aging
-
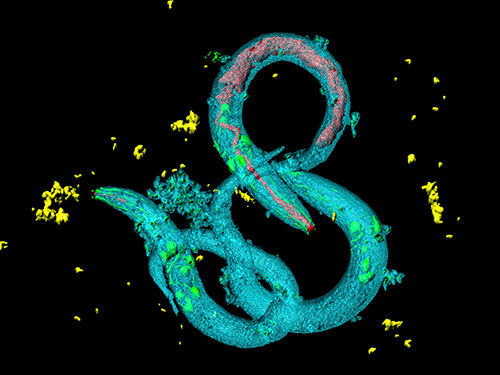 Tinkering with Roundworm Proteins Offers Hope for Anti-aging Drugs
- The somatic nuclear protein kinase VRK-1 increases the worm’s lifespan through AMPK activation, and this mechanism can be applied to promoting human longevity, the study reveals. -
KAIST researchers have been able to dial up and down creatures’ lifespans by altering the activity of proteins found in roundworm cells that tell them to convert sugar into energy when their cellular energy is running low. Humans also have these proteins, offering up the intriguing possibilities for developing longevity-promoting drugs. These new findings were published on July 1 in Science Advances.
The roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), a millimeter-long nematode commonly used in lab testing, enjoyed a boost in its lifespan when researchers tinkered with a couple of proteins involved in monitoring the energy use by its cells.
The proteins VRK-1 and AMPK work in tandem in roundworm cells, with the former telling the latter to get to work by sticking a phosphate molecule, composed of one phosphorus and four oxygen atoms, on it. In turn, AMPK’s role is to monitor energy levels in cells, when cellular energy is running low. In essence, VRK-1 regulates AMPK, and AMPK regulates the cellular energy status.
Using a range of different biological research tools, including introducing foreign genes into the worm, a group of researchers led by Professor Seung-Jae V. Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST were able to dial up and down the activity of the gene that tells cells to produce the VRK-1 protein. This gene has remained pretty much unchanged throughout evolution. Most complex organisms have this same gene, including humans.
Lead author of the study Sangsoon Park and his colleagues confirmed that the overexpression, or increased production, of the VRK-1 protein boosted the lifespan of the C. elegans, which normally lives just two to three weeks, and the inhibition of VRK-1 production reduced its lifespan.
The research team found that the activity of the VRK-1-to-AMPK cellular-energy monitoring process is increased in low cellular energy status by reduced mitochondrial respiration, the set of metabolic chemical reactions that make use of the oxygen the worm breathes to convert macronutrients from food into the energy “currency” that cells spend to do everything they need to do.
It is already known that mitochondria, the energy-producing engine rooms in cells, play a crucial role in aging, and declines in the functioning of mitochondria are associated with age-related diseases. At the same time, the mild inhibition of mitochondrial respiration has been shown to promote longevity in a range of species, including flies and mammals.
When the research team performed similar tinkering with cultured human cells, they found they could also replicate this ramping up and down of the VRK-1-to-AMPK process that occurs in roundworms.
“This raises the intriguing possibility that VRK-1 also functions as a factor in governing human longevity, and so perhaps we can start developing longevity-promoting drugs that alter the activity of VRK-1,” explained Professor Lee.
At the very least, the research points us in an interesting direction for investigating new therapeutic strategies to combat metabolic disorders by targeting the modulation of VRK-1. Metabolic disorders involve the disruption of chemical reactions in the body, including diseases of the mitochondria.
But before metabolic disorder therapeutics or longevity drugs can be contemplated by scientists, further research still needs to be carried out to better understand how VRK-1 works to activate AMPK, as well as figure out the precise mechanics of how AMPK controls cellular energy.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF), and the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of Korea.
Image credit: Seung-Jae V. LEE, KAIST.
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Park, S., et al. (2020) ‘VRK-1 extends life span by activation of AMPK via phosphorylation’. Science Advances, Volume 6. No. 27, eaaw7824. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw7824
Profile: Seung-Jae V. Lee, Ph.D.
Professor
seungjaevlee@kaist.ac.kr
https://sites.google.com/view/mgakaist
Molecular Genetics of Aging Laboratory
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.krDaejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.07.31 View 9112
Tinkering with Roundworm Proteins Offers Hope for Anti-aging Drugs
- The somatic nuclear protein kinase VRK-1 increases the worm’s lifespan through AMPK activation, and this mechanism can be applied to promoting human longevity, the study reveals. -
KAIST researchers have been able to dial up and down creatures’ lifespans by altering the activity of proteins found in roundworm cells that tell them to convert sugar into energy when their cellular energy is running low. Humans also have these proteins, offering up the intriguing possibilities for developing longevity-promoting drugs. These new findings were published on July 1 in Science Advances.
The roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), a millimeter-long nematode commonly used in lab testing, enjoyed a boost in its lifespan when researchers tinkered with a couple of proteins involved in monitoring the energy use by its cells.
The proteins VRK-1 and AMPK work in tandem in roundworm cells, with the former telling the latter to get to work by sticking a phosphate molecule, composed of one phosphorus and four oxygen atoms, on it. In turn, AMPK’s role is to monitor energy levels in cells, when cellular energy is running low. In essence, VRK-1 regulates AMPK, and AMPK regulates the cellular energy status.
Using a range of different biological research tools, including introducing foreign genes into the worm, a group of researchers led by Professor Seung-Jae V. Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST were able to dial up and down the activity of the gene that tells cells to produce the VRK-1 protein. This gene has remained pretty much unchanged throughout evolution. Most complex organisms have this same gene, including humans.
Lead author of the study Sangsoon Park and his colleagues confirmed that the overexpression, or increased production, of the VRK-1 protein boosted the lifespan of the C. elegans, which normally lives just two to three weeks, and the inhibition of VRK-1 production reduced its lifespan.
The research team found that the activity of the VRK-1-to-AMPK cellular-energy monitoring process is increased in low cellular energy status by reduced mitochondrial respiration, the set of metabolic chemical reactions that make use of the oxygen the worm breathes to convert macronutrients from food into the energy “currency” that cells spend to do everything they need to do.
It is already known that mitochondria, the energy-producing engine rooms in cells, play a crucial role in aging, and declines in the functioning of mitochondria are associated with age-related diseases. At the same time, the mild inhibition of mitochondrial respiration has been shown to promote longevity in a range of species, including flies and mammals.
When the research team performed similar tinkering with cultured human cells, they found they could also replicate this ramping up and down of the VRK-1-to-AMPK process that occurs in roundworms.
