AI
-
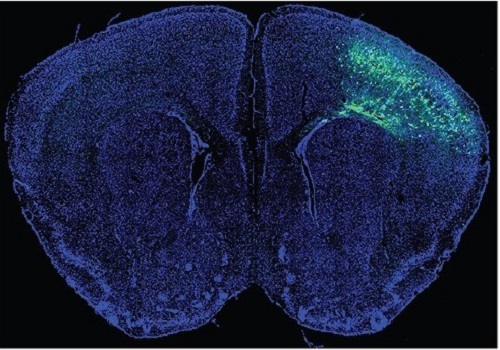 A Mechanism Underlying Most Common Cause of Epileptic Seizures Revealed
An interdisciplinary study shows that neurons carrying somatic mutations in MTOR can lead to focal epileptogenesis via non-cell-autonomous hyperexcitability of nearby nonmutated neurons
During fetal development, cells should migrate to the outer edge of the brain to form critical connections for information transfer and regulation in the body. When even a few cells fail to move to the correct location, the neurons become disorganized and this results in focal cortical dysplasia. This condition is the most common cause of seizures that cannot be controlled with medication in children and the second most common cause in adults.
Now, an interdisciplinary team studying neurogenetics, neural networks, and neurophysiology at KAIST has revealed how dysfunctions in even a small percentage of cells can cause disorder across the entire brain. They published their results on June 28 in Annals of Neurology.
The work builds on a previous finding, also by a KAIST scientists, who found that focal cortical dysplasia was caused by mutations in the cells involved in mTOR, a pathway that regulates signaling between neurons in the brain.
“Only 1 to 2% of neurons carrying mutations in the mTOR signaling pathway that regulates cell signaling in the brain have been found to include seizures in animal models of focal cortical dysplasia,” said Professor Jong-Woo Sohn from the Department of Biological Sciences. “The main challenge of this study was to explain how nearby non-mutated neurons are hyperexcitable.”
Initially, the researchers hypothesized that the mutated cells affected the number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in all neurons, mutated or not. These neural gates can trigger or halt activity, respectively, in other neurons. Seizures are a result of extreme activity, called hyperexcitability. If the mutated cells upend the balance and result in more excitatory cells, the researchers thought, it made sense that the cells would be more susceptible to hyperexcitability and, as a result, seizures.
“Contrary to our expectations, the synaptic input balance was not changed in either the mutated or non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. “We turned our attention to a protein overproduced by mutated neurons.”
The protein is adenosine kinase, which lowers the concentration of adenosine. This naturally occurring compound is an anticonvulsant and works to relax vessels. In mice engineered to have focal cortical dysplasia, the researchers injected adenosine to replace the levels lowered by the protein. It worked and the neurons became less excitable.
“We demonstrated that augmentation of adenosine signaling could attenuate the excitability of non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering.
The effect on the non-mutated neurons was the surprising part, according to Paik. “The seizure-triggering hyperexcitability originated not in the mutation-carrying neurons, but instead in the nearby non-mutated neurons,” he said.
The mutated neurons excreted more adenosine kinase, reducing the adenosine levels in the local environment of all the cells. With less adenosine, the non-mutated neurons became hyperexcitable, leading to seizures.
“While we need further investigate into the relationship between the concentration of adenosine and the increased excitation of nearby neurons, our results support the medical use of drugs to activate adenosine signaling as a possible treatment pathway for focal cortical dysplasia,” Professor Lee said.
The Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Korea Health Technology Research and Development Project, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation in Korea funded this work.
-Publication:Koh, H.Y., Jang, J., Ju, S.H., Kim, R., Cho, G.-B., Kim, D.S., Sohn, J.-W., Paik, S.-B. and Lee, J.H. (2021), ‘Non–Cell Autonomous Epileptogenesis in Focal Cortical Dysplasia’ Annals of Neurology, 90: 285 299. (https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26149)
-ProfileProfessor Jeong Ho Lee Translational Neurogenetics Labhttps://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/ Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering KAIST
Professor Se-Bum Paik Visual System and Neural Network Laboratory http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/ Department of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Jong-Woo Sohn Laboratory for Neurophysiology, https://sites.google.com/site/sohnlab2014/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
Dr. Hyun Yong Koh Translational Neurogenetics LabGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
Dr. Jaeson Jang Ph.D.Visual System and Neural Network LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST
Sang Hyeon Ju M.D.Laboratory for NeurophysiologyDepartment of Biological SciencesKAIST
2021.08.26 View 15021
A Mechanism Underlying Most Common Cause of Epileptic Seizures Revealed
An interdisciplinary study shows that neurons carrying somatic mutations in MTOR can lead to focal epileptogenesis via non-cell-autonomous hyperexcitability of nearby nonmutated neurons
During fetal development, cells should migrate to the outer edge of the brain to form critical connections for information transfer and regulation in the body. When even a few cells fail to move to the correct location, the neurons become disorganized and this results in focal cortical dysplasia. This condition is the most common cause of seizures that cannot be controlled with medication in children and the second most common cause in adults.
Now, an interdisciplinary team studying neurogenetics, neural networks, and neurophysiology at KAIST has revealed how dysfunctions in even a small percentage of cells can cause disorder across the entire brain. They published their results on June 28 in Annals of Neurology.
The work builds on a previous finding, also by a KAIST scientists, who found that focal cortical dysplasia was caused by mutations in the cells involved in mTOR, a pathway that regulates signaling between neurons in the brain.
“Only 1 to 2% of neurons carrying mutations in the mTOR signaling pathway that regulates cell signaling in the brain have been found to include seizures in animal models of focal cortical dysplasia,” said Professor Jong-Woo Sohn from the Department of Biological Sciences. “The main challenge of this study was to explain how nearby non-mutated neurons are hyperexcitable.”
Initially, the researchers hypothesized that the mutated cells affected the number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in all neurons, mutated or not. These neural gates can trigger or halt activity, respectively, in other neurons. Seizures are a result of extreme activity, called hyperexcitability. If the mutated cells upend the balance and result in more excitatory cells, the researchers thought, it made sense that the cells would be more susceptible to hyperexcitability and, as a result, seizures.
