BIO
-
 Professor Il-Doo Kim Named Scientist of the Year by the Journalists
Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering was named the 2019 Scientist of the Year by Korean science journalists. The award was conferred at the 2019 Science Press Night ceremony of the Korea Science Journalists Association (KSJA) on November 29.
Professor Kim focuses on developing nanofiber gas sensors for diagnosing diseases in advance by analyzing exhaled biomarkers with electrospinning technology. His outstanding research was praised and selected as one of the top 10 nanotechnology of 2019 by the Korea Nano Technology Research Society (KoNTRS), the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE).
Professor Kim was honored with the QIAN Baojun Fiber Award, which is awarded every two years by Donghua University in Shanghai, China to recognize outstanding contributions in fiber science and technology. Professor Kim was also elected as an academician of the Asia Pacific Academy of Materials (APAM) on November 21 in Guangzhou, China.
In May, Professor Kim was appointed as an associate editor of ACS Nano, a leading international research journal in the field of nanoscience. In his editorial published in the May issue of ACS Nano, Professor Kim introduced and shared the history of KAIST and its vision for the future with other members of the journal. He hopes this will help with promoting a closer relationship between the members of the journal and KAIST moving forward.
“Above all,” he said in his acceptance speech, “the greatest news for me as an educator is that the first PhD graduate from our lab, Dr. Seonjin Choi, was appointed as the youngest professor in the Division of Materials Science and Engineering at Hanyang University on September 1.”
2019.12.17 View 7570
Professor Il-Doo Kim Named Scientist of the Year by the Journalists
Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering was named the 2019 Scientist of the Year by Korean science journalists. The award was conferred at the 2019 Science Press Night ceremony of the Korea Science Journalists Association (KSJA) on November 29.
Professor Kim focuses on developing nanofiber gas sensors for diagnosing diseases in advance by analyzing exhaled biomarkers with electrospinning technology. His outstanding research was praised and selected as one of the top 10 nanotechnology of 2019 by the Korea Nano Technology Research Society (KoNTRS), the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE).
Professor Kim was honored with the QIAN Baojun Fiber Award, which is awarded every two years by Donghua University in Shanghai, China to recognize outstanding contributions in fiber science and technology. Professor Kim was also elected as an academician of the Asia Pacific Academy of Materials (APAM) on November 21 in Guangzhou, China.
In May, Professor Kim was appointed as an associate editor of ACS Nano, a leading international research journal in the field of nanoscience. In his editorial published in the May issue of ACS Nano, Professor Kim introduced and shared the history of KAIST and its vision for the future with other members of the journal. He hopes this will help with promoting a closer relationship between the members of the journal and KAIST moving forward.
“Above all,” he said in his acceptance speech, “the greatest news for me as an educator is that the first PhD graduate from our lab, Dr. Seonjin Choi, was appointed as the youngest professor in the Division of Materials Science and Engineering at Hanyang University on September 1.”
2019.12.17 View 7570 -
 Tungsten Suboxide Improves the Efficiency of Platinum in Hydrogen Production
< PhD Candidate Jinkyu Park and Professor Jinwoo Lee >
Researchers presented a new strategy for enhancing catalytic activity using tungsten suboxide as a single-atom catalyst (SAC). This strategy, which significantly improves hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in metal platinum (pt) by 16.3 times, sheds light on the development of new electrochemical catalyst technologies.
Hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. However, most of the conventional industrial hydrogen production methods come with environmental issues, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
Electrochemical water splitting is considered a potential approach for clean hydrogen production. Pt is one of the most commonly used catalysts to improve HER performance in electrochemical water splitting, but the high cost and scarcity of Pt remain key obstacles to mass commercial applications.
SACs, where all metal species are individually dispersed on a desired support material, have been identified as one way to reduce the amount of Pt usage, as they offer the maximum number of surface exposed Pt atoms.
Inspired by earlier studies, which mainly focused on SACs supported by carbon-based materials, a KAIST research team led by Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering investigated the influence of support materials on the performance of SACs.
Professor Lee and his researchers suggested mesoporous tungsten suboxide as a new support material for atomically dispersed Pt, as this was expected to provide high electronic conductivity and have a synergetic effect with Pt.
They compared the performance of single-atom Pt supported by carbon and tungsten suboxide respectively. The results revealed that the support effect occurred with tungsten suboxide, in which the mass activity of a single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide was 2.1 times greater than that of single-atom Pt supported by carbon, and 16.3 times higher than that of Pt nanoparticles supported by carbon.
The team indicated a change in the electronic structure of Pt via charge transfer from tungsten suboxide to Pt. This phenomenon was reported as a result of strong metal-support interaction between Pt and tungsten suboxide.
HER performance can be improved not only by changing the electronic structure of the supported metal, but also by inducing another support effect, the spillover effect, the research group reported. Hydrogen spillover is a phenomenon where adsorbed hydrogen migrates from one surface to another, and it occurs more easily as the Pt size becomes smaller.
The researchers compared the performance of single-atom Pt and Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide. The single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide exhibited a higher degree of hydrogen spillover phenomenon, which enhanced the Pt mass activity for hydrogen evolution up to 10.7 times compared to Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide.
Professor Lee said, “Choosing the right support material is important for improving electrocatalysis in hydrogen production. The tungsten suboxide catalyst we used to support Pt in our study implies that interactions between the well-matched metal and support can drastically enhance the efficiency of the process.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and introduced in the International Edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
Figure. Schematic representation of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of pseudo single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide
-Publication
Jinkyu Park, Dr. Seonggyu Lee, Hee-Eun Kim, Ara Cho, Seongbeen Kim, Dr. Youngjin Ye, Prof. Jeong Woo Han, Prof. Hyunjoo Lee, Dr. Jong Hyun Jang, and Prof. Jinwoo Lee. 2019. Investigation of the Support Effect in Atomically Dispersed Pt on WO3−x for Utilization of Pt in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. International Edition of Angewandte Chemie. Volume No. 58. Issue No. 45. 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908122
-ProfileProfessor Jinwoo LeeConvergence of Energy and Nano Science Laboratoryhttp://cens.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2019.10.28 View 16800
Tungsten Suboxide Improves the Efficiency of Platinum in Hydrogen Production
< PhD Candidate Jinkyu Park and Professor Jinwoo Lee >
Researchers presented a new strategy for enhancing catalytic activity using tungsten suboxide as a single-atom catalyst (SAC). This strategy, which significantly improves hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in metal platinum (pt) by 16.3 times, sheds light on the development of new electrochemical catalyst technologies.
Hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. However, most of the conventional industrial hydrogen production methods come with environmental issues, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
Electrochemical water splitting is considered a potential approach for clean hydrogen production. Pt is one of the most commonly used catalysts to improve HER performance in electrochemical water splitting, but the high cost and scarcity of Pt remain key obstacles to mass commercial applications.
SACs, where all metal species are individually dispersed on a desired support material, have been identified as one way to reduce the amount of Pt usage, as they offer the maximum number of surface exposed Pt atoms.
Inspired by earlier studies, which mainly focused on SACs supported by carbon-based materials, a KAIST research team led by Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering investigated the influence of support materials on the performance of SACs.
Professor Lee and his researchers suggested mesoporous tungsten suboxide as a new support material for atomically dispersed Pt, as this was expected to provide high electronic conductivity and have a synergetic effect with Pt.
They compared the performance of single-atom Pt supported by carbon and tungsten suboxide respectively. The results revealed that the support effect occurred with tungsten suboxide, in which the mass activity of a single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide was 2.1 times greater than that of single-atom Pt supported by carbon, and 16.3 times higher than that of Pt nanoparticles supported by carbon.
The team indicated a change in the electronic structure of Pt via charge transfer from tungsten suboxide to Pt. This phenomenon was reported as a result of strong metal-support interaction between Pt and tungsten suboxide.
HER performance can be improved not only by changing the electronic structure of the supported metal, but also by inducing another support effect, the spillover effect, the research group reported. Hydrogen spillover is a phenomenon where adsorbed hydrogen migrates from one surface to another, and it occurs more easily as the Pt size becomes smaller.
The researchers compared the performance of single-atom Pt and Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide. The single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide exhibited a higher degree of hydrogen spillover phenomenon, which enhanced the Pt mass activity for hydrogen evolution up to 10.7 times compared to Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide.
Professor Lee said, “Choosing the right support material is important for improving electrocatalysis in hydrogen production. The tungsten suboxide catalyst we used to support Pt in our study implies that interactions between the well-matched metal and support can drastically enhance the efficiency of the process.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and introduced in the International Edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
Figure. Schematic representation of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of pseudo single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide
-Publication
Jinkyu Park, Dr. Seonggyu Lee, Hee-Eun Kim, Ara Cho, Seongbeen Kim, Dr. Youngjin Ye, Prof. Jeong Woo Han, Prof. Hyunjoo Lee, Dr. Jong Hyun Jang, and Prof. Jinwoo Lee. 2019. Investigation of the Support Effect in Atomically Dispersed Pt on WO3−x for Utilization of Pt in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. International Edition of Angewandte Chemie. Volume No. 58. Issue No. 45. 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908122
-ProfileProfessor Jinwoo LeeConvergence of Energy and Nano Science Laboratoryhttp://cens.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2019.10.28 View 16800 -
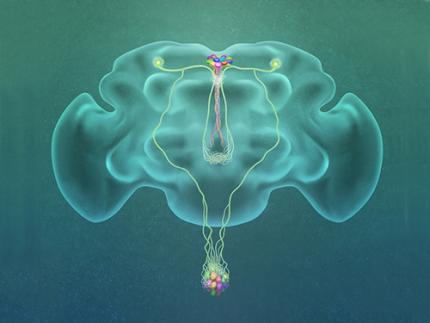 A Single, Master Switch for Sugar Levels?
When a fly eats sugar, a single brain cell sends simultaneous messages to stimulate one hormone and inhibit another to control glucose levels in the body. Further research into this control system with remarkable precision could shed light on the neural mechanisms of diabetes and obesity in humans .
A single neuron appears to monitor and control sugar levels in the fly body, according to research published this week in Nature. This new insight into the mechanisms in the fly brain that maintain a balance of two key hormones controlling glucose levels, insulin and glucagon, can provide a framework for understanding diabetes and obesity in humans.
Neurons that sense and respond to glucose were identified more than 50 years ago, but what they do in our body has remained unclear. Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and New York University School of Medicine have now found a single “glucose-sensing neuron” that appears to be the master controller in Drosophila, the vinegar fly, for maintaining an ideal glucose balance, called homeostasis.
Professor Greg Seong-Bae Suh, Dr. Yangkyun Oh and colleagues identified a key neuron that is excited by glucose, which they called CN neuron. This CN neuron has a unique shape – it has an axon (which is used to transmit information to downstream cells) that is bifurcated. One branch projects to insulin-producing cells, and sends a signal triggering the secretion of the insulin equivalent in flies. The other branch projects to glucagon-producing cells and sends a signal inhibiting the secretion of the glucagon equivalent.
When flies consume food, the levels of glucose in their body increase; this excites the CN neuron, which fires the simultaneous signals to stimulate insulin and inhibit glucagon secretion, thereby maintaining the appropriate balance between the hormones and sugar in the blood. The researchers were able to see this happening in the brain in real time by using a combination of cutting-edge fluorescent calcium imaging technology, as well as measuring hormone and sugar levels and applying highly sophisticated molecular genetic techniques.
When flies were not fed, however, the researchers observed a reduction in the activity of CN neuron, a reduction in insulin secretion and an increase in glucagon secretion. These findings indicate that these key hormones are under the direct control of the glucose-sensing neuron. Furthermore, when they silenced the CN neuron rendering dysfunctional CN neuron in flies, these animals experienced an imbalance, resulting in hyperglycemia – high levels of sugars in the blood, similar to what is observed in diabetes in humans. This further suggests that the CN neuron is critical to maintaining glucose homeostasis in animals.
While further research is required to investigate this process in humans, Suh notes this is a significant step forward in the fields of both neurobiology and endocrinology.
“This work lays the foundation for translational research to better understand how this delicate regulatory process is affected by diabetes, obesity, excessive nutrition and diets high in sugar,” Suh said.
Profile: Greg Seong-Bae Suh
seongbaesuh@kaist.ac.kr
Professor Department of Biological Sciences
KAIST
(Figure: A single glucose-excited CN neuron extends bifurcated axonal branches,
one of which innervates insulin producing cells and stimulates their activity an the other axonal branch projects to glucagon producing cells and inhibits their activity.)
2019.10.24 View 14883
A Single, Master Switch for Sugar Levels?