“This raises the intriguing possibility that VRK-1 also functions as a factor in governing human longevity, and so perhaps we can start developing longevity-promoting drugs that alter the activity of VRK-1,” explained Professor Lee.
At the very least, the research points us in an interesting direction for investigating new therapeutic strategies to combat metabolic disorders by targeting the modulation of VRK-1. Metabolic disorders involve the disruption of chemical reactions in the body, including diseases of the mitochondria.
But before metabolic disorder therapeutics or longevity drugs can be contemplated by scientists, further research still needs to be carried out to better understand how VRK-1 works to activate AMPK, as well as figure out the precise mechanics of how AMPK controls cellular energy.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF), and the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of Korea.
Image credit: Seung-Jae V. LEE, KAIST.
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Park, S., et al. (2020) ‘VRK-1 extends life span by activation of AMPK via phosphorylation’. Science Advances, Volume 6. No. 27, eaaw7824. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaw7824
Profile: Seung-Jae V. Lee, Ph.D.
Professor
seungjaevlee@kaist.ac.kr
https://sites.google.com/view/mgakaist
Molecular Genetics of Aging Laboratory
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.krDaejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.07.31 View 9112 -
 Unravelling Complex Brain Networks with Automated 3-D Neural Mapping
-Automated 3-D brain imaging data analysis technology offers more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of complex neural circuits.-
KAIST researchers developed a new algorithm for brain imaging data analysis that enables the precise and quantitative mapping of complex neural circuits onto a standardized 3-D reference atlas.
Brain imaging data analysis is indispensable in the studies of neuroscience. However, analysis of obtained brain imaging data has been heavily dependent on manual processing, which cannot guarantee the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of the results.
Conventional brain imaging data analysis typically begins with finding a 2-D brain atlas image that is visually similar to the experimentally obtained brain image. Then, the region-of-interest (ROI) of the atlas image is matched manually with the obtained image, and the number of labeled neurons in the ROI is counted.
Such a visual matching process between experimentally obtained brain images and 2-D brain atlas images has been one of the major sources of error in brain imaging data analysis, as the process is highly subjective, sample-specific, and susceptible to human error. Manual analysis processes for brain images are also laborious, and thus studying the complete 3-D neuronal organization on a whole-brain scale is a formidable task.
To address these issues, a KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering developed new brain imaging data analysis software named 'AMaSiNe (Automated 3-D Mapping of Single Neurons)', and introduced the algorithm in the May 26 issue of Cell Reports.
AMaSiNe automatically detects the positions of single neurons from multiple brain images, and accurately maps all the data onto a common standard 3-D reference space. The algorithm allows the direct comparison of brain data from different animals by automatically matching similar features from the images, and computing the image similarity score.
This feature-based quantitative image-to-image comparison technology improves the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of analysis results using only a small number of brain slice image samples, and helps standardize brain imaging data analyses.
Unlike other existing brain imaging data analysis methods, AMaSiNe can also automatically find the alignment conditions from misaligned and distorted brain images, and draw an accurate ROI, without any cumbersome manual validation process.
AMaSiNe has been further proved to produce consistent results with brain slice images stained utilizing various methods including DAPI, Nissl, and autofluorescence.
The two co-lead authors of this study, Jun Ho Song and Woochul Choi, exploited these benefits of AMaSiNe to investigate the topographic organization of neurons that project to the primary visual area (VISp) in various ROIs, such as the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGd), which could hardly be addressed without proper calibration and standardization of the brain slice image samples.
In collaboration with Professor Seung-Hee Lee's group of the Department of Biological Science, the researchers successfully observed the 3-D topographic neural projections to the VISp from LGd, and also demonstrated that these projections could not be observed when the slicing angle was not properly corrected by AMaSiNe. The results suggest that the precise correction of a slicing angle is essential for the investigation of complex and important brain structures.
AMaSiNe is widely applicable in the studies of various brain regions and other experimental conditions. For example, in the research team’s previous study jointly conducted with Professor Yang Dan’s group at UC Berkeley, the algorithm enabled the accurate analysis of the neuronal subsets in the substantia nigra and their projections to the whole brain. Their findings were published in Science on January 24.
AMaSiNe is of great interest to many neuroscientists in Korea and abroad, and is being actively used by a number of other research groups at KAIST, MIT, Harvard, Caltech, and UC San Diego.
Professor Paik said, “Our new algorithm allows the spatial organization of complex neural circuits to be found in a standardized 3-D reference atlas on a whole-brain scale. This will bring brain imaging data analysis to a new level.”
He continued, “More in-depth insights for understanding the function of brain circuits can be achieved by facilitating more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of neural circuits in various regions of the brain.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Figure and Image Credit: Professor Se-Bum Paik, KAIST
Figure and Image Usage Restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and images, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Song, J. H., et al. (2020). Precise Mapping of Single Neurons by Calibrated 3D Reconstruction of Brain Slices Reveals Topographic Projection in Mouse Visual Cortex. Cell Reports. Volume 31, 107682. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107682
Profile:
Se-Bum Paik
Assistant Professor
sbpaik@kaist.ac.kr
http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/
VSNN Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.06.08 View 10766
Unravelling Complex Brain Networks with Automated 3-D Neural Mapping
-Automated 3-D brain imaging data analysis technology offers more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of complex neural circuits.-
KAIST researchers developed a new algorithm for brain imaging data analysis that enables the precise and quantitative mapping of complex neural circuits onto a standardized 3-D reference atlas.
Brain imaging data analysis is indispensable in the studies of neuroscience. However, analysis of obtained brain imaging data has been heavily dependent on manual processing, which cannot guarantee the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of the results.
Conventional brain imaging data analysis typically begins with finding a 2-D brain atlas image that is visually similar to the experimentally obtained brain image. Then, the region-of-interest (ROI) of the atlas image is matched manually with the obtained image, and the number of labeled neurons in the ROI is counted.
Such a visual matching process between experimentally obtained brain images and 2-D brain atlas images has been one of the major sources of error in brain imaging data analysis, as the process is highly subjective, sample-specific, and susceptible to human error. Manual analysis processes for brain images are also laborious, and thus studying the complete 3-D neuronal organization on a whole-brain scale is a formidable task.
To address these issues, a KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering developed new brain imaging data analysis software named 'AMaSiNe (Automated 3-D Mapping of Single Neurons)', and introduced the algorithm in the May 26 issue of Cell Reports.