“Contrary to our expectations, the synaptic input balance was not changed in either the mutated or non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. “We turned our attention to a protein overproduced by mutated neurons.”
The protein is adenosine kinase, which lowers the concentration of adenosine. This naturally occurring compound is an anticonvulsant and works to relax vessels. In mice engineered to have focal cortical dysplasia, the researchers injected adenosine to replace the levels lowered by the protein. It worked and the neurons became less excitable.
“We demonstrated that augmentation of adenosine signaling could attenuate the excitability of non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering.
The effect on the non-mutated neurons was the surprising part, according to Paik. “The seizure-triggering hyperexcitability originated not in the mutation-carrying neurons, but instead in the nearby non-mutated neurons,” he said.
The mutated neurons excreted more adenosine kinase, reducing the adenosine levels in the local environment of all the cells. With less adenosine, the non-mutated neurons became hyperexcitable, leading to seizures.
“While we need further investigate into the relationship between the concentration of adenosine and the increased excitation of nearby neurons, our results support the medical use of drugs to activate adenosine signaling as a possible treatment pathway for focal cortical dysplasia,” Professor Lee said.
The Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Korea Health Technology Research and Development Project, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation in Korea funded this work.
-Publication:Koh, H.Y., Jang, J., Ju, S.H., Kim, R., Cho, G.-B., Kim, D.S., Sohn, J.-W., Paik, S.-B. and Lee, J.H. (2021), ‘Non–Cell Autonomous Epileptogenesis in Focal Cortical Dysplasia’ Annals of Neurology, 90: 285 299. (https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26149)
-ProfileProfessor Jeong Ho Lee Translational Neurogenetics Labhttps://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/ Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering KAIST
Professor Se-Bum Paik Visual System and Neural Network Laboratory http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/ Department of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Jong-Woo Sohn Laboratory for Neurophysiology, https://sites.google.com/site/sohnlab2014/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
Dr. Hyun Yong Koh Translational Neurogenetics LabGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
Dr. Jaeson Jang Ph.D.Visual System and Neural Network LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST
Sang Hyeon Ju M.D.Laboratory for NeurophysiologyDepartment of Biological SciencesKAIST
2021.08.26 View 15021 -
 KAIST KPC4IR Presents the AI Global Guide for Healthcare
The benchmark for the responsible usage of AI technology in the healthcare sector will promote clarity and high standards for technological applications
The KAIST Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) published 'Using AI to Support Healthcare Decisions: A Guide for Society.' This global guide is designed to serve as a benchmark for the responsible usage of AI technologies, and will promote clarity and high standards for technological applications in the healthcare sector. The guide details what should be considered when making clinical decisions to help reduce the chances of the AI giving false or misleading results.
The KPC4IR presented the guide in collaboration with the Lloyd’s Register Foundation Institute for the Public Understanding of Risk at the National University of Singapore (NUS IPUR) and Sense about Science, a non-profit organization in the UK specialized in science communication, during the 2021 SIG-KDD (Special Interest Group on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining) Conference on August 15.
AI technology is being widely used in the healthcare sector and has already proved its accuracy and efficiency in diagnosing and predicting diseases. Despite its huge impact on our daily lives in every sector of society, AI technology has some drawbacks and comes with risks, especially due to biased algorithms.
“We focused on the ‘reliability’ of AI applications in the healthcare sector to make all data well represented, in good quality. The technology will eventually innovate to better serve the people’s new demand, especially critical demands for safety and precision in healthcare services. This global guide will help both developers and people’s understanding of the appropriate technology applications,” says Director So Young Kim at the KPC4IR.
The guide, for instance, says that to scrutinize quality and reliability, the source of the data must be clearly known; the data must have been collected or selected for the purpose it’s being used for; the limitations and assumptions for that purpose have been clearly stated; the biases have been addressed; and it has been properly tested in the real world. It also reflects the importance of the representativeness of data that will affect the accuracy of the AI applications.
“By being transparent and demonstrating the steps taken to check that the AI is reliable, researchers and developers can help give people confidence about providing their data,” the guide states.
For this guide, the KPC4IR and its collaborators collected data after working with numerous experts from the Graduate School of AI at KAIST, the Science and Technology Policy Institute in Korea, Asan Medical Center in Seoul, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, and AI solution companies.
2021.08.17 View 9487
KAIST KPC4IR Presents the AI Global Guide for Healthcare
The benchmark for the responsible usage of AI technology in the healthcare sector will promote clarity and high standards for technological applications
The KAIST Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) published 'Using AI to Support Healthcare Decisions: A Guide for Society.' This global guide is designed to serve as a benchmark for the responsible usage of AI technologies, and will promote clarity and high standards for technological applications in the healthcare sector. The guide details what should be considered when making clinical decisions to help reduce the chances of the AI giving false or misleading results.
The KPC4IR presented the guide in collaboration with the Lloyd’s Register Foundation Institute for the Public Understanding of Risk at the National University of Singapore (NUS IPUR) and Sense about Science, a non-profit organization in the UK specialized in science communication, during the 2021 SIG-KDD (Special Interest Group on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining) Conference on August 15.
AI technology is being widely used in the healthcare sector and has already proved its accuracy and efficiency in diagnosing and predicting diseases. Despite its huge impact on our daily lives in every sector of society, AI technology has some drawbacks and comes with risks, especially due to biased algorithms.
“We focused on the ‘reliability’ of AI applications in the healthcare sector to make all data well represented, in good quality. The technology will eventually innovate to better serve the people’s new demand, especially critical demands for safety and precision in healthcare services. This global guide will help both developers and people’s understanding of the appropriate technology applications,” says Director So Young Kim at the KPC4IR.
The guide, for instance, says that to scrutinize quality and reliability, the source of the data must be clearly known; the data must have been collected or selected for the purpose it’s being used for; the limitations and assumptions for that purpose have been clearly stated; the biases have been addressed; and it has been properly tested in the real world. It also reflects the importance of the representativeness of data that will affect the accuracy of the AI applications.