When a fly eats sugar, a single brain cell sends simultaneous messages to stimulate one hormone and inhibit another to control glucose levels in the body. Further research into this control system with remarkable precision could shed light on the neural mechanisms of diabetes and obesity in humans .
A single neuron appears to monitor and control sugar levels in the fly body, according to research published this week in Nature. This new insight into the mechanisms in the fly brain that maintain a balance of two key hormones controlling glucose levels, insulin and glucagon, can provide a framework for understanding diabetes and obesity in humans.
Neurons that sense and respond to glucose were identified more than 50 years ago, but what they do in our body has remained unclear. Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and New York University School of Medicine have now found a single “glucose-sensing neuron” that appears to be the master controller in Drosophila, the vinegar fly, for maintaining an ideal glucose balance, called homeostasis.
Professor Greg Seong-Bae Suh, Dr. Yangkyun Oh and colleagues identified a key neuron that is excited by glucose, which they called CN neuron. This CN neuron has a unique shape – it has an axon (which is used to transmit information to downstream cells) that is bifurcated. One branch projects to insulin-producing cells, and sends a signal triggering the secretion of the insulin equivalent in flies. The other branch projects to glucagon-producing cells and sends a signal inhibiting the secretion of the glucagon equivalent.
When flies consume food, the levels of glucose in their body increase; this excites the CN neuron, which fires the simultaneous signals to stimulate insulin and inhibit glucagon secretion, thereby maintaining the appropriate balance between the hormones and sugar in the blood. The researchers were able to see this happening in the brain in real time by using a combination of cutting-edge fluorescent calcium imaging technology, as well as measuring hormone and sugar levels and applying highly sophisticated molecular genetic techniques.
When flies were not fed, however, the researchers observed a reduction in the activity of CN neuron, a reduction in insulin secretion and an increase in glucagon secretion. These findings indicate that these key hormones are under the direct control of the glucose-sensing neuron. Furthermore, when they silenced the CN neuron rendering dysfunctional CN neuron in flies, these animals experienced an imbalance, resulting in hyperglycemia – high levels of sugars in the blood, similar to what is observed in diabetes in humans. This further suggests that the CN neuron is critical to maintaining glucose homeostasis in animals.
While further research is required to investigate this process in humans, Suh notes this is a significant step forward in the fields of both neurobiology and endocrinology.
“This work lays the foundation for translational research to better understand how this delicate regulatory process is affected by diabetes, obesity, excessive nutrition and diets high in sugar,” Suh said.
Profile: Greg Seong-Bae Suh
seongbaesuh@kaist.ac.kr
Professor Department of Biological Sciences
KAIST
(Figure: A single glucose-excited CN neuron extends bifurcated axonal branches,
one of which innervates insulin producing cells and stimulates their activity an the other axonal branch projects to glucagon producing cells and inhibits their activity.)
2019.10.24 View 14883 -
 A Mathematical Model Reveals Long-Distance Cell Communication Mechanism
How can tens of thousands of people in a large football stadium all clap together with the same beat even though they can only hear the people near them clapping?
A combination of a partial differential equation and a synthetic circuit in microbes answers this question. An interdisciplinary collaborative team of Professor Jae Kyoung Kim at KAIST, Professor Krešimir Josić at the University of Houston, and Professor Matt Bennett at Rice University has identified how a large community can communicate with each other almost simultaneously even with very short distance signaling. The research was reported at Nature Chemical Biology.
Cells often communicate using signaling molecules, which can travel only a short distance. Nevertheless, the cells can also communicate over large distances to spur collective action. The team revealed a cell communication mechanism that quickly forms a network of local interactions to spur collective action, even in large communities.
The research team used an engineered transcriptional circuit of combined positive and negative feedback loops in E. coli, which can periodically release two types of signaling molecules: activator and repressor. As the signaling molecules travel over a short distance, cells can only talk to their nearest neighbors. However, cell communities synchronize oscillatory gene expression in spatially extended systems as long as the transcriptional circuit contains a positive feedback loop for the activator.
Professor Kim said that analyzing and understanding such high-dimensional dynamics was extremely difficult. He explained, “That’s why we used high-dimensional partial differential equation to describe the system based on the interactions among various types of molecules.” Surprisingly, the mathematical model accurately simulates the synthesis of the signaling molecules in the cell and their spatial diffusion throughout the chamber and their effect on neighboring cells.
The team simplified the high-dimensional system into a one-dimensional orbit, noting that the system repeats periodically. This allowed them to discover that cells can make one voice when they lowered their own voice and listened to the others. “It turns out the positive feedback loop reduces the distance between moving points and finally makes them move all together. That’s why you clap louder when you hear applause from nearby neighbors and everyone eventually claps together at almost the same time,” said Professor Kim.
Professor Kim added, “Math is a powerful as it simplifies complex thing so that we can find an essential underlying property. This finding would not have been possible without the simplification of complex systems using mathematics."
The National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Robert A. Welch Foundation, the Hamill Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the T.J. Park Science Fellowship of POSCO supported the research.
(Figure: Complex molecular interactions among microbial consortia is simplified as interactions among points on a limit cycle (right).)
2019.10.15 View 21985
A Mathematical Model Reveals Long-Distance Cell Communication Mechanism
How can tens of thousands of people in a large football stadium all clap together with the same beat even though they can only hear the people near them clapping?
A combination of a partial differential equation and a synthetic circuit in microbes answers this question. An interdisciplinary collaborative team of Professor Jae Kyoung Kim at KAIST, Professor Krešimir Josić at the University of Houston, and Professor Matt Bennett at Rice University has identified how a large community can communicate with each other almost simultaneously even with very short distance signaling. The research was reported at Nature Chemical Biology.
Cells often communicate using signaling molecules, which can travel only a short distance. Nevertheless, the cells can also communicate over large distances to spur collective action. The team revealed a cell communication mechanism that quickly forms a network of local interactions to spur collective action, even in large communities.
The research team used an engineered transcriptional circuit of combined positive and negative feedback loops in E. coli, which can periodically release two types of signaling molecules: activator and repressor. As the signaling molecules travel over a short distance, cells can only talk to their nearest neighbors. However, cell communities synchronize oscillatory gene expression in spatially extended systems as long as the transcriptional circuit contains a positive feedback loop for the activator.
Professor Kim said that analyzing and understanding such high-dimensional dynamics was extremely difficult. He explained, “That’s why we used high-dimensional partial differential equation to describe the system based on the interactions among various types of molecules.” Surprisingly, the mathematical model accurately simulates the synthesis of the signaling molecules in the cell and their spatial diffusion throughout the chamber and their effect on neighboring cells.