AMaSiNe automatically detects the positions of single neurons from multiple brain images, and accurately maps all the data onto a common standard 3-D reference space. The algorithm allows the direct comparison of brain data from different animals by automatically matching similar features from the images, and computing the image similarity score.
This feature-based quantitative image-to-image comparison technology improves the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of analysis results using only a small number of brain slice image samples, and helps standardize brain imaging data analyses.
Unlike other existing brain imaging data analysis methods, AMaSiNe can also automatically find the alignment conditions from misaligned and distorted brain images, and draw an accurate ROI, without any cumbersome manual validation process.
AMaSiNe has been further proved to produce consistent results with brain slice images stained utilizing various methods including DAPI, Nissl, and autofluorescence.
The two co-lead authors of this study, Jun Ho Song and Woochul Choi, exploited these benefits of AMaSiNe to investigate the topographic organization of neurons that project to the primary visual area (VISp) in various ROIs, such as the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGd), which could hardly be addressed without proper calibration and standardization of the brain slice image samples.
In collaboration with Professor Seung-Hee Lee's group of the Department of Biological Science, the researchers successfully observed the 3-D topographic neural projections to the VISp from LGd, and also demonstrated that these projections could not be observed when the slicing angle was not properly corrected by AMaSiNe. The results suggest that the precise correction of a slicing angle is essential for the investigation of complex and important brain structures.
AMaSiNe is widely applicable in the studies of various brain regions and other experimental conditions. For example, in the research team’s previous study jointly conducted with Professor Yang Dan’s group at UC Berkeley, the algorithm enabled the accurate analysis of the neuronal subsets in the substantia nigra and their projections to the whole brain. Their findings were published in Science on January 24.
AMaSiNe is of great interest to many neuroscientists in Korea and abroad, and is being actively used by a number of other research groups at KAIST, MIT, Harvard, Caltech, and UC San Diego.
Professor Paik said, “Our new algorithm allows the spatial organization of complex neural circuits to be found in a standardized 3-D reference atlas on a whole-brain scale. This will bring brain imaging data analysis to a new level.”
He continued, “More in-depth insights for understanding the function of brain circuits can be achieved by facilitating more reliable and standardized analysis of the spatial organization of neural circuits in various regions of the brain.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Figure and Image Credit: Professor Se-Bum Paik, KAIST
Figure and Image Usage Restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and images, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Song, J. H., et al. (2020). Precise Mapping of Single Neurons by Calibrated 3D Reconstruction of Brain Slices Reveals Topographic Projection in Mouse Visual Cortex. Cell Reports. Volume 31, 107682. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107682
Profile:
Se-Bum Paik
Assistant Professor
sbpaik@kaist.ac.kr
http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/
VSNN Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.06.08 View 10766 -
 Professor Sue-Hyun Lee Listed Among WEF 2020 Young Scientists
Professor Sue-Hyun Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering joined the World Economic Forum (WEF)’s Young Scientists Community on May 26. The class of 2020 comprises 25 leading researchers from 14 countries across the world who are at the forefront of scientific problem-solving and social change. Professor Lee was the only Korean on this year’s roster.
The WEF created the Young Scientists Community in 2008 to engage leaders from the public and private sectors with science and the role it plays in society. The WEF selects rising-star academics, 40 and under, from various fields every year, and helps them become stronger ambassadors for science, especially in tackling pressing global challenges including cybersecurity, climate change, poverty, and pandemics.
Professor Lee is researching how memories are encoded, recalled, and updated, and how emotional processes affect human memory, in order to ultimately direct the development of therapeutic methods to treat mental disorders. She has made significant contributions to resolving ongoing debates over the maintenance and changes of memory traces in the brain.
In recognition of her research excellence, leadership, and commitment to serving society, the President and the Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST nominated Professor Lee to the WEF’s Class of 2020 Young Scientists Selection Committee. The Committee also acknowledged Professor Lee’s achievements and potential for expanding the boundaries of knowledge and practical applications of science, and accepted her into the Community.
During her three-year membership in the Community, Professor Lee will be committed to participating in WEF-initiated activities and events related to promising therapeutic interventions for mental disorders and future directions of artificial intelligence.
Seven of this year’s WEF Young Scientists are from Asia, including Professor Lee, while eight are based in Europe. Six study in the Americas, two work in South Africa, and the remaining two in the Middle East. Fourteen, more than half, of the newly announced 25 Young Scientists are women.
(END)
2020.05.26 View 8459
Professor Sue-Hyun Lee Listed Among WEF 2020 Young Scientists
Professor Sue-Hyun Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering joined the World Economic Forum (WEF)’s Young Scientists Community on May 26. The class of 2020 comprises 25 leading researchers from 14 countries across the world who are at the forefront of scientific problem-solving and social change. Professor Lee was the only Korean on this year’s roster.
The WEF created the Young Scientists Community in 2008 to engage leaders from the public and private sectors with science and the role it plays in society. The WEF selects rising-star academics, 40 and under, from various fields every year, and helps them become stronger ambassadors for science, especially in tackling pressing global challenges including cybersecurity, climate change, poverty, and pandemics.
Professor Lee is researching how memories are encoded, recalled, and updated, and how emotional processes affect human memory, in order to ultimately direct the development of therapeutic methods to treat mental disorders. She has made significant contributions to resolving ongoing debates over the maintenance and changes of memory traces in the brain.
In recognition of her research excellence, leadership, and commitment to serving society, the President and the Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST nominated Professor Lee to the WEF’s Class of 2020 Young Scientists Selection Committee. The Committee also acknowledged Professor Lee’s achievements and potential for expanding the boundaries of knowledge and practical applications of science, and accepted her into the Community.
During her three-year membership in the Community, Professor Lee will be committed to participating in WEF-initiated activities and events related to promising therapeutic interventions for mental disorders and future directions of artificial intelligence.
Seven of this year’s WEF Young Scientists are from Asia, including Professor Lee, while eight are based in Europe. Six study in the Americas, two work in South Africa, and the remaining two in the Middle East. Fourteen, more than half, of the newly announced 25 Young Scientists are women.