“By being transparent and demonstrating the steps taken to check that the AI is reliable, researchers and developers can help give people confidence about providing their data,” the guide states.
For this guide, the KPC4IR and its collaborators collected data after working with numerous experts from the Graduate School of AI at KAIST, the Science and Technology Policy Institute in Korea, Asan Medical Center in Seoul, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, and AI solution companies.
2021.08.17 View 9487 -
 KPC4IR Helping to Create Global Standards for Virtual Transactions
KPC4IR will join the task force for the Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards
The KAIST Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will participate in a global initiative to create global standards for virtual asset transactions. As a member of the GI-TRUST (Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards) task force, the KPC4IR will develop technical standards and relevant policies that support the global implementation of the travel rule for virtual assets in compliance with the recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF).
The FATF is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1989 by the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering. In June 2019, the FATF extended its Recommendation 16, commonly known as the “travel rule,” to virtual asset services providers (VASPs), requiring both financial institutions and VASPs to aggregate information on the senders and recipients of wire transfers and exchange this information between parties to create a suitable audit trail.
According to the FATF’s recommendation and the G20’s support, jurisdictions, especially G20 member countries, have now applied the travel rule to their respective local laws. Korea also amended the Act on Reporting and Using Specified Financial Transaction Information in March 2020 to include virtual assets in their regulatory scope by March 2022.
The GI-TRUST task force will collaborate with global and local organizations developing travel rule technologies and offer a neutral assessment of proposed solutions. Their activities are aimed at standardizing related authentication protocols and security technologies that help VASPs comply with the travel rule.
The task force will also aid in the pilot testing of travel rule solutions for certain VASPs in Korea. Afterwards, the task force will report on the performance and reliability of the tested travel rule solutions for actual virtual asset transactions, in compliance with the FATF’s guidance.
Besides the KPC4IR, the GI-TRUST task force includes the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC), International Digital Asset Exchange Association (IDAXA), and Korea Blockchain Association (KBCA).
Director of the KPC4IR Professor So Young Kim will co-chair the task force. Professor Kim said their approach should be prudential in dealing with the regulations that rely on secure real-name data on top of the opposing governance style of pseudonymization, distribution, and recombination.
She explained, “KAIST has designed the co-evolution of technologies and institutions in conjunction with the global leaders’ groups such as the World Economic Forum and the EC Joint Research Center.”
She expects KAIST’s interdisciplinary, global cooperation to untie the entangled problem between regulations and technologies that obstruct future pathways.
2021.07.30 View 10072
KPC4IR Helping to Create Global Standards for Virtual Transactions
KPC4IR will join the task force for the Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards
The KAIST Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will participate in a global initiative to create global standards for virtual asset transactions. As a member of the GI-TRUST (Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards) task force, the KPC4IR will develop technical standards and relevant policies that support the global implementation of the travel rule for virtual assets in compliance with the recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF).
The FATF is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1989 by the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering. In June 2019, the FATF extended its Recommendation 16, commonly known as the “travel rule,” to virtual asset services providers (VASPs), requiring both financial institutions and VASPs to aggregate information on the senders and recipients of wire transfers and exchange this information between parties to create a suitable audit trail.
According to the FATF’s recommendation and the G20’s support, jurisdictions, especially G20 member countries, have now applied the travel rule to their respective local laws. Korea also amended the Act on Reporting and Using Specified Financial Transaction Information in March 2020 to include virtual assets in their regulatory scope by March 2022.
The GI-TRUST task force will collaborate with global and local organizations developing travel rule technologies and offer a neutral assessment of proposed solutions. Their activities are aimed at standardizing related authentication protocols and security technologies that help VASPs comply with the travel rule.
The task force will also aid in the pilot testing of travel rule solutions for certain VASPs in Korea. Afterwards, the task force will report on the performance and reliability of the tested travel rule solutions for actual virtual asset transactions, in compliance with the FATF’s guidance.
Besides the KPC4IR, the GI-TRUST task force includes the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC), International Digital Asset Exchange Association (IDAXA), and Korea Blockchain Association (KBCA).
Director of the KPC4IR Professor So Young Kim will co-chair the task force. Professor Kim said their approach should be prudential in dealing with the regulations that rely on secure real-name data on top of the opposing governance style of pseudonymization, distribution, and recombination.
She explained, “KAIST has designed the co-evolution of technologies and institutions in conjunction with the global leaders’ groups such as the World Economic Forum and the EC Joint Research Center.”
She expects KAIST’s interdisciplinary, global cooperation to untie the entangled problem between regulations and technologies that obstruct future pathways.
2021.07.30 View 10072 -
 VP Sang Yup Lee Honored with the Pony Chung Innovation Award
Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee became the recipient of the Innovation Award by the Pony Chung Foundation that was established to honor the late Se-yung Chung, the former chairman of Hyundai Development Company. He will receive 200 million KRW in prize money. Chairman Chung developed Korea’s first domestically manufactured automobile, ‘Pony,’ in the mid-1970s that became the cornerstone of Korea’s auto industry today.
Distinguished Professor Lee, from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, is a pioneering scholar in the field of systems metabolic engineering who developed various micro-organisms for producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds.
He recently was elected as a foreign member of the Royal Society in the UK and is the first Korean ever elected into the National Academy of Inventors (NAI) in the US as well as one of 13 scholars elected as an International Member of both the National Academy of Sciences (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) in the US.
2021.07.13 View 11848
VP Sang Yup Lee Honored with the Pony Chung Innovation Award
Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee became the recipient of the Innovation Award by the Pony Chung Foundation that was established to honor the late Se-yung Chung, the former chairman of Hyundai Development Company. He will receive 200 million KRW in prize money. Chairman Chung developed Korea’s first domestically manufactured automobile, ‘Pony,’ in the mid-1970s that became the cornerstone of Korea’s auto industry today.
Distinguished Professor Lee, from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, is a pioneering scholar in the field of systems metabolic engineering who developed various micro-organisms for producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds.
