AI
-
 Yuji Roh Awarded 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship
KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh of the School of Electrical Engineering (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) was selected as a recipient of the 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship.
< KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) >
The Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that recognizes outstanding graduate students for their exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. This year, 36 people from around the world received the fellowship, and Yuji Roh from KAIST EE is the only recipient from universities in Korea. Each selected fellow will receive a $10,000 scholarship and an opportunity to intern at Microsoft under the guidance of an experienced researcher.
Yuji Roh was named a fellow in the field of “Machine Learning” for her outstanding achievements in Trustworthy AI. Her research highlights include designing a state-of-the-art fair training framework using batch selection and developing novel algorithms for both fair and robust training. Her works have been presented at the top machine learning conferences ICML, ICLR, and NeurIPS among others. She also co-presented a tutorial on Trustworthy AI at the top data mining conference ACM SIGKDD. She is currently interning at the NVIDIA Research AI Algorithms Group developing large-scale real-world fair AI frameworks.
The list of fellowship recipients and the interview videos are displayed on the Microsoft webpage and Youtube.
The list of recipients: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/academic-program/phd-fellowship/2022-recipients/
Interview (Global): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T4Q-XwOOoJc
Interview (Asia): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwq3R1XU8UE
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair batch selection framework]
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair and robust training framework]
2022.10.28 View 16272
Yuji Roh Awarded 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship
KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh of the School of Electrical Engineering (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) was selected as a recipient of the 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship.
< KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) >
The Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that recognizes outstanding graduate students for their exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. This year, 36 people from around the world received the fellowship, and Yuji Roh from KAIST EE is the only recipient from universities in Korea. Each selected fellow will receive a $10,000 scholarship and an opportunity to intern at Microsoft under the guidance of an experienced researcher.
Yuji Roh was named a fellow in the field of “Machine Learning” for her outstanding achievements in Trustworthy AI. Her research highlights include designing a state-of-the-art fair training framework using batch selection and developing novel algorithms for both fair and robust training. Her works have been presented at the top machine learning conferences ICML, ICLR, and NeurIPS among others. She also co-presented a tutorial on Trustworthy AI at the top data mining conference ACM SIGKDD. She is currently interning at the NVIDIA Research AI Algorithms Group developing large-scale real-world fair AI frameworks.
The list of fellowship recipients and the interview videos are displayed on the Microsoft webpage and Youtube.
The list of recipients: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/academic-program/phd-fellowship/2022-recipients/
Interview (Global): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T4Q-XwOOoJc
Interview (Asia): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwq3R1XU8UE
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair batch selection framework]
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair and robust training framework]
2022.10.28 View 16272 -
 KAIST develops biocompatible adhesive applicable to hair transplants
Aside from being used as a new medical adhesive, the new material can be applied to developing a new method of hair transplants, which cannot be repeated multiple times using current method of implanting the wholly intact follicles into the skin.
Medical adhesives are materials that can be applied to various uses such as wound healing, hemostasis, vascular anastomosis, and tissue engineering, and is expected to contribute greatly to the development of minimally invasive surgery and organ transplants. However, adhesives with high adhesion, low toxicity, and capable of decomposing in the body are rare. Adhesives based on natural proteins, such as fibrin and collagen, have high biocompatibility but insufficient adhesive strength. Synthetic polymer adhesives based on urethane or acrylic have greater adhesion but do not decompose well and may cause an inflammatory reaction in the body.
A joint research team led by Professor Myungeun Seo and Professor Haeshin Lee from the KAIST Department of Chemistry developed a bio-friendly adhesive from biocompatible polymers using tannic acid, the source of astringency in wine.
The research team focused on tannic acid, a natural polyphenolic product. Tannic acid is a polyphenol present in large amounts in fruit peels, nuts, and cacao. It has a high affinity and coating ability on other substances, and we sense the astringent taste in wine when tannic acid sticks to the surface of our tongue. When tannic acid is mixed with hydrophilic polymers, they form coacervates, or small droplets of jelly-like fluids that sink. If the polymers used are biocompatible, the mixture can be applied as a medical adhesive with low toxicity. However, coacervates are fundamentally fluid-like and cannot withstand large forces, which limits their adhesive capabilities. Thus, while research to utilize it as an adhesive has been actively discussed, a biodegradable material exhibiting strong adhesion due to its high shear strength has not yet been developed.
The research team figured out a way to enhance adhesion by mixing two biocompatible FDA-approved polymers, polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polylactic acid (PLA). While PEG, which is used widely in eyedrops and cream, is hydrophilic, PLA, a well-known bioplastic derived from lactic acid, is insoluble in water. The team combined the two into a block copolymer, which forms hydrophilic PLA aggregates in water with PEG blocks surrounding them. A coacervate created by mixing the micelles and tannic acid would behave like a solid due to the hard PLA components, and show an elastic modulus improved by a thousand times compared to PEG, enabling it to withstand much greater force as an adhesive.
Figure 1. (Above) Principle of biodegradable adhesive made by mixing poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) diblock copolymer and tannic acid in water. Yellow coacervate is precipitated through hydrogen bonding between the block copolymer micelles and tannic acid, and exhibits adhesion. After heat treatment, hydrogen bonds are rearranged to further improve adhesion. (Bottom) Adhesion comparison. Compared to using poly(ethylene glycol) polymer (d), it can support 10 times more weight when using block copolymer (e) and 60 times more weight after heat treatment (f). The indicated G' values represent the elastic modulus of the material.
Furthermore, the research team observed that the material’s mechanical properties can be improved by over a hundred times through a heating and cooling process that is used to heat-treat metals. They also discovered that this is due to the enforced interactions between micelle and tannic acid arrays.
The research team used the fact that the material shows minimal irritation to the skin and decomposes well in the body to demonstrate its possible application as an adhesive for hair transplantation through an animal experiment. Professor Haeshin Lee, who has pioneered various application fields including medical adhesives, hemostatic agents, and browning shampoo, focused on the adhesive capacities and low toxicity of polyphenols like tannic acid, and now looks forward to it improving the limitations of current hair transplant methods, which still involve follicle transfer and are difficult to be repeated multiple times.
Figure 2. (a) Overview of a hair transplantation method using a biodegradable adhesive (right) compared to a conventional hair transplantation method (left) that transplants hair containing hair follicles. After applying an adhesive to the tip of the hair, it is fixed to the skin by implanting it through a subcutaneous injection, and repeated treatment is possible. (b) Initial animal test results. One day after 15 hair transplantation, 12 strands of hair remain. If you pull the 3 strands of hair, you can see that the whole body is pulled up, indicating that it is firmly implanted into the skin. All strands of hair applied without the new adhesive material fell off, and in the case of adhesive without heat treatment, the efficiency was 1/7.
This research was conducted by first co-authors Dr. Jongmin Park (currently a senior researcher at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology) from Professor Myeongeun Seo’s team and Dr. Eunsook Park from Professor Haeshin Lee’s team in the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and through joint research with the teams led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The research was published online on August 22 in the international journal Au (JACS Au) under the title Biodegradable Block Copolymer-Tannic Acid Glue.
This study was funded by the Support Research Under Protection Project of the National Research Foundation (NRF), Leading Research Center Support Project (Research Center for Multiscale Chiral Structure), Biodegradable Plastics Commercialization and Demonstration Project by the Ministry of Trade and Industry, and institutional funding from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology.
2022.10.07 View 13687
KAIST develops biocompatible adhesive applicable to hair transplants
Aside from being used as a new medical adhesive, the new material can be applied to developing a new method of hair transplants, which cannot be repeated multiple times using current method of implanting the wholly intact follicles into the skin.
Medical adhesives are materials that can be applied to various uses such as wound healing, hemostasis, vascular anastomosis, and tissue engineering, and is expected to contribute greatly to the development of minimally invasive surgery and organ transplants. However, adhesives with high adhesion, low toxicity, and capable of decomposing in the body are rare. Adhesives based on natural proteins, such as fibrin and collagen, have high biocompatibility but insufficient adhesive strength. Synthetic polymer adhesives based on urethane or acrylic have greater adhesion but do not decompose well and may cause an inflammatory reaction in the body.
