CAS
-
 KAIST develops technology for selective RNA modification in living cells and animals
· A team led by Professor Won Do Heo from the Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, has developed a pioneering technology that selectively acetylates specific RNA molecules in living cells and tissues.
· The platform uses RNA-targeting CRISPR tools in combination with RNA-modifying enzymes to chemically modify only the intended RNA.
· The method opens new possibilities for gene therapy by enabling precise control of disease-related RNA without affecting the rest of the transcriptome.
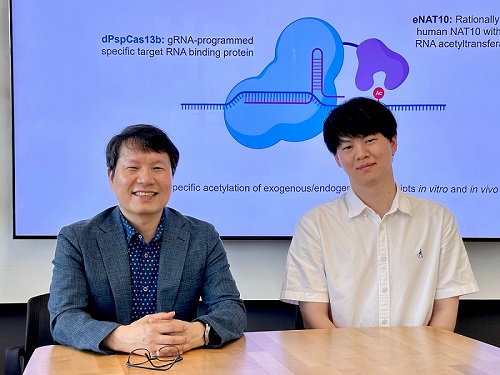
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Won Do Heo and Jihwan Yu, a Ph.D. Candidate of the Department of Biological Sciences >
CRISPR-Cas13, a powerful RNA-targeting technology is gaining increasing attention as a next-generation gene therapy platform due to its precision and reduced side effects. Utilizing this system, researchers at KAIST have now developed the world’s first technology capable of selectively acetylating (chemically modifying) specific RNA molecules among countless transcripts within living cells. This breakthrough enables precise, programmable control of RNA function and is expected to open new avenues in RNA-based therapeutic development.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professor Won Do Heo in the Department of Biological Sciences has recently developed a groundbreaking technology capable of selectively acetylating specific RNA molecules within the human body using the CRISPR-Cas13 system—an RNA-targeting platform gaining increasing attention in the fields of gene regulation and RNA-based therapeutics.
RNA molecules can undergo chemical modifications—the addition of specific chemical groups—which alter their function and behavior without changing the underlying nucleotide sequence. However, some of these modifications, a critical layer of post-transcriptional gene regulation, remain poorly understood. Among them, N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) has been particularly enigmatic, with ongoing debate about its existence and function in human messenger RNA (mRNA), the RNA that encodes proteins.
To address this gap, the KAIST research team developed a targeted RNA acetylation system, named dCas13-eNAT10. This platform combines a catalytically inactive Cas13 enzyme (dCas13) that guides the system to specific RNA targets, with a hyperactive variant of the NAT10 enzyme (eNAT10), which performs RNA acetylation. This approach enables precise acetylation of only the desired RNA molecules among the vast pool of transcripts within the cell.
< Figure 1. Development of hyperactive variant eNAT10 through NAT10 protein engineering. By engineering the NAT10 protein, which performs RNA acetylation in human cells, based on its domain and structure, eNAT10 was developed, showing approximately a 3-fold increase in RNA acetylation activity compared to the wild-type enzyme. >
Using this system, the researchers demonstrated that guide RNAs could direct the dCas13-eNAT10 complex to acetylate specific RNA targets, and acetylation significantly increased protein expression from the modified mRNA. Moreover, the study revealed, for the first time, that RNA acetylation plays a role in intracellular RNA localization, facilitating the export of RNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm—a critical step in gene expression regulation.
To validate its therapeutic potential, the team successfully delivered the targeted RNA acetylation system into the livers of live mice using adeno-associated virus (AAV), a commonly used gene therapy vector. This marks the first demonstration of in vivo RNA modification, extending the applicability of RNA chemical modification tools from cell culture models to living organisms.
< Figure 2. Acetylation of various RNA in cells using dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein. Utilizing the CRISPR-Cas13 system, which can precisely target specific RNA through guide RNA, a dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein was created, demonstrating its ability to specifically acetylate various endogenous RNA at different locations within cells. >
Professor Won Do Heo, who previously developed COVID-19 treatment technology using RNA gene scissors and technology to activate RNA gene scissors with light, stated, "Existing RNA chemical modification research faced difficulties in controlling specificity, temporality, and spatiality. However, this new technology allows selective acetylation of desired RNA, opening the door for accurate and detailed research into the functions of RNA acetylation." He added, "The RNA chemical modification technology developed in this study can be widely used as an RNA-based therapeutic agent and a tool for regulating RNA functions in living organisms in the future."
< Figure 3. In vivo delivery of targeted RNA acetylation system. The targeted RNA acetylation system was encoded in an AAV vector, commonly used in gene therapy, and delivered intravenously to adult mice, showing that target RNA in liver tissue was specifically acetylated according to the guide RNA. >
This research, with Ph.D. candidate Jihwan Yu from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST as the first author, was published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology on June 2, 2025. (Title: Programmable RNA acetylation with CRISPR-Cas13, Impact factor: 12.9, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-025-01922-3)
This research was supported by the Samsung Future Technology Foundation and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.06.10 View 1082
KAIST develops technology for selective RNA modification in living cells and animals
· A team led by Professor Won Do Heo from the Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, has developed a pioneering technology that selectively acetylates specific RNA molecules in living cells and tissues.
· The platform uses RNA-targeting CRISPR tools in combination with RNA-modifying enzymes to chemically modify only the intended RNA.
· The method opens new possibilities for gene therapy by enabling precise control of disease-related RNA without affecting the rest of the transcriptome.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Won Do Heo and Jihwan Yu, a Ph.D. Candidate of the Department of Biological Sciences >
CRISPR-Cas13, a powerful RNA-targeting technology is gaining increasing attention as a next-generation gene therapy platform due to its precision and reduced side effects. Utilizing this system, researchers at KAIST have now developed the world’s first technology capable of selectively acetylating (chemically modifying) specific RNA molecules among countless transcripts within living cells. This breakthrough enables precise, programmable control of RNA function and is expected to open new avenues in RNA-based therapeutic development.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professor Won Do Heo in the Department of Biological Sciences has recently developed a groundbreaking technology capable of selectively acetylating specific RNA molecules within the human body using the CRISPR-Cas13 system—an RNA-targeting platform gaining increasing attention in the fields of gene regulation and RNA-based therapeutics.
RNA molecules can undergo chemical modifications—the addition of specific chemical groups—which alter their function and behavior without changing the underlying nucleotide sequence. However, some of these modifications, a critical layer of post-transcriptional gene regulation, remain poorly understood. Among them, N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) has been particularly enigmatic, with ongoing debate about its existence and function in human messenger RNA (mRNA), the RNA that encodes proteins.
To address this gap, the KAIST research team developed a targeted RNA acetylation system, named dCas13-eNAT10. This platform combines a catalytically inactive Cas13 enzyme (dCas13) that guides the system to specific RNA targets, with a hyperactive variant of the NAT10 enzyme (eNAT10), which performs RNA acetylation. This approach enables precise acetylation of only the desired RNA molecules among the vast pool of transcripts within the cell.
< Figure 1. Development of hyperactive variant eNAT10 through NAT10 protein engineering. By engineering the NAT10 protein, which performs RNA acetylation in human cells, based on its domain and structure, eNAT10 was developed, showing approximately a 3-fold increase in RNA acetylation activity compared to the wild-type enzyme. >
Using this system, the researchers demonstrated that guide RNAs could direct the dCas13-eNAT10 complex to acetylate specific RNA targets, and acetylation significantly increased protein expression from the modified mRNA. Moreover, the study revealed, for the first time, that RNA acetylation plays a role in intracellular RNA localization, facilitating the export of RNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm—a critical step in gene expression regulation.
To validate its therapeutic potential, the team successfully delivered the targeted RNA acetylation system into the livers of live mice using adeno-associated virus (AAV), a commonly used gene therapy vector. This marks the first demonstration of in vivo RNA modification, extending the applicability of RNA chemical modification tools from cell culture models to living organisms.
< Figure 2. Acetylation of various RNA in cells using dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein. Utilizing the CRISPR-Cas13 system, which can precisely target specific RNA through guide RNA, a dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein was created, demonstrating its ability to specifically acetylate various endogenous RNA at different locations within cells. >
Professor Won Do Heo, who previously developed COVID-19 treatment technology using RNA gene scissors and technology to activate RNA gene scissors with light, stated, "Existing RNA chemical modification research faced difficulties in controlling specificity, temporality, and spatiality. However, this new technology allows selective acetylation of desired RNA, opening the door for accurate and detailed research into the functions of RNA acetylation." He added, "The RNA chemical modification technology developed in this study can be widely used as an RNA-based therapeutic agent and a tool for regulating RNA functions in living organisms in the future."
< Figure 3. In vivo delivery of targeted RNA acetylation system. The targeted RNA acetylation system was encoded in an AAV vector, commonly used in gene therapy, and delivered intravenously to adult mice, showing that target RNA in liver tissue was specifically acetylated according to the guide RNA. >
This research, with Ph.D. candidate Jihwan Yu from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST as the first author, was published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology on June 2, 2025. (Title: Programmable RNA acetylation with CRISPR-Cas13, Impact factor: 12.9, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-025-01922-3)
This research was supported by the Samsung Future Technology Foundation and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.06.10 View 1082 -
 KAIST Identifies Master Regulator Blocking Immunotherapy, Paving the Way for a New Lung Cancer Treatment
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, a class of immunotherapies that help immune cells attack cancer more effectively, have revolutionized cancer treatment. However, fewer than 20% of patients respond to these treatments, highlighting the urgent need for new strategies tailored to both responders and non-responders.
KAIST researchers have discovered that 'DEAD-box helicases 54 (DDX54)', a type of RNA-binding protein, is the master regulator that hinders the effectiveness of immunotherapy—opening a new path for lung cancer treatment. This breakthrough technology has been transferred to faculty startup BioRevert Inc., where it is currently being developed as a companion therapeutic and is expected to enter clinical trials by 2028.
