aging
-
 KAIST Predicts Diseases by Early Detection of Aging Signals in Liver Tissue
- KAIST-KRIBB Develops ‘FiNi-seq’ Technology to Capture Characteristics of Fibrotic Microenvironments Accumulated in Liver Tissue and Dynamic Changes of Early Aging Cells
- Elucidation of the Spatial Ecosystem of Aged Liver Tissue, where Reprogramming of Senescent Cells and Immune Exhaustion Progresses, at the Single-Cell Genome and Epigenome Levels
< (From left) Professor Jong-Eun Park of KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE), Dr. Chuna Kim of KRIBB, Dr. Kwon Yong Tak of KAIST GSMSE, Ph.D. Candidate Juyeon Kim of KRIBB, Ph.D. Candidate Myungsun Park of KAIST GSMSE >
Aging and chronic diseases involve the gradual accumulation of subtle tissue changes over a long period. Therefore, there are still limitations in quantitatively understanding these changes within organs and linking them to early signs of disease onset. In response, Korean researchers have successfully developed a platform technology that accurately captures localized changes that first occur within tissue, significantly aiding in faster disease discovery and prediction, and in setting personalized treatment targets.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on June 12th that a joint research team led by Professor Jong-Eun Park of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST and Dr. Chuna Kim of the Aging Convergence Research Center at the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB, President Seok-Yoon Kwon) has developed ‘FiNi-seq (Fibrotic Niche enrichment sequencing)’ technology. This technology captures fibrotic microenvironments locally occurring in aged liver tissue and enables precise analysis at the single-cell transcriptome level*.
*Single-cell transcriptome analysis: A method to measure how actively each cell uses which genes, allowing identification and function of individual diseased cells.
The researchers developed a method to selectively enrich early aging microenvironments where regeneration is delayed and fibrosis accumulates, by physically selecting regions with high tissue degradation resistance in aged liver tissue.
In this process, high-resolution identification of fibrosis-related endothelial cells, fibroblasts interacting with the immune system, and immune-exhausted cells such as PD-1 highly expressing CD8 T cells, which were difficult to capture with existing single-cell analysis technologies, was possible.
In particular, the research team confirmed through ‘FiNi-seq’ technology that specific cells observed in fibrotic areas within aged liver tissue secondarily age the surrounding environment through secreted factors, and that this leads to the expansion of the aged environment.
Furthermore, they also elucidated the mechanism by which endothelial cells lose their tissue-specific identity and induce innate immune responses, promoting immune cell infiltration. Through spatial transcriptome analysis, the spatial distribution of fibroblasts interacting with immune cells was quantified, revealing their involvement in tissue regeneration, induction of inflammatory responses, and progression to chronic fibrosis.
The research team performed integrated analysis of multi-omics\* data to obtain transcriptome and epigenome information, precisely interpreting the microenvironment of aged liver tissue and its spatial heterogeneity, and confirming how these changes are connected to the intrahepatic vascular structure.
*Multi-omics: An integrated analysis method for various biological information within an organism, such as genes, proteins, metabolites, and cell information.
The newly developed ‘FiNi-seq’ technology is expected to be a useful platform for high-resolution capture of pathophysiological signals in most chronic liver diseases, including the aging process that causes fibrosis.
< Figure 1. Isolation of fibrotic regions from aged liver tissue, followed by single-cell transcriptome analysis and validation in a fibrosis model. >
The first author, Dr. Kwon Yong Tak of KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE), a hepatologist at Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, designed this study to lay the groundwork for early diagnosis and treatment of fibrosis progression, the most important clinical prognostic indicator in chronic liver disease, while pursuing his Ph.D. at KAIST KAIST GSMSE with support from the physician-scientist training program. Co-first author Myungsun Park, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST KAIST GSMSE, was responsible for the technical implementation of FiNi-seq technology, and Juyeon Kim, a Ph.D. candidate at KRIBB's Aging Convergence Research Center, was responsible for imaging analysis of aged tissue, playing a key role in the research.
Dr. Chuna Kim of KRIBB stated, “Through this study, we were able to precisely elucidate the cellular composition and spatial characteristics of the fibrotic microenvironment observed in aged liver tissue at the single-cell level.”
< Figure 2. Spatially defined stepwise progression patterns of aging-related regions within the liver and identification of regulatory factors inducing them. >
Professor Jong-Eun Park of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering said, “As an analytical technology that can capture subtle changes occurring in the early stages of aging and chronic diseases, it is expected to play a significant role in finding effective treatment targets in the future. Also, we plan to expand this research to chronic diseases in other organs such as the lungs and kidneys, as well as various liver disease models.”
This research was published in the international journal ‘Nature Aging’ on May 5, 2025, with Dr. Kwon Yong Tak of KAIST KAIST GSMSE, Ph.D. Candidate Juyeon Kim of KRIBB, and Ph.D. Candidate Myungsun Park of KAIST as co-first authors.
*Paper Title: Quasi-spatial single-cell transcriptome based on physical tissue properties defines early aging associated niche in liver
*DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-025-00857-7
This research was supported by several domestic institutions, including the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), KIST, POSCO Science Fellowship, and the Convergence Medical Scientist Training Program.
2025.06.12 View 1943
KAIST Predicts Diseases by Early Detection of Aging Signals in Liver Tissue
- KAIST-KRIBB Develops ‘FiNi-seq’ Technology to Capture Characteristics of Fibrotic Microenvironments Accumulated in Liver Tissue and Dynamic Changes of Early Aging Cells
- Elucidation of the Spatial Ecosystem of Aged Liver Tissue, where Reprogramming of Senescent Cells and Immune Exhaustion Progresses, at the Single-Cell Genome and Epigenome Levels
< (From left) Professor Jong-Eun Park of KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE), Dr. Chuna Kim of KRIBB, Dr. Kwon Yong Tak of KAIST GSMSE, Ph.D. Candidate Juyeon Kim of KRIBB, Ph.D. Candidate Myungsun Park of KAIST GSMSE >
Aging and chronic diseases involve the gradual accumulation of subtle tissue changes over a long period. Therefore, there are still limitations in quantitatively understanding these changes within organs and linking them to early signs of disease onset. In response, Korean researchers have successfully developed a platform technology that accurately captures localized changes that first occur within tissue, significantly aiding in faster disease discovery and prediction, and in setting personalized treatment targets.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on June 12th that a joint research team led by Professor Jong-Eun Park of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST and Dr. Chuna Kim of the Aging Convergence Research Center at the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB, President Seok-Yoon Kwon) has developed ‘FiNi-seq (Fibrotic Niche enrichment sequencing)’ technology. This technology captures fibrotic microenvironments locally occurring in aged liver tissue and enables precise analysis at the single-cell transcriptome level*.
*Single-cell transcriptome analysis: A method to measure how actively each cell uses which genes, allowing identification and function of individual diseased cells.
The researchers developed a method to selectively enrich early aging microenvironments where regeneration is delayed and fibrosis accumulates, by physically selecting regions with high tissue degradation resistance in aged liver tissue.
In this process, high-resolution identification of fibrosis-related endothelial cells, fibroblasts interacting with the immune system, and immune-exhausted cells such as PD-1 highly expressing CD8 T cells, which were difficult to capture with existing single-cell analysis technologies, was possible.
In particular, the research team confirmed through ‘FiNi-seq’ technology that specific cells observed in fibrotic areas within aged liver tissue secondarily age the surrounding environment through secreted factors, and that this leads to the expansion of the aged environment.
Furthermore, they also elucidated the mechanism by which endothelial cells lose their tissue-specific identity and induce innate immune responses, promoting immune cell infiltration. Through spatial transcriptome analysis, the spatial distribution of fibroblasts interacting with immune cells was quantified, revealing their involvement in tissue regeneration, induction of inflammatory responses, and progression to chronic fibrosis.
The research team performed integrated analysis of multi-omics\* data to obtain transcriptome and epigenome information, precisely interpreting the microenvironment of aged liver tissue and its spatial heterogeneity, and confirming how these changes are connected to the intrahepatic vascular structure.
*Multi-omics: An integrated analysis method for various biological information within an organism, such as genes, proteins, metabolites, and cell information.
The newly developed ‘FiNi-seq’ technology is expected to be a useful platform for high-resolution capture of pathophysiological signals in most chronic liver diseases, including the aging process that causes fibrosis.
