Ion+engine
-
 KAIST Develops AI-Driven Performance Prediction Model to Advance Space Electric Propulsion Technology
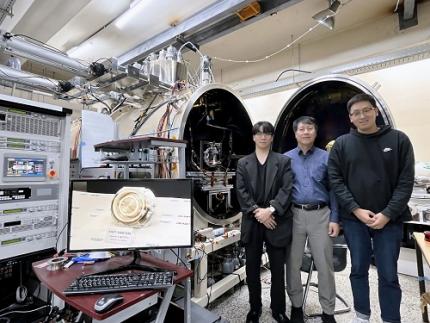
< (From left) PhD candidate Youngho Kim, Professor Wonho Choe, and PhD candidate Jaehong Park from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering >
Hall thrusters, a key space technology for missions like SpaceX's Starlink constellation and NASA's Psyche asteroid mission, are high-efficiency electric propulsion devices using plasma technology*. The KAIST research team announced that the AI-designed Hall thruster developed for CubeSats will be installed on the KAIST-Hall Effect Rocket Orbiter (K-HERO) CubeSat to demonstrate its in-orbit performance during the fourth launch of the Korean Launch Vehicle called Nuri rocket (KSLV-2) scheduled for November this year.
*Plasma is one of the four states of matter, where gases are heated to high energies, causing them to separate into charged ions and electrons. Plasma is used not only in space electric propulsion but also in semiconductor manufacturing, display processes, and sterilization devices.
On February 3rd, the research team from the KAIST Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering’s Electric Propulsion Laboratory, led by Professor Wonho Choe, announced the development of an AI-based technique to accurately predict the performance of Hall thrusters, the engines of satellites and space probes.
Hall thrusters provide high fuel efficiency, requiring minimal propellant to achieve significant acceleration of spacecrafts or satellites while producing substantial thrust relative to power consumption. Due to these advantages, Hall thrusters are widely used in various space missions, including the formation flight of satellite constellations, deorbiting maneuvers for space debris mitigation, and deep space missions such as asteroid exploration.
As the space industry continues to grow during the NewSpace era, the demand for Hall thrusters suited to diverse missions is increasing. To rapidly develop highly efficient, mission-optimized Hall thrusters, it is essential to predict thruster performance accurately from the design phase.
However, conventional methods have limitations, as they struggle to handle the complex plasma phenomena within Hall thrusters or are only applicable under specific conditions, leading to lower prediction accuracy.
The research team developed an AI-based performance prediction technique with high accuracy, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with the iterative design, fabrication, and testing of thrusters. Since 2003, Professor Wonho Choe’s team has been leading research on electric propulsion development in Korea. The team applied a neural network ensemble model to predict thruster performance using 18,000 Hall thruster training data points generated from their in-house numerical simulation tool.
The in-house numerical simulation tool, developed to model plasma physics and thrust performance, played a crucial role in providing high-quality training data. The simulation’s accuracy was validated through comparisons with experimental data from ten KAIST in-house Hall thrusters, with an average prediction error of less than 10%.
< Figure 1. This research has been selected as the cover article for the March 2025 issue (Volume 7, Issue 3) of the AI interdisciplinary journal, Advanced Intelligent Systems. >
The trained neural network ensemble model acts as a digital twin, accurately predicting the Hall thruster performance within seconds based on thruster design variables.
Notably, it offers detailed analyses of performance parameters such as thrust and discharge current, accounting for Hall thruster design variables like propellant flow rate and magnetic field—factors that are challenging to evaluate using traditional scaling laws.
This AI model demonstrated an average prediction error of less than 5% for the in-house 700 W and 1 kW KAIST Hall thrusters and less than 9% for a 5 kW high-power Hall thruster developed by the University of Michigan and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory. This confirms the broad applicability of the AI prediction method across different power levels of Hall thrusters.
Professor Wonho Choe stated, “The AI-based prediction technique developed by our team is highly accurate and is already being utilized in the analysis of thrust performance and the development of highly efficient, low-power Hall thrusters for satellites and spacecraft. This AI approach can also be applied beyond Hall thrusters to various industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, surface processing, and coating, through ion beam sources.”