< Photo 1. (From left) Researcher Jungeun Lee, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and Postdoctoral Researcher Jeong-Ryeol Gong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 8 that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering had identified DDX54 as a critical factor that determines the immune evasion capacity of lung cancer cells. They demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 enhances immune cell infiltration into tumors and significantly improves the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy using anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies is considered a powerful approach in cancer treatment. However, its low response rate limits the number of patients who actually benefit.
To identify likely responders, tumor mutational burden (TMB) has recently been approved by the FDA as a key biomarker for immunotherapy. Cancers with high mutation rates are thought to be more responsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, even tumors with high TMB can display an “immune-desert” phenotype—where immune cell infiltration is severely limited—resulting in poor treatment responses.
< Figure 1. DDX54 was identified as the master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy by orchestrating suppression of immune cell infiltration through cancer tissues as lung cancer cells become immune-evasive >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team compared transcriptome and genome data of lung cancer patients with immune evasion capabilities through gene regulatory network analysis (A) and discovered DDX54, a master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy (B-F).
This study is especially significant in that it successfully demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 in immune-desert lung tumors can overcome immunotherapy resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
The team used transcriptomic and genomic data from immune-evasive lung cancer patients and employed systems biology techniques to infer gene regulatory networks. Through this analysis, they identified DDX54 as a central regulator in the immune evasion of lung cancer cells.
In a syngeneic mouse model, the suppression of DDX54 led to significant increases in the infiltration of anti-cancer immune cells such as T cells and NK cells, and greatly improved the response to immunotherapy.
Single-cell transcriptomic and spatial transcriptomic analyses further showed that combination therapy targeting DDX54 promoted the differentiation of T cells and memory T cells that suppress tumors, while reducing the infiltration of regulatory T cells and exhausted T cells that support tumor growth.
< Figure 2. In the syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells, it was confirmed that inhibiting DDX54 reversed the immune-evasion ability of cancer cells and enhanced the sensitivity to anti-PD-1 therapy >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells exhibiting immunotherapy resistance, the treatment applied after DDX54 inhibition resulted in statistically significant inhibition of lung cancer growth (B-D) and a significant increase in immune cell infiltration into the tumor tissue (E, F).
The mechanism is believed to involve DDX54 suppression inactivating signaling pathways such as JAK-STAT, MYC, and NF-κB, thereby downregulating immune-evasive proteins CD38 and CD47. This also reduced the infiltration of circulating monocytes—which promote tumor development—and promoted the differentiation of M1 macrophages that play anti-tumor roles.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho stated, “We have, for the first time, identified a master regulatory factor that enables immune evasion in lung cancer cells. By targeting this factor, we developed a new therapeutic strategy that can induce responsiveness to immunotherapy in previously resistant cancers.”
He added, “The discovery of DDX54—hidden within the complex molecular networks of cancer cells—was made possible through the systematic integration of systems biology, combining IT and BT.”
The study, led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on April 2, 2025, with Jeong-Ryeol Gong being the first author, Jungeun Lee, a co-first author, and Younghyun Han, a co-author of the article.
< Figure 3. Single-cell transcriptome and spatial transcriptome analysis confirmed that knockdown of DDX54 increased immune cell infiltration into cancer tissues >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells that underwent immunotherapy in combination with DDX54 inhibition, single-cell transcriptome (H-L) and spatial transcriptome (A-G) analysis of immune cells infiltrating inside cancer tissues were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that anticancer immune cells such as T cells, B cells, and NK cells actively infiltrated the core of lung cancer tissues when DDX54 inhibition and immunotherapy were concurrently administered.
(Paper title: “DDX54 downregulation enhances anti-PD1 therapy in immune-desert lung tumors with high tumor mutational burden,” DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2412310122)
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Research Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program.
< Figure 4. The identified master regulator DDX54 was confirmed to induce CD38 and CD47 expression through Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB activation. >
DDX54 activates the Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB pathways in lung cancer cells to increase CD38 and CD47 expression (A-G). This creates a cancer microenvironment that contributes to cancer development (H) and ultimately induces immune anticancer treatment resistance.
< Figure 5. It was confirmed that an immune-inflamed environment can be created by combining DDX54 inhibition and immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. >
When DDX54 inhibition and ICI therapy are simultaneously administered, the cancer cell characteristics change, the immune evasion ability is restored, and the environment is transformed into an ‘immune-activated’ environment in which immune cells easily infiltrate cancer tissues. This strengthens the anticancer immune response, thereby increasing the sensitivity of immunotherapy even in lung cancer tissues that previously had low responsiveness to immunotherapy.
2025.04.08 View 4991
KAIST Identifies Master Regulator Blocking Immunotherapy, Paving the Way for a New Lung Cancer Treatment
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, a class of immunotherapies that help immune cells attack cancer more effectively, have revolutionized cancer treatment. However, fewer than 20% of patients respond to these treatments, highlighting the urgent need for new strategies tailored to both responders and non-responders.
KAIST researchers have discovered that 'DEAD-box helicases 54 (DDX54)', a type of RNA-binding protein, is the master regulator that hinders the effectiveness of immunotherapy—opening a new path for lung cancer treatment. This breakthrough technology has been transferred to faculty startup BioRevert Inc., where it is currently being developed as a companion therapeutic and is expected to enter clinical trials by 2028.
< Photo 1. (From left) Researcher Jungeun Lee, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and Postdoctoral Researcher Jeong-Ryeol Gong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 8 that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering had identified DDX54 as a critical factor that determines the immune evasion capacity of lung cancer cells. They demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 enhances immune cell infiltration into tumors and significantly improves the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy using anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies is considered a powerful approach in cancer treatment. However, its low response rate limits the number of patients who actually benefit.
To identify likely responders, tumor mutational burden (TMB) has recently been approved by the FDA as a key biomarker for immunotherapy. Cancers with high mutation rates are thought to be more responsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, even tumors with high TMB can display an “immune-desert” phenotype—where immune cell infiltration is severely limited—resulting in poor treatment responses.
< Figure 1. DDX54 was identified as the master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy by orchestrating suppression of immune cell infiltration through cancer tissues as lung cancer cells become immune-evasive >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team compared transcriptome and genome data of lung cancer patients with immune evasion capabilities through gene regulatory network analysis (A) and discovered DDX54, a master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy (B-F).
This study is especially significant in that it successfully demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 in immune-desert lung tumors can overcome immunotherapy resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
The team used transcriptomic and genomic data from immune-evasive lung cancer patients and employed systems biology techniques to infer gene regulatory networks. Through this analysis, they identified DDX54 as a central regulator in the immune evasion of lung cancer cells.
In a syngeneic mouse model, the suppression of DDX54 led to significant increases in the infiltration of anti-cancer immune cells such as T cells and NK cells, and greatly improved the response to immunotherapy.
Single-cell transcriptomic and spatial transcriptomic analyses further showed that combination therapy targeting DDX54 promoted the differentiation of T cells and memory T cells that suppress tumors, while reducing the infiltration of regulatory T cells and exhausted T cells that support tumor growth.
< Figure 2. In the syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells, it was confirmed that inhibiting DDX54 reversed the immune-evasion ability of cancer cells and enhanced the sensitivity to anti-PD-1 therapy >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells exhibiting immunotherapy resistance, the treatment applied after DDX54 inhibition resulted in statistically significant inhibition of lung cancer growth (B-D) and a significant increase in immune cell infiltration into the tumor tissue (E, F).
The mechanism is believed to involve DDX54 suppression inactivating signaling pathways such as JAK-STAT, MYC, and NF-κB, thereby downregulating immune-evasive proteins CD38 and CD47. This also reduced the infiltration of circulating monocytes—which promote tumor development—and promoted the differentiation of M1 macrophages that play anti-tumor roles.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho stated, “We have, for the first time, identified a master regulatory factor that enables immune evasion in lung cancer cells. By targeting this factor, we developed a new therapeutic strategy that can induce responsiveness to immunotherapy in previously resistant cancers.”
He added, “The discovery of DDX54—hidden within the complex molecular networks of cancer cells—was made possible through the systematic integration of systems biology, combining IT and BT.”
The study, led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on April 2, 2025, with Jeong-Ryeol Gong being the first author, Jungeun Lee, a co-first author, and Younghyun Han, a co-author of the article.
< Figure 3. Single-cell transcriptome and spatial transcriptome analysis confirmed that knockdown of DDX54 increased immune cell infiltration into cancer tissues >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells that underwent immunotherapy in combination with DDX54 inhibition, single-cell transcriptome (H-L) and spatial transcriptome (A-G) analysis of immune cells infiltrating inside cancer tissues were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that anticancer immune cells such as T cells, B cells, and NK cells actively infiltrated the core of lung cancer tissues when DDX54 inhibition and immunotherapy were concurrently administered.
(Paper title: “DDX54 downregulation enhances anti-PD1 therapy in immune-desert lung tumors with high tumor mutational burden,” DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2412310122)
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Research Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program.
< Figure 4. The identified master regulator DDX54 was confirmed to induce CD38 and CD47 expression through Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB activation. >
DDX54 activates the Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB pathways in lung cancer cells to increase CD38 and CD47 expression (A-G). This creates a cancer microenvironment that contributes to cancer development (H) and ultimately induces immune anticancer treatment resistance.
< Figure 5. It was confirmed that an immune-inflamed environment can be created by combining DDX54 inhibition and immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. >
When DDX54 inhibition and ICI therapy are simultaneously administered, the cancer cell characteristics change, the immune evasion ability is restored, and the environment is transformed into an ‘immune-activated’ environment in which immune cells easily infiltrate cancer tissues. This strengthens the anticancer immune response, thereby increasing the sensitivity of immunotherapy even in lung cancer tissues that previously had low responsiveness to immunotherapy.
2025.04.08 View 4991 -
 KAIST Holds 2025 Commencement Ceremony
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) held its 2025 Commencement Ceremony at the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex on the Daejeon Main Campus at 2 p.m. on the 14th of February.