(END)
2020.05.26 View 8459 -
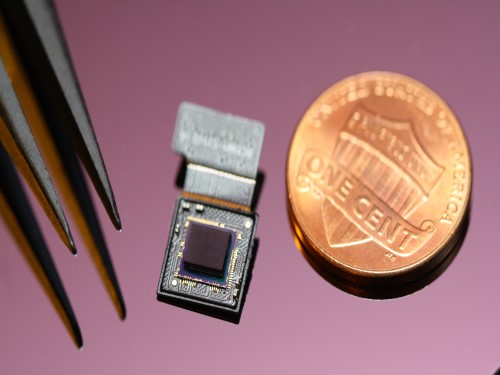 Ultrathin but Fully Packaged High-Resolution Camera
- Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera captures super-resolution images. -
The unique structures of biological vision systems in nature inspired scientists to design ultracompact imaging systems. A research group led by Professor Ki-Hun Jeong have made an ultracompact camera that captures high-contrast and high-resolution images. Fully packaged with micro-optical elements such as inverted micro-lenses, multilayered pinhole arrays, and gap spacers on the image sensor, the camera boasts a total track length of 740 μm and a field of view of 73°.
Inspired by the eye structures of the paper wasp species Xenos peckii, the research team completely suppressed optical noise between micro-lenses while reducing camera thickness. The camera has successfully demonstrated high-contrast clear array images acquired from tiny micro lenses. To further enhance the image quality of the captured image, the team combined the arrayed images into one image through super-resolution imaging.
An insect’s compound eye has superior visual characteristics, such as a wide viewing angle, high motion sensitivity, and a large depth of field while maintaining a small volume of visual structure with a small focal length. Among them, the eyes of Xenos peckii and an endoparasite found on paper wasps have hundreds of photoreceptors in a single lens unlike conventional compound eyes. In particular, the eye structures of an adult Xenos peckii exhibit hundreds of photoreceptors on an individual eyelet and offer engineering inspiration for ultrathin cameras or imaging applications because they have higher visual acuity than other compound eyes.
For instance, Xenos peckii’s eye-inspired cameras provide a 50 times higher spatial resolution than those based on arthropod eyes. In addition, the effective image resolution of the Xenos peckii’s eye can be further improved using the image overlaps between neighboring eyelets. This unique structure offers higher visual resolution than other insect eyes.
The team achieved high-contrast and super-resolution imaging through a novel arrayed design of micro-optical elements comprising multilayered aperture arrays and inverted micro-lens arrays directly stacked over an image sensor. This optical component was integrated with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor.
This is first demonstration of super-resolution imaging which acquires a single integrated image with high contrast and high resolving power reconstructed from high-contrast array images. It is expected that this ultrathin arrayed camera can be applied for further developing mobile devices, advanced surveillance vehicles, and endoscopes.
Professor Jeong said, “This research has led to technological advances in imaging technology. We will continue to strive to make significant impacts on multidisciplinary research projects in the fields of microtechnology and nanotechnology, seeking inspiration from natural photonic structures.”
This work was featured in Light Science & Applications last month and was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of and the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kisoo Kim, Kyung-Won Jang, Jae-Kwan Ryu, and Ki-Hun Jeong. (2020) “Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera for high-contrast and high-resolution imaging”. Light Science & Applications. Volume 9. Article 28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0261-8
Profile:
Ki-Hun Jeong
Professor
kjeong@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Kisoo Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
kisoo.kim1@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.23 View 12845
Ultrathin but Fully Packaged High-Resolution Camera
- Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera captures super-resolution images. -
The unique structures of biological vision systems in nature inspired scientists to design ultracompact imaging systems. A research group led by Professor Ki-Hun Jeong have made an ultracompact camera that captures high-contrast and high-resolution images. Fully packaged with micro-optical elements such as inverted micro-lenses, multilayered pinhole arrays, and gap spacers on the image sensor, the camera boasts a total track length of 740 μm and a field of view of 73°.
Inspired by the eye structures of the paper wasp species Xenos peckii, the research team completely suppressed optical noise between micro-lenses while reducing camera thickness. The camera has successfully demonstrated high-contrast clear array images acquired from tiny micro lenses. To further enhance the image quality of the captured image, the team combined the arrayed images into one image through super-resolution imaging.
An insect’s compound eye has superior visual characteristics, such as a wide viewing angle, high motion sensitivity, and a large depth of field while maintaining a small volume of visual structure with a small focal length. Among them, the eyes of Xenos peckii and an endoparasite found on paper wasps have hundreds of photoreceptors in a single lens unlike conventional compound eyes. In particular, the eye structures of an adult Xenos peckii exhibit hundreds of photoreceptors on an individual eyelet and offer engineering inspiration for ultrathin cameras or imaging applications because they have higher visual acuity than other compound eyes.
For instance, Xenos peckii’s eye-inspired cameras provide a 50 times higher spatial resolution than those based on arthropod eyes. In addition, the effective image resolution of the Xenos peckii’s eye can be further improved using the image overlaps between neighboring eyelets. This unique structure offers higher visual resolution than other insect eyes.
The team achieved high-contrast and super-resolution imaging through a novel arrayed design of micro-optical elements comprising multilayered aperture arrays and inverted micro-lens arrays directly stacked over an image sensor. This optical component was integrated with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor.
This is first demonstration of super-resolution imaging which acquires a single integrated image with high contrast and high resolving power reconstructed from high-contrast array images. It is expected that this ultrathin arrayed camera can be applied for further developing mobile devices, advanced surveillance vehicles, and endoscopes.
Professor Jeong said, “This research has led to technological advances in imaging technology. We will continue to strive to make significant impacts on multidisciplinary research projects in the fields of microtechnology and nanotechnology, seeking inspiration from natural photonic structures.”
This work was featured in Light Science & Applications last month and was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of and the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kisoo Kim, Kyung-Won Jang, Jae-Kwan Ryu, and Ki-Hun Jeong. (2020) “Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera for high-contrast and high-resolution imaging”. Light Science & Applications. Volume 9. Article 28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0261-8
Profile:
Ki-Hun Jeong
Professor
kjeong@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Kisoo Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
kisoo.kim1@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.23 View 12845 -
 Professor Jong Chul Ye Appointed as Distinguished Lecturer of IEEE EMBS
Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was appointed as a distinguished lecturer by the International Association of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS). Professor Ye was invited to deliver a lecture on his leading research on artificial intelligence (AI) technology in medical video restoration. He will serve a term of two years beginning in 2020.
IEEE EMBS's distinguished lecturer program is designed to educate researchers around the world on the latest trends and technology in biomedical engineering. Sponsored by IEEE, its members can attend lectures on the distinguished professor's research subject.
Professor Ye said, "We are at a time where the importance of AI in medical imaging is increasing.” He added, “I am proud to be appointed as a distinguished lecturer of the IEEE EMBS in recognition of my contributions to this field.”