< Figure 1. Isolation of fibrotic regions from aged liver tissue, followed by single-cell transcriptome analysis and validation in a fibrosis model. >
The first author, Dr. Kwon Yong Tak of KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE), a hepatologist at Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, designed this study to lay the groundwork for early diagnosis and treatment of fibrosis progression, the most important clinical prognostic indicator in chronic liver disease, while pursuing his Ph.D. at KAIST KAIST GSMSE with support from the physician-scientist training program. Co-first author Myungsun Park, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST KAIST GSMSE, was responsible for the technical implementation of FiNi-seq technology, and Juyeon Kim, a Ph.D. candidate at KRIBB's Aging Convergence Research Center, was responsible for imaging analysis of aged tissue, playing a key role in the research.
Dr. Chuna Kim of KRIBB stated, “Through this study, we were able to precisely elucidate the cellular composition and spatial characteristics of the fibrotic microenvironment observed in aged liver tissue at the single-cell level.”
< Figure 2. Spatially defined stepwise progression patterns of aging-related regions within the liver and identification of regulatory factors inducing them. >
Professor Jong-Eun Park of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering said, “As an analytical technology that can capture subtle changes occurring in the early stages of aging and chronic diseases, it is expected to play a significant role in finding effective treatment targets in the future. Also, we plan to expand this research to chronic diseases in other organs such as the lungs and kidneys, as well as various liver disease models.”
This research was published in the international journal ‘Nature Aging’ on May 5, 2025, with Dr. Kwon Yong Tak of KAIST KAIST GSMSE, Ph.D. Candidate Juyeon Kim of KRIBB, and Ph.D. Candidate Myungsun Park of KAIST as co-first authors.
*Paper Title: Quasi-spatial single-cell transcriptome based on physical tissue properties defines early aging associated niche in liver
*DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-025-00857-7
This research was supported by several domestic institutions, including the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), KIST, POSCO Science Fellowship, and the Convergence Medical Scientist Training Program.
2025.06.12 View 1943 -
 KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 11505
KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 11505 -
 A KAIST Team Develops Face-Conforming LED Mask Showing 340% Improved Efficacy in Deep Skin Elasticity
- A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee has developed a deep skin-stimulating LED mask which has been verified in clinical trials to improve dermis elasticity by 340%.
< Figure 1. Overall concept of face-fit surface-lighting micro-LEDs (FSLED) mask. a. Optical image of the FSLED mask showing uniform surface-lighting. schematic illustration of the FSLED mask. The 2D to 3D transformation procedure b. Difference in cosmetic effect on deep skin elasticity, wrinkles, and sagging between FSLED mask and CLED mask. (improvement percentage in eight weeks) >
Conventional LED masks, with their rigid design, fail to conform closely to the skin's contours. This limitation causes substantial light reflection, with up to 90% reflected over a distance of 2 cm, reducing light penetration and limiting stimulation of the deep skin layers essential for effective skin rejuvenation.
To address these challenges, Professor Lee's team developed a face-conforming surface lighting micro-LED (FSLED) mask, which can provide uniform photostimulation to the dermis. The key technology lies in the mask's ability to deliver uniform light to deep skin tissues while maintaining a conformal skin attachment. This is achieved through a 3D origami structure, integrated with 3,770 micro-LEDs and flexible surface light-diffusion layer, minimizing the gaps between the light source and the skin.
In clinical trials involving 33 participants, the FSLED mask demonstrated a 340% improvement in deep skin elasticity compared to conventional LED masks, proving its efficacy in significantly reducing skin wrinkles, sagging and aging.
Professor Keon Jae Lee said, “The FSLED mask provides cosmetic benefits to the entire facial dermis without the side effects of low-temperature burns, making home-care anti-aging treatment that enhances the quality of human life possible. The product is being manufactured by Fronics, KAIST startup company, and will be distributed globally through Amorepacific's network, with sales starting in November.”
This result titled “Clinical Validation of Face-fit Surface-lighting Micro Light-emitting Diode Mask for Skin Anti-aging Treatment”, in which Min Seo Kim, a student of the Master-Doctorate integrated program, and Jaehun An, a Ph.D. candidate, in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering of KAIST, took part as co-first authors, was published in Advanced Materials on October 22nd, 2024 (DOI: 10.1002/adma.202411651).
Introductory Video: Face-conforming surface LED mask for skin anti-aging ( https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kSccLwx8N_w )
2024.10.29 View 8683
A KAIST Team Develops Face-Conforming LED Mask Showing 340% Improved Efficacy in Deep Skin Elasticity
- A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee has developed a deep skin-stimulating LED mask which has been verified in clinical trials to improve dermis elasticity by 340%.
< Figure 1. Overall concept of face-fit surface-lighting micro-LEDs (FSLED) mask. a. Optical image of the FSLED mask showing uniform surface-lighting. schematic illustration of the FSLED mask. The 2D to 3D transformation procedure b. Difference in cosmetic effect on deep skin elasticity, wrinkles, and sagging between FSLED mask and CLED mask. (improvement percentage in eight weeks) >
Conventional LED masks, with their rigid design, fail to conform closely to the skin's contours. This limitation causes substantial light reflection, with up to 90% reflected over a distance of 2 cm, reducing light penetration and limiting stimulation of the deep skin layers essential for effective skin rejuvenation.
To address these challenges, Professor Lee's team developed a face-conforming surface lighting micro-LED (FSLED) mask, which can provide uniform photostimulation to the dermis. The key technology lies in the mask's ability to deliver uniform light to deep skin tissues while maintaining a conformal skin attachment. This is achieved through a 3D origami structure, integrated with 3,770 micro-LEDs and flexible surface light-diffusion layer, minimizing the gaps between the light source and the skin.
In clinical trials involving 33 participants, the FSLED mask demonstrated a 340% improvement in deep skin elasticity compared to conventional LED masks, proving its efficacy in significantly reducing skin wrinkles, sagging and aging.
Professor Keon Jae Lee said, “The FSLED mask provides cosmetic benefits to the entire facial dermis without the side effects of low-temperature burns, making home-care anti-aging treatment that enhances the quality of human life possible. The product is being manufactured by Fronics, KAIST startup company, and will be distributed globally through Amorepacific's network, with sales starting in November.”
This result titled “Clinical Validation of Face-fit Surface-lighting Micro Light-emitting Diode Mask for Skin Anti-aging Treatment”, in which Min Seo Kim, a student of the Master-Doctorate integrated program, and Jaehun An, a Ph.D. candidate, in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering of KAIST, took part as co-first authors, was published in Advanced Materials on October 22nd, 2024 (DOI: 10.1002/adma.202411651).
Introductory Video: Face-conforming surface LED mask for skin anti-aging ( https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kSccLwx8N_w )
2024.10.29 View 8683 -
 KAIST Succeeds in the Real-time Observation of Organoids using Holotomography
Organoids, which are 3D miniature organs that mimic the structure and function of human organs, play an essential role in disease research and drug development. A Korean research team has overcome the limitations of existing imaging technologies, succeeding in the real-time, high-resolution observation of living organoids.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 14th of October that Professor YongKeun Park’s research team from the Department of Physics, in collaboration with the Genome Editing Research Center (Director Bon-Kyoung Koo) of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS President Do-Young Noh) and Tomocube Inc., has developed an imaging technology using holotomography to observe live, small intestinal organoids in real time at a high resolution.
Existing imaging techniques have struggled to observe living organoids in high resolution over extended periods and often required additional treatments like fluorescent staining.
< Figure 1. Overview of the low-coherence HT workflow. Using holotomography, 3D morphological restoration and quantitative analysis of organoids can be performed. In order to improve the limited field of view, which is a limitation of the microscope, our research team utilized a large-area field of view combination algorithm and made a 3D restoration by acquiring multi-focus holographic images for 3D measurements. After that, the organoids were compartmentalized to divide the parts necessary for analysis and quantitatively evaluated the protein concentration measurable from the refractive index and the survival rate of the organoids. >
The research team introduced holotomography technology to address these issues, which provides high-resolution images without the need for fluorescent staining and allows for the long-term observation of dynamic changes in real time without causing cell damage.
The team validated this technology using small intestinal organoids from experimental mice and were able to observe various cell structures inside the organoids in detail. They also captured dynamic changes such as growth processes, cell division, and cell death in real time using holotomography.