A joint research team led by Professor Myungeun Seo and Professor Haeshin Lee from the KAIST Department of Chemistry developed a bio-friendly adhesive from biocompatible polymers using tannic acid, the source of astringency in wine.
The research team focused on tannic acid, a natural polyphenolic product. Tannic acid is a polyphenol present in large amounts in fruit peels, nuts, and cacao. It has a high affinity and coating ability on other substances, and we sense the astringent taste in wine when tannic acid sticks to the surface of our tongue. When tannic acid is mixed with hydrophilic polymers, they form coacervates, or small droplets of jelly-like fluids that sink. If the polymers used are biocompatible, the mixture can be applied as a medical adhesive with low toxicity. However, coacervates are fundamentally fluid-like and cannot withstand large forces, which limits their adhesive capabilities. Thus, while research to utilize it as an adhesive has been actively discussed, a biodegradable material exhibiting strong adhesion due to its high shear strength has not yet been developed.
The research team figured out a way to enhance adhesion by mixing two biocompatible FDA-approved polymers, polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polylactic acid (PLA). While PEG, which is used widely in eyedrops and cream, is hydrophilic, PLA, a well-known bioplastic derived from lactic acid, is insoluble in water. The team combined the two into a block copolymer, which forms hydrophilic PLA aggregates in water with PEG blocks surrounding them. A coacervate created by mixing the micelles and tannic acid would behave like a solid due to the hard PLA components, and show an elastic modulus improved by a thousand times compared to PEG, enabling it to withstand much greater force as an adhesive.
Figure 1. (Above) Principle of biodegradable adhesive made by mixing poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) diblock copolymer and tannic acid in water. Yellow coacervate is precipitated through hydrogen bonding between the block copolymer micelles and tannic acid, and exhibits adhesion. After heat treatment, hydrogen bonds are rearranged to further improve adhesion. (Bottom) Adhesion comparison. Compared to using poly(ethylene glycol) polymer (d), it can support 10 times more weight when using block copolymer (e) and 60 times more weight after heat treatment (f). The indicated G' values represent the elastic modulus of the material.
Furthermore, the research team observed that the material’s mechanical properties can be improved by over a hundred times through a heating and cooling process that is used to heat-treat metals. They also discovered that this is due to the enforced interactions between micelle and tannic acid arrays.
The research team used the fact that the material shows minimal irritation to the skin and decomposes well in the body to demonstrate its possible application as an adhesive for hair transplantation through an animal experiment. Professor Haeshin Lee, who has pioneered various application fields including medical adhesives, hemostatic agents, and browning shampoo, focused on the adhesive capacities and low toxicity of polyphenols like tannic acid, and now looks forward to it improving the limitations of current hair transplant methods, which still involve follicle transfer and are difficult to be repeated multiple times.
Figure 2. (a) Overview of a hair transplantation method using a biodegradable adhesive (right) compared to a conventional hair transplantation method (left) that transplants hair containing hair follicles. After applying an adhesive to the tip of the hair, it is fixed to the skin by implanting it through a subcutaneous injection, and repeated treatment is possible. (b) Initial animal test results. One day after 15 hair transplantation, 12 strands of hair remain. If you pull the 3 strands of hair, you can see that the whole body is pulled up, indicating that it is firmly implanted into the skin. All strands of hair applied without the new adhesive material fell off, and in the case of adhesive without heat treatment, the efficiency was 1/7.
This research was conducted by first co-authors Dr. Jongmin Park (currently a senior researcher at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology) from Professor Myeongeun Seo’s team and Dr. Eunsook Park from Professor Haeshin Lee’s team in the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and through joint research with the teams led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The research was published online on August 22 in the international journal Au (JACS Au) under the title Biodegradable Block Copolymer-Tannic Acid Glue.
This study was funded by the Support Research Under Protection Project of the National Research Foundation (NRF), Leading Research Center Support Project (Research Center for Multiscale Chiral Structure), Biodegradable Plastics Commercialization and Demonstration Project by the Ministry of Trade and Industry, and institutional funding from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology.
2022.10.07 View 13687 -
 NYC-KAIST Cooperation Agreement Signed in New York for KAIST NYU Joint Campus
A ceremony was held to celebrate the signing of the Cooperative Agreement between NYC and KAIST and the presentation of the signage for KAIST NYU Joint Campus at NYU’s Kimmel Center in Manhattan.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYU President Andrew Hamilton (right)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) signed a cooperative agreement with the City of New York and had an official showing of the signage for the Joint Campus of KAIST and New York University (NYU) on September 21 at 4:00 pm (Eastern Standard Time) at NYU’s Kimmel Center in New York City with the NYC Mayor Eric Adams, the Korean Minister of Science and ICT Dr. Lee Jong-ho, NYU Chairman William Berkley, NYU President Andrew Hamilton, and other distinguished guests in attendance.
KAIST and NYU signed a Memorandum of Understanding in June about building a joint campus in an effort to educate global talent. As a follow-up measure, NYU has provided KAIST with space to begin joint research programs and held a ceremony to present the signage designed for the future KAIST NYU Campus. In line with these efforts, KAIST has also signed an agreement with New York City, the administrative authority in charge of the establishment of the campus, for mutual cooperation.
NYU is a prestigious university headquartered in Manhattan, New York. It has nurtured outstanding talents in the humanities, art, and basic sciences, including 38 Nobel Prize winners, 5 Fields Prize winners, 26 Pulitzer Prize winners, and 38 Academy Award winners to be deserving of the evaluation.
The proposed joint campus is to be centered on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) by combining NYU's excellent basic sciences and convergence research capabilities with KAIST's globally renowned science and technology capabilities. The joint initiative is expected to launch in 2023; its programs will focus on areas such as AI Basic Science, AI Convergence Brain Science, AI-Applied Cyber Security, Cyber Security, and Sustainable High-Tech Smart City/Climate Change in order to lead the Digital Era and to solve the problems that surfaced following the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, in order to prepare for the Post-AI Era, it was decided to create the “New Engineering” program for undergraduate program that employs a hyper-convergence learning model that combines project-based, problem-solving learning (PBL, PSL) pedagogy.
▲ Biomedical Engineering- Research and development of technology to respond to the entire cycle (prevention-treatment-diagnosis-prediction) for a new infectious disease (Disease X) by converging new technologies such as IT and NT with biomedical technologies
▲ AI Convergence Neuroscience- Research on brain-machine interaction and brain-based machine learning through AI technology convergence
▲ AI Science- Algorithm development and in-depth research in preparation for the post AI era
▲ Sustainability and Climate Change- R&DB for advanced smart cities, sustainability for the global environment and carbon zero
▲ Next-generation Wireless Communications- From ICT to AIT: Research on 6G/7G related technologies, new communications theories, and etc.
▲ Cyber Security- Advanced research on protection of digital information and information safety/reliability
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYC Mayor Eric Adams (right)
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus has started enlisting professors and researchers from both institutions to participate in the collaboration. The campus will also function as the headquarter that will oversee the operation of the joint research program. At Daejeon, KAIST is also setting up a location for NYU on its main campus to provide space for NYU researchers upon their visit to KAIST.
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus, which has begun to take basic shape with the space for collaboration rendered this time, is to be upgraded to “KAIST New York Campus” in the future to function also as an industry-academic cooperation campus in which that promotes strategic cooperation with industries and expands start-up opportunities. To this end, the related procedures from the detailing of the establishment plans through a preliminary feasibility studies, to deliberation and decision on whether to proceed with the establishment by the KAIST Board of Trustees, will be taken.
The KAIST NYU Campus is expected to serve as a stepping stone for the outstanding talents of KAIST to pursue their dreams in the global market and research environment while seizing the attention of the world-class talents drawn to New York at the same time. In addition, by combining NYU's strong basic academic capabilities with KAIST’s strengths, it is expected to contribute to achieving 'global innovation' by creating synergies in various fields such as education, research, and entrepreneurship. The future KAIST-NYU Campus is also expected to encompass an industry-academic cooperation campus with industrial partners and startups.
Meanwhile, KAIST is planning to expand its excellent scientific and technological capabilities to the global stage through the cooperative agreement with New York City, and to prepare a pathway for KAIST students, faculty, and startups to enter their respective fields in the global markets. In the future, KAIST plans to explore areas of cooperation in different fields, such as education, economy, society, and culture, to prepare and implement detailed cooperation plans.