< A scene from KAIST Commencement 2025 - Guests of Honor and Administrative Professors Entering the Stage headed by the color guards of the ELKA (Encouraging Leaders of KAIST) >
At this ceremony, a total of 3,144 degrees were conferred, including 785 doctorates, 1,643 masters, and 716 bachelors. With this, KAIST has produced a total of 81,156 advanced science and technology personnel, including 17,313 doctorates, 41,566 masters, and 22,277 bachelors since its establishment in 1971.
Changyu Lee from the School of Computing received the Minister of Science and ICT Award, and the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Award went to Lance Khizner Dabu Gragasin, an international student from the Philippines of the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering. The President’s Award was given to Seoyeong Yang of the Department of Biological Sciences, and the Alumni Association President’s Award and the Development Foundation Chairman’s Award was given to Gahyeon Bae of the Department of Industrial Design and Buyeon Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, respectively.
Minister of Science and ICT Sang-Im Yoo joined the ceremony to deliver a congratulatory speech and to present the awards to outstanding graduates.
< Minister Sang-Im Yoo of the Ministry of Science, Technology and ICT giving his congratulatory message at KAIST Commencement 2025 >
The valedictorian speeches were given by Minjae Kim of the School of Computing, who has practiced the value of sharing that learning is not competition but cooperation, and Mohammed Haruna Hamza of the Department of Aerospace Engineering, a Nigerian international student. Mr. Hamza is the first foreign student to represent the graduating class as valedictorian since the founding of KAIST.
Hamza lost his home and school in his home country due to a terrorist group’s bombing and moved south, but despite the adversity, he continued his studies while pursuing his dream of becoming an aerospace engineer. As a result of his efforts, Hamza was invited by the Korean government to study at KAIST. He expressed his determination to pursue his dream by saying, “I am grateful for the people and experiences that helped me overcome my adversity. The future is the result of the decisions we make today.”
A Pakistani international student was chosen as one of this year's "Most Talked about Graduates of the Year". It is Ali Syed Sheraz who wore his doctoral cap at this year’s commencement ceremony. Ali, a single father who left his one-year-old son behind in his home country, working as a university lecturer. He joined the Ph.D. program in mechanical engineering in 2019 with a passion for mechanical energy.
Ali’s academic journey was full of challenges and growth. Due to COVID-19, his research was suspended for six months, and he had difficulty continuing his studies undergoing three surgeries after a bicycle accident, including a surgery for a fractured elbow, a nose surgery, and removal of kidney stones.
However, he accepted these failure and hardship as a process of growth and participated in the ‘Failed Project Showcase’ and ‘Failure Essay Contest’ held by the KAIST Failure Society, sharing his experiences and growing into a more solid researcher.
< Most Talked about Graduate Graduate of the Year - Syed Sheraz Ali >
Despite experiencing various hardships, he found lessons to learn from them and changed his perspective, which made him unafraid of taking on new challenges. He showed through his own example that failure is not just stumbling blocks but can be a stepping stone to success by looking at his studies and personal life positively.
Furthermore, after becoming the president of the Muslim Student Association, Ali introduced halal menus to the cafeteria on campus so that more Muslim students could eat comfortably. Thanks to this change, his time at KAIST has become an opportunity to understand and experience various cultures more.
Ali is researching artificial muscles (soft actuators) with the world's highest bending strain using MXene, an artificial muscle nanomaterial that can move smoothly, in Professor Il-kwon Oh's lab.
Ali said, "After completing my Ph.D., I plan to develop soft robots, healthcare electronics, and next-generation tactile technology based on MXene, a next-generation 2D material. It is important for my juniors not to be afraid of failure and to have a challenging attitude."
Another 'Most Talked about Graduate of the Year', Mr. Sung-Hyun Jung, who graduated with a master's degree from the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management, is the CEO of Promedius, a medical AI startup, and has commercialized an osteoporosis diagnosis software based on chest X-rays using AI, and grown it into a leading company in the bone health field.
CEO Jung's challenge shows that KAIST's management education is not just theoretical but practical enough to be applied immediately in the field. CEO Jung, who is also the father of three daughters, experienced business failure in China during the period when the conflict between Korea and China was intensifying.
He moved to Silicon Valley in the United States to revive his business and tried to acquire even small businesses, but the reality was not easy. He worked hard, standing 14 hours a day in a kimchi factory and a restaurant kitchen to make a living. After finishing his life in the United States, CEO Jung returned to Korea and had the opportunity to join Lunit, a global medical AI leader founded by KAIST graduates. CEO Jung experienced the growth of the global medical AI market firsthand with unit Chairman Seungwook Paek.
When he entered the Master's Program at the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management in 2023 to acquire more specialized knowledge, CEO Jung had just transferred to Promedius and was in a crisis situation with only about 6 months left before the company's funds were exhausted.
While considering a change in business direction because he judged that it would be difficult to survive with existing business items, he learned keywords and investment review perspectives that venture capital (VC) pays attention to in Professor Hoonje Cho’s ‘Bio-innovation Business Startup Strategy and Practice’ class. He attracted 11.4 billion won in investment by applying the investment proposal he wrote based on what he learned from the class to actual practice.
< Most Talked about Graduate of the Year - Sung-Hyun Jung >
In addition, he applied the innovation strategy in the medical field he learned in Professor Kihwan Park’s ‘Innovation and Marketing in Bio and Pharmaceutics’ to the field of osteoporosis, and achieved the result of being selected as the first Asian company to be a corporate advisory committee member of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF). Through this, he established the company as a representative global entity in the osteoporosis field in just one year.
CEO Jung, who applied what he learned from KAIST to actual management and achieved results in the global market in a short period of time, said, “I want to prove that KAIST education is not limited to theory, but is very practical.” He said, “I want to let people know that my life, once full of hardship, got on the track toward success after encountering KAIST,” and expressed his ambition, saying, “My long-term goal is to create a world-class company that is recognized globally.”
In addition, an honorary doctorate was awarded to Chairman Joong Keun Lee of Booyoung Group at the commencement ceremony.
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who is an entrepreneur that led Booyoung Group, a leading general construction company, received the honorary doctorate in business administration, for leading the development of domestic housing welfare, education, and culture.
KAIST Provost Gyunmin Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee spared no effort in providing dedicated support for the development of domestic science and technology and the cultivation of future talents. He is awarded the honorary doctorate in recognition of his social responsibility in various fields, including scholarships and support for educational facilities, as well as domestic and international education, culture, veterans affairs, and overseas support.”
Since founding Booyoung Group in 1983, Chairman Lee has boldly entered the rental housing business, a field that large construction companies had avoided, and has played a significant role in improving the quality of life of ordinary citizens by supplying 230,000 households out of 383 complexes and approximately 300,000 households nationwide as rental housing, thereby contributing greatly to the stability of national housing.
< Chairman Joong Keun Lee giving his acceptance speech for his honorary Doctorate >
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who has been offering hope for a sustainable future, said, “I am honored to receive an honorary doctorate from KAIST, and I hope that KAIST students will nurture their dreams and talents and grow into global talents who will contribute to national development.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee has been carrying out various social contribution activities, and in particular, through supporting academic infrastructure, which is the core of national competitiveness, we can see his deep interest in and sense of responsibility for the development of science and technology in our country.” He added, “I am truly delighted to have him as a member of the KAIST family, and I congratulate him on behalf of all members, including our students.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee also delivered a message of encouragement at the ceremony to charge the graduates to, “Find and keep a dream of your own, be on the lookout for opportunities, don’t be afraid of making mistakes, and do not shy away from taking on challenging tasks.” He added, “Even if you fail, don’t give up. Keep on trying so that you will get to that stage of radiate your own light on the stages where anything is possible.” (End)
2025.02.14 View 5879
KAIST Holds 2025 Commencement Ceremony
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) held its 2025 Commencement Ceremony at the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex on the Daejeon Main Campus at 2 p.m. on the 14th of February.
< A scene from KAIST Commencement 2025 - Guests of Honor and Administrative Professors Entering the Stage headed by the color guards of the ELKA (Encouraging Leaders of KAIST) >
At this ceremony, a total of 3,144 degrees were conferred, including 785 doctorates, 1,643 masters, and 716 bachelors. With this, KAIST has produced a total of 81,156 advanced science and technology personnel, including 17,313 doctorates, 41,566 masters, and 22,277 bachelors since its establishment in 1971.
Changyu Lee from the School of Computing received the Minister of Science and ICT Award, and the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Award went to Lance Khizner Dabu Gragasin, an international student from the Philippines of the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering. The President’s Award was given to Seoyeong Yang of the Department of Biological Sciences, and the Alumni Association President’s Award and the Development Foundation Chairman’s Award was given to Gahyeon Bae of the Department of Industrial Design and Buyeon Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, respectively.
Minister of Science and ICT Sang-Im Yoo joined the ceremony to deliver a congratulatory speech and to present the awards to outstanding graduates.
< Minister Sang-Im Yoo of the Ministry of Science, Technology and ICT giving his congratulatory message at KAIST Commencement 2025 >
The valedictorian speeches were given by Minjae Kim of the School of Computing, who has practiced the value of sharing that learning is not competition but cooperation, and Mohammed Haruna Hamza of the Department of Aerospace Engineering, a Nigerian international student. Mr. Hamza is the first foreign student to represent the graduating class as valedictorian since the founding of KAIST.
Hamza lost his home and school in his home country due to a terrorist group’s bombing and moved south, but despite the adversity, he continued his studies while pursuing his dream of becoming an aerospace engineer. As a result of his efforts, Hamza was invited by the Korean government to study at KAIST. He expressed his determination to pursue his dream by saying, “I am grateful for the people and experiences that helped me overcome my adversity. The future is the result of the decisions we make today.”
A Pakistani international student was chosen as one of this year's "Most Talked about Graduates of the Year". It is Ali Syed Sheraz who wore his doctoral cap at this year’s commencement ceremony. Ali, a single father who left his one-year-old son behind in his home country, working as a university lecturer. He joined the Ph.D. program in mechanical engineering in 2019 with a passion for mechanical energy.
Ali’s academic journey was full of challenges and growth. Due to COVID-19, his research was suspended for six months, and he had difficulty continuing his studies undergoing three surgeries after a bicycle accident, including a surgery for a fractured elbow, a nose surgery, and removal of kidney stones.