(END)
2020.02.27 View 7194
Professor Jong Chul Ye Appointed as Distinguished Lecturer of IEEE EMBS
Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was appointed as a distinguished lecturer by the International Association of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS). Professor Ye was invited to deliver a lecture on his leading research on artificial intelligence (AI) technology in medical video restoration. He will serve a term of two years beginning in 2020.
IEEE EMBS's distinguished lecturer program is designed to educate researchers around the world on the latest trends and technology in biomedical engineering. Sponsored by IEEE, its members can attend lectures on the distinguished professor's research subject.
Professor Ye said, "We are at a time where the importance of AI in medical imaging is increasing.” He added, “I am proud to be appointed as a distinguished lecturer of the IEEE EMBS in recognition of my contributions to this field.”
(END)
2020.02.27 View 7194 -
 Scientists Discover the Mechanism of DNA High-Order Structure Formation
(Molecular structures of Abo1 in different energy states (left), Demonstration of an Abo1-assisted histone loading onto DNA by the DNA curtain assay. )
The genetic material of our cells—DNA—exists in a high-order structure called “chromatin”. Chromatin consists of DNA wrapped around histone proteins and efficiently packs DNA into a small volume. Moreover, using a spool and thread analogy, chromatin allows DNA to be locally wound or unwound, thus enabling genes to be enclosed or exposed. The misregulation of chromatin structures results in aberrant gene expression and can ultimately lead to developmental disorders or cancers. Despite the importance of DNA high-order structures, the complexity of the underlying machinery has circumvented molecular dissection.
For the first time, molecular biologists have uncovered how one particular mechanism uses energy to ensure proper histone placement onto DNA to form chromatin. They published their results on Dec. 17 in Nature Communications.
The study focused on proteins called histone chaperones. Histone chaperones are responsible for adding and removing specific histones at specific times during the DNA packaging process. The wrong histone at the wrong time and place could result in the misregulation of gene expression or aberrant DNA replication. Thus, histone chaperones are key players in the assembly and disassembly of chromatin.
“In order to carefully control the assembly and disassembly of chromatin units, histone chaperones act as molecular escorts that prevent histone aggregation and undesired interactions,” said Professor Ji-Joon Song in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “We set out to understand how a unique histone chaperone uses chemical energy to assemble or disassemble chromatin.”
Song and his team looked to Abo1, the only known histone chaperone that utilizes cellular energy (ATP). While Abo1 is found in yeast, it has an analogous partner in other organisms, including humans, called ATAD2. Both use ATP, which is produced through a cellular process where enzymes break down a molecule’s phosphate bond. ATP energy is typically used to power other cellular processes, but it is a rare partner for histone chaperones.
“This was an interesting problem in the field because all other histone chaperones studied to date do not use ATP,” Song said.
By imaging Abo1 with a single-molecule fluorescence imaging technique known as the DNA curtain assay, the researchers could examine the protein interactions at the single-molecule level. The technique allows scientists to arrange the DNA molecules and proteins on a single layer of a microfluidic chamber and examine the layer with fluorescence microscopy.
The researchers found through real-time observation that Abo1 is ring-shaped and changes its structure to accommodate a specific histone and deposit it on DNA. Moreover, they found that the accommodating structural changes are powered by ADP.
“We discovered a mechanism by which Abo1 accommodates histone substrates, ultimately allowing it to function as a unique energy-dependent histone chaperone,” Song said. “We also found that despite looking like a protein disassembly machine, Abo1 actually loads histone substrates onto DNA to facilitate chromatin assembly.”
The researchers plan to continue exploring how energy-dependent histone chaperones bind and release histones, with the ultimate goal of developing therapeutics that can target cancer-causing misbehavior by Abo1’s analogous human counterpart, ATAD2.
-Profile
Professor Ji-Joon Song
Department of Biological Sciences KI for the BioCentury (https://kis.kaist.ac.kr/index.php?mid=KIB_O) KAIST
2020.01.07 View 7366
Scientists Discover the Mechanism of DNA High-Order Structure Formation
(Molecular structures of Abo1 in different energy states (left), Demonstration of an Abo1-assisted histone loading onto DNA by the DNA curtain assay. )
The genetic material of our cells—DNA—exists in a high-order structure called “chromatin”. Chromatin consists of DNA wrapped around histone proteins and efficiently packs DNA into a small volume. Moreover, using a spool and thread analogy, chromatin allows DNA to be locally wound or unwound, thus enabling genes to be enclosed or exposed. The misregulation of chromatin structures results in aberrant gene expression and can ultimately lead to developmental disorders or cancers. Despite the importance of DNA high-order structures, the complexity of the underlying machinery has circumvented molecular dissection.
For the first time, molecular biologists have uncovered how one particular mechanism uses energy to ensure proper histone placement onto DNA to form chromatin. They published their results on Dec. 17 in Nature Communications.
The study focused on proteins called histone chaperones. Histone chaperones are responsible for adding and removing specific histones at specific times during the DNA packaging process. The wrong histone at the wrong time and place could result in the misregulation of gene expression or aberrant DNA replication. Thus, histone chaperones are key players in the assembly and disassembly of chromatin.
“In order to carefully control the assembly and disassembly of chromatin units, histone chaperones act as molecular escorts that prevent histone aggregation and undesired interactions,” said Professor Ji-Joon Song in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “We set out to understand how a unique histone chaperone uses chemical energy to assemble or disassemble chromatin.”
Song and his team looked to Abo1, the only known histone chaperone that utilizes cellular energy (ATP). While Abo1 is found in yeast, it has an analogous partner in other organisms, including humans, called ATAD2. Both use ATP, which is produced through a cellular process where enzymes break down a molecule’s phosphate bond. ATP energy is typically used to power other cellular processes, but it is a rare partner for histone chaperones.
“This was an interesting problem in the field because all other histone chaperones studied to date do not use ATP,” Song said.
By imaging Abo1 with a single-molecule fluorescence imaging technique known as the DNA curtain assay, the researchers could examine the protein interactions at the single-molecule level. The technique allows scientists to arrange the DNA molecules and proteins on a single layer of a microfluidic chamber and examine the layer with fluorescence microscopy.
The researchers found through real-time observation that Abo1 is ring-shaped and changes its structure to accommodate a specific histone and deposit it on DNA. Moreover, they found that the accommodating structural changes are powered by ADP.
“We discovered a mechanism by which Abo1 accommodates histone substrates, ultimately allowing it to function as a unique energy-dependent histone chaperone,” Song said. “We also found that despite looking like a protein disassembly machine, Abo1 actually loads histone substrates onto DNA to facilitate chromatin assembly.”
