Kim+Il+Doo
-
 Core Technology for Lithium Air Secondary Battery Developed
KAIST-Kyonggi University joint research team developed composite catalyst out of nano fiber and graphene
Five times improvement in capacity compared to lithium-ion secondary battery, driving 800 km at maximum
The core technology for lithium air secondary battery, the next generation high capacity battery, has been developed.
A research team formed by KAIST Department of Materials Science’s Professors Il-Doo Kim and Seokwoo Jeon, and Kyonggi University Department of Materials Science’s Professor Yong-Joon Park has created a lithium air secondary battery, with five times greater storage than the lithium-ion secondary battery, by developing a nano fiber-graphene composite catalyst. The research results are published in the August 8th online edition of Nano Letters.
A cathode of a lithium-ion battery consists of graphite and an anode of the battery consists of a lithium transition metal oxide. Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in mobile phones and laptops. However, lithium-ion batteries cannot support electric vehicles, providing energy for only 160 kilometers on one full charge. The lithium air secondary battery just developed by the research team uses lithium on the cathode and oxygen on the anode. It is earning a popular acknowledgement among the next generation secondary battery research community for having lightweight mass and high energy density.
However, lithium-ion batteries remain difficult to commercialize because of their short lifespan. Lithium and oxygen meet up to form lithium oxide (Li2O2) at discharge, and decompose again at charge. In a traditional lithium air battery, this cycle does not occur smoothly and results in high resistance, thereby reducing the lifespan of the battery. It is thus essential to develop high efficiency catalyst that facilitates the formation and decomposition of lithium oxides.
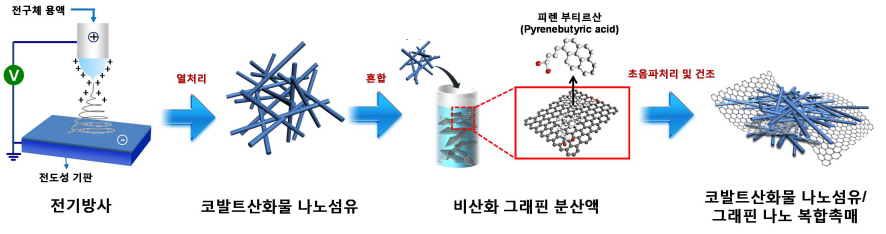
The research team used electric radiation to develop a nano composite catalyst by mixing cobalt oxide nano fiber and graphene. The performance of the battery has been maximized by settling nonoxidative graphene, which has high specific surface area and electrical conductivity, on catalyst active cobalt oxide nano fiber. Applying the nano composite catalyst on both poles of the lithium air battery resulted in an improved lifespan of over 80 recharge cycles with capacity greater than 100mAh/g, five times greater than a lithium ion battery. The newly discovered charge-discharge property is the highest among the reported performances of the lithium air battery so far.
The lithium air battery is cheap to make, as the main materials are metal oxide and graphene. “There are yet more issues to resolve such as stability, but we will collaborate with other organizations to open up the era of electronic vehicles,” said Professor Il-Doo Kim. “We hope to contribute to vitalizing the fields of next generation lithium air battery by leading nanocatalyst synthesis technology, one of the core materials in the fields of secondary battery,” Professor Kim spoke of his aspiration.
The graduate students participated in the research are Won-Hee Ryu, a postdoctorate at KAIST Department of Materials Science, Sungho Song, a PhD candidate at KAIST Department of Materials Science, and Taek-Han Yoon, a graduate student at Kyonggi University.
Picture I: Schematic Diagram of Lithium Air Battery Made of Nano Composite Catalysts
Picture II: Images of Cobalt Oxide Nano Fibers and Graphene Nano Composite Catalysts
Picture III: Images of Manufacturing Process of Cobalt Oxide Nano Fibers and Graphene Nano Composite Catalysts for Lithium Air Battery
2013.10.18 View 12303
Core Technology for Lithium Air Secondary Battery Developed
KAIST-Kyonggi University joint research team developed composite catalyst out of nano fiber and graphene
Five times improvement in capacity compared to lithium-ion secondary battery, driving 800 km at maximum
The core technology for lithium air secondary battery, the next generation high capacity battery, has been developed.
