department+of+biological+sciences
-
 KAIST Research Team Proves How a Neurotransmitter may be the Key in Controlling Alzheimer’s Toxicity
With nearly 50 million dementia patients worldwide, and Alzheimers’s disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Its main symptom is the impairment of general cognitive abilities, including the ability to speak or to remember. The importance of finding a cure is widely understood with increasingly aging population and the life expectancy being ever-extended. However, even the cause of the grim disease is yet to be given a clear definition.
A KAIST research team in the Department of Chemistry led by professor Mi Hee Lim took on a lead to discovered a new role for somatostatin, a protein-based neurotransmitter, in reducing the toxicity caused in the pathogenic mechanism taken towards development of Alzheimer’s disease. The study was published in the July issue of Nature Chemistry under the title, “Conformational and functional changes of the native neuropeptide somatostatin occur in the presence of copper and amyloid-β”.
According to the amyloid hypothesis, the abnormal deposition of Aβ proteins causes death of neuronal cells. While Aβ agglomerations make up most of the aged plaques through fibrosis, in recent studies, high concentrations of transitional metal were found in the plaques from Alzheimer’s patients.
This suggests a close interaction between metallic ions and Aβ, which accelerates the fibrosis of proteins. Copper in particular is a redox-activating transition metal that can produce large amounts of oxygen and cause serious oxidative stress on cell organelles. Aβ proteins and transition metals can closely interact with neurotransmitters at synapses, but the direct effects of such abnormalities on the structure and function of neurotransmitters are yet to be understood.
Figure 1. Functional shift of somatostatin (SST) by factors in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.
Figure 2. Somatostatin’s loss-of-function as neurotransmitter. a. Schematic diagram of SST auto-aggregation due to Alzheimer's pathological factors. b. SST’s aggregation by copper ions. c. Coordination-prediction structure and N-terminal folding of copper-SST. d. Inhibition of SST receptor binding specificity by metals.
In their research, Professor Lim’s team discovered that when somatostatin, the protein-based neurotransmitter, is met with copper, Aβ, and metal-Aβ complexes, self-aggregates and ceases to perform its innate function of transmitting neural signals, but begins to attenuate the toxicity and agglomeration of metal-Aβ complexes.
Figure 3. Gain-of-function of somatostatin (SST) in the dementia setting. a. Prediction of docking of SST and amyloid beta. b. SST making metal-amyloid beta aggregates into an amorphous form. c. Cytotoxic mitigation effect of SST. d. SST mitigating the interaction between amyloid beta protein with the cell membrane.
This research, by Dr. Jiyeon Han et al. from the KAIST Department of Chemistry, revealed the coordination structure between copper and somatostatin at a molecular level through which it suggested the agglomeration mechanism, and discovered the effects of somatostatin on Aβ agglomeration path depending on the presence or absence of metals. The team has further confirmed somatostatin’s receptor binding, interactions with cell membranes, and effects on cell toxicity for the first time to receive international attention.
Professor Mi Hee Lim said, “This research has great significance in having discovered a new role of neurotransmitters in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.” “We expect this research to contribute to defining the pathogenic network of neurodegenerative diseases caused by aging, and to the development of future biomarkers and medicine,” she added.
This research was conducted jointly by Professor Seung-Hee Lee’s team of KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, Professor Kiyoung Park’s Team of KAIST Department of Chemistry, and Professor Yulong Li’s team of Peking University.
The research was funded by Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and KAIST.
For more information about the research team, visit the website: https://sites.google.com/site/miheelimlab/1-professor-mi-hee-lim.
2022.07.29 View 15917
KAIST Research Team Proves How a Neurotransmitter may be the Key in Controlling Alzheimer’s Toxicity
With nearly 50 million dementia patients worldwide, and Alzheimers’s disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Its main symptom is the impairment of general cognitive abilities, including the ability to speak or to remember. The importance of finding a cure is widely understood with increasingly aging population and the life expectancy being ever-extended. However, even the cause of the grim disease is yet to be given a clear definition.
A KAIST research team in the Department of Chemistry led by professor Mi Hee Lim took on a lead to discovered a new role for somatostatin, a protein-based neurotransmitter, in reducing the toxicity caused in the pathogenic mechanism taken towards development of Alzheimer’s disease. The study was published in the July issue of Nature Chemistry under the title, “Conformational and functional changes of the native neuropeptide somatostatin occur in the presence of copper and amyloid-β”.
According to the amyloid hypothesis, the abnormal deposition of Aβ proteins causes death of neuronal cells. While Aβ agglomerations make up most of the aged plaques through fibrosis, in recent studies, high concentrations of transitional metal were found in the plaques from Alzheimer’s patients.
This suggests a close interaction between metallic ions and Aβ, which accelerates the fibrosis of proteins. Copper in particular is a redox-activating transition metal that can produce large amounts of oxygen and cause serious oxidative stress on cell organelles. Aβ proteins and transition metals can closely interact with neurotransmitters at synapses, but the direct effects of such abnormalities on the structure and function of neurotransmitters are yet to be understood.
Figure 1. Functional shift of somatostatin (SST) by factors in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.
Figure 2. Somatostatin’s loss-of-function as neurotransmitter. a. Schematic diagram of SST auto-aggregation due to Alzheimer's pathological factors. b. SST’s aggregation by copper ions. c. Coordination-prediction structure and N-terminal folding of copper-SST. d. Inhibition of SST receptor binding specificity by metals.
In their research, Professor Lim’s team discovered that when somatostatin, the protein-based neurotransmitter, is met with copper, Aβ, and metal-Aβ complexes, self-aggregates and ceases to perform its innate function of transmitting neural signals, but begins to attenuate the toxicity and agglomeration of metal-Aβ complexes.
Figure 3. Gain-of-function of somatostatin (SST) in the dementia setting. a. Prediction of docking of SST and amyloid beta. b. SST making metal-amyloid beta aggregates into an amorphous form. c. Cytotoxic mitigation effect of SST. d. SST mitigating the interaction between amyloid beta protein with the cell membrane.
This research, by Dr. Jiyeon Han et al. from the KAIST Department of Chemistry, revealed the coordination structure between copper and somatostatin at a molecular level through which it suggested the agglomeration mechanism, and discovered the effects of somatostatin on Aβ agglomeration path depending on the presence or absence of metals. The team has further confirmed somatostatin’s receptor binding, interactions with cell membranes, and effects on cell toxicity for the first time to receive international attention.
Professor Mi Hee Lim said, “This research has great significance in having discovered a new role of neurotransmitters in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.” “We expect this research to contribute to defining the pathogenic network of neurodegenerative diseases caused by aging, and to the development of future biomarkers and medicine,” she added.
