Sang+Yup+Lee
-
 KAIST Develops Microbial Liquid Egg Substitute
A team of researchers published a paper on developing a substitute for eggs using microorganisms, grabbing international attention. It is expected that the development of egg substitutes using non-animal raw materials will solve the problems of factory farming, which causes problems like increased emission of greenhouse gas and waste, and contribute to building a sustainable food system that allows easy protein intake.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi from the Biological Process Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering have published a paper on the development of an "Eco-Friendly Liquid Egg Substitute Derived from Microorganisms."
Eggs play a crucial role in various culinary applications due to their unique physicochemical properties such as gelling, foaming, and emulsifying, while also providing essential nutrients. However, traditional egg production is not only unethical and resource-intensive but also has significant environmental impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions and waste issues. Additionally, factors such as wars and trade regulations have led to significant increases in egg prices, highlighting food security concerns. In response to these issues, there has been growing interest in egg substitutes made from non-animal sources to establish a sustainable food system.
Although there has been progress in developing non-animal protein-based egg substitutes, no substitute has been able to fully replicate the essential functional properties of liquid eggs, such as gelling and foaming, while also providing complete nutrition. In this context, the research team aimed to develop a liquid egg substitute using microbial biomass, which has a protein content comparable to that of meat per unit dry mass. Various microorganisms, such as yeast, Bacillus, lactic acid bacteria, and other probiotics, have been proven safe through long-term human consumption. Microbial biomass requires fewer resources like water and land during production, and possesses high-quality nutrients, making it a promising sustainable food resource.
< Figure 1. Comparison of heat treatment results of microbial pellets and microbial lysates >
However, the semi-solid microbial biomass recovered through microbial cultivation was observed to turn liquid upon heating, unlike liquid egg. To address this, the research team devised a microbial lysate by breaking down the cell walls and cell membranes of microorganisms, which correspond to the eggshell. They found that the microbial lysate's proteins coagulated when heated and formed a gel similar to that of liquid egg. The gel formed from the heated microbial lysate was found to have microscopic structures and physical properties similar to those of boiled eggs. The addition of microbial-derived edible enzymes or plant-based materials allowed for the adjustment of its properties, enabling the creation of various textures.
Furthermore, the researchers demonstrated that the microbial lysate could form stable foams widely used in baking, such as meringues (made from egg whites). They successfully baked meringue cookies using this lysate, showing its potential as a functional liquid egg substitute.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee stated, "This substitute has excellent nutritional components, making it suitable for regular food consumption. It is especially promising as emergency food for long-term space travel, wartime situations, and other emergencies. More importantly, it contributes to securing a sustainable food system."
< Figure 2. Example of foaming ability of microbial lysate and meringue cookie production >
< Figure 3. Example of foaming ability of microbial lysate and meringue cookie production >
The paper was published online in the journal npj Science of Food, issued by Nature.
- Paper Title: Microbial lysates repurposed as liquid egg substitutes
- Authors: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Da-Hee Ahn, Seok Yeong Jung, YuHyun Lee, and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT's project for developing eco-friendly chemical technologies to replace petroleum (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and the Rural Development Administration's Agricultural Microorganisms Project Group (Director: Professor Pan-sik Jang, Seoul National University) for developing protein production technology from inorganic substances through microbial metabolic system control (Project Leader: Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, KAIST).
2024.07.05 View 369
KAIST Develops Microbial Liquid Egg Substitute
A team of researchers published a paper on developing a substitute for eggs using microorganisms, grabbing international attention. It is expected that the development of egg substitutes using non-animal raw materials will solve the problems of factory farming, which causes problems like increased emission of greenhouse gas and waste, and contribute to building a sustainable food system that allows easy protein intake.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi from the Biological Process Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering have published a paper on the development of an "Eco-Friendly Liquid Egg Substitute Derived from Microorganisms."
Eggs play a crucial role in various culinary applications due to their unique physicochemical properties such as gelling, foaming, and emulsifying, while also providing essential nutrients. However, traditional egg production is not only unethical and resource-intensive but also has significant environmental impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions and waste issues. Additionally, factors such as wars and trade regulations have led to significant increases in egg prices, highlighting food security concerns. In response to these issues, there has been growing interest in egg substitutes made from non-animal sources to establish a sustainable food system.
Although there has been progress in developing non-animal protein-based egg substitutes, no substitute has been able to fully replicate the essential functional properties of liquid eggs, such as gelling and foaming, while also providing complete nutrition. In this context, the research team aimed to develop a liquid egg substitute using microbial biomass, which has a protein content comparable to that of meat per unit dry mass. Various microorganisms, such as yeast, Bacillus, lactic acid bacteria, and other probiotics, have been proven safe through long-term human consumption. Microbial biomass requires fewer resources like water and land during production, and possesses high-quality nutrients, making it a promising sustainable food resource.
< Figure 1. Comparison of heat treatment results of microbial pellets and microbial lysates >
However, the semi-solid microbial biomass recovered through microbial cultivation was observed to turn liquid upon heating, unlike liquid egg. To address this, the research team devised a microbial lysate by breaking down the cell walls and cell membranes of microorganisms, which correspond to the eggshell. They found that the microbial lysate's proteins coagulated when heated and formed a gel similar to that of liquid egg. The gel formed from the heated microbial lysate was found to have microscopic structures and physical properties similar to those of boiled eggs. The addition of microbial-derived edible enzymes or plant-based materials allowed for the adjustment of its properties, enabling the creation of various textures.
Furthermore, the researchers demonstrated that the microbial lysate could form stable foams widely used in baking, such as meringues (made from egg whites). They successfully baked meringue cookies using this lysate, showing its potential as a functional liquid egg substitute.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee stated, "This substitute has excellent nutritional components, making it suitable for regular food consumption. It is especially promising as emergency food for long-term space travel, wartime situations, and other emergencies. More importantly, it contributes to securing a sustainable food system."
< Figure 2. Example of foaming ability of microbial lysate and meringue cookie production >
< Figure 3. Example of foaming ability of microbial lysate and meringue cookie production >
The paper was published online in the journal npj Science of Food, issued by Nature.
- Paper Title: Microbial lysates repurposed as liquid egg substitutes
- Authors: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Da-Hee Ahn, Seok Yeong Jung, YuHyun Lee, and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT's project for developing eco-friendly chemical technologies to replace petroleum (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and the Rural Development Administration's Agricultural Microorganisms Project Group (Director: Professor Pan-sik Jang, Seoul National University) for developing protein production technology from inorganic substances through microbial metabolic system control (Project Leader: Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, KAIST).
