engineering
-
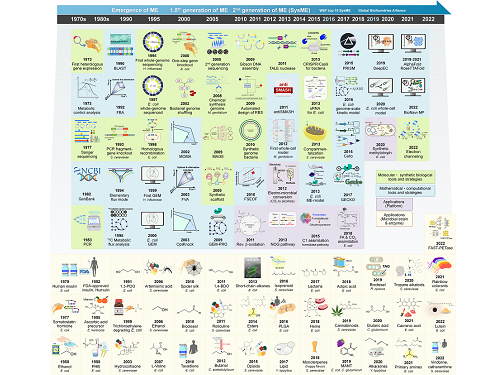 Overview of the 30-year history of metabolic engineering
< Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST >
A research team comprised of Gi Bae Kim, Dr. So Young Choi, Dr. In Jin Cho, Da-Hee Ahn, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported the 30-year history of metabolic engineering, highlighting examples of recent progress in the field and contributions to sustainability and health. Their paper “Metabolic engineering for sustainability and health” was published online in the 40th anniversary special issue of Trends in Biotechnology on January 10, 2023.
Metabolic engineering, a discipline of engineering that modifies cell phenotypes through molecular and genetic-level manipulations to improve cellular activities, has been studied since the early 1990s, and has progressed significantly over the past 30 years. In particular, metabolic engineering has enabled the engineering of microorganisms for the development of microbial cell factories capable of efficiently producing chemicals and materials as well as degrading recalcitrant contaminants.
This review article revisited how metabolic engineering has advanced over the past 30 years, from the advent of genetic engineering techniques such as recombinant DNA technologies to recent breakthroughs in systems metabolic engineering and data science aided by artificial intelligence. The research team highlighted momentous events and achievements in metabolic engineering, providing both trends and future directions in the field. Metabolic engineering’s contributions to bio-based sustainable chemicals and clean energy, health, and bioremediation were also reviewed. Finally, the research team shared their perspectives on the future challenges impacting metabolic engineering than must be overcome in order to achieve advancements in sustainability and health.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Replacing fossil resource-based chemical processes with bio-based sustainable processes for the production of chemicals, fuels, and materials using metabolic engineering has become our essential task for the future. By looking back on the 30+ years of metabolic engineering, we aimed to highlight the contributions of metabolic engineering to achieve sustainability and good health.” He added, “Metabolic engineering will play an increasingly important role as a key solution to the climate crisis, environmental pollution, food and energy shortages, and health problems in aging societies.”
< Figure: Metabolic Engineering Timeline >
2023.01.25 View 11636
Overview of the 30-year history of metabolic engineering
< Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST >
A research team comprised of Gi Bae Kim, Dr. So Young Choi, Dr. In Jin Cho, Da-Hee Ahn, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported the 30-year history of metabolic engineering, highlighting examples of recent progress in the field and contributions to sustainability and health. Their paper “Metabolic engineering for sustainability and health” was published online in the 40th anniversary special issue of Trends in Biotechnology on January 10, 2023.
Metabolic engineering, a discipline of engineering that modifies cell phenotypes through molecular and genetic-level manipulations to improve cellular activities, has been studied since the early 1990s, and has progressed significantly over the past 30 years. In particular, metabolic engineering has enabled the engineering of microorganisms for the development of microbial cell factories capable of efficiently producing chemicals and materials as well as degrading recalcitrant contaminants.
This review article revisited how metabolic engineering has advanced over the past 30 years, from the advent of genetic engineering techniques such as recombinant DNA technologies to recent breakthroughs in systems metabolic engineering and data science aided by artificial intelligence. The research team highlighted momentous events and achievements in metabolic engineering, providing both trends and future directions in the field. Metabolic engineering’s contributions to bio-based sustainable chemicals and clean energy, health, and bioremediation were also reviewed. Finally, the research team shared their perspectives on the future challenges impacting metabolic engineering than must be overcome in order to achieve advancements in sustainability and health.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Replacing fossil resource-based chemical processes with bio-based sustainable processes for the production of chemicals, fuels, and materials using metabolic engineering has become our essential task for the future. By looking back on the 30+ years of metabolic engineering, we aimed to highlight the contributions of metabolic engineering to achieve sustainability and good health.” He added, “Metabolic engineering will play an increasingly important role as a key solution to the climate crisis, environmental pollution, food and energy shortages, and health problems in aging societies.”
< Figure: Metabolic Engineering Timeline >
2023.01.25 View 11636 -
 A Quick but Clingy Creepy-Crawler that will MARVEL You
Engineered by KAIST Mechanics, a quadrupedal robot climbs steel walls and crawls across metal ceilings at the fastest speed that the world has ever seen.
< Photo 1. (From left) KAIST ME Prof. Hae-Won Park, Ph.D. Student Yong Um, Ph.D. Student Seungwoo Hong >
- Professor Hae-Won Park's team at the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal robot that can move at a high speed on ferrous walls and ceilings.
- It is expected to make a wide variety of contributions as it is to be used to conduct inspections and repairs of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, and transmission towers, offering an alternative to dangerous or risky activities required in hazardous environments while maintaining productivity and efficiency through automation and unmanning of such operations.
- The study was published as the cover paper of the December issue of Science Robotics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that a research team led by Professor Hae-Won Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal walking robot that can move at high speed on steel walls and ceilings named M.A.R.V.E.L. - rightly so as it is a Magnetically Adhesive Robot for Versatile and Expeditious Locomotion as described in their paper, “Agile and Versatile Climbing on Ferromagnetic Surfaces with a Quadrupedal Robot.” (DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.add1017)
To make this happen, Professor Park's research team developed a foot pad that can quickly turn the magnetic adhesive force on and off while retaining high adhesive force even on an uneven surface through the use of the Electro-Permanent Magnet (EPM), a device that can magnetize and demagnetize an electromagnet with little power, and the Magneto-Rheological Elastomer (MRE), an elastic material made by mixing a magnetic response factor, such as iron powder, with an elastic material, such as rubber, which they mounted on a small quadrupedal robot they made in-house, at their own laboratory. These walking robots are expected to be put into a wide variety of usage, including being programmed to perform inspections, repairs, and maintenance tasks on large structures made of steel, such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, large storage areas, and construction sites.
This study, in which Seungwoo Hong and Yong Um of the Department of Mechanical Engineering participated as co-first authors, was published as the cover paper in the December issue of Science Robotics.
< Image on the Cover of 2022 December issue of Science Robotics >
Existing wall-climbing robots use wheels or endless tracks, so their mobility is limited on surfaces with steps or irregularities. On the other hand, walking robots for climbing can expect improved mobility in obstacle terrain, but have disadvantages in that they have significantly slower moving speeds or cannot perform various movements.
In order to enable fast movement of the walking robot, the sole of the foot must have strong adhesion force and be able to control the adhesion to quickly switch from sticking to the surface or to be off of it. In addition, it is necessary to maintain the adhesion force even on a rough or uneven surface.
To solve this problem, the research team used the EPM and MRE for the first time in designing the soles of walking robots. An EPM is a magnet that can turn on and off the electromagnetic force with a short current pulse. Unlike general electromagnets, it has the advantage that it does not require energy to maintain the magnetic force. The research team proposed a new EPM with a rectangular structure arrangement, enabling faster switching while significantly lowering the voltage required for switching compared to existing electromagnets.
In addition, the research team was able to increase the frictional force without significantly reducing the magnetic force of the sole by covering the sole with an MRE. The proposed sole weighs only 169 g, but provides a vertical gripping force of about *535 Newtons (N) and a frictional force of 445 N, which is sufficient gripping force for a quadrupedal robot weighing 8 kg.
* 535 N converted to kg is 54.5 kg, and 445 N is 45.4 kg. In other words, even if an external force of up to 54.5 kg in the vertical direction and up to 45.4 kg in the horizontal direction is applied (or even if a corresponding weight is hung), the sole of the foot does not come off the steel plate.
MARVEL climbed up a vertical wall at high speed at a speed of 70 cm per second, and was able to walk while hanging upside down from the ceiling at a maximum speed of 50 cm per second. This is the world's fastest speed for a walking climbing robot. In addition, the research team demonstrated that the robot can climb at a speed of up to 35 cm even on a surface that is painted, dirty with dust and the rust-tainted surfaces of water tanks, proving the robot's performance in a real environment. It was experimentally demonstrated that the robot not only exhibited high speed, but also can switch from floor to wall and from wall to ceiling, and overcome 5-cm high obstacles protruding from walls without difficulty.
