Cell
-
 A KAIST Research Team Develops Diesel Reforming Catalyst Enabling Hydrogen Production for Future Mobile Fuel Cells
This catalyst capability allowing stable hydrogen production from commercial diesel is expected to be applied in mobile fuel cell systems in the future hydrogen economy
On August 16, a joint research team led by Professors Joongmyeon Bae and Kang Taek Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) announced the successful development of a highly active and durable reforming catalyst allowing hydrogen production from commercial diesel.
Fuel reforming is a hydrogen production technique that extracts hydrogen from hydrocarbons through catalytic reactions. Diesel, being a liquid fuel, has a high storage density for hydrogen and is easy to transport and store. There have therefore been continuous research efforts to apply hydrogel supply systems using diesel reformation in mobile fuel cells, such as for auxiliary power in heavy trucks or air-independent propulsion (AIP) systems in submarines.
However, diesel is a mixture of high hydrocarbons including long-chained paraffin, double-bonded olefin, and aromatic hydrocarbons with benzene groups, and it requires a highly active catalyst to effectively break them down. In addition, the catalyst must be extremely durable against caulking and sintering, as they are often the main causes of catalyst degradation. Such challenges have limited the use of diesel reformation technologies to date.
The joint research team successfully developed a highly active and durable diesel reforming catalyst through elution (a heat treatment method used to uniformly grow active metals retained in an oxide support as ions in the form of metal nanoparticles), forming alloy nanoparticles. The design was based on the fact that eluted nanoparticles strongly interact with the support, allowing a high degree of dispersion at high temperatures, and that producing an alloy from dissimilar metals can increase the performance of catalysts through a synergistic effect.
The research team introduced a solution combustion synthesis method to produce a multi-component catalyst with a trace amount of platinum (Pt) and ruthenium (Ru) penetrated into a ceria (CeO2) lattice, which is a structure commonly used as a support for catalysts in redox reactions. When exposed to a diesel reforming reaction environment, the catalyst induces Pt-Ru alloy nanoparticle formation upon Pt and Ru elution onto the support surface.
In addition to the catalyst analysis, the research team also succeeded in characterizing the behaviour of active metal elution and alloy formation from an energetic perspective using a density functional theory-based calculation. In a performance comparison test between the Pt-Ru alloy catalyst against existing single-metal catalysts, the reforming activity was shown to have improved, as it showed a 100% fuel conversion rate even at a low temperature (600oC, compared to the original 800oC). In a long-term durability test (800oC, 200 hours), the catalyst showed commercial stability by successfully producing hydrogen from commercial diesel without performance degradation.
The study was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jaemyung Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering as the first author. Ph.D. candidate Changho Yeon of KIER, Dr. Jiwoo Oh of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Gwangwoo Han of KIER, Ph.D. candidate Jeong Do Yoo of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Dr. Hyung Joong Yun of the Korea Basic Science Institute contributed as co-authors. Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of KIER and Professors Kang Taek Lee and Joongmyeon Bae of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering contributed as corresponding authors. The research was published in the online version of Applied Catalysis B: Environmental (IF 24.319, JCR 0.93%) on June 17, under the title “Highly Active and Stable Catalyst with Exsolved PtRu Alloy Nanoparticles for Hydrogen Production via Commercial Diesel Reforming”.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae said, “The fact that hydrogen can be stably produced from commercial diesel makes this a very meaningful achievement, and we look forward to this technology contributing to the active introduction of mobile fuel cell systems in the early hydrogen economy.” He added, “Our approach to catalyst design may be applied not only to reforming reactions, but also in various other fields.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through funding from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
Figure. Schematic diagram of high-performance diesel reforming catalyst with eluted platinum-ruthenium alloy nanoparticles and long-term durability verification experiment results for commercial diesel reforming reaction
2022.09.07 View 5309
A KAIST Research Team Develops Diesel Reforming Catalyst Enabling Hydrogen Production for Future Mobile Fuel Cells
This catalyst capability allowing stable hydrogen production from commercial diesel is expected to be applied in mobile fuel cell systems in the future hydrogen economy
On August 16, a joint research team led by Professors Joongmyeon Bae and Kang Taek Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) announced the successful development of a highly active and durable reforming catalyst allowing hydrogen production from commercial diesel.
Fuel reforming is a hydrogen production technique that extracts hydrogen from hydrocarbons through catalytic reactions. Diesel, being a liquid fuel, has a high storage density for hydrogen and is easy to transport and store. There have therefore been continuous research efforts to apply hydrogel supply systems using diesel reformation in mobile fuel cells, such as for auxiliary power in heavy trucks or air-independent propulsion (AIP) systems in submarines.
However, diesel is a mixture of high hydrocarbons including long-chained paraffin, double-bonded olefin, and aromatic hydrocarbons with benzene groups, and it requires a highly active catalyst to effectively break them down. In addition, the catalyst must be extremely durable against caulking and sintering, as they are often the main causes of catalyst degradation. Such challenges have limited the use of diesel reformation technologies to date.
The joint research team successfully developed a highly active and durable diesel reforming catalyst through elution (a heat treatment method used to uniformly grow active metals retained in an oxide support as ions in the form of metal nanoparticles), forming alloy nanoparticles. The design was based on the fact that eluted nanoparticles strongly interact with the support, allowing a high degree of dispersion at high temperatures, and that producing an alloy from dissimilar metals can increase the performance of catalysts through a synergistic effect.
The research team introduced a solution combustion synthesis method to produce a multi-component catalyst with a trace amount of platinum (Pt) and ruthenium (Ru) penetrated into a ceria (CeO2) lattice, which is a structure commonly used as a support for catalysts in redox reactions. When exposed to a diesel reforming reaction environment, the catalyst induces Pt-Ru alloy nanoparticle formation upon Pt and Ru elution onto the support surface.
In addition to the catalyst analysis, the research team also succeeded in characterizing the behaviour of active metal elution and alloy formation from an energetic perspective using a density functional theory-based calculation. In a performance comparison test between the Pt-Ru alloy catalyst against existing single-metal catalysts, the reforming activity was shown to have improved, as it showed a 100% fuel conversion rate even at a low temperature (600oC, compared to the original 800oC). In a long-term durability test (800oC, 200 hours), the catalyst showed commercial stability by successfully producing hydrogen from commercial diesel without performance degradation.
The study was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jaemyung Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering as the first author. Ph.D. candidate Changho Yeon of KIER, Dr. Jiwoo Oh of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Gwangwoo Han of KIER, Ph.D. candidate Jeong Do Yoo of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Dr. Hyung Joong Yun of the Korea Basic Science Institute contributed as co-authors. Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of KIER and Professors Kang Taek Lee and Joongmyeon Bae of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering contributed as corresponding authors. The research was published in the online version of Applied Catalysis B: Environmental (IF 24.319, JCR 0.93%) on June 17, under the title “Highly Active and Stable Catalyst with Exsolved PtRu Alloy Nanoparticles for Hydrogen Production via Commercial Diesel Reforming”.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae said, “The fact that hydrogen can be stably produced from commercial diesel makes this a very meaningful achievement, and we look forward to this technology contributing to the active introduction of mobile fuel cell systems in the early hydrogen economy.” He added, “Our approach to catalyst design may be applied not only to reforming reactions, but also in various other fields.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through funding from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
Figure. Schematic diagram of high-performance diesel reforming catalyst with eluted platinum-ruthenium alloy nanoparticles and long-term durability verification experiment results for commercial diesel reforming reaction
2022.09.07 View 5309 -
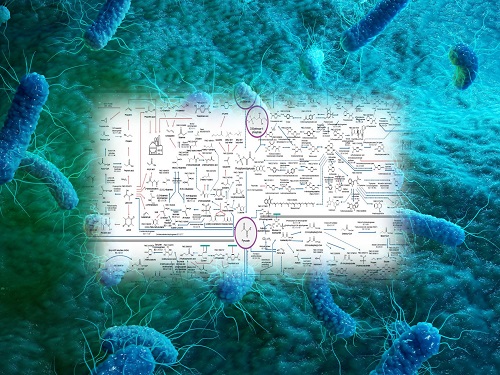 Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 6831
Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 6831 -
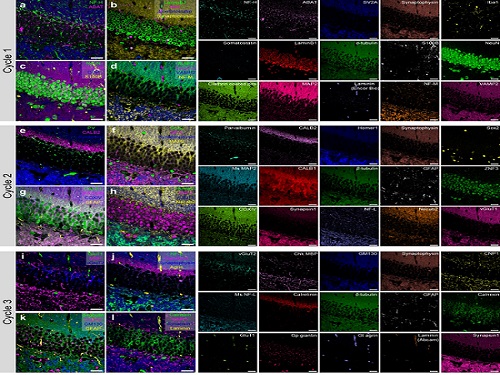 PICASSO Technique Drives Biological Molecules into Technicolor
The new imaging approach brings current imaging colors from four to more than 15 for mapping overlapping proteins
Pablo Picasso’s surreal cubist artistic style shifted common features into unrecognizable scenes, but a new imaging approach bearing his namesake may elucidate the most complicated subject: the brain. Employing artificial intelligence to clarify spectral color blending of tiny molecules used to stain specific proteins and other items of research interest, the PICASSO technique, allows researchers to use more than 15 colors to image and parse our overlapping proteins.