However, he accepted these failure and hardship as a process of growth and participated in the ‘Failed Project Showcase’ and ‘Failure Essay Contest’ held by the KAIST Failure Society, sharing his experiences and growing into a more solid researcher.
< Most Talked about Graduate Graduate of the Year - Syed Sheraz Ali >
Despite experiencing various hardships, he found lessons to learn from them and changed his perspective, which made him unafraid of taking on new challenges. He showed through his own example that failure is not just stumbling blocks but can be a stepping stone to success by looking at his studies and personal life positively.
Furthermore, after becoming the president of the Muslim Student Association, Ali introduced halal menus to the cafeteria on campus so that more Muslim students could eat comfortably. Thanks to this change, his time at KAIST has become an opportunity to understand and experience various cultures more.
Ali is researching artificial muscles (soft actuators) with the world's highest bending strain using MXene, an artificial muscle nanomaterial that can move smoothly, in Professor Il-kwon Oh's lab.
Ali said, "After completing my Ph.D., I plan to develop soft robots, healthcare electronics, and next-generation tactile technology based on MXene, a next-generation 2D material. It is important for my juniors not to be afraid of failure and to have a challenging attitude."
Another 'Most Talked about Graduate of the Year', Mr. Sung-Hyun Jung, who graduated with a master's degree from the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management, is the CEO of Promedius, a medical AI startup, and has commercialized an osteoporosis diagnosis software based on chest X-rays using AI, and grown it into a leading company in the bone health field.
CEO Jung's challenge shows that KAIST's management education is not just theoretical but practical enough to be applied immediately in the field. CEO Jung, who is also the father of three daughters, experienced business failure in China during the period when the conflict between Korea and China was intensifying.
He moved to Silicon Valley in the United States to revive his business and tried to acquire even small businesses, but the reality was not easy. He worked hard, standing 14 hours a day in a kimchi factory and a restaurant kitchen to make a living. After finishing his life in the United States, CEO Jung returned to Korea and had the opportunity to join Lunit, a global medical AI leader founded by KAIST graduates. CEO Jung experienced the growth of the global medical AI market firsthand with unit Chairman Seungwook Paek.
When he entered the Master's Program at the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management in 2023 to acquire more specialized knowledge, CEO Jung had just transferred to Promedius and was in a crisis situation with only about 6 months left before the company's funds were exhausted.
While considering a change in business direction because he judged that it would be difficult to survive with existing business items, he learned keywords and investment review perspectives that venture capital (VC) pays attention to in Professor Hoonje Cho’s ‘Bio-innovation Business Startup Strategy and Practice’ class. He attracted 11.4 billion won in investment by applying the investment proposal he wrote based on what he learned from the class to actual practice.
< Most Talked about Graduate of the Year - Sung-Hyun Jung >
In addition, he applied the innovation strategy in the medical field he learned in Professor Kihwan Park’s ‘Innovation and Marketing in Bio and Pharmaceutics’ to the field of osteoporosis, and achieved the result of being selected as the first Asian company to be a corporate advisory committee member of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF). Through this, he established the company as a representative global entity in the osteoporosis field in just one year.
CEO Jung, who applied what he learned from KAIST to actual management and achieved results in the global market in a short period of time, said, “I want to prove that KAIST education is not limited to theory, but is very practical.” He said, “I want to let people know that my life, once full of hardship, got on the track toward success after encountering KAIST,” and expressed his ambition, saying, “My long-term goal is to create a world-class company that is recognized globally.”
In addition, an honorary doctorate was awarded to Chairman Joong Keun Lee of Booyoung Group at the commencement ceremony.
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who is an entrepreneur that led Booyoung Group, a leading general construction company, received the honorary doctorate in business administration, for leading the development of domestic housing welfare, education, and culture.
KAIST Provost Gyunmin Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee spared no effort in providing dedicated support for the development of domestic science and technology and the cultivation of future talents. He is awarded the honorary doctorate in recognition of his social responsibility in various fields, including scholarships and support for educational facilities, as well as domestic and international education, culture, veterans affairs, and overseas support.”
Since founding Booyoung Group in 1983, Chairman Lee has boldly entered the rental housing business, a field that large construction companies had avoided, and has played a significant role in improving the quality of life of ordinary citizens by supplying 230,000 households out of 383 complexes and approximately 300,000 households nationwide as rental housing, thereby contributing greatly to the stability of national housing.
< Chairman Joong Keun Lee giving his acceptance speech for his honorary Doctorate >
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who has been offering hope for a sustainable future, said, “I am honored to receive an honorary doctorate from KAIST, and I hope that KAIST students will nurture their dreams and talents and grow into global talents who will contribute to national development.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee has been carrying out various social contribution activities, and in particular, through supporting academic infrastructure, which is the core of national competitiveness, we can see his deep interest in and sense of responsibility for the development of science and technology in our country.” He added, “I am truly delighted to have him as a member of the KAIST family, and I congratulate him on behalf of all members, including our students.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee also delivered a message of encouragement at the ceremony to charge the graduates to, “Find and keep a dream of your own, be on the lookout for opportunities, don’t be afraid of making mistakes, and do not shy away from taking on challenging tasks.” He added, “Even if you fail, don’t give up. Keep on trying so that you will get to that stage of radiate your own light on the stages where anything is possible.” (End)
2025.02.14 View 5879 -
 A Way for Smartwatches to Detect Depression Risks Devised by KAIST and U of Michigan Researchers
- A international joint research team of KAIST and the University of Michigan developed a digital biomarker for predicting symptoms of depression based on data collected by smartwatches
- It has the potential to be used as a medical technology to replace the economically burdensome fMRI measurement test
- It is expected to expand the scope of digital health data analysis
The CORONA virus pandemic also brought about a pandemic of mental illness. Approximately one billion people worldwide suffer from various psychiatric conditions. Korea is one of more serious cases, with approximately 1.8 million patients exhibiting depression and anxiety disorders, and the total number of patients with clinical mental diseases has increased by 37% in five years to approximately 4.65 million. A joint research team from Korea and the US has developed a technology that uses biometric data collected through wearable devices to predict tomorrow's mood and, further, to predict the possibility of developing symptoms of depression.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the research results. Based on the biometric data collected by a smartwatch, a mathematical algorithm that solves the inverse problem to estimate the brain's circadian phase and sleep stages has been developed. This algorithm can estimate the degrees of circadian disruption, and these estimates can be used as the digital biomarkers to predict depression risks. >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of January that the research team under Professor Dae Wook Kim from the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and the team under Professor Daniel B. Forger from the Department of Mathematics at the University of Michigan in the United States have developed a technology to predict symptoms of depression such as sleep disorders, depression, loss of appetite, overeating, and decreased concentration in shift workers from the activity and heart rate data collected from smartwatches.
According to WHO, a promising new treatment direction for mental illness focuses on the sleep and circadian timekeeping system located in the hypothalamus of the brain, which directly affect impulsivity, emotional responses, decision-making, and overall mood.
However, in order to measure endogenous circadian rhythms and sleep states, blood or saliva must be drawn every 30 minutes throughout the night to measure changes in the concentration of the melatonin hormone in our bodies and polysomnography (PSG) must be performed. As such treatments requires hospitalization and most psychiatric patients only visit for outpatient treatment, there has been no significant progress in developing treatment methods that take these two factors into account. In addition, the cost of the PSG test, which is approximately $1000, leaves mental health treatment considering sleep and circadian rhythms out of reach for the socially disadvantaged.
The solution to overcome these problems is to employ wearable devices for the easier collection of biometric data such as heart rate, body temperature, and activity level in real time without spatial constraints. However, current wearable devices have the limitation of providing only indirect information on biomarkers required by medical staff, such as the phase of the circadian clock.
The joint research team developed a filtering technology that accurately estimates the phase of the circadian clock, which changes daily, such as heart rate and activity time series data collected from a smartwatch. This is an implementation of a digital twin that precisely describes the circadian rhythm in the brain, and it can be used to estimate circadian rhythm disruption.
< Figure 2. The suprachiasmatic nucleus located in the hypothalamus of the brain is the central biological clock that regulates the 24-hour physiological rhythm and plays a key role in maintaining the body’s circadian rhythm. If the phase of this biological clock is disrupted, it affects various parts of the brain, which can cause psychiatric conditions such as depression. >
The possibility of using the digital twin of this circadian clock to predict the symptoms of depression was verified through collaboration with the research team of Professor Srijan Sen of the Michigan Neuroscience Institute and Professor Amy Bohnert of the Department of Psychiatry of the University of Michigan.
The collaborative research team conducted a large-scale prospective cohort study involving approximately 800 shift workers and showed that the circadian rhythm disruption digital biomarker estimated through the technology can predict tomorrow's mood as well as six symptoms, including sleep problems, appetite changes, decreased concentration, and suicidal thoughts, which are representative symptoms of depression.
< Figure 3. The circadian rhythm of hormones such as melatonin regulates various physiological functions and behaviors such as heart rate and activity level. These physiological and behavioral signals can be measured in daily life through wearable devices. In order to estimate the body’s circadian rhythm inversely based on the measured biometric signals, a mathematical algorithm is needed. This algorithm plays a key role in accurately identifying the characteristics of circadian rhythms by extracting hidden physiological patterns from biosignals. >
Professor Dae Wook Kim said, "It is very meaningful to be able to conduct research that provides a clue for ways to apply wearable biometric data using mathematics that have not previously been utilized for actual disease management." He added, "We expect that this research will be able to present continuous and non-invasive mental health monitoring technology. This is expected to present a new paradigm for mental health care. By resolving some of the major problems socially disadvantaged people may face in current treatment practices, they may be able to take more active steps when experiencing symptoms of depression, such as seeking counsel before things get out of hand."
