imaging
-
 KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 7982
KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 7982 -
 KAIST Succeeds in the Real-time Observation of Organoids using Holotomography
Organoids, which are 3D miniature organs that mimic the structure and function of human organs, play an essential role in disease research and drug development. A Korean research team has overcome the limitations of existing imaging technologies, succeeding in the real-time, high-resolution observation of living organoids.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 14th of October that Professor YongKeun Park’s research team from the Department of Physics, in collaboration with the Genome Editing Research Center (Director Bon-Kyoung Koo) of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS President Do-Young Noh) and Tomocube Inc., has developed an imaging technology using holotomography to observe live, small intestinal organoids in real time at a high resolution.
Existing imaging techniques have struggled to observe living organoids in high resolution over extended periods and often required additional treatments like fluorescent staining.
< Figure 1. Overview of the low-coherence HT workflow. Using holotomography, 3D morphological restoration and quantitative analysis of organoids can be performed. In order to improve the limited field of view, which is a limitation of the microscope, our research team utilized a large-area field of view combination algorithm and made a 3D restoration by acquiring multi-focus holographic images for 3D measurements. After that, the organoids were compartmentalized to divide the parts necessary for analysis and quantitatively evaluated the protein concentration measurable from the refractive index and the survival rate of the organoids. >
The research team introduced holotomography technology to address these issues, which provides high-resolution images without the need for fluorescent staining and allows for the long-term observation of dynamic changes in real time without causing cell damage.
The team validated this technology using small intestinal organoids from experimental mice and were able to observe various cell structures inside the organoids in detail. They also captured dynamic changes such as growth processes, cell division, and cell death in real time using holotomography.
Additionally, the technology allowed for the precise analysis of the organoids' responses to drug treatments, verifying the survival of the cells.
The researchers believe that this breakthrough will open new horizons in organoid research, enabling the greater utilization of organoids in drug development, personalized medicine, and regenerative medicine.
Future research is expected to more accurately replicate the in vivo environment of organoids, contributing significantly to a more detailed understanding of various life phenomena at the cellular level through more precise 3D imaging.
< Figure 2. Real-time organoid morphology analysis. Using holotomography, it is possible to observe the lumen and villus development process of intestinal organoids in real time, which was difficult to observe with a conventional microscope. In addition, various information about intestinal organoids can be obtained by quantifying the size and protein amount of intestinal organoids through image analysis. >
Dr. Mahn Jae Lee, a graduate of KAIST's Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, currently at Chungnam National University Hospital and the first author of the paper, commented, "This research represents a new imaging technology that surpasses previous limitations and is expected to make a major contribution to disease modeling, personalized treatments, and drug development research using organoids."
The research results were published online in the international journal Experimental & Molecular Medicine on October 1, 2024, and the technology has been recognized for its applicability in various fields of life sciences. (Paper title: “Long-term three-dimensional high-resolution imaging of live unlabeled small intestinal organoids via low-coherence holotomography”)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, KAIST Institutes, and the Institute for Basic Science.
2024.10.14 View 3809
KAIST Succeeds in the Real-time Observation of Organoids using Holotomography
Organoids, which are 3D miniature organs that mimic the structure and function of human organs, play an essential role in disease research and drug development. A Korean research team has overcome the limitations of existing imaging technologies, succeeding in the real-time, high-resolution observation of living organoids.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 14th of October that Professor YongKeun Park’s research team from the Department of Physics, in collaboration with the Genome Editing Research Center (Director Bon-Kyoung Koo) of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS President Do-Young Noh) and Tomocube Inc., has developed an imaging technology using holotomography to observe live, small intestinal organoids in real time at a high resolution.
Existing imaging techniques have struggled to observe living organoids in high resolution over extended periods and often required additional treatments like fluorescent staining.
< Figure 1. Overview of the low-coherence HT workflow. Using holotomography, 3D morphological restoration and quantitative analysis of organoids can be performed. In order to improve the limited field of view, which is a limitation of the microscope, our research team utilized a large-area field of view combination algorithm and made a 3D restoration by acquiring multi-focus holographic images for 3D measurements. After that, the organoids were compartmentalized to divide the parts necessary for analysis and quantitatively evaluated the protein concentration measurable from the refractive index and the survival rate of the organoids. >
The research team introduced holotomography technology to address these issues, which provides high-resolution images without the need for fluorescent staining and allows for the long-term observation of dynamic changes in real time without causing cell damage.
The team validated this technology using small intestinal organoids from experimental mice and were able to observe various cell structures inside the organoids in detail. They also captured dynamic changes such as growth processes, cell division, and cell death in real time using holotomography.
Additionally, the technology allowed for the precise analysis of the organoids' responses to drug treatments, verifying the survival of the cells.
The researchers believe that this breakthrough will open new horizons in organoid research, enabling the greater utilization of organoids in drug development, personalized medicine, and regenerative medicine.
Future research is expected to more accurately replicate the in vivo environment of organoids, contributing significantly to a more detailed understanding of various life phenomena at the cellular level through more precise 3D imaging.
< Figure 2. Real-time organoid morphology analysis. Using holotomography, it is possible to observe the lumen and villus development process of intestinal organoids in real time, which was difficult to observe with a conventional microscope. In addition, various information about intestinal organoids can be obtained by quantifying the size and protein amount of intestinal organoids through image analysis. >
Dr. Mahn Jae Lee, a graduate of KAIST's Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, currently at Chungnam National University Hospital and the first author of the paper, commented, "This research represents a new imaging technology that surpasses previous limitations and is expected to make a major contribution to disease modeling, personalized treatments, and drug development research using organoids."
The research results were published online in the international journal Experimental & Molecular Medicine on October 1, 2024, and the technology has been recognized for its applicability in various fields of life sciences. (Paper title: “Long-term three-dimensional high-resolution imaging of live unlabeled small intestinal organoids via low-coherence holotomography”)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, KAIST Institutes, and the Institute for Basic Science.
2024.10.14 View 3809 -
 KAIST builds a high-resolution 3D holographic sensor using a single mask
Holographic cameras can provide more realistic images than ordinary cameras thanks to their ability to acquire 3D information about objects. However, existing holographic cameras use interferometers that measure the wavelength and refraction of light through the interference of light waves, which makes them complex and sensitive to their surrounding environment.
On August 23, a KAIST research team led by Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics announced a new leap forward in 3D holographic imaging sensor technology.
The team proposed an innovative holographic camera technology that does not use complex interferometry. Instead, it uses a mask to precisely measure the phase information of light and reconstruct the 3D information of an object with higher accuracy.
< Figure 1. Structure and principle of the proposed holographic camera. The amplitude and phase information of light scattered from a holographic camera can be measured. >
The team used a mask that fulfills certain mathematical conditions and incorporated it into an ordinary camera, and the light scattered from a laser is measured through the mask and analyzed using a computer. This does not require a complex interferometer and allows the phase information of light to be collected through a simplified optical system. With this technique, the mask that is placed between the two lenses and behind an object plays an important role. The mask selectively filters specific parts of light,, and the intensity of the light passing through the lens can be measured using an ordinary commercial camera. This technique combines the image data received from the camera with the unique pattern received from the mask and reconstructs an object’s precise 3D information using an algorithm.
This method allows a high-resolution 3D image of an object to be captured in any position. In practical situations, one can construct a laser-based holographic 3D image sensor by adding a mask with a simple design to a general image sensor. This makes the design and construction of the optical system much easier. In particular, this novel technology can capture high-resolution holographic images of objects moving at high speeds, which widens its potential field of application.
< Figure 2. A moving doll captured by a conventional camera and the proposed holographic camera. When taking a picture without focusing on the object, only a blurred image of the doll can be obtained from a general camera, but the proposed holographic camera can restore the blurred image of the doll into a clear image. >
The results of this study, conducted by Dr. Jeonghun Oh from the KAIST Department of Physics as the first author, were published in Nature Communications on August 12 under the title, "Non-interferometric stand-alone single-shot holographic camera using reciprocal diffractive imaging".
Dr. Oh said, “The holographic camera module we are suggesting can be built by adding a filter to an ordinary camera, which would allow even non-experts to handle it easily in everyday life if it were to be commercialized.” He added, “In particular, it is a promising candidate with the potential to replace existing remote sensing technologies.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation’s Leader Research Project, the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT’s Core Hologram Technology Support Project, and the Nano and Material Technology Development Project.
2023.09.05 View 7515
KAIST builds a high-resolution 3D holographic sensor using a single mask
Holographic cameras can provide more realistic images than ordinary cameras thanks to their ability to acquire 3D information about objects. However, existing holographic cameras use interferometers that measure the wavelength and refraction of light through the interference of light waves, which makes them complex and sensitive to their surrounding environment.
On August 23, a KAIST research team led by Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics announced a new leap forward in 3D holographic imaging sensor technology.