2024.07.05 View 369 -
 KAIST introduces microbial food as a strategy food production of the future
The global food crisis is increasing due to rapid population growth and declining food productivity to climate change. Moreover, today's food production and supply system emit a huge amount of carbon dioxide, reaching 30% of the total amount emitted by humanity, aggravating climate change. Sustainable and nutritious microbial food is attracting attention as a key to overcoming this impasse.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi of the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper that proposes a direction of research on ‘microbial food production from sustainable raw materials.’
Microbial food refers to various foods and food ingredients produced using microorganisms. Microbial biomass contains a large amount of protein per unit in dry mass, comparable to that of meat, and emits the smallest amount of carbon dioxide and is required to produce a unit mass compared to various livestock, fish, shellfish, and crops. Since the amount of water and space requirement is small, it can be an eco-friendly, sustainable and highly nutritious food resource.
Fermented foods are the most readily available microbial foods around us. Although the proportion of microbial biomass in fermented foods is small, compounds with relatively low nutritional value, such as carbohydrates, are consumed during the fermentation process, and as microorganisms proliferate, the content of nutrients with higher nutritional value, such as proteins and vitamins, increases.
Various food compounds isolated and purified from biomass or culture media obtained through microbial culture are also a branch of microbial food. Examples that can be found around us include various amino acids, including monosodium glutamate, food proteins, enzymes, flavoring compounds, food colorings, and bioactive substances.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram portraying various microbial biomass production strategies utlizing sustainable feedstocks >
Lastly, the most ultimate and fundamental form of microbial food can be said to be microbial biomass or extracts produced through microbial culture and foods cooked using them. A representative example is single-cell protein, which collectively refers to microbial biomass or microbial proteins extracted from it.
In this paper, the researchers comprehensively covered various non-edible raw materials and strategies for using them that can be used to produce microbial food in a more sustainable way. Furthermore, it covers various microbial foods that are actually produced in the industry using the relevant raw materials and their characteristics, as well as prospects for the production and generalization of sustainable microbial foods.
Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “Microbial foods produced from various sustainable raw materials will soon be commonly encountered at our tables.” Second author Seok Yeong Jung, a doctoral student, also said, “Microbial foods of the future will not be limited foods consumed only out of a sense of obligation to the environment, but will be complete foods that are consumed by choice because of their nutritional value and taste.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is time for the industry and academia, as well as the public and private sectors, to cooperate more closely so that more diverse microbial foods can be developed and supplied in order to create a sustainable society for ourselves and our descendants.”
< Figure 2. Compositions and environmental footprints of animal, plant and microbial biomass. >
This paper was published online on April 9 in ‘Nature Microbiology’ published by Nature.
※ Paper title: From sustainable feedstocks to microbial foods
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Seok Yeong Jung (second author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was conducted under the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (project leader KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project leader KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) of the Agricultural Microbiology Project Group (Director, Professor Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration.
2024.04.12 View 2065
KAIST introduces microbial food as a strategy food production of the future
The global food crisis is increasing due to rapid population growth and declining food productivity to climate change. Moreover, today's food production and supply system emit a huge amount of carbon dioxide, reaching 30% of the total amount emitted by humanity, aggravating climate change. Sustainable and nutritious microbial food is attracting attention as a key to overcoming this impasse.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi of the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper that proposes a direction of research on ‘microbial food production from sustainable raw materials.’
Microbial food refers to various foods and food ingredients produced using microorganisms. Microbial biomass contains a large amount of protein per unit in dry mass, comparable to that of meat, and emits the smallest amount of carbon dioxide and is required to produce a unit mass compared to various livestock, fish, shellfish, and crops. Since the amount of water and space requirement is small, it can be an eco-friendly, sustainable and highly nutritious food resource.
Fermented foods are the most readily available microbial foods around us. Although the proportion of microbial biomass in fermented foods is small, compounds with relatively low nutritional value, such as carbohydrates, are consumed during the fermentation process, and as microorganisms proliferate, the content of nutrients with higher nutritional value, such as proteins and vitamins, increases.
Various food compounds isolated and purified from biomass or culture media obtained through microbial culture are also a branch of microbial food. Examples that can be found around us include various amino acids, including monosodium glutamate, food proteins, enzymes, flavoring compounds, food colorings, and bioactive substances.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram portraying various microbial biomass production strategies utlizing sustainable feedstocks >
Lastly, the most ultimate and fundamental form of microbial food can be said to be microbial biomass or extracts produced through microbial culture and foods cooked using them. A representative example is single-cell protein, which collectively refers to microbial biomass or microbial proteins extracted from it.
In this paper, the researchers comprehensively covered various non-edible raw materials and strategies for using them that can be used to produce microbial food in a more sustainable way. Furthermore, it covers various microbial foods that are actually produced in the industry using the relevant raw materials and their characteristics, as well as prospects for the production and generalization of sustainable microbial foods.
Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “Microbial foods produced from various sustainable raw materials will soon be commonly encountered at our tables.” Second author Seok Yeong Jung, a doctoral student, also said, “Microbial foods of the future will not be limited foods consumed only out of a sense of obligation to the environment, but will be complete foods that are consumed by choice because of their nutritional value and taste.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is time for the industry and academia, as well as the public and private sectors, to cooperate more closely so that more diverse microbial foods can be developed and supplied in order to create a sustainable society for ourselves and our descendants.”
< Figure 2. Compositions and environmental footprints of animal, plant and microbial biomass. >
This paper was published online on April 9 in ‘Nature Microbiology’ published by Nature.
※ Paper title: From sustainable feedstocks to microbial foods
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Seok Yeong Jung (second author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was conducted under the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (project leader KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project leader KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) of the Agricultural Microbiology Project Group (Director, Professor Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration.
2024.04.12 View 2065 -
 KAIST Research Team Creates the Scent of Jasmine from Microorganisms
The fragrance of jasmine and ylang-ylang, used widely in the manufacturing of cosmetics, foods, and beverages, can be produced by direct extraction from their respective flowers. In reality, this makes it difficult for production to meet demand, so companies use benzyl acetate, a major aromatic component of the two fragrances that is chemically synthesized from raw materials derived from petroleum.
On February 26, a KAIST research team led by Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi from the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering revealed the development of the first microbial process to effectively produce benzyl acetate, an industrially useful compound, from renewable carbon sources such as glucose. The results were published in their paper titled “A microbial process for the production of benzyl acetate”.
< Figure 1. Production of benzyl acetate through co-culture of upstream and downstream strains harboring the benzoic acid-dependent pathway. >
The team, led by Distinguished Professor Lee, aimed to produce benzyl acetate through an environmentally friendly and sustainable method, and developed an Escherichia coli strand to convert glucose into benzyl acetate through system metabolic engineering*.
*System metabolic engineering: a field of research founded by Distinguished Professor Lee to effectively develop microbial cell plants, a core component of the bio-industry that will replace the existing chemical industry, which is highly dependent on petroleum.