< KAIST-New York City Cooperation Items (Example) >
▲ Education: Joint degree program with a university in New York City, training of key talents in the field of artificial intelligence, etc.
▲ Economy: A hub for technology startups, job creation in the tech sector, etc.
▲ Society: Economics, finance, media-related engineering research, etc.
▲ Culture: Diversity-based culture and art-tech research, etc.▲ Etc: Joint research in the field of artificial intelligence healthcare, etc.
As a global mecca for startups, education, and investment, New York has a well-developed global network for cultural diversity and successful career development, and has great power to attract various resources including funds and talented individuals. Based on this, it has established itself as a mecca of global tech companies and global top media groups, and is building the reputation as 'Silicon Alley' in addition to its legends of the ‘Wall Street'.
Dr. Andrew Hamilton, the president of NYU, said, “We’re delighted by our newly established partnership with KAIST. We see great potential in the opportunities to collaborate on development of courses, research, cutting edge technologies, university-level courses, degrees, entrepreneurship initiatives and industrial partnerships, and exchanges. We believe this partnership is very much in line with NYU’s commitment to global engagement and will make important contributions to New York’s tech sector. It’s exciting to think how much NYU and KAIST have much to learn from one another, and how much we may accomplish together.”
New York City Mayor Eric Adams said, “We’re proud to have helped facilitate this partnership between KAIST and New York University, which will be a real win for students and help drive continued innovation in our city.” He added, “From the time that senior members of our administration learned about this opportunity during a recent trip to South Korea, we have worked closely with KAIST to develop strategies for increasing their presence and investments in New York. This is the start of a relationship that I am confident will bring even more academic, business, and technological opportunities to the five boroughs.”
Dr. Kwang Hyung Lee, the president of KAIST, urged, “Based on the KAIST-NYU partnership, we must create an interdisciplinary hyper-convergence model of collaboration and use cutting-edge tools to create an innovative model for new type of problem-solving engineering education to prepare to solve the challenges facing the world.” He went on to stress, “The new fusion engineering degree program will leverage the unique strengths of the two institutions to provide a uniquely colored education not found anywhere else.” In addition, he added, “KAIST will utilize the advantages that are unique to the global city of New York to contribute to advancing the science and technology research in New York City and creating jobs in the tech sector to lead the renaissance of Silicon Alley.”
2022.09.27 View 15139
NYC-KAIST Cooperation Agreement Signed in New York for KAIST NYU Joint Campus
A ceremony was held to celebrate the signing of the Cooperative Agreement between NYC and KAIST and the presentation of the signage for KAIST NYU Joint Campus at NYU’s Kimmel Center in Manhattan.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYU President Andrew Hamilton (right)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) signed a cooperative agreement with the City of New York and had an official showing of the signage for the Joint Campus of KAIST and New York University (NYU) on September 21 at 4:00 pm (Eastern Standard Time) at NYU’s Kimmel Center in New York City with the NYC Mayor Eric Adams, the Korean Minister of Science and ICT Dr. Lee Jong-ho, NYU Chairman William Berkley, NYU President Andrew Hamilton, and other distinguished guests in attendance.
KAIST and NYU signed a Memorandum of Understanding in June about building a joint campus in an effort to educate global talent. As a follow-up measure, NYU has provided KAIST with space to begin joint research programs and held a ceremony to present the signage designed for the future KAIST NYU Campus. In line with these efforts, KAIST has also signed an agreement with New York City, the administrative authority in charge of the establishment of the campus, for mutual cooperation.
NYU is a prestigious university headquartered in Manhattan, New York. It has nurtured outstanding talents in the humanities, art, and basic sciences, including 38 Nobel Prize winners, 5 Fields Prize winners, 26 Pulitzer Prize winners, and 38 Academy Award winners to be deserving of the evaluation.
The proposed joint campus is to be centered on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) by combining NYU's excellent basic sciences and convergence research capabilities with KAIST's globally renowned science and technology capabilities. The joint initiative is expected to launch in 2023; its programs will focus on areas such as AI Basic Science, AI Convergence Brain Science, AI-Applied Cyber Security, Cyber Security, and Sustainable High-Tech Smart City/Climate Change in order to lead the Digital Era and to solve the problems that surfaced following the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, in order to prepare for the Post-AI Era, it was decided to create the “New Engineering” program for undergraduate program that employs a hyper-convergence learning model that combines project-based, problem-solving learning (PBL, PSL) pedagogy.
▲ Biomedical Engineering- Research and development of technology to respond to the entire cycle (prevention-treatment-diagnosis-prediction) for a new infectious disease (Disease X) by converging new technologies such as IT and NT with biomedical technologies
▲ AI Convergence Neuroscience- Research on brain-machine interaction and brain-based machine learning through AI technology convergence
▲ AI Science- Algorithm development and in-depth research in preparation for the post AI era
▲ Sustainability and Climate Change- R&DB for advanced smart cities, sustainability for the global environment and carbon zero
▲ Next-generation Wireless Communications- From ICT to AIT: Research on 6G/7G related technologies, new communications theories, and etc.
▲ Cyber Security- Advanced research on protection of digital information and information safety/reliability
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYC Mayor Eric Adams (right)
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus has started enlisting professors and researchers from both institutions to participate in the collaboration. The campus will also function as the headquarter that will oversee the operation of the joint research program. At Daejeon, KAIST is also setting up a location for NYU on its main campus to provide space for NYU researchers upon their visit to KAIST.
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus, which has begun to take basic shape with the space for collaboration rendered this time, is to be upgraded to “KAIST New York Campus” in the future to function also as an industry-academic cooperation campus in which that promotes strategic cooperation with industries and expands start-up opportunities. To this end, the related procedures from the detailing of the establishment plans through a preliminary feasibility studies, to deliberation and decision on whether to proceed with the establishment by the KAIST Board of Trustees, will be taken.
The KAIST NYU Campus is expected to serve as a stepping stone for the outstanding talents of KAIST to pursue their dreams in the global market and research environment while seizing the attention of the world-class talents drawn to New York at the same time. In addition, by combining NYU's strong basic academic capabilities with KAIST’s strengths, it is expected to contribute to achieving 'global innovation' by creating synergies in various fields such as education, research, and entrepreneurship. The future KAIST-NYU Campus is also expected to encompass an industry-academic cooperation campus with industrial partners and startups.
Meanwhile, KAIST is planning to expand its excellent scientific and technological capabilities to the global stage through the cooperative agreement with New York City, and to prepare a pathway for KAIST students, faculty, and startups to enter their respective fields in the global markets. In the future, KAIST plans to explore areas of cooperation in different fields, such as education, economy, society, and culture, to prepare and implement detailed cooperation plans.
< KAIST-New York City Cooperation Items (Example) >
▲ Education: Joint degree program with a university in New York City, training of key talents in the field of artificial intelligence, etc.
▲ Economy: A hub for technology startups, job creation in the tech sector, etc.
▲ Society: Economics, finance, media-related engineering research, etc.
▲ Culture: Diversity-based culture and art-tech research, etc.▲ Etc: Joint research in the field of artificial intelligence healthcare, etc.
As a global mecca for startups, education, and investment, New York has a well-developed global network for cultural diversity and successful career development, and has great power to attract various resources including funds and talented individuals. Based on this, it has established itself as a mecca of global tech companies and global top media groups, and is building the reputation as 'Silicon Alley' in addition to its legends of the ‘Wall Street'.
Dr. Andrew Hamilton, the president of NYU, said, “We’re delighted by our newly established partnership with KAIST. We see great potential in the opportunities to collaborate on development of courses, research, cutting edge technologies, university-level courses, degrees, entrepreneurship initiatives and industrial partnerships, and exchanges. We believe this partnership is very much in line with NYU’s commitment to global engagement and will make important contributions to New York’s tech sector. It’s exciting to think how much NYU and KAIST have much to learn from one another, and how much we may accomplish together.”
New York City Mayor Eric Adams said, “We’re proud to have helped facilitate this partnership between KAIST and New York University, which will be a real win for students and help drive continued innovation in our city.” He added, “From the time that senior members of our administration learned about this opportunity during a recent trip to South Korea, we have worked closely with KAIST to develop strategies for increasing their presence and investments in New York. This is the start of a relationship that I am confident will bring even more academic, business, and technological opportunities to the five boroughs.”