The new climbing quadrupedal robot is expected to be widely used for inspection, repair, and maintenance of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, oil pipelines, large storage areas, and construction sites. As the works required in these places involves risks such as falls, suffocation and other accidents that may result in serious injuries or casualties, the need for automation is of utmost urgency.
One of the first co-authors of the paper, a Ph.D. student, Yong Um of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, said, "By the use of the magnetic soles made up of the EPM and MRE and the non-linear model predictive controller suitable for climbing, the robot can speedily move through a variety of ferromagnetic surfaces including walls and ceilings, not just level grounds. We believe this would become a cornerstone that will expand the mobility and the places of pedal-mobile robots can venture into." He added, “These robots can be put into good use in executing dangerous and difficult tasks on steel structures in places like the shipbuilding yards.”
This research was carried out with support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers and Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering Co., Ltd..
< Figure 1. The quadrupedal robot (MARVEL) walking over various ferrous surfaces. (A) vertical wall (B) ceiling. (C) over obstacles on a vertical wall (D) making floor-to-wall and wall-to-ceiling transitions (E) moving over a storage tank (F) walking on a wall with a 2-kg weight and over a ceiling with a 3-kg load. >
< Figure 2. Description of the magnetic foot (A) Components of the magnet sole: ankle, Square Eletro-Permanent Magnet(S-EPM), MRE footpad. (B) Components of the S-EPM and MRE footpad. (C) Working principle of the S-EPM. When the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the left figure, magnetic flux comes out of the keeper and circulates through the steel plate, generating holding force (ON state). Conversely, if the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the figure on the right, the magnetic flux circulates inside the S-EPM and the holding force disappears (OFF state). >
Video Introduction: Agile and versatile climbing on ferromagnetic surfaces with a quadrupedal robot - YouTube
2022.12.30 View 18802
A Quick but Clingy Creepy-Crawler that will MARVEL You
Engineered by KAIST Mechanics, a quadrupedal robot climbs steel walls and crawls across metal ceilings at the fastest speed that the world has ever seen.
< Photo 1. (From left) KAIST ME Prof. Hae-Won Park, Ph.D. Student Yong Um, Ph.D. Student Seungwoo Hong >
- Professor Hae-Won Park's team at the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal robot that can move at a high speed on ferrous walls and ceilings.
- It is expected to make a wide variety of contributions as it is to be used to conduct inspections and repairs of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, and transmission towers, offering an alternative to dangerous or risky activities required in hazardous environments while maintaining productivity and efficiency through automation and unmanning of such operations.
- The study was published as the cover paper of the December issue of Science Robotics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that a research team led by Professor Hae-Won Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal walking robot that can move at high speed on steel walls and ceilings named M.A.R.V.E.L. - rightly so as it is a Magnetically Adhesive Robot for Versatile and Expeditious Locomotion as described in their paper, “Agile and Versatile Climbing on Ferromagnetic Surfaces with a Quadrupedal Robot.” (DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.add1017)
To make this happen, Professor Park's research team developed a foot pad that can quickly turn the magnetic adhesive force on and off while retaining high adhesive force even on an uneven surface through the use of the Electro-Permanent Magnet (EPM), a device that can magnetize and demagnetize an electromagnet with little power, and the Magneto-Rheological Elastomer (MRE), an elastic material made by mixing a magnetic response factor, such as iron powder, with an elastic material, such as rubber, which they mounted on a small quadrupedal robot they made in-house, at their own laboratory. These walking robots are expected to be put into a wide variety of usage, including being programmed to perform inspections, repairs, and maintenance tasks on large structures made of steel, such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, large storage areas, and construction sites.
This study, in which Seungwoo Hong and Yong Um of the Department of Mechanical Engineering participated as co-first authors, was published as the cover paper in the December issue of Science Robotics.
< Image on the Cover of 2022 December issue of Science Robotics >
Existing wall-climbing robots use wheels or endless tracks, so their mobility is limited on surfaces with steps or irregularities. On the other hand, walking robots for climbing can expect improved mobility in obstacle terrain, but have disadvantages in that they have significantly slower moving speeds or cannot perform various movements.
In order to enable fast movement of the walking robot, the sole of the foot must have strong adhesion force and be able to control the adhesion to quickly switch from sticking to the surface or to be off of it. In addition, it is necessary to maintain the adhesion force even on a rough or uneven surface.
To solve this problem, the research team used the EPM and MRE for the first time in designing the soles of walking robots. An EPM is a magnet that can turn on and off the electromagnetic force with a short current pulse. Unlike general electromagnets, it has the advantage that it does not require energy to maintain the magnetic force. The research team proposed a new EPM with a rectangular structure arrangement, enabling faster switching while significantly lowering the voltage required for switching compared to existing electromagnets.
In addition, the research team was able to increase the frictional force without significantly reducing the magnetic force of the sole by covering the sole with an MRE. The proposed sole weighs only 169 g, but provides a vertical gripping force of about *535 Newtons (N) and a frictional force of 445 N, which is sufficient gripping force for a quadrupedal robot weighing 8 kg.
* 535 N converted to kg is 54.5 kg, and 445 N is 45.4 kg. In other words, even if an external force of up to 54.5 kg in the vertical direction and up to 45.4 kg in the horizontal direction is applied (or even if a corresponding weight is hung), the sole of the foot does not come off the steel plate.
MARVEL climbed up a vertical wall at high speed at a speed of 70 cm per second, and was able to walk while hanging upside down from the ceiling at a maximum speed of 50 cm per second. This is the world's fastest speed for a walking climbing robot. In addition, the research team demonstrated that the robot can climb at a speed of up to 35 cm even on a surface that is painted, dirty with dust and the rust-tainted surfaces of water tanks, proving the robot's performance in a real environment. It was experimentally demonstrated that the robot not only exhibited high speed, but also can switch from floor to wall and from wall to ceiling, and overcome 5-cm high obstacles protruding from walls without difficulty.
The new climbing quadrupedal robot is expected to be widely used for inspection, repair, and maintenance of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, oil pipelines, large storage areas, and construction sites. As the works required in these places involves risks such as falls, suffocation and other accidents that may result in serious injuries or casualties, the need for automation is of utmost urgency.
One of the first co-authors of the paper, a Ph.D. student, Yong Um of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, said, "By the use of the magnetic soles made up of the EPM and MRE and the non-linear model predictive controller suitable for climbing, the robot can speedily move through a variety of ferromagnetic surfaces including walls and ceilings, not just level grounds. We believe this would become a cornerstone that will expand the mobility and the places of pedal-mobile robots can venture into." He added, “These robots can be put into good use in executing dangerous and difficult tasks on steel structures in places like the shipbuilding yards.”
This research was carried out with support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers and Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering Co., Ltd..
< Figure 1. The quadrupedal robot (MARVEL) walking over various ferrous surfaces. (A) vertical wall (B) ceiling. (C) over obstacles on a vertical wall (D) making floor-to-wall and wall-to-ceiling transitions (E) moving over a storage tank (F) walking on a wall with a 2-kg weight and over a ceiling with a 3-kg load. >
< Figure 2. Description of the magnetic foot (A) Components of the magnet sole: ankle, Square Eletro-Permanent Magnet(S-EPM), MRE footpad. (B) Components of the S-EPM and MRE footpad. (C) Working principle of the S-EPM. When the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the left figure, magnetic flux comes out of the keeper and circulates through the steel plate, generating holding force (ON state). Conversely, if the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the figure on the right, the magnetic flux circulates inside the S-EPM and the holding force disappears (OFF state). >
Video Introduction: Agile and versatile climbing on ferromagnetic surfaces with a quadrupedal robot - YouTube
2022.12.30 View 18802 -
 Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 15287
Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 15287 -
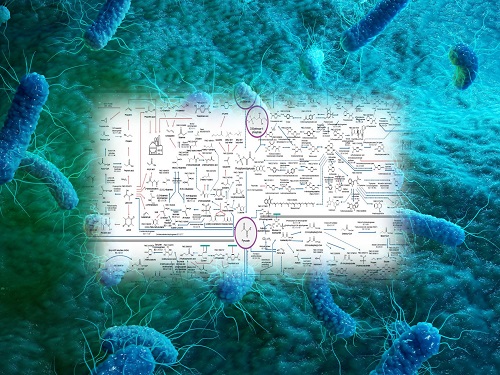 Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 16591
Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 16591 -
 Metabolically Engineered Bacterium Produces Lutein
A research group at KAIST has engineered a bacterial strain capable of producing lutein. The research team applied systems metabolic engineering strategies, including substrate channeling and electron channeling, to enhance the production of lutein in an engineered Escherichia coli strain. The strategies will be also useful for the efficient production of other industrially important natural products used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Figure: Systems metabolic engineering was employed to construct and optimize the metabolic pathways for lutein production, and substrate channeling and electron channeling strategies were additionally employed to increase the production of the lutein with high productivity.