< Figure 2. The AI-based prediction technique developed by the research team accurately predicts thrust performance based on design variables, making it highly valuable for the development of high-efficiency Hall thrusters. The neural network ensemble processes design variables, such as channel geometry and magnetic field information, and outputs key performance metrics like thrust and prediction accuracy, enabling efficient thruster design and performance analysis. >
Additionally, Professor Choe mentioned, “The CubeSat Hall thruster, developed using the AI technique in collaboration with our lab startup—Cosmo Bee, an electric propulsion company—will be tested in orbit this November aboard the K-HERO 3U (30 x 10 x 10 cm) CubeSat, scheduled for launch on the fourth flight of the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket.”
This research was published online in Advanced Intelligent Systems on December 25, 2024 with PhD candidate Jaehong Park as the first author and was selected as the journal’s cover article, highlighting its innovation.
< Figure 3. Image of the 150 W low-power Hall thruster for small and micro satellites, developed in collaboration with Cosmo Bee and the KAIST team. The thruster will be tested in orbit on the K-HERO CubeSat during the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket’s fourth launch in Q4 2025. >
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Space Pioneer Program (200mN High Thrust Electric Propulsion System Development).
(Paper Title: Predicting Performance of Hall Effect Ion Source Using Machine Learning, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202400555 )
< Figure 4. Graphs of the predicted thrust and discharge current of KAIST’s 700 W Hall thruster using the AI model (HallNN). The left image shows the Hall thruster operating in KAIST Electric Propulsion Laboratory’s vacuum chamber, while the center and right graphs present the prediction results for thrust and discharge current based on anode mass flow rate. The red lines represent AI predictions, and the blue dots represent experimental results, with a prediction error of less than 5%. >
2025.02.03 View 3475
KAIST Develops AI-Driven Performance Prediction Model to Advance Space Electric Propulsion Technology
< (From left) PhD candidate Youngho Kim, Professor Wonho Choe, and PhD candidate Jaehong Park from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering >
Hall thrusters, a key space technology for missions like SpaceX's Starlink constellation and NASA's Psyche asteroid mission, are high-efficiency electric propulsion devices using plasma technology*. The KAIST research team announced that the AI-designed Hall thruster developed for CubeSats will be installed on the KAIST-Hall Effect Rocket Orbiter (K-HERO) CubeSat to demonstrate its in-orbit performance during the fourth launch of the Korean Launch Vehicle called Nuri rocket (KSLV-2) scheduled for November this year.
*Plasma is one of the four states of matter, where gases are heated to high energies, causing them to separate into charged ions and electrons. Plasma is used not only in space electric propulsion but also in semiconductor manufacturing, display processes, and sterilization devices.
On February 3rd, the research team from the KAIST Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering’s Electric Propulsion Laboratory, led by Professor Wonho Choe, announced the development of an AI-based technique to accurately predict the performance of Hall thrusters, the engines of satellites and space probes.
Hall thrusters provide high fuel efficiency, requiring minimal propellant to achieve significant acceleration of spacecrafts or satellites while producing substantial thrust relative to power consumption. Due to these advantages, Hall thrusters are widely used in various space missions, including the formation flight of satellite constellations, deorbiting maneuvers for space debris mitigation, and deep space missions such as asteroid exploration.
As the space industry continues to grow during the NewSpace era, the demand for Hall thrusters suited to diverse missions is increasing. To rapidly develop highly efficient, mission-optimized Hall thrusters, it is essential to predict thruster performance accurately from the design phase.
However, conventional methods have limitations, as they struggle to handle the complex plasma phenomena within Hall thrusters or are only applicable under specific conditions, leading to lower prediction accuracy.
The research team developed an AI-based performance prediction technique with high accuracy, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with the iterative design, fabrication, and testing of thrusters. Since 2003, Professor Wonho Choe’s team has been leading research on electric propulsion development in Korea. The team applied a neural network ensemble model to predict thruster performance using 18,000 Hall thruster training data points generated from their in-house numerical simulation tool.
The in-house numerical simulation tool, developed to model plasma physics and thrust performance, played a crucial role in providing high-quality training data. The simulation’s accuracy was validated through comparisons with experimental data from ten KAIST in-house Hall thrusters, with an average prediction error of less than 10%.