The PICASSO developers, based in Korea, published their approach on May 5 in Nature Communications.
Fluorophores — the staining molecules — emit specific colors when excited by a light, but if more than four fluorophores are used, their emitted colors overlap and blend. Researchers previously developed techniques to correct this spectral overlap by precisely defining the matrix of mixed and unmixed images. This measurement depends on reference spectra, found by identifying clear images of only one fluorophore-stained specimen or of multiple, identically prepared specimens that only contain a single fluorophore each.
“Such reference spectra measurement could be complicated to perform in highly heterogeneous specimens, such as the brain, due to the highly varied emission spectra of fluorophores depending on the subregions from which the spectra were measured,” said co-corresponding author Young-Gyu Yoon, professor in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST. He explained that the subregions would each need their own spectra reference measurements, making for an inefficient, time-consuming process. “To address this problem, we developed an approach that does not require reference spectra measurements.”
The approach is the “Process of ultra-multiplexed Imaging of biomolecules viA the unmixing of the Signals of Spectrally Overlapping fluorophores,” also known as PICASSO. Ultra-multiplexed imaging refers to visualizing the numerous individual components of a unit. Like a cinema multiplex in which each theater plays a different movie, each protein in a cell has a different role. By staining with fluorophores, researchers can begin to understand those roles.
“We devised a strategy based on information theory; unmixing is performed by iteratively minimizing the mutual information between mixed images,” said co-corresponding author Jae-Byum Chang, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST. “This allows us to get away with the assumption that the spatial distribution of different proteins is mutually exclusive and enables accurate information unmixing.”
To demonstrate PICASSO’s capabilities, the researchers applied the technique to imaging a mouse brain. With a single round of staining, they performed 15-color multiplexed imaging of a mouse brain. Although small, mouse brains are still complex, multifaceted organs that can take significant resources to map. According to the researchers, PICASSO can improve the capabilities of other imaging techniques and allow for the use of even more fluorophore colors.
Using one such imaging technique in combination with PICASSO, the team achieved 45-color multiplexed imaging of the mouse brain in only three staining and imaging cycles, according to Yoon.
“PICASSO is a versatile tool for the multiplexed biomolecule imaging of cultured cells, tissue slices and clinical specimens,” Chang said. “We anticipate that PICASSO will be useful for a broad range of applications for which biomolecules’ spatial information is important. One such application the tool would be useful for is revealing the cellular heterogeneities of tumor microenvironments, especially the heterogeneous populations of immune cells, which are closely related to cancer prognoses and the efficacy of cancer therapies.”
The Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology supported this work. Spectral imaging was performed at the Korea Basic Science Institute Western Seoul Center.
-PublicationJunyoung Seo, Yeonbo Sim, Jeewon Kim, Hyunwoo Kim, In Cho, Hoyeon Nam, Yong-Gyu Yoon, Jae-Byum Chang, “PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatiallyoverlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements,” May 5, Nature Communications (doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30168-z)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Byum ChangDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
Professor Young-Gyu YoonSchool of Electrical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.06.22 View 4695
PICASSO Technique Drives Biological Molecules into Technicolor
The new imaging approach brings current imaging colors from four to more than 15 for mapping overlapping proteins
Pablo Picasso’s surreal cubist artistic style shifted common features into unrecognizable scenes, but a new imaging approach bearing his namesake may elucidate the most complicated subject: the brain. Employing artificial intelligence to clarify spectral color blending of tiny molecules used to stain specific proteins and other items of research interest, the PICASSO technique, allows researchers to use more than 15 colors to image and parse our overlapping proteins.
The PICASSO developers, based in Korea, published their approach on May 5 in Nature Communications.
Fluorophores — the staining molecules — emit specific colors when excited by a light, but if more than four fluorophores are used, their emitted colors overlap and blend. Researchers previously developed techniques to correct this spectral overlap by precisely defining the matrix of mixed and unmixed images. This measurement depends on reference spectra, found by identifying clear images of only one fluorophore-stained specimen or of multiple, identically prepared specimens that only contain a single fluorophore each.
“Such reference spectra measurement could be complicated to perform in highly heterogeneous specimens, such as the brain, due to the highly varied emission spectra of fluorophores depending on the subregions from which the spectra were measured,” said co-corresponding author Young-Gyu Yoon, professor in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST. He explained that the subregions would each need their own spectra reference measurements, making for an inefficient, time-consuming process. “To address this problem, we developed an approach that does not require reference spectra measurements.”
The approach is the “Process of ultra-multiplexed Imaging of biomolecules viA the unmixing of the Signals of Spectrally Overlapping fluorophores,” also known as PICASSO. Ultra-multiplexed imaging refers to visualizing the numerous individual components of a unit. Like a cinema multiplex in which each theater plays a different movie, each protein in a cell has a different role. By staining with fluorophores, researchers can begin to understand those roles.
“We devised a strategy based on information theory; unmixing is performed by iteratively minimizing the mutual information between mixed images,” said co-corresponding author Jae-Byum Chang, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST. “This allows us to get away with the assumption that the spatial distribution of different proteins is mutually exclusive and enables accurate information unmixing.”
To demonstrate PICASSO’s capabilities, the researchers applied the technique to imaging a mouse brain. With a single round of staining, they performed 15-color multiplexed imaging of a mouse brain. Although small, mouse brains are still complex, multifaceted organs that can take significant resources to map. According to the researchers, PICASSO can improve the capabilities of other imaging techniques and allow for the use of even more fluorophore colors.
Using one such imaging technique in combination with PICASSO, the team achieved 45-color multiplexed imaging of the mouse brain in only three staining and imaging cycles, according to Yoon.
“PICASSO is a versatile tool for the multiplexed biomolecule imaging of cultured cells, tissue slices and clinical specimens,” Chang said. “We anticipate that PICASSO will be useful for a broad range of applications for which biomolecules’ spatial information is important. One such application the tool would be useful for is revealing the cellular heterogeneities of tumor microenvironments, especially the heterogeneous populations of immune cells, which are closely related to cancer prognoses and the efficacy of cancer therapies.”
The Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology supported this work. Spectral imaging was performed at the Korea Basic Science Institute Western Seoul Center.