This research was conducted jointly by Professor Seung-Hee Lee’s team of KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, Professor Kiyoung Park’s Team of KAIST Department of Chemistry, and Professor Yulong Li’s team of Peking University.
The research was funded by Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and KAIST.
For more information about the research team, visit the website: https://sites.google.com/site/miheelimlab/1-professor-mi-hee-lim.
2022.07.29 View 15917 -
 A Mechanism Underlying Most Common Cause of Epileptic Seizures Revealed
An interdisciplinary study shows that neurons carrying somatic mutations in MTOR can lead to focal epileptogenesis via non-cell-autonomous hyperexcitability of nearby nonmutated neurons
During fetal development, cells should migrate to the outer edge of the brain to form critical connections for information transfer and regulation in the body. When even a few cells fail to move to the correct location, the neurons become disorganized and this results in focal cortical dysplasia. This condition is the most common cause of seizures that cannot be controlled with medication in children and the second most common cause in adults.
Now, an interdisciplinary team studying neurogenetics, neural networks, and neurophysiology at KAIST has revealed how dysfunctions in even a small percentage of cells can cause disorder across the entire brain. They published their results on June 28 in Annals of Neurology.
The work builds on a previous finding, also by a KAIST scientists, who found that focal cortical dysplasia was caused by mutations in the cells involved in mTOR, a pathway that regulates signaling between neurons in the brain.
“Only 1 to 2% of neurons carrying mutations in the mTOR signaling pathway that regulates cell signaling in the brain have been found to include seizures in animal models of focal cortical dysplasia,” said Professor Jong-Woo Sohn from the Department of Biological Sciences. “The main challenge of this study was to explain how nearby non-mutated neurons are hyperexcitable.”
Initially, the researchers hypothesized that the mutated cells affected the number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in all neurons, mutated or not. These neural gates can trigger or halt activity, respectively, in other neurons. Seizures are a result of extreme activity, called hyperexcitability. If the mutated cells upend the balance and result in more excitatory cells, the researchers thought, it made sense that the cells would be more susceptible to hyperexcitability and, as a result, seizures.
“Contrary to our expectations, the synaptic input balance was not changed in either the mutated or non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. “We turned our attention to a protein overproduced by mutated neurons.”
The protein is adenosine kinase, which lowers the concentration of adenosine. This naturally occurring compound is an anticonvulsant and works to relax vessels. In mice engineered to have focal cortical dysplasia, the researchers injected adenosine to replace the levels lowered by the protein. It worked and the neurons became less excitable.
“We demonstrated that augmentation of adenosine signaling could attenuate the excitability of non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering.
The effect on the non-mutated neurons was the surprising part, according to Paik. “The seizure-triggering hyperexcitability originated not in the mutation-carrying neurons, but instead in the nearby non-mutated neurons,” he said.
The mutated neurons excreted more adenosine kinase, reducing the adenosine levels in the local environment of all the cells. With less adenosine, the non-mutated neurons became hyperexcitable, leading to seizures.
“While we need further investigate into the relationship between the concentration of adenosine and the increased excitation of nearby neurons, our results support the medical use of drugs to activate adenosine signaling as a possible treatment pathway for focal cortical dysplasia,” Professor Lee said.
The Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Korea Health Technology Research and Development Project, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation in Korea funded this work.
-Publication:Koh, H.Y., Jang, J., Ju, S.H., Kim, R., Cho, G.-B., Kim, D.S., Sohn, J.-W., Paik, S.-B. and Lee, J.H. (2021), ‘Non–Cell Autonomous Epileptogenesis in Focal Cortical Dysplasia’ Annals of Neurology, 90: 285 299. (https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26149)
-ProfileProfessor Jeong Ho Lee Translational Neurogenetics Labhttps://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/ Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering KAIST
Professor Se-Bum Paik Visual System and Neural Network Laboratory http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/ Department of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Jong-Woo Sohn Laboratory for Neurophysiology, https://sites.google.com/site/sohnlab2014/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
Dr. Hyun Yong Koh Translational Neurogenetics LabGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
Dr. Jaeson Jang Ph.D.Visual System and Neural Network LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST
Sang Hyeon Ju M.D.Laboratory for NeurophysiologyDepartment of Biological SciencesKAIST
2021.08.26 View 14865
A Mechanism Underlying Most Common Cause of Epileptic Seizures Revealed
An interdisciplinary study shows that neurons carrying somatic mutations in MTOR can lead to focal epileptogenesis via non-cell-autonomous hyperexcitability of nearby nonmutated neurons
During fetal development, cells should migrate to the outer edge of the brain to form critical connections for information transfer and regulation in the body. When even a few cells fail to move to the correct location, the neurons become disorganized and this results in focal cortical dysplasia. This condition is the most common cause of seizures that cannot be controlled with medication in children and the second most common cause in adults.
Now, an interdisciplinary team studying neurogenetics, neural networks, and neurophysiology at KAIST has revealed how dysfunctions in even a small percentage of cells can cause disorder across the entire brain. They published their results on June 28 in Annals of Neurology.
The work builds on a previous finding, also by a KAIST scientists, who found that focal cortical dysplasia was caused by mutations in the cells involved in mTOR, a pathway that regulates signaling between neurons in the brain.
“Only 1 to 2% of neurons carrying mutations in the mTOR signaling pathway that regulates cell signaling in the brain have been found to include seizures in animal models of focal cortical dysplasia,” said Professor Jong-Woo Sohn from the Department of Biological Sciences. “The main challenge of this study was to explain how nearby non-mutated neurons are hyperexcitable.”
Initially, the researchers hypothesized that the mutated cells affected the number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in all neurons, mutated or not. These neural gates can trigger or halt activity, respectively, in other neurons. Seizures are a result of extreme activity, called hyperexcitability. If the mutated cells upend the balance and result in more excitatory cells, the researchers thought, it made sense that the cells would be more susceptible to hyperexcitability and, as a result, seizures.
“Contrary to our expectations, the synaptic input balance was not changed in either the mutated or non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. “We turned our attention to a protein overproduced by mutated neurons.”
The protein is adenosine kinase, which lowers the concentration of adenosine. This naturally occurring compound is an anticonvulsant and works to relax vessels. In mice engineered to have focal cortical dysplasia, the researchers injected adenosine to replace the levels lowered by the protein. It worked and the neurons became less excitable.
“We demonstrated that augmentation of adenosine signaling could attenuate the excitability of non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering.
The effect on the non-mutated neurons was the surprising part, according to Paik. “The seizure-triggering hyperexcitability originated not in the mutation-carrying neurons, but instead in the nearby non-mutated neurons,” he said.
The mutated neurons excreted more adenosine kinase, reducing the adenosine levels in the local environment of all the cells. With less adenosine, the non-mutated neurons became hyperexcitable, leading to seizures.
