School+of+Electrical+Engineering
-
 Scientists Develop Wireless Networks that Allow Brain Circuits to Be Controlled Remotely through the Internet
Wireless implantable devices and IoT could manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world due to their minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility
A new study shows that researchers can remotely control the brain circuits of numerous animals simultaneously and independently through the internet. The scientists believe this newly developed technology can speed up brain research and various neuroscience studies to uncover basic brain functions as well as the underpinnings of various neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers at KAIST, Washington University in St. Louis, and the University of Colorado, Boulder, created a wireless ecosystem with its own wireless implantable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure to enable high-throughput neuroscience experiments over the internet. This innovative technology could enable scientists to manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world. The study was published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering on November 25
“This novel technology is highly versatile and adaptive. It can remotely control numerous neural implants and laboratory tools in real-time or in a scheduled way without direct human interactions,” said Professor Jae-Woong Jeong of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and a senior author of the study. “These wireless neural devices and equipment integrated with IoT technology have enormous potential for science and medicine.”
The wireless ecosystem only requires a mini-computer that can be purchased for under $45, which connects to the internet and communicates with wireless multifunctional brain probes or other types of conventional laboratory equipment using IoT control modules. By optimally integrating the versatility and modular construction of both unique IoT hardware and software within a single ecosystem, this wireless technology offers new applications that have not been demonstrated before by a single standalone technology. This includes, but is not limited to minimalistic hardware, global remote access, selective and scheduled experiments, customizable automation, and high-throughput scalability.
“As long as researchers have internet access, they are able to trigger, customize, stop, validate, and store the outcomes of large experiments at any time and from anywhere in the world. They can remotely perform large-scale neuroscience experiments in animals deployed in multiple countries,” said one of the lead authors, Dr. Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado, Boulder. “The low cost of this system allows it to be easily adopted and can further fuel innovation across many laboratories,” Dr. Qazi added.
One of the significant advantages of this IoT neurotechnology is its ability to be mass deployed across the globe due to its minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility. Scientists across the world can quickly implement this technology within their existing laboratories with minimal budget concerns to achieve globally remote access, scalable experimental automation, or both, thus potentially reducing the time needed to unravel various neuroscientific challenges such as those associated with intractable neurological conditions.
Another senior author on the study, Professor Jordan McCall from the Department of Anesthesiology and Center for Clinical Pharmacology at Washington University in St. Louis, said this technology has the potential to change how basic neuroscience studies are performed. “One of the biggest limitations when trying to understand how the mammalian brain works is that we have to study these functions in unnatural conditions. This technology brings us one step closer to performing important studies without direct human interaction with the study subjects.”
The ability to remotely schedule experiments moves toward automating these types of experiments. Dr. Kyle Parker, an instructor at Washington University in St. Louis and another lead author on the study added, “This experimental automation can potentially help us reduce the number of animals used in biomedical research by reducing the variability introduced by various experimenters. This is especially important given our moral imperative to seek research designs that enable this reduction.”
The researchers believe this wireless technology may open new opportunities for many applications including brain research, pharmaceuticals, and telemedicine to treat diseases in the brain and other organs remotely. This remote automation technology could become even more valuable when many labs need to shut down, such as during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This work was supported by grants from the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the United States National Institute of Health, and Oak Ridge Associated Universities.
-PublicationRaza Qazi, Kyle Parker, Choong Yeon Kim, Jordan McCall, Jae-Woong Jeong et al. “Scalable and modular wireless-network infrastructure for large-scale behavioral neuroscience,” Nature Biomedical Engineering, November 25 2021 (doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00814-w)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Woong JeongBio-Integrated Electronics and Systems LabSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.11.29 View 17026
Scientists Develop Wireless Networks that Allow Brain Circuits to Be Controlled Remotely through the Internet
Wireless implantable devices and IoT could manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world due to their minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility
A new study shows that researchers can remotely control the brain circuits of numerous animals simultaneously and independently through the internet. The scientists believe this newly developed technology can speed up brain research and various neuroscience studies to uncover basic brain functions as well as the underpinnings of various neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers at KAIST, Washington University in St. Louis, and the University of Colorado, Boulder, created a wireless ecosystem with its own wireless implantable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure to enable high-throughput neuroscience experiments over the internet. This innovative technology could enable scientists to manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world. The study was published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering on November 25
“This novel technology is highly versatile and adaptive. It can remotely control numerous neural implants and laboratory tools in real-time or in a scheduled way without direct human interactions,” said Professor Jae-Woong Jeong of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and a senior author of the study. “These wireless neural devices and equipment integrated with IoT technology have enormous potential for science and medicine.”
The wireless ecosystem only requires a mini-computer that can be purchased for under $45, which connects to the internet and communicates with wireless multifunctional brain probes or other types of conventional laboratory equipment using IoT control modules. By optimally integrating the versatility and modular construction of both unique IoT hardware and software within a single ecosystem, this wireless technology offers new applications that have not been demonstrated before by a single standalone technology. This includes, but is not limited to minimalistic hardware, global remote access, selective and scheduled experiments, customizable automation, and high-throughput scalability.
“As long as researchers have internet access, they are able to trigger, customize, stop, validate, and store the outcomes of large experiments at any time and from anywhere in the world. They can remotely perform large-scale neuroscience experiments in animals deployed in multiple countries,” said one of the lead authors, Dr. Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado, Boulder. “The low cost of this system allows it to be easily adopted and can further fuel innovation across many laboratories,” Dr. Qazi added.
One of the significant advantages of this IoT neurotechnology is its ability to be mass deployed across the globe due to its minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility. Scientists across the world can quickly implement this technology within their existing laboratories with minimal budget concerns to achieve globally remote access, scalable experimental automation, or both, thus potentially reducing the time needed to unravel various neuroscientific challenges such as those associated with intractable neurological conditions.
Another senior author on the study, Professor Jordan McCall from the Department of Anesthesiology and Center for Clinical Pharmacology at Washington University in St. Louis, said this technology has the potential to change how basic neuroscience studies are performed. “One of the biggest limitations when trying to understand how the mammalian brain works is that we have to study these functions in unnatural conditions. This technology brings us one step closer to performing important studies without direct human interaction with the study subjects.”
The ability to remotely schedule experiments moves toward automating these types of experiments. Dr. Kyle Parker, an instructor at Washington University in St. Louis and another lead author on the study added, “This experimental automation can potentially help us reduce the number of animals used in biomedical research by reducing the variability introduced by various experimenters. This is especially important given our moral imperative to seek research designs that enable this reduction.”
The researchers believe this wireless technology may open new opportunities for many applications including brain research, pharmaceuticals, and telemedicine to treat diseases in the brain and other organs remotely. This remote automation technology could become even more valuable when many labs need to shut down, such as during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This work was supported by grants from the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the United States National Institute of Health, and Oak Ridge Associated Universities.