-PublicationJunyoung Seo, Yeonbo Sim, Jeewon Kim, Hyunwoo Kim, In Cho, Hoyeon Nam, Yong-Gyu Yoon, Jae-Byum Chang, “PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatiallyoverlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements,” May 5, Nature Communications (doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30168-z)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Byum ChangDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
Professor Young-Gyu YoonSchool of Electrical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.06.22 View 4695 -
 Mathematicians Identify a Key Source of Cell-to-Cell Variability in Cell Signaling
Systematic inferences identify a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics
Why do genetically identical cells respond differently to the same external stimuli, such as antibiotics? This long-standing mystery has been solved by KAIST and IBS mathematicians who have developed a new framework for analyzing cell responses to some stimuli. The team found that the cell-to-cell variability in antibiotic stress response increases as the effective length of the cell signaling pathway (i.e., the number of rate-limiting steps) increases. This finding could identify more effective chemotherapies to overcome the fractional killing of cancer cells caused by cell-to-cell variability.
Cells in the human body contain signal transduction systems that respond to various external stimuli such as antibiotics and changes in osmotic pressure. When an external stimulus is detected, various biochemical reactions occur sequentially. This leads to the expression of relevant genes, allowing the cells to respond to the perturbed external environment. Furthermore, signal transduction leads to a drug response (e.g., antibiotic resistance genes are expressed when antibiotic drugs are given).
However, even when the same external stimuli are detected, the responses of individual cells are greatly heterogeneous. This leads to the emergence of persister cells that are highly resistant to drugs. To identify potential sources of this cell-to cell variability, many studies have been conducted. However, most of the intermediate signal transduction reactions are unobservable with current experimental techniques.
A group of researchers including Dae Wook Kim and Hyukpyo Hong and led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences and IBS Biomedical Mathematics Group solved the mystery by exploiting queueing theory and Bayesian inference methodology. They proposed a queueing process that describes the signal transduction system in cells. Based on this, they developed Bayesian inference computational software using MBI (the Moment-based Bayesian Inference method). This enables the analysis of the signal transduction system without a direct observation of the intermediate steps. This study was published in Science Advances.
By analyzing experimental data from Escherichia coli using MBI, the research team found that cell-to-cell variability increases as the number of rate-limiting steps in the signaling pathway increases.
The rate-limiting steps denote the slowest steps (i.e., bottlenecks) in sequential biochemical reaction steps composing cell signaling pathways and thus dominates most of the signaling time. As the number of the rate-limiting steps increases, the intensity of the transduced signal becomes greatly heterogeneous even in a population of genetically identical cells. This finding is expected to provide a new paradigm for studying the heterogeneous antibiotic resistance of cells, which is a big challenge in cancer medicine.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help advance the understanding of cell-to-cell variability in response to external stimuli. I hope this finding facilitates the development of more effective chemotherapies.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Institute for Basic Science.
-Publication:Dae Wook Kim, Hyukpyo Hong, and Jae Kyoung Kim (2022) “Systematic inference identifies a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics: the rate-limiting step number,”Science Advances March 18, 2022 (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl4598)
-Profile:Professor Jae Kyoung Kimhttp://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr@umichkim on TwitterDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.03.29 View 4945
Mathematicians Identify a Key Source of Cell-to-Cell Variability in Cell Signaling
Systematic inferences identify a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics
Why do genetically identical cells respond differently to the same external stimuli, such as antibiotics? This long-standing mystery has been solved by KAIST and IBS mathematicians who have developed a new framework for analyzing cell responses to some stimuli. The team found that the cell-to-cell variability in antibiotic stress response increases as the effective length of the cell signaling pathway (i.e., the number of rate-limiting steps) increases. This finding could identify more effective chemotherapies to overcome the fractional killing of cancer cells caused by cell-to-cell variability.
Cells in the human body contain signal transduction systems that respond to various external stimuli such as antibiotics and changes in osmotic pressure. When an external stimulus is detected, various biochemical reactions occur sequentially. This leads to the expression of relevant genes, allowing the cells to respond to the perturbed external environment. Furthermore, signal transduction leads to a drug response (e.g., antibiotic resistance genes are expressed when antibiotic drugs are given).
However, even when the same external stimuli are detected, the responses of individual cells are greatly heterogeneous. This leads to the emergence of persister cells that are highly resistant to drugs. To identify potential sources of this cell-to cell variability, many studies have been conducted. However, most of the intermediate signal transduction reactions are unobservable with current experimental techniques.
A group of researchers including Dae Wook Kim and Hyukpyo Hong and led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences and IBS Biomedical Mathematics Group solved the mystery by exploiting queueing theory and Bayesian inference methodology. They proposed a queueing process that describes the signal transduction system in cells. Based on this, they developed Bayesian inference computational software using MBI (the Moment-based Bayesian Inference method). This enables the analysis of the signal transduction system without a direct observation of the intermediate steps. This study was published in Science Advances.
By analyzing experimental data from Escherichia coli using MBI, the research team found that cell-to-cell variability increases as the number of rate-limiting steps in the signaling pathway increases.
The rate-limiting steps denote the slowest steps (i.e., bottlenecks) in sequential biochemical reaction steps composing cell signaling pathways and thus dominates most of the signaling time. As the number of the rate-limiting steps increases, the intensity of the transduced signal becomes greatly heterogeneous even in a population of genetically identical cells. This finding is expected to provide a new paradigm for studying the heterogeneous antibiotic resistance of cells, which is a big challenge in cancer medicine.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help advance the understanding of cell-to-cell variability in response to external stimuli. I hope this finding facilitates the development of more effective chemotherapies.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Institute for Basic Science.
-Publication:Dae Wook Kim, Hyukpyo Hong, and Jae Kyoung Kim (2022) “Systematic inference identifies a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics: the rate-limiting step number,”Science Advances March 18, 2022 (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl4598)
-Profile:Professor Jae Kyoung Kimhttp://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr@umichkim on TwitterDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.03.29 View 4945 -
 A Mathematical Model Shows High Viral Transmissions Reduce the Progression Rates for Severe Covid-19
The model suggests a clue as to when a pandemic will turn into an endemic
A mathematical model demonstrated that high transmission rates among highly vaccinated populations of COVID-19 ultimately reduce the numbers of severe cases. This model suggests a clue as to when this pandemic will turn into an endemic.
With the future of the pandemic remaining uncertain, a research team of mathematicians and medical scientists analyzed a mathematical model that may predict how the changing transmission rate of COVID-19 would affect the settlement process of the virus as a mild respiratory virus.
The team led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the Department of Mathematical Science and Professor Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering used a new approach by dividing the human immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 into a shorter-term neutralizing antibody response and a longer-term T-cell immune response, and applying them each to a mathematical model. Additionally, the analysis was based on the fact that although breakthrough infection may occur frequently, the immune response of the patient will be boosted after recovery from each breakthrough infection.
The results showed that in an environment with a high vaccination rate, although COVID-19 cases may rise temporarily when the transmission rate increases, the ratio of critical cases would ultimately decline, thereby decreasing the total number of critical cases and in fact settling COVID-19 as a mild respiratory disease more quickly.
Conditions in which the number of cases may spike include relaxing social distancing measures or the rise of variants with higher transmission rates like the Omicron variant. This research did not take the less virulent characteristic of the Omicron variant into account but focused on the results of its high transmission rate, thereby predicting what may happen in the process of the endemic transition of COVID-19.
The research team pointed out the limitations of their mathematical model, such as the lack of consideration for age or patients with underlying diseases, and explained that the results of this study must be applied with care when compared against high-risk groups. Additionally, as medical systems may collapse when the number of cases rises sharply, this study must be interpreted with prudence and applied accordingly. The research team therefore emphasized that for policies that encourage a step-wise return to normality to succeed, the sustainable maintenance of public health systems is indispensable.
Professor Kim said, “We have drawn a counter-intuitive conclusion amid the unpredictable pandemic through an adequate mathematical model,” asserting the importance of applying mathematical models to medical research.
Professor Shin said, “Although the Omicron variant has become the dominant strain and the number of cases is rising rapidly in South Korea, it is important to use scientific approaches to predict the future and apply them to policies rather than fearing the current situation.”
The results of the research were published on medRxiv.org on February 11, under the title “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to severe COVID-19 during endemic transition.”
