions under the topic of “How regulation models can strengthen technical innovation and expansion.” President Steve Kang, Peter Sands, CEO of Standard Chartered Bank Group, Mark Weinberger, CEO of Ernest & Young, and Peter Terium, CEO of RWE, participated in the discussions.
The KAIST delegates also presented and participated in a session titled “From Trade Center to Innovative Hub” to discuss how to lead innovations in Asia, as well as “Marine Resources: Finding New Frontier” to address issues of how to develop and manage oceanic resources for potential growth.
President Kang said, “The World Economic Forum allows us to introduce the results of our innovative and creative research to global leaders and to demonstrate that our global position continues to grow.”
The WEF has been hosting Summer Davos Forum in China since 2007. About 1,500 participants from over 90 countries joined in this year’s summer forum under the theme of “Innovation: Inevitable Mainstream.” New strategies for innovations and solutions for global threats were suggested through presentations and discussions in 125 sessions.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an independent, international, and non-profit organization based in Geneva, Switzerland. It is committed to improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and government leaders to shape global, regional and industry agenda.
Among the meetings and forums organized by the WEF, its annual meeting held each January in Davos, a.k.a. the Davos Forum, has been the best known gathering. The Davos Forum brings together some 2,500 top business leaders, international political leaders, selected intellectuals and journalists to discuss the most pressing issues facing the world including health and environment.
2013.11.07 View 11562 -
 Top Ten Ways Biotechnology Could Improve Our Everyday Life
The Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology, one of the global networks under the World Economic Forum, which is composed of the world’s leading experts in the field of biotechnology, announced on February 25, 2013 that the council has indentified “ten most important biotechnologies” that could help meet rapidly growing demand for energy, food, nutrition, and health. These new technologies, the council said, also have the potential to increase productivity and create new jobs.
“The technologies selected by the members of the Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology represent almost all types of biotechnology.Utilization of waste, personalized medicine,and ocean agricultureare examples of the challenges where biotechnology can offer solutions,”said Sang Yup Lee, Chair of the Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology and Distinguished Professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST). He also added that “the members of the council concluded that regulatory certainty, public perception, and investment are the key enablers for the growth of biotechnology.”
These ideas will be further explored during “Biotechnology Week” at the World Economic Forum’s Blog (http://wef.ch/blog) from Monday, 25 February, 2013. The full list follows below:
Bio-based sustainable production of chemicals, energy, fuels and materials
Through the last century, human activity has depleted approximately half of the world’s reserves of fossil hydrocarbons. These reserves, which took over 600 million years to accumulate, are non-renewable and their extraction, refining and use contribute significantly to human emissions of greenhouse gases and the warming of our planet. In order to sustain human development going forward, a carbon-neutral alternative must be implemented. The key promising technology is biological synthesis; that is, bio-based production of chemicals, fuels and materials from plants that can be re-grown.
Engineering sustainable food production
The continuing increase in our numbers and affluence are posing growing challenges to the ability of humanity to produce adequate food (as well as feed, and now fuel). Although controversial, modern genetic modification of crops has supported growth in agricultural productivity. In 2011, 16.7 million farmers grew biotechnology-developed crops on almost 400 million acres in 29 countries, 19 of which were developing countries. Properly managed, such crops have the potential to lower both pesticide use and tilling which erodes soil.
Sea-water based bio-processes
Over 70% of the earth surface is covered by seawater, and it is the most abundant water source available on the planet. But we are yet to discover the full potential of it. For example with halliophic bacteria capable of growing in the seawater can be engineered to grow faster and produce useful products including chemicals, fuels and polymeric materials. Ocean agriculture is also a promising technology. It is based on the photosynthetic biomass from the oceans, like macroalgae and microalgae.