Dr. Kwang Hyung Lee, the president of KAIST, urged, “Based on the KAIST-NYU partnership, we must create an interdisciplinary hyper-convergence model of collaboration and use cutting-edge tools to create an innovative model for new type of problem-solving engineering education to prepare to solve the challenges facing the world.” He went on to stress, “The new fusion engineering degree program will leverage the unique strengths of the two institutions to provide a uniquely colored education not found anywhere else.” In addition, he added, “KAIST will utilize the advantages that are unique to the global city of New York to contribute to advancing the science and technology research in New York City and creating jobs in the tech sector to lead the renaissance of Silicon Alley.”
2022.09.27 View 15139 -
 Globally renowned stained-glass artist Fr. En Joon Kim appointed as a distinguished invited professor in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design
World-renowned master of stained-glass Father En Joong Kim was appointed to a two-year distinguished invited professorship in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design starting August 1, 2022
- Fr. Kim will share his life, spirit, and artistic capabilities with the members of KAIST through special lectures for undergraduate and graduate students, and through a stained-glass piece he will work on and donate to the KAIST Academic and Cultural Complex
- The 53-piece work of art will provide KAIST with fresh inspiration and add to its dynamic atmosphere
KAIST appointed the world-renowned stained-glass artist and priest Fr. En Joong Kim of the Dominican Order as a distinguished invited professor in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design. His term starts from August 1 of this year and ends on July 31, 2024.
The appointment aims to share the life, spirit, and artistic capabilities of Fr. Kim, who is internationally recognized for his creative work. The purpose of the appointment is not only to provide professional advice on lighting color and space, which are core contents of industrial design courses, but also to bring new inspiration to KAIST community.
Fr. Kim, who studied in the College of Fine Arts at Seoul National University, won the Korean Art Award in 1965, and later studied at the University of Fribourg in Switzerland and the Catholic University of Paris. Joining the Dominican Order in France in 1974, he started his career as both a priest and an artist, and continued his artistic activities via 200 exhibitions around the world and by working on the stained-glass windows of 50 European churches.
In recognition of the artistic merit of combining colorful tones with the beauty of blank spaces, a distinctive characteristic of Asian art, and Fr. Kim’s contributions to establishing such combinations, Passage Kim En Joong, an art gallery, was founded in Ambert, France in 2019, and for his artwork installed all over France, he was presented with the insignia of Officer in the Order of Arts and Letters by the French government in 2010.
Following the appointment, the KAIST Department of Industrial Design is preparing a special seminar lecture by Fr. Kim under the title “Search the Future”. Fr. Kim will share his experience and philosophy for pursuing aesthetic values and efforts. In addition, the department plans to set up a special studio for Fr. Kim to both work and interact with students, encouraging them to naturally communicate and share ideas together.
One of Fr. Kim's art piece being installed at the main administration building at KAIST.
In a studio at the KAIST Academic Cultural Complex (ACC), Fr. Kim is currently working on his 53-piece stained-glass project that, when finished, will be added to the ACC. KAISTians will be able to enjoy a master’s art on a daily basis as the 53 sheets of glasses combine to form one magnificent piece.
Fr. Kim said, “I am very happy to be a distinguished invited professor at KAIST, where excellent scientists are at work. It is my wish and prayer that my presence here may comfort the students’ hearts with artwork and art philosophy that carries sensitivity and sincerity, and that they may garner richer experiences.”
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said, “The purpose of research and art are similar in that they pioneer through endless contemplations and attempts. The art piece to be installed at ACC, which will combine 53 pieces of stained glass, resembles our school, where our members each with their own distinctive colors and textures come together create a harmonious new form known as KAIST.”
He added, “I hope that the artistic spirit of Fr. Kim, a world-class master, will be a beacon that would bring a new type of stimulation and ease here at KAIST”
KAIST also appointed world-renowned soprano Sumi Jo as a distinguished invited professor in the Graduate School of Culture Technology in October 2021, and SM Entertainment’s executive producer Soo-man Lee as a distinguished invited professor in the School of Computing in March 2022. KAIST continues to expand and incorporate science and technology into the fields of art and culture, and to establish itself as a place for joint research and creative endeavors.
2022.09.08 View 11526
Globally renowned stained-glass artist Fr. En Joon Kim appointed as a distinguished invited professor in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design
World-renowned master of stained-glass Father En Joong Kim was appointed to a two-year distinguished invited professorship in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design starting August 1, 2022
- Fr. Kim will share his life, spirit, and artistic capabilities with the members of KAIST through special lectures for undergraduate and graduate students, and through a stained-glass piece he will work on and donate to the KAIST Academic and Cultural Complex
- The 53-piece work of art will provide KAIST with fresh inspiration and add to its dynamic atmosphere
KAIST appointed the world-renowned stained-glass artist and priest Fr. En Joong Kim of the Dominican Order as a distinguished invited professor in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design. His term starts from August 1 of this year and ends on July 31, 2024.
The appointment aims to share the life, spirit, and artistic capabilities of Fr. Kim, who is internationally recognized for his creative work. The purpose of the appointment is not only to provide professional advice on lighting color and space, which are core contents of industrial design courses, but also to bring new inspiration to KAIST community.
Fr. Kim, who studied in the College of Fine Arts at Seoul National University, won the Korean Art Award in 1965, and later studied at the University of Fribourg in Switzerland and the Catholic University of Paris. Joining the Dominican Order in France in 1974, he started his career as both a priest and an artist, and continued his artistic activities via 200 exhibitions around the world and by working on the stained-glass windows of 50 European churches.
In recognition of the artistic merit of combining colorful tones with the beauty of blank spaces, a distinctive characteristic of Asian art, and Fr. Kim’s contributions to establishing such combinations, Passage Kim En Joong, an art gallery, was founded in Ambert, France in 2019, and for his artwork installed all over France, he was presented with the insignia of Officer in the Order of Arts and Letters by the French government in 2010.
Following the appointment, the KAIST Department of Industrial Design is preparing a special seminar lecture by Fr. Kim under the title “Search the Future”. Fr. Kim will share his experience and philosophy for pursuing aesthetic values and efforts. In addition, the department plans to set up a special studio for Fr. Kim to both work and interact with students, encouraging them to naturally communicate and share ideas together.
One of Fr. Kim's art piece being installed at the main administration building at KAIST.
In a studio at the KAIST Academic Cultural Complex (ACC), Fr. Kim is currently working on his 53-piece stained-glass project that, when finished, will be added to the ACC. KAISTians will be able to enjoy a master’s art on a daily basis as the 53 sheets of glasses combine to form one magnificent piece.
Fr. Kim said, “I am very happy to be a distinguished invited professor at KAIST, where excellent scientists are at work. It is my wish and prayer that my presence here may comfort the students’ hearts with artwork and art philosophy that carries sensitivity and sincerity, and that they may garner richer experiences.”
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said, “The purpose of research and art are similar in that they pioneer through endless contemplations and attempts. The art piece to be installed at ACC, which will combine 53 pieces of stained glass, resembles our school, where our members each with their own distinctive colors and textures come together create a harmonious new form known as KAIST.”
He added, “I hope that the artistic spirit of Fr. Kim, a world-class master, will be a beacon that would bring a new type of stimulation and ease here at KAIST”
KAIST also appointed world-renowned soprano Sumi Jo as a distinguished invited professor in the Graduate School of Culture Technology in October 2021, and SM Entertainment’s executive producer Soo-man Lee as a distinguished invited professor in the School of Computing in March 2022. KAIST continues to expand and incorporate science and technology into the fields of art and culture, and to establish itself as a place for joint research and creative endeavors.