The team simplified the high-dimensional system into a one-dimensional orbit, noting that the system repeats periodically. This allowed them to discover that cells can make one voice when they lowered their own voice and listened to the others. “It turns out the positive feedback loop reduces the distance between moving points and finally makes them move all together. That’s why you clap louder when you hear applause from nearby neighbors and everyone eventually claps together at almost the same time,” said Professor Kim.
Professor Kim added, “Math is a powerful as it simplifies complex thing so that we can find an essential underlying property. This finding would not have been possible without the simplification of complex systems using mathematics."
The National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Robert A. Welch Foundation, the Hamill Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the T.J. Park Science Fellowship of POSCO supported the research.
(Figure: Complex molecular interactions among microbial consortia is simplified as interactions among points on a limit cycle (right).)
2019.10.15 View 21985 -
 Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 8379
Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 8379 -
 Professor Hyun Gyu Park Appointed as Associate Editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Professor Hyun Gyu Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was appointed as an associate editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics, an international journal published by Elsevier.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics is one of the top SCI journals in the fields of chemistry and analytical science (IF 9.518 as of 2018). Professor Park was recognized and appointed as the associate editor for this journal due to his outstanding research achievements in the fields of nucleic acid engineering, biosensors, and nanobiotechnology.
Professor Park will serve as the associate editor from this October until December 2021.
(END)
2019.10.01 View 5077
Professor Hyun Gyu Park Appointed as Associate Editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Professor Hyun Gyu Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was appointed as an associate editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics, an international journal published by Elsevier.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics is one of the top SCI journals in the fields of chemistry and analytical science (IF 9.518 as of 2018). Professor Park was recognized and appointed as the associate editor for this journal due to his outstanding research achievements in the fields of nucleic acid engineering, biosensors, and nanobiotechnology.
Professor Park will serve as the associate editor from this October until December 2021.
(END)
2019.10.01 View 5077 -
 Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 7255
Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 7255 -
 Accurate Detection of Low-Level Somatic Mutation in Intractable Epilepsy
KAIST medical scientists have developed an advanced method for perfectly detecting low-level somatic mutation in patients with intractable epilepsy. Their study showed that deep sequencing replicates of major focal epilepsy genes accurately and efficiently identified low-level somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
According to the study, their diagnostic method could increase the accuracy up to 100%, unlike the conventional sequencing analysis, which stands at about 30% accuracy. This work was published in Acta Neuropathologica.
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder common in children. Approximately one third of child patients are diagnosed with intractable epilepsy despite adequate anti-epileptic medication treatment.
Somatic mutations in mTOR pathway genes, SLC35A2, and BRAF are the major genetic causes of intractable epilepsies. A clinical trial to target Focal Cortical Dysplasia type II (FCDII), the mTOR inhibitor is underway at Severance Hospital, their collaborator in Seoul, Korea. However, it is difficult to detect such somatic mutations causing intractable epilepsy because their mutational burden is less than 5%, which is similar to the level of sequencing artifacts. In the clinical field, this has remained a standing challenge for the genetic diagnosis of somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee’s team at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering analyzed paired brain and peripheral tissues from 232 intractable epilepsy patients with various brain pathologies at Severance Hospital using deep sequencing and extracted the major focal epilepsy genes.
They narrowed down target genes to eight major focal epilepsy genes, eliminating almost all of the false positive calls using deep targeted sequencing. As a result, the advanced method robustly increased the accuracy and enabled them to detect low-level somatic mutations in unmatched Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) brain samples, the most clinically relevant samples.
Professor Lee conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Dong Suk Kim and Hoon-Chul Kang at Severance Hospital of Yonsei University. He said, “This advanced method of genetic analysis will improve overall patient care by providing more comprehensive genetic counseling and informing decisions on alternative treatments.”
Professor Lee has investigated low-level somatic mutations arising in the brain for a decade. He is developing innovative diagnostics and therapeutics for untreatable brain disorders including intractable epilepsy and glioblastoma at a tech-startup called SoVarGen. “All of the technologies we used during the research were transferred to the company. This research gave us very good momentum to reach the next phase of our startup,” he remarked.
The work was supported by grants from the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Korean Health Technology R&D Project from the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development.
(Figure: Landscape of somatic and germline mutations identified in intractable epilepsy patients. a Signaling pathways for all of the mutated genes identified in this study. Bold: somatic mutation, Regular: germline mutation. b The distribution of variant allelic frequencies (VAFs) of identified somatic mutations. c The detecting rate and types of identified mutations according to histopathology. Yellow: somatic mutations, green: two-hit mutations, grey: germline mutations.)
2019.08.14 View 25565
Accurate Detection of Low-Level Somatic Mutation in Intractable Epilepsy
KAIST medical scientists have developed an advanced method for perfectly detecting low-level somatic mutation in patients with intractable epilepsy. Their study showed that deep sequencing replicates of major focal epilepsy genes accurately and efficiently identified low-level somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
According to the study, their diagnostic method could increase the accuracy up to 100%, unlike the conventional sequencing analysis, which stands at about 30% accuracy. This work was published in Acta Neuropathologica.
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder common in children. Approximately one third of child patients are diagnosed with intractable epilepsy despite adequate anti-epileptic medication treatment.
Somatic mutations in mTOR pathway genes, SLC35A2, and BRAF are the major genetic causes of intractable epilepsies. A clinical trial to target Focal Cortical Dysplasia type II (FCDII), the mTOR inhibitor is underway at Severance Hospital, their collaborator in Seoul, Korea. However, it is difficult to detect such somatic mutations causing intractable epilepsy because their mutational burden is less than 5%, which is similar to the level of sequencing artifacts. In the clinical field, this has remained a standing challenge for the genetic diagnosis of somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee’s team at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering analyzed paired brain and peripheral tissues from 232 intractable epilepsy patients with various brain pathologies at Severance Hospital using deep sequencing and extracted the major focal epilepsy genes.
They narrowed down target genes to eight major focal epilepsy genes, eliminating almost all of the false positive calls using deep targeted sequencing. As a result, the advanced method robustly increased the accuracy and enabled them to detect low-level somatic mutations in unmatched Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) brain samples, the most clinically relevant samples.