Additionally, the technology allowed for the precise analysis of the organoids' responses to drug treatments, verifying the survival of the cells.
The researchers believe that this breakthrough will open new horizons in organoid research, enabling the greater utilization of organoids in drug development, personalized medicine, and regenerative medicine.
Future research is expected to more accurately replicate the in vivo environment of organoids, contributing significantly to a more detailed understanding of various life phenomena at the cellular level through more precise 3D imaging.
< Figure 2. Real-time organoid morphology analysis. Using holotomography, it is possible to observe the lumen and villus development process of intestinal organoids in real time, which was difficult to observe with a conventional microscope. In addition, various information about intestinal organoids can be obtained by quantifying the size and protein amount of intestinal organoids through image analysis. >
Dr. Mahn Jae Lee, a graduate of KAIST's Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, currently at Chungnam National University Hospital and the first author of the paper, commented, "This research represents a new imaging technology that surpasses previous limitations and is expected to make a major contribution to disease modeling, personalized treatments, and drug development research using organoids."
The research results were published online in the international journal Experimental & Molecular Medicine on October 1, 2024, and the technology has been recognized for its applicability in various fields of life sciences. (Paper title: “Long-term three-dimensional high-resolution imaging of live unlabeled small intestinal organoids via low-coherence holotomography”)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, KAIST Institutes, and the Institute for Basic Science.
2024.10.14 View 6063
KAIST Succeeds in the Real-time Observation of Organoids using Holotomography
Organoids, which are 3D miniature organs that mimic the structure and function of human organs, play an essential role in disease research and drug development. A Korean research team has overcome the limitations of existing imaging technologies, succeeding in the real-time, high-resolution observation of living organoids.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 14th of October that Professor YongKeun Park’s research team from the Department of Physics, in collaboration with the Genome Editing Research Center (Director Bon-Kyoung Koo) of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS President Do-Young Noh) and Tomocube Inc., has developed an imaging technology using holotomography to observe live, small intestinal organoids in real time at a high resolution.
Existing imaging techniques have struggled to observe living organoids in high resolution over extended periods and often required additional treatments like fluorescent staining.
< Figure 1. Overview of the low-coherence HT workflow. Using holotomography, 3D morphological restoration and quantitative analysis of organoids can be performed. In order to improve the limited field of view, which is a limitation of the microscope, our research team utilized a large-area field of view combination algorithm and made a 3D restoration by acquiring multi-focus holographic images for 3D measurements. After that, the organoids were compartmentalized to divide the parts necessary for analysis and quantitatively evaluated the protein concentration measurable from the refractive index and the survival rate of the organoids. >
The research team introduced holotomography technology to address these issues, which provides high-resolution images without the need for fluorescent staining and allows for the long-term observation of dynamic changes in real time without causing cell damage.
The team validated this technology using small intestinal organoids from experimental mice and were able to observe various cell structures inside the organoids in detail. They also captured dynamic changes such as growth processes, cell division, and cell death in real time using holotomography.
Additionally, the technology allowed for the precise analysis of the organoids' responses to drug treatments, verifying the survival of the cells.
The researchers believe that this breakthrough will open new horizons in organoid research, enabling the greater utilization of organoids in drug development, personalized medicine, and regenerative medicine.
Future research is expected to more accurately replicate the in vivo environment of organoids, contributing significantly to a more detailed understanding of various life phenomena at the cellular level through more precise 3D imaging.
< Figure 2. Real-time organoid morphology analysis. Using holotomography, it is possible to observe the lumen and villus development process of intestinal organoids in real time, which was difficult to observe with a conventional microscope. In addition, various information about intestinal organoids can be obtained by quantifying the size and protein amount of intestinal organoids through image analysis. >
Dr. Mahn Jae Lee, a graduate of KAIST's Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, currently at Chungnam National University Hospital and the first author of the paper, commented, "This research represents a new imaging technology that surpasses previous limitations and is expected to make a major contribution to disease modeling, personalized treatments, and drug development research using organoids."
The research results were published online in the international journal Experimental & Molecular Medicine on October 1, 2024, and the technology has been recognized for its applicability in various fields of life sciences. (Paper title: “Long-term three-dimensional high-resolution imaging of live unlabeled small intestinal organoids via low-coherence holotomography”)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, KAIST Institutes, and the Institute for Basic Science.
2024.10.14 View 6063 -
 KAIST builds a high-resolution 3D holographic sensor using a single mask
Holographic cameras can provide more realistic images than ordinary cameras thanks to their ability to acquire 3D information about objects. However, existing holographic cameras use interferometers that measure the wavelength and refraction of light through the interference of light waves, which makes them complex and sensitive to their surrounding environment.
On August 23, a KAIST research team led by Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics announced a new leap forward in 3D holographic imaging sensor technology.
The team proposed an innovative holographic camera technology that does not use complex interferometry. Instead, it uses a mask to precisely measure the phase information of light and reconstruct the 3D information of an object with higher accuracy.
< Figure 1. Structure and principle of the proposed holographic camera. The amplitude and phase information of light scattered from a holographic camera can be measured. >
The team used a mask that fulfills certain mathematical conditions and incorporated it into an ordinary camera, and the light scattered from a laser is measured through the mask and analyzed using a computer. This does not require a complex interferometer and allows the phase information of light to be collected through a simplified optical system. With this technique, the mask that is placed between the two lenses and behind an object plays an important role. The mask selectively filters specific parts of light,, and the intensity of the light passing through the lens can be measured using an ordinary commercial camera. This technique combines the image data received from the camera with the unique pattern received from the mask and reconstructs an object’s precise 3D information using an algorithm.
This method allows a high-resolution 3D image of an object to be captured in any position. In practical situations, one can construct a laser-based holographic 3D image sensor by adding a mask with a simple design to a general image sensor. This makes the design and construction of the optical system much easier. In particular, this novel technology can capture high-resolution holographic images of objects moving at high speeds, which widens its potential field of application.
< Figure 2. A moving doll captured by a conventional camera and the proposed holographic camera. When taking a picture without focusing on the object, only a blurred image of the doll can be obtained from a general camera, but the proposed holographic camera can restore the blurred image of the doll into a clear image. >
The results of this study, conducted by Dr. Jeonghun Oh from the KAIST Department of Physics as the first author, were published in Nature Communications on August 12 under the title, "Non-interferometric stand-alone single-shot holographic camera using reciprocal diffractive imaging".
Dr. Oh said, “The holographic camera module we are suggesting can be built by adding a filter to an ordinary camera, which would allow even non-experts to handle it easily in everyday life if it were to be commercialized.” He added, “In particular, it is a promising candidate with the potential to replace existing remote sensing technologies.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation’s Leader Research Project, the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT’s Core Hologram Technology Support Project, and the Nano and Material Technology Development Project.
2023.09.05 View 9926
KAIST builds a high-resolution 3D holographic sensor using a single mask
Holographic cameras can provide more realistic images than ordinary cameras thanks to their ability to acquire 3D information about objects. However, existing holographic cameras use interferometers that measure the wavelength and refraction of light through the interference of light waves, which makes them complex and sensitive to their surrounding environment.
On August 23, a KAIST research team led by Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics announced a new leap forward in 3D holographic imaging sensor technology.
The team proposed an innovative holographic camera technology that does not use complex interferometry. Instead, it uses a mask to precisely measure the phase information of light and reconstruct the 3D information of an object with higher accuracy.
< Figure 1. Structure and principle of the proposed holographic camera. The amplitude and phase information of light scattered from a holographic camera can be measured. >
The team used a mask that fulfills certain mathematical conditions and incorporated it into an ordinary camera, and the light scattered from a laser is measured through the mask and analyzed using a computer. This does not require a complex interferometer and allows the phase information of light to be collected through a simplified optical system. With this technique, the mask that is placed between the two lenses and behind an object plays an important role. The mask selectively filters specific parts of light,, and the intensity of the light passing through the lens can be measured using an ordinary commercial camera. This technique combines the image data received from the camera with the unique pattern received from the mask and reconstructs an object’s precise 3D information using an algorithm.
This method allows a high-resolution 3D image of an object to be captured in any position. In practical situations, one can construct a laser-based holographic 3D image sensor by adding a mask with a simple design to a general image sensor. This makes the design and construction of the optical system much easier. In particular, this novel technology can capture high-resolution holographic images of objects moving at high speeds, which widens its potential field of application.