Lutein is classified as a xanthophyll chemical that is abundant in egg yolk, fruits, and vegetables. It protects the eye from oxidative damage from radiation and reduces the risk of eye diseases including macular degeneration and cataracts. Commercialized products featuring lutein are derived from the extracts of the marigold flower, which is known to harbor abundant amounts of lutein. However, the drawback of lutein production from nature is that it takes a long time to grow and harvest marigold flowers. Furthermore, it requires additional physical and chemical-based extractions with a low yield, which makes it economically unfeasible in terms of productivity. The high cost and low yield of these bioprocesses has made it difficult to readily meet the demand for lutein.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineers at KAIST, including researchers Dr. Seon Young Park, Ph.D. Candidate Hyunmin Eun, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The team’s study entitled “Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli with electron channeling for the production of natural products” was published in Nature Catalysis on August 5, 2022.
This research details the ability to produce lutein from E. coli with a high yield using a cheap carbon source, glycerol, via systems metabolic engineering. The research group focused on solving the bottlenecks of the biosynthetic pathway for lutein production constructed within an individual cell. First, using systems metabolic engineering, which is an integrated technology to engineer the metabolism of a microorganism, lutein was produced when the lutein biosynthesis pathway was introduced, albeit in very small amounts.
To improve the productivity of lutein production, the bottleneck enzymes within the metabolic pathway were first identified. It turned out that metabolic reactions that involve a promiscuous enzyme, an enzyme that is involved in two or more metabolic reactions, and electron-requiring cytochrome P450 enzymes are the main bottleneck steps of the pathway inhibiting lutein biosynthesis.
To overcome these challenges, substrate channeling, a strategy to artificially recruit enzymes in physical proximity within the cell in order to increase the local concentrations of substrates that can be converted into products, was employed to channel more metabolic flux towards the target chemical while reducing the formation of unwanted byproducts.
Furthermore, electron channeling, a strategy similar to substrate channeling but differing in terms of increasing the local concentrations of electrons required for oxidoreduction reactions mediated by P450 and its reductase partners, was applied to further streamline the metabolic flux towards lutein biosynthesis, which led to the highest titer of lutein production achieved in a bacterial host ever reported. The same electron channeling strategy was successfully applied for the production of other natural products including nootkatone and apigenin in E. coli, showcasing the general applicability of the strategy in the research field.
“It is expected that this microbial cell factory-based production of lutein will be able to replace the current plant extraction-based process,” said Dr. Seon Young Park, the first author of the paper. She explained that another important point of the research is that integrated metabolic engineering strategies developed from this study can be generally applicable for the efficient production of other natural products useful as pharmaceuticals or nutraceuticals.
“As maintaining good health in an aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” explained Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development funded by the Rural Development Administration of Korea, with further support from the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and by the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project of the National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea.
2022.08.05 View 11229
Metabolically Engineered Bacterium Produces Lutein
A research group at KAIST has engineered a bacterial strain capable of producing lutein. The research team applied systems metabolic engineering strategies, including substrate channeling and electron channeling, to enhance the production of lutein in an engineered Escherichia coli strain. The strategies will be also useful for the efficient production of other industrially important natural products used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Figure: Systems metabolic engineering was employed to construct and optimize the metabolic pathways for lutein production, and substrate channeling and electron channeling strategies were additionally employed to increase the production of the lutein with high productivity.
Lutein is classified as a xanthophyll chemical that is abundant in egg yolk, fruits, and vegetables. It protects the eye from oxidative damage from radiation and reduces the risk of eye diseases including macular degeneration and cataracts. Commercialized products featuring lutein are derived from the extracts of the marigold flower, which is known to harbor abundant amounts of lutein. However, the drawback of lutein production from nature is that it takes a long time to grow and harvest marigold flowers. Furthermore, it requires additional physical and chemical-based extractions with a low yield, which makes it economically unfeasible in terms of productivity. The high cost and low yield of these bioprocesses has made it difficult to readily meet the demand for lutein.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineers at KAIST, including researchers Dr. Seon Young Park, Ph.D. Candidate Hyunmin Eun, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The team’s study entitled “Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli with electron channeling for the production of natural products” was published in Nature Catalysis on August 5, 2022.
This research details the ability to produce lutein from E. coli with a high yield using a cheap carbon source, glycerol, via systems metabolic engineering. The research group focused on solving the bottlenecks of the biosynthetic pathway for lutein production constructed within an individual cell. First, using systems metabolic engineering, which is an integrated technology to engineer the metabolism of a microorganism, lutein was produced when the lutein biosynthesis pathway was introduced, albeit in very small amounts.
To improve the productivity of lutein production, the bottleneck enzymes within the metabolic pathway were first identified. It turned out that metabolic reactions that involve a promiscuous enzyme, an enzyme that is involved in two or more metabolic reactions, and electron-requiring cytochrome P450 enzymes are the main bottleneck steps of the pathway inhibiting lutein biosynthesis.
To overcome these challenges, substrate channeling, a strategy to artificially recruit enzymes in physical proximity within the cell in order to increase the local concentrations of substrates that can be converted into products, was employed to channel more metabolic flux towards the target chemical while reducing the formation of unwanted byproducts.
Furthermore, electron channeling, a strategy similar to substrate channeling but differing in terms of increasing the local concentrations of electrons required for oxidoreduction reactions mediated by P450 and its reductase partners, was applied to further streamline the metabolic flux towards lutein biosynthesis, which led to the highest titer of lutein production achieved in a bacterial host ever reported. The same electron channeling strategy was successfully applied for the production of other natural products including nootkatone and apigenin in E. coli, showcasing the general applicability of the strategy in the research field.
“It is expected that this microbial cell factory-based production of lutein will be able to replace the current plant extraction-based process,” said Dr. Seon Young Park, the first author of the paper. She explained that another important point of the research is that integrated metabolic engineering strategies developed from this study can be generally applicable for the efficient production of other natural products useful as pharmaceuticals or nutraceuticals.
“As maintaining good health in an aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” explained Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development funded by the Rural Development Administration of Korea, with further support from the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and by the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project of the National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea.
2022.08.05 View 11229 -
 An AI-based, Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated (IOI) GPS System to Bring Seismic Waves in the Terrains of Positioning Technology
KAIST breaks new grounds in positioning technology with an AI-integrated GPS board that works both indoors and out
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 8th that Professor Dong-Soo Han's research team (Intelligent Service Integration Lab) from the School of Computing has developed a GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors with quality precision regardless of the environment.
This Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated GPS System, or IOI GPS System, for short, uses the GPS signals outdoors and estimates locations indoors using signals from multiple sources like an inertial sensor, pressure sensors, geomagnetic sensors, and light sensors. To this end, the research team developed techniques to detect environmental changes such as entering a building, and methods to detect entrances, ground floors, stairs, elevators and levels of buildings by utilizing artificial intelligence techniques. Various landmark detecting techniques were also incorporated with pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR), a navigation tool for pedestrians, to devise the so-called “Sensor-Fusion Positioning Algorithm”.
To date, it was common to estimate locations based on wireless LAN signals or base station signals in a space where the GPS signal could not reach. However, the IOI GPS enables positioning even in buildings without signals nor indoor maps.
The algorithm developed by the research team can provide accurate floor information within a building where even big tech companies like Google and Apple's positioning services do not provide. Unlike other positioning methods that rely on visual data, geomagnetic positioning techniques, or wireless LAN, this system also has the advantage of not requiring any prior preparation. In other words, the foundation to enable the usage of a universal GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors anywhere in the world is now ready.
The research team also produced a circuit board for the purpose of operating the IOI GPS System, mounted with chips to receive and process GPS, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth signals, along with an inertial sensor, a barometer, a magnetometer, and a light sensor. The sensor-fusion positioning algorithm the lab has developed is also incorporated in the board.