Professor Lee conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Dong Suk Kim and Hoon-Chul Kang at Severance Hospital of Yonsei University. He said, “This advanced method of genetic analysis will improve overall patient care by providing more comprehensive genetic counseling and informing decisions on alternative treatments.”
Professor Lee has investigated low-level somatic mutations arising in the brain for a decade. He is developing innovative diagnostics and therapeutics for untreatable brain disorders including intractable epilepsy and glioblastoma at a tech-startup called SoVarGen. “All of the technologies we used during the research were transferred to the company. This research gave us very good momentum to reach the next phase of our startup,” he remarked.
The work was supported by grants from the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Korean Health Technology R&D Project from the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development.
(Figure: Landscape of somatic and germline mutations identified in intractable epilepsy patients. a Signaling pathways for all of the mutated genes identified in this study. Bold: somatic mutation, Regular: germline mutation. b The distribution of variant allelic frequencies (VAFs) of identified somatic mutations. c The detecting rate and types of identified mutations according to histopathology. Yellow: somatic mutations, green: two-hit mutations, grey: germline mutations.)
2019.08.14 View 25565 -
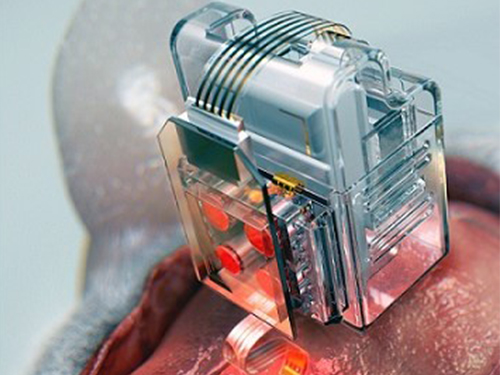 Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone
Researchers have developed a soft neural implant that can be wirelessly controlled using a smartphone. It is the first wireless neural device capable of indefinitely delivering multiple drugs and multiple colour lights, which neuroscientists believe can speed up efforts to uncover brain diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, addiction, depression, and pain.
A team under Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and his collaborators have invented a device that can control neural circuits using a tiny brain implant controlled by a smartphone. The device, using Lego-like replaceable drug cartridges and powerful, low-energy Bluetooth, can target specific neurons of interest using drugs and light for prolonged periods. This study was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“This novel device is the fruit of advanced electronics design and powerful micro and nanoscale engineering,” explained Professor Jeong. “We are interested in further developing this technology to make a brain implant for clinical applications.”
This technology significantly overshadows the conventional methods used by neuroscientists, which usually involve rigid metal tubes and optical fibers to deliver drugs and light. Apart from limiting the subject’s movement due to bulky equipment, their relatively rigid structure causes lesions in soft brain tissue over time, therefore making them not suitable for long-term implantation. Although some efforts have been made to partly mitigate adverse tissue response by incorporating soft probes and wireless platforms, the previous solutions were limited by their inability to deliver drugs for long periods of time as well as their bulky and complex control setups.
To achieve chronic wireless drug delivery, scientists had to solve the critical challenge of the exhaustion and evaporation of drugs. To combat this, the researchers invented a neural device with a replaceable drug cartridge, which could allow neuroscientists to study the same brain circuits for several months without worrying about running out of drugs.
These ‘plug-n-play’ drug cartridges were assembled into a brain implant for mice with a soft and ultrathin probe (with the thickness of a human hair), which consisted of microfluidic channels and tiny LEDs (smaller than a grain of salt), for unlimited drug doses and light delivery.
Controlled with an elegant and simple user interface on a smartphone, neuroscientists can easily trigger any specific combination or precise sequencing of light and drug delivery in any implanted target animal without the need to be physically inside the laboratory. Using these wireless neural devices, researchers can also easily setup fully automated animal studies where the behaviour of one animal could affect other animals by triggering light and/or drug delivery.
“The wireless neural device enables chronic chemical and optical neuromodulation that has never been achieved before,” said lead author Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado Boulder.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea, US National Institute of Health, National Institute on Drug Abuse, and Mallinckrodt Professorship.
(A neural implant with replaceable drug cartridges and Bluetooth low-energy can target specific neurons .)
(Micro LED controlling using smartphone application)
2019.08.07 View 28676
Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone
Researchers have developed a soft neural implant that can be wirelessly controlled using a smartphone. It is the first wireless neural device capable of indefinitely delivering multiple drugs and multiple colour lights, which neuroscientists believe can speed up efforts to uncover brain diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, addiction, depression, and pain.
A team under Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and his collaborators have invented a device that can control neural circuits using a tiny brain implant controlled by a smartphone. The device, using Lego-like replaceable drug cartridges and powerful, low-energy Bluetooth, can target specific neurons of interest using drugs and light for prolonged periods. This study was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“This novel device is the fruit of advanced electronics design and powerful micro and nanoscale engineering,” explained Professor Jeong. “We are interested in further developing this technology to make a brain implant for clinical applications.”
This technology significantly overshadows the conventional methods used by neuroscientists, which usually involve rigid metal tubes and optical fibers to deliver drugs and light. Apart from limiting the subject’s movement due to bulky equipment, their relatively rigid structure causes lesions in soft brain tissue over time, therefore making them not suitable for long-term implantation. Although some efforts have been made to partly mitigate adverse tissue response by incorporating soft probes and wireless platforms, the previous solutions were limited by their inability to deliver drugs for long periods of time as well as their bulky and complex control setups.
To achieve chronic wireless drug delivery, scientists had to solve the critical challenge of the exhaustion and evaporation of drugs. To combat this, the researchers invented a neural device with a replaceable drug cartridge, which could allow neuroscientists to study the same brain circuits for several months without worrying about running out of drugs.
These ‘plug-n-play’ drug cartridges were assembled into a brain implant for mice with a soft and ultrathin probe (with the thickness of a human hair), which consisted of microfluidic channels and tiny LEDs (smaller than a grain of salt), for unlimited drug doses and light delivery.
Controlled with an elegant and simple user interface on a smartphone, neuroscientists can easily trigger any specific combination or precise sequencing of light and drug delivery in any implanted target animal without the need to be physically inside the laboratory. Using these wireless neural devices, researchers can also easily setup fully automated animal studies where the behaviour of one animal could affect other animals by triggering light and/or drug delivery.
“The wireless neural device enables chronic chemical and optical neuromodulation that has never been achieved before,” said lead author Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado Boulder.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea, US National Institute of Health, National Institute on Drug Abuse, and Mallinckrodt Professorship.