-PublicationRaza Qazi, Kyle Parker, Choong Yeon Kim, Jordan McCall, Jae-Woong Jeong et al. “Scalable and modular wireless-network infrastructure for large-scale behavioral neuroscience,” Nature Biomedical Engineering, November 25 2021 (doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00814-w)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Woong JeongBio-Integrated Electronics and Systems LabSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.11.29 View 17026 -
 Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s Team Wins the Best Paper and the Methods Recognition Awards at the ACM CSCW
A research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee at the School of Electrical Engineering won the Best Paper Award and the Methods Recognition Award from ACM CSCW (International Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing) 2021 for their paper “Reflect, not Regret: Understanding Regretful Smartphone Use with App Feature-Level Analysis”.
Founded in 1986, CSCW has been a premier conference on HCI (Human Computer Interaction) and Social Computing. This year, 340 full papers were presented and the best paper awards are given to the top 1% papers of the submitted. Methods Recognition, which is a new award, is given “for strong examples of work that includes well developed, explained, or implemented methods, and methodological innovation.”
Hyunsung Cho (KAIST alumus and currently a PhD candidate at Carnegie Mellon University), Daeun Choi (KAIST undergraduate researcher), Donghwi Kim (KAIST PhD Candidate), Wan Ju Kang (KAIST PhD Candidate), and Professor Eun Kyoung Choe (University of Maryland and KAIST alumna) collaborated on this research.
The authors developed a tool that tracks and analyzes which features of a mobile app (e.g., Instagram’s following post, following story, recommended post, post upload, direct messaging, etc.) are in use based on a smartphone’s User Interface (UI) layout. Utilizing this novel method, the authors revealed which feature usage patterns result in regretful smartphone use.
Professor Lee said, “Although many people enjoy the benefits of smartphones, issues have emerged from the overuse of smartphones. With this feature level analysis, users can reflect on their smartphone usage based on finer grained analysis and this could contribute to digital wellbeing.”
2021.11.22 View 8927
Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s Team Wins the Best Paper and the Methods Recognition Awards at the ACM CSCW
A research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee at the School of Electrical Engineering won the Best Paper Award and the Methods Recognition Award from ACM CSCW (International Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing) 2021 for their paper “Reflect, not Regret: Understanding Regretful Smartphone Use with App Feature-Level Analysis”.
Founded in 1986, CSCW has been a premier conference on HCI (Human Computer Interaction) and Social Computing. This year, 340 full papers were presented and the best paper awards are given to the top 1% papers of the submitted. Methods Recognition, which is a new award, is given “for strong examples of work that includes well developed, explained, or implemented methods, and methodological innovation.”
Hyunsung Cho (KAIST alumus and currently a PhD candidate at Carnegie Mellon University), Daeun Choi (KAIST undergraduate researcher), Donghwi Kim (KAIST PhD Candidate), Wan Ju Kang (KAIST PhD Candidate), and Professor Eun Kyoung Choe (University of Maryland and KAIST alumna) collaborated on this research.
The authors developed a tool that tracks and analyzes which features of a mobile app (e.g., Instagram’s following post, following story, recommended post, post upload, direct messaging, etc.) are in use based on a smartphone’s User Interface (UI) layout. Utilizing this novel method, the authors revealed which feature usage patterns result in regretful smartphone use.
Professor Lee said, “Although many people enjoy the benefits of smartphones, issues have emerged from the overuse of smartphones. With this feature level analysis, users can reflect on their smartphone usage based on finer grained analysis and this could contribute to digital wellbeing.”
2021.11.22 View 8927 -
 3 KAIST PhD Candidates Selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows
PhD candidates Soo Ye Kim and Sanghyun Woo from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering and Hae Beom Lee from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI were selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows. The Google PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that supports graduate school students from around the world that have produced excellent achievements from promising computer science-related fields. The 75 selected fellows will receive ten thousand dollars of funding with the opportunity to discuss research and receive one-on-one feedback from experts in related fields at Google.
Kim and Woo were named fellows in the field of "Machine Perception, Speech Technology and Computer Vision" with research of deep learning based super-resolution and computer vision respectively. Lee was named a fellow in the field of "Machine Learning" for his research in meta-learning.
Kim's research includes the formulation of novel methods for super-resolution and HDR video restoration and deep joint frame interpolation and super-resolution methods. Many of her works have been presented in leading conferences in computer vision and AI such as CVPR, ICCV, and AAAI. In addition, she has been collaborating as a research intern with the Vision Group Team at Adobe Research to study depth map refinement techniques.
(Kim's research on deep learning based joint super-resolution and inverse tone-mapping framework for HDR videos)
Woo’s research includes an effective deep learning model design based on the attention mechanism and learning methods based on self-learning and simulators. His works have been also presented in leading conferences such as CVPR, ECCV, and NeurIPS. In particular, his work on the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) which was presented at ECCV in 2018 has surpassed over 2700 citations on Google Scholar after being referenced in many computer vision applications. He was also a recipient of Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship in 2020.
(Woo's research on attention mechanism based deep learning models)
Lee’s research focuses effectively overcoming various limitations of the existing meta-learning framework. Specifically, he proposed to deal with a realistic task distribution with imbalances, improved the practicality of meta-knowledge, and made meta-learning possible even in large-scale task scenarios. These various studies have been accepted to numerous top-tier machine learning conferences such as NeurIPS, ICML, and ICLR. In particular, one of his papers has been selected as an oral presentation at ICLR 2020 and another as a spotlight presentation at NeurIPS 2020.
(Lee's research on learning to balance and continual trajectory shifting)
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the award ceremony was held virtually at the Google PhD Fellowship Summit from August 31st to September 1st. The list of fellowship recipients is displayed on the Google webpage.
2021.10.18 View 6840
3 KAIST PhD Candidates Selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows
PhD candidates Soo Ye Kim and Sanghyun Woo from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering and Hae Beom Lee from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI were selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows. The Google PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that supports graduate school students from around the world that have produced excellent achievements from promising computer science-related fields. The 75 selected fellows will receive ten thousand dollars of funding with the opportunity to discuss research and receive one-on-one feedback from experts in related fields at Google.
Kim and Woo were named fellows in the field of "Machine Perception, Speech Technology and Computer Vision" with research of deep learning based super-resolution and computer vision respectively. Lee was named a fellow in the field of "Machine Learning" for his research in meta-learning.
Kim's research includes the formulation of novel methods for super-resolution and HDR video restoration and deep joint frame interpolation and super-resolution methods. Many of her works have been presented in leading conferences in computer vision and AI such as CVPR, ICCV, and AAAI. In addition, she has been collaborating as a research intern with the Vision Group Team at Adobe Research to study depth map refinement techniques.
