PHA
-
 KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 7442
KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 7442 -
 A Way for Smartwatches to Detect Depression Risks Devised by KAIST and U of Michigan Researchers
- A international joint research team of KAIST and the University of Michigan developed a digital biomarker for predicting symptoms of depression based on data collected by smartwatches
- It has the potential to be used as a medical technology to replace the economically burdensome fMRI measurement test
- It is expected to expand the scope of digital health data analysis
The CORONA virus pandemic also brought about a pandemic of mental illness. Approximately one billion people worldwide suffer from various psychiatric conditions. Korea is one of more serious cases, with approximately 1.8 million patients exhibiting depression and anxiety disorders, and the total number of patients with clinical mental diseases has increased by 37% in five years to approximately 4.65 million. A joint research team from Korea and the US has developed a technology that uses biometric data collected through wearable devices to predict tomorrow's mood and, further, to predict the possibility of developing symptoms of depression.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the research results. Based on the biometric data collected by a smartwatch, a mathematical algorithm that solves the inverse problem to estimate the brain's circadian phase and sleep stages has been developed. This algorithm can estimate the degrees of circadian disruption, and these estimates can be used as the digital biomarkers to predict depression risks. >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of January that the research team under Professor Dae Wook Kim from the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and the team under Professor Daniel B. Forger from the Department of Mathematics at the University of Michigan in the United States have developed a technology to predict symptoms of depression such as sleep disorders, depression, loss of appetite, overeating, and decreased concentration in shift workers from the activity and heart rate data collected from smartwatches.
According to WHO, a promising new treatment direction for mental illness focuses on the sleep and circadian timekeeping system located in the hypothalamus of the brain, which directly affect impulsivity, emotional responses, decision-making, and overall mood.
However, in order to measure endogenous circadian rhythms and sleep states, blood or saliva must be drawn every 30 minutes throughout the night to measure changes in the concentration of the melatonin hormone in our bodies and polysomnography (PSG) must be performed. As such treatments requires hospitalization and most psychiatric patients only visit for outpatient treatment, there has been no significant progress in developing treatment methods that take these two factors into account. In addition, the cost of the PSG test, which is approximately $1000, leaves mental health treatment considering sleep and circadian rhythms out of reach for the socially disadvantaged.
The solution to overcome these problems is to employ wearable devices for the easier collection of biometric data such as heart rate, body temperature, and activity level in real time without spatial constraints. However, current wearable devices have the limitation of providing only indirect information on biomarkers required by medical staff, such as the phase of the circadian clock.
The joint research team developed a filtering technology that accurately estimates the phase of the circadian clock, which changes daily, such as heart rate and activity time series data collected from a smartwatch. This is an implementation of a digital twin that precisely describes the circadian rhythm in the brain, and it can be used to estimate circadian rhythm disruption.
< Figure 2. The suprachiasmatic nucleus located in the hypothalamus of the brain is the central biological clock that regulates the 24-hour physiological rhythm and plays a key role in maintaining the body’s circadian rhythm. If the phase of this biological clock is disrupted, it affects various parts of the brain, which can cause psychiatric conditions such as depression. >
The possibility of using the digital twin of this circadian clock to predict the symptoms of depression was verified through collaboration with the research team of Professor Srijan Sen of the Michigan Neuroscience Institute and Professor Amy Bohnert of the Department of Psychiatry of the University of Michigan.
The collaborative research team conducted a large-scale prospective cohort study involving approximately 800 shift workers and showed that the circadian rhythm disruption digital biomarker estimated through the technology can predict tomorrow's mood as well as six symptoms, including sleep problems, appetite changes, decreased concentration, and suicidal thoughts, which are representative symptoms of depression.
< Figure 3. The circadian rhythm of hormones such as melatonin regulates various physiological functions and behaviors such as heart rate and activity level. These physiological and behavioral signals can be measured in daily life through wearable devices. In order to estimate the body’s circadian rhythm inversely based on the measured biometric signals, a mathematical algorithm is needed. This algorithm plays a key role in accurately identifying the characteristics of circadian rhythms by extracting hidden physiological patterns from biosignals. >
Professor Dae Wook Kim said, "It is very meaningful to be able to conduct research that provides a clue for ways to apply wearable biometric data using mathematics that have not previously been utilized for actual disease management." He added, "We expect that this research will be able to present continuous and non-invasive mental health monitoring technology. This is expected to present a new paradigm for mental health care. By resolving some of the major problems socially disadvantaged people may face in current treatment practices, they may be able to take more active steps when experiencing symptoms of depression, such as seeking counsel before things get out of hand."
< Figure 4. A mathematical algorithm was devised to circumvent the problems of estimating the phase of the brain's biological clock and sleep stages inversely from the biodata collected by a smartwatch. This algorithm can estimate the degree of daily circadian rhythm disruption, and this estimate can be used as a digital biomarker to predict depression symptoms. >
The results of this study, in which Professor Dae Wook Kim of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at KAIST participated as the joint first author and corresponding author, were published in the online version of the international academic journal npj Digital Medicine on December 5, 2024. (Paper title: The real-world association between digital markers of circadian disruption and mental health risks) DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01348-6
This study was conducted with the support of the KAIST's Research Support Program for New Faculty Members, the US National Science Foundation, the US National Institutes of Health, and the US Army Research Institute MURI Program.
2025.01.20 View 4571
A Way for Smartwatches to Detect Depression Risks Devised by KAIST and U of Michigan Researchers
- A international joint research team of KAIST and the University of Michigan developed a digital biomarker for predicting symptoms of depression based on data collected by smartwatches
- It has the potential to be used as a medical technology to replace the economically burdensome fMRI measurement test
- It is expected to expand the scope of digital health data analysis
The CORONA virus pandemic also brought about a pandemic of mental illness. Approximately one billion people worldwide suffer from various psychiatric conditions. Korea is one of more serious cases, with approximately 1.8 million patients exhibiting depression and anxiety disorders, and the total number of patients with clinical mental diseases has increased by 37% in five years to approximately 4.65 million. A joint research team from Korea and the US has developed a technology that uses biometric data collected through wearable devices to predict tomorrow's mood and, further, to predict the possibility of developing symptoms of depression.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the research results. Based on the biometric data collected by a smartwatch, a mathematical algorithm that solves the inverse problem to estimate the brain's circadian phase and sleep stages has been developed. This algorithm can estimate the degrees of circadian disruption, and these estimates can be used as the digital biomarkers to predict depression risks. >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of January that the research team under Professor Dae Wook Kim from the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and the team under Professor Daniel B. Forger from the Department of Mathematics at the University of Michigan in the United States have developed a technology to predict symptoms of depression such as sleep disorders, depression, loss of appetite, overeating, and decreased concentration in shift workers from the activity and heart rate data collected from smartwatches.
According to WHO, a promising new treatment direction for mental illness focuses on the sleep and circadian timekeeping system located in the hypothalamus of the brain, which directly affect impulsivity, emotional responses, decision-making, and overall mood.
However, in order to measure endogenous circadian rhythms and sleep states, blood or saliva must be drawn every 30 minutes throughout the night to measure changes in the concentration of the melatonin hormone in our bodies and polysomnography (PSG) must be performed. As such treatments requires hospitalization and most psychiatric patients only visit for outpatient treatment, there has been no significant progress in developing treatment methods that take these two factors into account. In addition, the cost of the PSG test, which is approximately $1000, leaves mental health treatment considering sleep and circadian rhythms out of reach for the socially disadvantaged.
The solution to overcome these problems is to employ wearable devices for the easier collection of biometric data such as heart rate, body temperature, and activity level in real time without spatial constraints. However, current wearable devices have the limitation of providing only indirect information on biomarkers required by medical staff, such as the phase of the circadian clock.
The joint research team developed a filtering technology that accurately estimates the phase of the circadian clock, which changes daily, such as heart rate and activity time series data collected from a smartwatch. This is an implementation of a digital twin that precisely describes the circadian rhythm in the brain, and it can be used to estimate circadian rhythm disruption.
< Figure 2. The suprachiasmatic nucleus located in the hypothalamus of the brain is the central biological clock that regulates the 24-hour physiological rhythm and plays a key role in maintaining the body’s circadian rhythm. If the phase of this biological clock is disrupted, it affects various parts of the brain, which can cause psychiatric conditions such as depression. >
The possibility of using the digital twin of this circadian clock to predict the symptoms of depression was verified through collaboration with the research team of Professor Srijan Sen of the Michigan Neuroscience Institute and Professor Amy Bohnert of the Department of Psychiatry of the University of Michigan.
The collaborative research team conducted a large-scale prospective cohort study involving approximately 800 shift workers and showed that the circadian rhythm disruption digital biomarker estimated through the technology can predict tomorrow's mood as well as six symptoms, including sleep problems, appetite changes, decreased concentration, and suicidal thoughts, which are representative symptoms of depression.
< Figure 3. The circadian rhythm of hormones such as melatonin regulates various physiological functions and behaviors such as heart rate and activity level. These physiological and behavioral signals can be measured in daily life through wearable devices. In order to estimate the body’s circadian rhythm inversely based on the measured biometric signals, a mathematical algorithm is needed. This algorithm plays a key role in accurately identifying the characteristics of circadian rhythms by extracting hidden physiological patterns from biosignals. >
Professor Dae Wook Kim said, "It is very meaningful to be able to conduct research that provides a clue for ways to apply wearable biometric data using mathematics that have not previously been utilized for actual disease management." He added, "We expect that this research will be able to present continuous and non-invasive mental health monitoring technology. This is expected to present a new paradigm for mental health care. By resolving some of the major problems socially disadvantaged people may face in current treatment practices, they may be able to take more active steps when experiencing symptoms of depression, such as seeking counsel before things get out of hand."
< Figure 4. A mathematical algorithm was devised to circumvent the problems of estimating the phase of the brain's biological clock and sleep stages inversely from the biodata collected by a smartwatch. This algorithm can estimate the degree of daily circadian rhythm disruption, and this estimate can be used as a digital biomarker to predict depression symptoms. >
The results of this study, in which Professor Dae Wook Kim of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at KAIST participated as the joint first author and corresponding author, were published in the online version of the international academic journal npj Digital Medicine on December 5, 2024. (Paper title: The real-world association between digital markers of circadian disruption and mental health risks) DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01348-6
This study was conducted with the support of the KAIST's Research Support Program for New Faculty Members, the US National Science Foundation, the US National Institutes of Health, and the US Army Research Institute MURI Program.