2022.09.08 View 11526 -
 Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 16658
Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 16658 -
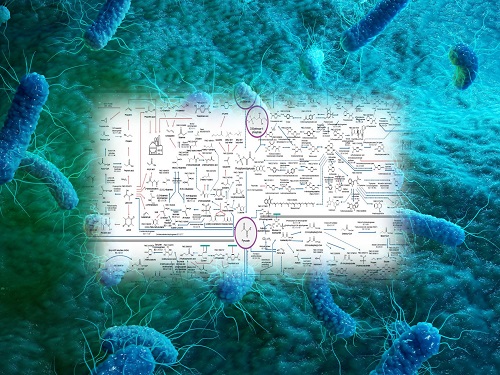 Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 18096
Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 18096 -
 KAIST Honors BMW and Hyundai with the 2022 Future Mobility of the Year Award
BMW ‘iVision Circular’, Commercial Vehicle-Hyundai Motors ‘Trailer Drone’ selected as winners of the international awards for concept cars established by KAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility to honor car makers that strive to present new visions in the field of eco-friendly design of automobiles and unmanned logistics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) hosted the “2022 Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) Awards” at the Convention Hall of the BEXCO International Motor Show at Busan in the afternoon of the 14th.
The Future Mobility of the Year Awards is an award ceremony that selects a model that showcases useful transportation technology and innovative service concepts for the future society among the set of concept cars exhibited at the motor show.
As a one-of-a-kind international concept car awards established by KAIST's Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility (Headed by Professor Jang In-Gwon), the auto journalists from 11 countries were invited to be the jurors to select the winner. With the inaugural awards ceremony held in 2019, over the past three years, automakers from around the globe, including internationally renowned automakers, such as, Volvo/Toyota (2019), Honda/Hyundai (2020), and Renault (2021), even a new start-up car manufacturer like Canoo, the winner of last year’s award for commercial vehicles, were honored for their award-winning works.
At this year’s awards ceremony, the 4th of its kind, BMW's “iVision Circular” and Hyundai's “'Trailer Drone” were selected as the best concept cars of the year, the former from the Private Mobility category and the latter from the Public & Commercial Vehicles category.
The jury consisting of 16 domestic and foreign auto journalists, including BBC Top Gear's Paul Horrell and Car Magazine’s Georg Kacher, evaluated 53 concept car contestants that made their entry last year. The jurors’ general comment was that while the trend of the global automobile market flowing fast towards electric vehicles, this year's award-winning works presented a new vision in the field of eco-friendly design and unmanned logistics.
Private Mobility Categry Winner: BMW iVision Circular
BMW's 'iVision Circular', the winner of the Private Mobility category, is an eco-friendly compact car in which all parts of the vehicle are designed with recycled and/or natural materials. It has received favorable reviews for its in-depth implementation of the concept of a futuristic eco-friendly car by manufacturing the tires from natural rubber and adopting a design that made recycling of its parts very easily when the car is to be disposed of.
Public & Commercial Vehicles Categry Winner: Hyundai Trailer Drone
Hyundai Motor Company’s “Trailer Drone”, the winner of the Public & Commercial Vehicles category, is an eco-friendly autonomous driving truck that can transport large-scale logistics from a port to a destination without a human driver while two unmanned vehicles push and drag a trailer. The concept car won supports from a large number of judges for the blueprint it presented for a groundbreaking logistics service that applied both eco-friendly hydrogen fuel cell and fully autonomous driving technology.
Jurors from overseas congratulated the development team of BMW and Hyundai Motor Company via a video message for providing a new direction for the global automobile industry as it strives to transform in line with the changes in the post-pandemic era.
Professor Bo-won Kim, the Vice President for Planning and Budget of KAIST, who presented the awards, said, “It is time for the K-Mobility wave to sweep over the global mobility industry.” “KAIST will lead in the various fields of mobility technologies to support global automakers,” he added.
Splitting the center are KAIST Vice President Bo-Won Kim on the right, and Seong-Kwon Lee,
the Deputy Mayor of the City of Busan on the left. To Kim's left is the Senior VP of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, Jean-Philippe Parain, and to Lee's Right is Sangyup Lee,
the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive VP of Hyundai Motors.
At the ceremony, along with KAIST officials, including Vice President Bo-Won Kim and Professor In-Gwon Jang, the Head of Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility, are the Deputy Mayor Seong-Kwon Lee of the City of Busan and the figures from the automobile industry, including Jean-Philippe Parain, the Senior Vice President of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, who is visiting Korea to receive the '2022 Future Mobility' award, and Sangyup Lee, the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive Vice President of Hyundai Motor Company, were in the attendance.
More information about the awards ceremony and winning works are available at the official website of this year's Future Mobility Awards (www.fmoty.org).
Profile:In-Gwon Jang, Ph.D.Presidentthe Organizing Committeethe Future Mobility of the Year Awardshttp://www.fmoty.org/
Head ProfessorKAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobilityhttps://gt.kaist.ac.kr
2022.07.14 View 17666
KAIST Honors BMW and Hyundai with the 2022 Future Mobility of the Year Award
BMW ‘iVision Circular’, Commercial Vehicle-Hyundai Motors ‘Trailer Drone’ selected as winners of the international awards for concept cars established by KAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility to honor car makers that strive to present new visions in the field of eco-friendly design of automobiles and unmanned logistics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) hosted the “2022 Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) Awards” at the Convention Hall of the BEXCO International Motor Show at Busan in the afternoon of the 14th.
The Future Mobility of the Year Awards is an award ceremony that selects a model that showcases useful transportation technology and innovative service concepts for the future society among the set of concept cars exhibited at the motor show.
As a one-of-a-kind international concept car awards established by KAIST's Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility (Headed by Professor Jang In-Gwon), the auto journalists from 11 countries were invited to be the jurors to select the winner. With the inaugural awards ceremony held in 2019, over the past three years, automakers from around the globe, including internationally renowned automakers, such as, Volvo/Toyota (2019), Honda/Hyundai (2020), and Renault (2021), even a new start-up car manufacturer like Canoo, the winner of last year’s award for commercial vehicles, were honored for their award-winning works.
At this year’s awards ceremony, the 4th of its kind, BMW's “iVision Circular” and Hyundai's “'Trailer Drone” were selected as the best concept cars of the year, the former from the Private Mobility category and the latter from the Public & Commercial Vehicles category.
The jury consisting of 16 domestic and foreign auto journalists, including BBC Top Gear's Paul Horrell and Car Magazine’s Georg Kacher, evaluated 53 concept car contestants that made their entry last year. The jurors’ general comment was that while the trend of the global automobile market flowing fast towards electric vehicles, this year's award-winning works presented a new vision in the field of eco-friendly design and unmanned logistics.
Private Mobility Categry Winner: BMW iVision Circular
BMW's 'iVision Circular', the winner of the Private Mobility category, is an eco-friendly compact car in which all parts of the vehicle are designed with recycled and/or natural materials. It has received favorable reviews for its in-depth implementation of the concept of a futuristic eco-friendly car by manufacturing the tires from natural rubber and adopting a design that made recycling of its parts very easily when the car is to be disposed of.
Public & Commercial Vehicles Categry Winner: Hyundai Trailer Drone
Hyundai Motor Company’s “Trailer Drone”, the winner of the Public & Commercial Vehicles category, is an eco-friendly autonomous driving truck that can transport large-scale logistics from a port to a destination without a human driver while two unmanned vehicles push and drag a trailer. The concept car won supports from a large number of judges for the blueprint it presented for a groundbreaking logistics service that applied both eco-friendly hydrogen fuel cell and fully autonomous driving technology.
Jurors from overseas congratulated the development team of BMW and Hyundai Motor Company via a video message for providing a new direction for the global automobile industry as it strives to transform in line with the changes in the post-pandemic era.
Professor Bo-won Kim, the Vice President for Planning and Budget of KAIST, who presented the awards, said, “It is time for the K-Mobility wave to sweep over the global mobility industry.” “KAIST will lead in the various fields of mobility technologies to support global automakers,” he added.
Splitting the center are KAIST Vice President Bo-Won Kim on the right, and Seong-Kwon Lee,
the Deputy Mayor of the City of Busan on the left. To Kim's left is the Senior VP of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, Jean-Philippe Parain, and to Lee's Right is Sangyup Lee,
the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive VP of Hyundai Motors.
At the ceremony, along with KAIST officials, including Vice President Bo-Won Kim and Professor In-Gwon Jang, the Head of Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility, are the Deputy Mayor Seong-Kwon Lee of the City of Busan and the figures from the automobile industry, including Jean-Philippe Parain, the Senior Vice President of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, who is visiting Korea to receive the '2022 Future Mobility' award, and Sangyup Lee, the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive Vice President of Hyundai Motor Company, were in the attendance.