< Figure 4. A mathematical algorithm was devised to circumvent the problems of estimating the phase of the brain's biological clock and sleep stages inversely from the biodata collected by a smartwatch. This algorithm can estimate the degree of daily circadian rhythm disruption, and this estimate can be used as a digital biomarker to predict depression symptoms. >
The results of this study, in which Professor Dae Wook Kim of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at KAIST participated as the joint first author and corresponding author, were published in the online version of the international academic journal npj Digital Medicine on December 5, 2024. (Paper title: The real-world association between digital markers of circadian disruption and mental health risks) DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01348-6
This study was conducted with the support of the KAIST's Research Support Program for New Faculty Members, the US National Science Foundation, the US National Institutes of Health, and the US Army Research Institute MURI Program.
2025.01.20 View 7273
A Way for Smartwatches to Detect Depression Risks Devised by KAIST and U of Michigan Researchers
- A international joint research team of KAIST and the University of Michigan developed a digital biomarker for predicting symptoms of depression based on data collected by smartwatches
- It has the potential to be used as a medical technology to replace the economically burdensome fMRI measurement test
- It is expected to expand the scope of digital health data analysis
The CORONA virus pandemic also brought about a pandemic of mental illness. Approximately one billion people worldwide suffer from various psychiatric conditions. Korea is one of more serious cases, with approximately 1.8 million patients exhibiting depression and anxiety disorders, and the total number of patients with clinical mental diseases has increased by 37% in five years to approximately 4.65 million. A joint research team from Korea and the US has developed a technology that uses biometric data collected through wearable devices to predict tomorrow's mood and, further, to predict the possibility of developing symptoms of depression.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the research results. Based on the biometric data collected by a smartwatch, a mathematical algorithm that solves the inverse problem to estimate the brain's circadian phase and sleep stages has been developed. This algorithm can estimate the degrees of circadian disruption, and these estimates can be used as the digital biomarkers to predict depression risks. >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of January that the research team under Professor Dae Wook Kim from the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and the team under Professor Daniel B. Forger from the Department of Mathematics at the University of Michigan in the United States have developed a technology to predict symptoms of depression such as sleep disorders, depression, loss of appetite, overeating, and decreased concentration in shift workers from the activity and heart rate data collected from smartwatches.
According to WHO, a promising new treatment direction for mental illness focuses on the sleep and circadian timekeeping system located in the hypothalamus of the brain, which directly affect impulsivity, emotional responses, decision-making, and overall mood.
However, in order to measure endogenous circadian rhythms and sleep states, blood or saliva must be drawn every 30 minutes throughout the night to measure changes in the concentration of the melatonin hormone in our bodies and polysomnography (PSG) must be performed. As such treatments requires hospitalization and most psychiatric patients only visit for outpatient treatment, there has been no significant progress in developing treatment methods that take these two factors into account. In addition, the cost of the PSG test, which is approximately $1000, leaves mental health treatment considering sleep and circadian rhythms out of reach for the socially disadvantaged.
The solution to overcome these problems is to employ wearable devices for the easier collection of biometric data such as heart rate, body temperature, and activity level in real time without spatial constraints. However, current wearable devices have the limitation of providing only indirect information on biomarkers required by medical staff, such as the phase of the circadian clock.
The joint research team developed a filtering technology that accurately estimates the phase of the circadian clock, which changes daily, such as heart rate and activity time series data collected from a smartwatch. This is an implementation of a digital twin that precisely describes the circadian rhythm in the brain, and it can be used to estimate circadian rhythm disruption.
< Figure 2. The suprachiasmatic nucleus located in the hypothalamus of the brain is the central biological clock that regulates the 24-hour physiological rhythm and plays a key role in maintaining the body’s circadian rhythm. If the phase of this biological clock is disrupted, it affects various parts of the brain, which can cause psychiatric conditions such as depression. >
The possibility of using the digital twin of this circadian clock to predict the symptoms of depression was verified through collaboration with the research team of Professor Srijan Sen of the Michigan Neuroscience Institute and Professor Amy Bohnert of the Department of Psychiatry of the University of Michigan.
The collaborative research team conducted a large-scale prospective cohort study involving approximately 800 shift workers and showed that the circadian rhythm disruption digital biomarker estimated through the technology can predict tomorrow's mood as well as six symptoms, including sleep problems, appetite changes, decreased concentration, and suicidal thoughts, which are representative symptoms of depression.
< Figure 3. The circadian rhythm of hormones such as melatonin regulates various physiological functions and behaviors such as heart rate and activity level. These physiological and behavioral signals can be measured in daily life through wearable devices. In order to estimate the body’s circadian rhythm inversely based on the measured biometric signals, a mathematical algorithm is needed. This algorithm plays a key role in accurately identifying the characteristics of circadian rhythms by extracting hidden physiological patterns from biosignals. >
Professor Dae Wook Kim said, "It is very meaningful to be able to conduct research that provides a clue for ways to apply wearable biometric data using mathematics that have not previously been utilized for actual disease management." He added, "We expect that this research will be able to present continuous and non-invasive mental health monitoring technology. This is expected to present a new paradigm for mental health care. By resolving some of the major problems socially disadvantaged people may face in current treatment practices, they may be able to take more active steps when experiencing symptoms of depression, such as seeking counsel before things get out of hand."
< Figure 4. A mathematical algorithm was devised to circumvent the problems of estimating the phase of the brain's biological clock and sleep stages inversely from the biodata collected by a smartwatch. This algorithm can estimate the degree of daily circadian rhythm disruption, and this estimate can be used as a digital biomarker to predict depression symptoms. >
The results of this study, in which Professor Dae Wook Kim of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at KAIST participated as the joint first author and corresponding author, were published in the online version of the international academic journal npj Digital Medicine on December 5, 2024. (Paper title: The real-world association between digital markers of circadian disruption and mental health risks) DOI: 10.1038/s41746-024-01348-6
This study was conducted with the support of the KAIST's Research Support Program for New Faculty Members, the US National Science Foundation, the US National Institutes of Health, and the US Army Research Institute MURI Program.
2025.01.20 View 7273 -
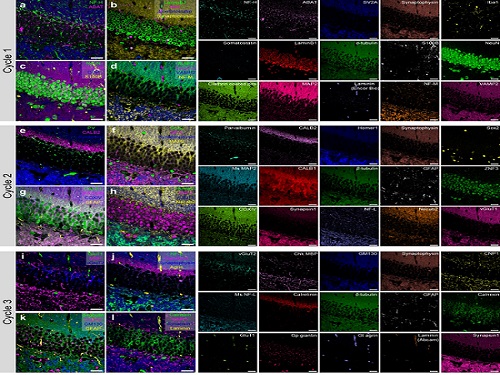 PICASSO Technique Drives Biological Molecules into Technicolor
The new imaging approach brings current imaging colors from four to more than 15 for mapping overlapping proteins
Pablo Picasso’s surreal cubist artistic style shifted common features into unrecognizable scenes, but a new imaging approach bearing his namesake may elucidate the most complicated subject: the brain. Employing artificial intelligence to clarify spectral color blending of tiny molecules used to stain specific proteins and other items of research interest, the PICASSO technique, allows researchers to use more than 15 colors to image and parse our overlapping proteins.
The PICASSO developers, based in Korea, published their approach on May 5 in Nature Communications.
Fluorophores — the staining molecules — emit specific colors when excited by a light, but if more than four fluorophores are used, their emitted colors overlap and blend. Researchers previously developed techniques to correct this spectral overlap by precisely defining the matrix of mixed and unmixed images. This measurement depends on reference spectra, found by identifying clear images of only one fluorophore-stained specimen or of multiple, identically prepared specimens that only contain a single fluorophore each.
“Such reference spectra measurement could be complicated to perform in highly heterogeneous specimens, such as the brain, due to the highly varied emission spectra of fluorophores depending on the subregions from which the spectra were measured,” said co-corresponding author Young-Gyu Yoon, professor in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST. He explained that the subregions would each need their own spectra reference measurements, making for an inefficient, time-consuming process. “To address this problem, we developed an approach that does not require reference spectra measurements.”
The approach is the “Process of ultra-multiplexed Imaging of biomolecules viA the unmixing of the Signals of Spectrally Overlapping fluorophores,” also known as PICASSO. Ultra-multiplexed imaging refers to visualizing the numerous individual components of a unit. Like a cinema multiplex in which each theater plays a different movie, each protein in a cell has a different role. By staining with fluorophores, researchers can begin to understand those roles.
“We devised a strategy based on information theory; unmixing is performed by iteratively minimizing the mutual information between mixed images,” said co-corresponding author Jae-Byum Chang, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST. “This allows us to get away with the assumption that the spatial distribution of different proteins is mutually exclusive and enables accurate information unmixing.”
To demonstrate PICASSO’s capabilities, the researchers applied the technique to imaging a mouse brain. With a single round of staining, they performed 15-color multiplexed imaging of a mouse brain. Although small, mouse brains are still complex, multifaceted organs that can take significant resources to map. According to the researchers, PICASSO can improve the capabilities of other imaging techniques and allow for the use of even more fluorophore colors.
Using one such imaging technique in combination with PICASSO, the team achieved 45-color multiplexed imaging of the mouse brain in only three staining and imaging cycles, according to Yoon.
“PICASSO is a versatile tool for the multiplexed biomolecule imaging of cultured cells, tissue slices and clinical specimens,” Chang said. “We anticipate that PICASSO will be useful for a broad range of applications for which biomolecules’ spatial information is important. One such application the tool would be useful for is revealing the cellular heterogeneities of tumor microenvironments, especially the heterogeneous populations of immune cells, which are closely related to cancer prognoses and the efficacy of cancer therapies.”
The Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology supported this work. Spectral imaging was performed at the Korea Basic Science Institute Western Seoul Center.
