%CE%BCLED
-
 KAIST researchers devises a technology to utilize ultrahigh-resolution micro-LED with 40% reduced self-generated heat
In the digitized modern life, various forms of future displays, such as wearable and rollable displays are required. More and more people are wanting to connect to the virtual world whenever and wherever with the use of their smartglasses or smartwatches. Even further, we’ve been hearing about medical diagnosis kit on a shirt and a theatre-hat. However, it is not quite here in our hands yet due to technical limitations of being unable to fit as many pixels as a limited surface area of a glasses while keeping the power consumption at the a level that a hand held battery can supply, all the while the resolution of 4K+ is needed in order to perfectly immerse the users into the augmented or virtual reality through a wireless smartglasses or whatever the device.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd that Professor Sang Hyeon Kim's research team of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering re-examined the phenomenon of efficiency degradation of micro-LEDs with pixels in a size of micrometers (μm, one millionth of a meter) and found that it was possible to fundamentally resolve the problem by the use of epitaxial structure engineering.
Epitaxy refers to the process of stacking gallium nitride crystals that are used as a light emitting body on top of an ultrapure silicon or sapphire substrate used for μLEDs as a medium.
μLED is being actively studied because it has the advantages of superior brightness, contrast ratio, and lifespan compared to OLED. In 2018, Samsung Electronics commercialized a product equipped with μLED called 'The Wall'. And there is a prospect that Apple may be launching a μLED-mounted product in 2025.
In order to manufacture μLEDs, pixels are formed by cutting the epitaxial structure grown on a wafer into a cylinder or cuboid shape through an etching process, and this etching process is accompanied by a plasma-based process. However, these plasmas generate defects on the side of the pixel during the pixel formation process.
Therefore, as the pixel size becomes smaller and the resolution increases, the ratio of the surface area to the volume of the pixel increases, and defects on the side of the device that occur during processing further reduce the device efficiency of the μLED. Accordingly, a considerable amount of research has been conducted on mitigating or removing sidewall defects, but this method has a limit to the degree of improvement as it must be done at the post-processing stage after the grown of the epitaxial structure is finished.
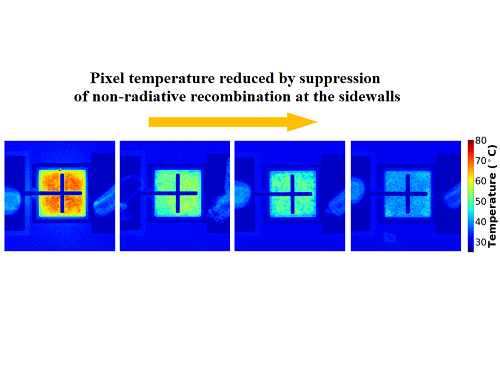
The research team identified that there is a difference in the current moving to the sidewall of the μLED depending on the epitaxial structure during μLED device operation, and based on the findings, the team built a structure that is not sensitive to sidewall defects to solve the problem of reduced efficiency due to miniaturization of μLED devices. In addition, the proposed structure reduced the self-generated heat while the device was running by about 40% compared to the existing structure, which is also of great significance in commercialization of ultrahigh-resolution μLED displays.
This study, which was led by Woo Jin Baek of Professor Sang Hyeon Kim's research team at the KAIST School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering as the first author with guidance by Professor Sang Hyeon Kim and Professor Dae-Myeong Geum of the Chungbuk National University (who was with the team as a postdoctoral researcher at the time) as corresponding authors, was published in the international journal, 'Nature Communications' on March 17th. (Title of the paper: Ultra-low-current driven InGaN blue micro light-emitting diodes for electrically efficient and self-heating relaxed microdisplay).
Professor Sang Hyeon Kim said, "This technological development has great meaning in identifying the cause of the drop in efficiency, which was an obstacle to miniaturization of μLED, and solving it with the design of the epitaxial structure.“ He added, ”We are looking forward to it being used in manufacturing of ultrahigh-resolution displays in the future."
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Future Technology Incubation Center.
Figure 1. Image of electroluminescence distribution of μLEDs fabricated from epitaxial structures with quantum barriers of different thicknesses while the current is running
Figure 2. Thermal distribution images of devices fabricated with different epitaxial structures under the same amount of light.
Figure 3. Normalized external quantum efficiency of the device fabricated with the optimized epitaxial structure by sizes.