When the accuracy of the IOI GPS board was tested in the N1 building of KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon, it achieved an accuracy of about 95% in floor estimation and an accuracy of about 3 to 6 meters in distance estimation. As for the indoor/outdoor transition, the navigational mode change was completed in about 0.3 seconds. When it was combined with the PDR technique, the estimation accuracy improved further down to a scope of one meter.
The research team is now working on assembling a tag with a built-in positioning board and applying it to location-based docent services for visitors at museums, science centers, and art galleries. The IOI GPS tag can be used for the purpose of tracking children and/or the elderly, and it can also be used to locate people or rescue workers lost in disaster-ridden or hazardous sites. On a different note, the sensor-fusion positioning algorithm and positioning board for vehicles are also under development for the tracking of vehicles entering indoor areas like underground parking lots.
When the IOI GPS board for vehicles is manufactured, the research team will work to collaborate with car manufacturers and car rental companies, and will also develop a sensor-fusion positioning algorithm for smartphones. Telecommunication companies seeking to diversify their programs in the field of location-based services will also be interested in the use the IOI GPS.
Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing, who leads the research team, said, “This is the first time to develop an indoor/outdoor integrated GPS system that can pinpoint locations in a building where there is no wireless signal or an indoor map, and there are an infinite number of areas it can be applied to. When the integration with the Korea Augmentation Satellite System (KASS) and the Korean GPS (KPS) System that began this year, is finally completed, Korea can become the leader in the field of GPS both indoors and outdoors, and we also have plans to manufacture semi-conductor chips for the IOI GPS System to keep the tech-gap between Korea and the followers.”
He added, "The guidance services at science centers, museums, and art galleries that uses IOI GPS tags can provide a set of data that would be very helpful for analyzing the visitors’ viewing traces. It is an essential piece of information required when the time comes to decide when to organize the next exhibit. We will be working on having it applied to the National Science Museum, first.”
The projects to develop the IOI GPS system and the trace analysis system for science centers were supported through Science, Culture, Exhibits and Services Capability Enhancement Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile: Dong-Soo Han, Ph.D.Professorddsshhan@kaist.ac.krhttp://isilab.kaist.ac.kr
Intelligent Service Integration Lab.School of Computing
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 12808
An AI-based, Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated (IOI) GPS System to Bring Seismic Waves in the Terrains of Positioning Technology
KAIST breaks new grounds in positioning technology with an AI-integrated GPS board that works both indoors and out
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 8th that Professor Dong-Soo Han's research team (Intelligent Service Integration Lab) from the School of Computing has developed a GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors with quality precision regardless of the environment.
This Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated GPS System, or IOI GPS System, for short, uses the GPS signals outdoors and estimates locations indoors using signals from multiple sources like an inertial sensor, pressure sensors, geomagnetic sensors, and light sensors. To this end, the research team developed techniques to detect environmental changes such as entering a building, and methods to detect entrances, ground floors, stairs, elevators and levels of buildings by utilizing artificial intelligence techniques. Various landmark detecting techniques were also incorporated with pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR), a navigation tool for pedestrians, to devise the so-called “Sensor-Fusion Positioning Algorithm”.
To date, it was common to estimate locations based on wireless LAN signals or base station signals in a space where the GPS signal could not reach. However, the IOI GPS enables positioning even in buildings without signals nor indoor maps.
The algorithm developed by the research team can provide accurate floor information within a building where even big tech companies like Google and Apple's positioning services do not provide. Unlike other positioning methods that rely on visual data, geomagnetic positioning techniques, or wireless LAN, this system also has the advantage of not requiring any prior preparation. In other words, the foundation to enable the usage of a universal GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors anywhere in the world is now ready.
The research team also produced a circuit board for the purpose of operating the IOI GPS System, mounted with chips to receive and process GPS, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth signals, along with an inertial sensor, a barometer, a magnetometer, and a light sensor. The sensor-fusion positioning algorithm the lab has developed is also incorporated in the board.
When the accuracy of the IOI GPS board was tested in the N1 building of KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon, it achieved an accuracy of about 95% in floor estimation and an accuracy of about 3 to 6 meters in distance estimation. As for the indoor/outdoor transition, the navigational mode change was completed in about 0.3 seconds. When it was combined with the PDR technique, the estimation accuracy improved further down to a scope of one meter.
The research team is now working on assembling a tag with a built-in positioning board and applying it to location-based docent services for visitors at museums, science centers, and art galleries. The IOI GPS tag can be used for the purpose of tracking children and/or the elderly, and it can also be used to locate people or rescue workers lost in disaster-ridden or hazardous sites. On a different note, the sensor-fusion positioning algorithm and positioning board for vehicles are also under development for the tracking of vehicles entering indoor areas like underground parking lots.
When the IOI GPS board for vehicles is manufactured, the research team will work to collaborate with car manufacturers and car rental companies, and will also develop a sensor-fusion positioning algorithm for smartphones. Telecommunication companies seeking to diversify their programs in the field of location-based services will also be interested in the use the IOI GPS.
Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing, who leads the research team, said, “This is the first time to develop an indoor/outdoor integrated GPS system that can pinpoint locations in a building where there is no wireless signal or an indoor map, and there are an infinite number of areas it can be applied to. When the integration with the Korea Augmentation Satellite System (KASS) and the Korean GPS (KPS) System that began this year, is finally completed, Korea can become the leader in the field of GPS both indoors and outdoors, and we also have plans to manufacture semi-conductor chips for the IOI GPS System to keep the tech-gap between Korea and the followers.”
He added, "The guidance services at science centers, museums, and art galleries that uses IOI GPS tags can provide a set of data that would be very helpful for analyzing the visitors’ viewing traces. It is an essential piece of information required when the time comes to decide when to organize the next exhibit. We will be working on having it applied to the National Science Museum, first.”
The projects to develop the IOI GPS system and the trace analysis system for science centers were supported through Science, Culture, Exhibits and Services Capability Enhancement Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile: Dong-Soo Han, Ph.D.Professorddsshhan@kaist.ac.krhttp://isilab.kaist.ac.kr
Intelligent Service Integration Lab.School of Computing
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 12808 -
 VP Sang Yup Lee Receives Honorary Doctorate from DTU
Vice President for Research, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, was awarded an honorary doctorate from the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) during the DTU Commemoration Day 2022 on April 29. The event drew distinguished guests, students, and faculty including HRH The Crown Prince Frederik Andre Henrik Christian and DTU President Anders Bjarklev.
Professor Lee was recognized for his exceptional scholarship in the field of systems metabolic engineering, which led to the development of microcell factories capable of producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds, many for the first time.
Professor Lee said in his acceptance speech that KAIST’s continued partnership with DTU in the field of biotechnology will lead to significant contributions in the global efforts to respond to climate change and promote green growth.
DTU CPO and CSO Dina Petronovic Nielson, who heads DTU Biosustain, also lauded Professor Lee saying, “It is not only a great honor for Professor Lee to be induced at DTU but also great honor for DTU to have him.”
Professor Lee also gave commemorative lectures at DTU Biosustain in Lingby and the Bio Innovation Research Institute at the Novo Nordisk Foundation in Copenhagen while in Denmark.
DTU, one of the leading science and technology universities in Europe, has been awarding honorary doctorates since 1921, including to Nobel laureate in chemistry Professor Frances Arnold at Caltech. Professor Lee is the first Korean to receive an honorary doctorate from DTU.
2022.05.03 View 11871
VP Sang Yup Lee Receives Honorary Doctorate from DTU
Vice President for Research, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, was awarded an honorary doctorate from the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) during the DTU Commemoration Day 2022 on April 29. The event drew distinguished guests, students, and faculty including HRH The Crown Prince Frederik Andre Henrik Christian and DTU President Anders Bjarklev.
Professor Lee was recognized for his exceptional scholarship in the field of systems metabolic engineering, which led to the development of microcell factories capable of producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds, many for the first time.
Professor Lee said in his acceptance speech that KAIST’s continued partnership with DTU in the field of biotechnology will lead to significant contributions in the global efforts to respond to climate change and promote green growth.
DTU CPO and CSO Dina Petronovic Nielson, who heads DTU Biosustain, also lauded Professor Lee saying, “It is not only a great honor for Professor Lee to be induced at DTU but also great honor for DTU to have him.”