-PublicationJunyoung Seo, Yeonbo Sim, Jeewon Kim, Hyunwoo Kim, In Cho, Hoyeon Nam, Yong-Gyu Yoon, Jae-Byum Chang, “PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatiallyoverlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements,” May 5, Nature Communications (doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30168-z)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Byum ChangDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
Professor Young-Gyu YoonSchool of Electrical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.06.22 View 11392
PICASSO Technique Drives Biological Molecules into Technicolor
The new imaging approach brings current imaging colors from four to more than 15 for mapping overlapping proteins
Pablo Picasso’s surreal cubist artistic style shifted common features into unrecognizable scenes, but a new imaging approach bearing his namesake may elucidate the most complicated subject: the brain. Employing artificial intelligence to clarify spectral color blending of tiny molecules used to stain specific proteins and other items of research interest, the PICASSO technique, allows researchers to use more than 15 colors to image and parse our overlapping proteins.
The PICASSO developers, based in Korea, published their approach on May 5 in Nature Communications.
Fluorophores — the staining molecules — emit specific colors when excited by a light, but if more than four fluorophores are used, their emitted colors overlap and blend. Researchers previously developed techniques to correct this spectral overlap by precisely defining the matrix of mixed and unmixed images. This measurement depends on reference spectra, found by identifying clear images of only one fluorophore-stained specimen or of multiple, identically prepared specimens that only contain a single fluorophore each.
“Such reference spectra measurement could be complicated to perform in highly heterogeneous specimens, such as the brain, due to the highly varied emission spectra of fluorophores depending on the subregions from which the spectra were measured,” said co-corresponding author Young-Gyu Yoon, professor in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST. He explained that the subregions would each need their own spectra reference measurements, making for an inefficient, time-consuming process. “To address this problem, we developed an approach that does not require reference spectra measurements.”
The approach is the “Process of ultra-multiplexed Imaging of biomolecules viA the unmixing of the Signals of Spectrally Overlapping fluorophores,” also known as PICASSO. Ultra-multiplexed imaging refers to visualizing the numerous individual components of a unit. Like a cinema multiplex in which each theater plays a different movie, each protein in a cell has a different role. By staining with fluorophores, researchers can begin to understand those roles.
“We devised a strategy based on information theory; unmixing is performed by iteratively minimizing the mutual information between mixed images,” said co-corresponding author Jae-Byum Chang, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST. “This allows us to get away with the assumption that the spatial distribution of different proteins is mutually exclusive and enables accurate information unmixing.”
To demonstrate PICASSO’s capabilities, the researchers applied the technique to imaging a mouse brain. With a single round of staining, they performed 15-color multiplexed imaging of a mouse brain. Although small, mouse brains are still complex, multifaceted organs that can take significant resources to map. According to the researchers, PICASSO can improve the capabilities of other imaging techniques and allow for the use of even more fluorophore colors.
Using one such imaging technique in combination with PICASSO, the team achieved 45-color multiplexed imaging of the mouse brain in only three staining and imaging cycles, according to Yoon.
“PICASSO is a versatile tool for the multiplexed biomolecule imaging of cultured cells, tissue slices and clinical specimens,” Chang said. “We anticipate that PICASSO will be useful for a broad range of applications for which biomolecules’ spatial information is important. One such application the tool would be useful for is revealing the cellular heterogeneities of tumor microenvironments, especially the heterogeneous populations of immune cells, which are closely related to cancer prognoses and the efficacy of cancer therapies.”
The Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology supported this work. Spectral imaging was performed at the Korea Basic Science Institute Western Seoul Center.
-PublicationJunyoung Seo, Yeonbo Sim, Jeewon Kim, Hyunwoo Kim, In Cho, Hoyeon Nam, Yong-Gyu Yoon, Jae-Byum Chang, “PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatiallyoverlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements,” May 5, Nature Communications (doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30168-z)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Byum ChangDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
Professor Young-Gyu YoonSchool of Electrical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.06.22 View 11392 -
 AI Weather Forecasting Research Center Opens
The Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI in collaboration with the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences (NIMS) under the National Meteorological Administration launched the AI Weather Forecasting Research Center last month.
The KAIST AI Weather Forecasting Research Center headed by Professor Seyoung Yoon was established with funding from from the AlphaWeather Development Research Project of the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences. KAIST was finally selected asas the project facilitator.
AlphaWeather is an AI system that utilizes and analyzes approximately approximately 150,000 ,000 pieces of weather information per hour to help weather forecasters produce accurate weather forecasts. The research center is composed of three research teams with the following goals: (a) developdevelop AI technology for precipitation nowcasting, (b) developdevelop AI technology for accelerating physical process-based numerical models, and (c) develop dAI technology for supporting weather forecasters. The teams consist of 15 staff member members from NIMS and 61 researchers from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST.
The research center is developing an AI algorithm for precipitation nowcasting (with up to six hours of lead time), which uses satellite images, radar reflectivity, and data collected from weather stations. It is also developing an AI algorithm for correcting biases in the prediction results from multiple numerical models. Finally, it is Finally, it is developing AI technology that supports weather forecasters by standardizing and automating repetitive manual processes. After verification, the the results obtained will be used by by the Korean National Weather Service as a next-generation forecasting/special-reporting system intelligence engine from 2026.
2022.01.10 View 7234
AI Weather Forecasting Research Center Opens
The Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI in collaboration with the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences (NIMS) under the National Meteorological Administration launched the AI Weather Forecasting Research Center last month.
The KAIST AI Weather Forecasting Research Center headed by Professor Seyoung Yoon was established with funding from from the AlphaWeather Development Research Project of the National Institute of Meteorological Sciences. KAIST was finally selected asas the project facilitator.
AlphaWeather is an AI system that utilizes and analyzes approximately approximately 150,000 ,000 pieces of weather information per hour to help weather forecasters produce accurate weather forecasts. The research center is composed of three research teams with the following goals: (a) developdevelop AI technology for precipitation nowcasting, (b) developdevelop AI technology for accelerating physical process-based numerical models, and (c) develop dAI technology for supporting weather forecasters. The teams consist of 15 staff member members from NIMS and 61 researchers from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST.
The research center is developing an AI algorithm for precipitation nowcasting (with up to six hours of lead time), which uses satellite images, radar reflectivity, and data collected from weather stations. It is also developing an AI algorithm for correcting biases in the prediction results from multiple numerical models. Finally, it is Finally, it is developing AI technology that supports weather forecasters by standardizing and automating repetitive manual processes. After verification, the the results obtained will be used by by the Korean National Weather Service as a next-generation forecasting/special-reporting system intelligence engine from 2026.
2022.01.10 View 7234 -
 Professor Jihee Kim Wins the Lucas Prize for Her Income Inequality Theory
Professor Jihee Kim from the School of Business and Technology Management at KAIST was announced as one of two winners of the 2021 Robert E. Lucas Jr. Prize. Professor Kim was recognized for having provided an empirical analysis on engines of income growth, sources of income inequality, and their rich interplay in her paper published in the Journal of Political Economy (JPE) in October 2018. The co-author of this study, Professor Charles I. Jones at Stanford University, was honored to be another awardee of this year’s Lucas Prize.
The Robert E. Lucas Jr. Prize, simply known as the Lucas Prize, is awarded biannually for the most interesting paper in the area of Dynamic Economics published in the leading economics journal JPE in the preceding two years. The prize was established in 2016 in celebration of the 1995 Nobel Prize in Economics Laureate Dr. Lucas’s seminal contributions to economics. The two former prizes were presented in 2019 and 2017 respectively.
Professor Kim and Professor Jones, in their award-winning paper titled 'A Schumpeterian Model of Top Income Inequality', observed that top income inequality was relatively low and stable between 1960 and 1980, but then rose sharply in some countries, including the United States and the United Kingdom.
The authors focused on entrepreneurial activities and the resulting income as the driving force of income inequality. They assumed that the forces that increased the efforts of fast-growing entrepreneurs to improve their products or increased productivity of their efforts could increase income inequality. On the other hand, the forces that enhanced creative destruction or that raised the rate at which high-growth entrepreneurs lost that status could decrease income inequality, according to the authors’ theory.
Professor Kim explained, “Various economic forces due to globalization, the advancement in AI and IT technologies, taxes, and policies related to innovation blocking may explain the varied patterns in income inequality.”
“Through follow-up research, I will continue developing economic theory models that can analyze the impact of changes such as income tax rates and salary negotiations on income inequality,” she added.
Professor Kim received her bachelor’s degree from the KAIST School of Computing in 2005 and pursued her graduates studies at Stanford University, acquiring a master’s degree in economics in 2011 and a doctoral degree in management science and engineering in 2013.
(END)
2021.03.26 View 9073
Professor Jihee Kim Wins the Lucas Prize for Her Income Inequality Theory
Professor Jihee Kim from the School of Business and Technology Management at KAIST was announced as one of two winners of the 2021 Robert E. Lucas Jr. Prize. Professor Kim was recognized for having provided an empirical analysis on engines of income growth, sources of income inequality, and their rich interplay in her paper published in the Journal of Political Economy (JPE) in October 2018. The co-author of this study, Professor Charles I. Jones at Stanford University, was honored to be another awardee of this year’s Lucas Prize.
The Robert E. Lucas Jr. Prize, simply known as the Lucas Prize, is awarded biannually for the most interesting paper in the area of Dynamic Economics published in the leading economics journal JPE in the preceding two years. The prize was established in 2016 in celebration of the 1995 Nobel Prize in Economics Laureate Dr. Lucas’s seminal contributions to economics. The two former prizes were presented in 2019 and 2017 respectively.
Professor Kim and Professor Jones, in their award-winning paper titled 'A Schumpeterian Model of Top Income Inequality', observed that top income inequality was relatively low and stable between 1960 and 1980, but then rose sharply in some countries, including the United States and the United Kingdom.
The authors focused on entrepreneurial activities and the resulting income as the driving force of income inequality. They assumed that the forces that increased the efforts of fast-growing entrepreneurs to improve their products or increased productivity of their efforts could increase income inequality. On the other hand, the forces that enhanced creative destruction or that raised the rate at which high-growth entrepreneurs lost that status could decrease income inequality, according to the authors’ theory.
Professor Kim explained, “Various economic forces due to globalization, the advancement in AI and IT technologies, taxes, and policies related to innovation blocking may explain the varied patterns in income inequality.”
“Through follow-up research, I will continue developing economic theory models that can analyze the impact of changes such as income tax rates and salary negotiations on income inequality,” she added.