This research was funded by the Institute of Basic Science, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-PublicationHyukpyo Hong, Ji Yun Noh, Hyojung Lee, Sunhwa Choi, Boseung Choi, Jae Kyung Kim, Eui-Cheol Shin, “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to
severe COVID-19 during endemic transition,” medRxiv, February 9, 2022 (doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.09.22270633)
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
Professor Eui-Cheol ShinGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.02.22 View 5237
A Mathematical Model Shows High Viral Transmissions Reduce the Progression Rates for Severe Covid-19
The model suggests a clue as to when a pandemic will turn into an endemic
A mathematical model demonstrated that high transmission rates among highly vaccinated populations of COVID-19 ultimately reduce the numbers of severe cases. This model suggests a clue as to when this pandemic will turn into an endemic.
With the future of the pandemic remaining uncertain, a research team of mathematicians and medical scientists analyzed a mathematical model that may predict how the changing transmission rate of COVID-19 would affect the settlement process of the virus as a mild respiratory virus.
The team led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the Department of Mathematical Science and Professor Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering used a new approach by dividing the human immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 into a shorter-term neutralizing antibody response and a longer-term T-cell immune response, and applying them each to a mathematical model. Additionally, the analysis was based on the fact that although breakthrough infection may occur frequently, the immune response of the patient will be boosted after recovery from each breakthrough infection.
The results showed that in an environment with a high vaccination rate, although COVID-19 cases may rise temporarily when the transmission rate increases, the ratio of critical cases would ultimately decline, thereby decreasing the total number of critical cases and in fact settling COVID-19 as a mild respiratory disease more quickly.
Conditions in which the number of cases may spike include relaxing social distancing measures or the rise of variants with higher transmission rates like the Omicron variant. This research did not take the less virulent characteristic of the Omicron variant into account but focused on the results of its high transmission rate, thereby predicting what may happen in the process of the endemic transition of COVID-19.
The research team pointed out the limitations of their mathematical model, such as the lack of consideration for age or patients with underlying diseases, and explained that the results of this study must be applied with care when compared against high-risk groups. Additionally, as medical systems may collapse when the number of cases rises sharply, this study must be interpreted with prudence and applied accordingly. The research team therefore emphasized that for policies that encourage a step-wise return to normality to succeed, the sustainable maintenance of public health systems is indispensable.
Professor Kim said, “We have drawn a counter-intuitive conclusion amid the unpredictable pandemic through an adequate mathematical model,” asserting the importance of applying mathematical models to medical research.
Professor Shin said, “Although the Omicron variant has become the dominant strain and the number of cases is rising rapidly in South Korea, it is important to use scientific approaches to predict the future and apply them to policies rather than fearing the current situation.”
The results of the research were published on medRxiv.org on February 11, under the title “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to severe COVID-19 during endemic transition.”
This research was funded by the Institute of Basic Science, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-PublicationHyukpyo Hong, Ji Yun Noh, Hyojung Lee, Sunhwa Choi, Boseung Choi, Jae Kyung Kim, Eui-Cheol Shin, “Increasing viral transmission paradoxically reduces progression rates to
severe COVID-19 during endemic transition,” medRxiv, February 9, 2022 (doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.09.22270633)
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
Professor Eui-Cheol ShinGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.02.22 View 5237 -
 Five Projects Ranked in the Top 100 for National R&D Excellence
Five KAIST research projects were selected as the 2021 Top 100 for National R&D Excellence by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of Science & Technology Evaluation and Planning.
The five projects are:-The development of E. coli that proliferates with only formic acid and carbon dioxide by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-An original reverse aging technology that restores an old human skin cell into a younger one by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering-The development of next-generation high-efficiency perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells by Professor Byungha Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering-Research on the effects of ultrafine dust in the atmosphere has on energy consumption by Professor Jiyong Eom from the School of Business and Technology Management-Research on a molecular trigger that controls the phase transformation of bio materials by Professor Myungchul Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Started in 2006, an Evaluation Committee composed of experts in industries, universities, and research institutes has made the preliminary selections of the most outstanding research projects based on their significance as a scientific and technological development and their socioeconomic effects. The finalists went through an open public evaluation. The final 100 studies are from six fields: 18 from mechanics & materials, 26 from biology & marine sciences, 19 from ICT & electronics, 10 from interdisciplinary research, and nine from natural science and infrastructure.
The selected 100 studies will receive a certificate and an award plaque from the minister of MSIT as well as additional points for business and institutional evaluations according to appropriate regulations, and the selected researchers will be strongly recommended as candidates for national meritorious awards.
In particular, to help the 100 selected research projects become more accessible for the general public, their main contents will be provided in a free e-book ‘The Top 100 for National R&D Excellence of 2021’ that will be available from online booksellers.
2022.02.17 View 5518
Five Projects Ranked in the Top 100 for National R&D Excellence
Five KAIST research projects were selected as the 2021 Top 100 for National R&D Excellence by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of Science & Technology Evaluation and Planning.
The five projects are:-The development of E. coli that proliferates with only formic acid and carbon dioxide by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-An original reverse aging technology that restores an old human skin cell into a younger one by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering-The development of next-generation high-efficiency perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells by Professor Byungha Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering-Research on the effects of ultrafine dust in the atmosphere has on energy consumption by Professor Jiyong Eom from the School of Business and Technology Management-Research on a molecular trigger that controls the phase transformation of bio materials by Professor Myungchul Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Started in 2006, an Evaluation Committee composed of experts in industries, universities, and research institutes has made the preliminary selections of the most outstanding research projects based on their significance as a scientific and technological development and their socioeconomic effects. The finalists went through an open public evaluation. The final 100 studies are from six fields: 18 from mechanics & materials, 26 from biology & marine sciences, 19 from ICT & electronics, 10 from interdisciplinary research, and nine from natural science and infrastructure.
The selected 100 studies will receive a certificate and an award plaque from the minister of MSIT as well as additional points for business and institutional evaluations according to appropriate regulations, and the selected researchers will be strongly recommended as candidates for national meritorious awards.
In particular, to help the 100 selected research projects become more accessible for the general public, their main contents will be provided in a free e-book ‘The Top 100 for National R&D Excellence of 2021’ that will be available from online booksellers.
2022.02.17 View 5518 -
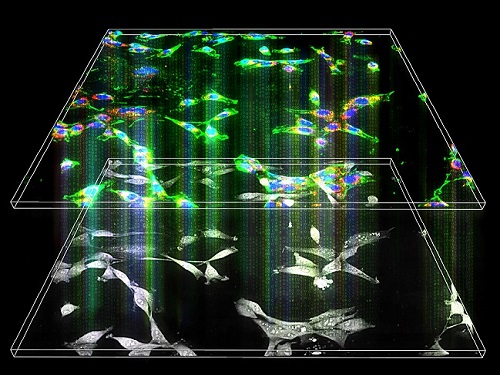 Label-Free Multiplexed Microtomography of Endogenous Subcellular Dynamics Using Deep Learning
AI-based holographic microscopy allows molecular imaging without introducing exogenous labeling agents
A research team upgraded the 3D microtomography observing dynamics of label-free live cells in multiplexed fluorescence imaging. The AI-powered 3D holotomographic microscopy extracts various molecular information from live unlabeled biological cells in real time without exogenous labeling or staining agents.
Professor YongKeum Park’s team and the startup Tomocube encoded 3D refractive index tomograms using the refractive index as a means of measurement. Then they decoded the information with a deep learning-based model that infers multiple 3D fluorescence tomograms from the refractive index measurements of the corresponding subcellular targets, thereby achieving multiplexed micro tomography. This study was reported in Nature Cell Biology online on December 7, 2021.
Fluorescence microscopy is the most widely used optical microscopy technique due to its high biochemical specificity. However, it needs to genetically manipulate or to stain cells with fluorescent labels in order to express fluorescent proteins. These labeling processes inevitably affect the intrinsic physiology of cells. It also has challenges in long-term measuring due to photobleaching and phototoxicity. The overlapped spectra of multiplexed fluorescence signals also hinder the viewing of various structures at the same time. More critically, it took several hours to observe the cells after preparing them.