More information about the awards ceremony and winning works are available at the official website of this year's Future Mobility Awards (www.fmoty.org).
Profile:In-Gwon Jang, Ph.D.Presidentthe Organizing Committeethe Future Mobility of the Year Awardshttp://www.fmoty.org/
Head ProfessorKAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobilityhttps://gt.kaist.ac.kr
2022.07.14 View 17666 -
 The 1st Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp bridges KAIST and Silicon Valley, US
Twenty KAIST students gave a go at selling their business ideas to investors at Silicon Valley on the “Pitch Day” at 2022 Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp.
From Tuesday, June 21 to Monday, July 4, 2022, KAIST held the first Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp (GESC).
The 2022 GESC, which was organized in collaboration with Stanford Technology Ventures Program (STVP), KOTRA Silicon Valley IT Center, and KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, was a pilot program that offered opportunities of experiencing and learning about the cases of startup companies in Silicon Valley and a chance to expand businesses to Silicon Valley through networking.
Twenty KAIST students, including pre-startup entrepreneurs and students interested in global entrepreneurship with less than one year of business experience were selected. The first week of the program was organized by Startup KAIST while the second week program was organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning (GSP) at KAIST in collaboration with the Stanford Technology Venture Program (STVP), KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, and KOTRA at Silicon Valley.
Dr. Mo-Yun Lei Fong, the Executive Director of STVP, said, “The program offered an opportunity for us to realize our vision of empowering aspiring entrepreneurs to become global citizens who create and scale responsible innovation. By collaborating with KAIST and offering entrepreneurial insights to Korean students, we are able to have a positive impact on a global scale.” Mo added, “The program also enabled STVP to build bridges, learn from the students, and refine our culturally relevant curriculum by understanding Korean culture and ideas.”
On the “Pitch Day” on July 1, following a special talk by Dr. Chong-Moon Lee, the Chairman of AmBex Venture Partners, the students presented their team business ideas such as an AI-assisted, noise-canceling pillow devised for better sleep, a metaverse dating application, an XR virtual conferencing system, and an AI language tutoring application to the entice global investors’ curiosity. The invited investors, majorly based in Silicon Valley, commented that all the presentation was very exciting, and the level of pitches was beyond the expectation considering that the students have given only two weeks.
Ms. Seunghee Lee of the team “Bored KAIST Yacht Club”, which was awarded the first prize, explained, “our item, called ‘Meta-Everland’, is a service that offers real-time dating experiences similar to off-line dates. The GESC taught me that anybody can launch a startup as long as they are willing. Developing a business model from ideation and taking it to the actual pitching was challenging, but it was a very thrilling experience at the same time.” Lee added, “Most importantly, over the course of the program and the final pitch, I found out that an interesting idea can attract investors interest even at a very early stage of the launching.”
Mr. Byunghoon Hwang, a student who attended the program said, “Having learned the thoughts and attitudes the people at the front line of Silicon Valley, my views on career and launching of a start-up have been expanded a lot.”
Ms. Marina Mondragon, another attendee at the program, also said that the program was very meaningful because she was able to learn the difference between the ecosystem for the new start-up businesses at Korea and at Silicon Valley through her talks with the CEOs at Silicon Valley.
The program was co-organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST International Office and Startup of KAIST. Dr. Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President for KAIST International Office, who guided students in Silicon Valley, said, “I believe the GESC program broadened the views and entrepreneurial mindset of students. After joining this program, students stepped forward to become a founder of startups.” In addition, Dr. Young-Tae Kim, the Associate Vice President of the Institute for Startup KAIST, addressed “Startup KAIST will support business items founded via the program through various other programs in order to enhance their competitiveness in the global market.”
The GSP and Startup KAIST will continuously revamp the program by selecting distinguished fellows to join the program and coming up with innovative startup items.
Profile:
Sooa Lee, Ph.D.
Research Assistant Professor
slee900@kaist.ac.kr
Center for Global Strategies and Planning
Office of Global Initiatives
KAIST International Office
https://io.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.05 View 14880
The 1st Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp bridges KAIST and Silicon Valley, US
Twenty KAIST students gave a go at selling their business ideas to investors at Silicon Valley on the “Pitch Day” at 2022 Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp.
From Tuesday, June 21 to Monday, July 4, 2022, KAIST held the first Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp (GESC).
The 2022 GESC, which was organized in collaboration with Stanford Technology Ventures Program (STVP), KOTRA Silicon Valley IT Center, and KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, was a pilot program that offered opportunities of experiencing and learning about the cases of startup companies in Silicon Valley and a chance to expand businesses to Silicon Valley through networking.
Twenty KAIST students, including pre-startup entrepreneurs and students interested in global entrepreneurship with less than one year of business experience were selected. The first week of the program was organized by Startup KAIST while the second week program was organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning (GSP) at KAIST in collaboration with the Stanford Technology Venture Program (STVP), KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, and KOTRA at Silicon Valley.
Dr. Mo-Yun Lei Fong, the Executive Director of STVP, said, “The program offered an opportunity for us to realize our vision of empowering aspiring entrepreneurs to become global citizens who create and scale responsible innovation. By collaborating with KAIST and offering entrepreneurial insights to Korean students, we are able to have a positive impact on a global scale.” Mo added, “The program also enabled STVP to build bridges, learn from the students, and refine our culturally relevant curriculum by understanding Korean culture and ideas.”
On the “Pitch Day” on July 1, following a special talk by Dr. Chong-Moon Lee, the Chairman of AmBex Venture Partners, the students presented their team business ideas such as an AI-assisted, noise-canceling pillow devised for better sleep, a metaverse dating application, an XR virtual conferencing system, and an AI language tutoring application to the entice global investors’ curiosity. The invited investors, majorly based in Silicon Valley, commented that all the presentation was very exciting, and the level of pitches was beyond the expectation considering that the students have given only two weeks.
Ms. Seunghee Lee of the team “Bored KAIST Yacht Club”, which was awarded the first prize, explained, “our item, called ‘Meta-Everland’, is a service that offers real-time dating experiences similar to off-line dates. The GESC taught me that anybody can launch a startup as long as they are willing. Developing a business model from ideation and taking it to the actual pitching was challenging, but it was a very thrilling experience at the same time.” Lee added, “Most importantly, over the course of the program and the final pitch, I found out that an interesting idea can attract investors interest even at a very early stage of the launching.”
Mr. Byunghoon Hwang, a student who attended the program said, “Having learned the thoughts and attitudes the people at the front line of Silicon Valley, my views on career and launching of a start-up have been expanded a lot.”
Ms. Marina Mondragon, another attendee at the program, also said that the program was very meaningful because she was able to learn the difference between the ecosystem for the new start-up businesses at Korea and at Silicon Valley through her talks with the CEOs at Silicon Valley.
The program was co-organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST International Office and Startup of KAIST. Dr. Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President for KAIST International Office, who guided students in Silicon Valley, said, “I believe the GESC program broadened the views and entrepreneurial mindset of students. After joining this program, students stepped forward to become a founder of startups.” In addition, Dr. Young-Tae Kim, the Associate Vice President of the Institute for Startup KAIST, addressed “Startup KAIST will support business items founded via the program through various other programs in order to enhance their competitiveness in the global market.”
The GSP and Startup KAIST will continuously revamp the program by selecting distinguished fellows to join the program and coming up with innovative startup items.
Profile:
Sooa Lee, Ph.D.
Research Assistant Professor
slee900@kaist.ac.kr
Center for Global Strategies and Planning
Office of Global Initiatives
KAIST International Office
https://io.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.05 View 14880 -
 KAIST & LG U+ Team Up for Quantum Computing Solution for Ultra-Space 6G Satellite Networking
KAIST quantum computer scientists have optimized ultra-space 6G Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite networking, finding the shortest path to transfer data from a city to another place via multi-satellite hops.
The research team led by Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Dongsu Han in partnership with LG U+ verified the possibility of ultra-performance and precision communication with satellite networks using D-Wave, the first commercialized quantum computer.
Satellite network optimization has remained challenging since the network needs to be reconfigured whenever satellites approach other satellites within the connection range in a three-dimensional space. Moreover, LEO satellites orbiting at 200~2000 km above the Earth change their positions dynamically, whereas Geo-Stationary Orbit (GSO) satellites do not change their positions. Thus, LEO satellite network optimization needs to be solved in real time.