Professor Kim received her bachelor’s degree from the KAIST School of Computing in 2005 and pursued her graduates studies at Stanford University, acquiring a master’s degree in economics in 2011 and a doctoral degree in management science and engineering in 2013.
(END)
2021.03.26 View 9073 -
 Sturdy Fabric-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Takes Us One Step Closer to Wearable Electronics
KAIST researchers presented a highly flexible but sturdy wearable piezoelectric harvester using the simple and easy fabrication process of hot pressing and tape casting. This energy harvester, which has record high interfacial adhesion strength, will take us one step closer to being able to manufacture embedded wearable electronics.
A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong said that the novelty of this result lies in its simplicity, applicability, durability, and its new characterization of wearable electronic devices.
Wearable devices are increasingly being used in a wide array of applications from small electronics to embedded devices such as sensors, actuators, displays, and energy harvesters.
Despite their many advantages, high costs and complex fabrication processes remained challenges for reaching commercialization. In addition, their durability was frequently questioned. To address these issues, Professor Hong’s team developed a new fabrication process and analysis technology for testing the mechanical properties of affordable wearable devices.
For this process, the research team used a hot pressing and tape casting procedure to connect the fabric structures of polyester and a polymer film. Hot pressing has usually been used when making batteries and fuel cells due to its high adhesiveness. Above all, the process takes only two to three minutes.
The newly developed fabrication process will enable the direct application of a device into general garments using hot pressing just as graphic patches can be attached to garments using a heat press.
In particular, when the polymer film is hot pressed onto a fabric below its crystallization temperature, it transforms into an amorphous state. In this state, it compactly attaches to the concave surface of the fabric and infiltrates into the gaps between the transverse wefts and longitudinal warps. These features result in high interfacial adhesion strength. For this reason, hot pressing has the potential to reduce the cost of fabrication through the direct application of fabric-based wearable devices to common garments.
In addition to the conventional durability test of bending cycles, the newly introduced surface and interfacial cutting analysis system proved the high mechanical durability of the fabric-based wearable device by measuring the high interfacial adhesion strength between the fabric and the polymer film. Professor Hong said the study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of wearable devices using fabrics and polymers.
He added that his team first used the surface and interfacial cutting analysis system (SAICAS) in the field of wearable electronics to test the mechanical properties of polymer-based wearable devices. Their surface and interfacial cutting analysis system is more precise than conventional methods (peel test, tape test, and microstretch test) because it qualitatively and quantitatively measures the adhesion strength.
Professor Hong explained, “This study could enable the commercialization of highly durable wearable devices based on the analysis of their interfacial adhesion strength. Our study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of other devices using fabrics and polymers. We look forward to fabric-based wearable electronics hitting the market very soon.”
The results of this study were registered as a domestic patent in Korea last year, and published in Nano Energy this month. This study has been conducted through collaboration with Professor Yong Min Lee in the Department of Energy Science and Engineering at DGIST, Professor Kwangsoo No in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, and Professor Seunghwa Ryu in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST.
This study was supported by the High-Risk High-Return Project and the Global Singularity Research Project at KAIST, the National Research Foundation, and the Ministry of Science and ICT in Korea.
-Publication:
Jaegyu Kim, Seoungwoo Byun, Sangryun Lee, Jeongjae Ryu, Seongwoo Cho, Chungik Oh, Hongjun Kim, Kwangsoo No, Seunghwa Ryu, Yong Min Lee, Seungbum Hong*, Nano Energy 75 (2020), 104992.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104992
-Profile: Professor Seungbum Hong
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2020.09.17 View 14994
Sturdy Fabric-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Takes Us One Step Closer to Wearable Electronics
KAIST researchers presented a highly flexible but sturdy wearable piezoelectric harvester using the simple and easy fabrication process of hot pressing and tape casting. This energy harvester, which has record high interfacial adhesion strength, will take us one step closer to being able to manufacture embedded wearable electronics.
A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong said that the novelty of this result lies in its simplicity, applicability, durability, and its new characterization of wearable electronic devices.
Wearable devices are increasingly being used in a wide array of applications from small electronics to embedded devices such as sensors, actuators, displays, and energy harvesters.
Despite their many advantages, high costs and complex fabrication processes remained challenges for reaching commercialization. In addition, their durability was frequently questioned. To address these issues, Professor Hong’s team developed a new fabrication process and analysis technology for testing the mechanical properties of affordable wearable devices.
For this process, the research team used a hot pressing and tape casting procedure to connect the fabric structures of polyester and a polymer film. Hot pressing has usually been used when making batteries and fuel cells due to its high adhesiveness. Above all, the process takes only two to three minutes.
The newly developed fabrication process will enable the direct application of a device into general garments using hot pressing just as graphic patches can be attached to garments using a heat press.
In particular, when the polymer film is hot pressed onto a fabric below its crystallization temperature, it transforms into an amorphous state. In this state, it compactly attaches to the concave surface of the fabric and infiltrates into the gaps between the transverse wefts and longitudinal warps. These features result in high interfacial adhesion strength. For this reason, hot pressing has the potential to reduce the cost of fabrication through the direct application of fabric-based wearable devices to common garments.
In addition to the conventional durability test of bending cycles, the newly introduced surface and interfacial cutting analysis system proved the high mechanical durability of the fabric-based wearable device by measuring the high interfacial adhesion strength between the fabric and the polymer film. Professor Hong said the study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of wearable devices using fabrics and polymers.
He added that his team first used the surface and interfacial cutting analysis system (SAICAS) in the field of wearable electronics to test the mechanical properties of polymer-based wearable devices. Their surface and interfacial cutting analysis system is more precise than conventional methods (peel test, tape test, and microstretch test) because it qualitatively and quantitatively measures the adhesion strength.
Professor Hong explained, “This study could enable the commercialization of highly durable wearable devices based on the analysis of their interfacial adhesion strength. Our study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of other devices using fabrics and polymers. We look forward to fabric-based wearable electronics hitting the market very soon.”
The results of this study were registered as a domestic patent in Korea last year, and published in Nano Energy this month. This study has been conducted through collaboration with Professor Yong Min Lee in the Department of Energy Science and Engineering at DGIST, Professor Kwangsoo No in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, and Professor Seunghwa Ryu in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST.
This study was supported by the High-Risk High-Return Project and the Global Singularity Research Project at KAIST, the National Research Foundation, and the Ministry of Science and ICT in Korea.
-Publication:
Jaegyu Kim, Seoungwoo Byun, Sangryun Lee, Jeongjae Ryu, Seongwoo Cho, Chungik Oh, Hongjun Kim, Kwangsoo No, Seunghwa Ryu, Yong Min Lee, Seungbum Hong*, Nano Energy 75 (2020), 104992.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104992
-Profile: Professor Seungbum Hong
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2020.09.17 View 14994 -
 Professor Ji-Hyun Lee Awarded the Sasada Prize
Professor Ji-Hyun Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology was awarded the Sasada Prize during the 24th annual Conference of Computer-Aided Architectural Design Research in Asia (CAADRIA) held in Wellington, New Zealand on April 15.
The Sasada Award honors the late Professor Tsuyoshi Sasada (1941-2005), the former Professor of Osaka University and co-founder and fellow of CAADRIA. It is given to an individual who has contributed to the next generation of researchers and academics, to the wider profession and practice in computer-aided design and research, and has earned recognition in the academic community.
Professor Lee was recognized for her development of CAAD (Computer-Aided Architectural Design) through her research work on the land price precision system using case-based reasoning. Her research team proposed a model for estimating the average apartment price in an administrative district after collecting 40 variables from the six major Korean cities, excluding Seoul and Ulsan. Their follow-up studies showed the possibility of replacing existing experts’ predictions.
Professor Lee has been steadily researching for 20 years on case-based reasoning (CBR), a field of artificial intelligence, and has published more than 40 papers in the field of CBR. Meanwhile, the CAAD Future 2019 event will be held at KAIST in June.
2019.04.23 View 8120
Professor Ji-Hyun Lee Awarded the Sasada Prize
Professor Ji-Hyun Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology was awarded the Sasada Prize during the 24th annual Conference of Computer-Aided Architectural Design Research in Asia (CAADRIA) held in Wellington, New Zealand on April 15.
The Sasada Award honors the late Professor Tsuyoshi Sasada (1941-2005), the former Professor of Osaka University and co-founder and fellow of CAADRIA. It is given to an individual who has contributed to the next generation of researchers and academics, to the wider profession and practice in computer-aided design and research, and has earned recognition in the academic community.
Professor Lee was recognized for her development of CAAD (Computer-Aided Architectural Design) through her research work on the land price precision system using case-based reasoning. Her research team proposed a model for estimating the average apartment price in an administrative district after collecting 40 variables from the six major Korean cities, excluding Seoul and Ulsan. Their follow-up studies showed the possibility of replacing existing experts’ predictions.
Professor Lee has been steadily researching for 20 years on case-based reasoning (CBR), a field of artificial intelligence, and has published more than 40 papers in the field of CBR. Meanwhile, the CAAD Future 2019 event will be held at KAIST in June.
2019.04.23 View 8120 -
 Distinguished Professor Lee Named International Fellow of the CAS
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was awarded the title of distinguished professor and international fellow from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and honorary professor from its affiliated organization the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology (TIB).
The CAS recognized Distinguished Professor Lee for his significant contributions to biotechnology. He has made significant pioneering academic achievements in the area of systems metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals from microorganisms. Not only did he develop the first and best source technology in that field, but also came out with processes for the production of biofuel and environmentally-friendly chemicals.”
As a global leader in systems metabolic engineering, Distinguished Professor Lee has also been appointed as an honorary professor at Jiangnan University in Wuxi, China.
Distinguished Professor Lee was listed in the ‘Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014’ selected by the renowned international journal Nature Biotechnology. Moreover, he was the first Asian recipient of the James E. Bailey Award in 2016 and Marvin J. Johnson Award in 2012, which are given to scholars in the field of biotechnology.