2025.01.20 View 4571 -
 KAIST finds ways for Bacteria to produce PET-like materials
Among various eco-friendly polymers, polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) stand out for their excellent biodegradability and biocompatibility. They decompose naturally in soil and marine environments and are used in applications such as food packaging and medical products. However, natural PHA produced to date has faced challenges meeting various physical property requirements, such as durability and thermal stability, and has been limited in its commercial application due to low production concentrations. In light of this, KAIST researchers have recently developed a technology that could play a crucial role in solving the environmental pollution problem caused by plastics.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on August 26th that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, including Dr. Youngjoon Lee and master's student Minju Kang, has successfully developed a microbial strain that efficiently produces aromatic polyester* using systems metabolic engineering.
※ Aromatic polyester: A polymer containing aromatic compounds (specific carbon ring structures like benzene) and ester bonds.
In this study, the research team used metabolic engineering to enhance the metabolic flux of the biosynthetic pathway for the aromatic monomer phenyllactate (PhLA) in E. coli. They manipulated the metabolic pathway to increase the polymer fraction accumulated within the cells and employed computer simulations to predict the structure of PHA synthase and improve the enzyme based on the structure-function relationship.
Through subsequent fermentation optimization, the team achieved the world’s highest concentration (12.3±0.1 g/L) for the efficient production of poly (PhLA) and successfully produced polyester through a 30L scale fed-batch fermentation, demonstrating the possibility of industrial-level production. The produced aromatic polyesters showed enhanced thermal properties, improved mechanical properties, and potential for use as drug delivery carriers.
< Figure 1. Development schematics of aromatic polyester producing microorganisms >
The research team also demonstrated that an exogenous phasin protein* plays a crucial role in increasing the intracellular polymer accumulation fraction, which is directly related to the economic feasibility and efficiency of non-natural PHA production. They improved PHA synthase using a rational enzyme design approach, predicting the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme through homology modeling (a method of predicting the three-dimensional structure of a new protein based on the structure of similar proteins) followed by molecular docking simulations (simulations that predict how well a monomer can bind to an enzyme) and molecular dynamics simulations (simulations that predict how molecules move and interact over time) to upgrade the enzyme into a mutant enzyme with enhanced monomer polymerization efficiency.
※ Exogenous phasin protein: Phasin is a protein related to PHA production, interacting with the cytoplasmic environment on the surface of granules of PHA, and playing a role in polymer accumulation and controlling the number and size of granules. In this study, genes encoding phasin proteins derived from various natural PHA-producing microorganisms were selected and introduced.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, co-first author of the paper, explained, "The significance of this study lies in the fact that we have achieved the world's highest concentration of microbial-based aromatic polyester production using eco-friendly materials and methods. This technology is expected to play a crucial role in addressing the environmental pollution caused by plastics." Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee added, "This study, which presents various strategies for the high-efficiency production of useful polymers via systems metabolic engineering, is expected to make a significant contribution to solving climate change issues, particularly the recent plastic problem."
< Figure 2. Detailed development strategy for aromatic polyester producing microorganisms >
The research findings were published on August 21st in Trends in Biotechnology, published by Cell, an international academic journal.
※ Paper Title: “Microbial production of an aromatic homopolyester”
※ Author Information: Youngjoon Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Minju Kang (KAIST, co-first author), Woo Dae Jang (KAIST, second author), So Young Choi (KAIST, third author), Jung Eun Yang (KAIST, fourth author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), totaling six authors.
This research was supported by the "Development of Next-Generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading the Bio-based Chemicals Industry" project led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST, under the eco-friendly chemical technology development project aimed at substituting petroleum, funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT. It was also supported by the "Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic Using Microbial Cell Factories" project (Project Leader: Si Jae Park, Ewha Woman’s University).
2024.08.28 View 5058
KAIST finds ways for Bacteria to produce PET-like materials
Among various eco-friendly polymers, polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) stand out for their excellent biodegradability and biocompatibility. They decompose naturally in soil and marine environments and are used in applications such as food packaging and medical products. However, natural PHA produced to date has faced challenges meeting various physical property requirements, such as durability and thermal stability, and has been limited in its commercial application due to low production concentrations. In light of this, KAIST researchers have recently developed a technology that could play a crucial role in solving the environmental pollution problem caused by plastics.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on August 26th that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, including Dr. Youngjoon Lee and master's student Minju Kang, has successfully developed a microbial strain that efficiently produces aromatic polyester* using systems metabolic engineering.
※ Aromatic polyester: A polymer containing aromatic compounds (specific carbon ring structures like benzene) and ester bonds.
In this study, the research team used metabolic engineering to enhance the metabolic flux of the biosynthetic pathway for the aromatic monomer phenyllactate (PhLA) in E. coli. They manipulated the metabolic pathway to increase the polymer fraction accumulated within the cells and employed computer simulations to predict the structure of PHA synthase and improve the enzyme based on the structure-function relationship.
Through subsequent fermentation optimization, the team achieved the world’s highest concentration (12.3±0.1 g/L) for the efficient production of poly (PhLA) and successfully produced polyester through a 30L scale fed-batch fermentation, demonstrating the possibility of industrial-level production. The produced aromatic polyesters showed enhanced thermal properties, improved mechanical properties, and potential for use as drug delivery carriers.
< Figure 1. Development schematics of aromatic polyester producing microorganisms >
The research team also demonstrated that an exogenous phasin protein* plays a crucial role in increasing the intracellular polymer accumulation fraction, which is directly related to the economic feasibility and efficiency of non-natural PHA production. They improved PHA synthase using a rational enzyme design approach, predicting the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme through homology modeling (a method of predicting the three-dimensional structure of a new protein based on the structure of similar proteins) followed by molecular docking simulations (simulations that predict how well a monomer can bind to an enzyme) and molecular dynamics simulations (simulations that predict how molecules move and interact over time) to upgrade the enzyme into a mutant enzyme with enhanced monomer polymerization efficiency.
※ Exogenous phasin protein: Phasin is a protein related to PHA production, interacting with the cytoplasmic environment on the surface of granules of PHA, and playing a role in polymer accumulation and controlling the number and size of granules. In this study, genes encoding phasin proteins derived from various natural PHA-producing microorganisms were selected and introduced.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, co-first author of the paper, explained, "The significance of this study lies in the fact that we have achieved the world's highest concentration of microbial-based aromatic polyester production using eco-friendly materials and methods. This technology is expected to play a crucial role in addressing the environmental pollution caused by plastics." Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee added, "This study, which presents various strategies for the high-efficiency production of useful polymers via systems metabolic engineering, is expected to make a significant contribution to solving climate change issues, particularly the recent plastic problem."
< Figure 2. Detailed development strategy for aromatic polyester producing microorganisms >
The research findings were published on August 21st in Trends in Biotechnology, published by Cell, an international academic journal.
※ Paper Title: “Microbial production of an aromatic homopolyester”
※ Author Information: Youngjoon Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Minju Kang (KAIST, co-first author), Woo Dae Jang (KAIST, second author), So Young Choi (KAIST, third author), Jung Eun Yang (KAIST, fourth author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), totaling six authors.
This research was supported by the "Development of Next-Generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading the Bio-based Chemicals Industry" project led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST, under the eco-friendly chemical technology development project aimed at substituting petroleum, funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT. It was also supported by the "Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic Using Microbial Cell Factories" project (Project Leader: Si Jae Park, Ewha Woman’s University).
2024.08.28 View 5058 -
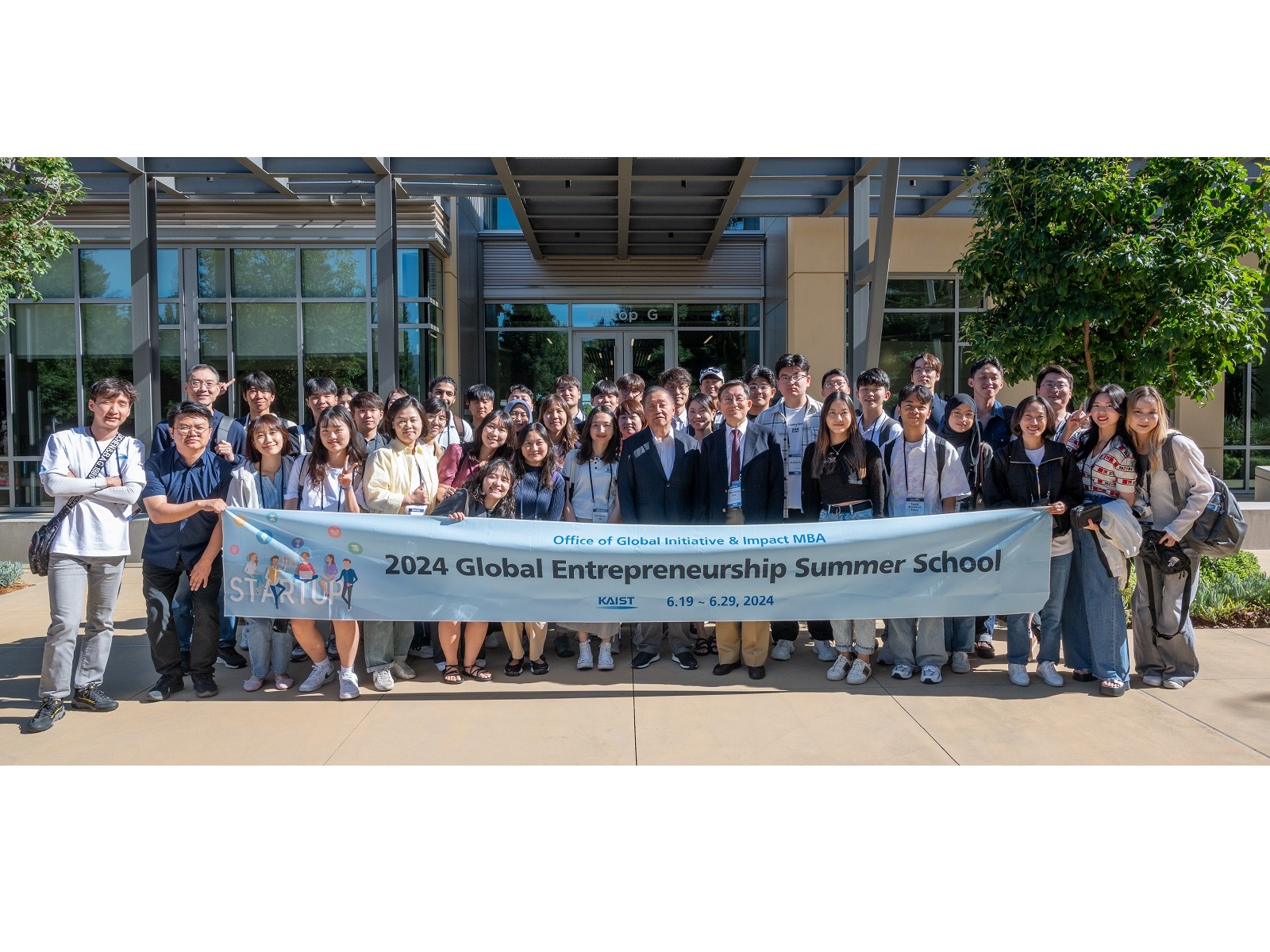 The 3rd Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (GESS 2024) Successfully Completed in Silicon Valley
The 2024 Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (2024 KAIST GESS), hosted by the Office of Global Initiatives under the KAIST International Office (Director Man-Sung Yim), was held for the third time. This program allows students to visit Silicon Valley, a global startup hub, to directly experience its famous startup ecosystem and develop their capabilities for global expansion. A total of 20 students were selected through applications, interviews, final presentations, mentoring, and peer evaluations. Additionally, 17 students from the KAIST Impact MBA course at the KAIST Business School also participated.