“While we need further investigate into the relationship between the concentration of adenosine and the increased excitation of nearby neurons, our results support the medical use of drugs to activate adenosine signaling as a possible treatment pathway for focal cortical dysplasia,” Professor Lee said.
The Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Korea Health Technology Research and Development Project, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation in Korea funded this work.
-Publication:Koh, H.Y., Jang, J., Ju, S.H., Kim, R., Cho, G.-B., Kim, D.S., Sohn, J.-W., Paik, S.-B. and Lee, J.H. (2021), ‘Non–Cell Autonomous Epileptogenesis in Focal Cortical Dysplasia’ Annals of Neurology, 90: 285 299. (https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26149)
-ProfileProfessor Jeong Ho Lee Translational Neurogenetics Labhttps://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/ Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering KAIST
Professor Se-Bum Paik Visual System and Neural Network Laboratory http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/ Department of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Jong-Woo Sohn Laboratory for Neurophysiology, https://sites.google.com/site/sohnlab2014/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
Dr. Hyun Yong Koh Translational Neurogenetics LabGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
Dr. Jaeson Jang Ph.D.Visual System and Neural Network LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST
Sang Hyeon Ju M.D.Laboratory for NeurophysiologyDepartment of Biological SciencesKAIST
2021.08.26 View 14865 -
 What Fuels a “Domino Effect” in Cancer Drug Resistance?
KAIST researchers have identified mechanisms that relay prior acquired resistance to the first-line chemotherapy to the second-line targeted therapy, fueling a “domino effect” in cancer drug resistance. Their study featured in the February 7 edition of Science Advances suggests a new strategy for improving the second-line setting of cancer treatment for patients who showed resistance to anti-cancer drugs.
Resistance to cancer drugs is often managed in the clinic by chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Unlike chemotherapy that works by repressing fast-proliferating cells, targeted therapy blocks a single oncogenic pathway to halt tumor growth. In many cases, targeted therapy is engaged as a maintenance therapy or employed in the second-line after front-line chemotherapy.
A team of researchers led by Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the KAIST Institute for Health Science and Technology (KIHST) has discovered an unexpected resistance signature that occurs between chemotherapy and targeted therapy. The team further identified a set of integrated mechanisms that promotes this kind of sequential therapy resistance.
“There have been multiple clinical accounts reflecting that targeted therapies tend to be least successful in patients who have exhausted all standard treatments,” said the first author of the paper Mark Borris D. Aldonza. He continued, “These accounts ignited our hypothesis that failed responses to some chemotherapies might speed up the evolution of resistance to other drugs, particularly those with specific targets.”
Aldonza and his colleagues extracted large amounts of drug-resistance information from the open-source database the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC), which contains thousands of drug response data entries from various human cancer cell lines. Their big data analysis revealed that cancer cell lines resistant to chemotherapies classified as anti-mitotic drugs (AMDs), toxins that inhibit overacting cell division, are also resistant to a class of targeted therapies called epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs).
In all of the cancer types analyzed, more than 84 percent of those resistant to AMDs, representatively ‘paclitaxel’, were also resistant to at least nine EGFR-TKIs. In lung, pancreatic, and breast cancers where paclitaxel is often used as a first-line, standard-of-care regimen, greater than 92 percent showed resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Professor Kim said, “It is surprising to see that such collateral resistance can occur specifically between two chemically different classes of drugs.”
To figure out how failed responses to paclitaxel leads to resistance to EGFR-TKIs, the team validated co-resistance signatures that they found in the database by generating and analyzing a subset of slow-doubling, paclitaxel-resistant cancer models called ‘persisters’.
The results demonstrated that paclitaxel-resistant cancers remodel their stress response by first becoming more stem cell-like, evolving the ability to self-renew to adapt to more stressful conditions like drug exposures. More surprisingly, when the researchers characterized the metabolic state of the cells, EGFR-TKI persisters derived from paclitaxel-resistant cancer cells showed high dependencies to energy-producing processes such as glycolysis and glutaminolysis.
“We found that, without an energy stimulus like glucose, these cells transform to becoming more senescent, a characteristic of cells that have arrested cell division. However, this senescence is controlled by stem cell factors, which the paclitaxel-resistant cancers use to escape from this arrested state given a favorable condition to re-grow,” said Aldonza.
Professor Kim explained, “Before this research, there was no reason to expect that acquiring the cancer stem cell phenotype that dramatically leads to a cascade of changes in cellular states affecting metabolism and cell death is linked with drug-specific sequential resistance between two classes of therapies.”
He added, “The expansion of our work to other working models of drug resistance in a much more clinically-relevant setting, perhaps in clinical trials, will take on increasing importance, as sequential treatment strategies will continue to be adapted to various forms of anti-cancer therapy regimens.”
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2016R1C1B2009886), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project (KAISTHEALTHCARE42) funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT). Undergraduate student Aldonza participated in this research project and presented the findings as the lead author as part of the Undergraduate Research Participation (URP) Program at KAIST.
< Figure 1. Schematic overview of the study. >
< Figure 2. Big data analysis revealing co-resistance signatures between classes of anti-cancer drugs. >
Publication:
Aldonza et al. (2020) Prior acquired resistance to paclitaxel relays diverse EGFR-targeted therapy persistence mechanisms. Science Advances, Vol. 6, No. 6, eaav7416. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav7416
Profile: Prof. Yoosik Kim, MA, PhD
ysyoosik@kaist.ac.kr
https://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Bio Network Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Mark Borris D. Aldonza
borris@kaist.ac.kr
Undergraduate Student
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.10 View 16711
What Fuels a “Domino Effect” in Cancer Drug Resistance?
KAIST researchers have identified mechanisms that relay prior acquired resistance to the first-line chemotherapy to the second-line targeted therapy, fueling a “domino effect” in cancer drug resistance. Their study featured in the February 7 edition of Science Advances suggests a new strategy for improving the second-line setting of cancer treatment for patients who showed resistance to anti-cancer drugs.
Resistance to cancer drugs is often managed in the clinic by chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Unlike chemotherapy that works by repressing fast-proliferating cells, targeted therapy blocks a single oncogenic pathway to halt tumor growth. In many cases, targeted therapy is engaged as a maintenance therapy or employed in the second-line after front-line chemotherapy.
A team of researchers led by Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the KAIST Institute for Health Science and Technology (KIHST) has discovered an unexpected resistance signature that occurs between chemotherapy and targeted therapy. The team further identified a set of integrated mechanisms that promotes this kind of sequential therapy resistance.