The research team developed a metabolic pathway that biosynthesizes benzyl acetate from benzoic acid derived from glucose, and successfully produced benzyl acetate by co-culturing** the strain.
**co-culture: simultaneously synthesizing two or more types of microorganisms in a mixture
However, it has been confirmed that the enzyme used to convert benzoic acid into benzyl acetate in this co-culturing technique acts non-specifically on an intermediate product during benzoic acid biosynthesis, producing a by-product called cinnamyl acetate. This process consumes the intermediate product needed for benzoic acid biosynthesis, thereby reducing the production efficiency of the target compound, benzyl acetate.
To overcome this problem, Distinguished Professor Lee and his team devised a delayed co-culture method, where they first produced benzoic acid in the earlier stages of fermentation by only culturing the top strain that produces benzoic acid from glucose, and later inoculated the bottom strain to convert the accumulated benzoic acid in the culture medium into benzyl acetate.
By applying this co-culture technique, the team suppressed the formation of by-products without further strain improvement or applying additional enzymes, and multiplied the concentration of the target compound by 10 times, producing 2.2 g/L of benzyl acetate. In addition, the team confirmed its potential for the commercial production of benzyl acetate through a technical economic analysis on this microbial process.
< Figure 2. Delayed co-culture of the Bn1 and Bn-BnAc3 strains for improved production of benzyl acetate through the benzoic acid-independent pathway.>
Research Professor Keyong Rok Choi, who was the first author of this paper, said, “This work is significant in that we have developed an effective microbial process to produce the industrially useful compound benzyl acetate, and also in that we have suggested a new approach to overcome the target chemical efficiency diminution and by-product formation issues caused commonly through non-specific enzyme activities during metabolic engineering.”
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “If we can increase the variety and number of microbial processes that produce useful chemicals through sustainable methods and at the same time develop effective strategies to solve chronic and inevitable problems that arise during microbial strain development, we will be able to accelerate the transition from the petrochemical industry into the eco-friendly and sustainable bio-industry.
This work was published online in Nature Chemical Engineering, issued by Nature.
This research was supported by the ‘Implementation of Intelligent Cell Factory Technology (PI: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) Project by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the ‘Development of Protein Production Technology from Inorganic Substances through Microbiological Metabolic System Control’ (PI: Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) by the Agricultural Microbiological Project Group at the Rural Development Administration.
2024.03.05 View 2051
KAIST Research Team Creates the Scent of Jasmine from Microorganisms
The fragrance of jasmine and ylang-ylang, used widely in the manufacturing of cosmetics, foods, and beverages, can be produced by direct extraction from their respective flowers. In reality, this makes it difficult for production to meet demand, so companies use benzyl acetate, a major aromatic component of the two fragrances that is chemically synthesized from raw materials derived from petroleum.
On February 26, a KAIST research team led by Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi from the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering revealed the development of the first microbial process to effectively produce benzyl acetate, an industrially useful compound, from renewable carbon sources such as glucose. The results were published in their paper titled “A microbial process for the production of benzyl acetate”.
< Figure 1. Production of benzyl acetate through co-culture of upstream and downstream strains harboring the benzoic acid-dependent pathway. >
The team, led by Distinguished Professor Lee, aimed to produce benzyl acetate through an environmentally friendly and sustainable method, and developed an Escherichia coli strand to convert glucose into benzyl acetate through system metabolic engineering*.
*System metabolic engineering: a field of research founded by Distinguished Professor Lee to effectively develop microbial cell plants, a core component of the bio-industry that will replace the existing chemical industry, which is highly dependent on petroleum.
The research team developed a metabolic pathway that biosynthesizes benzyl acetate from benzoic acid derived from glucose, and successfully produced benzyl acetate by co-culturing** the strain.
**co-culture: simultaneously synthesizing two or more types of microorganisms in a mixture
However, it has been confirmed that the enzyme used to convert benzoic acid into benzyl acetate in this co-culturing technique acts non-specifically on an intermediate product during benzoic acid biosynthesis, producing a by-product called cinnamyl acetate. This process consumes the intermediate product needed for benzoic acid biosynthesis, thereby reducing the production efficiency of the target compound, benzyl acetate.
To overcome this problem, Distinguished Professor Lee and his team devised a delayed co-culture method, where they first produced benzoic acid in the earlier stages of fermentation by only culturing the top strain that produces benzoic acid from glucose, and later inoculated the bottom strain to convert the accumulated benzoic acid in the culture medium into benzyl acetate.
By applying this co-culture technique, the team suppressed the formation of by-products without further strain improvement or applying additional enzymes, and multiplied the concentration of the target compound by 10 times, producing 2.2 g/L of benzyl acetate. In addition, the team confirmed its potential for the commercial production of benzyl acetate through a technical economic analysis on this microbial process.
< Figure 2. Delayed co-culture of the Bn1 and Bn-BnAc3 strains for improved production of benzyl acetate through the benzoic acid-independent pathway.>
Research Professor Keyong Rok Choi, who was the first author of this paper, said, “This work is significant in that we have developed an effective microbial process to produce the industrially useful compound benzyl acetate, and also in that we have suggested a new approach to overcome the target chemical efficiency diminution and by-product formation issues caused commonly through non-specific enzyme activities during metabolic engineering.”
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “If we can increase the variety and number of microbial processes that produce useful chemicals through sustainable methods and at the same time develop effective strategies to solve chronic and inevitable problems that arise during microbial strain development, we will be able to accelerate the transition from the petrochemical industry into the eco-friendly and sustainable bio-industry.
This work was published online in Nature Chemical Engineering, issued by Nature.
This research was supported by the ‘Implementation of Intelligent Cell Factory Technology (PI: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) Project by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the ‘Development of Protein Production Technology from Inorganic Substances through Microbiological Metabolic System Control’ (PI: Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) by the Agricultural Microbiological Project Group at the Rural Development Administration.
2024.03.05 View 2051 -
 KAIST to begin Joint Research to Develop Next-Generation LiDAR System with Hyundai Motor Group
< (From left) Jong-Soo Lee, Executive Vice President at Hyundai Motor, Sang-Yup Lee, Senior Vice President for Research at KAIST >
The ‘Hyundai Motor Group-KAIST On-Chip LiDAR Joint Research Lab’ was opened at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon to develop LiDAR sensors for advanced autonomous vehicles.
The joint research lab aims to develop high-performance and compact on-chip sensors and new signal detection technology, which are essential in the increasingly competitive autonomous driving market. On-chip sensors, which utilize semiconductor manufacturing technology to add various functions, can reduce the size of LiDAR systems compared to conventional methods and secure price competitiveness through mass production using semiconductor fabrication processes.