Before starting the Silicon Valley program, participants received mentoring on business model development and pitching advice from a senior entrepreneur at KAIST for about two months, beginning last May. Afterward, they developed business items for each team at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon. For seven days, starting from June 23rd, workshops were held under the themes of global entrepreneurship, learning through failure, capital and network, and startup culture at KOTRA Silicon Valley Trade Center, JP Morgan, and Plug and Play Tech Center. This program's lecture series provided prospective entrepreneurs with the opportunity to systematically learn the mindset and gain the experience needed to start a global business.
The participants also visited local companies and gained experience in the field of global technology startups. Visits included Bear Robotics (CEO John Ha), Soundable Health (CEO Cathering Song), ImpriMed (CEO Sungwon Lim), Phantom AI (CEO Hyunggi Cho), B Garage (CEO Aiden Kim), and Simple Steps (CEO Doyeon Kim). Lectures contained vivid experiences from Silicon Valley CEOs and company tours boosted the students' passion for entrepreneurship. In particular, Doyeon Kim, CEO of Simple Steps, which helps prevent career breaks for Korean female immigrants in Silicon Valley and allows talented female immigrants to demonstrate their abilities in society, said, “As a KAIST alumna entrepreneur, it was meaningful to share my experience with this generation of students who dream of starting a global business and creating social enterprises in the United States.”
This program also included a tour of Silicon Valley's big tech companies that have made a significant impact on the digital ecosystem through technological advancement and innovation. This included Broadcom, which maintains a strong global presence in the semiconductor and infrastructure software technology fields. At the invitation of Chairman Hock Tan, GESS participants had the opportunity to attend his lecture and ask questions. Chairman Tan, who received an honorary doctorate in engineering from KAIST last February, emphasized that experiencing failure and giving consistent effort over a long period of time are more important than anything else in order to grow as a global entrepreneur, and that technologies influencing the global market evolve over generations.
< Photo. Group photo of GESS 2024 participants at Broadcom with Chairman Hock Tan (center) ⓒBroadcom>
As part of this program, participants conducted a volunteer program called 'Let's play with AI+ Tech' with the Sunnyvale community in Silicon Valley and Foothill College to help grow together with the community. Through this program, GESS participants cultivated the virtues of a global leader. In this volunteer activity, low-income elementary school students and parents from the Sunnyvale community participated in chatbot training led by KAIST students, providing an opportunity to work with underprivileged groups in the local community.
In the final pitching event, the highlight of the program, local venture investors from Silicon Valley were invited as judges and evaluated the pitches for each team's business items. The participating students, who developed their own business models while receiving advice through face-to-face mentoring from a professional accelerator in Silicon Valley, showcased their creative and innovative ideas, presenting themselves as future global entrepreneurs. Merey Makhmutova (BS in Civil and Environmental Engineering) from the K-Bridge team, who won the final pitch, expressed her ambition: “Even before GESS pitch day, our team kept refining the pitch deck as we attended the lectures and benefitted from the mentoring. Our intense teamwork was a significant reason why we ultimately won first prize.” She added that K-Bridge aims to win an award at the upcoming UKC Pitching Competition and expressed her gratitude for being able to participate in this program. Arseniy Kan (BS in Electrical Engineering) from the KAIST Enablers team, who took second place, said, “The 2024 KAIST GESS Program became the most unforgettable and precious opportunity of my lifetime, and I dream of using this opportunity as a stepping stone to becoming a global entrepreneur.“ Additionally, Kangster (CEO Kang Kim), who won the Impact MBA final pitching session, had the opportunity to secure a meeting with a local investment company after their GESS final pitch.
The 2024 KAIST GESS was held in cooperation with the KAIST International Office, the KAIST College of Business, and Startup KAIST. Director Man-Sung Yim from the Office of Global Initiatives, who hosted the event, said, “KAIST students will grow into leaders with global influence and contribute to the international community by creating global value. At the same time, we hope to raise the international status of our university.” Professor Sangchan Park, who led the 17 Impact MBA students in this educational program, added, “Meeting with companies leading the global market and visiting Silicon Valley has been a valuable learning experience for students aiming to start a global startup.”
KAIST plans to continue promoting its global entrepreneurship education program by enriching its curriculum each year and helping students grow into entrepreneurs with the virtues of global leaders.
2024.07.03 View 7241
The 3rd Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (GESS 2024) Successfully Completed in Silicon Valley
The 2024 Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (2024 KAIST GESS), hosted by the Office of Global Initiatives under the KAIST International Office (Director Man-Sung Yim), was held for the third time. This program allows students to visit Silicon Valley, a global startup hub, to directly experience its famous startup ecosystem and develop their capabilities for global expansion. A total of 20 students were selected through applications, interviews, final presentations, mentoring, and peer evaluations. Additionally, 17 students from the KAIST Impact MBA course at the KAIST Business School also participated.
Before starting the Silicon Valley program, participants received mentoring on business model development and pitching advice from a senior entrepreneur at KAIST for about two months, beginning last May. Afterward, they developed business items for each team at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon. For seven days, starting from June 23rd, workshops were held under the themes of global entrepreneurship, learning through failure, capital and network, and startup culture at KOTRA Silicon Valley Trade Center, JP Morgan, and Plug and Play Tech Center. This program's lecture series provided prospective entrepreneurs with the opportunity to systematically learn the mindset and gain the experience needed to start a global business.
The participants also visited local companies and gained experience in the field of global technology startups. Visits included Bear Robotics (CEO John Ha), Soundable Health (CEO Cathering Song), ImpriMed (CEO Sungwon Lim), Phantom AI (CEO Hyunggi Cho), B Garage (CEO Aiden Kim), and Simple Steps (CEO Doyeon Kim). Lectures contained vivid experiences from Silicon Valley CEOs and company tours boosted the students' passion for entrepreneurship. In particular, Doyeon Kim, CEO of Simple Steps, which helps prevent career breaks for Korean female immigrants in Silicon Valley and allows talented female immigrants to demonstrate their abilities in society, said, “As a KAIST alumna entrepreneur, it was meaningful to share my experience with this generation of students who dream of starting a global business and creating social enterprises in the United States.”
This program also included a tour of Silicon Valley's big tech companies that have made a significant impact on the digital ecosystem through technological advancement and innovation. This included Broadcom, which maintains a strong global presence in the semiconductor and infrastructure software technology fields. At the invitation of Chairman Hock Tan, GESS participants had the opportunity to attend his lecture and ask questions. Chairman Tan, who received an honorary doctorate in engineering from KAIST last February, emphasized that experiencing failure and giving consistent effort over a long period of time are more important than anything else in order to grow as a global entrepreneur, and that technologies influencing the global market evolve over generations.
< Photo. Group photo of GESS 2024 participants at Broadcom with Chairman Hock Tan (center) ⓒBroadcom>
As part of this program, participants conducted a volunteer program called 'Let's play with AI+ Tech' with the Sunnyvale community in Silicon Valley and Foothill College to help grow together with the community. Through this program, GESS participants cultivated the virtues of a global leader. In this volunteer activity, low-income elementary school students and parents from the Sunnyvale community participated in chatbot training led by KAIST students, providing an opportunity to work with underprivileged groups in the local community.
In the final pitching event, the highlight of the program, local venture investors from Silicon Valley were invited as judges and evaluated the pitches for each team's business items. The participating students, who developed their own business models while receiving advice through face-to-face mentoring from a professional accelerator in Silicon Valley, showcased their creative and innovative ideas, presenting themselves as future global entrepreneurs. Merey Makhmutova (BS in Civil and Environmental Engineering) from the K-Bridge team, who won the final pitch, expressed her ambition: “Even before GESS pitch day, our team kept refining the pitch deck as we attended the lectures and benefitted from the mentoring. Our intense teamwork was a significant reason why we ultimately won first prize.” She added that K-Bridge aims to win an award at the upcoming UKC Pitching Competition and expressed her gratitude for being able to participate in this program. Arseniy Kan (BS in Electrical Engineering) from the KAIST Enablers team, who took second place, said, “The 2024 KAIST GESS Program became the most unforgettable and precious opportunity of my lifetime, and I dream of using this opportunity as a stepping stone to becoming a global entrepreneur.“ Additionally, Kangster (CEO Kang Kim), who won the Impact MBA final pitching session, had the opportunity to secure a meeting with a local investment company after their GESS final pitch.
The 2024 KAIST GESS was held in cooperation with the KAIST International Office, the KAIST College of Business, and Startup KAIST. Director Man-Sung Yim from the Office of Global Initiatives, who hosted the event, said, “KAIST students will grow into leaders with global influence and contribute to the international community by creating global value. At the same time, we hope to raise the international status of our university.” Professor Sangchan Park, who led the 17 Impact MBA students in this educational program, added, “Meeting with companies leading the global market and visiting Silicon Valley has been a valuable learning experience for students aiming to start a global startup.”
KAIST plans to continue promoting its global entrepreneurship education program by enriching its curriculum each year and helping students grow into entrepreneurs with the virtues of global leaders.