“There have been multiple clinical accounts reflecting that targeted therapies tend to be least successful in patients who have exhausted all standard treatments,” said the first author of the paper Mark Borris D. Aldonza. He continued, “These accounts ignited our hypothesis that failed responses to some chemotherapies might speed up the evolution of resistance to other drugs, particularly those with specific targets.”
Aldonza and his colleagues extracted large amounts of drug-resistance information from the open-source database the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC), which contains thousands of drug response data entries from various human cancer cell lines. Their big data analysis revealed that cancer cell lines resistant to chemotherapies classified as anti-mitotic drugs (AMDs), toxins that inhibit overacting cell division, are also resistant to a class of targeted therapies called epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs).
In all of the cancer types analyzed, more than 84 percent of those resistant to AMDs, representatively ‘paclitaxel’, were also resistant to at least nine EGFR-TKIs. In lung, pancreatic, and breast cancers where paclitaxel is often used as a first-line, standard-of-care regimen, greater than 92 percent showed resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Professor Kim said, “It is surprising to see that such collateral resistance can occur specifically between two chemically different classes of drugs.”
To figure out how failed responses to paclitaxel leads to resistance to EGFR-TKIs, the team validated co-resistance signatures that they found in the database by generating and analyzing a subset of slow-doubling, paclitaxel-resistant cancer models called ‘persisters’.
The results demonstrated that paclitaxel-resistant cancers remodel their stress response by first becoming more stem cell-like, evolving the ability to self-renew to adapt to more stressful conditions like drug exposures. More surprisingly, when the researchers characterized the metabolic state of the cells, EGFR-TKI persisters derived from paclitaxel-resistant cancer cells showed high dependencies to energy-producing processes such as glycolysis and glutaminolysis.
“We found that, without an energy stimulus like glucose, these cells transform to becoming more senescent, a characteristic of cells that have arrested cell division. However, this senescence is controlled by stem cell factors, which the paclitaxel-resistant cancers use to escape from this arrested state given a favorable condition to re-grow,” said Aldonza.
Professor Kim explained, “Before this research, there was no reason to expect that acquiring the cancer stem cell phenotype that dramatically leads to a cascade of changes in cellular states affecting metabolism and cell death is linked with drug-specific sequential resistance between two classes of therapies.”
He added, “The expansion of our work to other working models of drug resistance in a much more clinically-relevant setting, perhaps in clinical trials, will take on increasing importance, as sequential treatment strategies will continue to be adapted to various forms of anti-cancer therapy regimens.”
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2016R1C1B2009886), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project (KAISTHEALTHCARE42) funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT). Undergraduate student Aldonza participated in this research project and presented the findings as the lead author as part of the Undergraduate Research Participation (URP) Program at KAIST.
< Figure 1. Schematic overview of the study. >
< Figure 2. Big data analysis revealing co-resistance signatures between classes of anti-cancer drugs. >
Publication:
Aldonza et al. (2020) Prior acquired resistance to paclitaxel relays diverse EGFR-targeted therapy persistence mechanisms. Science Advances, Vol. 6, No. 6, eaav7416. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav7416
Profile: Prof. Yoosik Kim, MA, PhD
ysyoosik@kaist.ac.kr
https://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Bio Network Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Mark Borris D. Aldonza
borris@kaist.ac.kr
Undergraduate Student
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.10 View 16711 -
 Two Professors Receive the Asan Medical Award
(Professor Ho Min Kim and Chair Profesor Eunjoon Kim (from far right)
Chair Professor Eunjoon Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences and Professor Ho Min Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science & Engineering won the 11th Asan Medical Award in the areas of basic medicine and young medical scholar on March 21.
The Asan Medical Award has been recognizing the most distinguished scholars in the areas of basic and clinical medicines annually since 2007.
Chair Professor Kim won the 300 million KRW award in recognition of his research in the mechanism of synaptic brain dysfunction and its relation with neural diseases.
The young medical scholar’s award recognizes a promising scholar under the age of 40. Professor Kim won the award for identifying the key protein structure and molecular mechanism controlling immunocytes and neurons. He earned a 50 million KRW prize.
2018.03.26 View 10677
Two Professors Receive the Asan Medical Award
(Professor Ho Min Kim and Chair Profesor Eunjoon Kim (from far right)
Chair Professor Eunjoon Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences and Professor Ho Min Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science & Engineering won the 11th Asan Medical Award in the areas of basic medicine and young medical scholar on March 21.
The Asan Medical Award has been recognizing the most distinguished scholars in the areas of basic and clinical medicines annually since 2007.
Chair Professor Kim won the 300 million KRW award in recognition of his research in the mechanism of synaptic brain dysfunction and its relation with neural diseases.
The young medical scholar’s award recognizes a promising scholar under the age of 40. Professor Kim won the award for identifying the key protein structure and molecular mechanism controlling immunocytes and neurons. He earned a 50 million KRW prize.
2018.03.26 View 10677 -
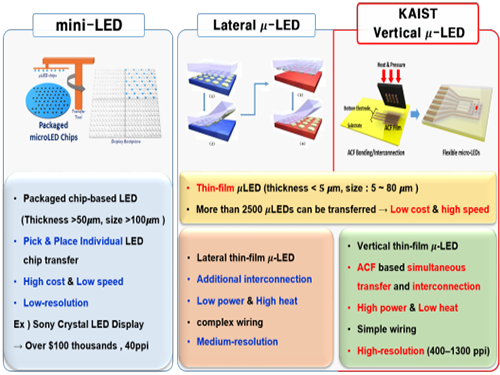 Developing Flexible Vertical Micro LED
A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences has developed flexible vertical micro LEDs (f-VLEDs) using anisotropic conductive film (ACF)-based transfer and interconnection technology. The team also succeeded in controlling animal behavior via optogenetic stimulation of the f-VLEDs.
Flexible micro LEDs have become a strong candidate for the next-generation display due to their ultra-low power consumption, fast response speed, and excellent flexibility. However, the previous micro LED technology had critical issues such as poor device efficiency, low thermal reliability, and the lack of interconnection technology for high-resolution micro LED displays.
The research team has designed new transfer equipment and fabricated a f-VLED array (50ⅹ50) using simultaneous transfer and interconnection through the precise alignment of ACF bonding process. These f-VLEDs (thickness: 5 ㎛, size: below 80 ㎛) achieved optical power density (30 mW/mm2) three times higher than that of lateral micro LEDs, improving thermal reliability and lifetime by reducing heat generation within the thin film LEDs.
These f-VLEDs can be applied to optogenetics for controlling the behavior of neuron cells and brains. In contrast to the electrical stimulation that activates all of the neurons in brain, optogenetics can stimulate specific excitatory or inhibitory neurons within the localized cortical areas of the brain, which facilitates precise analysis, high-resolution mapping, and neuron modulation of animal brains. (Refer to the author’s previous ACS Nano paper of “Optogenetic Mapping of Functional Connectivity in Freely Moving Mice via Insertable Wrapping Electrode Array Beneath the Skull.” )
In this work, they inserted the innovative f-VLEDs into the narrow space between the skull and the brain surface and succeeded in controlling mouse behavior by illuminating motor neurons on two-dimensional cortical areas located deep below the brain surface.