He recently was elected as a foreign member of the Royal Society in the UK and is the first Korean ever elected into the National Academy of Inventors (NAI) in the US as well as one of 13 scholars elected as an International Member of both the National Academy of Sciences (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) in the US.
2021.07.13 View 11848 -
 Professor Jung Receives the Hansong Science Award
Professor Yousung Jung of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has been selected as the recipient of the 5th Hansong Science Award in Chemistry. The award recognizes young and mid-career scholars who made outstanding achievement in physics, chemistry, and life sciences. Recipients receive 50 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Jung was recognized for finding a new way to predict synthesis potentials when designing data-based materials and molecules through AI-powered inverse technology. Conventionally, new material discovery mainly relied on a method where the new materials were proposed by an expert’s intuition or experimental trial, then synthesized to measure the properties of the material before it was used. However, this method took a lot of time, which resulted in an inefficient discovery process.
Professor Jung’s AI reverse design technology is reported to be more efficient for discovering new materials by finding crystal structures with desired properties using data and AI algorithms.
"AI reverse design technology can accelerate the development of new materials and new drugs," Professor Jung said. "It can be used as an algorithm for future autonomous laboratories implemented by robots, algorithms, and data without human intervention," he added.
2021.07.13 View 8387
Professor Jung Receives the Hansong Science Award
Professor Yousung Jung of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has been selected as the recipient of the 5th Hansong Science Award in Chemistry. The award recognizes young and mid-career scholars who made outstanding achievement in physics, chemistry, and life sciences. Recipients receive 50 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Jung was recognized for finding a new way to predict synthesis potentials when designing data-based materials and molecules through AI-powered inverse technology. Conventionally, new material discovery mainly relied on a method where the new materials were proposed by an expert’s intuition or experimental trial, then synthesized to measure the properties of the material before it was used. However, this method took a lot of time, which resulted in an inefficient discovery process.
Professor Jung’s AI reverse design technology is reported to be more efficient for discovering new materials by finding crystal structures with desired properties using data and AI algorithms.
"AI reverse design technology can accelerate the development of new materials and new drugs," Professor Jung said. "It can be used as an algorithm for future autonomous laboratories implemented by robots, algorithms, and data without human intervention," he added.
2021.07.13 View 8387 -
 Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-PublicationPark, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-ProfileProfessor Seongjun ParkBio and Neural Interfaces LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.13 View 13075
Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-PublicationPark, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-ProfileProfessor Seongjun ParkBio and Neural Interfaces LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.13 View 13075 -
 Repurposed Drugs Present New Strategy for Treating COVID-19
Virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assays identifies best therapeutic medication candidates
A joint research group from KAIST and Institut Pasteur Korea has identified repurposed drugs for COVID-19 treatment through virtual screening and cell-based assays. The research team suggested the strategy for virtual screening with greatly reduced false positives by incorporating pre-docking filtering based on shape similarity and post-docking filtering based on interaction similarity. This strategy will help develop therapeutic medications for COVID-19 and other antiviral diseases more rapidly. This study was reported at the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS).
Researchers screened 6,218 drugs from a collection of FDA-approved drugs or those under clinical trial and identified 38 potential repurposed drugs for COVID-19 with this strategy. Among them, seven compounds inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication in Vero cells. Three of these drugs, emodin, omipalisib, and tipifarnib, showed anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity in human lung cells, Calu-3.
Drug repurposing is a practical strategy for developing antiviral drugs in a short period of time, especially during a global pandemic. In many instances, drug repurposing starts with the virtual screening of approved drugs. However, the actual hit rate of virtual screening is low and most of the predicted drug candidates are false positives.
The research group developed effective filtering algorithms before and after the docking simulations to improve the hit rates. In the pre-docking filtering process, compounds with similar shapes to the known active compounds for each target protein were selected and used for docking simulations. In the post-docking filtering process, the chemicals identified through their docking simulations were evaluated considering the docking energy and the similarity of the protein-ligand interactions with the known active compounds.
The experimental results showed that the virtual screening strategy reached a high hit rate of 18.4%, leading to the identification of seven potential drugs out of the 38 drugs initially selected.
“We plan to conduct further preclinical trials for optimizing drug concentrations as one of the three candidates didn’t resolve the toxicity issues in preclinical trials,” said Woo Dae Jang, one of the researchers from KAIST.
“The most important part of this research is that we developed a platform technology that can rapidly identify novel compounds for COVID-19 treatment. If we use this technology, we will be able to quickly respond to new infectious diseases as well as variants of the coronavirus,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the KAIST Mobile Clinic Module Project funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The National Culture Collection for Pathogens in Korea provided the SARS-CoV-2 (NCCP43326).
-PublicationWoo Dae Jang, Sangeun Jeon, Seungtaek Kim, and Sang Yup Lee. Drugs repurposed for COVID-19 by virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (https://doi/org/10.1073/pnas.2024302118)
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.08 View 15864
Repurposed Drugs Present New Strategy for Treating COVID-19
Virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assays identifies best therapeutic medication candidates
A joint research group from KAIST and Institut Pasteur Korea has identified repurposed drugs for COVID-19 treatment through virtual screening and cell-based assays. The research team suggested the strategy for virtual screening with greatly reduced false positives by incorporating pre-docking filtering based on shape similarity and post-docking filtering based on interaction similarity. This strategy will help develop therapeutic medications for COVID-19 and other antiviral diseases more rapidly. This study was reported at the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS).
Researchers screened 6,218 drugs from a collection of FDA-approved drugs or those under clinical trial and identified 38 potential repurposed drugs for COVID-19 with this strategy. Among them, seven compounds inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication in Vero cells. Three of these drugs, emodin, omipalisib, and tipifarnib, showed anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity in human lung cells, Calu-3.
Drug repurposing is a practical strategy for developing antiviral drugs in a short period of time, especially during a global pandemic. In many instances, drug repurposing starts with the virtual screening of approved drugs. However, the actual hit rate of virtual screening is low and most of the predicted drug candidates are false positives.