The team proposed an innovative holographic camera technology that does not use complex interferometry. Instead, it uses a mask to precisely measure the phase information of light and reconstruct the 3D information of an object with higher accuracy.
< Figure 1. Structure and principle of the proposed holographic camera. The amplitude and phase information of light scattered from a holographic camera can be measured. >
The team used a mask that fulfills certain mathematical conditions and incorporated it into an ordinary camera, and the light scattered from a laser is measured through the mask and analyzed using a computer. This does not require a complex interferometer and allows the phase information of light to be collected through a simplified optical system. With this technique, the mask that is placed between the two lenses and behind an object plays an important role. The mask selectively filters specific parts of light,, and the intensity of the light passing through the lens can be measured using an ordinary commercial camera. This technique combines the image data received from the camera with the unique pattern received from the mask and reconstructs an object’s precise 3D information using an algorithm.
This method allows a high-resolution 3D image of an object to be captured in any position. In practical situations, one can construct a laser-based holographic 3D image sensor by adding a mask with a simple design to a general image sensor. This makes the design and construction of the optical system much easier. In particular, this novel technology can capture high-resolution holographic images of objects moving at high speeds, which widens its potential field of application.
< Figure 2. A moving doll captured by a conventional camera and the proposed holographic camera. When taking a picture without focusing on the object, only a blurred image of the doll can be obtained from a general camera, but the proposed holographic camera can restore the blurred image of the doll into a clear image. >
The results of this study, conducted by Dr. Jeonghun Oh from the KAIST Department of Physics as the first author, were published in Nature Communications on August 12 under the title, "Non-interferometric stand-alone single-shot holographic camera using reciprocal diffractive imaging".
Dr. Oh said, “The holographic camera module we are suggesting can be built by adding a filter to an ordinary camera, which would allow even non-experts to handle it easily in everyday life if it were to be commercialized.” He added, “In particular, it is a promising candidate with the potential to replace existing remote sensing technologies.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation’s Leader Research Project, the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT’s Core Hologram Technology Support Project, and the Nano and Material Technology Development Project.
2023.09.05 View 7515 -
 KAIST researchers find the key to overcome the limits in X-ray microscopy
X-ray microscopes have the advantage of penetrating most substances, so internal organs and skeletons can be observed non-invasively through chest X-rays or CT scans. Recently, studies to increase the resolution of X-ray imaging technology are being actively conducted in order to precisely observe the internal structure of semiconductors and batteries at the nanoscale.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that a joint research team led by Professor YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics and Dr. Jun Lim of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory has succeeded in developing a core technology that can overcome the resolution limitations of existing X-ray microscopes.
d
This study, in which Dr. KyeoReh Lee participated as the first author, was published on 6th of April in “Light: Science and Application”, a world-renowned academic journal in optics and photonics. (Paper title: Direct high-resolution X-ray imaging exploiting pseudorandomness).
X-ray nanomicroscopes do not have refractive lenses. In an X-ray microscope, a circular grating called a concentric zone plate is used instead of a lens. The resolution of an image obtained using the zone plate is determined by the quality of the nanostructure that comprises the plate. There are several difficulties in fabricating and maintaining these nanostructures, which set the limit to the level of resolution for X-ray microscopy.
The research team developed a new X-ray nanomicroscopy technology to overcome this problem. The X-ray lens proposed by the research team is in the form of numerous holes punched in a thin tungsten film, and generates random diffraction patterns by diffracting incident X-rays. The research team mathematically identified that, paradoxically, the high-resolution information of the sample was fully contained in these random diffraction patterns, and actually succeeded in extracting the information and imaging the internal states of the samples.
The imaging method using the mathematical properties of random diffraction was proposed and implemented in the visible light band for the first time by Dr. KyeoReh Lee and Professor YongKeun Park in 2016*. This study uses the results of previous studies to solve the difficult, lingering problem in the field of the X-ray imaging. ※ "Exploiting the speckle-correlation scattering matrix for a compact reference-free holographic image sensor." Nature communications 7.1 (2016): 13359.
The resolution of the image of the constructed sample has no direct correlation with the size of the pattern etched on the random lens used. Based on this idea, the research team succeeded in acquiring images with 14 nm resolution (approximately 1/7 the size of the coronavirus) by using random lenses made in a circular pattern with a diameter of 300 nm.
The imaging technology developed by this research team is a key fundamental technology that can enhance the resolution of X-ray nanomicroscopy, which has been blocked by limitations of the production of existing zone plates.
The first author and one of the co-corresponding author, Dr. KyeoReh Lee of KAIST Department of Physics, said, “In this study, the resolution was limited to 14 nm, but if the next-generation X-ray light source and high-performance X-ray detector are used, the resolution would exceed that of the conventional X-ray nano-imaging and approach the resolution of an electron microscope.” and added, “Unlike an electron microscope, X-rays can observe the internal structure without damaging the sample, so it will be able to present a new standard for non-invasive nanostructure observation processes such as quality inspections for semiconductors.”.
The co-corresponding author, Dr. Jun Lim of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, said, “In the same context, the developed image technology is expected to greatly increase the performance in the 4th generation multipurpose radiation accelerator which is set to be established in Ochang of the Northern Chungcheong Province.”
This research was conducted with the support through the Research Leader Program and the Sejong Science Fellowship of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
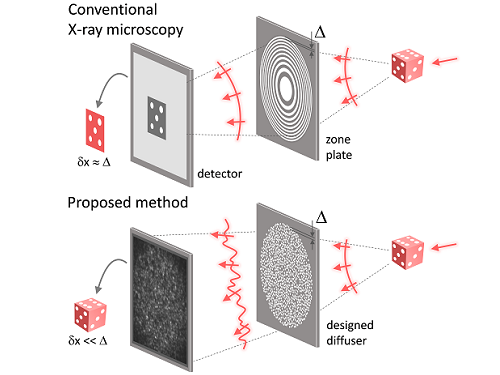
Fig. 1. Designed diffuser as X-ray imaging lens. a, Schematic of full-field transmission X-ray microscopy. The attenuation (amplitude) map of a sample is measured. The image resolution (dx) is limited by the outermost zone width of the zone plate (D). b, Schematic of the proposed method. A designed diffuser is used instead of a zone plate. The image resolution is finer than the hole size of the diffuser (dx << D).
Fig. 2. The left panel is a surface electron microscopy (SEM) image of the X-ray diffuser used in the experiment. The middle panel shows the design of the X-ray diffuser, and there is an inset in the middle of the panel that shows a corresponding part of the SEM image. The right panel shows an experimental random X-ray diffraction pattern, also known as a speckle pattern, obtained from the X-ray diffuser.
Fig. 3. Images taken from the proposed randomness-based X-ray imaging (bottom) and the corresponding surface electron microscope (SEM) images (top).
2023.04.12 View 7398
KAIST researchers find the key to overcome the limits in X-ray microscopy
X-ray microscopes have the advantage of penetrating most substances, so internal organs and skeletons can be observed non-invasively through chest X-rays or CT scans. Recently, studies to increase the resolution of X-ray imaging technology are being actively conducted in order to precisely observe the internal structure of semiconductors and batteries at the nanoscale.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that a joint research team led by Professor YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics and Dr. Jun Lim of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory has succeeded in developing a core technology that can overcome the resolution limitations of existing X-ray microscopes.
d
This study, in which Dr. KyeoReh Lee participated as the first author, was published on 6th of April in “Light: Science and Application”, a world-renowned academic journal in optics and photonics. (Paper title: Direct high-resolution X-ray imaging exploiting pseudorandomness).
X-ray nanomicroscopes do not have refractive lenses. In an X-ray microscope, a circular grating called a concentric zone plate is used instead of a lens. The resolution of an image obtained using the zone plate is determined by the quality of the nanostructure that comprises the plate. There are several difficulties in fabricating and maintaining these nanostructures, which set the limit to the level of resolution for X-ray microscopy.
The research team developed a new X-ray nanomicroscopy technology to overcome this problem. The X-ray lens proposed by the research team is in the form of numerous holes punched in a thin tungsten film, and generates random diffraction patterns by diffracting incident X-rays. The research team mathematically identified that, paradoxically, the high-resolution information of the sample was fully contained in these random diffraction patterns, and actually succeeded in extracting the information and imaging the internal states of the samples.
The imaging method using the mathematical properties of random diffraction was proposed and implemented in the visible light band for the first time by Dr. KyeoReh Lee and Professor YongKeun Park in 2016*. This study uses the results of previous studies to solve the difficult, lingering problem in the field of the X-ray imaging. ※ "Exploiting the speckle-correlation scattering matrix for a compact reference-free holographic image sensor." Nature communications 7.1 (2016): 13359.