Professor Lee said, “The flexible vertical micro LED can be used in low-power smart watches, mobile displays, and wearable lighting. In addition, these flexible optoelectronic devices are suitable for biomedical applications such as brain science, phototherapeutic treatment, and contact lens biosensors.”
He recently established a startup company ( FRONICS Inc. ) based on micro LED technology and is looking for global partnerships for commercialization. This result entitled “ Optogenetic Control of Body Movements via Flexible Vertical Light-Emitting Diodes on Brain Surface ” was published in the February 2018 issue of Nano Energy.
Figure 1. Comparison of μ-LEDs Technology
2018.01.29 View 14240
Developing Flexible Vertical Micro LED
A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences has developed flexible vertical micro LEDs (f-VLEDs) using anisotropic conductive film (ACF)-based transfer and interconnection technology. The team also succeeded in controlling animal behavior via optogenetic stimulation of the f-VLEDs.
Flexible micro LEDs have become a strong candidate for the next-generation display due to their ultra-low power consumption, fast response speed, and excellent flexibility. However, the previous micro LED technology had critical issues such as poor device efficiency, low thermal reliability, and the lack of interconnection technology for high-resolution micro LED displays.
The research team has designed new transfer equipment and fabricated a f-VLED array (50ⅹ50) using simultaneous transfer and interconnection through the precise alignment of ACF bonding process. These f-VLEDs (thickness: 5 ㎛, size: below 80 ㎛) achieved optical power density (30 mW/mm2) three times higher than that of lateral micro LEDs, improving thermal reliability and lifetime by reducing heat generation within the thin film LEDs.
These f-VLEDs can be applied to optogenetics for controlling the behavior of neuron cells and brains. In contrast to the electrical stimulation that activates all of the neurons in brain, optogenetics can stimulate specific excitatory or inhibitory neurons within the localized cortical areas of the brain, which facilitates precise analysis, high-resolution mapping, and neuron modulation of animal brains. (Refer to the author’s previous ACS Nano paper of “Optogenetic Mapping of Functional Connectivity in Freely Moving Mice via Insertable Wrapping Electrode Array Beneath the Skull.” )
In this work, they inserted the innovative f-VLEDs into the narrow space between the skull and the brain surface and succeeded in controlling mouse behavior by illuminating motor neurons on two-dimensional cortical areas located deep below the brain surface.
Professor Lee said, “The flexible vertical micro LED can be used in low-power smart watches, mobile displays, and wearable lighting. In addition, these flexible optoelectronic devices are suitable for biomedical applications such as brain science, phototherapeutic treatment, and contact lens biosensors.”
He recently established a startup company ( FRONICS Inc. ) based on micro LED technology and is looking for global partnerships for commercialization. This result entitled “ Optogenetic Control of Body Movements via Flexible Vertical Light-Emitting Diodes on Brain Surface ” was published in the February 2018 issue of Nano Energy.
Figure 1. Comparison of μ-LEDs Technology
2018.01.29 View 14240 -
 Meditox Donates 600 Million KRW Scholarship
On February 17, a Korean biopharmaceutical company Meditox, headed by Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Hyun-Ho Jeong, signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with KAIST to establish the “Meditox Fellowship” and donated a total of 600 million Korean won (KRW) to the university to assist in promoting more scientists in the field of biology.
Meditox CEO Hyun-Ho Jeong, KAIST President Steve Kang, Dean of Life Science and Bioengineering College Jung-Hoe Kim, and Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences Byung-Ha Oh participated in the agreement ceremony.
According to the MOU, Meditox will donate 60,000,000 KRW over a ten year period, from which KAIST can draw on to grant scholarships for master’s and doctoral students.
The “Meditox Fellowship” will support promising and enthusiastic students whose finances limit their studies. The first scholarship students for 2016 were: Kwang-Uk Min, In-suk Yeo, Sung-ryung- Lee, Si-on Lee, and Jung-hyun Kim.
Meditox CEO Jeong, who graduated from KAIST’s Department of Biological Sciences, said, "I felt it was important to start the Meditox Fellowship at my alma mater to contribute to the cultivation of outstanding scientists in the field of biological sciences."
He also said that he would plan to launch projects that aim to support not only those who receive the scholarship but also the development of Korea’s biological sciences in general.
President Steve Kang (right) and Chief Executive Officer Hyun-Ho Jeong (left) of Meditox hold the signed memorandum of understanding together.
2016.02.18 View 11657
Meditox Donates 600 Million KRW Scholarship
On February 17, a Korean biopharmaceutical company Meditox, headed by Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Hyun-Ho Jeong, signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with KAIST to establish the “Meditox Fellowship” and donated a total of 600 million Korean won (KRW) to the university to assist in promoting more scientists in the field of biology.
Meditox CEO Hyun-Ho Jeong, KAIST President Steve Kang, Dean of Life Science and Bioengineering College Jung-Hoe Kim, and Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences Byung-Ha Oh participated in the agreement ceremony.
According to the MOU, Meditox will donate 60,000,000 KRW over a ten year period, from which KAIST can draw on to grant scholarships for master’s and doctoral students.
The “Meditox Fellowship” will support promising and enthusiastic students whose finances limit their studies. The first scholarship students for 2016 were: Kwang-Uk Min, In-suk Yeo, Sung-ryung- Lee, Si-on Lee, and Jung-hyun Kim.
Meditox CEO Jeong, who graduated from KAIST’s Department of Biological Sciences, said, "I felt it was important to start the Meditox Fellowship at my alma mater to contribute to the cultivation of outstanding scientists in the field of biological sciences."
He also said that he would plan to launch projects that aim to support not only those who receive the scholarship but also the development of Korea’s biological sciences in general.
President Steve Kang (right) and Chief Executive Officer Hyun-Ho Jeong (left) of Meditox hold the signed memorandum of understanding together.
2016.02.18 View 11657 -
 IdeasLab Presents Biotechnology Solutions for Aging Populations at 2016 Davos Forum
KAIST researchers will discuss how biological sciences and health technologies can address challenges and opportunities posed by aging populations in an era of increasing longevity.
Many countries around the world today are experiencing the rapid growth of aging populations, with a decline in fertility rate and longer life expectancy.
At this year's Annual Meeting of the World Economic Forum (a.k.a. Davos Forum) on January 20-23, 2016 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland, four researchers in the field of biological sciences and biotechnology at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) will discuss the implications of an aging population and explore possible solutions to provide better health care services to the elderly.