Non-resource draining zero waste bio-processing
The sustainable goal of zero waste may become a reality with biotechnology. Waste streams can be processed at bio-refineries and turned into valuable chemicals and fuels, thereby closing the loop of production with no net waste. Advances in biotechnology are now allowing lower cost, less draining inputs to be used, including methane, and waste heat. These advances are simplifying waste streams with the potential to reduce toxicity as well as support their use in other processes, moving society progressively closer to the sustainable goal of zero waste.
Using carbon dioxide as a raw material
Biotechnology is poised to contribute solutions to mitigate the growing threat of rising CO2 levels. Recent advances are rapidly increasing our understanding of how living organisms consume and use CO2. By harnessing the power of these natural biological systems, scientists are engineering a new wave of approaches to convert waste CO2 and C1 molecules into energy, fuels, chemicals, and new materials.
Regenerative medicine
Regenerative medicine has become increasingly important due to both increased longevity and treatment of injury. Tissue engineering based on various bio-materials has been developed to speed up the regenerative medicine. Recently, stem cells, especially the induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS), have provided another great opportunity for regenerative medicine. Combination of tissue engineering and stem cell (including iPS) technologies will allow replacements of damaged or old human organs with functional ones in the near future.
Rapid and precise development and manufacturing of medicine and vaccines
A global pandemic remains one of the most real and serious threats to humanity. Biotechnology has the potential to rapidly identify biological threats, develop and manufacture potential cures. Leading edge biotechnology is now offering the potential to rapidly produce therapeutics and vaccines against virtually any target. These technologies, including messenger therapeutics, targeted immunotherapies, conjugated nanoparticles, and structure-based engineering, have already produced candidates with substantial potential to improve human health globally.
Accurate, fast, cheap, and personalized diagnostics and prognostics
Identification of better targets and combining nanotechnology and information technology it will be possible to develop rapid, accurate, personalized and inexpensive diagnostics and prognostics systems.
Bio-tech improvements to soil and water
Arable land and fresh water are two of the most important, yet limited, resources on earth. Abuse and mis-appropriation have threatened these resources, as the demand on them has increased. Advances in biotechnology have already yielded technologies that can restore the vitality and viability of these resources. A new generation of technologies: bio-remediation, bio-regeneration and bio-augmentation are being developed, offering the potential to not only further restore these resources, but also augment their potential.
Advanced healthcare through genome sequencing
It took more than 13 years and $1.5 billion to sequence the first human genome and today we can sequence a complete human genome in a single day for less than $1,000. When we analyze the roughly 3 billion base pairs in such a sequence we find that we differ from each other in several million of these base pairs. In the vast majority of cases these difference do not cause any issues but in rare cases they cause disease, or susceptibility to disease. Medical research and practice will increasingly be driven by our understanding of such genetic variations together with their phenotypic consequences.
2013.03.19 View 12456
Top Ten Ways Biotechnology Could Improve Our Everyday Life
The Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology, one of the global networks under the World Economic Forum, which is composed of the world’s leading experts in the field of biotechnology, announced on February 25, 2013 that the council has indentified “ten most important biotechnologies” that could help meet rapidly growing demand for energy, food, nutrition, and health. These new technologies, the council said, also have the potential to increase productivity and create new jobs.
“The technologies selected by the members of the Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology represent almost all types of biotechnology.Utilization of waste, personalized medicine,and ocean agricultureare examples of the challenges where biotechnology can offer solutions,”said Sang Yup Lee, Chair of the Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology and Distinguished Professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST). He also added that “the members of the council concluded that regulatory certainty, public perception, and investment are the key enablers for the growth of biotechnology.”
These ideas will be further explored during “Biotechnology Week” at the World Economic Forum’s Blog (http://wef.ch/blog) from Monday, 25 February, 2013. The full list follows below:
Bio-based sustainable production of chemicals, energy, fuels and materials
Through the last century, human activity has depleted approximately half of the world’s reserves of fossil hydrocarbons. These reserves, which took over 600 million years to accumulate, are non-renewable and their extraction, refining and use contribute significantly to human emissions of greenhouse gases and the warming of our planet. In order to sustain human development going forward, a carbon-neutral alternative must be implemented. The key promising technology is biological synthesis; that is, bio-based production of chemicals, fuels and materials from plants that can be re-grown.
