Eui-Cheol+Shin
-
 Activation of Bystander Immune Cells during Acute Hepatitis A.
A KAIST research team has identified a process of tissue damage caused by bystander immune cells in acute viral infections. This research will pave the way for research to understand the principles of tissue damage in viral infections and immune diseases, and can point toward a possible therapeutic target for the treatment.
Upon viral infection, viral replication itself destroys human cells, but in some cases, viral replication is not the direct cause of the tissue damage. In particular, the destruction of infected cells is the primary cause of tissue damage during non-cytopathic viral infections such as hepatitis A virus, hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. However, the underlying pathological mechanisms involved in the tissue damage during viral infections have not been fully elucidated.
Specificity is one of the most important characteristics of the immune system. In general, infection from a certain virus specifically activates immune cells targeting the virus, while other immune cells specific to different viruses remain inactive.
An immune cell not specific to an infected virus is called a bystander immune cell. A phenomenon that activates irrelevant immune cells not originally targeting the infecting virus, called the activation of bystander immune cells, is already known to the world; however, its clinical significance has not been investigated thoroughly.
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and Professor Su-Hyung Park from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering analyzed patients with acute hepatitis A, in collaboration with Chung-Ang University Hospital.
The team found not only immune cells specifically targeting the hepatitis A virus were activated, but also bystander immune cells were activated and involved in the damaging of liver tissues during acute hepatitis A.
According to the research, when a person is infected with hepatitis A virus, hepatitis A virus-infected cells produce IL-15, which induces the activation of bystander immune cells. Activated bystander immune cells exert innate-like cytotoxicity, triggered by activating receptors NKG2D and NKp30 and this can lead to liver injury.
Through describing the cause of excessive tissue damage during acute viral hepatitis, the research outcome is expected to provide critical contributions for the development of potential therapeutic intervention that can minimize tissue damage caused by viral hepatitis and immune disorders.
Professor Shin said, “This is a novel research case that discovered the clinical significance of bystander immune cell activation, which was previously unknown. We will continue to work on establishing treatments which could prevent tissue damage in viral and immune diseases in the future.”
This research was published in Immunity on January 2.
Figure 1. Graphical abstract
2018.03.06 View 7368
Activation of Bystander Immune Cells during Acute Hepatitis A.
A KAIST research team has identified a process of tissue damage caused by bystander immune cells in acute viral infections. This research will pave the way for research to understand the principles of tissue damage in viral infections and immune diseases, and can point toward a possible therapeutic target for the treatment.
Upon viral infection, viral replication itself destroys human cells, but in some cases, viral replication is not the direct cause of the tissue damage. In particular, the destruction of infected cells is the primary cause of tissue damage during non-cytopathic viral infections such as hepatitis A virus, hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. However, the underlying pathological mechanisms involved in the tissue damage during viral infections have not been fully elucidated.
Specificity is one of the most important characteristics of the immune system. In general, infection from a certain virus specifically activates immune cells targeting the virus, while other immune cells specific to different viruses remain inactive.
An immune cell not specific to an infected virus is called a bystander immune cell. A phenomenon that activates irrelevant immune cells not originally targeting the infecting virus, called the activation of bystander immune cells, is already known to the world; however, its clinical significance has not been investigated thoroughly.
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and Professor Su-Hyung Park from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering analyzed patients with acute hepatitis A, in collaboration with Chung-Ang University Hospital.
The team found not only immune cells specifically targeting the hepatitis A virus were activated, but also bystander immune cells were activated and involved in the damaging of liver tissues during acute hepatitis A.
According to the research, when a person is infected with hepatitis A virus, hepatitis A virus-infected cells produce IL-15, which induces the activation of bystander immune cells. Activated bystander immune cells exert innate-like cytotoxicity, triggered by activating receptors NKG2D and NKp30 and this can lead to liver injury.
Through describing the cause of excessive tissue damage during acute viral hepatitis, the research outcome is expected to provide critical contributions for the development of potential therapeutic intervention that can minimize tissue damage caused by viral hepatitis and immune disorders.
Professor Shin said, “This is a novel research case that discovered the clinical significance of bystander immune cell activation, which was previously unknown. We will continue to work on establishing treatments which could prevent tissue damage in viral and immune diseases in the future.”
This research was published in Immunity on January 2.
Figure 1. Graphical abstract
2018.03.06 View 7368 -
 Cellular Mechanism for Severe Viral Hepatitis Identified
(Professor Shin(left) and Professor Jung)
KAIST medical scientists identified a cellular mechanism causing inflammatory changes in regulatory T cells that can lead to severe viral hepatitis. Research on this mechanism will help further understand the nature of various inflammatory diseases and lead to the development of relevant clinical treatments.