The resolution of the image of the constructed sample has no direct correlation with the size of the pattern etched on the random lens used. Based on this idea, the research team succeeded in acquiring images with 14 nm resolution (approximately 1/7 the size of the coronavirus) by using random lenses made in a circular pattern with a diameter of 300 nm.
The imaging technology developed by this research team is a key fundamental technology that can enhance the resolution of X-ray nanomicroscopy, which has been blocked by limitations of the production of existing zone plates.
The first author and one of the co-corresponding author, Dr. KyeoReh Lee of KAIST Department of Physics, said, “In this study, the resolution was limited to 14 nm, but if the next-generation X-ray light source and high-performance X-ray detector are used, the resolution would exceed that of the conventional X-ray nano-imaging and approach the resolution of an electron microscope.” and added, “Unlike an electron microscope, X-rays can observe the internal structure without damaging the sample, so it will be able to present a new standard for non-invasive nanostructure observation processes such as quality inspections for semiconductors.”.
The co-corresponding author, Dr. Jun Lim of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, said, “In the same context, the developed image technology is expected to greatly increase the performance in the 4th generation multipurpose radiation accelerator which is set to be established in Ochang of the Northern Chungcheong Province.”
This research was conducted with the support through the Research Leader Program and the Sejong Science Fellowship of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Fig. 1. Designed diffuser as X-ray imaging lens. a, Schematic of full-field transmission X-ray microscopy. The attenuation (amplitude) map of a sample is measured. The image resolution (dx) is limited by the outermost zone width of the zone plate (D). b, Schematic of the proposed method. A designed diffuser is used instead of a zone plate. The image resolution is finer than the hole size of the diffuser (dx << D).
Fig. 2. The left panel is a surface electron microscopy (SEM) image of the X-ray diffuser used in the experiment. The middle panel shows the design of the X-ray diffuser, and there is an inset in the middle of the panel that shows a corresponding part of the SEM image. The right panel shows an experimental random X-ray diffraction pattern, also known as a speckle pattern, obtained from the X-ray diffuser.
Fig. 3. Images taken from the proposed randomness-based X-ray imaging (bottom) and the corresponding surface electron microscope (SEM) images (top).
2023.04.12 View 7398 -
 PICASSO Technique Drives Biological Molecules into Technicolor
The new imaging approach brings current imaging colors from four to more than 15 for mapping overlapping proteins
Pablo Picasso’s surreal cubist artistic style shifted common features into unrecognizable scenes, but a new imaging approach bearing his namesake may elucidate the most complicated subject: the brain. Employing artificial intelligence to clarify spectral color blending of tiny molecules used to stain specific proteins and other items of research interest, the PICASSO technique, allows researchers to use more than 15 colors to image and parse our overlapping proteins.
The PICASSO developers, based in Korea, published their approach on May 5 in Nature Communications.
Fluorophores — the staining molecules — emit specific colors when excited by a light, but if more than four fluorophores are used, their emitted colors overlap and blend. Researchers previously developed techniques to correct this spectral overlap by precisely defining the matrix of mixed and unmixed images. This measurement depends on reference spectra, found by identifying clear images of only one fluorophore-stained specimen or of multiple, identically prepared specimens that only contain a single fluorophore each.
“Such reference spectra measurement could be complicated to perform in highly heterogeneous specimens, such as the brain, due to the highly varied emission spectra of fluorophores depending on the subregions from which the spectra were measured,” said co-corresponding author Young-Gyu Yoon, professor in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST. He explained that the subregions would each need their own spectra reference measurements, making for an inefficient, time-consuming process. “To address this problem, we developed an approach that does not require reference spectra measurements.”
The approach is the “Process of ultra-multiplexed Imaging of biomolecules viA the unmixing of the Signals of Spectrally Overlapping fluorophores,” also known as PICASSO. Ultra-multiplexed imaging refers to visualizing the numerous individual components of a unit. Like a cinema multiplex in which each theater plays a different movie, each protein in a cell has a different role. By staining with fluorophores, researchers can begin to understand those roles.
“We devised a strategy based on information theory; unmixing is performed by iteratively minimizing the mutual information between mixed images,” said co-corresponding author Jae-Byum Chang, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST. “This allows us to get away with the assumption that the spatial distribution of different proteins is mutually exclusive and enables accurate information unmixing.”
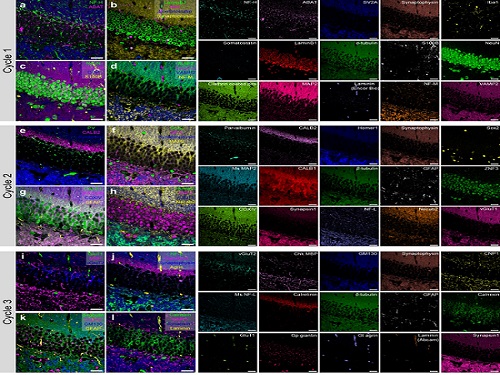
To demonstrate PICASSO’s capabilities, the researchers applied the technique to imaging a mouse brain. With a single round of staining, they performed 15-color multiplexed imaging of a mouse brain. Although small, mouse brains are still complex, multifaceted organs that can take significant resources to map. According to the researchers, PICASSO can improve the capabilities of other imaging techniques and allow for the use of even more fluorophore colors.
Using one such imaging technique in combination with PICASSO, the team achieved 45-color multiplexed imaging of the mouse brain in only three staining and imaging cycles, according to Yoon.
“PICASSO is a versatile tool for the multiplexed biomolecule imaging of cultured cells, tissue slices and clinical specimens,” Chang said. “We anticipate that PICASSO will be useful for a broad range of applications for which biomolecules’ spatial information is important. One such application the tool would be useful for is revealing the cellular heterogeneities of tumor microenvironments, especially the heterogeneous populations of immune cells, which are closely related to cancer prognoses and the efficacy of cancer therapies.”
The Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology supported this work. Spectral imaging was performed at the Korea Basic Science Institute Western Seoul Center.
-PublicationJunyoung Seo, Yeonbo Sim, Jeewon Kim, Hyunwoo Kim, In Cho, Hoyeon Nam, Yong-Gyu Yoon, Jae-Byum Chang, “PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatiallyoverlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements,” May 5, Nature Communications (doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30168-z)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Byum ChangDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
Professor Young-Gyu YoonSchool of Electrical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.06.22 View 10265
PICASSO Technique Drives Biological Molecules into Technicolor
The new imaging approach brings current imaging colors from four to more than 15 for mapping overlapping proteins
Pablo Picasso’s surreal cubist artistic style shifted common features into unrecognizable scenes, but a new imaging approach bearing his namesake may elucidate the most complicated subject: the brain. Employing artificial intelligence to clarify spectral color blending of tiny molecules used to stain specific proteins and other items of research interest, the PICASSO technique, allows researchers to use more than 15 colors to image and parse our overlapping proteins.
The PICASSO developers, based in Korea, published their approach on May 5 in Nature Communications.
Fluorophores — the staining molecules — emit specific colors when excited by a light, but if more than four fluorophores are used, their emitted colors overlap and blend. Researchers previously developed techniques to correct this spectral overlap by precisely defining the matrix of mixed and unmixed images. This measurement depends on reference spectra, found by identifying clear images of only one fluorophore-stained specimen or of multiple, identically prepared specimens that only contain a single fluorophore each.
“Such reference spectra measurement could be complicated to perform in highly heterogeneous specimens, such as the brain, due to the highly varied emission spectra of fluorophores depending on the subregions from which the spectra were measured,” said co-corresponding author Young-Gyu Yoon, professor in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST. He explained that the subregions would each need their own spectra reference measurements, making for an inefficient, time-consuming process. “To address this problem, we developed an approach that does not require reference spectra measurements.”
The approach is the “Process of ultra-multiplexed Imaging of biomolecules viA the unmixing of the Signals of Spectrally Overlapping fluorophores,” also known as PICASSO. Ultra-multiplexed imaging refers to visualizing the numerous individual components of a unit. Like a cinema multiplex in which each theater plays a different movie, each protein in a cell has a different role. By staining with fluorophores, researchers can begin to understand those roles.
“We devised a strategy based on information theory; unmixing is performed by iteratively minimizing the mutual information between mixed images,” said co-corresponding author Jae-Byum Chang, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST. “This allows us to get away with the assumption that the spatial distribution of different proteins is mutually exclusive and enables accurate information unmixing.”
To demonstrate PICASSO’s capabilities, the researchers applied the technique to imaging a mouse brain. With a single round of staining, they performed 15-color multiplexed imaging of a mouse brain. Although small, mouse brains are still complex, multifaceted organs that can take significant resources to map. According to the researchers, PICASSO can improve the capabilities of other imaging techniques and allow for the use of even more fluorophore colors.
Using one such imaging technique in combination with PICASSO, the team achieved 45-color multiplexed imaging of the mouse brain in only three staining and imaging cycles, according to Yoon.