The research group developed effective filtering algorithms before and after the docking simulations to improve the hit rates. In the pre-docking filtering process, compounds with similar shapes to the known active compounds for each target protein were selected and used for docking simulations. In the post-docking filtering process, the chemicals identified through their docking simulations were evaluated considering the docking energy and the similarity of the protein-ligand interactions with the known active compounds.
The experimental results showed that the virtual screening strategy reached a high hit rate of 18.4%, leading to the identification of seven potential drugs out of the 38 drugs initially selected.
“We plan to conduct further preclinical trials for optimizing drug concentrations as one of the three candidates didn’t resolve the toxicity issues in preclinical trials,” said Woo Dae Jang, one of the researchers from KAIST.
“The most important part of this research is that we developed a platform technology that can rapidly identify novel compounds for COVID-19 treatment. If we use this technology, we will be able to quickly respond to new infectious diseases as well as variants of the coronavirus,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the KAIST Mobile Clinic Module Project funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The National Culture Collection for Pathogens in Korea provided the SARS-CoV-2 (NCCP43326).
-PublicationWoo Dae Jang, Sangeun Jeon, Seungtaek Kim, and Sang Yup Lee. Drugs repurposed for COVID-19 by virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (https://doi/org/10.1073/pnas.2024302118)
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.08 View 15864 -
 Prof. Sang Wan Lee Selected for 2021 IBM Academic Award
Professor Sang Wan Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2021 IBM Global University Program Academic Award. The award recognizes individual faculty members whose emerging science and technology contains significant interest for universities and IBM.
Professor Lee, whose research focuses on artificial intelligence and computational neuroscience, won the award for his research proposal titled A Neuroscience-Inspired Approach for Metacognitive Reinforcement Learning. IBM provides a gift of $40,000 to the recipient’s institution in recognition of the selection of the project but not as a contract for services.
Professor Lee’s project aims to exploit the unique characteristics of human reinforcement learning. Specifically, he plans to examines the hypothesis that metacognition, a human’s ability to estimate their uncertainty level, serves to guide sample-efficient and near-optimal exploration, making it possible to achieve an optimal balance between model-based and model-free reinforcement learning.
He was also selected as the winner of the Google Research Award in 2016 and has been working with DeepMind and University College London to conduct basic research on decision-making brain science to establish a theory on frontal lobe meta-enhance learning.
"We plan to conduct joint research for utilizing brain-based artificial intelligence technology and frontal lobe meta-enhanced learning technology modeling in collaboration with an international research team including IBM, DeepMind, MIT, and Oxford,” Professor Lee said.
2021.06.25 View 14020
Prof. Sang Wan Lee Selected for 2021 IBM Academic Award
Professor Sang Wan Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2021 IBM Global University Program Academic Award. The award recognizes individual faculty members whose emerging science and technology contains significant interest for universities and IBM.
Professor Lee, whose research focuses on artificial intelligence and computational neuroscience, won the award for his research proposal titled A Neuroscience-Inspired Approach for Metacognitive Reinforcement Learning. IBM provides a gift of $40,000 to the recipient’s institution in recognition of the selection of the project but not as a contract for services.
Professor Lee’s project aims to exploit the unique characteristics of human reinforcement learning. Specifically, he plans to examines the hypothesis that metacognition, a human’s ability to estimate their uncertainty level, serves to guide sample-efficient and near-optimal exploration, making it possible to achieve an optimal balance between model-based and model-free reinforcement learning.
He was also selected as the winner of the Google Research Award in 2016 and has been working with DeepMind and University College London to conduct basic research on decision-making brain science to establish a theory on frontal lobe meta-enhance learning.
"We plan to conduct joint research for utilizing brain-based artificial intelligence technology and frontal lobe meta-enhanced learning technology modeling in collaboration with an international research team including IBM, DeepMind, MIT, and Oxford,” Professor Lee said.
2021.06.25 View 14020 -
 KAIST-SM Entertainment Joint Research for Metaverse
“Culture scientist will play a role in the future of the entertainment industry”
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee and SM Entertainment Founder and Chief Executive Producer Soo-Man Lee signed an MOU on joint research of the metaverse on June 23 at the Daejeon campus. SM Entertainment is the powerhouse of K-pop and Lee is a pioneering figure who helped Korean pop culture emerge into a global phenomenon.
The KAIST-SM metaverse partnership will bring out new culture technology that will lead the virtual entertainment industry by creating more dynamic and vivid digital technologies. KAIST will utilize its AI, robot, and network technologies, while SM will provide its content production expertise for this metaverse research.
President Lee said, “SM artists have mesmerized global audiences and opened new markets for K-Pop. Combining the creativity and cultural imagination of SM with technologies from KAIST, together we will make significant contributions to the advancement of virtual reality as well as the global entertainment industry.”
The Graduate School of Culture Technology has been engaging in a variety of creative projects incorporating science and technology for decades and will now actively participate in this metaverse project with SM.
CEP Lee explained, “The power of celebrities and avatars will rule the future entertainment industry. SM will make a leap forward to be a ‘first mover’ in the digital entertainment industry with this partnership with KAIST. This partnership will shape the new digital future of the entertainment industry boosted by cutting-edge technologies.”
CEP Lee also delivered a special lecture for the KAIST community via Zoom. Saying that producers in the future will be ‘culture scientists’, he stressed the importance of technology converging with culture.
“The key factor for K-pop’s success lies in the impressive technology of Korea. SM places a high priority on developing cultural technology and creating new artists and products combining this technology,” added Lee, citing the hologram contents of Beyond Live concerts and the new 4+4 girl group composed of four girls and four avatars called ‘Aespa.’
2021.06.25 View 8326
KAIST-SM Entertainment Joint Research for Metaverse
“Culture scientist will play a role in the future of the entertainment industry”
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee and SM Entertainment Founder and Chief Executive Producer Soo-Man Lee signed an MOU on joint research of the metaverse on June 23 at the Daejeon campus. SM Entertainment is the powerhouse of K-pop and Lee is a pioneering figure who helped Korean pop culture emerge into a global phenomenon.