KAIST will host an IdeasLab twice on the theme "Biotechnology Solutions for Ageing Populations" on January 21st and 23rd, respectively.
Professor Byung-Kwan Cho of the Biological Sciences Department will give a presentation on "Rejuvenation via the Microbiome," explaining how microorganisms in the human gut play an important role in preventing aging, or even rejuvenating it.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department will talk about "Traditional Medicine Reimagined through Modern Systems Biology." Professor Lee will introduce his research results published in Nature Biotechnology (March 6, 2015) and some more new results. He discovered the mechanisms of traditional oriental medicine's (TOM) efficacy by applying systems biology to study structural similarities between natural and nontoxic multi-compounds in the medicine and human metabolites. He will discuss TOM's multi-target approach, which is based on the synergistic combinations of multi-compounds to treat symptoms of a disease, can contribute to the development of new drugs, cosmetics, and nutrients.
Professor Youn-Kyung Lim of the Industrial Design Department will speak about a mobile and the Internet of Things-based health care service called "Dr. M" in her presentation on "Advanced Mobile Healthcare Systems."
Professor Daesoo Kim of the Biological Sciences Department will share his research on human's happiness and greed in the context of nueroscience and behavioral and biological sciences in a talk entitled "A Neural Switch for Being Happy with Less on a Crowded Planet."
KAIST has hosted IdeasLabs several times at the Summer Davos Forum in China, but this is the first time it will participate in the Davos Forum in January.
Professor Lee said, "Just like climate change, the issue of how to address aging populations has become a major global issue. We will share some exciting research results and hope to have in depth discussion on this issue with the leaders attending the Davos Forum. KAIST will engage actively in finding solutions that benefit not only Korea but also the international community."
2016.01.19 View 12459
IdeasLab Presents Biotechnology Solutions for Aging Populations at 2016 Davos Forum
KAIST researchers will discuss how biological sciences and health technologies can address challenges and opportunities posed by aging populations in an era of increasing longevity.
Many countries around the world today are experiencing the rapid growth of aging populations, with a decline in fertility rate and longer life expectancy.
At this year's Annual Meeting of the World Economic Forum (a.k.a. Davos Forum) on January 20-23, 2016 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland, four researchers in the field of biological sciences and biotechnology at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) will discuss the implications of an aging population and explore possible solutions to provide better health care services to the elderly.
KAIST will host an IdeasLab twice on the theme "Biotechnology Solutions for Ageing Populations" on January 21st and 23rd, respectively.
Professor Byung-Kwan Cho of the Biological Sciences Department will give a presentation on "Rejuvenation via the Microbiome," explaining how microorganisms in the human gut play an important role in preventing aging, or even rejuvenating it.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department will talk about "Traditional Medicine Reimagined through Modern Systems Biology." Professor Lee will introduce his research results published in Nature Biotechnology (March 6, 2015) and some more new results. He discovered the mechanisms of traditional oriental medicine's (TOM) efficacy by applying systems biology to study structural similarities between natural and nontoxic multi-compounds in the medicine and human metabolites. He will discuss TOM's multi-target approach, which is based on the synergistic combinations of multi-compounds to treat symptoms of a disease, can contribute to the development of new drugs, cosmetics, and nutrients.
Professor Youn-Kyung Lim of the Industrial Design Department will speak about a mobile and the Internet of Things-based health care service called "Dr. M" in her presentation on "Advanced Mobile Healthcare Systems."
Professor Daesoo Kim of the Biological Sciences Department will share his research on human's happiness and greed in the context of nueroscience and behavioral and biological sciences in a talk entitled "A Neural Switch for Being Happy with Less on a Crowded Planet."
KAIST has hosted IdeasLabs several times at the Summer Davos Forum in China, but this is the first time it will participate in the Davos Forum in January.
Professor Lee said, "Just like climate change, the issue of how to address aging populations has become a major global issue. We will share some exciting research results and hope to have in depth discussion on this issue with the leaders attending the Davos Forum. KAIST will engage actively in finding solutions that benefit not only Korea but also the international community."
2016.01.19 View 12459 -
 Professor YongKeun Park Produces Undergraduate Students with International Achievements
Three undergraduate students under the supervision of Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics, KAIST, have published papers in globally renowned academic journals.
The most recent publication was made by YoungJu Jo, a senior in physics. Jo’s paper entitled “Angle-resolved light scattering of individual rod-shaped bacteria based on Fourier transform light scattering” was published in the May 28th edition of Scientific Reports.
Analyzing bacteria is a very important task in the field of health and food hygiene, but using the conventional biochemical methods of analysis takes days. However, observation with Jo’s newly developed method using light scattering analyzes bacteria within a matter of seconds.
SangYeon Cho from the Department of Chemistry also published papers in Cell (2012) and Nature (2013), respectively, under the guidance of Professor Park. SangYeon Cho’s outstanding research achievements were recognized by Harvard and MIT. He was accepted with a full scholarship to Harvard-MIT Health Sciences and Technology Graduate School. He will begin his graduate studies at Harvard-MIT this September.
Last March, SeoEun Lee from the Department of Biology was the recipient of the Best Paper Award by the Optical Society of Korea. She plans to pursue a doctoral degree at the College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University in New York.
Professor Park said, “Undergraduate students, who are learning a variety of subjects concurrently, are at the most creative time of their lives. KAIST has offered many opportunities to undergraduate students to partake in various research programs.”
- Picture (a) and (b): Rod-shaped bacteria’s phase image and light-scattering patterns
- Picture (c): Quantitative analysis to illustrate the extraction of information from bacteria
2014.06.03 View 14826
Professor YongKeun Park Produces Undergraduate Students with International Achievements
Three undergraduate students under the supervision of Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics, KAIST, have published papers in globally renowned academic journals.
The most recent publication was made by YoungJu Jo, a senior in physics. Jo’s paper entitled “Angle-resolved light scattering of individual rod-shaped bacteria based on Fourier transform light scattering” was published in the May 28th edition of Scientific Reports.
Analyzing bacteria is a very important task in the field of health and food hygiene, but using the conventional biochemical methods of analysis takes days. However, observation with Jo’s newly developed method using light scattering analyzes bacteria within a matter of seconds.
SangYeon Cho from the Department of Chemistry also published papers in Cell (2012) and Nature (2013), respectively, under the guidance of Professor Park. SangYeon Cho’s outstanding research achievements were recognized by Harvard and MIT. He was accepted with a full scholarship to Harvard-MIT Health Sciences and Technology Graduate School. He will begin his graduate studies at Harvard-MIT this September.