“PICASSO is a versatile tool for the multiplexed biomolecule imaging of cultured cells, tissue slices and clinical specimens,” Chang said. “We anticipate that PICASSO will be useful for a broad range of applications for which biomolecules’ spatial information is important. One such application the tool would be useful for is revealing the cellular heterogeneities of tumor microenvironments, especially the heterogeneous populations of immune cells, which are closely related to cancer prognoses and the efficacy of cancer therapies.”
The Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology supported this work. Spectral imaging was performed at the Korea Basic Science Institute Western Seoul Center.
-PublicationJunyoung Seo, Yeonbo Sim, Jeewon Kim, Hyunwoo Kim, In Cho, Hoyeon Nam, Yong-Gyu Yoon, Jae-Byum Chang, “PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatiallyoverlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements,” May 5, Nature Communications (doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30168-z)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Byum ChangDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
Professor Young-Gyu YoonSchool of Electrical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.06.22 View 10265 -
 AI Light-Field Camera Reads 3D Facial Expressions
Machine-learned, light-field camera reads facial expressions from high-contrast illumination invariant 3D facial images
A joint research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong and Doheon Lee from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering reported the development of a technique for facial expression detection by merging near-infrared light-field camera techniques with artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
Unlike a conventional camera, the light-field camera contains micro-lens arrays in front of the image sensor, which makes the camera small enough to fit into a smart phone, while allowing it to acquire the spatial and directional information of the light with a single shot. The technique has received attention as it can reconstruct images in a variety of ways including multi-views, refocusing, and 3D image acquisition, giving rise to many potential applications.
However, the optical crosstalk between shadows caused by external light sources in the environment and the micro-lens has limited existing light-field cameras from being able to provide accurate image contrast and 3D reconstruction.
The joint research team applied a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) in the near-IR range to stabilize the accuracy of 3D image reconstruction that previously depended on environmental light. When an external light source is shone on a face at 0-, 30-, and 60-degree angles, the light field camera reduces 54% of image reconstruction errors. Additionally, by inserting a light-absorbing layer for visible and near-IR wavelengths between the micro-lens arrays, the team could minimize optical crosstalk while increasing the image contrast by 2.1 times.
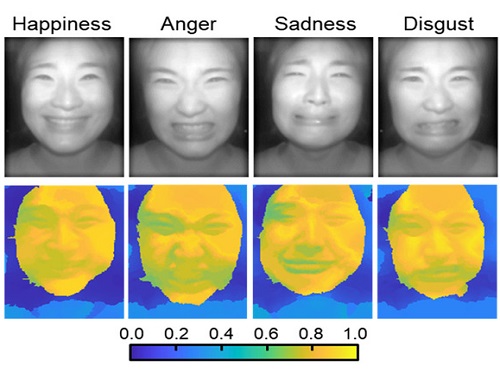
Through this technique, the team could overcome the limitations of existing light-field cameras and was able to develop their NIR-based light-field camera (NIR-LFC), optimized for the 3D image reconstruction of facial expressions. Using the NIR-LFC, the team acquired high-quality 3D reconstruction images of facial expressions expressing various emotions regardless of the lighting conditions of the surrounding environment.
The facial expressions in the acquired 3D images were distinguished through machine learning with an average of 85% accuracy – a statistically significant figure compared to when 2D images were used. Furthermore, by calculating the interdependency of distance information that varies with facial expression in 3D images, the team could identify the information a light-field camera utilizes to distinguish human expressions.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong said, “The sub-miniature light-field camera developed by the research team has the potential to become the new platform to quantitatively analyze the facial expressions and emotions of humans.” To highlight the significance of this research, he added, “It could be applied in various fields including mobile healthcare, field diagnosis, social cognition, and human-machine interactions.”
This research was published in Advanced Intelligent Systems online on December 16, under the title, “Machine-Learned Light-field Camera that Reads Facial Expression from High-Contrast and Illumination Invariant 3D Facial Images.” This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
-Publication“Machine-learned light-field camera that reads fascial expression from high-contrast and illumination invariant 3D facial images,” Sang-In Bae, Sangyeon Lee, Jae-Myeong Kwon, Hyun-Kyung Kim. Kyung-Won Jang, Doheon Lee, Ki-Hun Jeong, Advanced Intelligent Systems, December 16, 2021 (doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202100182)
ProfileProfessor Ki-Hun JeongBiophotonic LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Doheon LeeDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2022.01.21 View 12757
AI Light-Field Camera Reads 3D Facial Expressions
Machine-learned, light-field camera reads facial expressions from high-contrast illumination invariant 3D facial images
A joint research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong and Doheon Lee from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering reported the development of a technique for facial expression detection by merging near-infrared light-field camera techniques with artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
Unlike a conventional camera, the light-field camera contains micro-lens arrays in front of the image sensor, which makes the camera small enough to fit into a smart phone, while allowing it to acquire the spatial and directional information of the light with a single shot. The technique has received attention as it can reconstruct images in a variety of ways including multi-views, refocusing, and 3D image acquisition, giving rise to many potential applications.
However, the optical crosstalk between shadows caused by external light sources in the environment and the micro-lens has limited existing light-field cameras from being able to provide accurate image contrast and 3D reconstruction.
The joint research team applied a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) in the near-IR range to stabilize the accuracy of 3D image reconstruction that previously depended on environmental light. When an external light source is shone on a face at 0-, 30-, and 60-degree angles, the light field camera reduces 54% of image reconstruction errors. Additionally, by inserting a light-absorbing layer for visible and near-IR wavelengths between the micro-lens arrays, the team could minimize optical crosstalk while increasing the image contrast by 2.1 times.
Through this technique, the team could overcome the limitations of existing light-field cameras and was able to develop their NIR-based light-field camera (NIR-LFC), optimized for the 3D image reconstruction of facial expressions. Using the NIR-LFC, the team acquired high-quality 3D reconstruction images of facial expressions expressing various emotions regardless of the lighting conditions of the surrounding environment.
The facial expressions in the acquired 3D images were distinguished through machine learning with an average of 85% accuracy – a statistically significant figure compared to when 2D images were used. Furthermore, by calculating the interdependency of distance information that varies with facial expression in 3D images, the team could identify the information a light-field camera utilizes to distinguish human expressions.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong said, “The sub-miniature light-field camera developed by the research team has the potential to become the new platform to quantitatively analyze the facial expressions and emotions of humans.” To highlight the significance of this research, he added, “It could be applied in various fields including mobile healthcare, field diagnosis, social cognition, and human-machine interactions.”
This research was published in Advanced Intelligent Systems online on December 16, under the title, “Machine-Learned Light-field Camera that Reads Facial Expression from High-Contrast and Illumination Invariant 3D Facial Images.” This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
-Publication“Machine-learned light-field camera that reads fascial expression from high-contrast and illumination invariant 3D facial images,” Sang-In Bae, Sangyeon Lee, Jae-Myeong Kwon, Hyun-Kyung Kim. Kyung-Won Jang, Doheon Lee, Ki-Hun Jeong, Advanced Intelligent Systems, December 16, 2021 (doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202100182)
ProfileProfessor Ki-Hun JeongBiophotonic LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Doheon LeeDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2022.01.21 View 12757 -
 Observing Individual Atoms in 3D Nanomaterials and Their Surfaces
Atoms are the basic building blocks for all materials. To tailor functional properties, it is essential to accurately determine their atomic structures. KAIST researchers observed the 3D atomic structure of a nanoparticle at the atom level via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography.
Using a platinum nanoparticle as a model system, a research team led by Professor Yongsoo Yang demonstrated that an atomicity-based deep learning approach can reliably identify the 3D surface atomic structure with a precision of 15 picometers (only about 1/3 of a hydrogen atom’s radius). The atomic displacement, strain, and facet analysis revealed that the surface atomic structure and strain are related to both the shape of the nanoparticle and the particle-substrate interface.
Combined with quantum mechanical calculations such as density functional theory, the ability to precisely identify surface atomic structure will serve as a powerful key for understanding catalytic performance and oxidation effect.
“We solved the problem of determining the 3D surface atomic structure of nanomaterials in a reliable manner. It has been difficult to accurately measure the surface atomic structures due to the ‘missing wedge problem’ in electron tomography, which arises from geometrical limitations, allowing only part of a full tomographic angular range to be measured. We resolved the problem using a deep learning-based approach,” explained Professor Yang.
The missing wedge problem results in elongation and ringing artifacts, negatively affecting the accuracy of the atomic structure determined from the tomogram, especially for identifying the surface structures. The missing wedge problem has been the main roadblock for the precise determination of the 3D surface atomic structures of nanomaterials.
The team used atomic electron tomography (AET), which is basically a very high-resolution CT scan for nanomaterials using transmission electron microscopes. AET allows individual atom level 3D atomic structural determination.