2024.07.03 View 7241 -
 KAIST researchers developed a novel ultra-low power memory for neuromorphic computing
A team of Korean researchers is making headlines by developing a new memory device that can be used to replace existing memory or used in implementing neuromorphic computing for next-generation artificial intelligence hardware for its low processing costs and its ultra-low power consumption.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 4th that Professor Shinhyun Choi's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a next-generation phase change memory* device featuring ultra-low-power consumption that can replace DRAM and NAND flash memory.
☞ Phase change memory: A memory device that stores and/or processes information by changing the crystalline states of materials to be amorphous or crystalline using heat, thereby changing its resistance state.
Existing phase change memory has the problems such as expensive fabrication process for making highly scaled device and requiring substantial amount of power for operation. To solve these problems, Professor Choi’s research team developed an ultra-low power phase change memory device by electrically forming a very small nanometer (nm) scale phase changeable filament without expensive fabrication processes. This new development has the groundbreaking advantage of not only having a very low processing cost but also of enabling operating with ultra-low power consumption.
DRAM, one of the most popularly used memory, is very fast, but has volatile characteristics in which data disappears when the power is turned off. NAND flash memory, a storage device, has relatively slow read/write speeds, but it has non-volatile characteristic that enables it to preserve the data even when the power is cut off.
Phase change memory, on the other hand, combines the advantages of both DRAM and NAND flash memory, offering high speed and non-volatile characteristics. For this reason, phase change memory is being highlighted as the next-generation memory that can replace existing memory, and is being actively researched as a memory technology or neuromorphic computing technology that mimics the human brain.
However, conventional phase change memory devices require a substantial amount of power to operate, making it difficult to make practical large-capacity memory products or realize a neuromorphic computing system. In order to maximize the thermal efficiency for memory device operation, previous research efforts focused on reducing the power consumption by shrinking the physical size of the device through the use of the state-of-the-art lithography technologies, but they were met with limitations in terms of practicality as the degree of improvement in power consumption was minimal whereas the cost and the difficulty of fabrication increased with each improvement.
In order to solve the power consumption problem of phase change memory, Professor Shinhyun Choi’s research team created a method to electrically form phase change materials in extremely small area, successfully implementing an ultra-low-power phase change memory device that consumes 15 times less power than a conventional phase change memory device fabricated with the expensive lithography tool.
< Figure 1. Illustrations of the ultra-low power phase change memory device developed through this study and the comparison of power consumption by the newly developed phase change memory device compared to conventional phase change memory devices. >
Professor Shinhyun Choi expressed strong confidence in how this research will span out in the future in the new field of research saying, "The phase change memory device we have developed is significant as it offers a novel approach to solve the lingering problems in producing a memory device at a greatly improved manufacturing cost and energy efficiency. We expect the results of our study to become the foundation of future electronic engineering, enabling various applications including high-density three-dimensional vertical memory and neuromorphic computing systems as it opened up the possibilities to choose from a variety of materials.” He went on to add, “I would like to thank the National Research Foundation of Korea and the National NanoFab Center for supporting this research.”
This study, in which See-On Park, a student of MS-PhD Integrated Program, and Seokman Hong, a doctoral student of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, participated as first authors, was published on April 4 in the April issue of the renowned international academic journal Nature. (Paper title: Phase-Change Memory via a Phase-Changeable Self-Confined Nano-Filament)
This research was conducted with support from the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project, PIM AI Semiconductor Core Technology Development (Device) Project, Excellent Emerging Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Semiconductor Process-based Nanomedical Devices Development Project of the National NanoFab Center.
2024.04.04 View 7083
KAIST researchers developed a novel ultra-low power memory for neuromorphic computing
A team of Korean researchers is making headlines by developing a new memory device that can be used to replace existing memory or used in implementing neuromorphic computing for next-generation artificial intelligence hardware for its low processing costs and its ultra-low power consumption.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 4th that Professor Shinhyun Choi's research team in the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a next-generation phase change memory* device featuring ultra-low-power consumption that can replace DRAM and NAND flash memory.
☞ Phase change memory: A memory device that stores and/or processes information by changing the crystalline states of materials to be amorphous or crystalline using heat, thereby changing its resistance state.
Existing phase change memory has the problems such as expensive fabrication process for making highly scaled device and requiring substantial amount of power for operation. To solve these problems, Professor Choi’s research team developed an ultra-low power phase change memory device by electrically forming a very small nanometer (nm) scale phase changeable filament without expensive fabrication processes. This new development has the groundbreaking advantage of not only having a very low processing cost but also of enabling operating with ultra-low power consumption.
DRAM, one of the most popularly used memory, is very fast, but has volatile characteristics in which data disappears when the power is turned off. NAND flash memory, a storage device, has relatively slow read/write speeds, but it has non-volatile characteristic that enables it to preserve the data even when the power is cut off.
Phase change memory, on the other hand, combines the advantages of both DRAM and NAND flash memory, offering high speed and non-volatile characteristics. For this reason, phase change memory is being highlighted as the next-generation memory that can replace existing memory, and is being actively researched as a memory technology or neuromorphic computing technology that mimics the human brain.
However, conventional phase change memory devices require a substantial amount of power to operate, making it difficult to make practical large-capacity memory products or realize a neuromorphic computing system. In order to maximize the thermal efficiency for memory device operation, previous research efforts focused on reducing the power consumption by shrinking the physical size of the device through the use of the state-of-the-art lithography technologies, but they were met with limitations in terms of practicality as the degree of improvement in power consumption was minimal whereas the cost and the difficulty of fabrication increased with each improvement.
In order to solve the power consumption problem of phase change memory, Professor Shinhyun Choi’s research team created a method to electrically form phase change materials in extremely small area, successfully implementing an ultra-low-power phase change memory device that consumes 15 times less power than a conventional phase change memory device fabricated with the expensive lithography tool.
< Figure 1. Illustrations of the ultra-low power phase change memory device developed through this study and the comparison of power consumption by the newly developed phase change memory device compared to conventional phase change memory devices. >
Professor Shinhyun Choi expressed strong confidence in how this research will span out in the future in the new field of research saying, "The phase change memory device we have developed is significant as it offers a novel approach to solve the lingering problems in producing a memory device at a greatly improved manufacturing cost and energy efficiency. We expect the results of our study to become the foundation of future electronic engineering, enabling various applications including high-density three-dimensional vertical memory and neuromorphic computing systems as it opened up the possibilities to choose from a variety of materials.” He went on to add, “I would like to thank the National Research Foundation of Korea and the National NanoFab Center for supporting this research.”
This study, in which See-On Park, a student of MS-PhD Integrated Program, and Seokman Hong, a doctoral student of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, participated as first authors, was published on April 4 in the April issue of the renowned international academic journal Nature. (Paper title: Phase-Change Memory via a Phase-Changeable Self-Confined Nano-Filament)
This research was conducted with support from the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project, PIM AI Semiconductor Core Technology Development (Device) Project, Excellent Emerging Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Semiconductor Process-based Nanomedical Devices Development Project of the National NanoFab Center.
2024.04.04 View 7083 -
 A biohybrid system to extract 20 times more bioplastic from CO2 developed by KAIST researchers
As the issues surrounding global climate change intensify, more attention and determined efforts are required to re-grasp the issue as a state of “crisis” and respond to it properly. Among the various methods of recycling CO2, the electrochemical CO2 conversion technology is a technology that can convert CO2 into useful chemical substances using electrical energy. Since it is easy to operate facilities and can use the electricity from renewable sources like the solar cells or the wind power, it has received a lot of attention as an eco-friendly technology can contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and achieve carbon neutrality.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 30th that the joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering succeeded in developing a technology that produces bioplastics from CO2 with high efficiency by developing a hybrid system that interlinked the electrochemical CO2 conversion and microbial bio conversion methods together. The results of the research, which showed the world's highest productivity by more than 20 times compared to similar systems, were published online on March 27th in the "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS)".
※ Paper title: Biohybrid CO2 electrolysis for the direct synthesis of polyesters from CO2
※ Author information: Jinkyu Lim (currently at Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, co-first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Won Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Hyunjoo Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author)
For the efficient conversion of CO2, high-efficiency electrode catalysts and systems are actively being developed. As conversion products, only compounds containing one or up to three carbon atoms are produced on a limited basis. Compounds of one carbon, such as CO, formic acid, and ethylene, are produced with relatively high efficiency. Liquid compounds of several carbons, such as ethanol, acetic acid, and propanol, can also be produced by these systems, but due to the nature of the chemical reaction that requires more electrons, there are limitations involving the conversion efficiency and the product selection.
Accordingly, a joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a technology to produce bioplastics from CO2 by linking electrochemical conversion technology with bioconversion method that uses microorganisms.
This electrochemical-bio hybrid system is in the form of having an electrolyzer, in which electrochemical conversion reactions occur, connected to a fermenter, in which microorganisms are cultured. When CO2 is converted to formic acid in the electrolyzer, and it is fed into the fermenter in which the microbes like the Cupriavidus necator, in this case, consumes the carbon source to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a microbial-derived bioplastic.
According to the research results of the existing hybrid concepts, there was a disadvantage of having low productivity or stopping at a non-continuous process due to problems of low efficiency of the electrolysis and irregular results arising from the culturing conditions of the microbes.
In order to overcome these problems, the joint research team made formic acid with a gas diffusion electrode using gaseous CO2. In addition, the team developed a 'physiologically compatible catholyte' that can be used as a culture medium for microorganisms as well as an electrolyte that allows the electrolysis to occur sufficiently without inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, without having to have a additional separation and purification process, which allowed the acide to be supplied directly to microorganisms.
Through this, the electrolyte solution containing formic acid made from CO2 enters the fermentation tank, is used for microbial culture, and enters the electrolyzer to be circulated, maximizing the utilization of the electrolyte solution and remaining formic acid. In addition, a filter was installed to ensure that only the electrolyte solution with any and all microorganisms that can affect the electrosis filtered out is supplied back to the electrolyzer, and that the microorganisms exist only in the fermenter, designing the two system to work well together with utmost efficiency.
Through the developed hybrid system, the produced bioplastic, poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), of up to 83% of the cell dry weight was produced from CO2, which produced 1.38g of PHB from a 4 cm2 electrode, which is the world's first gram(g) level production and is more than 20 times more productive than previous research. In addition, the hybrid system is expected to be applied to various industrial processes in the future as it shows promises of the continuous culture system.