3D holographic microscopy, also known as holotomography, is providing new ways to quantitatively image live cells without pretreatments such as staining. Holotomography can accurately and quickly measure the morphological and structural information of cells, but only provides limited biochemical and molecular information.
The 'AI microscope' created in this process takes advantage of the features of both holographic microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. That is, a specific image from a fluorescence microscope can be obtained without a fluorescent label. Therefore, the microscope can observe many types of cellular structures in their natural state in 3D and at the same time as fast as one millisecond, and long-term measurements over several days are also possible.
The Tomocube-KAIST team showed that fluorescence images can be directly and precisely predicted from holotomographic images in various cells and conditions. Using the quantitative relationship between the spatial distribution of the refractive index found by AI and the major structures in cells, it was possible to decipher the spatial distribution of the refractive index. And surprisingly, it confirmed that this relationship is constant regardless of cell type.
Professor Park said, “We were able to develop a new concept microscope that combines the advantages of several microscopes with the multidisciplinary research of AI, optics, and biology. It will be immediately applicable for new types of cells not included in the existing data and is expected to be widely applicable for various biological and medical research.”
When comparing the molecular image information extracted by AI with the molecular image information physically obtained by fluorescence staining in 3D space, it showed a 97% or more conformity, which is a level that is difficult to distinguish with the naked eye.
“Compared to the sub-60% accuracy of the fluorescence information extracted from the model developed by the Google AI team, it showed significantly higher performance,” Professor Park added.
This work was supported by the KAIST Up program, the BK21+ program, Tomocube, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Health & Welfare.
-Publication
Hyun-seok Min, Won-Do Heo, YongKeun Park, et al. “Label-free multiplexed microtomography of endogenous subcellular dynamics using generalizable deep learning,” Nature Cell Biology (doi.org/10.1038/s41556-021-00802-x) published online December 07 2021.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
Department of Physics
KAIST
2022.02.09 View 5425
Label-Free Multiplexed Microtomography of Endogenous Subcellular Dynamics Using Deep Learning
AI-based holographic microscopy allows molecular imaging without introducing exogenous labeling agents
A research team upgraded the 3D microtomography observing dynamics of label-free live cells in multiplexed fluorescence imaging. The AI-powered 3D holotomographic microscopy extracts various molecular information from live unlabeled biological cells in real time without exogenous labeling or staining agents.
Professor YongKeum Park’s team and the startup Tomocube encoded 3D refractive index tomograms using the refractive index as a means of measurement. Then they decoded the information with a deep learning-based model that infers multiple 3D fluorescence tomograms from the refractive index measurements of the corresponding subcellular targets, thereby achieving multiplexed micro tomography. This study was reported in Nature Cell Biology online on December 7, 2021.
Fluorescence microscopy is the most widely used optical microscopy technique due to its high biochemical specificity. However, it needs to genetically manipulate or to stain cells with fluorescent labels in order to express fluorescent proteins. These labeling processes inevitably affect the intrinsic physiology of cells. It also has challenges in long-term measuring due to photobleaching and phototoxicity. The overlapped spectra of multiplexed fluorescence signals also hinder the viewing of various structures at the same time. More critically, it took several hours to observe the cells after preparing them.
3D holographic microscopy, also known as holotomography, is providing new ways to quantitatively image live cells without pretreatments such as staining. Holotomography can accurately and quickly measure the morphological and structural information of cells, but only provides limited biochemical and molecular information.
The 'AI microscope' created in this process takes advantage of the features of both holographic microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. That is, a specific image from a fluorescence microscope can be obtained without a fluorescent label. Therefore, the microscope can observe many types of cellular structures in their natural state in 3D and at the same time as fast as one millisecond, and long-term measurements over several days are also possible.
The Tomocube-KAIST team showed that fluorescence images can be directly and precisely predicted from holotomographic images in various cells and conditions. Using the quantitative relationship between the spatial distribution of the refractive index found by AI and the major structures in cells, it was possible to decipher the spatial distribution of the refractive index. And surprisingly, it confirmed that this relationship is constant regardless of cell type.
Professor Park said, “We were able to develop a new concept microscope that combines the advantages of several microscopes with the multidisciplinary research of AI, optics, and biology. It will be immediately applicable for new types of cells not included in the existing data and is expected to be widely applicable for various biological and medical research.”
When comparing the molecular image information extracted by AI with the molecular image information physically obtained by fluorescence staining in 3D space, it showed a 97% or more conformity, which is a level that is difficult to distinguish with the naked eye.
“Compared to the sub-60% accuracy of the fluorescence information extracted from the model developed by the Google AI team, it showed significantly higher performance,” Professor Park added.
This work was supported by the KAIST Up program, the BK21+ program, Tomocube, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Health & Welfare.
-Publication
Hyun-seok Min, Won-Do Heo, YongKeun Park, et al. “Label-free multiplexed microtomography of endogenous subcellular dynamics using generalizable deep learning,” Nature Cell Biology (doi.org/10.1038/s41556-021-00802-x) published online December 07 2021.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
Department of Physics
KAIST
2022.02.09 View 5425 -
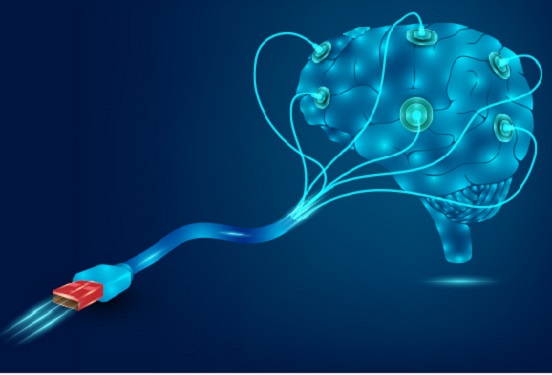 Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-PublicationPark, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-ProfileProfessor Seongjun ParkBio and Neural Interfaces LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.13 View 6877
Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-PublicationPark, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-ProfileProfessor Seongjun ParkBio and Neural Interfaces LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.13 View 6877 -