The KAIST-SM metaverse partnership will bring out new culture technology that will lead the virtual entertainment industry by creating more dynamic and vivid digital technologies. KAIST will utilize its AI, robot, and network technologies, while SM will provide its content production expertise for this metaverse research.
President Lee said, “SM artists have mesmerized global audiences and opened new markets for K-Pop. Combining the creativity and cultural imagination of SM with technologies from KAIST, together we will make significant contributions to the advancement of virtual reality as well as the global entertainment industry.”
The Graduate School of Culture Technology has been engaging in a variety of creative projects incorporating science and technology for decades and will now actively participate in this metaverse project with SM.
CEP Lee explained, “The power of celebrities and avatars will rule the future entertainment industry. SM will make a leap forward to be a ‘first mover’ in the digital entertainment industry with this partnership with KAIST. This partnership will shape the new digital future of the entertainment industry boosted by cutting-edge technologies.”
CEP Lee also delivered a special lecture for the KAIST community via Zoom. Saying that producers in the future will be ‘culture scientists’, he stressed the importance of technology converging with culture.
“The key factor for K-pop’s success lies in the impressive technology of Korea. SM places a high priority on developing cultural technology and creating new artists and products combining this technology,” added Lee, citing the hologram contents of Beyond Live concerts and the new 4+4 girl group composed of four girls and four avatars called ‘Aespa.’
2021.06.25 View 8326 -
 Krafton Matches Alumni Donations to Raise 11 Billion KRW for SW Developers
Alumni donations from the School of Computing, including Baemin and Devsisters, continue to grow
Alumni from the KAIST School of Computing who are current and former developers at the leading game company Krafton, established by KAIST alumna Byung-Gyu Chang, made an agreement to help raise 11 billion KRW during a ceremony on June 4. The funds raised in the matching grant will be used to nurture software developers.
Krafton Chairman Chang donated 10 billion won last January. His donation inspired other alumni working at Krafton as well as its former developers. Eleven KAIST alumni raised 5.5 billion KRW in two months and discussed the matching grant idea with Chairman Chang.
The Krafton matching grant ceremony was attended by President Kwang Hyung Lee, Provost and Executive Vice President Seung Seob Lee, Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee, Head of the School of Computing Sukyoung Ryu, Krafton Chairman Byung-gyu Chang, and KAIST alumnus from Krafton Seung-woo Shin. Other alumni donors including Krafton CEO Changhan Kim joined the ceremony online.
Krafton CEO Changhan Kim said, “Just as our alma mater played an important role in growing our company, we hope that our donation could help support good developers. This will not only help our company, but advance our industry.”
KAIST and Krafton also signed a business agreement to foster competitive developers. Krafton said it plans to continue giving back to society through the matching grant program.
Head of the School of Computing Sukyoung Ryu thanked Chairman Chang and alumni who took part in the fund raising, saying, “To take the lead in rapidly changing computer technology, we desperately need more top students, faculty members, and facilities. We need more resources and infrastructure for interdisciplinary research.”
The School of Computing has seen significant growth recently. Its number of undergraduate students has increased from 450 in 2016 to more than 900 in 2021. With this donation, the school will expand its current buildings to provide diverse educational and mentoring programs in more spacious facilities.
Seung-woo Shin (Class of ’92), who joined Krafton’s matching grant, said, “I have always been thankful for the people I met and what I learned at KAIST. I was moved by the idea of giving back to the school.”
Seong-jung Ryu (Class of ’97) said, “This donation reminded me of the good times I had back then. I thought it was crucial that the department’s facilities be extended, so I naturally wanted to take part.”
Alumni donations, especially from the School of Computing, have also continued to grow more recently. Woowa Brothers Corp. CEO Beom-Jun Kim, the developer of the meal delivery app ‘Baemin’ donated 100 million KRW in April. Baemin became the most used app in the country during the COVID-19 pandemic.
He explained, “I have been thinking about ways to give something to the next generation, rather than ‘paying back’ those who helped me in the past.”
Encouraged by Baemin’s donation, alumni couple Ha-Yeon Seo and Dong-Hun Hahn from the School of Computing and eleven alumni engineers working at Devsisters Corp. also followed suit.
2021.06.09 View 12219
Krafton Matches Alumni Donations to Raise 11 Billion KRW for SW Developers
Alumni donations from the School of Computing, including Baemin and Devsisters, continue to grow
Alumni from the KAIST School of Computing who are current and former developers at the leading game company Krafton, established by KAIST alumna Byung-Gyu Chang, made an agreement to help raise 11 billion KRW during a ceremony on June 4. The funds raised in the matching grant will be used to nurture software developers.
Krafton Chairman Chang donated 10 billion won last January. His donation inspired other alumni working at Krafton as well as its former developers. Eleven KAIST alumni raised 5.5 billion KRW in two months and discussed the matching grant idea with Chairman Chang.
The Krafton matching grant ceremony was attended by President Kwang Hyung Lee, Provost and Executive Vice President Seung Seob Lee, Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee, Head of the School of Computing Sukyoung Ryu, Krafton Chairman Byung-gyu Chang, and KAIST alumnus from Krafton Seung-woo Shin. Other alumni donors including Krafton CEO Changhan Kim joined the ceremony online.
Krafton CEO Changhan Kim said, “Just as our alma mater played an important role in growing our company, we hope that our donation could help support good developers. This will not only help our company, but advance our industry.”
KAIST and Krafton also signed a business agreement to foster competitive developers. Krafton said it plans to continue giving back to society through the matching grant program.
Head of the School of Computing Sukyoung Ryu thanked Chairman Chang and alumni who took part in the fund raising, saying, “To take the lead in rapidly changing computer technology, we desperately need more top students, faculty members, and facilities. We need more resources and infrastructure for interdisciplinary research.”
The School of Computing has seen significant growth recently. Its number of undergraduate students has increased from 450 in 2016 to more than 900 in 2021. With this donation, the school will expand its current buildings to provide diverse educational and mentoring programs in more spacious facilities.