The corresponding authors, Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted that “The results of this research are technologies that can be applied to the production of various chemical substances as well as bioplastics, and are expected to be used as key parts needed in achieving carbon neutrality in the future.”
This research was received and performed with the supports from the CO2 Reduction Catalyst and Energy Device Technology Development Project, the Heterogeneous Atomic Catalyst Control Project, and the Next-generation Biorefinery Source Technology Development Project to lead the Biochemical Industry of the Oil-replacement Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram and photo of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system.
(A) A conceptual scheme and (B) a photograph of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system. (C) A detailed scheme of reaction inside the system. Gaseous CO2 was converted to formate in the electrolyzer, and the formate was converted to PHB by the cells in the fermenter. The catholyte was developed so that it is compatible with both CO2 electrolysis and fermentation and was continuously circulated.
2023.03.30 View 9970
A biohybrid system to extract 20 times more bioplastic from CO2 developed by KAIST researchers
As the issues surrounding global climate change intensify, more attention and determined efforts are required to re-grasp the issue as a state of “crisis” and respond to it properly. Among the various methods of recycling CO2, the electrochemical CO2 conversion technology is a technology that can convert CO2 into useful chemical substances using electrical energy. Since it is easy to operate facilities and can use the electricity from renewable sources like the solar cells or the wind power, it has received a lot of attention as an eco-friendly technology can contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and achieve carbon neutrality.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 30th that the joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering succeeded in developing a technology that produces bioplastics from CO2 with high efficiency by developing a hybrid system that interlinked the electrochemical CO2 conversion and microbial bio conversion methods together. The results of the research, which showed the world's highest productivity by more than 20 times compared to similar systems, were published online on March 27th in the "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS)".
※ Paper title: Biohybrid CO2 electrolysis for the direct synthesis of polyesters from CO2
※ Author information: Jinkyu Lim (currently at Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, co-first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Won Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Hyunjoo Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author)
For the efficient conversion of CO2, high-efficiency electrode catalysts and systems are actively being developed. As conversion products, only compounds containing one or up to three carbon atoms are produced on a limited basis. Compounds of one carbon, such as CO, formic acid, and ethylene, are produced with relatively high efficiency. Liquid compounds of several carbons, such as ethanol, acetic acid, and propanol, can also be produced by these systems, but due to the nature of the chemical reaction that requires more electrons, there are limitations involving the conversion efficiency and the product selection.
Accordingly, a joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a technology to produce bioplastics from CO2 by linking electrochemical conversion technology with bioconversion method that uses microorganisms.
This electrochemical-bio hybrid system is in the form of having an electrolyzer, in which electrochemical conversion reactions occur, connected to a fermenter, in which microorganisms are cultured. When CO2 is converted to formic acid in the electrolyzer, and it is fed into the fermenter in which the microbes like the Cupriavidus necator, in this case, consumes the carbon source to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a microbial-derived bioplastic.
According to the research results of the existing hybrid concepts, there was a disadvantage of having low productivity or stopping at a non-continuous process due to problems of low efficiency of the electrolysis and irregular results arising from the culturing conditions of the microbes.
In order to overcome these problems, the joint research team made formic acid with a gas diffusion electrode using gaseous CO2. In addition, the team developed a 'physiologically compatible catholyte' that can be used as a culture medium for microorganisms as well as an electrolyte that allows the electrolysis to occur sufficiently without inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, without having to have a additional separation and purification process, which allowed the acide to be supplied directly to microorganisms.
Through this, the electrolyte solution containing formic acid made from CO2 enters the fermentation tank, is used for microbial culture, and enters the electrolyzer to be circulated, maximizing the utilization of the electrolyte solution and remaining formic acid. In addition, a filter was installed to ensure that only the electrolyte solution with any and all microorganisms that can affect the electrosis filtered out is supplied back to the electrolyzer, and that the microorganisms exist only in the fermenter, designing the two system to work well together with utmost efficiency.
Through the developed hybrid system, the produced bioplastic, poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), of up to 83% of the cell dry weight was produced from CO2, which produced 1.38g of PHB from a 4 cm2 electrode, which is the world's first gram(g) level production and is more than 20 times more productive than previous research. In addition, the hybrid system is expected to be applied to various industrial processes in the future as it shows promises of the continuous culture system.
The corresponding authors, Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted that “The results of this research are technologies that can be applied to the production of various chemical substances as well as bioplastics, and are expected to be used as key parts needed in achieving carbon neutrality in the future.”
This research was received and performed with the supports from the CO2 Reduction Catalyst and Energy Device Technology Development Project, the Heterogeneous Atomic Catalyst Control Project, and the Next-generation Biorefinery Source Technology Development Project to lead the Biochemical Industry of the Oil-replacement Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram and photo of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system.
(A) A conceptual scheme and (B) a photograph of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system. (C) A detailed scheme of reaction inside the system. Gaseous CO2 was converted to formate in the electrolyzer, and the formate was converted to PHB by the cells in the fermenter. The catholyte was developed so that it is compatible with both CO2 electrolysis and fermentation and was continuously circulated.
2023.03.30 View 9970 -
 Scientists re-writes FDA-recommended equation to improve estimation of drug-drug interaction
Drugs absorbed into the body are metabolized and thus removed by enzymes from several organs like the liver. How fast a drug is cleared out of the system can be affected by other drugs that are taken together because added substance can increase the amount of enzyme secretion in the body. This dramatically decreases the concentration of a drug, reducing its efficacy, often leading to the failure of having any effect at all. Therefore, accurately predicting the clearance rate in the presence of drug-drug interaction* is critical in the process of drug prescription and development of a new drug in order to ensure its efficacy and/or to avoid unwanted side-effects.
*Drug-drug interaction: In terms of metabolism, drug-drug interaction is a phenomenon in which one drug changes the metabolism of another drug to promote or inhibit its excretion from the body when two or more drugs are taken together. As a result, it increases the toxicity of medicines or causes loss of efficacy.
Since it is practically impossible to evaluate all interactions between new drug candidates and all marketed drugs during the development process, the FDA recommends indirect evaluation of drug interactions using a formula suggested in their guidance, first published in 1997, revised in January of 2020, in order to evaluate drug interactions and minimize side effects of having to use more than one type of drugs at once.
The formula relies on the 110-year-old Michaelis-Menten (MM) model, which has a fundamental limit of making a very broad and groundless assumption on the part of the presence of the enzymes that metabolizes the drug. While MM equation has been one of the most widely known equations in biochemistry used in more than 220,000 published papers, the MM equation is accurate only when the concentration of the enzyme that metabolizes the drug is almost non-existent, causing the accuracy of the equation highly unsatisfactory – only 38 percent of the predictions had less than two-fold errors.
“To make up for the gap, researcher resorted to plugging in scientifically unjustified constants into the equation,” Professor Jung-woo Chae of Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy said. “This is comparable to having to have the epicyclic orbits introduced to explain the motion of the planets back in the days in order to explain the now-defunct Ptolemaic theory, because it was 'THE' theory back then.”
< (From left) Ph.D. student Yun Min Song (KAIST, co-first authors), Professor Sang Kyum Kim (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Jae Kyoung Kim, CI (KAIST, co-corresponding author), Professor Jung-woo Chae (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Ph.D. students Quyen Thi Tran and Ngoc-Anh Thi Vu (Chungnam National University, co-first authors) >
A joint research team composed of mathematicians from the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and pharmacological scientists from the Chungnam National University reported that they identified the major causes of the FDA-recommended equation’s inaccuracies and presented a solution.
When estimating the gut bioavailability (Fg), which is the key parameter of the equation, the fraction absorbed from the gut lumen (Fa) is usually assumed to be 1. However, many experiments have shown that Fa is less than 1, obviously since it can’t be expected that all of the orally taken drugs to be completely absorbed by the intestines. To solve this problem, the research team used an “estimated Fa” value based on factors such as the drug’s transit time, intestine radius, and permeability values and used it to re-calculate Fg.
Also, taking a different approach from the MM equation, the team used an alternative model they derived in a previous study back in 2020, which can more accurately predict the drug metabolism rate regardless of the enzyme concentration. Combining these changes, the modified equation with re-calculated Fg had a dramatically increased accuracy of the resulting estimate. The existing FDA formula predicted drug interactions within a 2-fold margin of error at the rate of 38%, whereas the accuracy rate of the revised formula reached 80%.
“Such drastic improvement in drug-drug interaction prediction accuracy is expected to make great contribution to increasing the success rate of new drug development and drug efficacy in clinical trials. As the results of this study were published in one of the top clinical pharmacology journal, it is expected that the FDA guidance will be revised according to the results of this study.” said Professor Sang Kyum Kim from Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy.
Furthermore, this study highlights the importance of collaborative research between research groups in vastly different disciplines, in a field that is as dynamic as drug interactions.
“Thanks to the collaborative research between mathematics and pharmacy, we were able to recify the formula that we have accepted to be the right answer for so long to finally grasp on the leads toward healthier life for mankind.,” said Professor Jae Kyung Kim. He continued, “I hope seeing a ‘K-formula’ entered into the US FDA guidance one day.”
The results of this study were published in the online edition of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (IF 7.051), an authoritative journal in the field of clinical pharmacology, on December 15, 2022 (Korean time).
Thesis Title: Beyond the Michaelis-Menten: Accurate Prediction of Drug Interactions through Cytochrome P450 3A4 Induction (doi: 10.1002/cpt.2824)
< Figure 1. The formula proposed by the FDA guidance for predicting drug-drug interactions (top) and the formula newly derived by the researchers (bottom). AUCR (the ratio of substrate area under the plasma concentration-time curve) represents the rate of change in drug concentration due to drug interactions. The research team more than doubled the accuracy of drug interaction prediction compared to the existing formula. >
< Figure 2. Existing FDA formulas tend to underestimate the extent of drug-drug interactions (gray dots) than the actual measured values. On the other hand, the newly derived equation (red dot) has a prediction rate that is within the error range of 2 times (0.5 to 2 times) of the measured value, and is more than twice as high as the existing equation. The solid line in the figure represents the predicted value that matches the measured value. The dotted line represents the predicted value with an error of 0.5 to 2 times. >
For further information or to request media assistance, please contact Jae Kyoung Kim at Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science (IBS) (jaekkim@ibs.re.kr) or William I. Suh at the IBS Communications Team (willisuh@ibs.re.kr).
