energy+harvester
-
 Sturdy Fabric-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Takes Us One Step Closer to Wearable Electronics
KAIST researchers presented a highly flexible but sturdy wearable piezoelectric harvester using the simple and easy fabrication process of hot pressing and tape casting. This energy harvester, which has record high interfacial adhesion strength, will take us one step closer to being able to manufacture embedded wearable electronics.
A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong said that the novelty of this result lies in its simplicity, applicability, durability, and its new characterization of wearable electronic devices.
Wearable devices are increasingly being used in a wide array of applications from small electronics to embedded devices such as sensors, actuators, displays, and energy harvesters.
Despite their many advantages, high costs and complex fabrication processes remained challenges for reaching commercialization. In addition, their durability was frequently questioned. To address these issues, Professor Hong’s team developed a new fabrication process and analysis technology for testing the mechanical properties of affordable wearable devices.
For this process, the research team used a hot pressing and tape casting procedure to connect the fabric structures of polyester and a polymer film. Hot pressing has usually been used when making batteries and fuel cells due to its high adhesiveness. Above all, the process takes only two to three minutes.
The newly developed fabrication process will enable the direct application of a device into general garments using hot pressing just as graphic patches can be attached to garments using a heat press.
In particular, when the polymer film is hot pressed onto a fabric below its crystallization temperature, it transforms into an amorphous state. In this state, it compactly attaches to the concave surface of the fabric and infiltrates into the gaps between the transverse wefts and longitudinal warps. These features result in high interfacial adhesion strength. For this reason, hot pressing has the potential to reduce the cost of fabrication through the direct application of fabric-based wearable devices to common garments.
In addition to the conventional durability test of bending cycles, the newly introduced surface and interfacial cutting analysis system proved the high mechanical durability of the fabric-based wearable device by measuring the high interfacial adhesion strength between the fabric and the polymer film. Professor Hong said the study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of wearable devices using fabrics and polymers.
He added that his team first used the surface and interfacial cutting analysis system (SAICAS) in the field of wearable electronics to test the mechanical properties of polymer-based wearable devices. Their surface and interfacial cutting analysis system is more precise than conventional methods (peel test, tape test, and microstretch test) because it qualitatively and quantitatively measures the adhesion strength.
Professor Hong explained, “This study could enable the commercialization of highly durable wearable devices based on the analysis of their interfacial adhesion strength. Our study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of other devices using fabrics and polymers. We look forward to fabric-based wearable electronics hitting the market very soon.”
The results of this study were registered as a domestic patent in Korea last year, and published in Nano Energy this month. This study has been conducted through collaboration with Professor Yong Min Lee in the Department of Energy Science and Engineering at DGIST, Professor Kwangsoo No in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, and Professor Seunghwa Ryu in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST.
This study was supported by the High-Risk High-Return Project and the Global Singularity Research Project at KAIST, the National Research Foundation, and the Ministry of Science and ICT in Korea.
-Publication:
Jaegyu Kim, Seoungwoo Byun, Sangryun Lee, Jeongjae Ryu, Seongwoo Cho, Chungik Oh, Hongjun Kim, Kwangsoo No, Seunghwa Ryu, Yong Min Lee, Seungbum Hong*, Nano Energy 75 (2020), 104992.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104992
-Profile: Professor Seungbum Hong
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2020.09.17 View 14213
Sturdy Fabric-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Takes Us One Step Closer to Wearable Electronics
KAIST researchers presented a highly flexible but sturdy wearable piezoelectric harvester using the simple and easy fabrication process of hot pressing and tape casting. This energy harvester, which has record high interfacial adhesion strength, will take us one step closer to being able to manufacture embedded wearable electronics.
A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong said that the novelty of this result lies in its simplicity, applicability, durability, and its new characterization of wearable electronic devices.
Wearable devices are increasingly being used in a wide array of applications from small electronics to embedded devices such as sensors, actuators, displays, and energy harvesters.
Despite their many advantages, high costs and complex fabrication processes remained challenges for reaching commercialization. In addition, their durability was frequently questioned. To address these issues, Professor Hong’s team developed a new fabrication process and analysis technology for testing the mechanical properties of affordable wearable devices.
For this process, the research team used a hot pressing and tape casting procedure to connect the fabric structures of polyester and a polymer film. Hot pressing has usually been used when making batteries and fuel cells due to its high adhesiveness. Above all, the process takes only two to three minutes.
The newly developed fabrication process will enable the direct application of a device into general garments using hot pressing just as graphic patches can be attached to garments using a heat press.
In particular, when the polymer film is hot pressed onto a fabric below its crystallization temperature, it transforms into an amorphous state. In this state, it compactly attaches to the concave surface of the fabric and infiltrates into the gaps between the transverse wefts and longitudinal warps. These features result in high interfacial adhesion strength. For this reason, hot pressing has the potential to reduce the cost of fabrication through the direct application of fabric-based wearable devices to common garments.
In addition to the conventional durability test of bending cycles, the newly introduced surface and interfacial cutting analysis system proved the high mechanical durability of the fabric-based wearable device by measuring the high interfacial adhesion strength between the fabric and the polymer film. Professor Hong said the study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of wearable devices using fabrics and polymers.
He added that his team first used the surface and interfacial cutting analysis system (SAICAS) in the field of wearable electronics to test the mechanical properties of polymer-based wearable devices. Their surface and interfacial cutting analysis system is more precise than conventional methods (peel test, tape test, and microstretch test) because it qualitatively and quantitatively measures the adhesion strength.
Professor Hong explained, “This study could enable the commercialization of highly durable wearable devices based on the analysis of their interfacial adhesion strength. Our study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of other devices using fabrics and polymers. We look forward to fabric-based wearable electronics hitting the market very soon.”