“The main idea behind this deep learning-based approach is atomicity—the fact that all matter is composed of atoms. This means that true atomic resolution electron tomogram should only contain sharp 3D atomic potentials convolved with the electron beam profile,” said Professor Yang.
“A deep neural network can be trained using simulated tomograms that suffer from missing wedges as inputs, and the ground truth 3D atomic volumes as targets. The trained deep learning network effectively augments the imperfect tomograms and removes the artifacts resulting from the missing wedge problem.”
The precision of 3D atomic structure can be enhanced by nearly 70% by applying the deep learning-based augmentation. The accuracy of surface atom identification was also significantly improved.
Structure-property relationships of functional nanomaterials, especially the ones that strongly depend on the surface structures, such as catalytic properties for fuel-cell applications, can now be revealed at one of the most fundamental scales: the atomic scale.
Professor Yang concluded, “We would like to fully map out the 3D atomic structure with higher precision and better elemental specificity. And not being limited to atomic structures, we aim to measure the physical, chemical, and functional properties of nanomaterials at the 3D atomic scale by further advancing electron tomography techniques.”
This research, reported at Nature Communications, was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research M3I3 Project.
-Publication
Juhyeok Lee, Chaehwa Jeong & Yongsoo Yang
“Single-atom level determination of 3-dimensional surface atomic structure via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography”
Nature Communications
-Profile
Professor Yongsoo Yang
Department of Physics
Multi-Dimensional Atomic Imaging Lab (MDAIL)
http://mdail.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
2021.05.12 View 12582
Observing Individual Atoms in 3D Nanomaterials and Their Surfaces
Atoms are the basic building blocks for all materials. To tailor functional properties, it is essential to accurately determine their atomic structures. KAIST researchers observed the 3D atomic structure of a nanoparticle at the atom level via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography.
Using a platinum nanoparticle as a model system, a research team led by Professor Yongsoo Yang demonstrated that an atomicity-based deep learning approach can reliably identify the 3D surface atomic structure with a precision of 15 picometers (only about 1/3 of a hydrogen atom’s radius). The atomic displacement, strain, and facet analysis revealed that the surface atomic structure and strain are related to both the shape of the nanoparticle and the particle-substrate interface.
Combined with quantum mechanical calculations such as density functional theory, the ability to precisely identify surface atomic structure will serve as a powerful key for understanding catalytic performance and oxidation effect.
“We solved the problem of determining the 3D surface atomic structure of nanomaterials in a reliable manner. It has been difficult to accurately measure the surface atomic structures due to the ‘missing wedge problem’ in electron tomography, which arises from geometrical limitations, allowing only part of a full tomographic angular range to be measured. We resolved the problem using a deep learning-based approach,” explained Professor Yang.
The missing wedge problem results in elongation and ringing artifacts, negatively affecting the accuracy of the atomic structure determined from the tomogram, especially for identifying the surface structures. The missing wedge problem has been the main roadblock for the precise determination of the 3D surface atomic structures of nanomaterials.
The team used atomic electron tomography (AET), which is basically a very high-resolution CT scan for nanomaterials using transmission electron microscopes. AET allows individual atom level 3D atomic structural determination.
“The main idea behind this deep learning-based approach is atomicity—the fact that all matter is composed of atoms. This means that true atomic resolution electron tomogram should only contain sharp 3D atomic potentials convolved with the electron beam profile,” said Professor Yang.
“A deep neural network can be trained using simulated tomograms that suffer from missing wedges as inputs, and the ground truth 3D atomic volumes as targets. The trained deep learning network effectively augments the imperfect tomograms and removes the artifacts resulting from the missing wedge problem.”
The precision of 3D atomic structure can be enhanced by nearly 70% by applying the deep learning-based augmentation. The accuracy of surface atom identification was also significantly improved.
Structure-property relationships of functional nanomaterials, especially the ones that strongly depend on the surface structures, such as catalytic properties for fuel-cell applications, can now be revealed at one of the most fundamental scales: the atomic scale.
Professor Yang concluded, “We would like to fully map out the 3D atomic structure with higher precision and better elemental specificity. And not being limited to atomic structures, we aim to measure the physical, chemical, and functional properties of nanomaterials at the 3D atomic scale by further advancing electron tomography techniques.”
This research, reported at Nature Communications, was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research M3I3 Project.
-Publication
Juhyeok Lee, Chaehwa Jeong & Yongsoo Yang
“Single-atom level determination of 3-dimensional surface atomic structure via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography”
Nature Communications
-Profile
Professor Yongsoo Yang
Department of Physics
Multi-Dimensional Atomic Imaging Lab (MDAIL)
http://mdail.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
2021.05.12 View 12582 -
 Streamlining the Process of Materials Discovery
The materials platform M3I3 reduces the time for materials discovery by reverse engineering future materials using multiscale/multimodal imaging and machine learning of the processing-structure-properties relationship
Developing new materials and novel processes has continued to change the world. The M3I3 Initiative at KAIST has led to new insights into advancing materials development by implementing breakthroughs in materials imaging that have created a paradigm shift in the discovery of materials. The Initiative features the multiscale modeling and imaging of structure and property relationships and materials hierarchies combined with the latest material-processing data.
The research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong analyzed the materials research projects reported by leading global institutes and research groups, and derived a quantitative model using machine learning with a scientific interpretation. This process embodies the research goal of the M3I3: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration.
The researchers discussed the role of multiscale materials and molecular imaging combined with machine learning and also presented a future outlook for developments and the major challenges of M3I3. By building this model, the research team envisions creating desired sets of properties for materials and obtaining the optimum processing recipes to synthesize them.
“The development of various microscopy and diffraction tools with the ability to map the structure, property, and performance of materials at multiscale levels and in real time enabled us to think that materials imaging could radically accelerate materials discovery and development,” says Professor Hong.
“We plan to build an M3I3 repository of searchable structural and property maps using FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) principles to standardize best practices as well as streamline the training of early career researchers.”
One of the examples that shows the power of structure-property imaging at the nanoscale is the development of future materials for emerging nonvolatile memory devices. Specifically, the research team focused on microscopy using photons, electrons, and physical probes on the multiscale structural hierarchy, as well as structure-property relationships to enhance the performance of memory devices.
“M3I3 is an algorithm for performing the reverse engineering of future materials. Reverse engineering starts by analyzing the structure and composition of cutting-edge materials or products. Once the research team determines the performance of our targeted future materials, we need to know the candidate structures and compositions for producing the future materials.”
The research team has built a data-driven experimental design based on traditional NCM (nickel, cobalt, and manganese) cathode materials. With this, the research team expanded their future direction for achieving even higher discharge capacity, which can be realized via Li-rich cathodes.
However, one of the major challenges was the limitation of available data that describes the Li-rich cathode properties. To mitigate this problem, the researchers proposed two solutions: First, they should build a machine-learning-guided data generator for data augmentation. Second, they would use a machine-learning method based on ‘transfer learning.’ Since the NCM cathode database shares a common feature with a Li-rich cathode, one could consider repurposing the NCM trained model for assisting the Li-rich prediction. With the pretrained model and transfer learning, the team expects to achieve outstanding predictions for Li-rich cathodes even with the small data set.
With advances in experimental imaging and the availability of well-resolved information and big data, along with significant advances in high-performance computing and a worldwide thrust toward a general, collaborative, integrative, and on-demand research platform, there is a clear confluence in the required capabilities of advancing the M3I3 Initiative.
Professor Hong said, “Once we succeed in using the inverse “property−structure−processing” solver to develop cathode, anode, electrolyte, and membrane materials for high energy density Li-ion batteries, we will expand our scope of materials to battery/fuel cells, aerospace, automobiles, food, medicine, and cosmetic materials.”
The review was published in ACS Nano in March. This study was conducted through collaborations with Dr. Chi Hao Liow, Professor Jong Min Yuk, Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Professor Yongsoo Yang, Professor EunAe Cho, Professor Pyuck-Pa Choi, and Professor Hyuck Mo Lee at KAIST, Professor Joshua C. Agar at Lehigh University, Dr. Sergei V. Kalinin at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Professor Peter W. Voorhees at Northwestern University, and Professor Peter Littlewood at the University of Chicago (Article title: Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics, and Integration).This work was supported by the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program for 2019 and 2020.