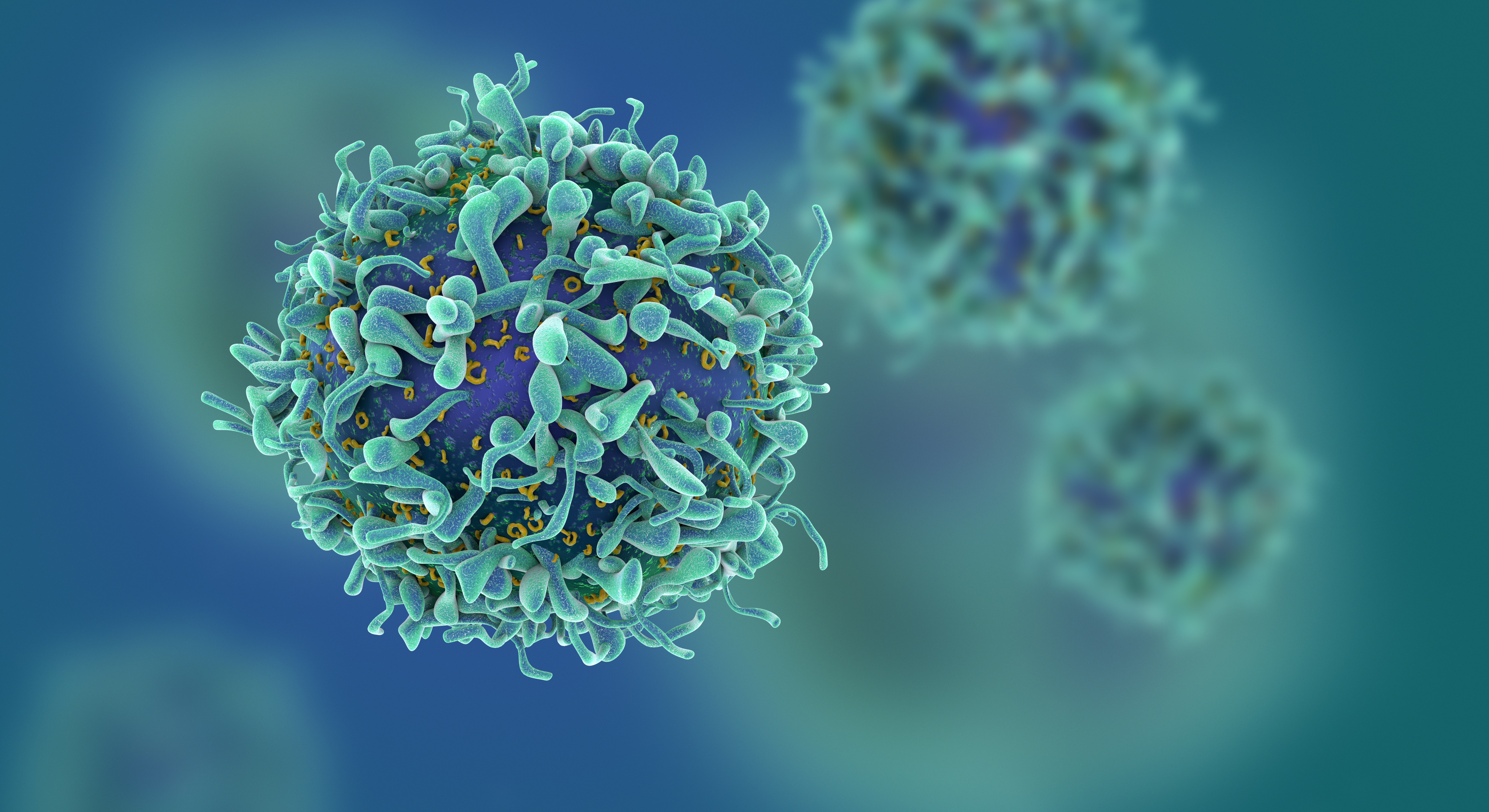 Study of T Cells from COVID-19 Convalescents Guides Vaccine Strategies
Researchers confirm that most COVID-19 patients in their convalescent stage carry stem cell-like memory T cells for months
A KAIST immunology research team found that most convalescent patients of COVID-19 develop and maintain T cell memory for over 10 months regardless of the severity of their symptoms. In addition, memory T cells proliferate rapidly after encountering their cognate antigen and accomplish their multifunctional roles. This study provides new insights for effective vaccine strategies against COVID-19, considering the self-renewal capacity and multipotency of memory T cells.
COVID-19 is a disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. When patients recover from COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2-specific adaptive immune memory is developed. The adaptive immune system consists of two principal components: B cells that produce antibodies and T cells that eliminate infected cells. The current results suggest that the protective immune function of memory T cells will be implemented upon re-exposure to SARS-CoV-2.
Recently, the role of memory T cells against SARS-CoV-2 has been gaining attention as neutralizing antibodies wane after recovery. Although memory T cells cannot prevent the infection itself, they play a central role in preventing the severe progression of COVID-19. However, the longevity and functional maintenance of SARS-CoV-2-specific memory T cells remain unknown.
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and his collaborators investigated the characteristics and functions of stem cell-like memory T cells, which are expected to play a crucial role in long-term immunity. Researchers analyzed the generation of stem cell-like memory T cells and multi-cytokine producing polyfunctional memory T cells, using cutting-edge immunological techniques.
This research is significant in that revealing the long-term immunity of COVID-19 convalescent patients provides an indicator regarding the long-term persistence of T cell immunity, one of the main goals of future vaccine development, as well as evaluating the long-term efficacy of currently available COVID-19 vaccines.
The research team is presently conducting a follow-up study to identify the memory T cell formation and functional characteristics of those who received COVID-19 vaccines, and to understand the immunological effect of COVID-19 vaccines by comparing the characteristics of memory T cells from vaccinated individuals with those of COVID-19 convalescent patients.
PhD candidate Jae Hyung Jung and Dr. Min-Seok Rha, a clinical fellow at Yonsei Severance Hospital, who led the study together explained, “Our analysis will enhance the understanding of COVID-19 immunity and establish an index for COVID-19 vaccine-induced memory T cells.”
“This study is the world’s longest longitudinal study on differentiation and functions of memory T cells among COVID-19 convalescent patients. The research on the temporal dynamics of immune responses has laid the groundwork for building a strategy for next-generation vaccine development,” Professor Shin added. This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and KAIST, and was published in Nature Communications on June 30.
-Publication:
Jung, J.H., Rha, MS., Sa, M. et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell memory is sustained in COVID-19 convalescent patients for 10 months with successful development of stem cell-like memory T cells. Nat Communications 12, 4043 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24377-1
-Profile:
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin
Laboratory of Immunology & Infectious Diseases (http://liid.kaist.ac.kr/)
Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
KAIST
2021.07.05 View 7637
Study of T Cells from COVID-19 Convalescents Guides Vaccine Strategies
Researchers confirm that most COVID-19 patients in their convalescent stage carry stem cell-like memory T cells for months
A KAIST immunology research team found that most convalescent patients of COVID-19 develop and maintain T cell memory for over 10 months regardless of the severity of their symptoms. In addition, memory T cells proliferate rapidly after encountering their cognate antigen and accomplish their multifunctional roles. This study provides new insights for effective vaccine strategies against COVID-19, considering the self-renewal capacity and multipotency of memory T cells.
COVID-19 is a disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. When patients recover from COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2-specific adaptive immune memory is developed. The adaptive immune system consists of two principal components: B cells that produce antibodies and T cells that eliminate infected cells. The current results suggest that the protective immune function of memory T cells will be implemented upon re-exposure to SARS-CoV-2.
Recently, the role of memory T cells against SARS-CoV-2 has been gaining attention as neutralizing antibodies wane after recovery. Although memory T cells cannot prevent the infection itself, they play a central role in preventing the severe progression of COVID-19. However, the longevity and functional maintenance of SARS-CoV-2-specific memory T cells remain unknown.
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and his collaborators investigated the characteristics and functions of stem cell-like memory T cells, which are expected to play a crucial role in long-term immunity. Researchers analyzed the generation of stem cell-like memory T cells and multi-cytokine producing polyfunctional memory T cells, using cutting-edge immunological techniques.
This research is significant in that revealing the long-term immunity of COVID-19 convalescent patients provides an indicator regarding the long-term persistence of T cell immunity, one of the main goals of future vaccine development, as well as evaluating the long-term efficacy of currently available COVID-19 vaccines.
The research team is presently conducting a follow-up study to identify the memory T cell formation and functional characteristics of those who received COVID-19 vaccines, and to understand the immunological effect of COVID-19 vaccines by comparing the characteristics of memory T cells from vaccinated individuals with those of COVID-19 convalescent patients.
PhD candidate Jae Hyung Jung and Dr. Min-Seok Rha, a clinical fellow at Yonsei Severance Hospital, who led the study together explained, “Our analysis will enhance the understanding of COVID-19 immunity and establish an index for COVID-19 vaccine-induced memory T cells.”
“This study is the world’s longest longitudinal study on differentiation and functions of memory T cells among COVID-19 convalescent patients. The research on the temporal dynamics of immune responses has laid the groundwork for building a strategy for next-generation vaccine development,” Professor Shin added. This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and KAIST, and was published in Nature Communications on June 30.