< Figure 1. This research has been selected as the cover article for the March 2025 issue (Volume 7, Issue 3) of the AI interdisciplinary journal, Advanced Intelligent Systems. >
The trained neural network ensemble model acts as a digital twin, accurately predicting the Hall thruster performance within seconds based on thruster design variables.
Notably, it offers detailed analyses of performance parameters such as thrust and discharge current, accounting for Hall thruster design variables like propellant flow rate and magnetic field—factors that are challenging to evaluate using traditional scaling laws.
This AI model demonstrated an average prediction error of less than 5% for the in-house 700 W and 1 kW KAIST Hall thrusters and less than 9% for a 5 kW high-power Hall thruster developed by the University of Michigan and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory. This confirms the broad applicability of the AI prediction method across different power levels of Hall thrusters.
Professor Wonho Choe stated, “The AI-based prediction technique developed by our team is highly accurate and is already being utilized in the analysis of thrust performance and the development of highly efficient, low-power Hall thrusters for satellites and spacecraft. This AI approach can also be applied beyond Hall thrusters to various industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, surface processing, and coating, through ion beam sources.”
< Figure 2. The AI-based prediction technique developed by the research team accurately predicts thrust performance based on design variables, making it highly valuable for the development of high-efficiency Hall thrusters. The neural network ensemble processes design variables, such as channel geometry and magnetic field information, and outputs key performance metrics like thrust and prediction accuracy, enabling efficient thruster design and performance analysis. >
Additionally, Professor Choe mentioned, “The CubeSat Hall thruster, developed using the AI technique in collaboration with our lab startup—Cosmo Bee, an electric propulsion company—will be tested in orbit this November aboard the K-HERO 3U (30 x 10 x 10 cm) CubeSat, scheduled for launch on the fourth flight of the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket.”
This research was published online in Advanced Intelligent Systems on December 25, 2024 with PhD candidate Jaehong Park as the first author and was selected as the journal’s cover article, highlighting its innovation.
< Figure 3. Image of the 150 W low-power Hall thruster for small and micro satellites, developed in collaboration with Cosmo Bee and the KAIST team. The thruster will be tested in orbit on the K-HERO CubeSat during the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket’s fourth launch in Q4 2025. >
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Space Pioneer Program (200mN High Thrust Electric Propulsion System Development).
(Paper Title: Predicting Performance of Hall Effect Ion Source Using Machine Learning, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202400555 )
< Figure 4. Graphs of the predicted thrust and discharge current of KAIST’s 700 W Hall thruster using the AI model (HallNN). The left image shows the Hall thruster operating in KAIST Electric Propulsion Laboratory’s vacuum chamber, while the center and right graphs present the prediction results for thrust and discharge current based on anode mass flow rate. The red lines represent AI predictions, and the blue dots represent experimental results, with a prediction error of less than 5%. >
2025.02.03 View 3475 -
 Scientist of October: Professor Jungwon Kim
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2020 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Kim was recognized for his contributions to expanding the horizons of the basics of precision engineering through his research on multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution sensors. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was selected as the recipient of this award in celebration of “Measurement Day”, which commemorates October 26 as the day in which King Sejong the Great established a volume measurement system.
Professor Kim discovered that the time difference between the pulse of light created by a laser and the pulse of the current produced by a light-emitting diode was as small as 100 attoseconds (10-16 seconds). He then developed a unique multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution Time-of-Flight (TOF) sensor that could take measurements of multiple points at the same time by sampling electric light. The sensor, with a measurement speed of 100 megahertz (100 million vibrations per second), a resolution of 180 picometers (1/5.5 billion meters), and a dynamic range of 150 decibels, overcame the limitations of both existing TOF techniques and laser interferometric techniques at the same time. The results of this research were published in Nature Photonics on February 10, 2020.
Professor Kim said, “I’d like to thank the graduate students who worked passionately with me, and KAIST for providing an environment in which I could fully focus on research. I am looking forward to the new and diverse applications in the field of machine manufacturing, such as studying the dynamic phenomena in microdevices, or taking ultraprecision measurement of shapes for advanced manufacturing.”
(END)
2020.10.15 View 11922
Scientist of October: Professor Jungwon Kim
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2020 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Kim was recognized for his contributions to expanding the horizons of the basics of precision engineering through his research on multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution sensors. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was selected as the recipient of this award in celebration of “Measurement Day”, which commemorates October 26 as the day in which King Sejong the Great established a volume measurement system.