Publication:
“Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration,” S. Hong, C. H. Liow, J. M. Yuk, H. R. Byon, Y. Yang, E. Cho, J. Yeom, G. Park, H. Kang, S. Kim, Y. Shim, M. Na, C. Jeong, G. Hwang, H. Kim, H. Kim, S. Eom, S. Cho, H. Jun, Y. Lee, A. Baucour, K. Bang, M. Kim, S. Yun, J. Ryu, Y. Han, A. Jetybayeva, P.-P. Choi, J. C. Agar, S. V. Kalinin, P. W. Voorhees, P. Littlewood, and H. M. Lee, ACS Nano 15, 3, 3971–3995 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c00211
Profile:
Seungbum Hong, PhD
Associate Professor
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2021.04.05 View 14141
Streamlining the Process of Materials Discovery
The materials platform M3I3 reduces the time for materials discovery by reverse engineering future materials using multiscale/multimodal imaging and machine learning of the processing-structure-properties relationship
Developing new materials and novel processes has continued to change the world. The M3I3 Initiative at KAIST has led to new insights into advancing materials development by implementing breakthroughs in materials imaging that have created a paradigm shift in the discovery of materials. The Initiative features the multiscale modeling and imaging of structure and property relationships and materials hierarchies combined with the latest material-processing data.
The research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong analyzed the materials research projects reported by leading global institutes and research groups, and derived a quantitative model using machine learning with a scientific interpretation. This process embodies the research goal of the M3I3: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration.
The researchers discussed the role of multiscale materials and molecular imaging combined with machine learning and also presented a future outlook for developments and the major challenges of M3I3. By building this model, the research team envisions creating desired sets of properties for materials and obtaining the optimum processing recipes to synthesize them.
“The development of various microscopy and diffraction tools with the ability to map the structure, property, and performance of materials at multiscale levels and in real time enabled us to think that materials imaging could radically accelerate materials discovery and development,” says Professor Hong.
“We plan to build an M3I3 repository of searchable structural and property maps using FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) principles to standardize best practices as well as streamline the training of early career researchers.”
One of the examples that shows the power of structure-property imaging at the nanoscale is the development of future materials for emerging nonvolatile memory devices. Specifically, the research team focused on microscopy using photons, electrons, and physical probes on the multiscale structural hierarchy, as well as structure-property relationships to enhance the performance of memory devices.
“M3I3 is an algorithm for performing the reverse engineering of future materials. Reverse engineering starts by analyzing the structure and composition of cutting-edge materials or products. Once the research team determines the performance of our targeted future materials, we need to know the candidate structures and compositions for producing the future materials.”
The research team has built a data-driven experimental design based on traditional NCM (nickel, cobalt, and manganese) cathode materials. With this, the research team expanded their future direction for achieving even higher discharge capacity, which can be realized via Li-rich cathodes.
However, one of the major challenges was the limitation of available data that describes the Li-rich cathode properties. To mitigate this problem, the researchers proposed two solutions: First, they should build a machine-learning-guided data generator for data augmentation. Second, they would use a machine-learning method based on ‘transfer learning.’ Since the NCM cathode database shares a common feature with a Li-rich cathode, one could consider repurposing the NCM trained model for assisting the Li-rich prediction. With the pretrained model and transfer learning, the team expects to achieve outstanding predictions for Li-rich cathodes even with the small data set.
With advances in experimental imaging and the availability of well-resolved information and big data, along with significant advances in high-performance computing and a worldwide thrust toward a general, collaborative, integrative, and on-demand research platform, there is a clear confluence in the required capabilities of advancing the M3I3 Initiative.
Professor Hong said, “Once we succeed in using the inverse “property−structure−processing” solver to develop cathode, anode, electrolyte, and membrane materials for high energy density Li-ion batteries, we will expand our scope of materials to battery/fuel cells, aerospace, automobiles, food, medicine, and cosmetic materials.”
The review was published in ACS Nano in March. This study was conducted through collaborations with Dr. Chi Hao Liow, Professor Jong Min Yuk, Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Professor Yongsoo Yang, Professor EunAe Cho, Professor Pyuck-Pa Choi, and Professor Hyuck Mo Lee at KAIST, Professor Joshua C. Agar at Lehigh University, Dr. Sergei V. Kalinin at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Professor Peter W. Voorhees at Northwestern University, and Professor Peter Littlewood at the University of Chicago (Article title: Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics, and Integration).This work was supported by the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program for 2019 and 2020.
Publication:
“Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration,” S. Hong, C. H. Liow, J. M. Yuk, H. R. Byon, Y. Yang, E. Cho, J. Yeom, G. Park, H. Kang, S. Kim, Y. Shim, M. Na, C. Jeong, G. Hwang, H. Kim, H. Kim, S. Eom, S. Cho, H. Jun, Y. Lee, A. Baucour, K. Bang, M. Kim, S. Yun, J. Ryu, Y. Han, A. Jetybayeva, P.-P. Choi, J. C. Agar, S. V. Kalinin, P. W. Voorhees, P. Littlewood, and H. M. Lee, ACS Nano 15, 3, 3971–3995 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c00211
Profile:
Seungbum Hong, PhD
Associate Professor
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2021.04.05 View 14141 -
 Microscopy Approach Poised to Offer New Insights into Liver Diseases
Researchers have developed a new way to visualize the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in mouse models of the disease. The new microscopy method provides a high-resolution 3D view that could lead to important new insights into NAFLD, a condition in which too much fat is stored in the liver.
“It is estimated that a quarter of the adult global population has NAFLD, yet an effective treatment strategy has not been found,” said professor Pilhan Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST. “NAFLD is associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes and can sometimes progress to liver failure in serious case.”
In the Optical Society (OSA) journal Biomedical Optics Express, Professor Kim and colleagues reported their new imaging technique and showed that it can be used to observe how tiny droplets of fat, or lipids, accumulate in the liver cells of living mice over time.
“It has been challenging to find a treatment strategy for NAFLD because most studies examine excised liver tissue that represents just one timepoint in disease progression,” said Professor Kim. “Our technique can capture details of lipid accumulation over time, providing a highly useful research tool for identifying the multiple parameters that likely contribute to the disease and could be targeted with treatment.”
Capturing the dynamics of NAFLD in living mouse models of the disease requires the ability to observe quickly changing interactions of biological components in intact tissue in real-time. To accomplish this, the researchers developed a custom intravital confocal and two-photon microscopy system that acquires images of multiple fluorescent labels at video-rate with cellular resolution.
“With video-rate imaging capability, the continuous movement of liver tissue in live mice due to breathing and heart beating could be tracked in real time and precisely compensated,” said Professor Kim. “This provided motion-artifact free high-resolution images of cellular and sub-cellular sized individual lipid droplets.”
The key to fast imaging was a polygonal mirror that rotated at more than 240 miles per hour to provide extremely fast laser scanning. The researchers also incorporated four different lasers and four high-sensitivity optical detectors into the setup so that they could acquire multi-color images to capture different color fluorescent probes used to label the lipid droplets and microvasculature in the livers of live mice.
“Our approach can capture real-time changes in cell behavior and morphology, vascular structure and function, and the spatiotemporal localization of biological components while directly visualizing of lipid droplet development in NAFLD progression,” said Professor Kim. “It also allows the analysis of the highly complex behaviors of various immune cells as NAFLD progresses.”
The researchers demonstrated their approach by using it to observe the development and spatial distribution of lipid droplets in individual mice with NAFLD induced by a methionine and choline-deficient diet. Next, they plan to use it to study how the liver microenvironment changes during NAFLD progression by imaging the same mouse over time. They also want to use their microscope technique to visualize various immune cells and lipid droplets to better understand the complex liver microenvironment in NAFLD progression.
2020.08.21 View 9784
Microscopy Approach Poised to Offer New Insights into Liver Diseases
Researchers have developed a new way to visualize the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in mouse models of the disease. The new microscopy method provides a high-resolution 3D view that could lead to important new insights into NAFLD, a condition in which too much fat is stored in the liver.
“It is estimated that a quarter of the adult global population has NAFLD, yet an effective treatment strategy has not been found,” said professor Pilhan Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST. “NAFLD is associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes and can sometimes progress to liver failure in serious case.”
In the Optical Society (OSA) journal Biomedical Optics Express, Professor Kim and colleagues reported their new imaging technique and showed that it can be used to observe how tiny droplets of fat, or lipids, accumulate in the liver cells of living mice over time.
“It has been challenging to find a treatment strategy for NAFLD because most studies examine excised liver tissue that represents just one timepoint in disease progression,” said Professor Kim. “Our technique can capture details of lipid accumulation over time, providing a highly useful research tool for identifying the multiple parameters that likely contribute to the disease and could be targeted with treatment.”
Capturing the dynamics of NAFLD in living mouse models of the disease requires the ability to observe quickly changing interactions of biological components in intact tissue in real-time. To accomplish this, the researchers developed a custom intravital confocal and two-photon microscopy system that acquires images of multiple fluorescent labels at video-rate with cellular resolution.
“With video-rate imaging capability, the continuous movement of liver tissue in live mice due to breathing and heart beating could be tracked in real time and precisely compensated,” said Professor Kim. “This provided motion-artifact free high-resolution images of cellular and sub-cellular sized individual lipid droplets.”