The joint research lab will consist of about 30 researchers, including the Hyundai-Kia Institute of Advanced Technology Development research team and KAIST professors Sanghyeon Kim, Sangsik Kim, Wanyeong Jung, and Hamza Kurt from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering, and will operate for four years until 2028.
KAIST will be leading the specialized work of each research team, such as for the development of silicon optoelectronic on-chip LiDAR components, the fabrication of high-speed, high-power integrated circuits to run the LiDAR systems, and the optimization and verification of LiDAR systems.
Hyundai Motor and Kia, together with Hyundai NGV, a specialized industry-academia cooperation institution, will oversee the operation of the joint research lab and provide support such as monitoring technological trends, suggesting research directions, deriving core ideas, and recommending technologies and experts to enhance research capabilities.
A Hyundai Motor Group official said, "We believe that this cooperation between Hyundai Motor Company and Kia, the leader in autonomous driving technology, and KAIST, the home of world-class technology, will hasten the achievement of fully autonomous driving." He added, "We will do our best to enable the lab to produce tangible results.”
Professor Sanghyeon Kim said, "The LiDAR sensor, which serves as the eyes of a car, is a core technology for future autonomous vehicle development that is essential for automobile companies to internalize."
2024.02.27 View 2662
KAIST to begin Joint Research to Develop Next-Generation LiDAR System with Hyundai Motor Group
< (From left) Jong-Soo Lee, Executive Vice President at Hyundai Motor, Sang-Yup Lee, Senior Vice President for Research at KAIST >
The ‘Hyundai Motor Group-KAIST On-Chip LiDAR Joint Research Lab’ was opened at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon to develop LiDAR sensors for advanced autonomous vehicles.
The joint research lab aims to develop high-performance and compact on-chip sensors and new signal detection technology, which are essential in the increasingly competitive autonomous driving market. On-chip sensors, which utilize semiconductor manufacturing technology to add various functions, can reduce the size of LiDAR systems compared to conventional methods and secure price competitiveness through mass production using semiconductor fabrication processes.
The joint research lab will consist of about 30 researchers, including the Hyundai-Kia Institute of Advanced Technology Development research team and KAIST professors Sanghyeon Kim, Sangsik Kim, Wanyeong Jung, and Hamza Kurt from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering, and will operate for four years until 2028.
KAIST will be leading the specialized work of each research team, such as for the development of silicon optoelectronic on-chip LiDAR components, the fabrication of high-speed, high-power integrated circuits to run the LiDAR systems, and the optimization and verification of LiDAR systems.
Hyundai Motor and Kia, together with Hyundai NGV, a specialized industry-academia cooperation institution, will oversee the operation of the joint research lab and provide support such as monitoring technological trends, suggesting research directions, deriving core ideas, and recommending technologies and experts to enhance research capabilities.
A Hyundai Motor Group official said, "We believe that this cooperation between Hyundai Motor Company and Kia, the leader in autonomous driving technology, and KAIST, the home of world-class technology, will hasten the achievement of fully autonomous driving." He added, "We will do our best to enable the lab to produce tangible results.”
Professor Sanghyeon Kim said, "The LiDAR sensor, which serves as the eyes of a car, is a core technology for future autonomous vehicle development that is essential for automobile companies to internalize."
2024.02.27 View 2662 -
 KAIST presents strategies for environmentally friendly and sustainable polyamides production
- Provides current research trends in bio-based polyamide production
- Research on bio-based polyamides production gains importance for achieving a carbon-neutral society
Global industries focused on carbon neutrality, under the slogan "Net-Zero," are gaining increasing attention. In particular, research on microbial production of polymers, replacing traditional chemical methods with biological approaches, is actively progressing.
Polyamides, represented by nylon, are linear polymers widely used in various industries such as automotive, electronics, textiles, and medical fields. They possess beneficial properties such as high tensile strength, electrical insulation, heat resistance, wear resistance, and biocompatibility. Since the commercialization of nylon in 1938, approximately 7 million tons of polyamides are produced worldwide annually. Considering their broad applications and significance, producing polyamides through bio-based methods holds considerable environmental and industrial importance.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, including Dr. Jong An Lee and doctoral candidate Ji Yeon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, published a paper titled "Current Advancements in Bio-Based Production of Polyamides”. The paper was featured on the cover of the monthly issue of "Trends in Chemistry” by Cell Press.
As part of climate change response technologies, bio-refineries involve using biotechnological and chemical methods to produce industrially important chemicals and biofuels from renewable biomass without relying on fossil resources. Notably, systems metabolic engineering, pioneered by KAIST's Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, is a research field that effectively manipulates microbial metabolic pathways to produce valuable chemicals, forming the core technology for bio-refineries. The research team has successfully developed high-performance strains producing a variety of compounds, including succinic acid, biodegradable plastics, biofuels, and natural products, using systems metabolic engineering tools and strategies.
The research team predicted that if bio-based polyamide production technology, which is widely used in the production of clothing and textiles, becomes widespread, it will attract attention as a future technology that can respond to the climate crisis due to its environment-friendly production technology. In this study, the research team comprehensively reviewed the bio-based polyamide production strategies. They provided insights into the advancements in polyamide monomer production using metabolically engineered microorganisms and highlighted the recent trends in bio-based polyamide advancements utilizing these monomers. Additionally, they reviewed the strategies for synthesizing bio-based polyamides through chemical conversion of natural oils and discussed the biodegradability and recycling of the polyamides. Furthermore, the paper presented the future direction in which metabolic engineering can be applied for the bio-based polyamide production, contributing to environmentally friendly and sustainable society.
Ji Yeon Kim, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, stated "The importance of utilizing systems metabolic engineering tools and strategies for bio-based polyamides production is becoming increasingly prominent in achieving carbon neutrality."
Professor Sang Yup Lee emphasized, "Amid growing concerns about climate change, the significance of environmentally friendly and sustainable industrial development is greater than ever. Systems metabolic engineering is expected to have a significant impact not only on the chemical industry but also in various fields."
< [Figure 1] A schematic overview of the overall process for polyamides production >
This paper by Dr. Jong An Lee, PhD student Ji Yeon Kim, Dr. Jung Ho Ahn, and Master Yeah-Ji Ahn from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was published in the December issue of 'Trends in Chemistry', an authoritative review journal in the field of chemistry published by Cell. It was published on December 7 as the cover paper and featured review.
※ Paper title: Current advancements in the bio-based production of polyamides
※ Author information: Jong An Lee, Ji Yeon Kim, Jung Ho Ahn, Yeah-Ji Ahn, and Sang Yup Lee
This research was conducted with the support from the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project and C1 gas refinery program by Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
< [Figure 2] Cover paper of the December issue of Trends in Chemistry >
2023.12.21 View 2338
KAIST presents strategies for environmentally friendly and sustainable polyamides production
- Provides current research trends in bio-based polyamide production
- Research on bio-based polyamides production gains importance for achieving a carbon-neutral society
Global industries focused on carbon neutrality, under the slogan "Net-Zero," are gaining increasing attention. In particular, research on microbial production of polymers, replacing traditional chemical methods with biological approaches, is actively progressing.