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
IBS was founded in 2011 by the government of the Republic of Korea with the sole purpose of driving forward the development of basic science in South Korea. IBS has 4 research institutes and 33 research centers as of January 2023. There are eleven physics, three mathematics, five chemistry, nine life science, two earth science, and three interdisciplinary research centers.
2023.01.18 View 12765
Scientists re-writes FDA-recommended equation to improve estimation of drug-drug interaction
Drugs absorbed into the body are metabolized and thus removed by enzymes from several organs like the liver. How fast a drug is cleared out of the system can be affected by other drugs that are taken together because added substance can increase the amount of enzyme secretion in the body. This dramatically decreases the concentration of a drug, reducing its efficacy, often leading to the failure of having any effect at all. Therefore, accurately predicting the clearance rate in the presence of drug-drug interaction* is critical in the process of drug prescription and development of a new drug in order to ensure its efficacy and/or to avoid unwanted side-effects.
*Drug-drug interaction: In terms of metabolism, drug-drug interaction is a phenomenon in which one drug changes the metabolism of another drug to promote or inhibit its excretion from the body when two or more drugs are taken together. As a result, it increases the toxicity of medicines or causes loss of efficacy.
Since it is practically impossible to evaluate all interactions between new drug candidates and all marketed drugs during the development process, the FDA recommends indirect evaluation of drug interactions using a formula suggested in their guidance, first published in 1997, revised in January of 2020, in order to evaluate drug interactions and minimize side effects of having to use more than one type of drugs at once.
The formula relies on the 110-year-old Michaelis-Menten (MM) model, which has a fundamental limit of making a very broad and groundless assumption on the part of the presence of the enzymes that metabolizes the drug. While MM equation has been one of the most widely known equations in biochemistry used in more than 220,000 published papers, the MM equation is accurate only when the concentration of the enzyme that metabolizes the drug is almost non-existent, causing the accuracy of the equation highly unsatisfactory – only 38 percent of the predictions had less than two-fold errors.
“To make up for the gap, researcher resorted to plugging in scientifically unjustified constants into the equation,” Professor Jung-woo Chae of Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy said. “This is comparable to having to have the epicyclic orbits introduced to explain the motion of the planets back in the days in order to explain the now-defunct Ptolemaic theory, because it was 'THE' theory back then.”
< (From left) Ph.D. student Yun Min Song (KAIST, co-first authors), Professor Sang Kyum Kim (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Jae Kyoung Kim, CI (KAIST, co-corresponding author), Professor Jung-woo Chae (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Ph.D. students Quyen Thi Tran and Ngoc-Anh Thi Vu (Chungnam National University, co-first authors) >
A joint research team composed of mathematicians from the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and pharmacological scientists from the Chungnam National University reported that they identified the major causes of the FDA-recommended equation’s inaccuracies and presented a solution.
When estimating the gut bioavailability (Fg), which is the key parameter of the equation, the fraction absorbed from the gut lumen (Fa) is usually assumed to be 1. However, many experiments have shown that Fa is less than 1, obviously since it can’t be expected that all of the orally taken drugs to be completely absorbed by the intestines. To solve this problem, the research team used an “estimated Fa” value based on factors such as the drug’s transit time, intestine radius, and permeability values and used it to re-calculate Fg.
Also, taking a different approach from the MM equation, the team used an alternative model they derived in a previous study back in 2020, which can more accurately predict the drug metabolism rate regardless of the enzyme concentration. Combining these changes, the modified equation with re-calculated Fg had a dramatically increased accuracy of the resulting estimate. The existing FDA formula predicted drug interactions within a 2-fold margin of error at the rate of 38%, whereas the accuracy rate of the revised formula reached 80%.
“Such drastic improvement in drug-drug interaction prediction accuracy is expected to make great contribution to increasing the success rate of new drug development and drug efficacy in clinical trials. As the results of this study were published in one of the top clinical pharmacology journal, it is expected that the FDA guidance will be revised according to the results of this study.” said Professor Sang Kyum Kim from Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy.
Furthermore, this study highlights the importance of collaborative research between research groups in vastly different disciplines, in a field that is as dynamic as drug interactions.
“Thanks to the collaborative research between mathematics and pharmacy, we were able to recify the formula that we have accepted to be the right answer for so long to finally grasp on the leads toward healthier life for mankind.,” said Professor Jae Kyung Kim. He continued, “I hope seeing a ‘K-formula’ entered into the US FDA guidance one day.”
The results of this study were published in the online edition of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (IF 7.051), an authoritative journal in the field of clinical pharmacology, on December 15, 2022 (Korean time).
Thesis Title: Beyond the Michaelis-Menten: Accurate Prediction of Drug Interactions through Cytochrome P450 3A4 Induction (doi: 10.1002/cpt.2824)
< Figure 1. The formula proposed by the FDA guidance for predicting drug-drug interactions (top) and the formula newly derived by the researchers (bottom). AUCR (the ratio of substrate area under the plasma concentration-time curve) represents the rate of change in drug concentration due to drug interactions. The research team more than doubled the accuracy of drug interaction prediction compared to the existing formula. >
< Figure 2. Existing FDA formulas tend to underestimate the extent of drug-drug interactions (gray dots) than the actual measured values. On the other hand, the newly derived equation (red dot) has a prediction rate that is within the error range of 2 times (0.5 to 2 times) of the measured value, and is more than twice as high as the existing equation. The solid line in the figure represents the predicted value that matches the measured value. The dotted line represents the predicted value with an error of 0.5 to 2 times. >
For further information or to request media assistance, please contact Jae Kyoung Kim at Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science (IBS) (jaekkim@ibs.re.kr) or William I. Suh at the IBS Communications Team (willisuh@ibs.re.kr).
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
IBS was founded in 2011 by the government of the Republic of Korea with the sole purpose of driving forward the development of basic science in South Korea. IBS has 4 research institutes and 33 research centers as of January 2023. There are eleven physics, three mathematics, five chemistry, nine life science, two earth science, and three interdisciplinary research centers.
2023.01.18 View 12765 -
 Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 12879
Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 12879 -
 A New Therapeutic Drug for Alzheimer’s Disease without Inflammatory Side Effects
Although Aduhelm, a monoclonal antibody targeting amyloid beta (Aβ), recently became the first US FDA approved drug for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) based on its ability to decrease Aβ plaque burden in AD patients, its effect on cognitive improvement is still controversial. Moreover, about 40% of the patients treated with this antibody experienced serious side effects including cerebral edemas (ARIA-E) and hemorrhages (ARIA-H) that are likely related to inflammatory responses in the brain when the Aβ antibody binds Fc receptors (FCR) of immune cells such as microglia and macrophages.
These inflammatory side effects can cause neuronal cell death and synapse elimination by activated microglia, and even have the potential to exacerbate cognitive impairment in AD patients. Thus, current Aβ antibody-based immunotherapy holds the inherent risk of doing more harm than good due to their inflammatory side effects.
To overcome these problems, a team of researchers at KAIST in South Korea has developed a novel fusion protein drug, αAβ-Gas6, which efficiently eliminates Aβ via an entirely different mechanism than Aβ antibody-based immunotherapy. In a mouse model of AD, αAβ-Gas6 not only removed Aβ with higher potency, but also circumvented the neurotoxic inflammatory side effects associated with conventional antibody treatments.
Their findings were published on August 4 in Nature Medicine.
Schematic of a chimeric Gas6 fusion protein. A single chain variable fragment (scFv) of
an Amyloid β (Aβ)-targeting monoclonal antibody is fused with a truncated receptor binding
domain of Gas6, a bridging molecule for the clearance of dead cells via TAM (TYRO3, AXL,
and MERTK) receptors, which are expressed by microglia and astrocytes.
“FcR activation by Aβ targeting antibodies induces microglia-mediated Aβ phagocytosis, but it also produces inflammatory signals, inevitably damaging brain tissues,” said paper authors Chan Hyuk Kim and Won-Suk Chung, associate professors in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST.
“Therefore, we utilized efferocytosis, a cellular process by which dead cells are removed by phagocytes as an alternative pathway for the clearance of Aβ in the brain,” Prof. Kim and Chung said. “Efferocytosis is accompanied by anti-inflammatory responses to maintain tissue homeostasis. To exploit this process, we engineered Gas6, a soluble adaptor protein that mediates efferocytosis via TAM phagocytic receptors in such a way that its target specificity was redirected from dead cells to Aβ plaques.”
The professors and their team demonstrated that the resulting αAβ-Gas6 induced Aβ engulfment by activating not only microglial but also astrocytic phagocytosis since TAM phagocytic receptors are highly expressed by these two major phagocytes in the brain. Importantly, αAβ-Gas6 promoted the robust uptake of Aβ without showing any signs of inflammation and neurotoxicity, which contrasts sharply with the treatment using an Aβ monoclonal antibody. Moreover, they showed that αAβ-Gas6 substantially reduced excessive synapse elimination by microglia, consequently leading to better behavioral rescues in AD model mice.
“By using a mouse model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), a cerebrovascular disorder caused by the deposition of Aβ within the walls of the brain’s blood vessels, we also showed that the intrathecal administration of Gas6 fusion protein significantly eliminated cerebrovascular amyloids, along with a reduction of microhemorrhages. These data demonstrate that aAb-Gas6 is a potent therapeutic agent in eliminating Aβ without exacerbating CAA-related microhemorrhages.”
The resulting αAβ-Gas6 clears Aβ oligomers and fibrils without causing neurotoxicity (a-b, neurons: red, and fragmented axons: yellow) and proinflammatory responses (c, TNF release), which are conversely exacerbated by the treatment of an Aβ-targeting monoclonal antibody (Aducanumab).
Professors Kim and Chung noted, “We believe our approach can be a breakthrough in treating AD without causing inflammatory side effects and synapse loss. Our approach holds promise as a novel therapeutic platform that is applicable to more than AD. By modifying the target-specificity of the fusion protein, the Gas6-fusion protein can be applied to various neurological disorders as well as autoimmune diseases affected by toxic molecules that should be removed without causing inflammatory responses.”
The number and total area of Aβ plaques (Thioflavin-T, green) were significantly reduced in αAβ-Gas6-treated AD mouse brains compared to Aducanumab-treated ones (a, b). The cognitive functions of AD model mice were significantly rescued by αAβ-Gas6 treatment, whereas Aducanumab-treated AD mice showed partial rescue in these cognitive tests (c-e).