-Publication:
Jung, J.H., Rha, MS., Sa, M. et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell memory is sustained in COVID-19 convalescent patients for 10 months with successful development of stem cell-like memory T cells. Nat Communications 12, 4043 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24377-1
-Profile:
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin
Laboratory of Immunology & Infectious Diseases (http://liid.kaist.ac.kr/)
Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
KAIST
2021.07.05 View 7637 -
 Research Day Highlights the Most Impactful Technologies of the Year
Technology Converting Full HD Image to 4-Times Higher UHD Via Deep Learning Cited as the Research of the Year
The technology converting a full HD image into a four-times higher UHD image in real time via AI deep learning was recognized as the Research of the Year. Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering who developed the technology won the Research of the Year Grand Prize during the 2021 KAIST Research Day ceremony on May 25. Professor Kim was lauded for conducting creative research on machine learning and deep learning-based image processing.
KAIST’s Research Day recognizes the most notable research outcomes of the year, while creating opportunities for researchers to immerse themselves into interdisciplinary research projects with their peers. The ceremony was broadcast online due to Covid-19 and announced the Ten R&D Achievement of the Year that are expected to make a significant impact.
To celebrate the award, Professor Kim gave a lecture on “Computational Imaging through Deep Learning for the Acquisition of High-Quality Images.” Focusing on the fact that advancements in artificial intelligence technology can show superior performance when used to convert low-quality videos to higher quality, he introduced some of the AI technologies that are currently being applied in the field of image restoration and quality improvement.
Professors Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and In-Cheol Park from the School of Electrical Engineering each received Research Awards, and Professor Junyong Noh from the Graduate School of Culture Technology was selected for the Innovation Award. Professors Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry and Hyungki Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering were awarded the Interdisciplinary Award as a team for their joint research.
Meanwhile, out of KAIST’s ten most notable R&D achievements, those from the field of natural and biological sciences included research on rare earth element-platinum nanoparticle catalysts by Professor Ryong Ryoo from the Department of Chemistry, real-time observations of the locational changes in all of the atoms in a molecule by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry, and an investigation on memory retention mechanisms after synapse removal from an astrocyte by Professor Won-Suk Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences.
Awardees from the engineering field were a wearable robot for paraplegics with the world’s best functionality and walking speed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, fair machine learning by Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering, and a generative adversarial networks processing unit (GANPU), an AI semiconductor that can learn from even mobiles by processing multiple and deep networks by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering.
Others selected as part of the ten research studies were the development of epigenetic reprogramming technology in tumour by Professor Pilnam Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, the development of an original technology for reverse cell aging by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, a heterogeneous metal element catalyst for atmospheric purification by Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and the Mobile Clinic Module (MCM): a negative pressure ward for epidemic hospitals by Professor Taek-jin Nam (reported at the Wall Street Journal) from the Department of Industrial Design.
2021.05.31 View 9630
Research Day Highlights the Most Impactful Technologies of the Year
Technology Converting Full HD Image to 4-Times Higher UHD Via Deep Learning Cited as the Research of the Year
The technology converting a full HD image into a four-times higher UHD image in real time via AI deep learning was recognized as the Research of the Year. Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering who developed the technology won the Research of the Year Grand Prize during the 2021 KAIST Research Day ceremony on May 25. Professor Kim was lauded for conducting creative research on machine learning and deep learning-based image processing.
KAIST’s Research Day recognizes the most notable research outcomes of the year, while creating opportunities for researchers to immerse themselves into interdisciplinary research projects with their peers. The ceremony was broadcast online due to Covid-19 and announced the Ten R&D Achievement of the Year that are expected to make a significant impact.
To celebrate the award, Professor Kim gave a lecture on “Computational Imaging through Deep Learning for the Acquisition of High-Quality Images.” Focusing on the fact that advancements in artificial intelligence technology can show superior performance when used to convert low-quality videos to higher quality, he introduced some of the AI technologies that are currently being applied in the field of image restoration and quality improvement.
Professors Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and In-Cheol Park from the School of Electrical Engineering each received Research Awards, and Professor Junyong Noh from the Graduate School of Culture Technology was selected for the Innovation Award. Professors Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry and Hyungki Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering were awarded the Interdisciplinary Award as a team for their joint research.
Meanwhile, out of KAIST’s ten most notable R&D achievements, those from the field of natural and biological sciences included research on rare earth element-platinum nanoparticle catalysts by Professor Ryong Ryoo from the Department of Chemistry, real-time observations of the locational changes in all of the atoms in a molecule by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry, and an investigation on memory retention mechanisms after synapse removal from an astrocyte by Professor Won-Suk Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences.
Awardees from the engineering field were a wearable robot for paraplegics with the world’s best functionality and walking speed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, fair machine learning by Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering, and a generative adversarial networks processing unit (GANPU), an AI semiconductor that can learn from even mobiles by processing multiple and deep networks by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering.
Others selected as part of the ten research studies were the development of epigenetic reprogramming technology in tumour by Professor Pilnam Kim from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, the development of an original technology for reverse cell aging by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, a heterogeneous metal element catalyst for atmospheric purification by Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and the Mobile Clinic Module (MCM): a negative pressure ward for epidemic hospitals by Professor Taek-jin Nam (reported at the Wall Street Journal) from the Department of Industrial Design.
2021.05.31 View 9630 -
 Professor Bumjoon Kim Named Scientist of the Month
Professor Bumjoon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering won January’s Scientist of the Month Award presented by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) on January 6. Professor Kim also received 10 million won in prize money.
Professor Kim was recognized for his research in the field of fuel cells. Since the first paper on fuel cells was published in 1839 by the German chemist Friedrich Schonbein, there has been an increase in the number of fields in which fuel cells are used, including national defense, aerospace engineering, and autonomous vehicles.
Professor Kim developed carbonized block copolymer particles with high durability and a high-performance fuel cell. Block copolymers are two different polymers cross-linked into a chain structure. Various nanostructures can be made effectively by using the attractive and repulsive forces between the chains.
Professor Kim used the membrane emulsification technique, employing a high-performance separation membrane to develop a platform that makes the mass production of highly durable carbonized particles possible, which he then used to develop high-performance energy devices like fuel cells.
The carbonized particles designed by Professor Kim and his research team were used to create the world’s more durable fuel cells that boast outstanding performance while using only five percent of the costly platinum needed for existing commercialized products.
The team’s research results were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society and Energy Environmental Science in May and July of last year.
“We have developed a fuel cell that ticks all the boxes including performance, durability, and cost,” said Professor Kim. “Related techniques will not be limited to fuel cells, but could also be applied to the development of various energy devices like solar cells and secondary cells,” he added.
(END)
2021.01.22 View 7153
Professor Bumjoon Kim Named Scientist of the Month
Professor Bumjoon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering won January’s Scientist of the Month Award presented by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) on January 6. Professor Kim also received 10 million won in prize money.
Professor Kim was recognized for his research in the field of fuel cells. Since the first paper on fuel cells was published in 1839 by the German chemist Friedrich Schonbein, there has been an increase in the number of fields in which fuel cells are used, including national defense, aerospace engineering, and autonomous vehicles.
Professor Kim developed carbonized block copolymer particles with high durability and a high-performance fuel cell. Block copolymers are two different polymers cross-linked into a chain structure. Various nanostructures can be made effectively by using the attractive and repulsive forces between the chains.
Professor Kim used the membrane emulsification technique, employing a high-performance separation membrane to develop a platform that makes the mass production of highly durable carbonized particles possible, which he then used to develop high-performance energy devices like fuel cells.
The carbonized particles designed by Professor Kim and his research team were used to create the world’s more durable fuel cells that boast outstanding performance while using only five percent of the costly platinum needed for existing commercialized products.
The team’s research results were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society and Energy Environmental Science in May and July of last year.
“We have developed a fuel cell that ticks all the boxes including performance, durability, and cost,” said Professor Kim. “Related techniques will not be limited to fuel cells, but could also be applied to the development of various energy devices like solar cells and secondary cells,” he added.
(END)
2021.01.22 View 7153 -
 Extremely Stable Perovskite Nanoparticles Films for Next-Generation Displays
Researchers have reported an extremely stable cross-linked perovskite nanoparticle that maintains a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) for 1.5 years in air and harsh liquid environments. This stable material’s design strategies, which addressed one of the most critical problems limiting their practical application, provide a breakthrough for the commercialization of perovskite nanoparticles in next-generation displays and bio-related applications.