(A neural implant with replaceable drug cartridges and Bluetooth low-energy can target specific neurons .)
(Micro LED controlling using smartphone application)
2019.08.07 View 28676 -
 Deciphering Brain Somatic Mutations Associated with Alzheimer's Disease
Researchers have found a potential link between non-inherited somatic mutations in the brain and the progression of Alzheimer’s disease
Researchers have identified somatic mutations in the brain that could contribute to the development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Their findings were published in the journal Nature Communications last week.
Decades worth of research has identified inherited mutations that lead to early-onset familial AD. Inherited mutations, however, are behind at most half the cases of late onset sporadic AD, in which there is no family history of the disease. But the genetic factors causing the other half of these sporadic cases have been unclear.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and colleagues analysed the DNA present in post-mortem hippocampal formations and in blood samples from people aged 70 to 96 with AD and age-matched controls. They specifically looked for non-inherited somatic mutations in their brains using high-depth whole exome sequencing.
The team developed a bioinformatics pipeline that enabled them to detect low-level brain somatic single nucleotide variations (SNVs) – mutations that involve the substitution of a single nucleotide with another nucleotide. Brain somatic SNVs have been reported on and accumulate throughout our lives and can sometimes be associated with a range of neurological diseases.
The number of somatic SNVs did not differ between individuals with AD and non-demented controls. Interestingly, somatic SNVs in AD brains arise about 4.8 times more slowly than in blood. When the team performed gene-set enrichment tests, 26.9 percent of the AD brain samples had pathogenic brain somatic SNVs known to be linked to hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins, which is one of major hallmarks of AD.
Then, they pinpointed a pathogenic SNV in the PIN1 gene, a cis/trans isomerase that balances phosphorylation in tau proteins, found in one AD patient’s brain. They found the mutation was 4.9 time more abundant in AT8-positive – a marker for hyper-phosphorylated tau proteins– neurons in the entorhinal cortex than the bulk hippocampal tissue. Furthermore, in a series of functional assays, they observed the mutation causing a loss of function in PIN1 and such haploinsufficiency increased the phosphorylation and aggregation of tau proteins.
“Our study provides new insights into the molecular genetic factors behind Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases potentially linked to somatic mutations in the brain,” said Professor Lee.
The team is planning to expand their study to a larger cohort in order to establish stronger links between these brain somatic mutations and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.
(Figure 1. Bioinformatic pipeline for detecting low-level brain somatic mutations in AD and non-AD.)
(Figure 2. Pathogenic brain somatic mutations associated with tau phosphorylation are significantly enriched in AD brains.)
(Figure 3. A pathogenic brain somatic mutation in PIN1 (c. 477 C>T) is a loss-of-function and related functional assays show its haploinsufficiency increases phosphorylation and aggregation of tau.)
2019.07.19 View 33293
Deciphering Brain Somatic Mutations Associated with Alzheimer's Disease
Researchers have found a potential link between non-inherited somatic mutations in the brain and the progression of Alzheimer’s disease
Researchers have identified somatic mutations in the brain that could contribute to the development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Their findings were published in the journal Nature Communications last week.
Decades worth of research has identified inherited mutations that lead to early-onset familial AD. Inherited mutations, however, are behind at most half the cases of late onset sporadic AD, in which there is no family history of the disease. But the genetic factors causing the other half of these sporadic cases have been unclear.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and colleagues analysed the DNA present in post-mortem hippocampal formations and in blood samples from people aged 70 to 96 with AD and age-matched controls. They specifically looked for non-inherited somatic mutations in their brains using high-depth whole exome sequencing.
The team developed a bioinformatics pipeline that enabled them to detect low-level brain somatic single nucleotide variations (SNVs) – mutations that involve the substitution of a single nucleotide with another nucleotide. Brain somatic SNVs have been reported on and accumulate throughout our lives and can sometimes be associated with a range of neurological diseases.
The number of somatic SNVs did not differ between individuals with AD and non-demented controls. Interestingly, somatic SNVs in AD brains arise about 4.8 times more slowly than in blood. When the team performed gene-set enrichment tests, 26.9 percent of the AD brain samples had pathogenic brain somatic SNVs known to be linked to hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins, which is one of major hallmarks of AD.
Then, they pinpointed a pathogenic SNV in the PIN1 gene, a cis/trans isomerase that balances phosphorylation in tau proteins, found in one AD patient’s brain. They found the mutation was 4.9 time more abundant in AT8-positive – a marker for hyper-phosphorylated tau proteins– neurons in the entorhinal cortex than the bulk hippocampal tissue. Furthermore, in a series of functional assays, they observed the mutation causing a loss of function in PIN1 and such haploinsufficiency increased the phosphorylation and aggregation of tau proteins.
“Our study provides new insights into the molecular genetic factors behind Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases potentially linked to somatic mutations in the brain,” said Professor Lee.
The team is planning to expand their study to a larger cohort in order to establish stronger links between these brain somatic mutations and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.
(Figure 1. Bioinformatic pipeline for detecting low-level brain somatic mutations in AD and non-AD.)
(Figure 2. Pathogenic brain somatic mutations associated with tau phosphorylation are significantly enriched in AD brains.)
(Figure 3. A pathogenic brain somatic mutation in PIN1 (c. 477 C>T) is a loss-of-function and related functional assays show its haploinsufficiency increases phosphorylation and aggregation of tau.)
2019.07.19 View 33293 -
 Mathematical Modeling Makes a Breakthrough for a New CRSD Medication
PhD Candidate Dae Wook Kim (Left) and Professor Jae Kyoung Kim (Right)
- Systems approach reveals photosensitivity and PER2 level as determinants of clock-modulator efficacy -
Mathematicians’ new modeling has identified major sources of interspecies and inter-individual variations in the clinical efficacy of a clock-modulating drug: photosensitivity and PER2 level. This enabled precision medicine for circadian disruption.
A KAIST mathematics research team led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim, in collaboration with Pfizer, applied a combination of mathematical modeling and simulation tools for circadian rhythms sleep disorders (CRSDs) to analyze the animal data generated by Pfizer. This study was reported in Molecular Systems Biology as the cover article on July 8.
Pharmaceutical companies have conducted extensive studies on animals to determine the candidacy of this new medication. However, the results of animal testing do not always translate to the same effects in human trials. Furthermore, even between humans, efficacy differs across individuals depending on an individual’s genetic and environmental factors, which require different treatment strategies.