< Figure 2. A moving doll captured by a conventional camera and the proposed holographic camera. When taking a picture without focusing on the object, only a blurred image of the doll can be obtained from a general camera, but the proposed holographic camera can restore the blurred image of the doll into a clear image. >
The results of this study, conducted by Dr. Jeonghun Oh from the KAIST Department of Physics as the first author, were published in Nature Communications on August 12 under the title, "Non-interferometric stand-alone single-shot holographic camera using reciprocal diffractive imaging".
Dr. Oh said, “The holographic camera module we are suggesting can be built by adding a filter to an ordinary camera, which would allow even non-experts to handle it easily in everyday life if it were to be commercialized.” He added, “In particular, it is a promising candidate with the potential to replace existing remote sensing technologies.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation’s Leader Research Project, the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT’s Core Hologram Technology Support Project, and the Nano and Material Technology Development Project.
2023.09.05 View 9926 -
 KAIST researchers find the key to overcome the limits in X-ray microscopy
X-ray microscopes have the advantage of penetrating most substances, so internal organs and skeletons can be observed non-invasively through chest X-rays or CT scans. Recently, studies to increase the resolution of X-ray imaging technology are being actively conducted in order to precisely observe the internal structure of semiconductors and batteries at the nanoscale.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that a joint research team led by Professor YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics and Dr. Jun Lim of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory has succeeded in developing a core technology that can overcome the resolution limitations of existing X-ray microscopes.
d
This study, in which Dr. KyeoReh Lee participated as the first author, was published on 6th of April in “Light: Science and Application”, a world-renowned academic journal in optics and photonics. (Paper title: Direct high-resolution X-ray imaging exploiting pseudorandomness).
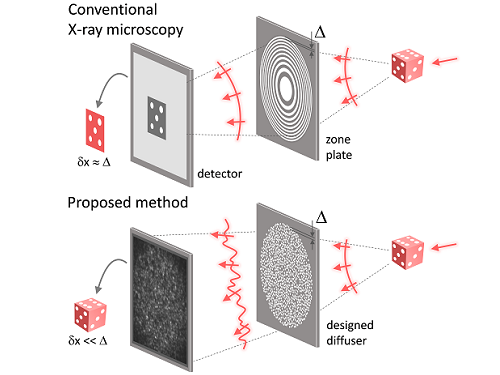
X-ray nanomicroscopes do not have refractive lenses. In an X-ray microscope, a circular grating called a concentric zone plate is used instead of a lens. The resolution of an image obtained using the zone plate is determined by the quality of the nanostructure that comprises the plate. There are several difficulties in fabricating and maintaining these nanostructures, which set the limit to the level of resolution for X-ray microscopy.
The research team developed a new X-ray nanomicroscopy technology to overcome this problem. The X-ray lens proposed by the research team is in the form of numerous holes punched in a thin tungsten film, and generates random diffraction patterns by diffracting incident X-rays. The research team mathematically identified that, paradoxically, the high-resolution information of the sample was fully contained in these random diffraction patterns, and actually succeeded in extracting the information and imaging the internal states of the samples.
The imaging method using the mathematical properties of random diffraction was proposed and implemented in the visible light band for the first time by Dr. KyeoReh Lee and Professor YongKeun Park in 2016*. This study uses the results of previous studies to solve the difficult, lingering problem in the field of the X-ray imaging. ※ "Exploiting the speckle-correlation scattering matrix for a compact reference-free holographic image sensor." Nature communications 7.1 (2016): 13359.
The resolution of the image of the constructed sample has no direct correlation with the size of the pattern etched on the random lens used. Based on this idea, the research team succeeded in acquiring images with 14 nm resolution (approximately 1/7 the size of the coronavirus) by using random lenses made in a circular pattern with a diameter of 300 nm.
The imaging technology developed by this research team is a key fundamental technology that can enhance the resolution of X-ray nanomicroscopy, which has been blocked by limitations of the production of existing zone plates.
The first author and one of the co-corresponding author, Dr. KyeoReh Lee of KAIST Department of Physics, said, “In this study, the resolution was limited to 14 nm, but if the next-generation X-ray light source and high-performance X-ray detector are used, the resolution would exceed that of the conventional X-ray nano-imaging and approach the resolution of an electron microscope.” and added, “Unlike an electron microscope, X-rays can observe the internal structure without damaging the sample, so it will be able to present a new standard for non-invasive nanostructure observation processes such as quality inspections for semiconductors.”.
The co-corresponding author, Dr. Jun Lim of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, said, “In the same context, the developed image technology is expected to greatly increase the performance in the 4th generation multipurpose radiation accelerator which is set to be established in Ochang of the Northern Chungcheong Province.”
This research was conducted with the support through the Research Leader Program and the Sejong Science Fellowship of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Fig. 1. Designed diffuser as X-ray imaging lens. a, Schematic of full-field transmission X-ray microscopy. The attenuation (amplitude) map of a sample is measured. The image resolution (dx) is limited by the outermost zone width of the zone plate (D). b, Schematic of the proposed method. A designed diffuser is used instead of a zone plate. The image resolution is finer than the hole size of the diffuser (dx << D).
Fig. 2. The left panel is a surface electron microscopy (SEM) image of the X-ray diffuser used in the experiment. The middle panel shows the design of the X-ray diffuser, and there is an inset in the middle of the panel that shows a corresponding part of the SEM image. The right panel shows an experimental random X-ray diffraction pattern, also known as a speckle pattern, obtained from the X-ray diffuser.
Fig. 3. Images taken from the proposed randomness-based X-ray imaging (bottom) and the corresponding surface electron microscope (SEM) images (top).
2023.04.12 View 8961
KAIST researchers find the key to overcome the limits in X-ray microscopy
X-ray microscopes have the advantage of penetrating most substances, so internal organs and skeletons can be observed non-invasively through chest X-rays or CT scans. Recently, studies to increase the resolution of X-ray imaging technology are being actively conducted in order to precisely observe the internal structure of semiconductors and batteries at the nanoscale.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that a joint research team led by Professor YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics and Dr. Jun Lim of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory has succeeded in developing a core technology that can overcome the resolution limitations of existing X-ray microscopes.
d
This study, in which Dr. KyeoReh Lee participated as the first author, was published on 6th of April in “Light: Science and Application”, a world-renowned academic journal in optics and photonics. (Paper title: Direct high-resolution X-ray imaging exploiting pseudorandomness).
X-ray nanomicroscopes do not have refractive lenses. In an X-ray microscope, a circular grating called a concentric zone plate is used instead of a lens. The resolution of an image obtained using the zone plate is determined by the quality of the nanostructure that comprises the plate. There are several difficulties in fabricating and maintaining these nanostructures, which set the limit to the level of resolution for X-ray microscopy.
The research team developed a new X-ray nanomicroscopy technology to overcome this problem. The X-ray lens proposed by the research team is in the form of numerous holes punched in a thin tungsten film, and generates random diffraction patterns by diffracting incident X-rays. The research team mathematically identified that, paradoxically, the high-resolution information of the sample was fully contained in these random diffraction patterns, and actually succeeded in extracting the information and imaging the internal states of the samples.
The imaging method using the mathematical properties of random diffraction was proposed and implemented in the visible light band for the first time by Dr. KyeoReh Lee and Professor YongKeun Park in 2016*. This study uses the results of previous studies to solve the difficult, lingering problem in the field of the X-ray imaging. ※ "Exploiting the speckle-correlation scattering matrix for a compact reference-free holographic image sensor." Nature communications 7.1 (2016): 13359.
The resolution of the image of the constructed sample has no direct correlation with the size of the pattern etched on the random lens used. Based on this idea, the research team succeeded in acquiring images with 14 nm resolution (approximately 1/7 the size of the coronavirus) by using random lenses made in a circular pattern with a diameter of 300 nm.
The imaging technology developed by this research team is a key fundamental technology that can enhance the resolution of X-ray nanomicroscopy, which has been blocked by limitations of the production of existing zone plates.
The first author and one of the co-corresponding author, Dr. KyeoReh Lee of KAIST Department of Physics, said, “In this study, the resolution was limited to 14 nm, but if the next-generation X-ray light source and high-performance X-ray detector are used, the resolution would exceed that of the conventional X-ray nano-imaging and approach the resolution of an electron microscope.” and added, “Unlike an electron microscope, X-rays can observe the internal structure without damaging the sample, so it will be able to present a new standard for non-invasive nanostructure observation processes such as quality inspections for semiconductors.”.