The researchers plan to continue exploring how energy-dependent histone chaperones bind and release histones, with the ultimate goal of developing therapeutics that can target cancer-causing misbehavior by Abo1’s analogous human counterpart, ATAD2.
-Profile
Professor Ji-Joon Song
Department of Biological Sciences KI for the BioCentury (https://kis.kaist.ac.kr/index.php?mid=KIB_O) KAIST
2020.01.07 View 7366 -
 New IEEE Fellow, Professor Jong Chul Ye
Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was named a new fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). IEEE announced this on December 1 in recognition of Professor Ye’s contributions to the development of signal processing and artificial intelligence (AI) technology in the field of biomedical imaging.
As the world’s largest society in the electrical and electronics field, IEEE names the top 0.1% of their members as fellows based on their research achievements.Professor Ye has published more than 100 research papers in world-leading journals in the biomedical imaging field, including those affiliated with IEEE.
He also gave a keynote talk at the yearly conference of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ISMRM) on medical AI technology. In addition, Professor Ye has been appointed to serve as the next chair of the Computational Imaging Technical Committee of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, and the chair of the IEEE Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2020 to be held in April in Iowa, USA.
Professor Ye said, “The importance of AI technology is developing in the biomedical imaging field. I feel proud that my contributions have been internationally recognized and allowed me to be named an IEEE fellow.”
2019.12.18 View 6646
New IEEE Fellow, Professor Jong Chul Ye
Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was named a new fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). IEEE announced this on December 1 in recognition of Professor Ye’s contributions to the development of signal processing and artificial intelligence (AI) technology in the field of biomedical imaging.
As the world’s largest society in the electrical and electronics field, IEEE names the top 0.1% of their members as fellows based on their research achievements.Professor Ye has published more than 100 research papers in world-leading journals in the biomedical imaging field, including those affiliated with IEEE.
He also gave a keynote talk at the yearly conference of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ISMRM) on medical AI technology. In addition, Professor Ye has been appointed to serve as the next chair of the Computational Imaging Technical Committee of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, and the chair of the IEEE Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2020 to be held in April in Iowa, USA.
Professor Ye said, “The importance of AI technology is developing in the biomedical imaging field. I feel proud that my contributions have been internationally recognized and allowed me to be named an IEEE fellow.”
2019.12.18 View 6646 -
 Professor YongKeun Park Wins the 2018 Fumio Okano Award
(Professor Park)
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics won the 2018 Fumio Okano Award in recognition of his contributions to 3D display technology development during the annual conference of the International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE) held last month in Orlando, Florida in the US.
The Fumio Okano Best 3D Paper Prize is presented annually in memory of Dr. Fumio Okano, a pioneer and innovator of 3D displays who passed away in 2013, for his contributions to the field of 3D TVs and displays. The award is sponsored by NHK-ES.
Professor Park and his team are developing novel technology for measuring and visualizing 3D images by applying random light scattering. He has published numerous papers on 3D holographic camera technology and 3000x enhanced performance of 3D holographic displays in renowned international journals such as Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, and Science Advances. His technology has drawn international attention from renowned media outlets including Newsweek and Forbes.
He has established two startups to commercialize his technology. Tomocube specializes in 3D imaging microscopes using holotomographic technology and the company exports their products to several countries including the US and Japan. The.Wave.Talk is exploring technology for examining pre-existing bacteria anywhere and anytime.
Professor Park’s innovations have already been recognized in and out of KAIST. In February, he was selected as the KAISTian of the Year for his outstanding research, commercialization, and startups. He was also decorated with the National Science Award in April by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Hong Jin-Ki Innovation Award later in May by the Yumin Cultural Foundation.
Professor Park said, “3D holography is emerging as a significant technology with growing potential and positive impacts on our daily lives. However, the current technology lags far behind the levels displayed in SF movies. We will do our utmost to reach this level with more commercialization."
2018.05.31 View 7529
Professor YongKeun Park Wins the 2018 Fumio Okano Award
(Professor Park)
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics won the 2018 Fumio Okano Award in recognition of his contributions to 3D display technology development during the annual conference of the International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE) held last month in Orlando, Florida in the US.
The Fumio Okano Best 3D Paper Prize is presented annually in memory of Dr. Fumio Okano, a pioneer and innovator of 3D displays who passed away in 2013, for his contributions to the field of 3D TVs and displays. The award is sponsored by NHK-ES.
Professor Park and his team are developing novel technology for measuring and visualizing 3D images by applying random light scattering. He has published numerous papers on 3D holographic camera technology and 3000x enhanced performance of 3D holographic displays in renowned international journals such as Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, and Science Advances. His technology has drawn international attention from renowned media outlets including Newsweek and Forbes.
He has established two startups to commercialize his technology. Tomocube specializes in 3D imaging microscopes using holotomographic technology and the company exports their products to several countries including the US and Japan. The.Wave.Talk is exploring technology for examining pre-existing bacteria anywhere and anytime.
Professor Park’s innovations have already been recognized in and out of KAIST. In February, he was selected as the KAISTian of the Year for his outstanding research, commercialization, and startups. He was also decorated with the National Science Award in April by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Hong Jin-Ki Innovation Award later in May by the Yumin Cultural Foundation.
Professor Park said, “3D holography is emerging as a significant technology with growing potential and positive impacts on our daily lives. However, the current technology lags far behind the levels displayed in SF movies. We will do our utmost to reach this level with more commercialization."
2018.05.31 View 7529 -
 Seong-Tae Kim Wins Robert-Wagner All-Conference Best Paper Award
(Ph.D. candidate Seong-Tae Kim)
Ph.D. candidate Seong-Tae Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering won the Robert Wagner All-Conference Best Student Paper Award during the 2018 International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE) Medical Imaging Conference, which was held in Houston last month.
Kim, supervised by Professor Yong Man Ro, received the award for his paper in the category of computer-aided diagnosis. His paper, titled “ICADx: Interpretable Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Breast Masses”, was selected as the best paper out of 900 submissions. The conference selects the best paper in nine different categories. His research provides new insights on diagnostic technology to detect breast cancer powered by deep learning.
2018.03.15 View 7709
Seong-Tae Kim Wins Robert-Wagner All-Conference Best Paper Award
(Ph.D. candidate Seong-Tae Kim)
Ph.D. candidate Seong-Tae Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering won the Robert Wagner All-Conference Best Student Paper Award during the 2018 International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE) Medical Imaging Conference, which was held in Houston last month.