The key to fast imaging was a polygonal mirror that rotated at more than 240 miles per hour to provide extremely fast laser scanning. The researchers also incorporated four different lasers and four high-sensitivity optical detectors into the setup so that they could acquire multi-color images to capture different color fluorescent probes used to label the lipid droplets and microvasculature in the livers of live mice.
“Our approach can capture real-time changes in cell behavior and morphology, vascular structure and function, and the spatiotemporal localization of biological components while directly visualizing of lipid droplet development in NAFLD progression,” said Professor Kim. “It also allows the analysis of the highly complex behaviors of various immune cells as NAFLD progresses.”
The researchers demonstrated their approach by using it to observe the development and spatial distribution of lipid droplets in individual mice with NAFLD induced by a methionine and choline-deficient diet. Next, they plan to use it to study how the liver microenvironment changes during NAFLD progression by imaging the same mouse over time. They also want to use their microscope technique to visualize various immune cells and lipid droplets to better understand the complex liver microenvironment in NAFLD progression.
2020.08.21 View 9784 -
 Unravelling Complex Brain Networks with Automated 3-D Neural Mapping
-Automated 3-D brain imaging data analysis technology offers more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of complex neural circuits.-
KAIST researchers developed a new algorithm for brain imaging data analysis that enables the precise and quantitative mapping of complex neural circuits onto a standardized 3-D reference atlas.
Brain imaging data analysis is indispensable in the studies of neuroscience. However, analysis of obtained brain imaging data has been heavily dependent on manual processing, which cannot guarantee the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of the results.
Conventional brain imaging data analysis typically begins with finding a 2-D brain atlas image that is visually similar to the experimentally obtained brain image. Then, the region-of-interest (ROI) of the atlas image is matched manually with the obtained image, and the number of labeled neurons in the ROI is counted.
Such a visual matching process between experimentally obtained brain images and 2-D brain atlas images has been one of the major sources of error in brain imaging data analysis, as the process is highly subjective, sample-specific, and susceptible to human error. Manual analysis processes for brain images are also laborious, and thus studying the complete 3-D neuronal organization on a whole-brain scale is a formidable task.
To address these issues, a KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering developed new brain imaging data analysis software named 'AMaSiNe (Automated 3-D Mapping of Single Neurons)', and introduced the algorithm in the May 26 issue of Cell Reports.
AMaSiNe automatically detects the positions of single neurons from multiple brain images, and accurately maps all the data onto a common standard 3-D reference space. The algorithm allows the direct comparison of brain data from different animals by automatically matching similar features from the images, and computing the image similarity score.
This feature-based quantitative image-to-image comparison technology improves the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of analysis results using only a small number of brain slice image samples, and helps standardize brain imaging data analyses.
Unlike other existing brain imaging data analysis methods, AMaSiNe can also automatically find the alignment conditions from misaligned and distorted brain images, and draw an accurate ROI, without any cumbersome manual validation process.
AMaSiNe has been further proved to produce consistent results with brain slice images stained utilizing various methods including DAPI, Nissl, and autofluorescence.
The two co-lead authors of this study, Jun Ho Song and Woochul Choi, exploited these benefits of AMaSiNe to investigate the topographic organization of neurons that project to the primary visual area (VISp) in various ROIs, such as the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGd), which could hardly be addressed without proper calibration and standardization of the brain slice image samples.
In collaboration with Professor Seung-Hee Lee's group of the Department of Biological Science, the researchers successfully observed the 3-D topographic neural projections to the VISp from LGd, and also demonstrated that these projections could not be observed when the slicing angle was not properly corrected by AMaSiNe. The results suggest that the precise correction of a slicing angle is essential for the investigation of complex and important brain structures.
AMaSiNe is widely applicable in the studies of various brain regions and other experimental conditions. For example, in the research team’s previous study jointly conducted with Professor Yang Dan’s group at UC Berkeley, the algorithm enabled the accurate analysis of the neuronal subsets in the substantia nigra and their projections to the whole brain. Their findings were published in Science on January 24.
AMaSiNe is of great interest to many neuroscientists in Korea and abroad, and is being actively used by a number of other research groups at KAIST, MIT, Harvard, Caltech, and UC San Diego.
Professor Paik said, “Our new algorithm allows the spatial organization of complex neural circuits to be found in a standardized 3-D reference atlas on a whole-brain scale. This will bring brain imaging data analysis to a new level.”
He continued, “More in-depth insights for understanding the function of brain circuits can be achieved by facilitating more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of neural circuits in various regions of the brain.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Figure and Image Credit: Professor Se-Bum Paik, KAIST
Figure and Image Usage Restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and images, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Song, J. H., et al. (2020). Precise Mapping of Single Neurons by Calibrated 3D Reconstruction of Brain Slices Reveals Topographic Projection in Mouse Visual Cortex. Cell Reports. Volume 31, 107682. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107682
Profile:
Se-Bum Paik
Assistant Professor
sbpaik@kaist.ac.kr
http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/
VSNN Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.06.08 View 14344
Unravelling Complex Brain Networks with Automated 3-D Neural Mapping
-Automated 3-D brain imaging data analysis technology offers more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of complex neural circuits.-
KAIST researchers developed a new algorithm for brain imaging data analysis that enables the precise and quantitative mapping of complex neural circuits onto a standardized 3-D reference atlas.
Brain imaging data analysis is indispensable in the studies of neuroscience. However, analysis of obtained brain imaging data has been heavily dependent on manual processing, which cannot guarantee the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of the results.
Conventional brain imaging data analysis typically begins with finding a 2-D brain atlas image that is visually similar to the experimentally obtained brain image. Then, the region-of-interest (ROI) of the atlas image is matched manually with the obtained image, and the number of labeled neurons in the ROI is counted.
Such a visual matching process between experimentally obtained brain images and 2-D brain atlas images has been one of the major sources of error in brain imaging data analysis, as the process is highly subjective, sample-specific, and susceptible to human error. Manual analysis processes for brain images are also laborious, and thus studying the complete 3-D neuronal organization on a whole-brain scale is a formidable task.
To address these issues, a KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering developed new brain imaging data analysis software named 'AMaSiNe (Automated 3-D Mapping of Single Neurons)', and introduced the algorithm in the May 26 issue of Cell Reports.
AMaSiNe automatically detects the positions of single neurons from multiple brain images, and accurately maps all the data onto a common standard 3-D reference space. The algorithm allows the direct comparison of brain data from different animals by automatically matching similar features from the images, and computing the image similarity score.
This feature-based quantitative image-to-image comparison technology improves the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of analysis results using only a small number of brain slice image samples, and helps standardize brain imaging data analyses.
Unlike other existing brain imaging data analysis methods, AMaSiNe can also automatically find the alignment conditions from misaligned and distorted brain images, and draw an accurate ROI, without any cumbersome manual validation process.
AMaSiNe has been further proved to produce consistent results with brain slice images stained utilizing various methods including DAPI, Nissl, and autofluorescence.
The two co-lead authors of this study, Jun Ho Song and Woochul Choi, exploited these benefits of AMaSiNe to investigate the topographic organization of neurons that project to the primary visual area (VISp) in various ROIs, such as the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGd), which could hardly be addressed without proper calibration and standardization of the brain slice image samples.
In collaboration with Professor Seung-Hee Lee's group of the Department of Biological Science, the researchers successfully observed the 3-D topographic neural projections to the VISp from LGd, and also demonstrated that these projections could not be observed when the slicing angle was not properly corrected by AMaSiNe. The results suggest that the precise correction of a slicing angle is essential for the investigation of complex and important brain structures.
AMaSiNe is widely applicable in the studies of various brain regions and other experimental conditions. For example, in the research team’s previous study jointly conducted with Professor Yang Dan’s group at UC Berkeley, the algorithm enabled the accurate analysis of the neuronal subsets in the substantia nigra and their projections to the whole brain. Their findings were published in Science on January 24.
AMaSiNe is of great interest to many neuroscientists in Korea and abroad, and is being actively used by a number of other research groups at KAIST, MIT, Harvard, Caltech, and UC San Diego.
Professor Paik said, “Our new algorithm allows the spatial organization of complex neural circuits to be found in a standardized 3-D reference atlas on a whole-brain scale. This will bring brain imaging data analysis to a new level.”
He continued, “More in-depth insights for understanding the function of brain circuits can be achieved by facilitating more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of neural circuits in various regions of the brain.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Figure and Image Credit: Professor Se-Bum Paik, KAIST
Figure and Image Usage Restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and images, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Song, J. H., et al. (2020). Precise Mapping of Single Neurons by Calibrated 3D Reconstruction of Brain Slices Reveals Topographic Projection in Mouse Visual Cortex. Cell Reports. Volume 31, 107682. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107682
Profile:
Se-Bum Paik
Assistant Professor
sbpaik@kaist.ac.kr
http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/
VSNN Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.06.08 View 14344 -
 Professor Sue-Hyun Lee Listed Among WEF 2020 Young Scientists
Professor Sue-Hyun Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering joined the World Economic Forum (WEF)’s Young Scientists Community on May 26. The class of 2020 comprises 25 leading researchers from 14 countries across the world who are at the forefront of scientific problem-solving and social change. Professor Lee was the only Korean on this year’s roster.