It is known that activated immune cells of patients with viral hepatitis destroy hepatocyte, but its regulatory mechanism has not yet been described.
Regulatory T cells inhibit activation of other immune cells and thus are important for homeostasis of the immune system. However, recent studies contradictorily show that immune inhibitory functions of regulatory T cells weaken in inflammatory conditions and the cells secrete inflammatory cytokines in response. Meanwhile, such a phenomenon was not observed in viral hepatitis including types A, B and C.
The team focused on changes in regulatory T cells in patients with viral hepatitis and discovered that regulatory T cells undergo inflammatory changes to secrete inflammatory cytokines (protein secreted by immune cells) called TNF. They also proved regulatory T cells that secrete TNF contribute to the progression of viral hepatitis.
The team confirmed that regulatory T cells of acute hepatitis A patients have reduced immune-inhibitory functions. Instead, their regulatory T cells secrete TNF. Through this research, the team identified a molecular mechanism for changes in regulatory T cells and identified the transcription factor regulating the process. Furthermore, the team found similar changes to be also present in hepatitis B and C patients.
A KAIST immunology research team led by Professors Eui-Cheol Shin and Min Kyung Jung at the Graduate School of Medical Science & Engineering conducted this translational research with teams from Chungnam National University and Yonsei University to identify the mechanism in humans, instead of using animal models. The research was described in Gastroenterology last December.
Professor Shin said, “This is the first research on regulatory T cells that contributes to hepatocyte damage in viral hepatitis.” He continued, “It is significant for identifying the cells and the molecules that can be used as effective treatment targets for viral hepatitis in the future. This research was funded by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation.
(Figure1: Treg cells from acute hepatitis A (AHA) patients produce tumor necrosis factor (TNF) andhave reduced suppressive activity. These changes are due to a decrease in FoxP3 transcription factor and an increase in RORγt transcription factor. TNF-producing Treg cells are associated with severe liver injury in AHA patients.)
(Figure 2: A higher proportion of Treg cells from patients with acute hepatitis A, compared with healthy controls, produced TNF upon stimulation with anti-CD3 and anti-CD2. This study reports the presence and the significance of TNF-producing Treg cells for the first time in human patients.)
2018.01.18 View 9232
Cellular Mechanism for Severe Viral Hepatitis Identified
(Professor Shin(left) and Professor Jung)
KAIST medical scientists identified a cellular mechanism causing inflammatory changes in regulatory T cells that can lead to severe viral hepatitis. Research on this mechanism will help further understand the nature of various inflammatory diseases and lead to the development of relevant clinical treatments.
It is known that activated immune cells of patients with viral hepatitis destroy hepatocyte, but its regulatory mechanism has not yet been described.
Regulatory T cells inhibit activation of other immune cells and thus are important for homeostasis of the immune system. However, recent studies contradictorily show that immune inhibitory functions of regulatory T cells weaken in inflammatory conditions and the cells secrete inflammatory cytokines in response. Meanwhile, such a phenomenon was not observed in viral hepatitis including types A, B and C.
The team focused on changes in regulatory T cells in patients with viral hepatitis and discovered that regulatory T cells undergo inflammatory changes to secrete inflammatory cytokines (protein secreted by immune cells) called TNF. They also proved regulatory T cells that secrete TNF contribute to the progression of viral hepatitis.
The team confirmed that regulatory T cells of acute hepatitis A patients have reduced immune-inhibitory functions. Instead, their regulatory T cells secrete TNF. Through this research, the team identified a molecular mechanism for changes in regulatory T cells and identified the transcription factor regulating the process. Furthermore, the team found similar changes to be also present in hepatitis B and C patients.
A KAIST immunology research team led by Professors Eui-Cheol Shin and Min Kyung Jung at the Graduate School of Medical Science & Engineering conducted this translational research with teams from Chungnam National University and Yonsei University to identify the mechanism in humans, instead of using animal models. The research was described in Gastroenterology last December.
Professor Shin said, “This is the first research on regulatory T cells that contributes to hepatocyte damage in viral hepatitis.” He continued, “It is significant for identifying the cells and the molecules that can be used as effective treatment targets for viral hepatitis in the future. This research was funded by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation.
(Figure1: Treg cells from acute hepatitis A (AHA) patients produce tumor necrosis factor (TNF) andhave reduced suppressive activity. These changes are due to a decrease in FoxP3 transcription factor and an increase in RORγt transcription factor. TNF-producing Treg cells are associated with severe liver injury in AHA patients.)
(Figure 2: A higher proportion of Treg cells from patients with acute hepatitis A, compared with healthy controls, produced TNF upon stimulation with anti-CD3 and anti-CD2. This study reports the presence and the significance of TNF-producing Treg cells for the first time in human patients.)