2023.03.23 View 8152
KAIST researchers devises a technology to utilize ultrahigh-resolution micro-LED with 40% reduced self-generated heat
In the digitized modern life, various forms of future displays, such as wearable and rollable displays are required. More and more people are wanting to connect to the virtual world whenever and wherever with the use of their smartglasses or smartwatches. Even further, we’ve been hearing about medical diagnosis kit on a shirt and a theatre-hat. However, it is not quite here in our hands yet due to technical limitations of being unable to fit as many pixels as a limited surface area of a glasses while keeping the power consumption at the a level that a hand held battery can supply, all the while the resolution of 4K+ is needed in order to perfectly immerse the users into the augmented or virtual reality through a wireless smartglasses or whatever the device.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd that Professor Sang Hyeon Kim's research team of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering re-examined the phenomenon of efficiency degradation of micro-LEDs with pixels in a size of micrometers (μm, one millionth of a meter) and found that it was possible to fundamentally resolve the problem by the use of epitaxial structure engineering.
Epitaxy refers to the process of stacking gallium nitride crystals that are used as a light emitting body on top of an ultrapure silicon or sapphire substrate used for μLEDs as a medium.
μLED is being actively studied because it has the advantages of superior brightness, contrast ratio, and lifespan compared to OLED. In 2018, Samsung Electronics commercialized a product equipped with μLED called 'The Wall'. And there is a prospect that Apple may be launching a μLED-mounted product in 2025.
In order to manufacture μLEDs, pixels are formed by cutting the epitaxial structure grown on a wafer into a cylinder or cuboid shape through an etching process, and this etching process is accompanied by a plasma-based process. However, these plasmas generate defects on the side of the pixel during the pixel formation process.
Therefore, as the pixel size becomes smaller and the resolution increases, the ratio of the surface area to the volume of the pixel increases, and defects on the side of the device that occur during processing further reduce the device efficiency of the μLED. Accordingly, a considerable amount of research has been conducted on mitigating or removing sidewall defects, but this method has a limit to the degree of improvement as it must be done at the post-processing stage after the grown of the epitaxial structure is finished.
The research team identified that there is a difference in the current moving to the sidewall of the μLED depending on the epitaxial structure during μLED device operation, and based on the findings, the team built a structure that is not sensitive to sidewall defects to solve the problem of reduced efficiency due to miniaturization of μLED devices. In addition, the proposed structure reduced the self-generated heat while the device was running by about 40% compared to the existing structure, which is also of great significance in commercialization of ultrahigh-resolution μLED displays.
This study, which was led by Woo Jin Baek of Professor Sang Hyeon Kim's research team at the KAIST School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering as the first author with guidance by Professor Sang Hyeon Kim and Professor Dae-Myeong Geum of the Chungbuk National University (who was with the team as a postdoctoral researcher at the time) as corresponding authors, was published in the international journal, 'Nature Communications' on March 17th. (Title of the paper: Ultra-low-current driven InGaN blue micro light-emitting diodes for electrically efficient and self-heating relaxed microdisplay).
Professor Sang Hyeon Kim said, "This technological development has great meaning in identifying the cause of the drop in efficiency, which was an obstacle to miniaturization of μLED, and solving it with the design of the epitaxial structure.“ He added, ”We are looking forward to it being used in manufacturing of ultrahigh-resolution displays in the future."
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Future Technology Incubation Center.
Figure 1. Image of electroluminescence distribution of μLEDs fabricated from epitaxial structures with quantum barriers of different thicknesses while the current is running
Figure 2. Thermal distribution images of devices fabricated with different epitaxial structures under the same amount of light.
Figure 3. Normalized external quantum efficiency of the device fabricated with the optimized epitaxial structure by sizes.
2023.03.23 View 8152 -
 KAIST researchers develops a tech to enable production of ultrahigh-resolution LED with sub-micrometer scale pixels
Ultrahigh-resolution displays are an essential element for developing next-generation electronic products such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and smart watches, and can be applied not only to head-mounted displays, but also to smart glasses and smart lenses. The technology developed through this research is expected to be used to make such next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and other various sub-micro optoelectronic devices.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd that Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team of KAIST Department of Physics developed the core technology for an ultrahigh resolution light-emitting diode (LED) display that can realize 0.5 micron-scale pixels smaller than 1/100 of the average hair thickness (about 100 microns) using focused ion beams.
Commonly, pixelation of ultrahigh-resolution LED displays usually relies on the etching method that physically cuts the area around the pixel, but as the pixel becomes smaller due to the occurrence of various defects around it, leading to side-effects of having leakage of current increased and light-emission efficiency decreased. In addition, various complex processes such as patterning for pixelation and post-processing for prevention of leakage current are required.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team developed a technology that can create pixels down to the size of a microscale without the complicated pre- and post-processing using a focused ion beam. This method has the advantage of being able to freely set the shape of the emitting pixel without causing any structural deformation on the material surface by controlling the intensity of the focused ion beam.
The focused ion beam technology has been widely used for ultrahigh-magnification imaging and nanostructure fabrication in fields such as materials engineering and biology. However, when a focused ion beam is used on a light emitting body such as an LED, light emission of a portion hit by the beam and a surrounding area rapidly decreases, which has been a barrier to fabricating a nano-scale light emitting structure. Upon facing this issue, Professor Cho's research team began the research on the idea that if they turned things around to use these problematic phenomena, they can be used in ultra-fine pixelation method on a sub-micron scale.