A research team formed by KAIST Department of Materials Science’s Professors Il-Doo Kim and Seokwoo Jeon, and Kyonggi University Department of Materials Science’s Professor Yong-Joon Park has created a lithium air secondary battery, with five times greater storage than the lithium-ion secondary battery, by developing a nano fiber-graphene composite catalyst. The research results are published in the August 8th online edition of Nano Letters.
A cathode of a lithium-ion battery consists of graphite and an anode of the battery consists of a lithium transition metal oxide. Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in mobile phones and laptops. However, lithium-ion batteries cannot support electric vehicles, providing energy for only 160 kilometers on one full charge. The lithium air secondary battery just developed by the research team uses lithium on the cathode and oxygen on the anode. It is earning a popular acknowledgement among the next generation secondary battery research community for having lightweight mass and high energy density.
However, lithium-ion batteries remain difficult to commercialize because of their short lifespan. Lithium and oxygen meet up to form lithium oxide (Li2O2) at discharge, and decompose again at charge. In a traditional lithium air battery, this cycle does not occur smoothly and results in high resistance, thereby reducing the lifespan of the battery. It is thus essential to develop high efficiency catalyst that facilitates the formation and decomposition of lithium oxides.
The research team used electric radiation to develop a nano composite catalyst by mixing cobalt oxide nano fiber and graphene. The performance of the battery has been maximized by settling nonoxidative graphene, which has high specific surface area and electrical conductivity, on catalyst active cobalt oxide nano fiber. Applying the nano composite catalyst on both poles of the lithium air battery resulted in an improved lifespan of over 80 recharge cycles with capacity greater than 100mAh/g, five times greater than a lithium ion battery. The newly discovered charge-discharge property is the highest among the reported performances of the lithium air battery so far.
The lithium air battery is cheap to make, as the main materials are metal oxide and graphene. “There are yet more issues to resolve such as stability, but we will collaborate with other organizations to open up the era of electronic vehicles,” said Professor Il-Doo Kim. “We hope to contribute to vitalizing the fields of next generation lithium air battery by leading nanocatalyst synthesis technology, one of the core materials in the fields of secondary battery,” Professor Kim spoke of his aspiration.
The graduate students participated in the research are Won-Hee Ryu, a postdoctorate at KAIST Department of Materials Science, Sungho Song, a PhD candidate at KAIST Department of Materials Science, and Taek-Han Yoon, a graduate student at Kyonggi University.
Picture I: Schematic Diagram of Lithium Air Battery Made of Nano Composite Catalysts
Picture II: Images of Cobalt Oxide Nano Fibers and Graphene Nano Composite Catalysts
Picture III: Images of Manufacturing Process of Cobalt Oxide Nano Fibers and Graphene Nano Composite Catalysts for Lithium Air Battery
2013.10.18 View 12303 -
 Nanofiber sensor detects diabetes or lung cancer faster and easier
Metal-oxide nanofiber based chemiresistive gas sensors offer greater usability for portable real-time breath tests that can be available on smart phones or tablet PCs in the near future.
Daejeon, Republic of Korea, June 11, 2013 -- Today"s technological innovation enables smartphone users to diagnose serious diseases such as diabetes or lung cancer quickly and effectively by simply breathing into a small gadget, a nanofiber breathing sensor, mounted on the phones.
Il-Doo Kim, Associate Professor of Materials Science and Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), and his research team have recently published a cover paper entitled "Thin-Wall Assembled SnO2 Fibers Functionalized by Catalytic Pt Nanoparticles and their Superior Exhaled Breath-Sensing Properties for the Diagnosis of Diabetes," in an academic journal, Advanced Functional Materials (May 20th issue), on the development of a highly sensitive exhaled breath sensor by using hierarchical SnO2 fibers that are assembled from wrinkled thin SnO2 nanotubes.