Polyamides, represented by nylon, are linear polymers widely used in various industries such as automotive, electronics, textiles, and medical fields. They possess beneficial properties such as high tensile strength, electrical insulation, heat resistance, wear resistance, and biocompatibility. Since the commercialization of nylon in 1938, approximately 7 million tons of polyamides are produced worldwide annually. Considering their broad applications and significance, producing polyamides through bio-based methods holds considerable environmental and industrial importance.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, including Dr. Jong An Lee and doctoral candidate Ji Yeon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, published a paper titled "Current Advancements in Bio-Based Production of Polyamides”. The paper was featured on the cover of the monthly issue of "Trends in Chemistry” by Cell Press.
As part of climate change response technologies, bio-refineries involve using biotechnological and chemical methods to produce industrially important chemicals and biofuels from renewable biomass without relying on fossil resources. Notably, systems metabolic engineering, pioneered by KAIST's Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, is a research field that effectively manipulates microbial metabolic pathways to produce valuable chemicals, forming the core technology for bio-refineries. The research team has successfully developed high-performance strains producing a variety of compounds, including succinic acid, biodegradable plastics, biofuels, and natural products, using systems metabolic engineering tools and strategies.
The research team predicted that if bio-based polyamide production technology, which is widely used in the production of clothing and textiles, becomes widespread, it will attract attention as a future technology that can respond to the climate crisis due to its environment-friendly production technology. In this study, the research team comprehensively reviewed the bio-based polyamide production strategies. They provided insights into the advancements in polyamide monomer production using metabolically engineered microorganisms and highlighted the recent trends in bio-based polyamide advancements utilizing these monomers. Additionally, they reviewed the strategies for synthesizing bio-based polyamides through chemical conversion of natural oils and discussed the biodegradability and recycling of the polyamides. Furthermore, the paper presented the future direction in which metabolic engineering can be applied for the bio-based polyamide production, contributing to environmentally friendly and sustainable society.
Ji Yeon Kim, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, stated "The importance of utilizing systems metabolic engineering tools and strategies for bio-based polyamides production is becoming increasingly prominent in achieving carbon neutrality."
Professor Sang Yup Lee emphasized, "Amid growing concerns about climate change, the significance of environmentally friendly and sustainable industrial development is greater than ever. Systems metabolic engineering is expected to have a significant impact not only on the chemical industry but also in various fields."
< [Figure 1] A schematic overview of the overall process for polyamides production >
This paper by Dr. Jong An Lee, PhD student Ji Yeon Kim, Dr. Jung Ho Ahn, and Master Yeah-Ji Ahn from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was published in the December issue of 'Trends in Chemistry', an authoritative review journal in the field of chemistry published by Cell. It was published on December 7 as the cover paper and featured review.
※ Paper title: Current advancements in the bio-based production of polyamides
※ Author information: Jong An Lee, Ji Yeon Kim, Jung Ho Ahn, Yeah-Ji Ahn, and Sang Yup Lee
This research was conducted with the support from the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project and C1 gas refinery program by Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
< [Figure 2] Cover paper of the December issue of Trends in Chemistry >
2023.12.21 View 2338 -
 KAIST introduces eco-friendly technologies for plastic production and biodegradation
- A research team under Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper in Nature Microbiology on the overview and trends of plastic production and degradation technology using microorganisms.
- Eco-friendly and sustainable plastic production and degradation technology using microorganisms as a core technology to achieve a plastic circular economy was presented.
Plastic is one of the important materials in modern society, with approximately 460 million tons produced annually and with expected production reaching approximately 1.23 billion tons in 2060. However, since 1950, plastic waste totaling more than 6.3 billion tons has been generated, and it is believed that more than 140 million tons of plastic waste has accumulated in the aquatic environment. Recently, the seriousness of microplastic pollution has emerged, not only posing a risk to the marine ecosystem and human health, but also worsening global warming by inhibiting the activity of marine plankton, which play an important role in lowering the Earth's carbon dioxide concentration.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee announced on December 11 that a research team under Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering had published a paper titled 'Sustainable production and degradation of plastics using microbes', which covers the latest technologies for producing plastics and processing waste plastics in an eco-friendly manner using microorganisms.
As the international community moves to solve this plastic problem, various efforts are being made, including 175 countries participating to conclude a legally binding agreement with the goal of ending plastic pollution by 2024. Various technologies are being developed for sustainable plastic production and processing, and among them, biotechnology using microorganisms is attracting attention.
Microorganisms have the ability to naturally produce or decompose certain compounds, and this ability is maximized through biotechnologies such as metabolic engineering and enzyme engineering to produce plastics from renewable biomass resources instead of fossil raw materials and to decompose waste plastics.
Accordingly, the research team comprehensively analyzed the latest microorganism-based technologies for the sustainable production and decomposition of plastics and presented how they actually contribute to solving the plastic problem. Based on this, they presented limitations, prospects, and research directions of the technologies for achieving a circular economy for plastics.
Microorganism-based technologies for various plastics range from widely used synthetic plastics such as polyethylene (PE) to promising bioplastics such as natural polymers derived from microorganisms (polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)) that are completely biodegradable in the natural environment and do not pose a risk of microplastic generation. Commercialization statuses and latest technologies were also discussed. In addition, the technology to decompose these plastics using microorganisms and their enzymes and the upcycling technology to convert them into other useful compounds after decomposition were introduced, highlighting the competitiveness and potential of technology using microorganisms.
First author So Young Choi, a research assistant professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, said, “In the future, we will be able to easily find eco-friendly plastics made using microorganisms all around us,” and corresponding author Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Plastic can be made more sustainable. It is important to use plastics responsibly to protect the environment and simultaneously achieve economic and social development through the new plastics industry, and we look forward to the improved performance of microbial metabolic engineering technology.”
This paper was published on November 30th in the online edition of Nature Microbiology.
※ Paper Title : Sustainable production and degradation of plastics using microbes
Authors: So Young Choi, Youngjoon Lee, Hye Eun Yu, In Jin Cho, Minju Kang & Sang Yup Lee
2023.12.11 View 2501
KAIST introduces eco-friendly technologies for plastic production and biodegradation
- A research team under Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper in Nature Microbiology on the overview and trends of plastic production and degradation technology using microorganisms.
- Eco-friendly and sustainable plastic production and degradation technology using microorganisms as a core technology to achieve a plastic circular economy was presented.