Professors Kim and Chung founded “Illimis Therapeutics” based on this strategy of designing chimeric Gas6 fusion proteins that would remove toxic aggregates from the nervous system. Through this company, they are planning to further develop various Gas6-fusion proteins not only for Ab but also for Tau to treat AD symptoms.
This work was supported by KAIST and the Korea Health Technology R&D Project that was administered by the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) and the Korea Dementia Research Center (KDRC) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare (MOHW) and the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), and KAIST.
Other contributors include Hyuncheol Jung and Se Young Lee, Sungjoon Lim, Hyeong Ryeol Choi, Yeseong Choi, Minjin Kim, Segi Kim, the Department of Biological Sciences, and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST).
To receive more up-to-date information on this new development, follow “Illimis Therapeutics” on twitter @Illimistx.
2022.08.05 View 11975
A New Therapeutic Drug for Alzheimer’s Disease without Inflammatory Side Effects
Although Aduhelm, a monoclonal antibody targeting amyloid beta (Aβ), recently became the first US FDA approved drug for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) based on its ability to decrease Aβ plaque burden in AD patients, its effect on cognitive improvement is still controversial. Moreover, about 40% of the patients treated with this antibody experienced serious side effects including cerebral edemas (ARIA-E) and hemorrhages (ARIA-H) that are likely related to inflammatory responses in the brain when the Aβ antibody binds Fc receptors (FCR) of immune cells such as microglia and macrophages.
These inflammatory side effects can cause neuronal cell death and synapse elimination by activated microglia, and even have the potential to exacerbate cognitive impairment in AD patients. Thus, current Aβ antibody-based immunotherapy holds the inherent risk of doing more harm than good due to their inflammatory side effects.
To overcome these problems, a team of researchers at KAIST in South Korea has developed a novel fusion protein drug, αAβ-Gas6, which efficiently eliminates Aβ via an entirely different mechanism than Aβ antibody-based immunotherapy. In a mouse model of AD, αAβ-Gas6 not only removed Aβ with higher potency, but also circumvented the neurotoxic inflammatory side effects associated with conventional antibody treatments.
Their findings were published on August 4 in Nature Medicine.
Schematic of a chimeric Gas6 fusion protein. A single chain variable fragment (scFv) of
an Amyloid β (Aβ)-targeting monoclonal antibody is fused with a truncated receptor binding
domain of Gas6, a bridging molecule for the clearance of dead cells via TAM (TYRO3, AXL,
and MERTK) receptors, which are expressed by microglia and astrocytes.
“FcR activation by Aβ targeting antibodies induces microglia-mediated Aβ phagocytosis, but it also produces inflammatory signals, inevitably damaging brain tissues,” said paper authors Chan Hyuk Kim and Won-Suk Chung, associate professors in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST.
“Therefore, we utilized efferocytosis, a cellular process by which dead cells are removed by phagocytes as an alternative pathway for the clearance of Aβ in the brain,” Prof. Kim and Chung said. “Efferocytosis is accompanied by anti-inflammatory responses to maintain tissue homeostasis. To exploit this process, we engineered Gas6, a soluble adaptor protein that mediates efferocytosis via TAM phagocytic receptors in such a way that its target specificity was redirected from dead cells to Aβ plaques.”
The professors and their team demonstrated that the resulting αAβ-Gas6 induced Aβ engulfment by activating not only microglial but also astrocytic phagocytosis since TAM phagocytic receptors are highly expressed by these two major phagocytes in the brain. Importantly, αAβ-Gas6 promoted the robust uptake of Aβ without showing any signs of inflammation and neurotoxicity, which contrasts sharply with the treatment using an Aβ monoclonal antibody. Moreover, they showed that αAβ-Gas6 substantially reduced excessive synapse elimination by microglia, consequently leading to better behavioral rescues in AD model mice.
“By using a mouse model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), a cerebrovascular disorder caused by the deposition of Aβ within the walls of the brain’s blood vessels, we also showed that the intrathecal administration of Gas6 fusion protein significantly eliminated cerebrovascular amyloids, along with a reduction of microhemorrhages. These data demonstrate that aAb-Gas6 is a potent therapeutic agent in eliminating Aβ without exacerbating CAA-related microhemorrhages.”
The resulting αAβ-Gas6 clears Aβ oligomers and fibrils without causing neurotoxicity (a-b, neurons: red, and fragmented axons: yellow) and proinflammatory responses (c, TNF release), which are conversely exacerbated by the treatment of an Aβ-targeting monoclonal antibody (Aducanumab).
Professors Kim and Chung noted, “We believe our approach can be a breakthrough in treating AD without causing inflammatory side effects and synapse loss. Our approach holds promise as a novel therapeutic platform that is applicable to more than AD. By modifying the target-specificity of the fusion protein, the Gas6-fusion protein can be applied to various neurological disorders as well as autoimmune diseases affected by toxic molecules that should be removed without causing inflammatory responses.”
The number and total area of Aβ plaques (Thioflavin-T, green) were significantly reduced in αAβ-Gas6-treated AD mouse brains compared to Aducanumab-treated ones (a, b). The cognitive functions of AD model mice were significantly rescued by αAβ-Gas6 treatment, whereas Aducanumab-treated AD mice showed partial rescue in these cognitive tests (c-e).
Professors Kim and Chung founded “Illimis Therapeutics” based on this strategy of designing chimeric Gas6 fusion proteins that would remove toxic aggregates from the nervous system. Through this company, they are planning to further develop various Gas6-fusion proteins not only for Ab but also for Tau to treat AD symptoms.
This work was supported by KAIST and the Korea Health Technology R&D Project that was administered by the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) and the Korea Dementia Research Center (KDRC) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare (MOHW) and the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), and KAIST.
Other contributors include Hyuncheol Jung and Se Young Lee, Sungjoon Lim, Hyeong Ryeol Choi, Yeseong Choi, Minjin Kim, Segi Kim, the Department of Biological Sciences, and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST).
To receive more up-to-date information on this new development, follow “Illimis Therapeutics” on twitter @Illimistx.
2022.08.05 View 11975 -
 New Polymer Mesophase Structure Discovered
Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymer sequence
Polymers, large molecules made up of repeating smaller molecules called monomers, are found in nearly everything we use in our day-to-day lives. Polymers can be natural or created synthetically. Natural polymers, also called biopolymers, include DNA, proteins, and materials like silk, gelatin, and collagen. Synthetic polymers make up many different kinds of materials, including plastic, that are used in constructing everything from toys to industrial fiber cables to brake pads.
As polymers are formed through a process called polymerization, the monomers are connected through a chain. As the chain develops, the structure of the polymer determines its unique physical and chemical properties. Researchers are continually studying polymers, how they form, how they are structured, and how they develop these unique properties. By understanding this information, scientists can develop new uses for polymers and create new materials that can be used in a wide variety of industries.
In a paper published in Nature Communications on May 4, researchers describe a new structure found in an aqueous solution of an amphiphilic copolymer, called a bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase, that has been discovered through a random copolymer sequence.
“A new mesophase is an important discovery as it shows a new way for molecules to self-organize,” said Professor Myungeun Seo at the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. “We were particularly thrilled to identify this bilayer-folded lamellar phase because pure bilayer membranes are difficult to fold thermodynamically.”
Researchers think that this mesophase structure comes from the sequence of the monomers within the copolymer. The way the different monomers arrange themselves in the chain that makes up a copolymer is important and can have implications for what the copolymer can do. Many copolymers are random, which means that their structure relies on how the monomers interact with each other. In this case, the interaction between the hydrophobic monomers associates the copolymer chains to conceal the hydrophobic domain from water. As the structure gets more complex, researchers have found that a visible order develops so that monomers can be matched up with the right pair.
“While we tend to think random means disorder, here we showed that a periodic order can spontaneously arise from the random copolymer sequence based on their collective behavior,” said Professor Seo. “We believe this comes from the sequence matching problem: finding a perfectly complementary pair for a long sequence is nearly impossible.”
This is what creates the unique structure of this newly discovered mesophase. The copolymer spontaneously folds and creates a multilamellar structure that is separated by water. A multilamellar structure refers to plate-like folds and the folded layers stack on top of each other. The resulting mesophase is birefringent, meaning light refracts through it, it is similar to liquid crystalline, and viscoelastic, which means that it is both viscous and elastic at the same time.
Looking ahead, researchers hope to learn more about this new mesophase and figure out how to control the outcome. Once more is understood about the mesophase and how it is formed, it’s possible that new mesophases could be discovered as more sequences are researched. “One of the obvious questions for us is how to control the folding frequency and adjust the folded height, which we are currently working to address. Ultimately, we want to understand how different multinary sequences can associate with another to create order and apply the knowledge to develop new materials,” said Professor Seo. The National Research Foundation, the Ministry of Education, and the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea funded this research.
-PublicationMinjoong Shin, Hayeon Kim, Geonhyeong Park, Jongmin Park, Hyungju Ahn, Dong Ki Yoon, Eunji Lee, Myungeun Seo, “Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymersequence,” May 4, 2022, Nature Communications (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30122-z)
-ProfileProfessor Myungeun SeoMacromolecular Materials Chemistry Lab (https://nanopsg.kaist.ac.kr/)Department of ChemistryCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.06.17 View 8620
New Polymer Mesophase Structure Discovered
Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymer sequence
Polymers, large molecules made up of repeating smaller molecules called monomers, are found in nearly everything we use in our day-to-day lives. Polymers can be natural or created synthetically. Natural polymers, also called biopolymers, include DNA, proteins, and materials like silk, gelatin, and collagen. Synthetic polymers make up many different kinds of materials, including plastic, that are used in constructing everything from toys to industrial fiber cables to brake pads.
As polymers are formed through a process called polymerization, the monomers are connected through a chain. As the chain develops, the structure of the polymer determines its unique physical and chemical properties. Researchers are continually studying polymers, how they form, how they are structured, and how they develop these unique properties. By understanding this information, scientists can develop new uses for polymers and create new materials that can be used in a wide variety of industries.
In a paper published in Nature Communications on May 4, researchers describe a new structure found in an aqueous solution of an amphiphilic copolymer, called a bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase, that has been discovered through a random copolymer sequence.
“A new mesophase is an important discovery as it shows a new way for molecules to self-organize,” said Professor Myungeun Seo at the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. “We were particularly thrilled to identify this bilayer-folded lamellar phase because pure bilayer membranes are difficult to fold thermodynamically.”