Professor Lee also gave commemorative lectures at DTU Biosustain in Lingby and the Bio Innovation Research Institute at the Novo Nordisk Foundation in Copenhagen while in Denmark.
DTU, one of the leading science and technology universities in Europe, has been awarding honorary doctorates since 1921, including to Nobel laureate in chemistry Professor Frances Arnold at Caltech. Professor Lee is the first Korean to receive an honorary doctorate from DTU.
2022.05.03 View 11871 -
 President Lee Presents Plans to Nurture Next-Generation Talents
President Lee stressed that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during a news conference
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during an online news conference marking the 1st anniversary of him becoming the president on February 15.
He said that nurturing physician-scientists is the most critical mission for KAIST to help the nation create a new growth engine. He said KAIST will help the nation drive the bio-industry and provide medical science resources for the nation’s health sector. To this end, he said that KAIST will open its Medical Science and Technology School by 2026.
“We plan to expand the current Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering into a new Medical Science and Technology School that will focus entirely on a condensed MD-PhD course converging the fields of AI, bio, and physics,” he said.
The school aims to foster medical scientists whose research results will eventually be commercialized. He said that the university is now discussing revisions to related laws and regulations with the government and other universities.
To supply human resources to the semiconductor industry, President Lee said the university will add a campus in Pyongtaek City that will serve as an advanced convergence research hub in the field of next generation semiconductors in collaboration with Samsung Electronics and the city of Pyongtaek. The three-stage opening plan projected the final opening of the campus by 2036. During the first stage, which will be completed by 2026, it will construct the campus infrastructure in Pyongtaek city where Samsung Semiconductors runs two massive semiconductor complexes. By 2031, it plans to launch the open research platform including a future cities research center and future vehicles research center. The campus will open the global industrial collaboration cluster hub by 2036.
In the global arena, President Lee said he is working to open the New York campus with stakeholders in the United States. He announced the plan last December that was endorsed by New York-based entrepreneur Hee-Nam Bae, the chairman of Big Continent Inc. President Lee and Chairman Lee signed an MOU for the funding to open the campus in New York.
“We are discussing how to facilitate the plan and best accommodate the interests and potential of our students. Many ideas and plans are on the table and we think it will take longer than expected to finalize the plan,” explained President Lee.
However, he added that the basic idea is to offer art tech and health technology programs as well as an AI-based finance MBA at the New York campus, in addition to it serving as the startup accelerator of KAIST.
President Lee stressed the importance of technology commercialization when successfully launching KAIST Holdings last month to help spinoffs of KAIST labs accelerate their end results. He said that KAIST Holdings will build a virtuous supporting system to commercialize the technology startups coming from KAIST.
“We plan to list at least 10 KAIST startups on the KOSDAQ and two on the NASDAQ by 2031. KAIST Holdings also aims to nurture companies valued at a total of one billion KRW and earn 100 billion KRW in technology fees by 2031.
2022.02.17 View 12615
President Lee Presents Plans to Nurture Next-Generation Talents
President Lee stressed that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during a news conference
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said that nurturing medical scientists, semiconductor R&D personnel, startup entrepreneurs, and global innovators are key missions he will continue to pursue during an online news conference marking the 1st anniversary of him becoming the president on February 15.
He said that nurturing physician-scientists is the most critical mission for KAIST to help the nation create a new growth engine. He said KAIST will help the nation drive the bio-industry and provide medical science resources for the nation’s health sector. To this end, he said that KAIST will open its Medical Science and Technology School by 2026.
“We plan to expand the current Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering into a new Medical Science and Technology School that will focus entirely on a condensed MD-PhD course converging the fields of AI, bio, and physics,” he said.
The school aims to foster medical scientists whose research results will eventually be commercialized. He said that the university is now discussing revisions to related laws and regulations with the government and other universities.
To supply human resources to the semiconductor industry, President Lee said the university will add a campus in Pyongtaek City that will serve as an advanced convergence research hub in the field of next generation semiconductors in collaboration with Samsung Electronics and the city of Pyongtaek. The three-stage opening plan projected the final opening of the campus by 2036. During the first stage, which will be completed by 2026, it will construct the campus infrastructure in Pyongtaek city where Samsung Semiconductors runs two massive semiconductor complexes. By 2031, it plans to launch the open research platform including a future cities research center and future vehicles research center. The campus will open the global industrial collaboration cluster hub by 2036.
In the global arena, President Lee said he is working to open the New York campus with stakeholders in the United States. He announced the plan last December that was endorsed by New York-based entrepreneur Hee-Nam Bae, the chairman of Big Continent Inc. President Lee and Chairman Lee signed an MOU for the funding to open the campus in New York.
“We are discussing how to facilitate the plan and best accommodate the interests and potential of our students. Many ideas and plans are on the table and we think it will take longer than expected to finalize the plan,” explained President Lee.
However, he added that the basic idea is to offer art tech and health technology programs as well as an AI-based finance MBA at the New York campus, in addition to it serving as the startup accelerator of KAIST.
President Lee stressed the importance of technology commercialization when successfully launching KAIST Holdings last month to help spinoffs of KAIST labs accelerate their end results. He said that KAIST Holdings will build a virtuous supporting system to commercialize the technology startups coming from KAIST.
“We plan to list at least 10 KAIST startups on the KOSDAQ and two on the NASDAQ by 2031. KAIST Holdings also aims to nurture companies valued at a total of one billion KRW and earn 100 billion KRW in technology fees by 2031.
2022.02.17 View 12615 -
 Seven Faculty Members Elected to Join the National Academy of Engineering of Korea
< Clockwise from top left: Professor Doo-Hwan Bae, Professor Seung Seob Lee, Professor Kyung Cheol Choi, Professor JaeYong Choung >
Seven KAIST faculty members have been elected as National Academy of Engineering of Korea (NAEK) members and associate members. NAEK, the most prestigious engineering society in Korea, elects new members with a minimum of 15 years of experience in engineering in academia and business every year.
In 2022, 24 members were newly elected from academia, including four KAIST faculty members: Professor Doo-Hwan Bae from the SW Education Center, KAIST Provost and Executive Vice President Seung Seob Lee, Professor JaeYong Choung from the School of Business and Technology Management, and Professor Kyung Cheol Choi of the School of Electrical Engineering. In the business sector, 21 members were elected as members in business, including Vice Chairman Jong-hee Han of Samsung Electronics, CEO Hyeon-Mo Ku of KT, President Sang-Ryul Lee of the Korea Aerospace Research Institute, President Kyo Won Jin of SK Hynix, CEO Eunkang Song of Capstone Partners, and Executive Vice President Se-hoon Kim of Hyundai Motor Company.
Among the newly elected 40 associate members from academia, three KAIST professors were listed: Professor Sukyoung Ryu from the School of Computing, Professor Joongmyeon Bae from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Professor EunAe Cho from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. Another 44 members were elected as associate members in business, including Vice Chairman Hag-Dong Kim of POSCO, President Seong-Hyeon Cho of Mando Corp, President Siyoung Choi of Samsung Electronics, President Joo Sun Choi of Samsung Display, and Chairman Byung-Gyu Chang of Krafton.
NAEK evaluates candidates not only on their academic achievements, but on various other criteria including technological achievements, patents, the nurturing of talents, and contributions to the advancements of the industry. Candidates are then elected through written ballots by the members of NAEK. There are now 294 members and 360 associate members of NAEK.
2022.01.14 View 7106
Seven Faculty Members Elected to Join the National Academy of Engineering of Korea
< Clockwise from top left: Professor Doo-Hwan Bae, Professor Seung Seob Lee, Professor Kyung Cheol Choi, Professor JaeYong Choung >
Seven KAIST faculty members have been elected as National Academy of Engineering of Korea (NAEK) members and associate members. NAEK, the most prestigious engineering society in Korea, elects new members with a minimum of 15 years of experience in engineering in academia and business every year.
In 2022, 24 members were newly elected from academia, including four KAIST faculty members: Professor Doo-Hwan Bae from the SW Education Center, KAIST Provost and Executive Vice President Seung Seob Lee, Professor JaeYong Choung from the School of Business and Technology Management, and Professor Kyung Cheol Choi of the School of Electrical Engineering. In the business sector, 21 members were elected as members in business, including Vice Chairman Jong-hee Han of Samsung Electronics, CEO Hyeon-Mo Ku of KT, President Sang-Ryul Lee of the Korea Aerospace Research Institute, President Kyo Won Jin of SK Hynix, CEO Eunkang Song of Capstone Partners, and Executive Vice President Se-hoon Kim of Hyundai Motor Company.