The research team used a focused ion beam whose intensity was softened to the extent that the surface was not shaved, and found that not only the light-emission rapidly decreased in the area hit by the focused ion beam, but also the local resistance greatly increased. As a result, while the surface of the LED is kept flat, the portion hit by the focused ion beam is optically and electrically isolated, enabling pixelation for independent operation.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho, who led the research, said, “We have newly developed a technology that can create sub-micron-scale pixels without complicated processes using a focused ion beam, which will be a base technology that can be applied to next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and nano-photoelectronic devices.”
This research in which the Master's student Ji-Hwan Moon and the Ph.D. student Baul Kim of KAIST Department of Physics participated as co-first authors, was carried out with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea's Support Program for Mid-Career Researchers and the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation. It was published online in 'Advanced Materials' on February 13, and was also selected as the internal cover of the next offline edition. (Title: Electrically Driven Sub-Micron Light-Emitting Diode Arrays Using Maskless and Etching-Free Pixelation)
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the technology for ultrahigh density sub-micron-sized pixels through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation on an LED device
Figure 2. Ultra-high-density pixelation technology of micro light-emitting diodes (μLED) through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation
Figure 3. Rectangular pixels of different sizes (surface structure picture and luminescence picture) realized by a focused ion beam. Luminescence pictures of pixel arrays ranging in size from 20 µm x 20 µm to 0.5 µm x 0.5 µm, with surface flatness maintained.
2023.03.08 View 8626
KAIST researchers develops a tech to enable production of ultrahigh-resolution LED with sub-micrometer scale pixels
Ultrahigh-resolution displays are an essential element for developing next-generation electronic products such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and smart watches, and can be applied not only to head-mounted displays, but also to smart glasses and smart lenses. The technology developed through this research is expected to be used to make such next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and other various sub-micro optoelectronic devices.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd that Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team of KAIST Department of Physics developed the core technology for an ultrahigh resolution light-emitting diode (LED) display that can realize 0.5 micron-scale pixels smaller than 1/100 of the average hair thickness (about 100 microns) using focused ion beams.
Commonly, pixelation of ultrahigh-resolution LED displays usually relies on the etching method that physically cuts the area around the pixel, but as the pixel becomes smaller due to the occurrence of various defects around it, leading to side-effects of having leakage of current increased and light-emission efficiency decreased. In addition, various complex processes such as patterning for pixelation and post-processing for prevention of leakage current are required.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team developed a technology that can create pixels down to the size of a microscale without the complicated pre- and post-processing using a focused ion beam. This method has the advantage of being able to freely set the shape of the emitting pixel without causing any structural deformation on the material surface by controlling the intensity of the focused ion beam.
The focused ion beam technology has been widely used for ultrahigh-magnification imaging and nanostructure fabrication in fields such as materials engineering and biology. However, when a focused ion beam is used on a light emitting body such as an LED, light emission of a portion hit by the beam and a surrounding area rapidly decreases, which has been a barrier to fabricating a nano-scale light emitting structure. Upon facing this issue, Professor Cho's research team began the research on the idea that if they turned things around to use these problematic phenomena, they can be used in ultra-fine pixelation method on a sub-micron scale.
The research team used a focused ion beam whose intensity was softened to the extent that the surface was not shaved, and found that not only the light-emission rapidly decreased in the area hit by the focused ion beam, but also the local resistance greatly increased. As a result, while the surface of the LED is kept flat, the portion hit by the focused ion beam is optically and electrically isolated, enabling pixelation for independent operation.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho, who led the research, said, “We have newly developed a technology that can create sub-micron-scale pixels without complicated processes using a focused ion beam, which will be a base technology that can be applied to next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and nano-photoelectronic devices.”
This research in which the Master's student Ji-Hwan Moon and the Ph.D. student Baul Kim of KAIST Department of Physics participated as co-first authors, was carried out with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea's Support Program for Mid-Career Researchers and the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation. It was published online in 'Advanced Materials' on February 13, and was also selected as the internal cover of the next offline edition. (Title: Electrically Driven Sub-Micron Light-Emitting Diode Arrays Using Maskless and Etching-Free Pixelation)
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the technology for ultrahigh density sub-micron-sized pixels through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation on an LED device
Figure 2. Ultra-high-density pixelation technology of micro light-emitting diodes (μLED) through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation
Figure 3. Rectangular pixels of different sizes (surface structure picture and luminescence picture) realized by a focused ion beam. Luminescence pictures of pixel arrays ranging in size from 20 µm x 20 µm to 0.5 µm x 0.5 µm, with surface flatness maintained.
2023.03.08 View 8626