To overcome these obstacles, KAIST mathematicians and their collaborators developed adaptive chronotherapeutics to identify precise dosing regimens that could restore normal circadian phase under different conditions.
A circadian rhythm is a 24-hour cycle in the physiological processes of living creatures, including humans. A biological clock in the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus in the human brain sets the time for various human behaviors such as sleep.
A disruption of the endogenous timekeeping system caused by changes in one’s life pattern leads to advanced or delayed sleep-wake cycle phase and a desynchronization between sleep-wake rhythms, resulting in CRSDs. To restore the normal timing of sleep, timing of the circadian clock could be adjusted pharmacologically.
Pfizer identified PF-670462, which can adjust the timing of circadian clock by inhibiting the core clock kinase of the circadian clock (CK1d/e). However, the efficacy of PF-670462 significantly differs between nocturnal mice and diurnal monkeys, whose sleeping times are opposite.
The research team discovered the source of such interspecies variations in drug response by performing thousands of virtual experiments using a mathematical model, which describes biochemical interactions among clock molecules and PF-670462. The result suggests that the effect of PF-670462 is reduced by light exposure in diurnal primates more than in nocturnal mice. This indicates that the strong counteracting effect of light must be considered in order to effectively regulate the circadian clock of diurnal humans using PF-670462.
Furthermore, the team also found the source of inter-patients variations in drug efficacy using virtual patients whose circadian clocks were disrupted due to various mutations. The degree of perturbation in the endogenous level of the core clock molecule PER2 affects the efficacy.
This explains why the clinical outcomes of clock-modulating drugs are highly variable and certain subtypes are unresponsive to treatment. Furthermore, this points out the limitations of current treatment strategies tailored to only the patient’s sleep and wake time but not to the molecular cause of sleep disorders.
PhD candidate Dae Wook Kim, who is the first author, said that this motivates the team to develop an adaptive chronotherapy, which identifies a personalized optimal dosing time of day by tracking the sleep-wake up time of patients via a wearable device and allows for a precision medicine approach for CRSDs.
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim said, "As a mathematician, I am excited to help enable the advancement of a new drug candidate, which can improve the lives of so many patients. I hope this result promotes more collaborations in this translational research.”
This research was supported by a Pfizer grant to KAIST (G01160179), the Human Frontiers Science Program Organization (RGY0063/2017), and a National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea Grant (NRF-2016 RICIB 3008468 and NRF-2017-Fostering Core Leaders of the Future Basic Science Program/ Global Ph.D. Fellowship Program).
Figure 1. Interspecies and Inter-patients Variations in PF-670462 Efficacy
Figure 2. Journal Cover Page
Publication:
Dae Wook Kim, Cheng Chang, Xian Chen, Angela C Doran, Francois Gaudreault, Travis Wager, George J DeMarco, and Jae Kyoung Kim. 2019. Systems approach reveals photosensitivity and PER2 level as determinants of clock-modulator efficacy. Molecular Systems Biology. EMBO Press, Heidelberg, Germany, Vol. 15, Issue No. 7, Article, 16 pages. https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.20198838
Profile: Prof. Jae Kyoung Kim, PhD
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
Associate Professor
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Dae Wook Kim, PhD Candidate
0308kdo@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
PhD Candidate
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Dr. Cheng Chang, PhD
cheng.chang@pfizer.com
Associate Director of Clinical Pharmacology
Clinical Pharmacology, Global Product Development
Pfizer
https://www.pfizer.com/ Groton 06340, USA
(END)
2019.07.09 View 31983
Mathematical Modeling Makes a Breakthrough for a New CRSD Medication
PhD Candidate Dae Wook Kim (Left) and Professor Jae Kyoung Kim (Right)
- Systems approach reveals photosensitivity and PER2 level as determinants of clock-modulator efficacy -
Mathematicians’ new modeling has identified major sources of interspecies and inter-individual variations in the clinical efficacy of a clock-modulating drug: photosensitivity and PER2 level. This enabled precision medicine for circadian disruption.
A KAIST mathematics research team led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim, in collaboration with Pfizer, applied a combination of mathematical modeling and simulation tools for circadian rhythms sleep disorders (CRSDs) to analyze the animal data generated by Pfizer. This study was reported in Molecular Systems Biology as the cover article on July 8.
Pharmaceutical companies have conducted extensive studies on animals to determine the candidacy of this new medication. However, the results of animal testing do not always translate to the same effects in human trials. Furthermore, even between humans, efficacy differs across individuals depending on an individual’s genetic and environmental factors, which require different treatment strategies.
To overcome these obstacles, KAIST mathematicians and their collaborators developed adaptive chronotherapeutics to identify precise dosing regimens that could restore normal circadian phase under different conditions.
A circadian rhythm is a 24-hour cycle in the physiological processes of living creatures, including humans. A biological clock in the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus in the human brain sets the time for various human behaviors such as sleep.
A disruption of the endogenous timekeeping system caused by changes in one’s life pattern leads to advanced or delayed sleep-wake cycle phase and a desynchronization between sleep-wake rhythms, resulting in CRSDs. To restore the normal timing of sleep, timing of the circadian clock could be adjusted pharmacologically.
Pfizer identified PF-670462, which can adjust the timing of circadian clock by inhibiting the core clock kinase of the circadian clock (CK1d/e). However, the efficacy of PF-670462 significantly differs between nocturnal mice and diurnal monkeys, whose sleeping times are opposite.
The research team discovered the source of such interspecies variations in drug response by performing thousands of virtual experiments using a mathematical model, which describes biochemical interactions among clock molecules and PF-670462. The result suggests that the effect of PF-670462 is reduced by light exposure in diurnal primates more than in nocturnal mice. This indicates that the strong counteracting effect of light must be considered in order to effectively regulate the circadian clock of diurnal humans using PF-670462.
Furthermore, the team also found the source of inter-patients variations in drug efficacy using virtual patients whose circadian clocks were disrupted due to various mutations. The degree of perturbation in the endogenous level of the core clock molecule PER2 affects the efficacy.
This explains why the clinical outcomes of clock-modulating drugs are highly variable and certain subtypes are unresponsive to treatment. Furthermore, this points out the limitations of current treatment strategies tailored to only the patient’s sleep and wake time but not to the molecular cause of sleep disorders.