The research groups formulated the problem as a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO) problem and managed to solve the problem, incorporating the connectivity and link distance limits as the constraints.
The proposed optimization algorithm is reported to be much more efficient in terms of hop counts and path length than previously reported studies using classical solutions. These results verify that a satellite network can provide ultra-performance (over 1Gbps user-perceived speed), and ultra-precision (less than 5ms end-to-end latency) network services, which are comparable to terrestrial communication.
Once QUBO is applied, “ultra-space networking” is expected to be realized with 6G. Researchers said that an ultra-space network provides communication services for an object moving at up to 10 km altitude with an extreme speed (~ 1000 km/h). Optimized LEO satellite networks can provide 6G communication services to currently unavailable areas such as air flights and deserts.
Professor Rhee, who is also the CEO of Qunova Computing, noted, “Collaboration with LG U+ was meaningful as we were able to find an industrial application for a quantum computer. We look forward to more quantum application research on real problems such as in communications, drug and material discovery, logistics, and fintech industries.”
2022.06.17 View 11126
KAIST & LG U+ Team Up for Quantum Computing Solution for Ultra-Space 6G Satellite Networking
KAIST quantum computer scientists have optimized ultra-space 6G Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite networking, finding the shortest path to transfer data from a city to another place via multi-satellite hops.
The research team led by Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Dongsu Han in partnership with LG U+ verified the possibility of ultra-performance and precision communication with satellite networks using D-Wave, the first commercialized quantum computer.
Satellite network optimization has remained challenging since the network needs to be reconfigured whenever satellites approach other satellites within the connection range in a three-dimensional space. Moreover, LEO satellites orbiting at 200~2000 km above the Earth change their positions dynamically, whereas Geo-Stationary Orbit (GSO) satellites do not change their positions. Thus, LEO satellite network optimization needs to be solved in real time.
The research groups formulated the problem as a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO) problem and managed to solve the problem, incorporating the connectivity and link distance limits as the constraints.
The proposed optimization algorithm is reported to be much more efficient in terms of hop counts and path length than previously reported studies using classical solutions. These results verify that a satellite network can provide ultra-performance (over 1Gbps user-perceived speed), and ultra-precision (less than 5ms end-to-end latency) network services, which are comparable to terrestrial communication.
Once QUBO is applied, “ultra-space networking” is expected to be realized with 6G. Researchers said that an ultra-space network provides communication services for an object moving at up to 10 km altitude with an extreme speed (~ 1000 km/h). Optimized LEO satellite networks can provide 6G communication services to currently unavailable areas such as air flights and deserts.
Professor Rhee, who is also the CEO of Qunova Computing, noted, “Collaboration with LG U+ was meaningful as we were able to find an industrial application for a quantum computer. We look forward to more quantum application research on real problems such as in communications, drug and material discovery, logistics, and fintech industries.”
2022.06.17 View 11126 -
 Professor Jae-Woong Jeong Receives Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering was selected for the Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award, funded by the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation (Chairman Soo-il Kwak, honorary professor at Seoul National University Business School).
The Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award, presented for the first time in 2021, is an award newly founded by the donations of Chairman Soo-il Kwak of the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation, who aims to reward excellent KAIST scholars who have made outstanding academic achievements.
Every year, through the strict evaluations of the selection committee of the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation and the faculty reward recommendation board, KAIST will choose one faculty member that may represent the school with their excellent academic achievement, and reward them with a plaque and 100 million won.
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, the winner of this year’s award, developed the first IoT-based wireless remote brain neural network control system to overcome brain diseases, and has been leading the field. The research was published in 2021 in Nature Biomedical Engineering, one of world’s best scientific journals, and has been recognized as a novel technology that suggested a new vision for the automation of brain research and disease treatment. This study, led by Professor Jeong’s research team, was part of the KAIST College of Engineering Global Initiative Interdisciplinary Research Project, and was jointly studied by Washington University School of Medicine through an international research collaboration. The technology was introduced more than 60 times through both domestic and international media, including Medical Xpress, MBC News, and Maeil Business News.
Professor Jeong has also developed a wirelessly chargeable soft machine for brain transplants, and the results were published in Nature Communications. He thereby opened a new paradigm for implantable semi-permanent devices for transplants, and is making unprecedented research achievements.
2022.06.13 View 10199
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong Receives Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering was selected for the Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award, funded by the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation (Chairman Soo-il Kwak, honorary professor at Seoul National University Business School).
The Hyonwoo KAIST Academic Award, presented for the first time in 2021, is an award newly founded by the donations of Chairman Soo-il Kwak of the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation, who aims to reward excellent KAIST scholars who have made outstanding academic achievements.
Every year, through the strict evaluations of the selection committee of the HyonWoo Cultural Foundation and the faculty reward recommendation board, KAIST will choose one faculty member that may represent the school with their excellent academic achievement, and reward them with a plaque and 100 million won.
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, the winner of this year’s award, developed the first IoT-based wireless remote brain neural network control system to overcome brain diseases, and has been leading the field. The research was published in 2021 in Nature Biomedical Engineering, one of world’s best scientific journals, and has been recognized as a novel technology that suggested a new vision for the automation of brain research and disease treatment. This study, led by Professor Jeong’s research team, was part of the KAIST College of Engineering Global Initiative Interdisciplinary Research Project, and was jointly studied by Washington University School of Medicine through an international research collaboration. The technology was introduced more than 60 times through both domestic and international media, including Medical Xpress, MBC News, and Maeil Business News.
Professor Jeong has also developed a wirelessly chargeable soft machine for brain transplants, and the results were published in Nature Communications. He thereby opened a new paradigm for implantable semi-permanent devices for transplants, and is making unprecedented research achievements.
2022.06.13 View 10199 -
 Quantum Technology: the Next Game Changer?
The 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute Forum explores how quantum technology has evolved into a new growth engine for the future
The participants of the 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute (GSI) Forum on April 20 agreed that the emerging technology of quantum computing will be a game changer of the future. As KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said in his opening remarks, the future is quantum and that future is rapidly approaching. Keynote speakers and panelists presented their insights on the disruptive innovations we are already experiencing.
The three keynote speakers included Dr. Jerry M. Chow, IBM fellow and director of quantum infrastructure, Professor John Preskill from Caltech, and Professor Jungsang Kim from Duke University. They discussed the academic impact and industrial applications of quantum technology, and its prospects for the future.
Dr. Chow leads IBM Quantum’s hardware system development efforts, focusing on research and system deployment. Professor Preskill is one of the leading quantum information science and quantum computation scholars. He coined the term “quantum supremacy.” Professor Kim is the co-founder and CTO of IonQ Inc., which develops general-purpose trapped ion quantum computers and software to generate, optimize, and execute quantum circuits.
Two leading quantum scholars from KAIST, Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Youngik Sohn, and Professor Andreas Heinrich from the IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience also participated in the forum as panelists. Professor Rhee is the founder of the nation’s first quantum computing software company and leads the AI Quantum Computing IT Research Center at KAIST.
During the panel session, Professor Rhee said that although it is undeniable the quantum computing will be a game changer, there are several challenges. For instance, the first actual quantum computer is NISQ (Noisy intermediate-scale quantum era), which is still incomplete. However, it is expected to outperform a supercomputer. Until then, it is important to advance the accuracy of quantum computation in order to offer super computation speeds.
Professor Sohn, who worked at PsiQuantum, detailed how quantum computers will affect our society. He said that PsiQuantum is developing silicon photonics that will control photons. We can’t begin to imagine how silicon photonics will transform our society. Things will change slowly but the scale would be massive.
The keynote speakers presented how quantum cryptography communications and its sensing technology will serve as disruptive innovations. Dr. Chow stressed that to realize the potential growth and innovation, additional R&D is needed. More research groups and scholars should be nurtured. Only then will the rich R&D resources be able to create breakthroughs in quantum-related industries. Lastly, the commercialization of quantum computing must be advanced, which will enable the provision of diverse services. In addition, more technological and industrial infrastructure must be built to better accommodate quantum computing.