He is also one of 13 global scientists who are foreign members of the renowned academic societies the National Academy of Engineering and the National Academy of Sciences in the US. Furthermore, he received the ‘2017 Korea Best Scientist Award’ from the president of Korea in July. Finally, his founding field, systems metabolic engineering, was chosen as one of the ‘Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016’ by the World Economic Forum.
The Chinese Academy of Sciences, established in November 1949, is an academic organization that carries out research on basic sciences and natural sciences in China. It defined its science and technology system to include the fields of basic sciences, natural sciences, and high technology. While having a base in Beijing, its branch academies are located in 12 main cities along with 117 affiliates and 100 national key labs.
2017.10.26 View 13240
Distinguished Professor Lee Named International Fellow of the CAS
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was awarded the title of distinguished professor and international fellow from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and honorary professor from its affiliated organization the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology (TIB).
The CAS recognized Distinguished Professor Lee for his significant contributions to biotechnology. He has made significant pioneering academic achievements in the area of systems metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals from microorganisms. Not only did he develop the first and best source technology in that field, but also came out with processes for the production of biofuel and environmentally-friendly chemicals.”
As a global leader in systems metabolic engineering, Distinguished Professor Lee has also been appointed as an honorary professor at Jiangnan University in Wuxi, China.
Distinguished Professor Lee was listed in the ‘Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014’ selected by the renowned international journal Nature Biotechnology. Moreover, he was the first Asian recipient of the James E. Bailey Award in 2016 and Marvin J. Johnson Award in 2012, which are given to scholars in the field of biotechnology.
He is also one of 13 global scientists who are foreign members of the renowned academic societies the National Academy of Engineering and the National Academy of Sciences in the US. Furthermore, he received the ‘2017 Korea Best Scientist Award’ from the president of Korea in July. Finally, his founding field, systems metabolic engineering, was chosen as one of the ‘Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016’ by the World Economic Forum.
The Chinese Academy of Sciences, established in November 1949, is an academic organization that carries out research on basic sciences and natural sciences in China. It defined its science and technology system to include the fields of basic sciences, natural sciences, and high technology. While having a base in Beijing, its branch academies are located in 12 main cities along with 117 affiliates and 100 national key labs.
2017.10.26 View 13240 -
 KAIST AI Academy for LG CNS Employees
The Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering) at KAIST has collaborated with LG CNS to start a full-fledged KAIST AI Academy course after the two-week pilot course for employees of LG CNS, a Korean company specializing in IT services.
Approximately 100 employees participated in the first KAIST AI Academy course held over two weeks from August 24 to September 1. LG CNS is planning to enroll a total of 500 employees in this course by the end of the year.
Artificial intelligence is widely recognized as essential technology in various industries. In that sense, the KAIST AI Academy course was established to reinforce both the AI technology and the business ability of the company. In addition, it aims at leading employees to develop new business using novel technologies. The main contents of this course are as follows: i) discussing AI technology development and its influence on industries; ii) understanding AI technologies and acquiring the major technologies applicable to business; and iii) introducing cases of AI applications and deep learning.
During the course, seven professors with expertise in AI deep learning from the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering), including Jae-Gil Lee and Jinkyoo Park will be leading the class, including practical on-site educational programs.
Based on the accumulated business experience integrated with the latest AI technology, LG CNS has been making an effort to find new business opportunities to support companies that are hoping to make digital innovations.
The company aims to reinforce the AI capabilities of its employees and is planning to upgrade the course in a sustainable manner. It will also foster outside manpower by expanding the AI education to its clients who pursue manufacturing reinforcement and innovation in digital marketing.
Seong Wook Lee, the Director of the AI and Big Data Business Unit said, “As AI plays an important role in business services, LG CNS decided to open the KAIST AI Academy course to deliver better value to our clients by incorporating our AI-based business cases and KAIST’s up-to-date knowledge.”
2017.09.06 View 8272
KAIST AI Academy for LG CNS Employees
The Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering) at KAIST has collaborated with LG CNS to start a full-fledged KAIST AI Academy course after the two-week pilot course for employees of LG CNS, a Korean company specializing in IT services.
Approximately 100 employees participated in the first KAIST AI Academy course held over two weeks from August 24 to September 1. LG CNS is planning to enroll a total of 500 employees in this course by the end of the year.
Artificial intelligence is widely recognized as essential technology in various industries. In that sense, the KAIST AI Academy course was established to reinforce both the AI technology and the business ability of the company. In addition, it aims at leading employees to develop new business using novel technologies. The main contents of this course are as follows: i) discussing AI technology development and its influence on industries; ii) understanding AI technologies and acquiring the major technologies applicable to business; and iii) introducing cases of AI applications and deep learning.
During the course, seven professors with expertise in AI deep learning from the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering (Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering), including Jae-Gil Lee and Jinkyoo Park will be leading the class, including practical on-site educational programs.
Based on the accumulated business experience integrated with the latest AI technology, LG CNS has been making an effort to find new business opportunities to support companies that are hoping to make digital innovations.
The company aims to reinforce the AI capabilities of its employees and is planning to upgrade the course in a sustainable manner. It will also foster outside manpower by expanding the AI education to its clients who pursue manufacturing reinforcement and innovation in digital marketing.
Seong Wook Lee, the Director of the AI and Big Data Business Unit said, “As AI plays an important role in business services, LG CNS decided to open the KAIST AI Academy course to deliver better value to our clients by incorporating our AI-based business cases and KAIST’s up-to-date knowledge.”
2017.09.06 View 8272 -
 Professor Shin's Team Receives the Best Software Defined Network Solution Showcase Award
Professor Seungwon Shin of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team won the Best Software Defined Networking (SDN) Solution Showcase Award hosted by the SDN World Congress, one of the biggest network summits held in Europe with over 2,000 participants. This year the conference took place in The Hague, the Netherlands, October 10-14, 2016.
SDN is an approach to computer networking that allows network administrators to respond quickly to changing business requirements via a centralized control console and to support the dynamic, scalable computing and storage needs of more modern computing environments such as data centers.
Collaborating with researchers from Queen’s University in the United Kingdom and Huawei, a global information and communications technology solutions provider in China, Professor Shin’s team, which is led by doctoral students Seungsoo Lee, Changhoon Yoon, and Jaehyun Nam, implemented a SDN security project called “DELTA.” ATTORESEARCH, a Korean SDN architecture and applications provider, conducted testing and verification for the project.
DELTA is a new SDN security evaluation framework with two main functions. It can automatically recognize attack cases against SDN elements across diverse environments and can assist in identifying unknown security problems within a SDN deployment.
The DELTA project consists of a control plane, the part of a network that carries signaling traffic and is responsible for routing; a data plane, the part of a network that carries user traffic; and a control channel that connects the two aforementioned planes. These three components have their own agents installed, which are all controlled by an agent manger. The agent manger can automatically detect any spots where the network security is weak.
Specifically, the project aimes to defense attacks against OpenFlow protocol, one of the first SDN standards; SDN controllers, a network operating system that is based on protocols; and network switch devices that use OpenFlow protocol.
The DELTA project was registered with the Open Networking Foundation, a user-driven organization dedicated to the promotion and adoption of SDN through open standards development, as an open source SDN security evaluation tool. This project is the only open source SDN which has been led by Korean researchers.
The SDN World Congress 2016 recognized the need for and importance of the DELTA project by conferring upon it the Best Solution Showcase Award. The Open Networking Foundation also widely publicized this award news.
Professor Shin said:
“In recent years, SDN has been attracting a large amount of interest as an emerging technology, but there still have not many SDN projects in Korea. This award acknowledges the advancement of Korean SDN technology, showing the potential for Korea to become a leader in SDN research.”
Picture: Major Components of the DELTA Project: Agents and Agent Manger
2016.10.25 View 9768
Professor Shin's Team Receives the Best Software Defined Network Solution Showcase Award
Professor Seungwon Shin of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team won the Best Software Defined Networking (SDN) Solution Showcase Award hosted by the SDN World Congress, one of the biggest network summits held in Europe with over 2,000 participants. This year the conference took place in The Hague, the Netherlands, October 10-14, 2016.
SDN is an approach to computer networking that allows network administrators to respond quickly to changing business requirements via a centralized control console and to support the dynamic, scalable computing and storage needs of more modern computing environments such as data centers.
Collaborating with researchers from Queen’s University in the United Kingdom and Huawei, a global information and communications technology solutions provider in China, Professor Shin’s team, which is led by doctoral students Seungsoo Lee, Changhoon Yoon, and Jaehyun Nam, implemented a SDN security project called “DELTA.” ATTORESEARCH, a Korean SDN architecture and applications provider, conducted testing and verification for the project.
DELTA is a new SDN security evaluation framework with two main functions. It can automatically recognize attack cases against SDN elements across diverse environments and can assist in identifying unknown security problems within a SDN deployment.
The DELTA project consists of a control plane, the part of a network that carries signaling traffic and is responsible for routing; a data plane, the part of a network that carries user traffic; and a control channel that connects the two aforementioned planes. These three components have their own agents installed, which are all controlled by an agent manger. The agent manger can automatically detect any spots where the network security is weak.
Specifically, the project aimes to defense attacks against OpenFlow protocol, one of the first SDN standards; SDN controllers, a network operating system that is based on protocols; and network switch devices that use OpenFlow protocol.
The DELTA project was registered with the Open Networking Foundation, a user-driven organization dedicated to the promotion and adoption of SDN through open standards development, as an open source SDN security evaluation tool. This project is the only open source SDN which has been led by Korean researchers.
The SDN World Congress 2016 recognized the need for and importance of the DELTA project by conferring upon it the Best Solution Showcase Award. The Open Networking Foundation also widely publicized this award news.
Professor Shin said:
“In recent years, SDN has been attracting a large amount of interest as an emerging technology, but there still have not many SDN projects in Korea. This award acknowledges the advancement of Korean SDN technology, showing the potential for Korea to become a leader in SDN research.”
Picture: Major Components of the DELTA Project: Agents and Agent Manger
2016.10.25 View 9768