In the paper, the research team presented a morphological evolution of SnO2 fibers, called micro phase-separations, which takes place between polymers and other dissolved solutes when varying the flow rate of an electrospinning solution feed and applying a subsequent heat treatment afterward.
The morphological change results in nanofibers that are shaped like an open cylinder inside which thin-film SnO2 nanotubes are layered and then rolled up. A number of elongated pores ranging from 10 nanometers (nm) to 500 nm in length along the fiber direction were formed on the surface of the SnO2 fibers, allowing exhaled gas molecules to easily permeate the fibers. The inner and outer wall of SnO2 tubes is evenly coated with catalytic platinum (Pt) nanoparticles. According to the research team, highly porous SnO2 fibers, synthesized by eletrospinning at a high flow rate, showed five-fold higher acetone responses than that of the dense SnO2 nanofibers created under a low flow rate. The catalytic Pt coating shortened the fibers" gas response time dramatically as well.
The breath analysis for diabetes is largely based on an acetone breath test because acetone is one of the specific volatile organic compounds (VOC) produced in the human body to signal the onset of particular diseases. In other words, they are biomarkers to predict certain diseases such as acetone for diabetes, toluene for lung cancer, and ammonia for kidney malfunction. Breath analysis for medical evaluation has attracted much attention because it is less intrusive than conventional medical examination, as well as fast and convenient, and environmentally friendly, leaving almost no biohazard wastes.
Various gas-sensing techniques have been adopted to analyze VOCs including gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS), but these techniques are difficult to incorporate into portable real-time gas sensors because the testing equipment is bulky and expensive, and their operation is more complex. Metal-oxide based chemiresistive gas sensors, however, offer greater usability for portable real-time breath sensors.
Il-Doo Kim said, "Catalyst-loaded metal oxide nanofibers synthesized by electrospinning have a great potential for future exhaled breath sensor applications. From our research, we obtained the results that Pt-coated SnO2 fibers are able to identify promptly and accurately acetone or toluene even at very low concentration less than 100 parts per billion (ppb)."
The exhaled acetone level of diabetes patients exceeds 1.8 parts per million (ppm), which is two to six-fold higher than that (0.3-0.9 ppm) of healthy people. Therefore, a highly sensitive detection that responds to acetone below 1 ppm, in the presence of other exhaled gases as well as under the humid environment of human breath, is important for an accurate diagnosis of diabetes. In addition, Professor Kim said, "a trace concentration of toluene (30 ppb) in exhaled breath is regarded to be a distinctive early symptom of lung cancer, which we were able to detect with our prototype breath tester."
The research team has now been developing an array of breathing sensors using various catalysts and a number of semiconducting metal oxide fibers, which will offer patients a real-time easy diagnosis of diseases.
###
Youtube Link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t_Hr11dRryg
For further inquires:
Il-Doo Kim, Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Laboratory
Tel: +82-42-350-3329
Email: idkim@kaist.ac.kr
Clockwise from left to right: left upper shows a magnified SEM image of a broken thin-wall assembled SnO2 fiber. Left below is an array of breath sensors (Inset is an actual size of a breath sensor). The right is the cover of Advanced Functional Materials (May 20th issue) in which a research paper on the development of a highly sensitive exhaled breath sensor by using SnO2 fibers is published.
This is the microstructural evolution of SnO2 nanofibers as a function of flow rate during electrospinning.
2013.06.20 View 14552
Nanofiber sensor detects diabetes or lung cancer faster and easier
Metal-oxide nanofiber based chemiresistive gas sensors offer greater usability for portable real-time breath tests that can be available on smart phones or tablet PCs in the near future.
Daejeon, Republic of Korea, June 11, 2013 -- Today"s technological innovation enables smartphone users to diagnose serious diseases such as diabetes or lung cancer quickly and effectively by simply breathing into a small gadget, a nanofiber breathing sensor, mounted on the phones.