(Kim's research on deep learning based joint super-resolution and inverse tone-mapping framework for HDR videos)
Woo’s research includes an effective deep learning model design based on the attention mechanism and learning methods based on self-learning and simulators. His works have been also presented in leading conferences such as CVPR, ECCV, and NeurIPS. In particular, his work on the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) which was presented at ECCV in 2018 has surpassed over 2700 citations on Google Scholar after being referenced in many computer vision applications. He was also a recipient of Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship in 2020.
(Woo's research on attention mechanism based deep learning models)
Lee’s research focuses effectively overcoming various limitations of the existing meta-learning framework. Specifically, he proposed to deal with a realistic task distribution with imbalances, improved the practicality of meta-knowledge, and made meta-learning possible even in large-scale task scenarios. These various studies have been accepted to numerous top-tier machine learning conferences such as NeurIPS, ICML, and ICLR. In particular, one of his papers has been selected as an oral presentation at ICLR 2020 and another as a spotlight presentation at NeurIPS 2020.
(Lee's research on learning to balance and continual trajectory shifting)
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the award ceremony was held virtually at the Google PhD Fellowship Summit from August 31st to September 1st. The list of fellowship recipients is displayed on the Google webpage.
2021.10.18 View 6840 -
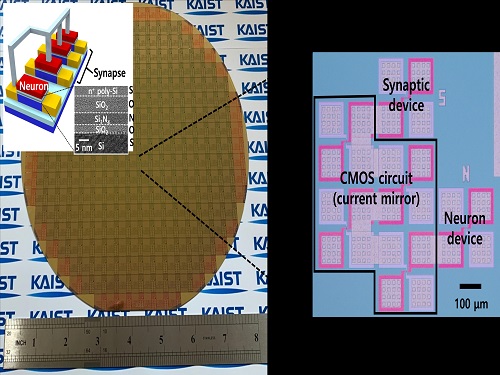 Brain-Inspired Highly Scalable Neuromorphic Hardware Presented
Neurons and synapses based on single transistor can dramatically reduce the hardware cost and accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware
KAIST researchers fabricated a brain-inspired highly scalable neuromorphic hardware by co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses. Using standard silicon complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, the neuromorphic hardware is expected to reduce chip cost and simplify fabrication procedures.
The research team led by Yang-Kyu Choi and Sung-Yool Choi produced a neurons and synapses based on single transistor for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware and showed the ability to recognize text and face images. This research was featured in Science Advances on August 4.
Neuromorphic hardware has attracted a great deal of attention because of its artificial intelligence functions, but consuming ultra-low power of less than 20 watts by mimicking the human brain. To make neuromorphic hardware work, a neuron that generates a spike when integrating a certain signal, and a synapse remembering the connection between two neurons are necessary, just like the biological brain. However, since neurons and synapses constructed on digital or analog circuits occupy a large space, there is a limit in terms of hardware efficiency and costs. Since the human brain consists of about 1011 neurons and 1014 synapses, it is necessary to improve the hardware cost in order to apply it to mobile and IoT devices.
To solve the problem, the research team mimicked the behavior of biological neurons and synapses with a single transistor, and co-integrated them onto an 8-inch wafer. The manufactured neuromorphic transistors have the same structure as the transistors for memory and logic that are currently mass-produced. In addition, the neuromorphic transistors proved for the first time that they can be implemented with a ‘Janus structure’ that functions as both neuron and synapse, just like coins have heads and tails.
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi said that this work can dramatically reduce the hardware cost by replacing the neurons and synapses that were based on complex digital and analog circuits with a single transistor. "We have demonstrated that neurons and synapses can be implemented using a single transistor," said Joon-Kyu Han, the first author. "By co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses on the same wafer using a standard CMOS process, the hardware cost of the neuromorphic hardware has been improved, which will accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware,” Han added.This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) and IC Design Education Center (IDEC).
-PublicationJoon-Kyu Han, Sung-Yool Choi, Yang-Kyu Choi, et al.“Cointegration of single-transistor neurons and synapses by nanoscale CMOS fabrication for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware,” Science Advances (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg8836)
-ProfileProfessor Yang-Kyu ChoiNano-Oriented Bio-Electronics Labhttps://sites.google.com/view/nobelab/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
Professor Sung-Yool ChoiMolecular and Nano Device Laboratoryhttps://www.mndl.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.08.05 View 12456
Brain-Inspired Highly Scalable Neuromorphic Hardware Presented
Neurons and synapses based on single transistor can dramatically reduce the hardware cost and accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware
KAIST researchers fabricated a brain-inspired highly scalable neuromorphic hardware by co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses. Using standard silicon complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, the neuromorphic hardware is expected to reduce chip cost and simplify fabrication procedures.
The research team led by Yang-Kyu Choi and Sung-Yool Choi produced a neurons and synapses based on single transistor for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware and showed the ability to recognize text and face images. This research was featured in Science Advances on August 4.
Neuromorphic hardware has attracted a great deal of attention because of its artificial intelligence functions, but consuming ultra-low power of less than 20 watts by mimicking the human brain. To make neuromorphic hardware work, a neuron that generates a spike when integrating a certain signal, and a synapse remembering the connection between two neurons are necessary, just like the biological brain. However, since neurons and synapses constructed on digital or analog circuits occupy a large space, there is a limit in terms of hardware efficiency and costs. Since the human brain consists of about 1011 neurons and 1014 synapses, it is necessary to improve the hardware cost in order to apply it to mobile and IoT devices.
To solve the problem, the research team mimicked the behavior of biological neurons and synapses with a single transistor, and co-integrated them onto an 8-inch wafer. The manufactured neuromorphic transistors have the same structure as the transistors for memory and logic that are currently mass-produced. In addition, the neuromorphic transistors proved for the first time that they can be implemented with a ‘Janus structure’ that functions as both neuron and synapse, just like coins have heads and tails.
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi said that this work can dramatically reduce the hardware cost by replacing the neurons and synapses that were based on complex digital and analog circuits with a single transistor. "We have demonstrated that neurons and synapses can be implemented using a single transistor," said Joon-Kyu Han, the first author. "By co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses on the same wafer using a standard CMOS process, the hardware cost of the neuromorphic hardware has been improved, which will accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware,” Han added.This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) and IC Design Education Center (IDEC).