Kim, supervised by Professor Yong Man Ro, received the award for his paper in the category of computer-aided diagnosis. His paper, titled “ICADx: Interpretable Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Breast Masses”, was selected as the best paper out of 900 submissions. The conference selects the best paper in nine different categories. His research provides new insights on diagnostic technology to detect breast cancer powered by deep learning.
2018.03.15 View 7709 -
 Meet the KAISTian of 2017, Professor YongKeun Park
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics is one of the star professors in KAIST. Rising to the academic stardom, Professor Park’s daily schedule is filled with series of business meetings in addition to lab meetings and lectures.
The year 2017 must have been special for him. During the year, he published numerous papers in international journals, such as Nature Photonics, Nature Communications and Science Advances. These high performances drew international attention from renowned media, including Newsweek and Forbes. Moreover, recognizing his research performance, he was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in his mid-30s. Noting that the members’ age ranges from late 50s to early 60s, Professor Park’s case considered to be quite exceptional.
Adding to his academic achievement, he has launched two startups powered of his own technologies. One is called Tomocube, a company specialized in 3-D imaging microscope using holotomography technology. His company is currently exporting the products to multiple countries, including the United States and Japan. The other one is The.Wave.Talk which has technologies for examining pre-existing bacteria anywhere and anytime.
His research career and entrepreneurship are well deserved recipient of many honors. At the 2018 kick-off ceremony, Professor Park was awarded the KAISTian of 2017 in recognition of his developing holographic measure and control technology as well as founding a new field for technology application.
KAISTian of the Year, first presented in 2001, is an award to recognize the achievements and exemplary contribution of KAIST member who has put significant effort nationally and internationally, enhancing the value of KAIST.
While receiving the award, he thanked his colleagues and his students who have achieved this far together. He said, “I would like to thank KAIST for providing environment for young professors like me so that we can engage themselves in research. Also, I would like to mention that I am an idea seeder and my students do the most of the research. So, I appreciate my students for their hard works, and it is very pleasure to have them. Lastly, I thank the professors for teaching these outstanding students. I feel great responsibility over this title. I will dedicate myself to make further progress in commercializing technology in KAIST.”
Expecting his successful startup cases as a model and great inspiration to students as well as professors, KAIST interviewed Professor Park.
Q What made you decide to found your startups?
A I believed that my research areas could be further used. As a professor, I believe that it is a university’s role to create added value through commercializing technology and creating startups.
Q You have co-founded two startups. What is your role in each company?
A So, basically I have two full-time jobs, professor in KAIST and CTO in Tomocube. After transferring the technology, I hold the position of advisor in The.Wave.Talk.
(Holographic images captured by the product Professor Park developed)
Q Do your students also participate in your companies or can they?
A No, the school and companies are separate spaces; in other words, they are not participating in my companies. They have trained my employees when transferring the technologies, but they are not directly working for the companies.
However, they can participate if they want to. If there’s a need to develop a certain technology, an industry-academia contract can be made. According to the agreement, students can work for the companies.
Q Were there any hardships when preparing the startups?
A At the initial stage, I did not have a financial problem, thanks to support from Startup KAIST. Yet, inviting capital is the beginning, and I think every step I made to operate, generate revenue, and so on is not easy.
Q Do you believe KAIST is startup-friendly?
A Yes, there’s no school like KAIST in Korea and any other country. Besides various programs to support startup activities, Startup KAIST has many professors equipped with a great deal of experience. Therefore, I believe that KAIST provides an excellent environment for both students and professors to create startups.
Q Do you have any suggestion to KAIST institutionally?
A Well, I would like to make a comment to students and professors in KAIST. I strongly recommend them to challenge themselves by launching startups if they have good ideas. Many students wish to begin their jobs in government-funded research institutes or major corporates, but I believe that engaging in a startup company will also give them valuable and very productive experience.
Unlike before, startup institutions are well established, so attracting good capital is not so hard. There are various activities offered by Startup KAIST, so it’s worthwhile giving it a try.
Q What is your goal for 2018 as a professor and entrepreneur?
A I don’t have a grand plan, but I will work harder to produce good students with new topics in KAIST while adding power to my companies to grow bigger.
By Se Yi Kim from the PR Office
2018.01.03 View 8629
Meet the KAISTian of 2017, Professor YongKeun Park
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics is one of the star professors in KAIST. Rising to the academic stardom, Professor Park’s daily schedule is filled with series of business meetings in addition to lab meetings and lectures.
The year 2017 must have been special for him. During the year, he published numerous papers in international journals, such as Nature Photonics, Nature Communications and Science Advances. These high performances drew international attention from renowned media, including Newsweek and Forbes. Moreover, recognizing his research performance, he was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in his mid-30s. Noting that the members’ age ranges from late 50s to early 60s, Professor Park’s case considered to be quite exceptional.
Adding to his academic achievement, he has launched two startups powered of his own technologies. One is called Tomocube, a company specialized in 3-D imaging microscope using holotomography technology. His company is currently exporting the products to multiple countries, including the United States and Japan. The other one is The.Wave.Talk which has technologies for examining pre-existing bacteria anywhere and anytime.
His research career and entrepreneurship are well deserved recipient of many honors. At the 2018 kick-off ceremony, Professor Park was awarded the KAISTian of 2017 in recognition of his developing holographic measure and control technology as well as founding a new field for technology application.
KAISTian of the Year, first presented in 2001, is an award to recognize the achievements and exemplary contribution of KAIST member who has put significant effort nationally and internationally, enhancing the value of KAIST.
While receiving the award, he thanked his colleagues and his students who have achieved this far together. He said, “I would like to thank KAIST for providing environment for young professors like me so that we can engage themselves in research. Also, I would like to mention that I am an idea seeder and my students do the most of the research. So, I appreciate my students for their hard works, and it is very pleasure to have them. Lastly, I thank the professors for teaching these outstanding students. I feel great responsibility over this title. I will dedicate myself to make further progress in commercializing technology in KAIST.”
Expecting his successful startup cases as a model and great inspiration to students as well as professors, KAIST interviewed Professor Park.
Q What made you decide to found your startups?
A I believed that my research areas could be further used. As a professor, I believe that it is a university’s role to create added value through commercializing technology and creating startups.
Q You have co-founded two startups. What is your role in each company?
A So, basically I have two full-time jobs, professor in KAIST and CTO in Tomocube. After transferring the technology, I hold the position of advisor in The.Wave.Talk.