Last March, SeoEun Lee from the Department of Biology was the recipient of the Best Paper Award by the Optical Society of Korea. She plans to pursue a doctoral degree at the College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University in New York.
Professor Park said, “Undergraduate students, who are learning a variety of subjects concurrently, are at the most creative time of their lives. KAIST has offered many opportunities to undergraduate students to partake in various research programs.”
- Picture (a) and (b): Rod-shaped bacteria’s phase image and light-scattering patterns
- Picture (c): Quantitative analysis to illustrate the extraction of information from bacteria
2014.06.03 View 14826 -
 The new era of personalized cancer diagnosis and treatment
Professor Tae-Young Yoon
- Succeeded in observing carcinogenic protein at the molecular level
- “Paved the way to customized cancer treatment through accurate analysis of carcinogenic protein”
The joint KAIST research team of Professor Tae Young Yoon of the Department of Physics and Professor Won Do Huh of the Department of Biological Sciences have developed the technology to monitor characteristics of carcinogenic protein in cancer tissue – for the first time in the world.
The technology makes it possible to analyse the mechanism of cancer development through a small amount of carcinogenic protein from a cancer patient. Therefore, a personalised approach to diagnosis and treatment using the knowledge of the specific mechanism of cancer development in the patient may be possible in the future.
Until recently, modern medicine could only speculate on the cause of cancer through statistics. Although developed countries, such as the United States, are known to use a large sequencing technology that analyses the patient’s DNA, identification of the interactions between proteins responsible for causing cancer remained an unanswered question for a long time in medicine.
Firstly, Professor Yoon’s research team has developed a fluorescent microscope that can observe even a single molecule. Then, the “Immunoprecipitation method”, a technology to extract a specific protein exploiting the high affinity between antigens and antibodies was developed. Using this technology and the microscope, “Real-Time Single Molecule co-Immunoprecipitation Method” was created. In this way, the team succeeded in observing the interactions between carcinogenic and other proteins at a molecular level, in real time.
To validate the developed technology, the team investigated Ras, a carcinogenic protein; its mutation statistically is known to cause around 30% of cancers.
The experimental results confirmed that 30-50% of Ras protein was expressed in mouse tumour and human cancer cells. In normal cells, less than 5% of Ras protein was expressed. Thus, the experiment showed that unusual increase in activation of Ras protein induces cancer.
The increase in the ratio of active Ras protein can be inferred from existing research data but the measurement of specific numerical data has never been done before.
The team suggested a new molecular level diagnosis technique of identifying the progress of cancer in patients through measuring the percentage of activated carcinogenic protein in cancer tissue.
Professor Yoon Tae-young said, “This newly developed technology does not require a separate procedure of protein expression or refining, hence the existing proteins in real biological tissues or cancer cells can be observed directly.” He also said, “Since carcinogenic protein can be analyzed accurately, it has opened up the path to customized cancer treatment in the future.”
“Since the observation is possible on a molecular level, the technology confers the advantage that researchers can carry out various examinations on a small sample of the cancer patient.” He added, “The clinical trial will start in December 2012 and in a few years customized cancer diagnosis and treatment will be possible.”
Meanwhile, the research has been published in Nature Communications (February 19). Many researchers from various fields have participated, regardless of the differences in their speciality, and successfully produced interdisciplinary research. Professor Tae Young Yoon of the Department of Physics and Professors Dae Sik Lim and Won Do Huh of Biological Sciences at KAIST, and Professor Chang Bong Hyun of Computational Science of KIAS contributed to developing the technique.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of observed interactions at the molecular level in real time using fluorescent microscope. The carcinogenic protein from a mouse tumour is fixed on the microchip, and its molecular characteristics are observed live.
Figure 2: Molecular interaction data using a molecular level fluorescent microscope. A signal in the form of spike is shown when two proteins combine. This is monitored live using an Electron Multiplying Charge Coupled Device (EMCCD). It shows signal results in bright dots.
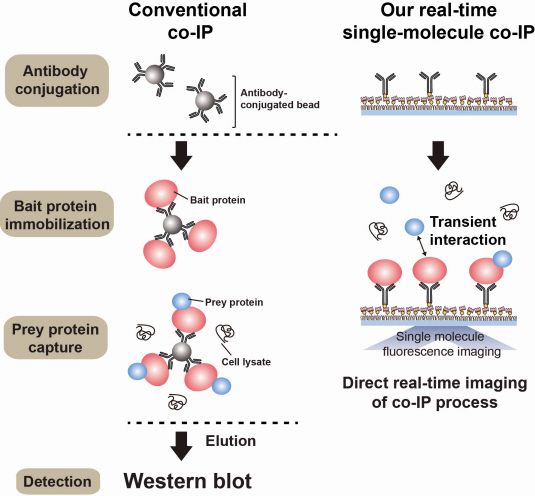
An organism has an immune system as a defence mechanism to foreign intruders. The immune system is activated when unwanted pathogens or foreign protein are in the body. Antibodies form in recognition of the specific antigen to protect itself. Organisms evolved to form antibodies with high specificity to a certain antigen. Antibodies only react to its complementary antigens. The field of molecular biology uses the affinity between antigens and antibodies to extract specific proteins; a technology called immunoprecipitation. Even in a mixture of many proteins, the protein sought can be extracted using antibodies. Thus immunoprecipitation is widely used to detect pathogens or to extract specific proteins.
Technology co-IP is a well-known example that uses immunoprecipitation. The research on interactions between proteins uses co-IP in general. The basis of fixing the antigen on the antibody to extract antigen protein is the same as immunoprecipitation. Then, researchers inject and observe its reaction with the partner protein to observe the interactions and precipitate the antibodies. If the reaction occurs, the partner protein will be found with the antibodies in the precipitations. If not, then the partner protein will not be found. This shows that the two proteins interact.
However, the traditional co-IP can be used to infer the interactions between the two proteins although the information of the dynamics on how the reaction occurs is lost. To overcome these shortcomings, the Real-Time Single Molecule co-IP Method enables observation on individual protein level in real time. Therefore, the significance of the new technique is in making observation of interactions more direct and quantitative.
Additional Figure 1: Comparison between Conventional co-IP and Real-Time Single Molecule co-IP
2013.04.01 View 20965
The new era of personalized cancer diagnosis and treatment
Professor Tae-Young Yoon
- Succeeded in observing carcinogenic protein at the molecular level
- “Paved the way to customized cancer treatment through accurate analysis of carcinogenic protein”
The joint KAIST research team of Professor Tae Young Yoon of the Department of Physics and Professor Won Do Huh of the Department of Biological Sciences have developed the technology to monitor characteristics of carcinogenic protein in cancer tissue – for the first time in the world.