Among the newly elected 40 associate members from academia, three KAIST professors were listed: Professor Sukyoung Ryu from the School of Computing, Professor Joongmyeon Bae from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Professor EunAe Cho from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. Another 44 members were elected as associate members in business, including Vice Chairman Hag-Dong Kim of POSCO, President Seong-Hyeon Cho of Mando Corp, President Siyoung Choi of Samsung Electronics, President Joo Sun Choi of Samsung Display, and Chairman Byung-Gyu Chang of Krafton.
NAEK evaluates candidates not only on their academic achievements, but on various other criteria including technological achievements, patents, the nurturing of talents, and contributions to the advancements of the industry. Candidates are then elected through written ballots by the members of NAEK. There are now 294 members and 360 associate members of NAEK.
2022.01.14 View 7106 -
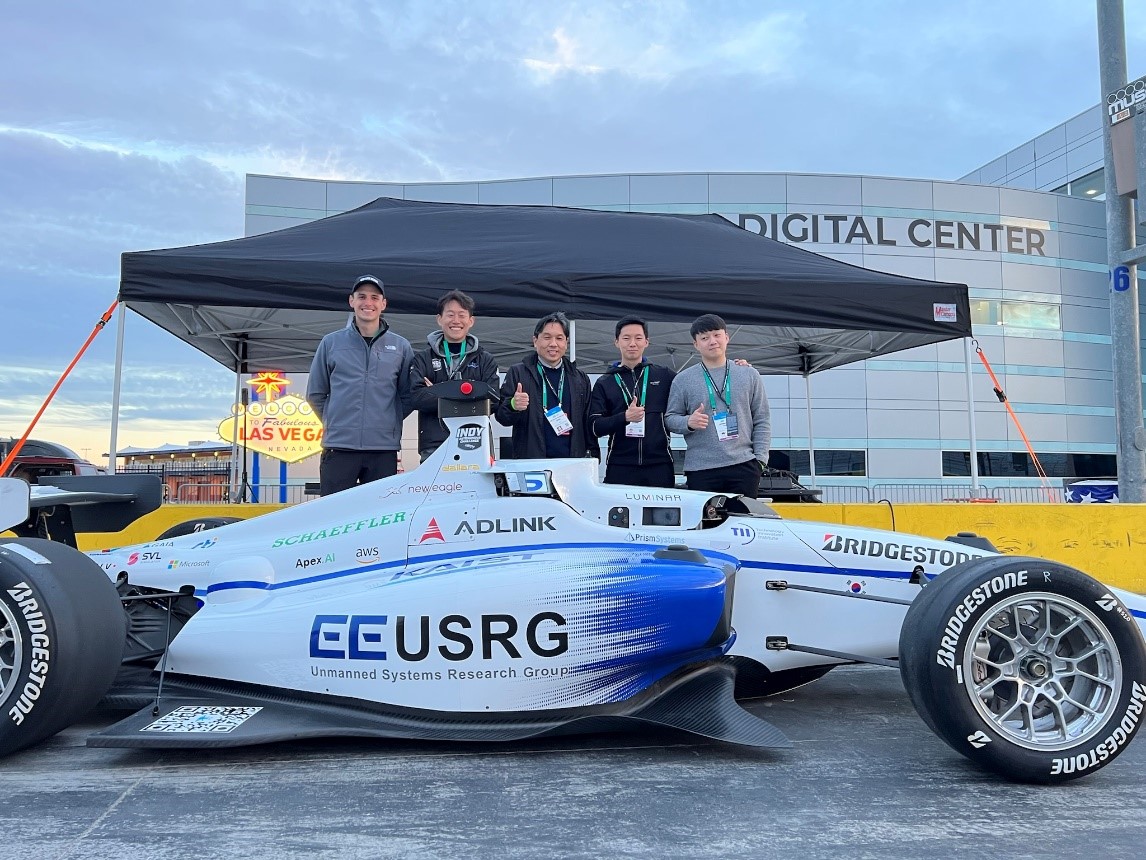 Team KAIST Makes Its Presence Felt in the Self-Driving Tech Industry
Team KAIST finishes 4th at the inaugural CES Autonomous Racing Competition
Team KAIST led by Professor Hyunchul Shim and Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG) placed fourth in an autonomous race car competition in Las Vegas last week, making its presence felt in the self-driving automotive tech industry.
Team KAIST, beat its first competitor, Auburn University, with speeds of up to 131 mph at the Autonomous Challenge at CES held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway. However, the team failed to advance to the final round when it lost to PoliMOVE, comprised of the Polytechnic University of Milan and the University of Alabama, the final winner of the $150,000 USD race.
A total of eight teams competed in the self-driving race. The race was conducted as a single elimination tournament consisting of multiple rounds of matches. Two cars took turns playing the role of defender and attacker, and each car attempted to outpace the other until one of them was unable to complete the mission.
Each team designed the algorithm to control its racecar, the Dallara-built AV-21, which can reach a speed of up to 173 mph, and make it safely drive around the track at high speeds without crashing into the other.
The event is the CES version of the Indy Autonomous Challenge, a competition that took place for the first time in October last year to encourage university students from around the world to develop complicated software for autonomous driving and advance relevant technologies. Team KAIST placed 4th at the Indy Autonomous Challenge, which qualified it to participate in this race.
“The technical level of the CES race is much higher than last October’s and we had a very tough race. We advanced to the semifinals for two consecutive races. I think our autonomous vehicle technology is proving itself to the world,” said Professor Shim.
Professor Shim’s research group has been working on the development of autonomous aerial and ground vehicles for the past 12 years. A self-driving car developed by the lab was certified by the South Korean government to run on public roads.
The vehicle the team used cost more than 1 million USD to build. Many of the other teams had to repair their vehicle more than once due to accidents and had to spend a lot on repairs. “We are the only one who did not have any accidents, and this is a testament to our technological prowess,” said Professor Shim.
He said the financial funding to purchase pricy parts and equipment for the racecar is always a challenge given the very tight research budget and absence of corporate sponsorships.
However, Professor Shim and his research group plan to participate in the next race in September and in the 2023 CES race.
“I think we need more systemic and proactive research and support systems to earn better results but there is nothing better than the group of passionate students who are taking part in this project with us,” Shim added.
2022.01.12 View 12032
Team KAIST Makes Its Presence Felt in the Self-Driving Tech Industry
Team KAIST finishes 4th at the inaugural CES Autonomous Racing Competition
Team KAIST led by Professor Hyunchul Shim and Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG) placed fourth in an autonomous race car competition in Las Vegas last week, making its presence felt in the self-driving automotive tech industry.
Team KAIST, beat its first competitor, Auburn University, with speeds of up to 131 mph at the Autonomous Challenge at CES held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway. However, the team failed to advance to the final round when it lost to PoliMOVE, comprised of the Polytechnic University of Milan and the University of Alabama, the final winner of the $150,000 USD race.
A total of eight teams competed in the self-driving race. The race was conducted as a single elimination tournament consisting of multiple rounds of matches. Two cars took turns playing the role of defender and attacker, and each car attempted to outpace the other until one of them was unable to complete the mission.
Each team designed the algorithm to control its racecar, the Dallara-built AV-21, which can reach a speed of up to 173 mph, and make it safely drive around the track at high speeds without crashing into the other.
The event is the CES version of the Indy Autonomous Challenge, a competition that took place for the first time in October last year to encourage university students from around the world to develop complicated software for autonomous driving and advance relevant technologies. Team KAIST placed 4th at the Indy Autonomous Challenge, which qualified it to participate in this race.
“The technical level of the CES race is much higher than last October’s and we had a very tough race. We advanced to the semifinals for two consecutive races. I think our autonomous vehicle technology is proving itself to the world,” said Professor Shim.
Professor Shim’s research group has been working on the development of autonomous aerial and ground vehicles for the past 12 years. A self-driving car developed by the lab was certified by the South Korean government to run on public roads.
The vehicle the team used cost more than 1 million USD to build. Many of the other teams had to repair their vehicle more than once due to accidents and had to spend a lot on repairs. “We are the only one who did not have any accidents, and this is a testament to our technological prowess,” said Professor Shim.