Engineering sustainable food production
The continuing increase in our numbers and affluence are posing growing challenges to the ability of humanity to produce adequate food (as well as feed, and now fuel). Although controversial, modern genetic modification of crops has supported growth in agricultural productivity. In 2011, 16.7 million farmers grew biotechnology-developed crops on almost 400 million acres in 29 countries, 19 of which were developing countries. Properly managed, such crops have the potential to lower both pesticide use and tilling which erodes soil.
Sea-water based bio-processes
Over 70% of the earth surface is covered by seawater, and it is the most abundant water source available on the planet. But we are yet to discover the full potential of it. For example with halliophic bacteria capable of growing in the seawater can be engineered to grow faster and produce useful products including chemicals, fuels and polymeric materials. Ocean agriculture is also a promising technology. It is based on the photosynthetic biomass from the oceans, like macroalgae and microalgae.
Non-resource draining zero waste bio-processing
The sustainable goal of zero waste may become a reality with biotechnology. Waste streams can be processed at bio-refineries and turned into valuable chemicals and fuels, thereby closing the loop of production with no net waste. Advances in biotechnology are now allowing lower cost, less draining inputs to be used, including methane, and waste heat. These advances are simplifying waste streams with the potential to reduce toxicity as well as support their use in other processes, moving society progressively closer to the sustainable goal of zero waste.
Using carbon dioxide as a raw material
Biotechnology is poised to contribute solutions to mitigate the growing threat of rising CO2 levels. Recent advances are rapidly increasing our understanding of how living organisms consume and use CO2. By harnessing the power of these natural biological systems, scientists are engineering a new wave of approaches to convert waste CO2 and C1 molecules into energy, fuels, chemicals, and new materials.
Regenerative medicine
Regenerative medicine has become increasingly important due to both increased longevity and treatment of injury. Tissue engineering based on various bio-materials has been developed to speed up the regenerative medicine. Recently, stem cells, especially the induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS), have provided another great opportunity for regenerative medicine. Combination of tissue engineering and stem cell (including iPS) technologies will allow replacements of damaged or old human organs with functional ones in the near future.
Rapid and precise development and manufacturing of medicine and vaccines
A global pandemic remains one of the most real and serious threats to humanity. Biotechnology has the potential to rapidly identify biological threats, develop and manufacture potential cures. Leading edge biotechnology is now offering the potential to rapidly produce therapeutics and vaccines against virtually any target. These technologies, including messenger therapeutics, targeted immunotherapies, conjugated nanoparticles, and structure-based engineering, have already produced candidates with substantial potential to improve human health globally.
Accurate, fast, cheap, and personalized diagnostics and prognostics
Identification of better targets and combining nanotechnology and information technology it will be possible to develop rapid, accurate, personalized and inexpensive diagnostics and prognostics systems.
Bio-tech improvements to soil and water
Arable land and fresh water are two of the most important, yet limited, resources on earth. Abuse and mis-appropriation have threatened these resources, as the demand on them has increased. Advances in biotechnology have already yielded technologies that can restore the vitality and viability of these resources. A new generation of technologies: bio-remediation, bio-regeneration and bio-augmentation are being developed, offering the potential to not only further restore these resources, but also augment their potential.
Advanced healthcare through genome sequencing
It took more than 13 years and $1.5 billion to sequence the first human genome and today we can sequence a complete human genome in a single day for less than $1,000. When we analyze the roughly 3 billion base pairs in such a sequence we find that we differ from each other in several million of these base pairs. In the vast majority of cases these difference do not cause any issues but in rare cases they cause disease, or susceptibility to disease. Medical research and practice will increasingly be driven by our understanding of such genetic variations together with their phenotypic consequences.
2013.03.19 View 12456