The technology makes it possible to analyse the mechanism of cancer development through a small amount of carcinogenic protein from a cancer patient. Therefore, a personalised approach to diagnosis and treatment using the knowledge of the specific mechanism of cancer development in the patient may be possible in the future.
Until recently, modern medicine could only speculate on the cause of cancer through statistics. Although developed countries, such as the United States, are known to use a large sequencing technology that analyses the patient’s DNA, identification of the interactions between proteins responsible for causing cancer remained an unanswered question for a long time in medicine.
Firstly, Professor Yoon’s research team has developed a fluorescent microscope that can observe even a single molecule. Then, the “Immunoprecipitation method”, a technology to extract a specific protein exploiting the high affinity between antigens and antibodies was developed. Using this technology and the microscope, “Real-Time Single Molecule co-Immunoprecipitation Method” was created. In this way, the team succeeded in observing the interactions between carcinogenic and other proteins at a molecular level, in real time.
To validate the developed technology, the team investigated Ras, a carcinogenic protein; its mutation statistically is known to cause around 30% of cancers.
The experimental results confirmed that 30-50% of Ras protein was expressed in mouse tumour and human cancer cells. In normal cells, less than 5% of Ras protein was expressed. Thus, the experiment showed that unusual increase in activation of Ras protein induces cancer.
The increase in the ratio of active Ras protein can be inferred from existing research data but the measurement of specific numerical data has never been done before.
The team suggested a new molecular level diagnosis technique of identifying the progress of cancer in patients through measuring the percentage of activated carcinogenic protein in cancer tissue.
Professor Yoon Tae-young said, “This newly developed technology does not require a separate procedure of protein expression or refining, hence the existing proteins in real biological tissues or cancer cells can be observed directly.” He also said, “Since carcinogenic protein can be analyzed accurately, it has opened up the path to customized cancer treatment in the future.”
“Since the observation is possible on a molecular level, the technology confers the advantage that researchers can carry out various examinations on a small sample of the cancer patient.” He added, “The clinical trial will start in December 2012 and in a few years customized cancer diagnosis and treatment will be possible.”
Meanwhile, the research has been published in Nature Communications (February 19). Many researchers from various fields have participated, regardless of the differences in their speciality, and successfully produced interdisciplinary research. Professor Tae Young Yoon of the Department of Physics and Professors Dae Sik Lim and Won Do Huh of Biological Sciences at KAIST, and Professor Chang Bong Hyun of Computational Science of KIAS contributed to developing the technique.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of observed interactions at the molecular level in real time using fluorescent microscope. The carcinogenic protein from a mouse tumour is fixed on the microchip, and its molecular characteristics are observed live.
Figure 2: Molecular interaction data using a molecular level fluorescent microscope. A signal in the form of spike is shown when two proteins combine. This is monitored live using an Electron Multiplying Charge Coupled Device (EMCCD). It shows signal results in bright dots.
An organism has an immune system as a defence mechanism to foreign intruders. The immune system is activated when unwanted pathogens or foreign protein are in the body. Antibodies form in recognition of the specific antigen to protect itself. Organisms evolved to form antibodies with high specificity to a certain antigen. Antibodies only react to its complementary antigens. The field of molecular biology uses the affinity between antigens and antibodies to extract specific proteins; a technology called immunoprecipitation. Even in a mixture of many proteins, the protein sought can be extracted using antibodies. Thus immunoprecipitation is widely used to detect pathogens or to extract specific proteins.
Technology co-IP is a well-known example that uses immunoprecipitation. The research on interactions between proteins uses co-IP in general. The basis of fixing the antigen on the antibody to extract antigen protein is the same as immunoprecipitation. Then, researchers inject and observe its reaction with the partner protein to observe the interactions and precipitate the antibodies. If the reaction occurs, the partner protein will be found with the antibodies in the precipitations. If not, then the partner protein will not be found. This shows that the two proteins interact.
However, the traditional co-IP can be used to infer the interactions between the two proteins although the information of the dynamics on how the reaction occurs is lost. To overcome these shortcomings, the Real-Time Single Molecule co-IP Method enables observation on individual protein level in real time. Therefore, the significance of the new technique is in making observation of interactions more direct and quantitative.
Additional Figure 1: Comparison between Conventional co-IP and Real-Time Single Molecule co-IP
2013.04.01 View 20965 -
 Ph.D. students Hyowon Park and Won Ma receive Grand Prizes in Mathematics and Biology respectively.
Researchers in KAIST received best paper awards in two out of three fields at this year’s award ceremony for the “Second Annual Best Thesis Paper Award” held collectively by the Korea University Presidents’ Federation (with Chairman DaeSoon Lee) and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (with Director GilSang Jung).
Two researchers from KAIST, Hyowon Park (Department of Mathematics) and Won Ma (Department of Biology) received best paper awards.
This prize, given by the both the Korea University Presidents’ Federation and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology since last year, is awarded to researchers and assistant professors who write the most outstanding thesis papers in the field of basic sciences.
Park, who received the best paper award this year, did research on graph braid groups. He was supervised by Professor Kihyung Ko, who received the best supervisor reward.
Ma, who received the best paper award in the field of biological science, researched about the Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder due to deficiency of the GIT1 synapse protein. His supervising professor also received the supervisor award.
The award ceremony was held in the auditorium of the S-OIL headquarters in Seoul on November 30.
Meanwhile, NASA researcher Jaehwa Lee received the best paper award in the field of earth science, and his supervising professor, Professor Jun Kim from Yonsei University who studies atmospheric science, received the best supervisor award.
2012.12.21 View 12261
Ph.D. students Hyowon Park and Won Ma receive Grand Prizes in Mathematics and Biology respectively.
Researchers in KAIST received best paper awards in two out of three fields at this year’s award ceremony for the “Second Annual Best Thesis Paper Award” held collectively by the Korea University Presidents’ Federation (with Chairman DaeSoon Lee) and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (with Director GilSang Jung).
Two researchers from KAIST, Hyowon Park (Department of Mathematics) and Won Ma (Department of Biology) received best paper awards.
This prize, given by the both the Korea University Presidents’ Federation and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology since last year, is awarded to researchers and assistant professors who write the most outstanding thesis papers in the field of basic sciences.
Park, who received the best paper award this year, did research on graph braid groups. He was supervised by Professor Kihyung Ko, who received the best supervisor reward.
Ma, who received the best paper award in the field of biological science, researched about the Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder due to deficiency of the GIT1 synapse protein. His supervising professor also received the supervisor award.
The award ceremony was held in the auditorium of the S-OIL headquarters in Seoul on November 30.
Meanwhile, NASA researcher Jaehwa Lee received the best paper award in the field of earth science, and his supervising professor, Professor Jun Kim from Yonsei University who studies atmospheric science, received the best supervisor award.
2012.12.21 View 12261