He said the financial funding to purchase pricy parts and equipment for the racecar is always a challenge given the very tight research budget and absence of corporate sponsorships.
However, Professor Shim and his research group plan to participate in the next race in September and in the 2023 CES race.
“I think we need more systemic and proactive research and support systems to earn better results but there is nothing better than the group of passionate students who are taking part in this project with us,” Shim added.
2022.01.12 View 12032 -
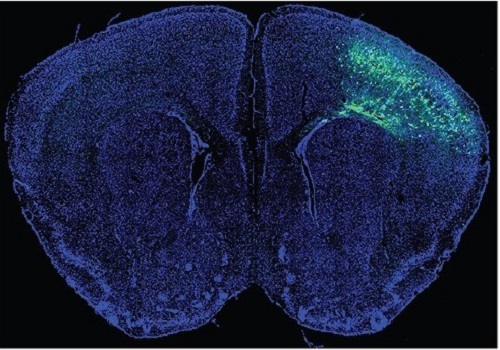 A Mechanism Underlying Most Common Cause of Epileptic Seizures Revealed
An interdisciplinary study shows that neurons carrying somatic mutations in MTOR can lead to focal epileptogenesis via non-cell-autonomous hyperexcitability of nearby nonmutated neurons
During fetal development, cells should migrate to the outer edge of the brain to form critical connections for information transfer and regulation in the body. When even a few cells fail to move to the correct location, the neurons become disorganized and this results in focal cortical dysplasia. This condition is the most common cause of seizures that cannot be controlled with medication in children and the second most common cause in adults.
Now, an interdisciplinary team studying neurogenetics, neural networks, and neurophysiology at KAIST has revealed how dysfunctions in even a small percentage of cells can cause disorder across the entire brain. They published their results on June 28 in Annals of Neurology.
The work builds on a previous finding, also by a KAIST scientists, who found that focal cortical dysplasia was caused by mutations in the cells involved in mTOR, a pathway that regulates signaling between neurons in the brain.
“Only 1 to 2% of neurons carrying mutations in the mTOR signaling pathway that regulates cell signaling in the brain have been found to include seizures in animal models of focal cortical dysplasia,” said Professor Jong-Woo Sohn from the Department of Biological Sciences. “The main challenge of this study was to explain how nearby non-mutated neurons are hyperexcitable.”
Initially, the researchers hypothesized that the mutated cells affected the number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in all neurons, mutated or not. These neural gates can trigger or halt activity, respectively, in other neurons. Seizures are a result of extreme activity, called hyperexcitability. If the mutated cells upend the balance and result in more excitatory cells, the researchers thought, it made sense that the cells would be more susceptible to hyperexcitability and, as a result, seizures.
“Contrary to our expectations, the synaptic input balance was not changed in either the mutated or non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. “We turned our attention to a protein overproduced by mutated neurons.”
The protein is adenosine kinase, which lowers the concentration of adenosine. This naturally occurring compound is an anticonvulsant and works to relax vessels. In mice engineered to have focal cortical dysplasia, the researchers injected adenosine to replace the levels lowered by the protein. It worked and the neurons became less excitable.
“We demonstrated that augmentation of adenosine signaling could attenuate the excitability of non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering.
The effect on the non-mutated neurons was the surprising part, according to Paik. “The seizure-triggering hyperexcitability originated not in the mutation-carrying neurons, but instead in the nearby non-mutated neurons,” he said.
The mutated neurons excreted more adenosine kinase, reducing the adenosine levels in the local environment of all the cells. With less adenosine, the non-mutated neurons became hyperexcitable, leading to seizures.
“While we need further investigate into the relationship between the concentration of adenosine and the increased excitation of nearby neurons, our results support the medical use of drugs to activate adenosine signaling as a possible treatment pathway for focal cortical dysplasia,” Professor Lee said.
The Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Korea Health Technology Research and Development Project, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation in Korea funded this work.
-Publication:Koh, H.Y., Jang, J., Ju, S.H., Kim, R., Cho, G.-B., Kim, D.S., Sohn, J.-W., Paik, S.-B. and Lee, J.H. (2021), ‘Non–Cell Autonomous Epileptogenesis in Focal Cortical Dysplasia’ Annals of Neurology, 90: 285 299. (https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26149)
-ProfileProfessor Jeong Ho Lee Translational Neurogenetics Labhttps://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/ Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering KAIST
Professor Se-Bum Paik Visual System and Neural Network Laboratory http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/ Department of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Jong-Woo Sohn Laboratory for Neurophysiology, https://sites.google.com/site/sohnlab2014/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
Dr. Hyun Yong Koh Translational Neurogenetics LabGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
Dr. Jaeson Jang Ph.D.Visual System and Neural Network LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST
Sang Hyeon Ju M.D.Laboratory for NeurophysiologyDepartment of Biological SciencesKAIST
2021.08.26 View 14940
A Mechanism Underlying Most Common Cause of Epileptic Seizures Revealed
An interdisciplinary study shows that neurons carrying somatic mutations in MTOR can lead to focal epileptogenesis via non-cell-autonomous hyperexcitability of nearby nonmutated neurons
During fetal development, cells should migrate to the outer edge of the brain to form critical connections for information transfer and regulation in the body. When even a few cells fail to move to the correct location, the neurons become disorganized and this results in focal cortical dysplasia. This condition is the most common cause of seizures that cannot be controlled with medication in children and the second most common cause in adults.
Now, an interdisciplinary team studying neurogenetics, neural networks, and neurophysiology at KAIST has revealed how dysfunctions in even a small percentage of cells can cause disorder across the entire brain. They published their results on June 28 in Annals of Neurology.
The work builds on a previous finding, also by a KAIST scientists, who found that focal cortical dysplasia was caused by mutations in the cells involved in mTOR, a pathway that regulates signaling between neurons in the brain.
“Only 1 to 2% of neurons carrying mutations in the mTOR signaling pathway that regulates cell signaling in the brain have been found to include seizures in animal models of focal cortical dysplasia,” said Professor Jong-Woo Sohn from the Department of Biological Sciences. “The main challenge of this study was to explain how nearby non-mutated neurons are hyperexcitable.”
Initially, the researchers hypothesized that the mutated cells affected the number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in all neurons, mutated or not. These neural gates can trigger or halt activity, respectively, in other neurons. Seizures are a result of extreme activity, called hyperexcitability. If the mutated cells upend the balance and result in more excitatory cells, the researchers thought, it made sense that the cells would be more susceptible to hyperexcitability and, as a result, seizures.
“Contrary to our expectations, the synaptic input balance was not changed in either the mutated or non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. “We turned our attention to a protein overproduced by mutated neurons.”
The protein is adenosine kinase, which lowers the concentration of adenosine. This naturally occurring compound is an anticonvulsant and works to relax vessels. In mice engineered to have focal cortical dysplasia, the researchers injected adenosine to replace the levels lowered by the protein. It worked and the neurons became less excitable.
“We demonstrated that augmentation of adenosine signaling could attenuate the excitability of non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering.
The effect on the non-mutated neurons was the surprising part, according to Paik. “The seizure-triggering hyperexcitability originated not in the mutation-carrying neurons, but instead in the nearby non-mutated neurons,” he said.
The mutated neurons excreted more adenosine kinase, reducing the adenosine levels in the local environment of all the cells. With less adenosine, the non-mutated neurons became hyperexcitable, leading to seizures.
“While we need further investigate into the relationship between the concentration of adenosine and the increased excitation of nearby neurons, our results support the medical use of drugs to activate adenosine signaling as a possible treatment pathway for focal cortical dysplasia,” Professor Lee said.
The Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Korea Health Technology Research and Development Project, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation in Korea funded this work.