(Holographic images captured by the product Professor Park developed)
Q Do your students also participate in your companies or can they?
A No, the school and companies are separate spaces; in other words, they are not participating in my companies. They have trained my employees when transferring the technologies, but they are not directly working for the companies.
However, they can participate if they want to. If there’s a need to develop a certain technology, an industry-academia contract can be made. According to the agreement, students can work for the companies.
Q Were there any hardships when preparing the startups?
A At the initial stage, I did not have a financial problem, thanks to support from Startup KAIST. Yet, inviting capital is the beginning, and I think every step I made to operate, generate revenue, and so on is not easy.
Q Do you believe KAIST is startup-friendly?
A Yes, there’s no school like KAIST in Korea and any other country. Besides various programs to support startup activities, Startup KAIST has many professors equipped with a great deal of experience. Therefore, I believe that KAIST provides an excellent environment for both students and professors to create startups.
Q Do you have any suggestion to KAIST institutionally?
A Well, I would like to make a comment to students and professors in KAIST. I strongly recommend them to challenge themselves by launching startups if they have good ideas. Many students wish to begin their jobs in government-funded research institutes or major corporates, but I believe that engaging in a startup company will also give them valuable and very productive experience.
Unlike before, startup institutions are well established, so attracting good capital is not so hard. There are various activities offered by Startup KAIST, so it’s worthwhile giving it a try.
Q What is your goal for 2018 as a professor and entrepreneur?
A I don’t have a grand plan, but I will work harder to produce good students with new topics in KAIST while adding power to my companies to grow bigger.
By Se Yi Kim from the PR Office
2018.01.03 View 8629 -
 Professor YongKeun Park Elected as a Fellow of the Optical Society
Professor YongKeun Park, from the Department of Physics at KAIST, was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in Washington, D.C. on September 12. Fellow membership is given to members who have made a significant contribution to the advancement of optics and photonics.
Professor Park was recognized for his research on digital holography and wavefront control technology.
Professor Park has been producing outstanding research outcomes in the field of holographic technology and light scattering control since joining KAIST in 2010. In particular, he developed and commercialized technology for a holographic telescope. He applied it to various medical and biological research projects, leading the field worldwide.
In the past, cells needed to be dyed with fluorescent materials to capture a 3-D image. However, Professor Park’s holotomography (HT) technology can capture 3-D images of living cells and tissues in real time without color dyeing. This technology allows diversified research in the biological and medical field.
Professor Park established a company, Tomocube, Inc. in 2015 to commercialize the technology. In 2016, he received funding from SoftBank Ventures and Hanmi Pharmaceutical. Currently, major institutes, including MIT, the University of Pittsburgh, the German Cancer Research Center, and Seoul National University Hospital are using his equipment.
Recently, Professor Park and his team developed technology based on light scattering measurements. With this technology, they established a company called The Wave Talk and received funding from various organizations, such as NAVER. Its first product is about to be released.
Professor Park said, “I am glad to become a fellow member based on the research outcomes I produced since I was appointed as a professor at KAIST. I would like to thank the excellent researchers as well as the school for its support. I will devote myself to continuously producing novel outcomes in both basic and applied fields.”
Professor Park has published nearly 100 papers in renowned journals including Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, Science Advances, and Physical Review Letters.
2017.10.18 View 8828
Professor YongKeun Park Elected as a Fellow of the Optical Society
Professor YongKeun Park, from the Department of Physics at KAIST, was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in Washington, D.C. on September 12. Fellow membership is given to members who have made a significant contribution to the advancement of optics and photonics.
Professor Park was recognized for his research on digital holography and wavefront control technology.
Professor Park has been producing outstanding research outcomes in the field of holographic technology and light scattering control since joining KAIST in 2010. In particular, he developed and commercialized technology for a holographic telescope. He applied it to various medical and biological research projects, leading the field worldwide.
In the past, cells needed to be dyed with fluorescent materials to capture a 3-D image. However, Professor Park’s holotomography (HT) technology can capture 3-D images of living cells and tissues in real time without color dyeing. This technology allows diversified research in the biological and medical field.
Professor Park established a company, Tomocube, Inc. in 2015 to commercialize the technology. In 2016, he received funding from SoftBank Ventures and Hanmi Pharmaceutical. Currently, major institutes, including MIT, the University of Pittsburgh, the German Cancer Research Center, and Seoul National University Hospital are using his equipment.
Recently, Professor Park and his team developed technology based on light scattering measurements. With this technology, they established a company called The Wave Talk and received funding from various organizations, such as NAVER. Its first product is about to be released.
Professor Park said, “I am glad to become a fellow member based on the research outcomes I produced since I was appointed as a professor at KAIST. I would like to thank the excellent researchers as well as the school for its support. I will devote myself to continuously producing novel outcomes in both basic and applied fields.”
Professor Park has published nearly 100 papers in renowned journals including Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, Science Advances, and Physical Review Letters.
2017.10.18 View 8828 -
 Professor Jinah Park Received the Prime Minister's Award
Professor Jinah Park of the School of Computing received the Prime Minister’s Citation Ribbon on April 21 at a ceremony celebrating the Day of Science and ICT. The awardee was selected by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and Korea Communications Commission.
Professor Park was recognized for her convergence R&D of a VR simulator for dental treatment with haptic feedback, in addition to her research on understanding 3D interaction behavior in VR environments. Her major academic contributions are in the field of medical imaging, where she developed a computational technique to analyze cardiac motion from tagging data.
Professor Park said she was very pleased to see her twenty-plus years of research on ways to converge computing into medical areas finally bear fruit. She also thanked her colleagues and students in her Computer Graphics and CGV Research Lab for working together to make this achievement possible.
2017.04.26 View 6769
Professor Jinah Park Received the Prime Minister's Award
Professor Jinah Park of the School of Computing received the Prime Minister’s Citation Ribbon on April 21 at a ceremony celebrating the Day of Science and ICT. The awardee was selected by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and Korea Communications Commission.
Professor Park was recognized for her convergence R&D of a VR simulator for dental treatment with haptic feedback, in addition to her research on understanding 3D interaction behavior in VR environments. Her major academic contributions are in the field of medical imaging, where she developed a computational technique to analyze cardiac motion from tagging data.
Professor Park said she was very pleased to see her twenty-plus years of research on ways to converge computing into medical areas finally bear fruit. She also thanked her colleagues and students in her Computer Graphics and CGV Research Lab for working together to make this achievement possible.
2017.04.26 View 6769