Il-Doo Kim, Associate Professor of Materials Science and Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), and his research team have recently published a cover paper entitled "Thin-Wall Assembled SnO2 Fibers Functionalized by Catalytic Pt Nanoparticles and their Superior Exhaled Breath-Sensing Properties for the Diagnosis of Diabetes," in an academic journal, Advanced Functional Materials (May 20th issue), on the development of a highly sensitive exhaled breath sensor by using hierarchical SnO2 fibers that are assembled from wrinkled thin SnO2 nanotubes.
In the paper, the research team presented a morphological evolution of SnO2 fibers, called micro phase-separations, which takes place between polymers and other dissolved solutes when varying the flow rate of an electrospinning solution feed and applying a subsequent heat treatment afterward.
The morphological change results in nanofibers that are shaped like an open cylinder inside which thin-film SnO2 nanotubes are layered and then rolled up. A number of elongated pores ranging from 10 nanometers (nm) to 500 nm in length along the fiber direction were formed on the surface of the SnO2 fibers, allowing exhaled gas molecules to easily permeate the fibers. The inner and outer wall of SnO2 tubes is evenly coated with catalytic platinum (Pt) nanoparticles. According to the research team, highly porous SnO2 fibers, synthesized by eletrospinning at a high flow rate, showed five-fold higher acetone responses than that of the dense SnO2 nanofibers created under a low flow rate. The catalytic Pt coating shortened the fibers" gas response time dramatically as well.
The breath analysis for diabetes is largely based on an acetone breath test because acetone is one of the specific volatile organic compounds (VOC) produced in the human body to signal the onset of particular diseases. In other words, they are biomarkers to predict certain diseases such as acetone for diabetes, toluene for lung cancer, and ammonia for kidney malfunction. Breath analysis for medical evaluation has attracted much attention because it is less intrusive than conventional medical examination, as well as fast and convenient, and environmentally friendly, leaving almost no biohazard wastes.
Various gas-sensing techniques have been adopted to analyze VOCs including gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS), but these techniques are difficult to incorporate into portable real-time gas sensors because the testing equipment is bulky and expensive, and their operation is more complex. Metal-oxide based chemiresistive gas sensors, however, offer greater usability for portable real-time breath sensors.
Il-Doo Kim said, "Catalyst-loaded metal oxide nanofibers synthesized by electrospinning have a great potential for future exhaled breath sensor applications. From our research, we obtained the results that Pt-coated SnO2 fibers are able to identify promptly and accurately acetone or toluene even at very low concentration less than 100 parts per billion (ppb)."
The exhaled acetone level of diabetes patients exceeds 1.8 parts per million (ppm), which is two to six-fold higher than that (0.3-0.9 ppm) of healthy people. Therefore, a highly sensitive detection that responds to acetone below 1 ppm, in the presence of other exhaled gases as well as under the humid environment of human breath, is important for an accurate diagnosis of diabetes. In addition, Professor Kim said, "a trace concentration of toluene (30 ppb) in exhaled breath is regarded to be a distinctive early symptom of lung cancer, which we were able to detect with our prototype breath tester."
The research team has now been developing an array of breathing sensors using various catalysts and a number of semiconducting metal oxide fibers, which will offer patients a real-time easy diagnosis of diseases.
###
Youtube Link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t_Hr11dRryg
For further inquires:
Il-Doo Kim, Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Laboratory
Tel: +82-42-350-3329
Email: idkim@kaist.ac.kr
Clockwise from left to right: left upper shows a magnified SEM image of a broken thin-wall assembled SnO2 fiber. Left below is an array of breath sensors (Inset is an actual size of a breath sensor). The right is the cover of Advanced Functional Materials (May 20th issue) in which a research paper on the development of a highly sensitive exhaled breath sensor by using SnO2 fibers is published.
This is the microstructural evolution of SnO2 nanofibers as a function of flow rate during electrospinning.
2013.06.20 View 14552