Professor Preskill believes that quantum computing will benefit humanity. He cited two basic reasons for his optimistic prediction: quantum complexity and quantum error corrections. He explained why quantum computing is so powerful: quantum computer can easily solve the problems classically considered difficult, such as factorization. In addition, quantum computer has the potential to efficiently simulate all of the physical processes taking place in nature.
Despite such dramatic advantages, why does it seem so difficult? Professor Preskill believes this is because we want qubits (quantum bits or ‘qubits’ are the basic unit of quantum information) to interact very strongly with each other. Because computations can fail, we don’t want qubits to interact with the environment unless we can control and predict them.
As for quantum computing in the NISQ era, he said that NISQ will be an exciting tool for exploring physics. Professor Preskill does not believe that NISQ will change the world alone, rather it is a step forward toward more powerful quantum technologies in the future. He added that a potentially transformable, scalable quantum computer could still be decades away.
Professor Preskill said that a large number of qubits, higher accuracy, and better quality will require a significant investment. He said if we expand with better ideas, we can make a better system. In the longer term, quantum technology will bring significant benefits to the technological sectors and society in the fields of materials, physics, chemistry, and energy production.
Professor Kim from Duke University presented on the practical applications of quantum computing, especially in the startup environment. He said that although there is no right answer for the early applications of quantum computing, developing new approaches to solve difficult problems and raising the accessibility of the technology will be important for ensuring the growth of technology-based startups.
2022.04.21 View 14024
Quantum Technology: the Next Game Changer?
The 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute Forum explores how quantum technology has evolved into a new growth engine for the future
The participants of the 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute (GSI) Forum on April 20 agreed that the emerging technology of quantum computing will be a game changer of the future. As KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said in his opening remarks, the future is quantum and that future is rapidly approaching. Keynote speakers and panelists presented their insights on the disruptive innovations we are already experiencing.
The three keynote speakers included Dr. Jerry M. Chow, IBM fellow and director of quantum infrastructure, Professor John Preskill from Caltech, and Professor Jungsang Kim from Duke University. They discussed the academic impact and industrial applications of quantum technology, and its prospects for the future.
Dr. Chow leads IBM Quantum’s hardware system development efforts, focusing on research and system deployment. Professor Preskill is one of the leading quantum information science and quantum computation scholars. He coined the term “quantum supremacy.” Professor Kim is the co-founder and CTO of IonQ Inc., which develops general-purpose trapped ion quantum computers and software to generate, optimize, and execute quantum circuits.
Two leading quantum scholars from KAIST, Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Youngik Sohn, and Professor Andreas Heinrich from the IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience also participated in the forum as panelists. Professor Rhee is the founder of the nation’s first quantum computing software company and leads the AI Quantum Computing IT Research Center at KAIST.
During the panel session, Professor Rhee said that although it is undeniable the quantum computing will be a game changer, there are several challenges. For instance, the first actual quantum computer is NISQ (Noisy intermediate-scale quantum era), which is still incomplete. However, it is expected to outperform a supercomputer. Until then, it is important to advance the accuracy of quantum computation in order to offer super computation speeds.
Professor Sohn, who worked at PsiQuantum, detailed how quantum computers will affect our society. He said that PsiQuantum is developing silicon photonics that will control photons. We can’t begin to imagine how silicon photonics will transform our society. Things will change slowly but the scale would be massive.
The keynote speakers presented how quantum cryptography communications and its sensing technology will serve as disruptive innovations. Dr. Chow stressed that to realize the potential growth and innovation, additional R&D is needed. More research groups and scholars should be nurtured. Only then will the rich R&D resources be able to create breakthroughs in quantum-related industries. Lastly, the commercialization of quantum computing must be advanced, which will enable the provision of diverse services. In addition, more technological and industrial infrastructure must be built to better accommodate quantum computing.
Professor Preskill believes that quantum computing will benefit humanity. He cited two basic reasons for his optimistic prediction: quantum complexity and quantum error corrections. He explained why quantum computing is so powerful: quantum computer can easily solve the problems classically considered difficult, such as factorization. In addition, quantum computer has the potential to efficiently simulate all of the physical processes taking place in nature.
Despite such dramatic advantages, why does it seem so difficult? Professor Preskill believes this is because we want qubits (quantum bits or ‘qubits’ are the basic unit of quantum information) to interact very strongly with each other. Because computations can fail, we don’t want qubits to interact with the environment unless we can control and predict them.
As for quantum computing in the NISQ era, he said that NISQ will be an exciting tool for exploring physics. Professor Preskill does not believe that NISQ will change the world alone, rather it is a step forward toward more powerful quantum technologies in the future. He added that a potentially transformable, scalable quantum computer could still be decades away.
Professor Preskill said that a large number of qubits, higher accuracy, and better quality will require a significant investment. He said if we expand with better ideas, we can make a better system. In the longer term, quantum technology will bring significant benefits to the technological sectors and society in the fields of materials, physics, chemistry, and energy production.
Professor Kim from Duke University presented on the practical applications of quantum computing, especially in the startup environment. He said that although there is no right answer for the early applications of quantum computing, developing new approaches to solve difficult problems and raising the accessibility of the technology will be important for ensuring the growth of technology-based startups.
2022.04.21 View 14024 -
 Professor June-Koo Rhee’s Team Wins the QHack Open Hackathon Science Challenge
The research team consisting of three master students Ju-Young Ryu, Jeung-rak Lee, and Eyel Elala in Professor June-Koo Rhee’s group from the KAIST IRTC of Quantum Computing for AI has won the first place at the QHack 2022 Open Hackathon Science Challenge.
The QHack 2022 Open Hackathon is one of the world’s prestigious quantum software hackathon events held by US Xanadu, in which 250 people from 100 countries participate. Major sponsors such as IBM Quantum, AWS, CERN QTI, and Google Quantum AI proposed challenging problems, and a winning team is selected judged on team projects in each of the 13 challenges.
The KAIST team supervised by Professor Rhee received the First Place prize on the Science Challenge which was organized by the CERN QTI of the European Communities. The team will be awarded an opportunity to tour CERN’s research lab in Europe for one week along with an online internship.
The students on the team presented a method for “Leaning Based Error Mitigation for VQE,” in which they implemented an LBEM protocol to lower the error in quantum computing, and leveraged the protocol in the VQU algorithm which is used to calculate the ground state energy of a given molecule.
Their research successfully demonstrated the ability to effectively mitigate the error in IBM Quantum hardware and the virtual error model. In conjunction, Professor June-Koo (Kevin) Rhee founded a quantum computing venture start-up, Qunova Computing(https://qunovacomputing.com), with technology tranfer from the KAIST ITRC of Quantum Computing for AI. Qunova Computing is one of the frontier of the quantum software industry in Korea.
2022.04.08 View 8201
Professor June-Koo Rhee’s Team Wins the QHack Open Hackathon Science Challenge
The research team consisting of three master students Ju-Young Ryu, Jeung-rak Lee, and Eyel Elala in Professor June-Koo Rhee’s group from the KAIST IRTC of Quantum Computing for AI has won the first place at the QHack 2022 Open Hackathon Science Challenge.
The QHack 2022 Open Hackathon is one of the world’s prestigious quantum software hackathon events held by US Xanadu, in which 250 people from 100 countries participate. Major sponsors such as IBM Quantum, AWS, CERN QTI, and Google Quantum AI proposed challenging problems, and a winning team is selected judged on team projects in each of the 13 challenges.
The KAIST team supervised by Professor Rhee received the First Place prize on the Science Challenge which was organized by the CERN QTI of the European Communities. The team will be awarded an opportunity to tour CERN’s research lab in Europe for one week along with an online internship.
The students on the team presented a method for “Leaning Based Error Mitigation for VQE,” in which they implemented an LBEM protocol to lower the error in quantum computing, and leveraged the protocol in the VQU algorithm which is used to calculate the ground state energy of a given molecule.
Their research successfully demonstrated the ability to effectively mitigate the error in IBM Quantum hardware and the virtual error model. In conjunction, Professor June-Koo (Kevin) Rhee founded a quantum computing venture start-up, Qunova Computing(https://qunovacomputing.com), with technology tranfer from the KAIST ITRC of Quantum Computing for AI. Qunova Computing is one of the frontier of the quantum software industry in Korea.
2022.04.08 View 8201