Plastic is one of the important materials in modern society, with approximately 460 million tons produced annually and with expected production reaching approximately 1.23 billion tons in 2060. However, since 1950, plastic waste totaling more than 6.3 billion tons has been generated, and it is believed that more than 140 million tons of plastic waste has accumulated in the aquatic environment. Recently, the seriousness of microplastic pollution has emerged, not only posing a risk to the marine ecosystem and human health, but also worsening global warming by inhibiting the activity of marine plankton, which play an important role in lowering the Earth's carbon dioxide concentration.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee announced on December 11 that a research team under Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering had published a paper titled 'Sustainable production and degradation of plastics using microbes', which covers the latest technologies for producing plastics and processing waste plastics in an eco-friendly manner using microorganisms.
As the international community moves to solve this plastic problem, various efforts are being made, including 175 countries participating to conclude a legally binding agreement with the goal of ending plastic pollution by 2024. Various technologies are being developed for sustainable plastic production and processing, and among them, biotechnology using microorganisms is attracting attention.
Microorganisms have the ability to naturally produce or decompose certain compounds, and this ability is maximized through biotechnologies such as metabolic engineering and enzyme engineering to produce plastics from renewable biomass resources instead of fossil raw materials and to decompose waste plastics.
Accordingly, the research team comprehensively analyzed the latest microorganism-based technologies for the sustainable production and decomposition of plastics and presented how they actually contribute to solving the plastic problem. Based on this, they presented limitations, prospects, and research directions of the technologies for achieving a circular economy for plastics.
Microorganism-based technologies for various plastics range from widely used synthetic plastics such as polyethylene (PE) to promising bioplastics such as natural polymers derived from microorganisms (polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)) that are completely biodegradable in the natural environment and do not pose a risk of microplastic generation. Commercialization statuses and latest technologies were also discussed. In addition, the technology to decompose these plastics using microorganisms and their enzymes and the upcycling technology to convert them into other useful compounds after decomposition were introduced, highlighting the competitiveness and potential of technology using microorganisms.
First author So Young Choi, a research assistant professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, said, “In the future, we will be able to easily find eco-friendly plastics made using microorganisms all around us,” and corresponding author Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Plastic can be made more sustainable. It is important to use plastics responsibly to protect the environment and simultaneously achieve economic and social development through the new plastics industry, and we look forward to the improved performance of microbial metabolic engineering technology.”
This paper was published on November 30th in the online edition of Nature Microbiology.
※ Paper Title : Sustainable production and degradation of plastics using microbes
Authors: So Young Choi, Youngjoon Lee, Hye Eun Yu, In Jin Cho, Minju Kang & Sang Yup Lee
2023.12.11 View 2501 -
 KAIST-UCSD researchers build an enzyme discovering AI
- A joint research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Bernhard Palsson of UCSD developed ‘DeepECtransformer’, an artificial intelligence that can predict Enzyme Commission (EC) number of proteins.
- The AI is tasked to discover new enzymes that have not been discovered yet, which would allow prediction for a total of 5,360 types of Enzyme Commission (EC) numbers
- It is expected to be used in the development of microbial cell factories that produce environmentally friendly chemicals as a core technology for analyzing the metabolic network of a genome.
While E. coli is one of the most studied organisms, the function of 30% of proteins that make up E. coli has not yet been clearly revealed. For this, an artificial intelligence was used to discover 464 types of enzymes from the proteins that were unknown, and the researchers went on to verify the predictions of 3 types of proteins were successfully identified through in vitro enzyme assay.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th that a joint research team comprised of Gi Bae Kim, Ji Yeon Kim, Dr. Jong An Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Dr. Charles J. Norsigian and Professor Bernhard O. Palsson of the Department of Bioengineering at UCSD has developed DeepECtransformer, an artificial intelligence that can predict the enzyme functions from the protein sequence, and has established a prediction system by utilizing the AI to quickly and accurately identify the enzyme function.
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biological reactions, and identifying the function of each enzyme is essential to understanding the various chemical reactions that exist in living organisms and the metabolic characteristics of those organisms. Enzyme Commission (EC) number is an enzyme function classification system designed by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and in order to understand the metabolic characteristics of various organisms, it is necessary to develop a technology that can quickly analyze enzymes and EC numbers of the enzymes present in the genome.
Various methodologies based on deep learning have been developed to analyze the features of biological sequences, including protein function prediction, but most of them have a problem of a black box, where the inference process of AI cannot be interpreted. Various prediction systems that utilize AI for enzyme function prediction have also been reported, but they do not solve this black box problem, or cannot interpret the reasoning process in fine-grained level (e.g., the level of amino acid residues in the enzyme sequence).
The joint team developed DeepECtransformer, an AI that utilizes deep learning and a protein homology analysis module to predict the enzyme function of a given protein sequence. To better understand the features of protein sequences, the transformer architecture, which is commonly used in natural language processing, was additionally used to extract important features about enzyme functions in the context of the entire protein sequence, which enabled the team to accurately predict the EC number of the enzyme. The developed DeepECtransformer can predict a total of 5360 EC numbers.
The joint team further analyzed the transformer architecture to understand the inference process of DeepECtransformer, and found that in the inference process, the AI utilizes information on catalytic active sites and/or the cofactor binding sites which are important for enzyme function. By analyzing the black box of DeepECtransformer, it was confirmed that the AI was able to identify the features that are important for enzyme function on its own during the learning process.
"By utilizing the prediction system we developed, we were able to predict the functions of enzymes that had not yet been identified and verify them experimentally," said Gi Bae Kim, the first author of the paper. "By using DeepECtransformer to identify previously unknown enzymes in living organisms, we will be able to more accurately analyze various facets involved in the metabolic processes of organisms, such as the enzymes needed to biosynthesize various useful compounds or the enzymes needed to biodegrade plastics." he added.
"DeepECtransformer, which quickly and accurately predicts enzyme functions, is a key technology in functional genomics, enabling us to analyze the function of entire enzymes at the systems level," said Professor Sang Yup Lee. He added, “We will be able to use it to develop eco-friendly microbial factories based on comprehensive genome-scale metabolic models, potentially minimizing missing information of metabolism.”
The joint team’s work on DeepECtransformer is described in the paper titled "Functional annotation of enzyme-encoding genes using deep learning with transformer layers" written by Gi Bae Kim, Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST and their colleagues. The paper was published via peer-review on the 14th of November on “Nature Communications”.
This research was conducted with the support by “the Development of next-generation biorefinery platform technologies for leading bio-based chemicals industry project (2022M3J5A1056072)” and by “Development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (2022M3J5A1056117)” from National Research Foundation supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST).
< Figure 1. The structure of DeepECtransformer's artificial neural network >
2023.11.24 View 1885
KAIST-UCSD researchers build an enzyme discovering AI
- A joint research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Bernhard Palsson of UCSD developed ‘DeepECtransformer’, an artificial intelligence that can predict Enzyme Commission (EC) number of proteins.