Researchers think that this mesophase structure comes from the sequence of the monomers within the copolymer. The way the different monomers arrange themselves in the chain that makes up a copolymer is important and can have implications for what the copolymer can do. Many copolymers are random, which means that their structure relies on how the monomers interact with each other. In this case, the interaction between the hydrophobic monomers associates the copolymer chains to conceal the hydrophobic domain from water. As the structure gets more complex, researchers have found that a visible order develops so that monomers can be matched up with the right pair.
“While we tend to think random means disorder, here we showed that a periodic order can spontaneously arise from the random copolymer sequence based on their collective behavior,” said Professor Seo. “We believe this comes from the sequence matching problem: finding a perfectly complementary pair for a long sequence is nearly impossible.”
This is what creates the unique structure of this newly discovered mesophase. The copolymer spontaneously folds and creates a multilamellar structure that is separated by water. A multilamellar structure refers to plate-like folds and the folded layers stack on top of each other. The resulting mesophase is birefringent, meaning light refracts through it, it is similar to liquid crystalline, and viscoelastic, which means that it is both viscous and elastic at the same time.
Looking ahead, researchers hope to learn more about this new mesophase and figure out how to control the outcome. Once more is understood about the mesophase and how it is formed, it’s possible that new mesophases could be discovered as more sequences are researched. “One of the obvious questions for us is how to control the folding frequency and adjust the folded height, which we are currently working to address. Ultimately, we want to understand how different multinary sequences can associate with another to create order and apply the knowledge to develop new materials,” said Professor Seo. The National Research Foundation, the Ministry of Education, and the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea funded this research.
-PublicationMinjoong Shin, Hayeon Kim, Geonhyeong Park, Jongmin Park, Hyungju Ahn, Dong Ki Yoon, Eunji Lee, Myungeun Seo, “Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymersequence,” May 4, 2022, Nature Communications (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30122-z)
-ProfileProfessor Myungeun SeoMacromolecular Materials Chemistry Lab (https://nanopsg.kaist.ac.kr/)Department of ChemistryCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.06.17 View 8620 -
 AI Weather Forecasting Research Center Opens
The Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI in collaboration with the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences (NIMS) under the National Meteorological Administration launched the AI Weather Forecasting Research Center last month.
The KAIST AI Weather Forecasting Research Center headed by Professor Seyoung Yoon was established with funding from from the AlphaWeather Development Research Project of the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences. KAIST was finally selected asas the project facilitator.
AlphaWeather is an AI system that utilizes and analyzes approximately approximately 150,000 ,000 pieces of weather information per hour to help weather forecasters produce accurate weather forecasts. The research center is composed of three research teams with the following goals: (a) developdevelop AI technology for precipitation nowcasting, (b) developdevelop AI technology for accelerating physical process-based numerical models, and (c) develop dAI technology for supporting weather forecasters. The teams consist of 15 staff member members from NIMS and 61 researchers from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST.
The research center is developing an AI algorithm for precipitation nowcasting (with up to six hours of lead time), which uses satellite images, radar reflectivity, and data collected from weather stations. It is also developing an AI algorithm for correcting biases in the prediction results from multiple numerical models. Finally, it is Finally, it is developing AI technology that supports weather forecasters by standardizing and automating repetitive manual processes. After verification, the the results obtained will be used by by the Korean National Weather Service as a next-generation forecasting/special-reporting system intelligence engine from 2026.
2022.01.10 View 6328
AI Weather Forecasting Research Center Opens
The Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI in collaboration with the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences (NIMS) under the National Meteorological Administration launched the AI Weather Forecasting Research Center last month.
The KAIST AI Weather Forecasting Research Center headed by Professor Seyoung Yoon was established with funding from from the AlphaWeather Development Research Project of the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences. KAIST was finally selected asas the project facilitator.
AlphaWeather is an AI system that utilizes and analyzes approximately approximately 150,000 ,000 pieces of weather information per hour to help weather forecasters produce accurate weather forecasts. The research center is composed of three research teams with the following goals: (a) developdevelop AI technology for precipitation nowcasting, (b) developdevelop AI technology for accelerating physical process-based numerical models, and (c) develop dAI technology for supporting weather forecasters. The teams consist of 15 staff member members from NIMS and 61 researchers from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST.
The research center is developing an AI algorithm for precipitation nowcasting (with up to six hours of lead time), which uses satellite images, radar reflectivity, and data collected from weather stations. It is also developing an AI algorithm for correcting biases in the prediction results from multiple numerical models. Finally, it is Finally, it is developing AI technology that supports weather forecasters by standardizing and automating repetitive manual processes. After verification, the the results obtained will be used by by the Korean National Weather Service as a next-generation forecasting/special-reporting system intelligence engine from 2026.
2022.01.10 View 6328 -
 A Study Shows Reactive Electrolyte Additives Improve Lithium Metal Battery Performance
Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives provide an opportunity to improve high-performance lithium metal batteries
A research team showed that electrolyte additives increase the lifetime of lithium metal batteries and remarkably improve the performance of fast charging and discharging. Professor Nam-Soon Choi’s team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST hierarchized the solid electrolyte interphase to make a dual-layer structure and showed groundbreaking run times for lithium metal batteries.
The team applied two electrolyte additives that have different reduction and adsorption properties to improve the functionality of the dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase. In addition, the team has confirmed that the structural stability of the nickel-rich cathode was achieved through the formation of a thin protective layer on the cathode. This study was reported in Energy Storage Materials.
Securing high-energy-density lithium metal batteries with a long lifespan and fast charging performance is vital for realizing their ubiquitous use as superior power sources for electric vehicles. Lithium metal batteries comprise a lithium metal anode that delivers 10 times higher capacity than the graphite anodes in lithium-ion batteries. Therefore, lithium metal is an indispensable anode material for realizing high-energy rechargeable batteries. However, undesirable reactions among the electrolytes with lithium metal anodes can reduce the power and this remains an impediment to achieving a longer battery lifespan. Previous studies only focused on the formation of the solid electrolyte interphase on the surface of the lithium metal anode.
The team designed a way to create a dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase to resolve the instability of the lithium metal anode by using electrolyte additives, depending on their electron accepting ability and adsorption tendencies. This hierarchical structure of the solid electrolyte interphase on the lithium metal anode has the potential to be further applied to lithium-alloy anodes, lithium storage structures, and anode-free technology to meet market expectations for electrolyte technology.
The batteries with lithium metal anodes and nickel-rich cathodes represented 80.9% of the initial capacity after 600 cycles and achieved a high Coulombic efficiency of 99.94%. These remarkable results contributed to the development of protective dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase technology for lithium metal anodes.
Professor Choi said that the research suggests a new direction for the development of electrolyte additives to regulate the unstable lithium metal anode-electrolyte interface, the biggest hurdle in research on lithium metal batteries.
She added that anode-free secondary battery technology is expected to be a game changer in the secondary battery market and electrolyte additive technology will contribute to the enhancement of anode-free secondary batteries through the stabilization of lithium metal anodes.
This research was funded by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change of the National Research Foundation in Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning and the Technology Innovation Program funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, and Hyundai Motor Company.
- PublicationSaehun Kim, Sung O Park, Min-Young Lee, Jeong-A Lee, Imanuel Kristanto, Tae Kyung Lee, Daeyeon Hwang, Juyoung Kim, Tae-Ung Wi, Hyun-Wook Lee, Sang Kyu Kwak, and NamSoon Choi, “Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives for high-performance lithium metal batteries,” Energy Storage Materials,45, 1-13 (2022), (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.10.031)
- ProfileProfessor Nam-Soon ChoiEnergy Materials LaboratoryDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.16 View 9474
A Study Shows Reactive Electrolyte Additives Improve Lithium Metal Battery Performance
Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives provide an opportunity to improve high-performance lithium metal batteries
A research team showed that electrolyte additives increase the lifetime of lithium metal batteries and remarkably improve the performance of fast charging and discharging. Professor Nam-Soon Choi’s team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST hierarchized the solid electrolyte interphase to make a dual-layer structure and showed groundbreaking run times for lithium metal batteries.
The team applied two electrolyte additives that have different reduction and adsorption properties to improve the functionality of the dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase. In addition, the team has confirmed that the structural stability of the nickel-rich cathode was achieved through the formation of a thin protective layer on the cathode. This study was reported in Energy Storage Materials.
Securing high-energy-density lithium metal batteries with a long lifespan and fast charging performance is vital for realizing their ubiquitous use as superior power sources for electric vehicles. Lithium metal batteries comprise a lithium metal anode that delivers 10 times higher capacity than the graphite anodes in lithium-ion batteries. Therefore, lithium metal is an indispensable anode material for realizing high-energy rechargeable batteries. However, undesirable reactions among the electrolytes with lithium metal anodes can reduce the power and this remains an impediment to achieving a longer battery lifespan. Previous studies only focused on the formation of the solid electrolyte interphase on the surface of the lithium metal anode.
The team designed a way to create a dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase to resolve the instability of the lithium metal anode by using electrolyte additives, depending on their electron accepting ability and adsorption tendencies. This hierarchical structure of the solid electrolyte interphase on the lithium metal anode has the potential to be further applied to lithium-alloy anodes, lithium storage structures, and anode-free technology to meet market expectations for electrolyte technology.
The batteries with lithium metal anodes and nickel-rich cathodes represented 80.9% of the initial capacity after 600 cycles and achieved a high Coulombic efficiency of 99.94%. These remarkable results contributed to the development of protective dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase technology for lithium metal anodes.
Professor Choi said that the research suggests a new direction for the development of electrolyte additives to regulate the unstable lithium metal anode-electrolyte interface, the biggest hurdle in research on lithium metal batteries.
She added that anode-free secondary battery technology is expected to be a game changer in the secondary battery market and electrolyte additive technology will contribute to the enhancement of anode-free secondary batteries through the stabilization of lithium metal anodes.
This research was funded by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change of the National Research Foundation in Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning and the Technology Innovation Program funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, and Hyundai Motor Company.
- PublicationSaehun Kim, Sung O Park, Min-Young Lee, Jeong-A Lee, Imanuel Kristanto, Tae Kyung Lee, Daeyeon Hwang, Juyoung Kim, Tae-Ung Wi, Hyun-Wook Lee, Sang Kyu Kwak, and NamSoon Choi, “Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives for high-performance lithium metal batteries,” Energy Storage Materials,45, 1-13 (2022), (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.10.031)
- ProfileProfessor Nam-Soon ChoiEnergy Materials LaboratoryDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.16 View 9474