2018.01.18 View 9232 -
 Regulatory T Cells Influence Liver Damage of Hepatitis A Patients
Liver damage becomes more severe with the decrease of regulatory T cells
“This research will aid the development of hepatitis A targeted drug,” said a KAIST researcher.
The KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering’s Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and his research team have identified the mechanism, explaining how the regulatory T cells are responsible for the body’s immune system and how they have induced liver damage of hepatitis A patients.
The research results were published online in the July 9th edition of ‘Gut,’ the world’s most prominent journal in the field of gastroenterology.
Hepatitis A is an acute form of hepatitis caused by hepatitis A virus. The virus spreads through oral contact and enters the body via digestive organs.
Regulatory T cells play an important role in maintaining the homeostasis of the body’s immune system by inhibiting the activation of other immune cells. In the case of chronic viral infections, regulatory T cells are known to contribute to the duration of the infection, weakening the immune response to virus infections. However, there has been no information on what roles the regulatory T cells perform in the case of acute viral infections.
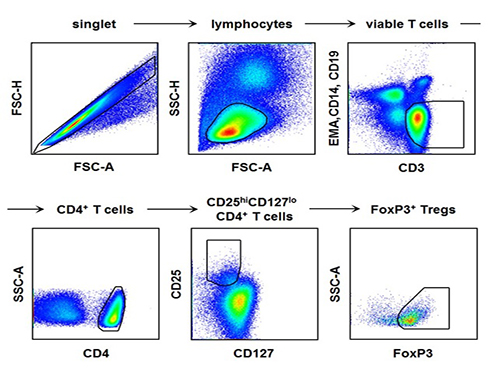
The research team used the fluorescence flow cytometry technique to determine the number and characteristics of a variety of immune cells, including regulatory T cells, in the blood of hepatitis A patients.
Consequently, the researchers confirmed that the decrease in the regulatory T cells immune inhibitory ability was consistent with a significant reduction in the number of regulatory T cells in the blood of hepatitis A patients. Furthermore, it was identified that the more noticeable decrease of regulatory T cells led to the occurrence of a more severe liver injury.
The analysis of hepatitis A patient’s blood proved that the cause of the decrease in the number and function of regulatory T cells was the increased expression of cell surface protein ‘Fas,’ which induces cell death.
Professor Shin said, “This study is the first case which proposes the mechanism for clinical aspects in not only hepatitis A, but also acute virus infection.” He added on the future prospect of the research that: “In the future, we can prevent tissue damage by inhibiting cell death of regulatory T cells for severe acute viral infections that do not have an effective treatment for the virus itself.”
[Picture]
The picture shows the process of fluorescence flow cytometry technique to study regulatory T cell in the blood of hepatitis A patients.
2014.08.11 View 11300
Regulatory T Cells Influence Liver Damage of Hepatitis A Patients
Liver damage becomes more severe with the decrease of regulatory T cells
“This research will aid the development of hepatitis A targeted drug,” said a KAIST researcher.
The KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering’s Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and his research team have identified the mechanism, explaining how the regulatory T cells are responsible for the body’s immune system and how they have induced liver damage of hepatitis A patients.
The research results were published online in the July 9th edition of ‘Gut,’ the world’s most prominent journal in the field of gastroenterology.
Hepatitis A is an acute form of hepatitis caused by hepatitis A virus. The virus spreads through oral contact and enters the body via digestive organs.
Regulatory T cells play an important role in maintaining the homeostasis of the body’s immune system by inhibiting the activation of other immune cells. In the case of chronic viral infections, regulatory T cells are known to contribute to the duration of the infection, weakening the immune response to virus infections. However, there has been no information on what roles the regulatory T cells perform in the case of acute viral infections.
The research team used the fluorescence flow cytometry technique to determine the number and characteristics of a variety of immune cells, including regulatory T cells, in the blood of hepatitis A patients.
Consequently, the researchers confirmed that the decrease in the regulatory T cells immune inhibitory ability was consistent with a significant reduction in the number of regulatory T cells in the blood of hepatitis A patients. Furthermore, it was identified that the more noticeable decrease of regulatory T cells led to the occurrence of a more severe liver injury.
The analysis of hepatitis A patient’s blood proved that the cause of the decrease in the number and function of regulatory T cells was the increased expression of cell surface protein ‘Fas,’ which induces cell death.
Professor Shin said, “This study is the first case which proposes the mechanism for clinical aspects in not only hepatitis A, but also acute virus infection.” He added on the future prospect of the research that: “In the future, we can prevent tissue damage by inhibiting cell death of regulatory T cells for severe acute viral infections that do not have an effective treatment for the virus itself.”
[Picture]
The picture shows the process of fluorescence flow cytometry technique to study regulatory T cell in the blood of hepatitis A patients.
2014.08.11 View 11300