Professor Kim discovered that the time difference between the pulse of light created by a laser and the pulse of the current produced by a light-emitting diode was as small as 100 attoseconds (10-16 seconds). He then developed a unique multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution Time-of-Flight (TOF) sensor that could take measurements of multiple points at the same time by sampling electric light. The sensor, with a measurement speed of 100 megahertz (100 million vibrations per second), a resolution of 180 picometers (1/5.5 billion meters), and a dynamic range of 150 decibels, overcame the limitations of both existing TOF techniques and laser interferometric techniques at the same time. The results of this research were published in Nature Photonics on February 10, 2020.
Professor Kim said, “I’d like to thank the graduate students who worked passionately with me, and KAIST for providing an environment in which I could fully focus on research. I am looking forward to the new and diverse applications in the field of machine manufacturing, such as studying the dynamic phenomena in microdevices, or taking ultraprecision measurement of shapes for advanced manufacturing.”
(END)
2020.10.15 View 11922 -
 Professor Suh Chosen for IT Young Engineer Award
(The ceremony photo of Professor Changho Suh)
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering received the IT Young Engineer Award on June 28. This award is hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the Institute of Electrical and Information Engineers (IEIE) and funded by the Haedong Science Foundation.
The IT Young Engineer Award is given to researchers under the age of 40 in Korea. The selection criteria include the researches’ technical practicability, their social and environmental contributions, and their creativity.
Professor Suh has shown outstanding academic performance in the field of telecommunications, distributed storage, and artificial intelligence and he has also contributed to technological commercialization. He published 23 papers in SCI journals and ten papers at top-level international conferences including the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems and the International Conference on Machine Learning. His papers were cited more than 4,100 times. He has also achieved 30 international patent registrations.
Currently, he is developing an autonomous driving system using an AI-tutor and deep learning technology.
Professor Suh said, “It is my great honor to receive the IT Young Engineer Award. I strive to continue guiding students and carrying out research in order to make a contribution to the fields of IT and AI.”
2018.07.04 View 9857
Professor Suh Chosen for IT Young Engineer Award
(The ceremony photo of Professor Changho Suh)
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering received the IT Young Engineer Award on June 28. This award is hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the Institute of Electrical and Information Engineers (IEIE) and funded by the Haedong Science Foundation.
The IT Young Engineer Award is given to researchers under the age of 40 in Korea. The selection criteria include the researches’ technical practicability, their social and environmental contributions, and their creativity.
Professor Suh has shown outstanding academic performance in the field of telecommunications, distributed storage, and artificial intelligence and he has also contributed to technological commercialization. He published 23 papers in SCI journals and ten papers at top-level international conferences including the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems and the International Conference on Machine Learning. His papers were cited more than 4,100 times. He has also achieved 30 international patent registrations.
Currently, he is developing an autonomous driving system using an AI-tutor and deep learning technology.
Professor Suh said, “It is my great honor to receive the IT Young Engineer Award. I strive to continue guiding students and carrying out research in order to make a contribution to the fields of IT and AI.”
2018.07.04 View 9857 -
 CLKIP Bearing Fruit in China
The Chongqing Liangjiang KAIST International Program (CLKIP) is rapidly gaining steam in China. CLKIP, an educational program operated in Chongqing internationally by KAIST since 2015, offers two majors, Electronic Information Engineering and Computer Science and Technology, applying the same curriculum as at KAIST.
To operate the program, KAIST assigns professors from the School of Electrical Engineering and the School of Computing to the program every year. They are in charge of one-third of the major courses, and transfer KAIST’s educational curriculum and know-how.
A total of 13 professors from Chongqing University of Technology (CQUT) have received or are receiving training on advanced education methodologies and technical know-how, including an on and offline integrated learning program, called Education 4.0 and large-scale internet open learning.As CLKIP is gaining in popularity, the number of students for its undergraduate courses keeps increasing, from 66 in 2015 to 172 in 2016 and 200 students in 2017, achieving the student volume for enrollment annually.
CLKIP selected seven exchange undergraduate students and five dual-degree students this fall, and they are currently studying in KAIST for either one semester or one full year.
CLKIP is located in Chongqing, one of the major direct-controlled municipalities and a focal point for notable government projects. The Korea-China industrial zone is also located in this area.