The co-corresponding author, Dr. Jun Lim of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, said, “In the same context, the developed image technology is expected to greatly increase the performance in the 4th generation multipurpose radiation accelerator which is set to be established in Ochang of the Northern Chungcheong Province.”
This research was conducted with the support through the Research Leader Program and the Sejong Science Fellowship of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Fig. 1. Designed diffuser as X-ray imaging lens. a, Schematic of full-field transmission X-ray microscopy. The attenuation (amplitude) map of a sample is measured. The image resolution (dx) is limited by the outermost zone width of the zone plate (D). b, Schematic of the proposed method. A designed diffuser is used instead of a zone plate. The image resolution is finer than the hole size of the diffuser (dx << D).
Fig. 2. The left panel is a surface electron microscopy (SEM) image of the X-ray diffuser used in the experiment. The middle panel shows the design of the X-ray diffuser, and there is an inset in the middle of the panel that shows a corresponding part of the SEM image. The right panel shows an experimental random X-ray diffraction pattern, also known as a speckle pattern, obtained from the X-ray diffuser.
Fig. 3. Images taken from the proposed randomness-based X-ray imaging (bottom) and the corresponding surface electron microscope (SEM) images (top).
2023.04.12 View 8961 -
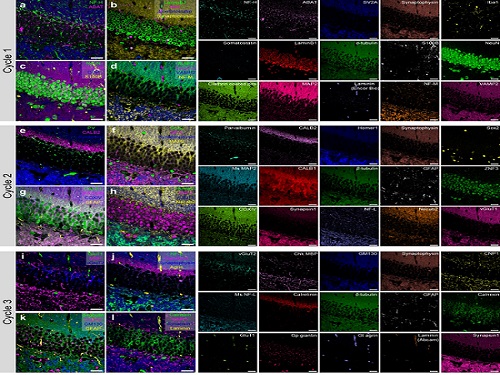 PICASSO Technique Drives Biological Molecules into Technicolor
The new imaging approach brings current imaging colors from four to more than 15 for mapping overlapping proteins
Pablo Picasso’s surreal cubist artistic style shifted common features into unrecognizable scenes, but a new imaging approach bearing his namesake may elucidate the most complicated subject: the brain. Employing artificial intelligence to clarify spectral color blending of tiny molecules used to stain specific proteins and other items of research interest, the PICASSO technique, allows researchers to use more than 15 colors to image and parse our overlapping proteins.
The PICASSO developers, based in Korea, published their approach on May 5 in Nature Communications.
Fluorophores — the staining molecules — emit specific colors when excited by a light, but if more than four fluorophores are used, their emitted colors overlap and blend. Researchers previously developed techniques to correct this spectral overlap by precisely defining the matrix of mixed and unmixed images. This measurement depends on reference spectra, found by identifying clear images of only one fluorophore-stained specimen or of multiple, identically prepared specimens that only contain a single fluorophore each.
“Such reference spectra measurement could be complicated to perform in highly heterogeneous specimens, such as the brain, due to the highly varied emission spectra of fluorophores depending on the subregions from which the spectra were measured,” said co-corresponding author Young-Gyu Yoon, professor in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST. He explained that the subregions would each need their own spectra reference measurements, making for an inefficient, time-consuming process. “To address this problem, we developed an approach that does not require reference spectra measurements.”
The approach is the “Process of ultra-multiplexed Imaging of biomolecules viA the unmixing of the Signals of Spectrally Overlapping fluorophores,” also known as PICASSO. Ultra-multiplexed imaging refers to visualizing the numerous individual components of a unit. Like a cinema multiplex in which each theater plays a different movie, each protein in a cell has a different role. By staining with fluorophores, researchers can begin to understand those roles.
“We devised a strategy based on information theory; unmixing is performed by iteratively minimizing the mutual information between mixed images,” said co-corresponding author Jae-Byum Chang, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST. “This allows us to get away with the assumption that the spatial distribution of different proteins is mutually exclusive and enables accurate information unmixing.”
To demonstrate PICASSO’s capabilities, the researchers applied the technique to imaging a mouse brain. With a single round of staining, they performed 15-color multiplexed imaging of a mouse brain. Although small, mouse brains are still complex, multifaceted organs that can take significant resources to map. According to the researchers, PICASSO can improve the capabilities of other imaging techniques and allow for the use of even more fluorophore colors.
Using one such imaging technique in combination with PICASSO, the team achieved 45-color multiplexed imaging of the mouse brain in only three staining and imaging cycles, according to Yoon.
“PICASSO is a versatile tool for the multiplexed biomolecule imaging of cultured cells, tissue slices and clinical specimens,” Chang said. “We anticipate that PICASSO will be useful for a broad range of applications for which biomolecules’ spatial information is important. One such application the tool would be useful for is revealing the cellular heterogeneities of tumor microenvironments, especially the heterogeneous populations of immune cells, which are closely related to cancer prognoses and the efficacy of cancer therapies.”
The Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology supported this work. Spectral imaging was performed at the Korea Basic Science Institute Western Seoul Center.
-PublicationJunyoung Seo, Yeonbo Sim, Jeewon Kim, Hyunwoo Kim, In Cho, Hoyeon Nam, Yong-Gyu Yoon, Jae-Byum Chang, “PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatiallyoverlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements,” May 5, Nature Communications (doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30168-z)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Byum ChangDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
Professor Young-Gyu YoonSchool of Electrical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.06.22 View 12289
PICASSO Technique Drives Biological Molecules into Technicolor
The new imaging approach brings current imaging colors from four to more than 15 for mapping overlapping proteins
Pablo Picasso’s surreal cubist artistic style shifted common features into unrecognizable scenes, but a new imaging approach bearing his namesake may elucidate the most complicated subject: the brain. Employing artificial intelligence to clarify spectral color blending of tiny molecules used to stain specific proteins and other items of research interest, the PICASSO technique, allows researchers to use more than 15 colors to image and parse our overlapping proteins.
The PICASSO developers, based in Korea, published their approach on May 5 in Nature Communications.
Fluorophores — the staining molecules — emit specific colors when excited by a light, but if more than four fluorophores are used, their emitted colors overlap and blend. Researchers previously developed techniques to correct this spectral overlap by precisely defining the matrix of mixed and unmixed images. This measurement depends on reference spectra, found by identifying clear images of only one fluorophore-stained specimen or of multiple, identically prepared specimens that only contain a single fluorophore each.
“Such reference spectra measurement could be complicated to perform in highly heterogeneous specimens, such as the brain, due to the highly varied emission spectra of fluorophores depending on the subregions from which the spectra were measured,” said co-corresponding author Young-Gyu Yoon, professor in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST. He explained that the subregions would each need their own spectra reference measurements, making for an inefficient, time-consuming process. “To address this problem, we developed an approach that does not require reference spectra measurements.”
The approach is the “Process of ultra-multiplexed Imaging of biomolecules viA the unmixing of the Signals of Spectrally Overlapping fluorophores,” also known as PICASSO. Ultra-multiplexed imaging refers to visualizing the numerous individual components of a unit. Like a cinema multiplex in which each theater plays a different movie, each protein in a cell has a different role. By staining with fluorophores, researchers can begin to understand those roles.
“We devised a strategy based on information theory; unmixing is performed by iteratively minimizing the mutual information between mixed images,” said co-corresponding author Jae-Byum Chang, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST. “This allows us to get away with the assumption that the spatial distribution of different proteins is mutually exclusive and enables accurate information unmixing.”
To demonstrate PICASSO’s capabilities, the researchers applied the technique to imaging a mouse brain. With a single round of staining, they performed 15-color multiplexed imaging of a mouse brain. Although small, mouse brains are still complex, multifaceted organs that can take significant resources to map. According to the researchers, PICASSO can improve the capabilities of other imaging techniques and allow for the use of even more fluorophore colors.
Using one such imaging technique in combination with PICASSO, the team achieved 45-color multiplexed imaging of the mouse brain in only three staining and imaging cycles, according to Yoon.
“PICASSO is a versatile tool for the multiplexed biomolecule imaging of cultured cells, tissue slices and clinical specimens,” Chang said. “We anticipate that PICASSO will be useful for a broad range of applications for which biomolecules’ spatial information is important. One such application the tool would be useful for is revealing the cellular heterogeneities of tumor microenvironments, especially the heterogeneous populations of immune cells, which are closely related to cancer prognoses and the efficacy of cancer therapies.”
The Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology supported this work. Spectral imaging was performed at the Korea Basic Science Institute Western Seoul Center.
-PublicationJunyoung Seo, Yeonbo Sim, Jeewon Kim, Hyunwoo Kim, In Cho, Hoyeon Nam, Yong-Gyu Yoon, Jae-Byum Chang, “PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatiallyoverlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements,” May 5, Nature Communications (doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30168-z)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Byum ChangDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
Professor Young-Gyu YoonSchool of Electrical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.06.22 View 12289 -
 Game Design Guide Book for Middle-Aged and Older Adult Players Helps Rewrite Gaming Culture
The online book ‘Game Design Guide for Adults in Their 50s and Older’ helps to increase accessibility for adult gamers
A KAIST multi-disciplinary research team published a game guide to respond to the new demands of senior gamers and expand the gaming market. The guide will be helpful for designing interfaces fit for senior groups as a way to minimize the cognitive burdens related to aging. It also helps readers understand older users’ cognitive abilities and socioemotional characteristics.
“This guide analyzed the game experience of players in their 50s and older and converted it into a game design element that can be easily referred to by game developers and designers,” explained Professor Young Im Do from the Graduate School of Culture Technology who led the research.
The gaming industry is paying attention to the emerging trend of ‘active aging’ and senior gamers. According to the National Purchase Diary Panel Inc., game play time increased significantly in the 45-64 age group compared to other age groups during the pandemic. Despite the growing number of senior gamers, it is still difficult for older novice players to start video games because most commercial games focus on younger players. For example, older players can feel frustrated if the game requires fast reflexes and accurate timing. Font sizes and objects that are too small as well as interfaces that are too complicated can be challenging for senior gamers.
The research team presents how to handle these difficulties in game design considering the visual-motor coordination of people in age groups ranging from their 20s to 80s. It also proposes various game elements such as audio-visual elements, cognitive and motor elements, game rules, stories and characters, social aspects, in-app purchases, and advertisements for senior groups. The guide also proposes a game service model and introduces examples of game prototypes that apply supportive technology.
For this guide, the researchers operated the “International Game Living Lab”, which is an open space for creating novel and innovative solutions by converging IT technology into daily life. In the lab, ordinary citizens, research institutes, companies, and local communities formed a cooperative network and actively participated in experiments, education, and discussions for finding solutions over three years.
Researchers in multi-disciplinary fields, including computer science, psychology, game design, and gerontechnology, covered various methodologies to understand the game experience of adults in their 50s and older. In order to profile players of this age group, three different approaches were performed: visual-motor coordination experiments, an EEG (Electroencephalogram) test, and a gameplay workshop. Then, they converted the results into practical knowledge that can be used in the gaming industry.
Professor Kyung Myun Lee from the School of Digital Humanities and Computational Social Sciences at KAIST, Professor Byungjoo Shin from Yonsei University, CEO Junyoung Shin of CareU, and CEO Minseok Doh of Heartverse participated in this online book which is available to the public at https://wikidocs.net/book/7356.
2022.06.10 View 7557
Game Design Guide Book for Middle-Aged and Older Adult Players Helps Rewrite Gaming Culture
The online book ‘Game Design Guide for Adults in Their 50s and Older’ helps to increase accessibility for adult gamers
A KAIST multi-disciplinary research team published a game guide to respond to the new demands of senior gamers and expand the gaming market. The guide will be helpful for designing interfaces fit for senior groups as a way to minimize the cognitive burdens related to aging. It also helps readers understand older users’ cognitive abilities and socioemotional characteristics.
“This guide analyzed the game experience of players in their 50s and older and converted it into a game design element that can be easily referred to by game developers and designers,” explained Professor Young Im Do from the Graduate School of Culture Technology who led the research.
The gaming industry is paying attention to the emerging trend of ‘active aging’ and senior gamers. According to the National Purchase Diary Panel Inc., game play time increased significantly in the 45-64 age group compared to other age groups during the pandemic. Despite the growing number of senior gamers, it is still difficult for older novice players to start video games because most commercial games focus on younger players. For example, older players can feel frustrated if the game requires fast reflexes and accurate timing. Font sizes and objects that are too small as well as interfaces that are too complicated can be challenging for senior gamers.
The research team presents how to handle these difficulties in game design considering the visual-motor coordination of people in age groups ranging from their 20s to 80s. It also proposes various game elements such as audio-visual elements, cognitive and motor elements, game rules, stories and characters, social aspects, in-app purchases, and advertisements for senior groups. The guide also proposes a game service model and introduces examples of game prototypes that apply supportive technology.
For this guide, the researchers operated the “International Game Living Lab”, which is an open space for creating novel and innovative solutions by converging IT technology into daily life. In the lab, ordinary citizens, research institutes, companies, and local communities formed a cooperative network and actively participated in experiments, education, and discussions for finding solutions over three years.
Researchers in multi-disciplinary fields, including computer science, psychology, game design, and gerontechnology, covered various methodologies to understand the game experience of adults in their 50s and older. In order to profile players of this age group, three different approaches were performed: visual-motor coordination experiments, an EEG (Electroencephalogram) test, and a gameplay workshop. Then, they converted the results into practical knowledge that can be used in the gaming industry.
Professor Kyung Myun Lee from the School of Digital Humanities and Computational Social Sciences at KAIST, Professor Byungjoo Shin from Yonsei University, CEO Junyoung Shin of CareU, and CEO Minseok Doh of Heartverse participated in this online book which is available to the public at https://wikidocs.net/book/7356.
2022.06.10 View 7557 -
 Five Projects Ranked in the Top 100 for National R&D Excellence
Five KAIST research projects were selected as the 2021 Top 100 for National R&D Excellence by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of Science & Technology Evaluation and Planning.
The five projects are:-The development of E. coli that proliferates with only formic acid and carbon dioxide by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-An original reverse aging technology that restores an old human skin cell into a younger one by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering-The development of next-generation high-efficiency perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells by Professor Byungha Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering-Research on the effects of ultrafine dust in the atmosphere has on energy consumption by Professor Jiyong Eom from the School of Business and Technology Management-Research on a molecular trigger that controls the phase transformation of bio materials by Professor Myungchul Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Started in 2006, an Evaluation Committee composed of experts in industries, universities, and research institutes has made the preliminary selections of the most outstanding research projects based on their significance as a scientific and technological development and their socioeconomic effects. The finalists went through an open public evaluation. The final 100 studies are from six fields: 18 from mechanics & materials, 26 from biology & marine sciences, 19 from ICT & electronics, 10 from interdisciplinary research, and nine from natural science and infrastructure.
The selected 100 studies will receive a certificate and an award plaque from the minister of MSIT as well as additional points for business and institutional evaluations according to appropriate regulations, and the selected researchers will be strongly recommended as candidates for national meritorious awards.
In particular, to help the 100 selected research projects become more accessible for the general public, their main contents will be provided in a free e-book ‘The Top 100 for National R&D Excellence of 2021’ that will be available from online booksellers.
2022.02.17 View 12599
Five Projects Ranked in the Top 100 for National R&D Excellence
Five KAIST research projects were selected as the 2021 Top 100 for National R&D Excellence by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of Science & Technology Evaluation and Planning.
The five projects are:-The development of E. coli that proliferates with only formic acid and carbon dioxide by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-An original reverse aging technology that restores an old human skin cell into a younger one by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering-The development of next-generation high-efficiency perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells by Professor Byungha Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering-Research on the effects of ultrafine dust in the atmosphere has on energy consumption by Professor Jiyong Eom from the School of Business and Technology Management-Research on a molecular trigger that controls the phase transformation of bio materials by Professor Myungchul Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Started in 2006, an Evaluation Committee composed of experts in industries, universities, and research institutes has made the preliminary selections of the most outstanding research projects based on their significance as a scientific and technological development and their socioeconomic effects. The finalists went through an open public evaluation. The final 100 studies are from six fields: 18 from mechanics & materials, 26 from biology & marine sciences, 19 from ICT & electronics, 10 from interdisciplinary research, and nine from natural science and infrastructure.