Seung-woo Shin (Class of ’92), who joined Krafton’s matching grant, said, “I have always been thankful for the people I met and what I learned at KAIST. I was moved by the idea of giving back to the school.”
Seong-jung Ryu (Class of ’97) said, “This donation reminded me of the good times I had back then. I thought it was crucial that the department’s facilities be extended, so I naturally wanted to take part.”
Alumni donations, especially from the School of Computing, have also continued to grow more recently. Woowa Brothers Corp. CEO Beom-Jun Kim, the developer of the meal delivery app ‘Baemin’ donated 100 million KRW in April. Baemin became the most used app in the country during the COVID-19 pandemic.
He explained, “I have been thinking about ways to give something to the next generation, rather than ‘paying back’ those who helped me in the past.”
Encouraged by Baemin’s donation, alumni couple Ha-Yeon Seo and Dong-Hun Hahn from the School of Computing and eleven alumni engineers working at Devsisters Corp. also followed suit.
2021.06.09 View 12219 -
 Natural Rainbow Colorants Microbially Produced
Integrated strategies of systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering led to the production of natural rainbow colorants comprising seven natural colorants from bacteria for the first time
A research group at KAIST has engineered bacterial strains capable of producing three carotenoids and four violacein derivatives, completing the seven colors in the rainbow spectrum. The research team integrated systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering strategies for the production of seven natural rainbow colorants in engineered Escherichia coli strains. The strategies will be also useful for the efficient production of other industrially important natural products used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Colorants are widely used in our lives and are directly related to human health when we eat food additives and wear cosmetics. However, most of these colorants are made from petroleum, causing unexpected side effects and health problems. Furthermore, they raise environmental concerns such as water pollution from dyeing fabric in the textiles industry. For these reasons, the demand for the production of natural colorants using microorganisms has increased, but could not be readily realized due to the high cost and low yield of the bioprocesses.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineers at KAIST including researchers Dr. Dongsoo Yang and Dr. Seon Young Park, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The team reported the study entitled “Production of rainbow colorants by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli” in Advanced Science online on May 5. It was selected as the journal cover of the July 7 issue.
This research reports for the first time the production of rainbow colorants comprising three carotenoids and four violacein derivatives from glucose or glycerol via systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering. The research group focused on the production of hydrophobic natural colorants useful for lipophilic food and dyeing garments. First, using systems metabolic engineering, which is an integrated technology to engineer the metabolism of a microorganism, three carotenoids comprising astaxanthin (red), -carotene (orange), and zeaxanthin (yellow), and four violacein derivatives comprising proviolacein (green), prodeoxyviolacein (blue), violacein (navy), and deoxyviolacein (purple) could be produced. Thus, the production of natural colorants covering the complete rainbow spectrum was achieved.
When hydrophobic colorants are produced from microorganisms, the colorants are accumulated inside the cell. As the accumulation capacity is limited, the hydrophobic colorants could not be produced with concentrations higher than the limit. In this regard, the researchers engineered the cell morphology and generated inner-membrane vesicles (spherical membranous structures) to increase the intracellular capacity for accumulating the natural colorants. To further promote production, the researchers generated outer-membrane vesicles to secrete the natural colorants, thus succeeding in efficiently producing all of seven rainbow colorants. It was even more impressive that the production of natural green and navy colorants was achieved for the first time.
“The production of the seven natural rainbow colorants that can replace the current petroleum-based synthetic colorants was achieved for the first time,” said Dr. Dongsoo Yang. He explained that another important point of the research is that integrated metabolic engineering strategies developed from this study can be generally applicable for the efficient production of other natural products useful as pharmaceuticals or nutraceuticals. “As maintaining good health in an aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” explained Distinguished Professor Lee.
This work was supported by the "Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ01550602)" Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
-Publication:Dongsoo Yang, Seon Young Park, and Sang Yup Lee. Production of rainbow colorants by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Advanced Science, 2100743.
-Profile Distinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.06.09 View 12527
Natural Rainbow Colorants Microbially Produced
Integrated strategies of systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering led to the production of natural rainbow colorants comprising seven natural colorants from bacteria for the first time
A research group at KAIST has engineered bacterial strains capable of producing three carotenoids and four violacein derivatives, completing the seven colors in the rainbow spectrum. The research team integrated systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering strategies for the production of seven natural rainbow colorants in engineered Escherichia coli strains. The strategies will be also useful for the efficient production of other industrially important natural products used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Colorants are widely used in our lives and are directly related to human health when we eat food additives and wear cosmetics. However, most of these colorants are made from petroleum, causing unexpected side effects and health problems. Furthermore, they raise environmental concerns such as water pollution from dyeing fabric in the textiles industry. For these reasons, the demand for the production of natural colorants using microorganisms has increased, but could not be readily realized due to the high cost and low yield of the bioprocesses.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineers at KAIST including researchers Dr. Dongsoo Yang and Dr. Seon Young Park, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The team reported the study entitled “Production of rainbow colorants by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli” in Advanced Science online on May 5. It was selected as the journal cover of the July 7 issue.
This research reports for the first time the production of rainbow colorants comprising three carotenoids and four violacein derivatives from glucose or glycerol via systems metabolic engineering and membrane engineering. The research group focused on the production of hydrophobic natural colorants useful for lipophilic food and dyeing garments. First, using systems metabolic engineering, which is an integrated technology to engineer the metabolism of a microorganism, three carotenoids comprising astaxanthin (red), -carotene (orange), and zeaxanthin (yellow), and four violacein derivatives comprising proviolacein (green), prodeoxyviolacein (blue), violacein (navy), and deoxyviolacein (purple) could be produced. Thus, the production of natural colorants covering the complete rainbow spectrum was achieved.
When hydrophobic colorants are produced from microorganisms, the colorants are accumulated inside the cell. As the accumulation capacity is limited, the hydrophobic colorants could not be produced with concentrations higher than the limit. In this regard, the researchers engineered the cell morphology and generated inner-membrane vesicles (spherical membranous structures) to increase the intracellular capacity for accumulating the natural colorants. To further promote production, the researchers generated outer-membrane vesicles to secrete the natural colorants, thus succeeding in efficiently producing all of seven rainbow colorants. It was even more impressive that the production of natural green and navy colorants was achieved for the first time.