Considering its location, CLKIP is more than just an international programs for educational cooperation. The program will provide opportunities to cooperate with Korean enterprises including Hyundai, SK Hynix, LG Chem and Hankook Tire. While cooperating in research and development as well as technical assistance, KAIST hopes that these enterprises will play a bridging role for KAIST alumni entering the Chinese market.
President Sung-Chul Shin said, “The success of CLKIP shows that KAIST programs for fostering future manpower and developing cutting-edge technologies do work in other countries. Based on this case, KAST will put more effort into transferring our innovative education systems abroad. We are also pushing ahead to establish a joint institute between KAIST and CQUT by 2018, which will become a foundation for facilitating the entry of KAIST’s cutting-edge technologies into the Chinese market.”
“KAIST aims to become an entrepreneurial university that creates value through technology commercialization. In this sense, KAIST plans to transfer advanced technologies to domestic and international companies located in the Liangjiang district,” he added.
2017.12.12 View 11348
CLKIP Bearing Fruit in China
The Chongqing Liangjiang KAIST International Program (CLKIP) is rapidly gaining steam in China. CLKIP, an educational program operated in Chongqing internationally by KAIST since 2015, offers two majors, Electronic Information Engineering and Computer Science and Technology, applying the same curriculum as at KAIST.
To operate the program, KAIST assigns professors from the School of Electrical Engineering and the School of Computing to the program every year. They are in charge of one-third of the major courses, and transfer KAIST’s educational curriculum and know-how.
A total of 13 professors from Chongqing University of Technology (CQUT) have received or are receiving training on advanced education methodologies and technical know-how, including an on and offline integrated learning program, called Education 4.0 and large-scale internet open learning.As CLKIP is gaining in popularity, the number of students for its undergraduate courses keeps increasing, from 66 in 2015 to 172 in 2016 and 200 students in 2017, achieving the student volume for enrollment annually.
CLKIP selected seven exchange undergraduate students and five dual-degree students this fall, and they are currently studying in KAIST for either one semester or one full year.
CLKIP is located in Chongqing, one of the major direct-controlled municipalities and a focal point for notable government projects. The Korea-China industrial zone is also located in this area.
Considering its location, CLKIP is more than just an international programs for educational cooperation. The program will provide opportunities to cooperate with Korean enterprises including Hyundai, SK Hynix, LG Chem and Hankook Tire. While cooperating in research and development as well as technical assistance, KAIST hopes that these enterprises will play a bridging role for KAIST alumni entering the Chinese market.
President Sung-Chul Shin said, “The success of CLKIP shows that KAIST programs for fostering future manpower and developing cutting-edge technologies do work in other countries. Based on this case, KAST will put more effort into transferring our innovative education systems abroad. We are also pushing ahead to establish a joint institute between KAIST and CQUT by 2018, which will become a foundation for facilitating the entry of KAIST’s cutting-edge technologies into the Chinese market.”
“KAIST aims to become an entrepreneurial university that creates value through technology commercialization. In this sense, KAIST plans to transfer advanced technologies to domestic and international companies located in the Liangjiang district,” he added.
2017.12.12 View 11348 -
 KAIST Dedicates Geocentrifuge Experiment Center
KAIST dedicated the KOCED Geo-Centrifuge Experiment Center for researches in monitoring natural disasters such as earthquake and embankment collapse through miniature simulation tests on Wednesday (April 9) after a two-year construction work.
The experiment center is part of the Korea Construction Engineering Development Collaboratory Program (KOCED) which has been sponsored by the Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs to build an infrastructure for construction engineering researches at a national level. The ministry plans to build a total of 5 similar centers nationwide by the end of the year.
On hand at the dedication ceremony were Jae-Choon Lee, President of the Korea Institute of Construction & Transportation Technology Evaluation and Planning, KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh, and scores of experts and administration officials.
The construction of the five-story building on an area of about 3,328 square meters cost 8.4 billion won (US$6.3 million).
The center is expected to serve as a major laboratory in the field of geotechnical engineering. It is equipped with such state-of-the-art facilities as geocentrifuge, a useful tool for studying flow in unsaturated soil under well-controlled, repeatable conditions, a bidirectional shaking-table that can reproduce earthquake-like wave; and robots that can reproduce construction procedures by remote control.