- The AI is tasked to discover new enzymes that have not been discovered yet, which would allow prediction for a total of 5,360 types of Enzyme Commission (EC) numbers
- It is expected to be used in the development of microbial cell factories that produce environmentally friendly chemicals as a core technology for analyzing the metabolic network of a genome.
While E. coli is one of the most studied organisms, the function of 30% of proteins that make up E. coli has not yet been clearly revealed. For this, an artificial intelligence was used to discover 464 types of enzymes from the proteins that were unknown, and the researchers went on to verify the predictions of 3 types of proteins were successfully identified through in vitro enzyme assay.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th that a joint research team comprised of Gi Bae Kim, Ji Yeon Kim, Dr. Jong An Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Dr. Charles J. Norsigian and Professor Bernhard O. Palsson of the Department of Bioengineering at UCSD has developed DeepECtransformer, an artificial intelligence that can predict the enzyme functions from the protein sequence, and has established a prediction system by utilizing the AI to quickly and accurately identify the enzyme function.
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biological reactions, and identifying the function of each enzyme is essential to understanding the various chemical reactions that exist in living organisms and the metabolic characteristics of those organisms. Enzyme Commission (EC) number is an enzyme function classification system designed by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and in order to understand the metabolic characteristics of various organisms, it is necessary to develop a technology that can quickly analyze enzymes and EC numbers of the enzymes present in the genome.
Various methodologies based on deep learning have been developed to analyze the features of biological sequences, including protein function prediction, but most of them have a problem of a black box, where the inference process of AI cannot be interpreted. Various prediction systems that utilize AI for enzyme function prediction have also been reported, but they do not solve this black box problem, or cannot interpret the reasoning process in fine-grained level (e.g., the level of amino acid residues in the enzyme sequence).
The joint team developed DeepECtransformer, an AI that utilizes deep learning and a protein homology analysis module to predict the enzyme function of a given protein sequence. To better understand the features of protein sequences, the transformer architecture, which is commonly used in natural language processing, was additionally used to extract important features about enzyme functions in the context of the entire protein sequence, which enabled the team to accurately predict the EC number of the enzyme. The developed DeepECtransformer can predict a total of 5360 EC numbers.
The joint team further analyzed the transformer architecture to understand the inference process of DeepECtransformer, and found that in the inference process, the AI utilizes information on catalytic active sites and/or the cofactor binding sites which are important for enzyme function. By analyzing the black box of DeepECtransformer, it was confirmed that the AI was able to identify the features that are important for enzyme function on its own during the learning process.
"By utilizing the prediction system we developed, we were able to predict the functions of enzymes that had not yet been identified and verify them experimentally," said Gi Bae Kim, the first author of the paper. "By using DeepECtransformer to identify previously unknown enzymes in living organisms, we will be able to more accurately analyze various facets involved in the metabolic processes of organisms, such as the enzymes needed to biosynthesize various useful compounds or the enzymes needed to biodegrade plastics." he added.
"DeepECtransformer, which quickly and accurately predicts enzyme functions, is a key technology in functional genomics, enabling us to analyze the function of entire enzymes at the systems level," said Professor Sang Yup Lee. He added, “We will be able to use it to develop eco-friendly microbial factories based on comprehensive genome-scale metabolic models, potentially minimizing missing information of metabolism.”
The joint team’s work on DeepECtransformer is described in the paper titled "Functional annotation of enzyme-encoding genes using deep learning with transformer layers" written by Gi Bae Kim, Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST and their colleagues. The paper was published via peer-review on the 14th of November on “Nature Communications”.
This research was conducted with the support by “the Development of next-generation biorefinery platform technologies for leading bio-based chemicals industry project (2022M3J5A1056072)” and by “Development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (2022M3J5A1056117)” from National Research Foundation supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST).
< Figure 1. The structure of DeepECtransformer's artificial neural network >
2023.11.24 View 1885 -
 KAIST proposes alternatives to chemical factories through “iBridge”
- A computer simulation program “iBridge” was developed at KAIST that can put together microbial cell factories quickly and efficiently to produce cosmetics and food additives, and raw materials for nylons
- Eco-friendly and sustainable fermentation process to establish an alternative to chemical plants
As climate change and environmental concerns intensify, sustainable microbial cell factories garner significant attention as candidates to replace chemical plants. To develop microorganisms to be used in the microbial cell factories, it is crucial to modify their metabolic processes to induce efficient target chemical production by modulating its gene expressions. Yet, the challenge persists in determining which gene expressions to amplify and suppress, and the experimental verification of these modification targets is a time- and resource-intensive process even for experts. The challenges were addressed by a team of researchers at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
It was announced on the 9th by the school that a method for building a microbial factory at low cost, quickly and efficiently, was presented by a novel computer simulation program developed by the team under Professor Lee’s guidance, which is named “iBridge”. This innovative system is designed to predict gene targets to either overexpress or downregulate in the goal of producing a desired compound to enable the cost-effective and efficient construction of microbial cell factories specifically tailored for producing the chemical compound in demand from renewable biomass.
Systems metabolic engineering is a field of research and engineering pioneered by KAIST’s Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee that seeks to produce valuable compounds in industrial demands using microorganisms that are re-configured by a combination of methods including, but not limited to, metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, systems biology, and fermentation engineering.
In order to improve microorganisms’ capability to produce useful compounds, it is essential to delete, suppress, or overexpress microbial genes. However, it is difficult even for the experts to identify the gene targets to modify without experimental confirmations for each of them, which can take up immeasurable amount of time and resources.