The WEF created the Young Scientists Community in 2008 to engage leaders from the public and private sectors with science and the role it plays in society. The WEF selects rising-star academics, 40 and under, from various fields every year, and helps them become stronger ambassadors for science, especially in tackling pressing global challenges including cybersecurity, climate change, poverty, and pandemics.
Professor Lee is researching how memories are encoded, recalled, and updated, and how emotional processes affect human memory, in order to ultimately direct the development of therapeutic methods to treat mental disorders. She has made significant contributions to resolving ongoing debates over the maintenance and changes of memory traces in the brain.
In recognition of her research excellence, leadership, and commitment to serving society, the President and the Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST nominated Professor Lee to the WEF’s Class of 2020 Young Scientists Selection Committee. The Committee also acknowledged Professor Lee’s achievements and potential for expanding the boundaries of knowledge and practical applications of science, and accepted her into the Community.
During her three-year membership in the Community, Professor Lee will be committed to participating in WEF-initiated activities and events related to promising therapeutic interventions for mental disorders and future directions of artificial intelligence.
Seven of this year’s WEF Young Scientists are from Asia, including Professor Lee, while eight are based in Europe. Six study in the Americas, two work in South Africa, and the remaining two in the Middle East. Fourteen, more than half, of the newly announced 25 Young Scientists are women.
(END)
2020.05.26 View 12792
Professor Sue-Hyun Lee Listed Among WEF 2020 Young Scientists
Professor Sue-Hyun Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering joined the World Economic Forum (WEF)’s Young Scientists Community on May 26. The class of 2020 comprises 25 leading researchers from 14 countries across the world who are at the forefront of scientific problem-solving and social change. Professor Lee was the only Korean on this year’s roster.
The WEF created the Young Scientists Community in 2008 to engage leaders from the public and private sectors with science and the role it plays in society. The WEF selects rising-star academics, 40 and under, from various fields every year, and helps them become stronger ambassadors for science, especially in tackling pressing global challenges including cybersecurity, climate change, poverty, and pandemics.
Professor Lee is researching how memories are encoded, recalled, and updated, and how emotional processes affect human memory, in order to ultimately direct the development of therapeutic methods to treat mental disorders. She has made significant contributions to resolving ongoing debates over the maintenance and changes of memory traces in the brain.
In recognition of her research excellence, leadership, and commitment to serving society, the President and the Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST nominated Professor Lee to the WEF’s Class of 2020 Young Scientists Selection Committee. The Committee also acknowledged Professor Lee’s achievements and potential for expanding the boundaries of knowledge and practical applications of science, and accepted her into the Community.
During her three-year membership in the Community, Professor Lee will be committed to participating in WEF-initiated activities and events related to promising therapeutic interventions for mental disorders and future directions of artificial intelligence.
Seven of this year’s WEF Young Scientists are from Asia, including Professor Lee, while eight are based in Europe. Six study in the Americas, two work in South Africa, and the remaining two in the Middle East. Fourteen, more than half, of the newly announced 25 Young Scientists are women.
(END)
2020.05.26 View 12792 -
 Ultrathin but Fully Packaged High-Resolution Camera
- Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera captures super-resolution images. -
The unique structures of biological vision systems in nature inspired scientists to design ultracompact imaging systems. A research group led by Professor Ki-Hun Jeong have made an ultracompact camera that captures high-contrast and high-resolution images. Fully packaged with micro-optical elements such as inverted micro-lenses, multilayered pinhole arrays, and gap spacers on the image sensor, the camera boasts a total track length of 740 μm and a field of view of 73°.
Inspired by the eye structures of the paper wasp species Xenos peckii, the research team completely suppressed optical noise between micro-lenses while reducing camera thickness. The camera has successfully demonstrated high-contrast clear array images acquired from tiny micro lenses. To further enhance the image quality of the captured image, the team combined the arrayed images into one image through super-resolution imaging.
An insect’s compound eye has superior visual characteristics, such as a wide viewing angle, high motion sensitivity, and a large depth of field while maintaining a small volume of visual structure with a small focal length. Among them, the eyes of Xenos peckii and an endoparasite found on paper wasps have hundreds of photoreceptors in a single lens unlike conventional compound eyes. In particular, the eye structures of an adult Xenos peckii exhibit hundreds of photoreceptors on an individual eyelet and offer engineering inspiration for ultrathin cameras or imaging applications because they have higher visual acuity than other compound eyes.
For instance, Xenos peckii’s eye-inspired cameras provide a 50 times higher spatial resolution than those based on arthropod eyes. In addition, the effective image resolution of the Xenos peckii’s eye can be further improved using the image overlaps between neighboring eyelets. This unique structure offers higher visual resolution than other insect eyes.
The team achieved high-contrast and super-resolution imaging through a novel arrayed design of micro-optical elements comprising multilayered aperture arrays and inverted micro-lens arrays directly stacked over an image sensor. This optical component was integrated with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor.
This is first demonstration of super-resolution imaging which acquires a single integrated image with high contrast and high resolving power reconstructed from high-contrast array images. It is expected that this ultrathin arrayed camera can be applied for further developing mobile devices, advanced surveillance vehicles, and endoscopes.
Professor Jeong said, “This research has led to technological advances in imaging technology. We will continue to strive to make significant impacts on multidisciplinary research projects in the fields of microtechnology and nanotechnology, seeking inspiration from natural photonic structures.”
This work was featured in Light Science & Applications last month and was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of and the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kisoo Kim, Kyung-Won Jang, Jae-Kwan Ryu, and Ki-Hun Jeong. (2020) “Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera for high-contrast and high-resolution imaging”. Light Science & Applications. Volume 9. Article 28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0261-8
Profile:
Ki-Hun Jeong
Professor
kjeong@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Kisoo Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
kisoo.kim1@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.23 View 18924
Ultrathin but Fully Packaged High-Resolution Camera
- Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera captures super-resolution images. -
The unique structures of biological vision systems in nature inspired scientists to design ultracompact imaging systems. A research group led by Professor Ki-Hun Jeong have made an ultracompact camera that captures high-contrast and high-resolution images. Fully packaged with micro-optical elements such as inverted micro-lenses, multilayered pinhole arrays, and gap spacers on the image sensor, the camera boasts a total track length of 740 μm and a field of view of 73°.
Inspired by the eye structures of the paper wasp species Xenos peckii, the research team completely suppressed optical noise between micro-lenses while reducing camera thickness. The camera has successfully demonstrated high-contrast clear array images acquired from tiny micro lenses. To further enhance the image quality of the captured image, the team combined the arrayed images into one image through super-resolution imaging.
An insect’s compound eye has superior visual characteristics, such as a wide viewing angle, high motion sensitivity, and a large depth of field while maintaining a small volume of visual structure with a small focal length. Among them, the eyes of Xenos peckii and an endoparasite found on paper wasps have hundreds of photoreceptors in a single lens unlike conventional compound eyes. In particular, the eye structures of an adult Xenos peckii exhibit hundreds of photoreceptors on an individual eyelet and offer engineering inspiration for ultrathin cameras or imaging applications because they have higher visual acuity than other compound eyes.
For instance, Xenos peckii’s eye-inspired cameras provide a 50 times higher spatial resolution than those based on arthropod eyes. In addition, the effective image resolution of the Xenos peckii’s eye can be further improved using the image overlaps between neighboring eyelets. This unique structure offers higher visual resolution than other insect eyes.
The team achieved high-contrast and super-resolution imaging through a novel arrayed design of micro-optical elements comprising multilayered aperture arrays and inverted micro-lens arrays directly stacked over an image sensor. This optical component was integrated with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor.
This is first demonstration of super-resolution imaging which acquires a single integrated image with high contrast and high resolving power reconstructed from high-contrast array images. It is expected that this ultrathin arrayed camera can be applied for further developing mobile devices, advanced surveillance vehicles, and endoscopes.
Professor Jeong said, “This research has led to technological advances in imaging technology. We will continue to strive to make significant impacts on multidisciplinary research projects in the fields of microtechnology and nanotechnology, seeking inspiration from natural photonic structures.”
This work was featured in Light Science & Applications last month and was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of and the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kisoo Kim, Kyung-Won Jang, Jae-Kwan Ryu, and Ki-Hun Jeong. (2020) “Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera for high-contrast and high-resolution imaging”. Light Science & Applications. Volume 9. Article 28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0261-8
Profile:
Ki-Hun Jeong
Professor
kjeong@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Kisoo Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
kisoo.kim1@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.23 View 18924