Geocentrifuge experiment allows detecting ground and structure motions easily and rapidly by simulation tests. Thus, it is widely used for various geotechnical engineering researches such as evaluation of seismic safety, soft ground movement, slope stability analysis, etc. The causes of the embankment collapse in New Orleans by Hurricane Katrina in 2005 were also revealed by the geocentrifuge experiment.
The geocentrifuge research facility is available for use by outside researchers, so scientists from other universities, research institutes and corporations can perform research and test their scientific and engineering hypotheses.
The center is divided into two sections, experiment building and research building. The experiment building is composed of a geocentrifuge laboratory, model-making rooms, workshops, a geotechnical engineering laboratory and specimen storehouse, while the research building has a control room, a video conference room, an electronic library and research rooms.
2009.04.09 View 13615
KAIST Dedicates Geocentrifuge Experiment Center
KAIST dedicated the KOCED Geo-Centrifuge Experiment Center for researches in monitoring natural disasters such as earthquake and embankment collapse through miniature simulation tests on Wednesday (April 9) after a two-year construction work.
The experiment center is part of the Korea Construction Engineering Development Collaboratory Program (KOCED) which has been sponsored by the Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs to build an infrastructure for construction engineering researches at a national level. The ministry plans to build a total of 5 similar centers nationwide by the end of the year.
On hand at the dedication ceremony were Jae-Choon Lee, President of the Korea Institute of Construction & Transportation Technology Evaluation and Planning, KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh, and scores of experts and administration officials.
The construction of the five-story building on an area of about 3,328 square meters cost 8.4 billion won (US$6.3 million).
The center is expected to serve as a major laboratory in the field of geotechnical engineering. It is equipped with such state-of-the-art facilities as geocentrifuge, a useful tool for studying flow in unsaturated soil under well-controlled, repeatable conditions, a bidirectional shaking-table that can reproduce earthquake-like wave; and robots that can reproduce construction procedures by remote control.
Geocentrifuge experiment allows detecting ground and structure motions easily and rapidly by simulation tests. Thus, it is widely used for various geotechnical engineering researches such as evaluation of seismic safety, soft ground movement, slope stability analysis, etc. The causes of the embankment collapse in New Orleans by Hurricane Katrina in 2005 were also revealed by the geocentrifuge experiment.
The geocentrifuge research facility is available for use by outside researchers, so scientists from other universities, research institutes and corporations can perform research and test their scientific and engineering hypotheses.
The center is divided into two sections, experiment building and research building. The experiment building is composed of a geocentrifuge laboratory, model-making rooms, workshops, a geotechnical engineering laboratory and specimen storehouse, while the research building has a control room, a video conference room, an electronic library and research rooms.
2009.04.09 View 13615 -
 President Nam-Pyo Suh won 'International award'
President Nam-Pyo Suh won ‘International award’
In recognition of distinguished scientific and industrial contributions to the field of production engineering, KAIST president Nam-Pyo Suh won ‘General Pierre Nicolau Award’ conferred by College International pour la Recherche en Productique (CIRP).
President Suh is a world-renowned scholar who has made excellent achievements at plastic manufacturing process, metal manufacturing process, wear and tear theory, design theory, etc. in the field of production and manufacturing technologies and also the founder of production/ design theory using axiom.
General Pierre Nicolau Award’ has been established to honor General Pierre Nicolau, a world-renowned French authority in the field of production engineering, and commemorate his contributions to the founding of CIRP.
2006.09.18 View 12526
President Nam-Pyo Suh won 'International award'
President Nam-Pyo Suh won ‘International award’
In recognition of distinguished scientific and industrial contributions to the field of production engineering, KAIST president Nam-Pyo Suh won ‘General Pierre Nicolau Award’ conferred by College International pour la Recherche en Productique (CIRP).
President Suh is a world-renowned scholar who has made excellent achievements at plastic manufacturing process, metal manufacturing process, wear and tear theory, design theory, etc. in the field of production and manufacturing technologies and also the founder of production/ design theory using axiom.
General Pierre Nicolau Award’ has been established to honor General Pierre Nicolau, a world-renowned French authority in the field of production engineering, and commemorate his contributions to the founding of CIRP.
2006.09.18 View 12526