-PublicationJoon-Kyu Han, Sung-Yool Choi, Yang-Kyu Choi, et al.“Cointegration of single-transistor neurons and synapses by nanoscale CMOS fabrication for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware,” Science Advances (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg8836)
-ProfileProfessor Yang-Kyu ChoiNano-Oriented Bio-Electronics Labhttps://sites.google.com/view/nobelab/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
Professor Sung-Yool ChoiMolecular and Nano Device Laboratoryhttps://www.mndl.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.08.05 View 12456 -
 Prof. Changho Suh Named the 2021 James L. Massey Awardee
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering was named the recipient of the 2021 James L.Massey Award. The award recognizes outstanding achievement in research and teaching by young scholars in the information theory community. The award is named in honor of James L. Massey, who was an internationally acclaimed pioneer in digital communications and revered teacher and mentor to communications engineers.
Professor Suh is a recipient of numerous awards, including the 2021 James L. Massey Research & Teaching Award for Young Scholars from the IEEE Information Theory Society, the 2019 AFOSR Grant, the 2019 Google Education Grant, the 2018 IEIE/IEEE Joint Award, the 2015 IEIE Haedong Young Engineer Award, the 2013 IEEE Communications Society Stephen O. Rice Prize, the 2011 David J. Sakrison Memorial Prize (the best dissertation award in UC Berkeley EECS), the 2009 IEEE ISIT Best Student Paper Award, the 2020 LINKGENESIS Best Teacher Award (the campus-wide Grand Prize in Teaching), and the four Departmental Teaching Awards (2013, 2019, 2020, 2021).
Dr. Suh is an IEEE Information Theory Society Distinguished Lecturer, the General Chair of the Inaugural IEEE East Asian School of Information Theory, and a Member of the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology. He is also an Associate Editor of Machine Learning for the IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, the Editor for the IEEE Information Theory Newsletter, a Column Editor for IEEE BITS the Information Theory Magazine, an Area Chair of NeurIPS 2021, and on the Senior Program Committee of IJCAI 2019–2021.
2021.07.27 View 9489
Prof. Changho Suh Named the 2021 James L. Massey Awardee
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering was named the recipient of the 2021 James L.Massey Award. The award recognizes outstanding achievement in research and teaching by young scholars in the information theory community. The award is named in honor of James L. Massey, who was an internationally acclaimed pioneer in digital communications and revered teacher and mentor to communications engineers.
Professor Suh is a recipient of numerous awards, including the 2021 James L. Massey Research & Teaching Award for Young Scholars from the IEEE Information Theory Society, the 2019 AFOSR Grant, the 2019 Google Education Grant, the 2018 IEIE/IEEE Joint Award, the 2015 IEIE Haedong Young Engineer Award, the 2013 IEEE Communications Society Stephen O. Rice Prize, the 2011 David J. Sakrison Memorial Prize (the best dissertation award in UC Berkeley EECS), the 2009 IEEE ISIT Best Student Paper Award, the 2020 LINKGENESIS Best Teacher Award (the campus-wide Grand Prize in Teaching), and the four Departmental Teaching Awards (2013, 2019, 2020, 2021).
Dr. Suh is an IEEE Information Theory Society Distinguished Lecturer, the General Chair of the Inaugural IEEE East Asian School of Information Theory, and a Member of the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology. He is also an Associate Editor of Machine Learning for the IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, the Editor for the IEEE Information Theory Newsletter, a Column Editor for IEEE BITS the Information Theory Magazine, an Area Chair of NeurIPS 2021, and on the Senior Program Committee of IJCAI 2019–2021.
2021.07.27 View 9489 -
 Prof. Junil Choi Receives the Neal Shepherd Memorial Award
Professor Junil Choi of the School of Electrical Engineering received the 2021 Neal Shepherd Memorial Award from the IEEE Vehicular Technology Society. The award recognizes the most outstanding paper relating to radio propagation published in major journals over the previous five years.
Professor Cho, the recipient of the 2015 IEEE Signal Processing Society’s and the 2019 IEEE Communications Society’s Best Paper Award, was selected as the awardee for his paper titled “The Impact of Beamwidth on Temporal Channel Variation in Vehicular Channels and Its Implications” in IEEE Transaction on Vehicular Technology in 2017.
In this paper, Professor Choi and his team derived the channel coherence time for a wireless channel as a function of the beamwidth, taking both Doppler effect and pointing error into consideration. The results showed that a nonzero optimal beamwidth exists that maximizes the channel coherence time. To reduce the impact of the overhead of doing realignment in every channel coherence time, the paper showed that the beams should be realigned every beam coherence time for the best performance.
Professor Choi said, “It is quite an honor to receive this prestigious award following Professor Joonhyun Kang who won the IEEE VTS’s Jack Neubauer Memorial Award this year. It shows that our university’s pursuit of excellence in advanced research is being well recognized.”
2021.07.26 View 7801
Prof. Junil Choi Receives the Neal Shepherd Memorial Award
Professor Junil Choi of the School of Electrical Engineering received the 2021 Neal Shepherd Memorial Award from the IEEE Vehicular Technology Society. The award recognizes the most outstanding paper relating to radio propagation published in major journals over the previous five years.
Professor Cho, the recipient of the 2015 IEEE Signal Processing Society’s and the 2019 IEEE Communications Society’s Best Paper Award, was selected as the awardee for his paper titled “The Impact of Beamwidth on Temporal Channel Variation in Vehicular Channels and Its Implications” in IEEE Transaction on Vehicular Technology in 2017.
In this paper, Professor Choi and his team derived the channel coherence time for a wireless channel as a function of the beamwidth, taking both Doppler effect and pointing error into consideration. The results showed that a nonzero optimal beamwidth exists that maximizes the channel coherence time. To reduce the impact of the overhead of doing realignment in every channel coherence time, the paper showed that the beams should be realigned every beam coherence time for the best performance.
Professor Choi said, “It is quite an honor to receive this prestigious award following Professor Joonhyun Kang who won the IEEE VTS’s Jack Neubauer Memorial Award this year. It shows that our university’s pursuit of excellence in advanced research is being well recognized.”
2021.07.26 View 7801 -
 Professor Kang’s Team Receives the IEEE Jack Newbauer Memorial Award
Professor Joonhyuk Kang of the School of Electrical Engineering received the IEEE Vehicular Technology Society’s 2021 Jack Neubauer Memorial Award for his team’s paper published in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. The Jack Neubauer Memorial Award recognizes the best paper published in the IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology journal in the last five years.
The team of authors, Professor Kang, Professor Sung-Ah Chung at Kyungpook National University, and Professor Osvaldo Simeone of King's College London reported their research titled Mobile Edge Computing via a UAV-Mounted Cloudlet: Optimization of Bit Allocation and Path Planning in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, Vol. 67, No. 3, pp. 2049-2063, in March 2018.
Their paper shows how the trajectory of aircraft is optimized and resources are allocated when unmanned aerial vehicles perform edge computing to help mobile device calculations. This paper has currently recorded nearly 400 citations (based on Google Scholar). "We are very happy to see the results of proposing edge computing using unmanned aerial vehicles by applying optimization theory, and conducting research on trajectory and resource utilization of unmanned aerial vehicles that minimize power consumption," said Professor Kang.