The results of this study were registered as a domestic patent in Korea last year, and published in Nano Energy this month. This study has been conducted through collaboration with Professor Yong Min Lee in the Department of Energy Science and Engineering at DGIST, Professor Kwangsoo No in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, and Professor Seunghwa Ryu in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST.
This study was supported by the High-Risk High-Return Project and the Global Singularity Research Project at KAIST, the National Research Foundation, and the Ministry of Science and ICT in Korea.
-Publication:
Jaegyu Kim, Seoungwoo Byun, Sangryun Lee, Jeongjae Ryu, Seongwoo Cho, Chungik Oh, Hongjun Kim, Kwangsoo No, Seunghwa Ryu, Yong Min Lee, Seungbum Hong*, Nano Energy 75 (2020), 104992.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104992
-Profile: Professor Seungbum Hong
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2020.09.17 View 14213 -
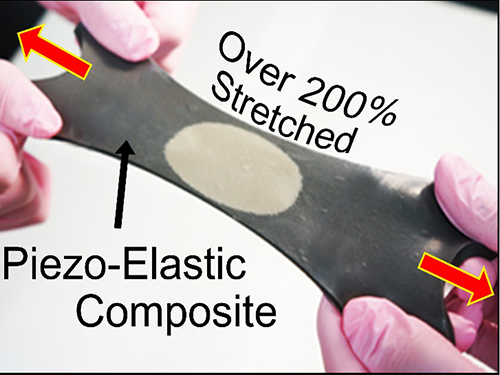 KAIST Researchers Develops Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee (http://fand.kaist.ac.kr) of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed a hyper-stretchable elastic-composite energy harvesting device called a nanogenerator.
Flexible electronics have come into the market and are enabling new technologies like flexible displays in mobile phone, wearable electronics, and the Internet of Things (IoTs). However, is the degree of flexibility enough for most applications? For many flexible devices, elasticity is a very important issue. For example, wearable/biomedical devices and electronic skins (e-skins) should stretch to conform to arbitrarily curved surfaces and moving body parts such as joints, diaphragms, and tendons. They must be able to withstand the repeated and prolonged mechanical stresses of stretching. In particular, the development of elastic energy devices is regarded as critical to establish power supplies in stretchable applications. Although several researchers have explored diverse stretchable electronics, due to the absence of the appropriate device structures and correspondingly electrodes, researchers have not developed ultra-stretchable and fully-reversible energy conversion devices properly.
Recently, researchers from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) have collaborated and demonstrated a facile methodology to obtain a high-performance and hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator (SEG) using very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes. Their stretchable piezoelectric generator can harvest mechanical energy to produce high power output (~4 V) with large elasticity (~250%) and excellent durability (over 104 cycles). These noteworthy results were achieved by the non-destructive stress- relaxation ability of the unique electrodes as well as the good piezoelectricity of the device components. The new SEG can be applied to a wide-variety of wearable energy-harvesters to transduce biomechanical-stretching energy from the body (or machines) to electrical energy.
Professor Lee said, “This exciting approach introduces an ultra-stretchable piezoelectric generator. It can open avenues for power supplies in universal wearable and biomedical applications as well as self-powered ultra-stretchable electronics.”
This result was published online in the March issue of Advanced Materials, which is entitled “A Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester.”
YouTube Link: “A hyper-stretchable energy harvester”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EBByFvPVRiU&feature=youtu.be
Figure: Top row: Schematics of hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator enabled by very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes.
Bottom row: The SEG energy harvester stretched by human hands over 200% strain.
2015.04.14 View 14243
KAIST Researchers Develops Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee (http://fand.kaist.ac.kr) of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed a hyper-stretchable elastic-composite energy harvesting device called a nanogenerator.
Flexible electronics have come into the market and are enabling new technologies like flexible displays in mobile phone, wearable electronics, and the Internet of Things (IoTs). However, is the degree of flexibility enough for most applications? For many flexible devices, elasticity is a very important issue. For example, wearable/biomedical devices and electronic skins (e-skins) should stretch to conform to arbitrarily curved surfaces and moving body parts such as joints, diaphragms, and tendons. They must be able to withstand the repeated and prolonged mechanical stresses of stretching. In particular, the development of elastic energy devices is regarded as critical to establish power supplies in stretchable applications. Although several researchers have explored diverse stretchable electronics, due to the absence of the appropriate device structures and correspondingly electrodes, researchers have not developed ultra-stretchable and fully-reversible energy conversion devices properly.
Recently, researchers from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) have collaborated and demonstrated a facile methodology to obtain a high-performance and hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator (SEG) using very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes. Their stretchable piezoelectric generator can harvest mechanical energy to produce high power output (~4 V) with large elasticity (~250%) and excellent durability (over 104 cycles). These noteworthy results were achieved by the non-destructive stress- relaxation ability of the unique electrodes as well as the good piezoelectricity of the device components. The new SEG can be applied to a wide-variety of wearable energy-harvesters to transduce biomechanical-stretching energy from the body (or machines) to electrical energy.
Professor Lee said, “This exciting approach introduces an ultra-stretchable piezoelectric generator. It can open avenues for power supplies in universal wearable and biomedical applications as well as self-powered ultra-stretchable electronics.”
This result was published online in the March issue of Advanced Materials, which is entitled “A Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester.”
YouTube Link: “A hyper-stretchable energy harvester”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EBByFvPVRiU&feature=youtu.be
Figure: Top row: Schematics of hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator enabled by very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes.
Bottom row: The SEG energy harvester stretched by human hands over 200% strain.
2015.04.14 View 14243