According to the research team led by Professor Byeong-Soo Bae, their development can survive in severe environments such as water, various polar solvents, and high temperature with high humidity without additional encapsulation. This development is expected to enable perovskite nanoparticles to be applied to high color purity display applications as a practical color converting material. This result was published as the inside front cover article in Advanced Materials.
Perovskites, which consist of organics, metals, and halogen elements, have emerged as key elements in various optoelectronic applications. The power conversion efficiency of photovoltaic cells based on perovskites light absorbers has been rapidly increased. Perovskites are also great promise as a light emitter in display applications because of their low material cost, facile wavelength tunability, high (PLQY), very narrow emission band width, and wider color gamut than inorganic semiconducting nanocrystals and organic emitters. Thanks to these advantages, perovskites have been identified as a key color-converting material for next-generation high color-purity displays. In particular, perovskites are the only luminescence material that meets Rec. 2020 which is a new color standard in display industry.
However, perovskites are very unstable against heat, moisture, and light, which makes them almost impossible to use in practical applications. To solve these problems, many researchers have attempted to physically prevent perovskites from coming into contact with water molecules by passivating the perovskite grain and nanoparticle surfaces with organic ligands or inorganic shell materials, or by fabricating perovskite-polymer nanocomposites. These methods require complex processes and have limited stability in ambient air and water. Furthermore, stable perovskite nanoparticles in the various chemical environments and high temperatures with high humidity have not been reported yet.
The research team in collaboration with Seoul National University develops siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films. Here, perovskite nanoparticles are chemically crosslinked with thermally stable siloxane molecules, thereby significantly improving the stability of the perovskite nanoparticles without the need for any additional protecting layer.
Siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited a high PLQY (> 70%) value, which can be maintained over 600 days in water, various chemicals (alcohol, strong acidic and basic solutions), and high temperatures with high humidity (85℃/85%). The research team investigated the mechanisms impacting the chemical crosslinking and water molecule-induced stabilization of perovskite nanoparticles through various photo-physical analysis and density-functional theory calculation.
The research team confirmed that displays based on their siloxane-perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited higher PLQY and a wider color gamut than those of Cd-based quantum dots and demonstrated perfect color converting properties on commercial mobile phone screens. Unlike what was commonly believed in the halide perovskite field, the composite films showed excellent bio-compatibility because the siloxane matrix prevents the toxicity of Pb in perovskite nanoparticle.
By using this technology, the instability of perovskite materials, which is the biggest challenge for practical applications, is greatly improved through simple encapsulation method.
“Perovskite nanoparticle is the only photoluminescent material that can meet the next generation display color standard. Nevertheless, there has been reluctant to commercialize it due to its moisture vulnerability. The newly developed siloxane encapsulation technology will trigger more research on perovskite nanoparticles as color conversion materials and will accelerate early commercialization,” Professor Bae said.
This work was supported by the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center (WMC) of the Engineering Research Center (ERC) Project, and the Leadership Research Program funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication:
Junho Jang, Young-Hoon Kim, Sunjoon Park, Dongsuk Yoo, Hyunjin Cho, Jinhyeong Jang, Han Beom Jeong, Hyunhwan Lee, Jong Min Yuk, Chan Beum Park, Duk Young Jeon, Yong-Hyun Kim, Byeong-Soo Bae, and Tae-Woo Lee. “Extremely Stable Luminescent Crosslinked Perovskite Nanoparticles under Harsh Environments over 1.5 Years” Advanced Materials, 2020, 2005255. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202005255.
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202005255
-Profile: Prof. Byeong-Soo Bae (Corresponding author)
bsbae@kaist.ac.kr
Lab. of Optical Materials & Coating
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
2020.12.29 View 8119
Extremely Stable Perovskite Nanoparticles Films for Next-Generation Displays
Researchers have reported an extremely stable cross-linked perovskite nanoparticle that maintains a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) for 1.5 years in air and harsh liquid environments. This stable material’s design strategies, which addressed one of the most critical problems limiting their practical application, provide a breakthrough for the commercialization of perovskite nanoparticles in next-generation displays and bio-related applications.
According to the research team led by Professor Byeong-Soo Bae, their development can survive in severe environments such as water, various polar solvents, and high temperature with high humidity without additional encapsulation. This development is expected to enable perovskite nanoparticles to be applied to high color purity display applications as a practical color converting material. This result was published as the inside front cover article in Advanced Materials.
Perovskites, which consist of organics, metals, and halogen elements, have emerged as key elements in various optoelectronic applications. The power conversion efficiency of photovoltaic cells based on perovskites light absorbers has been rapidly increased. Perovskites are also great promise as a light emitter in display applications because of their low material cost, facile wavelength tunability, high (PLQY), very narrow emission band width, and wider color gamut than inorganic semiconducting nanocrystals and organic emitters. Thanks to these advantages, perovskites have been identified as a key color-converting material for next-generation high color-purity displays. In particular, perovskites are the only luminescence material that meets Rec. 2020 which is a new color standard in display industry.
However, perovskites are very unstable against heat, moisture, and light, which makes them almost impossible to use in practical applications. To solve these problems, many researchers have attempted to physically prevent perovskites from coming into contact with water molecules by passivating the perovskite grain and nanoparticle surfaces with organic ligands or inorganic shell materials, or by fabricating perovskite-polymer nanocomposites. These methods require complex processes and have limited stability in ambient air and water. Furthermore, stable perovskite nanoparticles in the various chemical environments and high temperatures with high humidity have not been reported yet.
The research team in collaboration with Seoul National University develops siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films. Here, perovskite nanoparticles are chemically crosslinked with thermally stable siloxane molecules, thereby significantly improving the stability of the perovskite nanoparticles without the need for any additional protecting layer.
Siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited a high PLQY (> 70%) value, which can be maintained over 600 days in water, various chemicals (alcohol, strong acidic and basic solutions), and high temperatures with high humidity (85℃/85%). The research team investigated the mechanisms impacting the chemical crosslinking and water molecule-induced stabilization of perovskite nanoparticles through various photo-physical analysis and density-functional theory calculation.
The research team confirmed that displays based on their siloxane-perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited higher PLQY and a wider color gamut than those of Cd-based quantum dots and demonstrated perfect color converting properties on commercial mobile phone screens. Unlike what was commonly believed in the halide perovskite field, the composite films showed excellent bio-compatibility because the siloxane matrix prevents the toxicity of Pb in perovskite nanoparticle.
By using this technology, the instability of perovskite materials, which is the biggest challenge for practical applications, is greatly improved through simple encapsulation method.
“Perovskite nanoparticle is the only photoluminescent material that can meet the next generation display color standard. Nevertheless, there has been reluctant to commercialize it due to its moisture vulnerability. The newly developed siloxane encapsulation technology will trigger more research on perovskite nanoparticles as color conversion materials and will accelerate early commercialization,” Professor Bae said.
This work was supported by the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center (WMC) of the Engineering Research Center (ERC) Project, and the Leadership Research Program funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication:
Junho Jang, Young-Hoon Kim, Sunjoon Park, Dongsuk Yoo, Hyunjin Cho, Jinhyeong Jang, Han Beom Jeong, Hyunhwan Lee, Jong Min Yuk, Chan Beum Park, Duk Young Jeon, Yong-Hyun Kim, Byeong-Soo Bae, and Tae-Woo Lee. “Extremely Stable Luminescent Crosslinked Perovskite Nanoparticles under Harsh Environments over 1.5 Years” Advanced Materials, 2020, 2005255. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202005255.
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202005255
-Profile: Prof. Byeong-Soo Bae (Corresponding author)
bsbae@kaist.ac.kr
Lab. of Optical Materials & Coating
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
2020.12.29 View 8119