2021.07.12 View 9170
Professor Kang’s Team Receives the IEEE Jack Newbauer Memorial Award
Professor Joonhyuk Kang of the School of Electrical Engineering received the IEEE Vehicular Technology Society’s 2021 Jack Neubauer Memorial Award for his team’s paper published in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. The Jack Neubauer Memorial Award recognizes the best paper published in the IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology journal in the last five years.
The team of authors, Professor Kang, Professor Sung-Ah Chung at Kyungpook National University, and Professor Osvaldo Simeone of King's College London reported their research titled Mobile Edge Computing via a UAV-Mounted Cloudlet: Optimization of Bit Allocation and Path Planning in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, Vol. 67, No. 3, pp. 2049-2063, in March 2018.
Their paper shows how the trajectory of aircraft is optimized and resources are allocated when unmanned aerial vehicles perform edge computing to help mobile device calculations. This paper has currently recorded nearly 400 citations (based on Google Scholar). "We are very happy to see the results of proposing edge computing using unmanned aerial vehicles by applying optimization theory, and conducting research on trajectory and resource utilization of unmanned aerial vehicles that minimize power consumption," said Professor Kang.
2021.07.12 View 9170 -
 Wearable Device to Monitor Sweat in Real Time
An on-skin platform for the wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss, and temperature of sweat in real time
An electronic patch can monitor your sweating and check your health status. Even more, the soft microfluidic device that adheres to the surface of the skin, captures, stores, and performs biomarker analysis of sweat as it is released through the eccrine glands.
This wearable and wireless electronic device developed by Professor Kyeongha Kwon and her collaborators is a digital and wireless platform that could help track the so-called ‘filling process’ of sweat without having to visually examine the device. The platform was integrated with microfluidic systems to analyze the sweat’s components.
To monitor the sweat release rate in real time, the researchers created a ‘thermal flow sensing module.’ They designed a sophisticated microfluidic channel to allow the collected sweat to flow through a narrow passage and a heat source was placed on the outer surface of the channel to induce a heat exchange between the sweat and the heated channel.
As a result, the researchers could develop a wireless electronic patch that can measure the temperature difference in a specific location upstream and downstream of the heat source with an electronic circuit and convert it into a digital signal to measure the sweat release rate in real time. The patch accurately measured the perspiration rate in the range of 0-5 microliters/minute (μl/min), which was considered physiologically significant. The sensor can measure the flow of sweat directly and then use the information it collected to quantify total sweat loss. Moreover, the device features advanced microfluidic systems and colorimetric chemical reagents to gather pH measurements and determine the concentration of chloride, creatinine, and glucose in a user's sweat.
Professor Kwon said that these indicators could be used to diagnose various diseases related with sweating such as cystic fibrosis, diabetes, kidney dysfunction, and metabolic alkalosis. “As the sweat flowing in the microfluidic channel is completely separated from the electronic circuit, the new patch overcame the shortcomings of existing flow rate measuring devices, which were vulnerable to corrosion and aging,” she explained.
The patch can be easily attached to the skin with flexible circuit board printing technology and silicone sealing technology. It has an additional sensor that detects changes in skin temperature. Using a smartphone app, a user can check the data measured by the wearable patch in real time.
Professor Kwon added, “This patch can be widely used for personal hydration strategies, the detection of dehydration symptoms, and other health management purposes. It can also be used in a systematic drug delivery system, such as for measuring the blood flow rate in blood vessels near the skin’s surface or measuring a drug’s release rate in real time to calculate the exact dosage.”
-PublicationKyeongha Kwon, Jong Uk Kim, John A. Rogers, et al. “An on-skin platform for wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss and temperature of sweat in real time.” Nature Electronics (doi.org/10.1038/s41928-021-00556-2)
-ProfileProfessor Kyeongha KwonSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.06.25 View 12015
Wearable Device to Monitor Sweat in Real Time
An on-skin platform for the wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss, and temperature of sweat in real time
An electronic patch can monitor your sweating and check your health status. Even more, the soft microfluidic device that adheres to the surface of the skin, captures, stores, and performs biomarker analysis of sweat as it is released through the eccrine glands.
This wearable and wireless electronic device developed by Professor Kyeongha Kwon and her collaborators is a digital and wireless platform that could help track the so-called ‘filling process’ of sweat without having to visually examine the device. The platform was integrated with microfluidic systems to analyze the sweat’s components.
To monitor the sweat release rate in real time, the researchers created a ‘thermal flow sensing module.’ They designed a sophisticated microfluidic channel to allow the collected sweat to flow through a narrow passage and a heat source was placed on the outer surface of the channel to induce a heat exchange between the sweat and the heated channel.
As a result, the researchers could develop a wireless electronic patch that can measure the temperature difference in a specific location upstream and downstream of the heat source with an electronic circuit and convert it into a digital signal to measure the sweat release rate in real time. The patch accurately measured the perspiration rate in the range of 0-5 microliters/minute (μl/min), which was considered physiologically significant. The sensor can measure the flow of sweat directly and then use the information it collected to quantify total sweat loss. Moreover, the device features advanced microfluidic systems and colorimetric chemical reagents to gather pH measurements and determine the concentration of chloride, creatinine, and glucose in a user's sweat.
Professor Kwon said that these indicators could be used to diagnose various diseases related with sweating such as cystic fibrosis, diabetes, kidney dysfunction, and metabolic alkalosis. “As the sweat flowing in the microfluidic channel is completely separated from the electronic circuit, the new patch overcame the shortcomings of existing flow rate measuring devices, which were vulnerable to corrosion and aging,” she explained.
The patch can be easily attached to the skin with flexible circuit board printing technology and silicone sealing technology. It has an additional sensor that detects changes in skin temperature. Using a smartphone app, a user can check the data measured by the wearable patch in real time.
Professor Kwon added, “This patch can be widely used for personal hydration strategies, the detection of dehydration symptoms, and other health management purposes. It can also be used in a systematic drug delivery system, such as for measuring the blood flow rate in blood vessels near the skin’s surface or measuring a drug’s release rate in real time to calculate the exact dosage.”
-PublicationKyeongha Kwon, Jong Uk Kim, John A. Rogers, et al. “An on-skin platform for wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss and temperature of sweat in real time.” Nature Electronics (doi.org/10.1038/s41928-021-00556-2)
-ProfileProfessor Kyeongha KwonSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.06.25 View 12015 -
 Acoustic Graphene Plasmons Study Paves Way for Optoelectronic Applications
- The first images of mid-infrared optical waves compressed 1,000 times captured using a highly sensitive scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope. -
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new methodology for direct near-field optical imaging of acoustic graphene plasmon fields. This strategy will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of acoustic graphene plasmon platforms in next-generation, high-performance, graphene-based optoelectronic devices with enhanced light-matter interactions and lower propagation loss.