“The production of the seven natural rainbow colorants that can replace the current petroleum-based synthetic colorants was achieved for the first time,” said Dr. Dongsoo Yang. He explained that another important point of the research is that integrated metabolic engineering strategies developed from this study can be generally applicable for the efficient production of other natural products useful as pharmaceuticals or nutraceuticals. “As maintaining good health in an aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” explained Distinguished Professor Lee.
This work was supported by the "Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ01550602)" Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
-Publication:Dongsoo Yang, Seon Young Park, and Sang Yup Lee. Production of rainbow colorants by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Advanced Science, 2100743.
-Profile Distinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.06.09 View 12527 -
 Ultrafast, on-Chip PCR Could Speed Up Diagnoses during Pandemics
A rapid point-of-care diagnostic plasmofluidic chip can deliver result in only 8 minutes
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) has been the gold standard for diagnosis during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the PCR portion of the test requires bulky, expensive machines and takes about an hour to complete, making it difficult to quickly diagnose someone at a testing site. Now, researchers at KAIST have developed a plasmofluidic chip that can perform PCR in only about 8 minutes, which could speed up diagnoses during current and future pandemics.
The rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 and other highly contagious viral diseases is important for timely medical care, quarantining and contact tracing. Currently, RT-PCR uses enzymes to reverse transcribe tiny amounts of viral RNA to DNA, and then amplifies the DNA so that it can be detected by a fluorescent probe. It is the most sensitive and reliable diagnostic method.
But because the PCR portion of the test requires 30-40 cycles of heating and cooling in special machines, it takes about an hour to perform, and samples must typically be sent away to a lab, meaning that a patient usually has to wait a day or two to receive their diagnosis.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his colleagues wanted to develop a plasmofluidic PCR chip that could quickly heat and cool miniscule volumes of liquids, allowing accurate point-of-care diagnoses in a fraction of the time. The research was reported in ACS Nano on May 19.
The researchers devised a postage stamp-sized polydimethylsiloxane chip with a microchamber array for the PCR reactions. When a drop of a sample is added to the chip, a vacuum pulls the liquid into the microchambers, which are positioned above glass nanopillars with gold nanoislands. Any microbubbles, which could interfere with the PCR reaction, diffuse out through an air-permeable wall. When a white LED is turned on beneath the chip, the gold nanoislands on the nanopillars quickly convert light to heat, and then rapidly cool when the light is switched off.
The researchers tested the device on a piece of DNA containing a SARS-CoV-2 gene, accomplishing 40 heating and cooling cycles and fluorescence detection in only 5 minutes, with an additional 3 minutes for sample loading. The amplification efficiency was 91%, whereas a comparable conventional PCR process has an efficiency of 98%. With the reverse transcriptase step added prior to sample loading, the entire testing time with the new method could take 10-13 minutes, as opposed to about an hour for typical RT-PCR testing. The new device could provide many opportunities for rapid point-of-care diagnostics during a pandemic, the researchers say.
-Publication
Ultrafast and Real-Time Nanoplasmonic On-Chip Polymerase Chain Reaction for Rapid and Quantitative Molecular Diagnostics
ACS Nano (https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c02154)
-Professor
Ki-Hun Jeong
Biophotonics Laboratory
https://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineeinrg
KAIST
2021.06.08 View 12646
Ultrafast, on-Chip PCR Could Speed Up Diagnoses during Pandemics
A rapid point-of-care diagnostic plasmofluidic chip can deliver result in only 8 minutes
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) has been the gold standard for diagnosis during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the PCR portion of the test requires bulky, expensive machines and takes about an hour to complete, making it difficult to quickly diagnose someone at a testing site. Now, researchers at KAIST have developed a plasmofluidic chip that can perform PCR in only about 8 minutes, which could speed up diagnoses during current and future pandemics.
The rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 and other highly contagious viral diseases is important for timely medical care, quarantining and contact tracing. Currently, RT-PCR uses enzymes to reverse transcribe tiny amounts of viral RNA to DNA, and then amplifies the DNA so that it can be detected by a fluorescent probe. It is the most sensitive and reliable diagnostic method.
But because the PCR portion of the test requires 30-40 cycles of heating and cooling in special machines, it takes about an hour to perform, and samples must typically be sent away to a lab, meaning that a patient usually has to wait a day or two to receive their diagnosis.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his colleagues wanted to develop a plasmofluidic PCR chip that could quickly heat and cool miniscule volumes of liquids, allowing accurate point-of-care diagnoses in a fraction of the time. The research was reported in ACS Nano on May 19.
The researchers devised a postage stamp-sized polydimethylsiloxane chip with a microchamber array for the PCR reactions. When a drop of a sample is added to the chip, a vacuum pulls the liquid into the microchambers, which are positioned above glass nanopillars with gold nanoislands. Any microbubbles, which could interfere with the PCR reaction, diffuse out through an air-permeable wall. When a white LED is turned on beneath the chip, the gold nanoislands on the nanopillars quickly convert light to heat, and then rapidly cool when the light is switched off.
The researchers tested the device on a piece of DNA containing a SARS-CoV-2 gene, accomplishing 40 heating and cooling cycles and fluorescence detection in only 5 minutes, with an additional 3 minutes for sample loading. The amplification efficiency was 91%, whereas a comparable conventional PCR process has an efficiency of 98%. With the reverse transcriptase step added prior to sample loading, the entire testing time with the new method could take 10-13 minutes, as opposed to about an hour for typical RT-PCR testing. The new device could provide many opportunities for rapid point-of-care diagnostics during a pandemic, the researchers say.
-Publication
Ultrafast and Real-Time Nanoplasmonic On-Chip Polymerase Chain Reaction for Rapid and Quantitative Molecular Diagnostics
ACS Nano (https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c02154)
-Professor
Ki-Hun Jeong
Biophotonics Laboratory
https://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineeinrg
KAIST
2021.06.08 View 12646