The selected 100 studies will receive a certificate and an award plaque from the minister of MSIT as well as additional points for business and institutional evaluations according to appropriate regulations, and the selected researchers will be strongly recommended as candidates for national meritorious awards.
In particular, to help the 100 selected research projects become more accessible for the general public, their main contents will be provided in a free e-book ‘The Top 100 for National R&D Excellence of 2021’ that will be available from online booksellers.
2022.02.17 View 12599 -
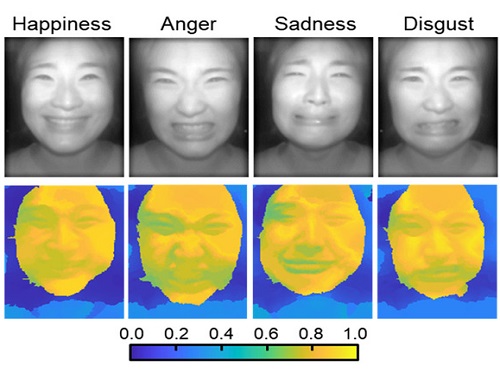 AI Light-Field Camera Reads 3D Facial Expressions
Machine-learned, light-field camera reads facial expressions from high-contrast illumination invariant 3D facial images
A joint research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong and Doheon Lee from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering reported the development of a technique for facial expression detection by merging near-infrared light-field camera techniques with artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
Unlike a conventional camera, the light-field camera contains micro-lens arrays in front of the image sensor, which makes the camera small enough to fit into a smart phone, while allowing it to acquire the spatial and directional information of the light with a single shot. The technique has received attention as it can reconstruct images in a variety of ways including multi-views, refocusing, and 3D image acquisition, giving rise to many potential applications.
However, the optical crosstalk between shadows caused by external light sources in the environment and the micro-lens has limited existing light-field cameras from being able to provide accurate image contrast and 3D reconstruction.
The joint research team applied a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) in the near-IR range to stabilize the accuracy of 3D image reconstruction that previously depended on environmental light. When an external light source is shone on a face at 0-, 30-, and 60-degree angles, the light field camera reduces 54% of image reconstruction errors. Additionally, by inserting a light-absorbing layer for visible and near-IR wavelengths between the micro-lens arrays, the team could minimize optical crosstalk while increasing the image contrast by 2.1 times.
Through this technique, the team could overcome the limitations of existing light-field cameras and was able to develop their NIR-based light-field camera (NIR-LFC), optimized for the 3D image reconstruction of facial expressions. Using the NIR-LFC, the team acquired high-quality 3D reconstruction images of facial expressions expressing various emotions regardless of the lighting conditions of the surrounding environment.
The facial expressions in the acquired 3D images were distinguished through machine learning with an average of 85% accuracy – a statistically significant figure compared to when 2D images were used. Furthermore, by calculating the interdependency of distance information that varies with facial expression in 3D images, the team could identify the information a light-field camera utilizes to distinguish human expressions.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong said, “The sub-miniature light-field camera developed by the research team has the potential to become the new platform to quantitatively analyze the facial expressions and emotions of humans.” To highlight the significance of this research, he added, “It could be applied in various fields including mobile healthcare, field diagnosis, social cognition, and human-machine interactions.”
This research was published in Advanced Intelligent Systems online on December 16, under the title, “Machine-Learned Light-field Camera that Reads Facial Expression from High-Contrast and Illumination Invariant 3D Facial Images.” This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
-Publication“Machine-learned light-field camera that reads fascial expression from high-contrast and illumination invariant 3D facial images,” Sang-In Bae, Sangyeon Lee, Jae-Myeong Kwon, Hyun-Kyung Kim. Kyung-Won Jang, Doheon Lee, Ki-Hun Jeong, Advanced Intelligent Systems, December 16, 2021 (doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202100182)
ProfileProfessor Ki-Hun JeongBiophotonic LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Doheon LeeDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2022.01.21 View 14589
AI Light-Field Camera Reads 3D Facial Expressions
Machine-learned, light-field camera reads facial expressions from high-contrast illumination invariant 3D facial images
A joint research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong and Doheon Lee from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering reported the development of a technique for facial expression detection by merging near-infrared light-field camera techniques with artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
Unlike a conventional camera, the light-field camera contains micro-lens arrays in front of the image sensor, which makes the camera small enough to fit into a smart phone, while allowing it to acquire the spatial and directional information of the light with a single shot. The technique has received attention as it can reconstruct images in a variety of ways including multi-views, refocusing, and 3D image acquisition, giving rise to many potential applications.
However, the optical crosstalk between shadows caused by external light sources in the environment and the micro-lens has limited existing light-field cameras from being able to provide accurate image contrast and 3D reconstruction.
The joint research team applied a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) in the near-IR range to stabilize the accuracy of 3D image reconstruction that previously depended on environmental light. When an external light source is shone on a face at 0-, 30-, and 60-degree angles, the light field camera reduces 54% of image reconstruction errors. Additionally, by inserting a light-absorbing layer for visible and near-IR wavelengths between the micro-lens arrays, the team could minimize optical crosstalk while increasing the image contrast by 2.1 times.
Through this technique, the team could overcome the limitations of existing light-field cameras and was able to develop their NIR-based light-field camera (NIR-LFC), optimized for the 3D image reconstruction of facial expressions. Using the NIR-LFC, the team acquired high-quality 3D reconstruction images of facial expressions expressing various emotions regardless of the lighting conditions of the surrounding environment.
The facial expressions in the acquired 3D images were distinguished through machine learning with an average of 85% accuracy – a statistically significant figure compared to when 2D images were used. Furthermore, by calculating the interdependency of distance information that varies with facial expression in 3D images, the team could identify the information a light-field camera utilizes to distinguish human expressions.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong said, “The sub-miniature light-field camera developed by the research team has the potential to become the new platform to quantitatively analyze the facial expressions and emotions of humans.” To highlight the significance of this research, he added, “It could be applied in various fields including mobile healthcare, field diagnosis, social cognition, and human-machine interactions.”
This research was published in Advanced Intelligent Systems online on December 16, under the title, “Machine-Learned Light-field Camera that Reads Facial Expression from High-Contrast and Illumination Invariant 3D Facial Images.” This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
-Publication“Machine-learned light-field camera that reads fascial expression from high-contrast and illumination invariant 3D facial images,” Sang-In Bae, Sangyeon Lee, Jae-Myeong Kwon, Hyun-Kyung Kim. Kyung-Won Jang, Doheon Lee, Ki-Hun Jeong, Advanced Intelligent Systems, December 16, 2021 (doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202100182)
ProfileProfessor Ki-Hun JeongBiophotonic LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Doheon LeeDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2022.01.21 View 14589 -
 A Genetic Change for Achieving a Long and Healthy Life
Researchers identified a single amino acid change in the tumor suppressor protein in PTEN that extends healthy periods while maintaining longevity
Living a long, healthy life is everyone’s wish, but it is not an easy one to achieve. Many aging studies are developing strategies to increase health spans, the period of life spent with good health, without chronic diseases and disabilities. Researchers at KAIST presented new insights for improving the health span by just regulating the activity of a protein.
A research group under Professor Seung-Jae V. Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences identified a single amino acid change in the tumor suppressor protein phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) that dramatically extends healthy periods while maintaining longevity. This study highlights the importance of the well-conserved tumor suppressor protein PTEN in health span regulation, which can be targeted to develop therapies for promoting healthy longevity in humans. The research was published in Nature Communications on September 24, 2021.
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) signaling (IIS) is one of the evolutionarily conserved aging-modulatory pathways present in life forms ranging from tiny roundworms to humans. The proper reduction of IIS leads to longevity in animals but often causes defects in multiple health parameters including impaired motility, reproduction, and growth.
The research team found that a specific amino acid change in the PTEN protein improves health status while retaining the longevity conferred by reduced IIS. They used the roundworm C. elegans, an excellent model animal that has been widely used for aging research, mainly because of its very short normal lifespan of about two to three weeks. The PTEN protein is a phosphatase that removes phosphate from lipids as well as proteins. Interestingly, the newly identified amino acid change delicately recalibrated the IIS by partially maintaining protein phosphatase activity while reducing lipid phosphatase activity.
As a result, the amino acid change in the PTEN protein maintained the activity of the longevity-promoting transcription factor Forkhead Box O (FOXO) protein while restricting the detrimental upregulation of another transcription factor, NRF2, leading to long and healthy life in animals with reduced IIS.