It was recently demonstrated that ‘graphene plasmons’ – collective oscillations of free electrons in graphene coupled to electromagnetic waves of light – can be used to trap and compress optical waves inside a very thin dielectric layer separating graphene from a metallic sheet. In such a configuration, graphene’s conduction electrons are “reflected” in the metal, so when the light waves “push” the electrons in graphene, their image charges in metal also start to oscillate. This new type of collective electronic oscillation mode is called ‘acoustic graphene plasmon (AGP)’.
The existence of AGP could previously be observed only via indirect methods such as far-field infrared spectroscopy and photocurrent mapping. This indirect observation was the price that researchers had to pay for the strong compression of optical waves inside nanometer-thin structures. It was believed that the intensity of electromagnetic fields outside the device was insufficient for direct near-field optical imaging of AGP.
Challenged by these limitations, three research groups combined their efforts to bring together a unique experimental technique using advanced nanofabrication methods. Their findings were published in Nature Communications on February 19.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering used a highly sensitive scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope (s-SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of the AGP waves propagating in a nanometer-thin waveguide, visualizing thousand-fold compression of mid-infrared light for the first time.
Professor Jang and a post-doc researcher in his group, Sergey G. Menabde, successfully obtained direct images of AGP waves by taking advantage of their rapidly decaying yet always present electric field above graphene. They showed that AGPs are detectable even when most of their energy is flowing inside the dielectric below the graphene.
This became possible due to the ultra-smooth surfaces inside the nano-waveguides where plasmonic waves can propagate at longer distances. The AGP mode probed by the researchers was up to 2.3 times more confined and exhibited a 1.4 times higher figure of merit in terms of the normalized propagation length compared to the graphene surface plasmon under similar conditions.
These ultra-smooth nanostructures of the waveguides used in the experiment were created using a template-stripping method by Professor Sang-Hyun Oh and a post-doc researcher, In-Ho Lee, from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Minnesota.
Professor Young Hee Lee and his researchers at the Center for Integrated Nanostructure Physics (CINAP) of the Institute of Basic Science (IBS) at Sungkyunkwan University synthesized the graphene with a monocrystalline structure, and this high-quality, large-area graphene enabled low-loss plasmonic propagation.
The chemical and physical properties of many important organic molecules can be detected and evaluated by their absorption signatures in the mid-infrared spectrum. However, conventional detection methods require a large number of molecules for successful detection, whereas the ultra-compressed AGP fields can provide strong light-matter interactions at the microscopic level, thus significantly improving the detection sensitivity down to a single molecule.
Furthermore, the study conducted by Professor Jang and the team demonstrated that the mid-infrared AGPs are inherently less sensitive to losses in graphene due to their fields being mostly confined within the dielectric. The research team’s reported results suggest that AGPs could become a promising platform for electrically tunable graphene-based optoelectronic devices that typically suffer from higher absorption rates in graphene such as metasurfaces, optical switches, photovoltaics, and other optoelectronic applications operating at infrared frequencies.
Professor Jang said, “Our research revealed that the ultra-compressed electromagnetic fields of acoustic graphene plasmons can be directly accessed through near-field optical microscopy methods. I hope this realization will motivate other researchers to apply AGPs to various problems where strong light-matter interactions and lower propagation loss are needed.”
This research was primarily funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics. The National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), Samsung Global Research Outreach (GRO) Program, and Institute for Basic Science of Korea (IBS) also supported the work.
Publication:
Menabde, S. G., et al. (2021) Real-space imaging of acoustic plasmons in large-area graphene grown by chemical vapor deposition. Nature Communications 12, Article No. 938. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21193-5
Profile:
Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
Associate Professorjang.minseok@kaist.ac.krhttp://jlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Min Seok Jang Research GroupSchool of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.16 View 16035
Acoustic Graphene Plasmons Study Paves Way for Optoelectronic Applications
- The first images of mid-infrared optical waves compressed 1,000 times captured using a highly sensitive scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope. -
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new methodology for direct near-field optical imaging of acoustic graphene plasmon fields. This strategy will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of acoustic graphene plasmon platforms in next-generation, high-performance, graphene-based optoelectronic devices with enhanced light-matter interactions and lower propagation loss.
It was recently demonstrated that ‘graphene plasmons’ – collective oscillations of free electrons in graphene coupled to electromagnetic waves of light – can be used to trap and compress optical waves inside a very thin dielectric layer separating graphene from a metallic sheet. In such a configuration, graphene’s conduction electrons are “reflected” in the metal, so when the light waves “push” the electrons in graphene, their image charges in metal also start to oscillate. This new type of collective electronic oscillation mode is called ‘acoustic graphene plasmon (AGP)’.
The existence of AGP could previously be observed only via indirect methods such as far-field infrared spectroscopy and photocurrent mapping. This indirect observation was the price that researchers had to pay for the strong compression of optical waves inside nanometer-thin structures. It was believed that the intensity of electromagnetic fields outside the device was insufficient for direct near-field optical imaging of AGP.
Challenged by these limitations, three research groups combined their efforts to bring together a unique experimental technique using advanced nanofabrication methods. Their findings were published in Nature Communications on February 19.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering used a highly sensitive scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope (s-SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of the AGP waves propagating in a nanometer-thin waveguide, visualizing thousand-fold compression of mid-infrared light for the first time.
Professor Jang and a post-doc researcher in his group, Sergey G. Menabde, successfully obtained direct images of AGP waves by taking advantage of their rapidly decaying yet always present electric field above graphene. They showed that AGPs are detectable even when most of their energy is flowing inside the dielectric below the graphene.
This became possible due to the ultra-smooth surfaces inside the nano-waveguides where plasmonic waves can propagate at longer distances. The AGP mode probed by the researchers was up to 2.3 times more confined and exhibited a 1.4 times higher figure of merit in terms of the normalized propagation length compared to the graphene surface plasmon under similar conditions.
These ultra-smooth nanostructures of the waveguides used in the experiment were created using a template-stripping method by Professor Sang-Hyun Oh and a post-doc researcher, In-Ho Lee, from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Minnesota.
Professor Young Hee Lee and his researchers at the Center for Integrated Nanostructure Physics (CINAP) of the Institute of Basic Science (IBS) at Sungkyunkwan University synthesized the graphene with a monocrystalline structure, and this high-quality, large-area graphene enabled low-loss plasmonic propagation.
The chemical and physical properties of many important organic molecules can be detected and evaluated by their absorption signatures in the mid-infrared spectrum. However, conventional detection methods require a large number of molecules for successful detection, whereas the ultra-compressed AGP fields can provide strong light-matter interactions at the microscopic level, thus significantly improving the detection sensitivity down to a single molecule.