-Publication:Koh, H.Y., Jang, J., Ju, S.H., Kim, R., Cho, G.-B., Kim, D.S., Sohn, J.-W., Paik, S.-B. and Lee, J.H. (2021), ‘Non–Cell Autonomous Epileptogenesis in Focal Cortical Dysplasia’ Annals of Neurology, 90: 285 299. (https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26149)
-ProfileProfessor Jeong Ho Lee Translational Neurogenetics Labhttps://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/ Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering KAIST
Professor Se-Bum Paik Visual System and Neural Network Laboratory http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/ Department of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Jong-Woo Sohn Laboratory for Neurophysiology, https://sites.google.com/site/sohnlab2014/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
Dr. Hyun Yong Koh Translational Neurogenetics LabGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
Dr. Jaeson Jang Ph.D.Visual System and Neural Network LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST
Sang Hyeon Ju M.D.Laboratory for NeurophysiologyDepartment of Biological SciencesKAIST
2021.08.26 View 14940 -
 3D Visualization and Quantification of Bioplastic PHA in a Living Bacterial Cell
3D holographic microscopy leads to in-depth analysis of bacterial cells accumulating the bacterial bioplastic, polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)
A research team at KAIST has observed how bioplastic granule is being accumulated in living bacteria cells through 3D holographic microscopy. Their 3D imaging and quantitative analysis of the bioplastic ‘polyhydroxyalkanoate’ (PHA) via optical diffraction tomography provides insights into biosynthesizing sustainable substitutes for petroleum-based plastics.
The bio-degradable polyester polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) is being touted as an eco-friendly bioplastic to replace existing synthetic plastics. While carrying similar properties to general-purpose plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene, PHA can be used in various industrial applications such as container packaging and disposable products.
PHA is synthesized by numerous bacteria as an energy and carbon storage material under unbalanced growth conditions in the presence of excess carbon sources. PHA exists in the form of insoluble granules in the cytoplasm. Previous studies on investigating in vivo PHA granules have been performed by using fluorescence microscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and electron cryotomography.
These techniques have generally relied on the statistical analysis of multiple 2D snapshots of fixed cells or the short-time monitoring of the cells. For the TEM analysis, cells need to be fixed and sectioned, and thus the investigation of living cells was not possible. Fluorescence-based techniques require fluorescence labeling or dye staining. Thus, indirect imaging with the use of reporter proteins cannot show the native state of PHAs or cells, and invasive exogenous dyes can affect the physiology and viability of the cells. Therefore, it was difficult to fully understand the formation of PHA granules in cells due to the technical limitations, and thus several mechanism models based on the observations have been only proposed.
The team of metabolic engineering researchers led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee and Physics Professor YongKeun Park, who established the startup Tomocube with his 3D holographic microscopy, reported the results of 3D quantitative label-free analysis of PHA granules in individual live bacterial cells by measuring the refractive index distributions using optical diffraction tomography. The formation and growth of PHA granules in the cells of Cupriavidus necator, the most-studied native PHA (specifically, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), also known as PHB) producer, and recombinant Escherichia coli harboring C. necator PHB biosynthesis pathway were comparatively examined.
From the reconstructed 3D refractive index distribution of the cells, the team succeeded in the 3D visualization and quantitative analysis of cells and intracellular PHA granules at a single-cell level. In particular, the team newly presented the concept of “in vivo PHA granule density.” Through the statistical analysis of hundreds of single cells accumulating PHA granules, the distinctive differences of density and localization of PHA granules in the two micro-organisms were found. Furthermore, the team identified the key protein that plays a major role in making the difference that enabled the characteristics of PHA granules in the recombinant E. coli to become similar to those of C. necator.
The research team also presented 3D time-lapse movies showing the actual processes of PHA granule formation combined with cell growth and division. Movies showing the living cells synthesizing and accumulating PHA granules in their native state had never been reported before.
Professor Lee said, “This study provides insights into the morphological and physical characteristics of in vivo PHA as well as the unique mechanisms of PHA granule formation that undergo the phase transition from soluble monomers into the insoluble polymer, followed by granule formation. Through this study, a deeper understanding of PHA granule formation within the bacterial cells is now possible, which has great significance in that a convergence study of biology and physics was achieved. This study will help develop various bioplastics production processes in the future.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (Grants NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program (Grant No. 2021M3A9I4022740) from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea to S.Y.L. This work was also supported by the KAIST Cross-Generation Collaborative Laboratory project.
-PublicationSo Young Choi, Jeonghun Oh, JaeHwang Jung, YongKeun Park, and Sang Yup Lee. Three-dimensional label-free visualization and quantification of polyhydroxyalkanoates in individualbacterial cell in its native state. PNAS(https://doi.org./10.1073/pnas.2103956118)
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic Engineering and Synthetic Biologyhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering KAIST
Endowed Chair Professor YongKeun ParkBiomedical Optics Laboratoryhttps://bmokaist.wordpress.com/
Department of PhysicsKAIST
2021.07.28 View 15262
3D Visualization and Quantification of Bioplastic PHA in a Living Bacterial Cell
3D holographic microscopy leads to in-depth analysis of bacterial cells accumulating the bacterial bioplastic, polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)
A research team at KAIST has observed how bioplastic granule is being accumulated in living bacteria cells through 3D holographic microscopy. Their 3D imaging and quantitative analysis of the bioplastic ‘polyhydroxyalkanoate’ (PHA) via optical diffraction tomography provides insights into biosynthesizing sustainable substitutes for petroleum-based plastics.
The bio-degradable polyester polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) is being touted as an eco-friendly bioplastic to replace existing synthetic plastics. While carrying similar properties to general-purpose plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene, PHA can be used in various industrial applications such as container packaging and disposable products.
PHA is synthesized by numerous bacteria as an energy and carbon storage material under unbalanced growth conditions in the presence of excess carbon sources. PHA exists in the form of insoluble granules in the cytoplasm. Previous studies on investigating in vivo PHA granules have been performed by using fluorescence microscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and electron cryotomography.
These techniques have generally relied on the statistical analysis of multiple 2D snapshots of fixed cells or the short-time monitoring of the cells. For the TEM analysis, cells need to be fixed and sectioned, and thus the investigation of living cells was not possible. Fluorescence-based techniques require fluorescence labeling or dye staining. Thus, indirect imaging with the use of reporter proteins cannot show the native state of PHAs or cells, and invasive exogenous dyes can affect the physiology and viability of the cells. Therefore, it was difficult to fully understand the formation of PHA granules in cells due to the technical limitations, and thus several mechanism models based on the observations have been only proposed.
The team of metabolic engineering researchers led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee and Physics Professor YongKeun Park, who established the startup Tomocube with his 3D holographic microscopy, reported the results of 3D quantitative label-free analysis of PHA granules in individual live bacterial cells by measuring the refractive index distributions using optical diffraction tomography. The formation and growth of PHA granules in the cells of Cupriavidus necator, the most-studied native PHA (specifically, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), also known as PHB) producer, and recombinant Escherichia coli harboring C. necator PHB biosynthesis pathway were comparatively examined.
From the reconstructed 3D refractive index distribution of the cells, the team succeeded in the 3D visualization and quantitative analysis of cells and intracellular PHA granules at a single-cell level. In particular, the team newly presented the concept of “in vivo PHA granule density.” Through the statistical analysis of hundreds of single cells accumulating PHA granules, the distinctive differences of density and localization of PHA granules in the two micro-organisms were found. Furthermore, the team identified the key protein that plays a major role in making the difference that enabled the characteristics of PHA granules in the recombinant E. coli to become similar to those of C. necator.
The research team also presented 3D time-lapse movies showing the actual processes of PHA granule formation combined with cell growth and division. Movies showing the living cells synthesizing and accumulating PHA granules in their native state had never been reported before.
Professor Lee said, “This study provides insights into the morphological and physical characteristics of in vivo PHA as well as the unique mechanisms of PHA granule formation that undergo the phase transition from soluble monomers into the insoluble polymer, followed by granule formation. Through this study, a deeper understanding of PHA granule formation within the bacterial cells is now possible, which has great significance in that a convergence study of biology and physics was achieved. This study will help develop various bioplastics production processes in the future.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (Grants NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program (Grant No. 2021M3A9I4022740) from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea to S.Y.L. This work was also supported by the KAIST Cross-Generation Collaborative Laboratory project.
-PublicationSo Young Choi, Jeonghun Oh, JaeHwang Jung, YongKeun Park, and Sang Yup Lee. Three-dimensional label-free visualization and quantification of polyhydroxyalkanoates in individualbacterial cell in its native state. PNAS(https://doi.org./10.1073/pnas.2103956118)
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic Engineering and Synthetic Biologyhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering KAIST
Endowed Chair Professor YongKeun ParkBiomedical Optics Laboratoryhttps://bmokaist.wordpress.com/
Department of PhysicsKAIST
2021.07.28 View 15262