Professor Lee said, “Our study raises the exciting possibility of simultaneously promoting longevity and health in humans by slightly tweaking the activity of one protein, PTEN.”
This work was supported by the MInistry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication:Hae-Eun H. Park, Wooseon Hwang, Seokjin Ham, Eunah Kim, Ozlem Altintas, Sangsoon Park, Heehwa G. Son, Yujin Lee, Dongyeop Lee, Won Do Heo, and Seung-Jae V. Lee. 2021. “A PTEN variant uncouples longevity from impaired fitness in Caenorhabditis elegans with reduced insulin/IGF-1 signaling,” Nature Communications, 12(1), 5631. (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25920-w)
-ProfileProfessor Seung-Jae V. LeeMolecular Genetics of Aging LaboratoryDepartment of Biological Sciences KAIST
2021.11.19 View 10149
A Genetic Change for Achieving a Long and Healthy Life
Researchers identified a single amino acid change in the tumor suppressor protein in PTEN that extends healthy periods while maintaining longevity
Living a long, healthy life is everyone’s wish, but it is not an easy one to achieve. Many aging studies are developing strategies to increase health spans, the period of life spent with good health, without chronic diseases and disabilities. Researchers at KAIST presented new insights for improving the health span by just regulating the activity of a protein.
A research group under Professor Seung-Jae V. Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences identified a single amino acid change in the tumor suppressor protein phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) that dramatically extends healthy periods while maintaining longevity. This study highlights the importance of the well-conserved tumor suppressor protein PTEN in health span regulation, which can be targeted to develop therapies for promoting healthy longevity in humans. The research was published in Nature Communications on September 24, 2021.
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) signaling (IIS) is one of the evolutionarily conserved aging-modulatory pathways present in life forms ranging from tiny roundworms to humans. The proper reduction of IIS leads to longevity in animals but often causes defects in multiple health parameters including impaired motility, reproduction, and growth.
The research team found that a specific amino acid change in the PTEN protein improves health status while retaining the longevity conferred by reduced IIS. They used the roundworm C. elegans, an excellent model animal that has been widely used for aging research, mainly because of its very short normal lifespan of about two to three weeks. The PTEN protein is a phosphatase that removes phosphate from lipids as well as proteins. Interestingly, the newly identified amino acid change delicately recalibrated the IIS by partially maintaining protein phosphatase activity while reducing lipid phosphatase activity.
As a result, the amino acid change in the PTEN protein maintained the activity of the longevity-promoting transcription factor Forkhead Box O (FOXO) protein while restricting the detrimental upregulation of another transcription factor, NRF2, leading to long and healthy life in animals with reduced IIS.
Professor Lee said, “Our study raises the exciting possibility of simultaneously promoting longevity and health in humans by slightly tweaking the activity of one protein, PTEN.”
This work was supported by the MInistry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication:Hae-Eun H. Park, Wooseon Hwang, Seokjin Ham, Eunah Kim, Ozlem Altintas, Sangsoon Park, Heehwa G. Son, Yujin Lee, Dongyeop Lee, Won Do Heo, and Seung-Jae V. Lee. 2021. “A PTEN variant uncouples longevity from impaired fitness in Caenorhabditis elegans with reduced insulin/IGF-1 signaling,” Nature Communications, 12(1), 5631. (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25920-w)
-ProfileProfessor Seung-Jae V. LeeMolecular Genetics of Aging LaboratoryDepartment of Biological Sciences KAIST
2021.11.19 View 10149 -
 Research Day Highlights the Most Impactful Technologies of the Year
Technology Converting Full HD Image to 4-Times Higher UHD Via Deep Learning Cited as the Research of the Year
The technology converting a full HD image into a four-times higher UHD image in real time via AI deep learning was recognized as the Research of the Year. Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering who developed the technology won the Research of the Year Grand Prize during the 2021 KAIST Research Day ceremony on May 25. Professor Kim was lauded for conducting creative research on machine learning and deep learning-based image processing.
KAIST’s Research Day recognizes the most notable research outcomes of the year, while creating opportunities for researchers to immerse themselves into interdisciplinary research projects with their peers. The ceremony was broadcast online due to Covid-19 and announced the Ten R&D Achievement of the Year that are expected to make a significant impact.
To celebrate the award, Professor Kim gave a lecture on “Computational Imaging through Deep Learning for the Acquisition of High-Quality Images.” Focusing on the fact that advancements in artificial intelligence technology can show superior performance when used to convert low-quality videos to higher quality, he introduced some of the AI technologies that are currently being applied in the field of image restoration and quality improvement.
Professors Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and In-Cheol Park from the School of Electrical Engineering each received Research Awards, and Professor Junyong Noh from the Graduate School of Culture Technology was selected for the Innovation Award. Professors Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry and Hyungki Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering were awarded the Interdisciplinary Award as a team for their joint research.
Meanwhile, out of KAIST’s ten most notable R&D achievements, those from the field of natural and biological sciences included research on rare earth element-platinum nanoparticle catalysts by Professor Ryong Ryoo from the Department of Chemistry, real-time observations of the locational changes in all of the atoms in a molecule by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry, and an investigation on memory retention mechanisms after synapse removal from an astrocyte by Professor Won-Suk Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences.
Awardees from the engineering field were a wearable robot for paraplegics with the world’s best functionality and walking speed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, fair machine learning by Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering, and a generative adversarial networks processing unit (GANPU), an AI semiconductor that can learn from even mobiles by processing multiple and deep networks by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering.
Others selected as part of the ten research studies were the development of epigenetic reprogramming technology in tumour by Professor Pilnam Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, the development of an original technology for reverse cell aging by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, a heterogeneous metal element catalyst for atmospheric purification by Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and the Mobile Clinic Module (MCM): a negative pressure ward for epidemic hospitals by Professor Taek-jin Nam (reported at the Wall Street Journal) from the Department of Industrial Design.
2021.05.31 View 17522
Research Day Highlights the Most Impactful Technologies of the Year
Technology Converting Full HD Image to 4-Times Higher UHD Via Deep Learning Cited as the Research of the Year
The technology converting a full HD image into a four-times higher UHD image in real time via AI deep learning was recognized as the Research of the Year. Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering who developed the technology won the Research of the Year Grand Prize during the 2021 KAIST Research Day ceremony on May 25. Professor Kim was lauded for conducting creative research on machine learning and deep learning-based image processing.
KAIST’s Research Day recognizes the most notable research outcomes of the year, while creating opportunities for researchers to immerse themselves into interdisciplinary research projects with their peers. The ceremony was broadcast online due to Covid-19 and announced the Ten R&D Achievement of the Year that are expected to make a significant impact.
To celebrate the award, Professor Kim gave a lecture on “Computational Imaging through Deep Learning for the Acquisition of High-Quality Images.” Focusing on the fact that advancements in artificial intelligence technology can show superior performance when used to convert low-quality videos to higher quality, he introduced some of the AI technologies that are currently being applied in the field of image restoration and quality improvement.
Professors Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and In-Cheol Park from the School of Electrical Engineering each received Research Awards, and Professor Junyong Noh from the Graduate School of Culture Technology was selected for the Innovation Award. Professors Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry and Hyungki Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering were awarded the Interdisciplinary Award as a team for their joint research.
Meanwhile, out of KAIST’s ten most notable R&D achievements, those from the field of natural and biological sciences included research on rare earth element-platinum nanoparticle catalysts by Professor Ryong Ryoo from the Department of Chemistry, real-time observations of the locational changes in all of the atoms in a molecule by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry, and an investigation on memory retention mechanisms after synapse removal from an astrocyte by Professor Won-Suk Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences.
Awardees from the engineering field were a wearable robot for paraplegics with the world’s best functionality and walking speed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, fair machine learning by Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering, and a generative adversarial networks processing unit (GANPU), an AI semiconductor that can learn from even mobiles by processing multiple and deep networks by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering.
Others selected as part of the ten research studies were the development of epigenetic reprogramming technology in tumour by Professor Pilnam Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, the development of an original technology for reverse cell aging by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, a heterogeneous metal element catalyst for atmospheric purification by Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and the Mobile Clinic Module (MCM): a negative pressure ward for epidemic hospitals by Professor Taek-jin Nam (reported at the Wall Street Journal) from the Department of Industrial Design.
2021.05.31 View 17522