Furthermore, the study conducted by Professor Jang and the team demonstrated that the mid-infrared AGPs are inherently less sensitive to losses in graphene due to their fields being mostly confined within the dielectric. The research team’s reported results suggest that AGPs could become a promising platform for electrically tunable graphene-based optoelectronic devices that typically suffer from higher absorption rates in graphene such as metasurfaces, optical switches, photovoltaics, and other optoelectronic applications operating at infrared frequencies.
Professor Jang said, “Our research revealed that the ultra-compressed electromagnetic fields of acoustic graphene plasmons can be directly accessed through near-field optical microscopy methods. I hope this realization will motivate other researchers to apply AGPs to various problems where strong light-matter interactions and lower propagation loss are needed.”
This research was primarily funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics. The National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), Samsung Global Research Outreach (GRO) Program, and Institute for Basic Science of Korea (IBS) also supported the work.
Publication:
Menabde, S. G., et al. (2021) Real-space imaging of acoustic plasmons in large-area graphene grown by chemical vapor deposition. Nature Communications 12, Article No. 938. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21193-5
Profile:
Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
Associate Professorjang.minseok@kaist.ac.krhttp://jlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Min Seok Jang Research GroupSchool of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.16 View 16035 -
 ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 34280
ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 34280 -
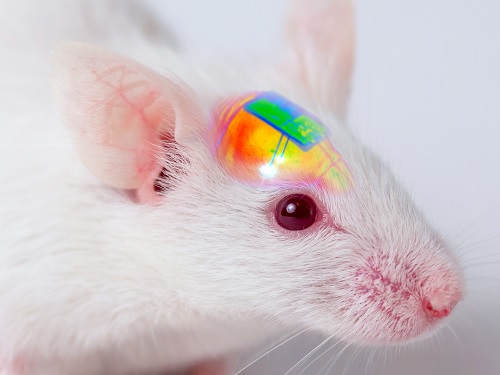 Wirelessly Rechargeable Soft Brain Implant Controls Brain Cells
Researchers have invented a smartphone-controlled soft brain implant that can be recharged wirelessly from outside the body. It enables long-term neural circuit manipulation without the need for periodic disruptive surgeries to replace the battery of the implant. Scientists believe this technology can help uncover and treat psychiatric disorders and neurodegenerative diseases such as addiction, depression, and Parkinson’s.
A group of KAIST researchers and collaborators have engineered a tiny brain implant that can be wirelessly recharged from outside the body to control brain circuits for long periods of time without battery replacement. The device is constructed of ultra-soft and bio-compliant polymers to help provide long-term compatibility with tissue. Geared with micrometer-sized LEDs (equivalent to the size of a grain of salt) mounted on ultrathin probes (the thickness of a human hair), it can wirelessly manipulate target neurons in the deep brain using light.
This study, led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, is a step forward from the wireless head-mounted implant neural device he developed in 2019. That previous version could indefinitely deliver multiple drugs and light stimulation treatment wirelessly by using a smartphone. For more, Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone.
For the new upgraded version, the research team came up with a fully implantable, soft optoelectronic system that can be remotely and selectively controlled by a smartphone. This research was published on January 22, 2021 in Nature Communications.
The new wireless charging technology addresses the limitations of current brain implants. Wireless implantable device technologies have recently become popular as alternatives to conventional tethered implants, because they help minimize stress and inflammation in freely-moving animals during brain studies, which in turn enhance the lifetime of the devices. However, such devices require either intermittent surgeries to replace discharged batteries, or special and bulky wireless power setups, which limit experimental options as well as the scalability of animal experiments.
“This powerful device eliminates the need for additional painful surgeries to replace an exhausted battery in the implant, allowing seamless chronic neuromodulation,” said Professor Jeong. “We believe that the same basic technology can be applied to various types of implants, including deep brain stimulators, and cardiac and gastric pacemakers, to reduce the burden on patients for long-term use within the body.”
To enable wireless battery charging and controls, researchers developed a tiny circuit that integrates a wireless energy harvester with a coil antenna and a Bluetooth low-energy chip. An alternating magnetic field can harmlessly penetrate through tissue, and generate electricity inside the device to charge the battery. Then the battery-powered Bluetooth implant delivers programmable patterns of light to brain cells using an “easy-to-use” smartphone app for real-time brain control.
“This device can be operated anywhere and anytime to manipulate neural circuits, which makes it a highly versatile tool for investigating brain functions,” said lead author Choong Yeon Kim, a researcher at KAIST.
Neuroscientists successfully tested these implants in rats and demonstrated their ability to suppress cocaine-induced behaviour after the rats were injected with cocaine. This was achieved by precise light stimulation of relevant target neurons in their brains using the smartphone-controlled LEDs. Furthermore, the battery in the implants could be repeatedly recharged while the rats were behaving freely, thus minimizing any physical interruption to the experiments.
“Wireless battery re-charging makes experimental procedures much less complicated,” said the co-lead author Min Jeong Ku, a researcher at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine.
“The fact that we can control a specific behaviour of animals, by delivering light stimulation into the brain just with a simple manipulation of smartphone app, watching freely moving animals nearby, is very interesting and stimulates a lot of imagination,” said Jeong-Hoon Kim, a professor of physiology at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine. “This technology will facilitate various avenues of brain research.”
The researchers believe this brain implant technology may lead to new opportunities for brain research and therapeutic intervention to treat diseases in the brain and other organs.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program.
-Profile
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong
https://www.jeongresearch.org/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.26 View 27518
Wirelessly Rechargeable Soft Brain Implant Controls Brain Cells
Researchers have invented a smartphone-controlled soft brain implant that can be recharged wirelessly from outside the body. It enables long-term neural circuit manipulation without the need for periodic disruptive surgeries to replace the battery of the implant. Scientists believe this technology can help uncover and treat psychiatric disorders and neurodegenerative diseases such as addiction, depression, and Parkinson’s.
A group of KAIST researchers and collaborators have engineered a tiny brain implant that can be wirelessly recharged from outside the body to control brain circuits for long periods of time without battery replacement. The device is constructed of ultra-soft and bio-compliant polymers to help provide long-term compatibility with tissue. Geared with micrometer-sized LEDs (equivalent to the size of a grain of salt) mounted on ultrathin probes (the thickness of a human hair), it can wirelessly manipulate target neurons in the deep brain using light.
This study, led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, is a step forward from the wireless head-mounted implant neural device he developed in 2019. That previous version could indefinitely deliver multiple drugs and light stimulation treatment wirelessly by using a smartphone. For more, Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone.