PhD candidate Dae Wook Kim, who is the first author, said that this motivates the team to develop an adaptive chronotherapy, which identifies a personalized optimal dosing time of day by tracking the sleep-wake up time of patients via a wearable device and allows for a precision medicine approach for CRSDs.
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim said, "As a mathematician, I am excited to help enable the advancement of a new drug candidate, which can improve the lives of so many patients. I hope this result promotes more collaborations in this translational research.”
This research was supported by a Pfizer grant to KAIST (G01160179), the Human Frontiers Science Program Organization (RGY0063/2017), and a National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea Grant (NRF-2016 RICIB 3008468 and NRF-2017-Fostering Core Leaders of the Future Basic Science Program/ Global Ph.D. Fellowship Program).
Figure 1. Interspecies and Inter-patients Variations in PF-670462 Efficacy
Figure 2. Journal Cover Page
Publication:
Dae Wook Kim, Cheng Chang, Xian Chen, Angela C Doran, Francois Gaudreault, Travis Wager, George J DeMarco, and Jae Kyoung Kim. 2019. Systems approach reveals photosensitivity and PER2 level as determinants of clock-modulator efficacy. Molecular Systems Biology. EMBO Press, Heidelberg, Germany, Vol. 15, Issue No. 7, Article, 16 pages. https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.20198838
Profile: Prof. Jae Kyoung Kim, PhD
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
Associate Professor
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Dae Wook Kim, PhD Candidate
0308kdo@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
PhD Candidate
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Dr. Cheng Chang, PhD
cheng.chang@pfizer.com
Associate Director of Clinical Pharmacology
Clinical Pharmacology, Global Product Development
Pfizer
https://www.pfizer.com/ Groton 06340, USA
(END)
2019.07.09 View 31983 -
 Deep Learning-Powered 'DeepEC' Helps Accurately Understand Enzyme Functions
(Figure: Overall scheme of DeepEC)
A deep learning-powered computational framework, ‘DeepEC,’ will allow the high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers, which is essential for the accurate understanding of enzyme functions.
A team of Dr. Jae Yong Ryu, Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST reported the computational framework powered by deep learning that predicts enzyme commission (EC) numbers with high precision in a high-throughput manner.
DeepEC takes a protein sequence as an input and accurately predicts EC numbers as an output. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions and EC numbers consisting of four level numbers (i.e., a.b.c.d) indicate biochemical reactions. Thus, the identification of EC numbers is critical for accurately understanding enzyme functions and metabolism.
EC numbers are usually given to a protein sequence encoding an enzyme during a genome annotation procedure. Because of the importance of EC numbers, several EC number prediction tools have been developed, but they have room for further improvement with respect to computation time, precision, coverage, and the total size of the files needed for the EC number prediction.
DeepEC uses three convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a major engine for the prediction of EC numbers, and also implements homology analysis for EC numbers if the three CNNs do not produce reliable EC numbers for a given protein sequence. DeepEC was developed by using a gold standard dataset covering 1,388,606 protein sequences and 4,669 EC numbers.
In particular, benchmarking studies of DeepEC and five other representative EC number prediction tools showed that DeepEC made the most precise and fastest predictions for EC numbers. DeepEC also required the smallest disk space for implementation, which makes it an ideal third-party software component.
Furthermore, DeepEC was the most sensitive in detecting enzymatic function loss as a result of mutations in domains/binding site residue of protein sequences; in this comparative analysis, all the domains or binding site residue were substituted with L-alanine residue in order to remove the protein function, which is known as the L-alanine scanning method.
This study was published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 20, 2019, entitled “Deep learning enables high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers.”
“DeepEC can be used as an independent tool and also as a third-party software component in combination with other computational platforms that examine metabolic reactions. DeepEC is freely available online,” said Professor Kim.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “With DeepEC, it has become possible to process ever-increasing volumes of protein sequence data more efficiently and more accurately.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea. This work was also funded by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean government, the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile:
-Professor Hyun Uk Kim (ehukim@kaist.ac.kr)
https://sites.google.com/view/ehukim
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (leesy@kaist.ac.kr)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
2019.07.09 View 32494
Deep Learning-Powered 'DeepEC' Helps Accurately Understand Enzyme Functions
(Figure: Overall scheme of DeepEC)
A deep learning-powered computational framework, ‘DeepEC,’ will allow the high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers, which is essential for the accurate understanding of enzyme functions.
A team of Dr. Jae Yong Ryu, Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST reported the computational framework powered by deep learning that predicts enzyme commission (EC) numbers with high precision in a high-throughput manner.
DeepEC takes a protein sequence as an input and accurately predicts EC numbers as an output. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions and EC numbers consisting of four level numbers (i.e., a.b.c.d) indicate biochemical reactions. Thus, the identification of EC numbers is critical for accurately understanding enzyme functions and metabolism.
EC numbers are usually given to a protein sequence encoding an enzyme during a genome annotation procedure. Because of the importance of EC numbers, several EC number prediction tools have been developed, but they have room for further improvement with respect to computation time, precision, coverage, and the total size of the files needed for the EC number prediction.
DeepEC uses three convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a major engine for the prediction of EC numbers, and also implements homology analysis for EC numbers if the three CNNs do not produce reliable EC numbers for a given protein sequence. DeepEC was developed by using a gold standard dataset covering 1,388,606 protein sequences and 4,669 EC numbers.
In particular, benchmarking studies of DeepEC and five other representative EC number prediction tools showed that DeepEC made the most precise and fastest predictions for EC numbers. DeepEC also required the smallest disk space for implementation, which makes it an ideal third-party software component.
Furthermore, DeepEC was the most sensitive in detecting enzymatic function loss as a result of mutations in domains/binding site residue of protein sequences; in this comparative analysis, all the domains or binding site residue were substituted with L-alanine residue in order to remove the protein function, which is known as the L-alanine scanning method.
This study was published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 20, 2019, entitled “Deep learning enables high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers.”
“DeepEC can be used as an independent tool and also as a third-party software component in combination with other computational platforms that examine metabolic reactions. DeepEC is freely available online,” said Professor Kim.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “With DeepEC, it has become possible to process ever-increasing volumes of protein sequence data more efficiently and more accurately.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea. This work was also funded by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean government, the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile:
-Professor Hyun Uk Kim (ehukim@kaist.ac.kr)
https://sites.google.com/view/ehukim
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (leesy@kaist.ac.kr)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
2019.07.09 View 32494