For the new upgraded version, the research team came up with a fully implantable, soft optoelectronic system that can be remotely and selectively controlled by a smartphone. This research was published on January 22, 2021 in Nature Communications.
The new wireless charging technology addresses the limitations of current brain implants. Wireless implantable device technologies have recently become popular as alternatives to conventional tethered implants, because they help minimize stress and inflammation in freely-moving animals during brain studies, which in turn enhance the lifetime of the devices. However, such devices require either intermittent surgeries to replace discharged batteries, or special and bulky wireless power setups, which limit experimental options as well as the scalability of animal experiments.
“This powerful device eliminates the need for additional painful surgeries to replace an exhausted battery in the implant, allowing seamless chronic neuromodulation,” said Professor Jeong. “We believe that the same basic technology can be applied to various types of implants, including deep brain stimulators, and cardiac and gastric pacemakers, to reduce the burden on patients for long-term use within the body.”
To enable wireless battery charging and controls, researchers developed a tiny circuit that integrates a wireless energy harvester with a coil antenna and a Bluetooth low-energy chip. An alternating magnetic field can harmlessly penetrate through tissue, and generate electricity inside the device to charge the battery. Then the battery-powered Bluetooth implant delivers programmable patterns of light to brain cells using an “easy-to-use” smartphone app for real-time brain control.
“This device can be operated anywhere and anytime to manipulate neural circuits, which makes it a highly versatile tool for investigating brain functions,” said lead author Choong Yeon Kim, a researcher at KAIST.
Neuroscientists successfully tested these implants in rats and demonstrated their ability to suppress cocaine-induced behaviour after the rats were injected with cocaine. This was achieved by precise light stimulation of relevant target neurons in their brains using the smartphone-controlled LEDs. Furthermore, the battery in the implants could be repeatedly recharged while the rats were behaving freely, thus minimizing any physical interruption to the experiments.
“Wireless battery re-charging makes experimental procedures much less complicated,” said the co-lead author Min Jeong Ku, a researcher at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine.
“The fact that we can control a specific behaviour of animals, by delivering light stimulation into the brain just with a simple manipulation of smartphone app, watching freely moving animals nearby, is very interesting and stimulates a lot of imagination,” said Jeong-Hoon Kim, a professor of physiology at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine. “This technology will facilitate various avenues of brain research.”
The researchers believe this brain implant technology may lead to new opportunities for brain research and therapeutic intervention to treat diseases in the brain and other organs.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program.
-Profile
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong
https://www.jeongresearch.org/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.26 View 27518 -
 Team USRG’s Winning Streak Continues at the AI Grand Challenge
Team USRG (Unmanned Systems Research Group) led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electrical Engineering has won the AI Grand Challenge 2020 held on Nov. 23 at Kintex in Ilsan, Kyonggi-do for the second consecutive year. The team received 7.7 million KRW in research funding from the Ministry of Science and ICT, the organizer of the challenge.
The team took a little over two minutes to complete the rescue operation mission of the challenge. The mission included swerving around seven obstacles, airdropping an aid package, and safely landing after identifying the landing spot. Their drone is the only one that successfully passed through a 10-meter tunnel out of five pre-qualified teams: three from universities and two from companies.
The AI Grand Challenge, which began in 2017, was designed to promote AI technology and its applications for addressing high-risk technical challenges, especially for conducting complex disaster relief operations.
For autonomous flying drones, swerving to avoid objects has always been an essential skill and a big challenge. For their flawless performance in the rescue operation, the team loaded an AI algorithm and upgraded their drone by improving the LiDAR-based localization system and a stronger propulsion system to carry more sensors. The drone weighs 2.4 kg and carries a small yet powerful computer with a GPU.
This AI-powered drone can complete rescue missions more efficiently in complicated and disastrous environments by precisely comprehending where the drone should go without needing GPS. The team also designed an all-in-one prop guard and installed a gripper onto the bottom of the drone to hold the aid package securely.
“We tried hard to improve our localization system better to resolve issues we had in the previous event,” said Professor Shim. Two PhD candidates, Han-Sob Lee and Bo-Sung Kim played a critical role in developing this drone.
After their two-year winning streak, their prize money now totals 2.4 billion KRW, equivalent to the winning prize of the DARPA Challenge. As the winning team, they will collaborate with other champions at the AI track challenge to develop rescue mission technology for a more complex environment.
“The importance of AI technology is continuing to grow and the government is providing large amounts of funding for research in this field. We would like to develop very competitive technology that will work in the real world,” Professor Shim added.
His group is investigating a wide array of AI technologies applicable to unmanned vehicles including indoor flying drones, self-driving cars, delivery robots, and a tram that circles the campus.
2020.12.01 View 9820
Team USRG’s Winning Streak Continues at the AI Grand Challenge
Team USRG (Unmanned Systems Research Group) led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electrical Engineering has won the AI Grand Challenge 2020 held on Nov. 23 at Kintex in Ilsan, Kyonggi-do for the second consecutive year. The team received 7.7 million KRW in research funding from the Ministry of Science and ICT, the organizer of the challenge.
The team took a little over two minutes to complete the rescue operation mission of the challenge. The mission included swerving around seven obstacles, airdropping an aid package, and safely landing after identifying the landing spot. Their drone is the only one that successfully passed through a 10-meter tunnel out of five pre-qualified teams: three from universities and two from companies.
The AI Grand Challenge, which began in 2017, was designed to promote AI technology and its applications for addressing high-risk technical challenges, especially for conducting complex disaster relief operations.
For autonomous flying drones, swerving to avoid objects has always been an essential skill and a big challenge. For their flawless performance in the rescue operation, the team loaded an AI algorithm and upgraded their drone by improving the LiDAR-based localization system and a stronger propulsion system to carry more sensors. The drone weighs 2.4 kg and carries a small yet powerful computer with a GPU.
This AI-powered drone can complete rescue missions more efficiently in complicated and disastrous environments by precisely comprehending where the drone should go without needing GPS. The team also designed an all-in-one prop guard and installed a gripper onto the bottom of the drone to hold the aid package securely.
“We tried hard to improve our localization system better to resolve issues we had in the previous event,” said Professor Shim. Two PhD candidates, Han-Sob Lee and Bo-Sung Kim played a critical role in developing this drone.
After their two-year winning streak, their prize money now totals 2.4 billion KRW, equivalent to the winning prize of the DARPA Challenge. As the winning team, they will collaborate with other champions at the AI track challenge to develop rescue mission technology for a more complex environment.
“The importance of AI technology is continuing to grow and the government is providing large amounts of funding for research in this field. We would like to develop very competitive technology that will work in the real world,” Professor Shim added.
His group is investigating a wide array of AI technologies applicable to unmanned vehicles including indoor flying drones, self-driving cars, delivery robots, and a tram that circles the campus.
2020.12.01 View 9820