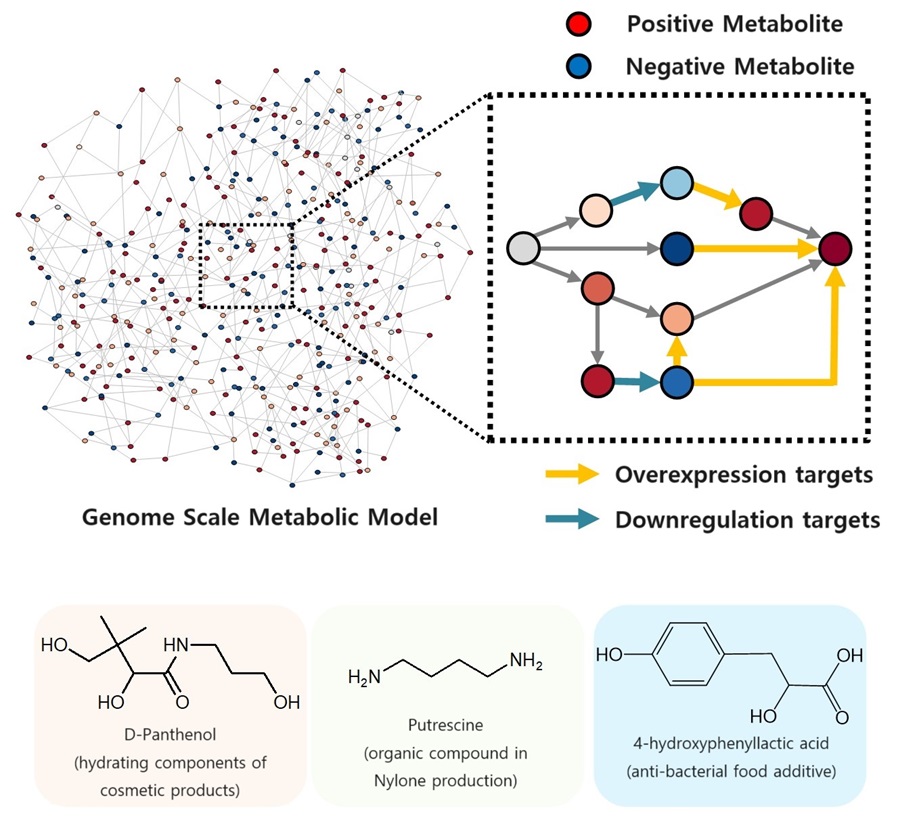
The newly developed iBridge identifies positive and negative metabolites within cells, which exert positive and/or negative impact on formation of the products, by calculating the sum of covariances of their outgoing (consuming) reaction fluxes for a target chemical. Subsequently, it pinpoints "bridge" reactions responsible for converting negative metabolites into positive ones as candidates for overexpression, while identifying the opposites as targets for downregulation.
The research team successfully utilized the iBridge simulation to establish E. coli microbial cell factories each capable of producing three of the compounds that are in high demands at a production capacity that has not been reported around the world. They developed E. coli strains that can each produce panthenol, a moisturizing agent found in many cosmetics, putrescine, which is one of the key components in nylon production, and 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid, an anti-bacterial food additive. In addition to these three compounds, the study presents predictions for overexpression and suppression genes to construct microbial factories for 298 other industrially valuable compounds.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, emphasized the accelerated construction of various microbial factories the newly developed simulation enabled. He stated, "With the use of this simulation, multiple microbial cell factories have been established significantly faster than it would have been using the conventional methods. Microbial cell factories producing a wider range of valuable compounds can now be constructed quickly using this technology."
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "Systems metabolic engineering is a crucial technology for addressing the current climate change issues." He added, "This simulation could significantly expedite the transition from resorting to conventional chemical factories to utilizing environmentally friendly microbial factories."
< Figure. Conceptual diagram of the flow of iBridge simulation >
The team’s work on iBridge is described in a paper titled "Genome-Wide Identification of Overexpression and Downregulation Gene Targets Based on the Sum of Covariances of the Outgoing Reaction Fluxes" written by Dr. Won Jun Kim, and Dr. Youngjoon Lee of the Bioprocess Research Center and Professors Hyun Uk Kim and Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST. The paper was published via peer-review on the 6th of November on “Cell Systems” by Cell Press.
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic using Microbial Cell Factories Project (Project Leader: Research Professor So Young Choi, KAIST) of the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.11.09 View 2680
KAIST proposes alternatives to chemical factories through “iBridge”
- A computer simulation program “iBridge” was developed at KAIST that can put together microbial cell factories quickly and efficiently to produce cosmetics and food additives, and raw materials for nylons
- Eco-friendly and sustainable fermentation process to establish an alternative to chemical plants
As climate change and environmental concerns intensify, sustainable microbial cell factories garner significant attention as candidates to replace chemical plants. To develop microorganisms to be used in the microbial cell factories, it is crucial to modify their metabolic processes to induce efficient target chemical production by modulating its gene expressions. Yet, the challenge persists in determining which gene expressions to amplify and suppress, and the experimental verification of these modification targets is a time- and resource-intensive process even for experts. The challenges were addressed by a team of researchers at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
It was announced on the 9th by the school that a method for building a microbial factory at low cost, quickly and efficiently, was presented by a novel computer simulation program developed by the team under Professor Lee’s guidance, which is named “iBridge”. This innovative system is designed to predict gene targets to either overexpress or downregulate in the goal of producing a desired compound to enable the cost-effective and efficient construction of microbial cell factories specifically tailored for producing the chemical compound in demand from renewable biomass.
Systems metabolic engineering is a field of research and engineering pioneered by KAIST’s Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee that seeks to produce valuable compounds in industrial demands using microorganisms that are re-configured by a combination of methods including, but not limited to, metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, systems biology, and fermentation engineering.
In order to improve microorganisms’ capability to produce useful compounds, it is essential to delete, suppress, or overexpress microbial genes. However, it is difficult even for the experts to identify the gene targets to modify without experimental confirmations for each of them, which can take up immeasurable amount of time and resources.
The newly developed iBridge identifies positive and negative metabolites within cells, which exert positive and/or negative impact on formation of the products, by calculating the sum of covariances of their outgoing (consuming) reaction fluxes for a target chemical. Subsequently, it pinpoints "bridge" reactions responsible for converting negative metabolites into positive ones as candidates for overexpression, while identifying the opposites as targets for downregulation.
The research team successfully utilized the iBridge simulation to establish E. coli microbial cell factories each capable of producing three of the compounds that are in high demands at a production capacity that has not been reported around the world. They developed E. coli strains that can each produce panthenol, a moisturizing agent found in many cosmetics, putrescine, which is one of the key components in nylon production, and 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid, an anti-bacterial food additive. In addition to these three compounds, the study presents predictions for overexpression and suppression genes to construct microbial factories for 298 other industrially valuable compounds.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, emphasized the accelerated construction of various microbial factories the newly developed simulation enabled. He stated, "With the use of this simulation, multiple microbial cell factories have been established significantly faster than it would have been using the conventional methods. Microbial cell factories producing a wider range of valuable compounds can now be constructed quickly using this technology."
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "Systems metabolic engineering is a crucial technology for addressing the current climate change issues." He added, "This simulation could significantly expedite the transition from resorting to conventional chemical factories to utilizing environmentally friendly microbial factories."
< Figure. Conceptual diagram of the flow of iBridge simulation >
The team’s work on iBridge is described in a paper titled "Genome-Wide Identification of Overexpression and Downregulation Gene Targets Based on the Sum of Covariances of the Outgoing Reaction Fluxes" written by Dr. Won Jun Kim, and Dr. Youngjoon Lee of the Bioprocess Research Center and Professors Hyun Uk Kim and Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST. The paper was published via peer-review on the 6th of November on “Cell Systems” by Cell Press.
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic using Microbial Cell Factories Project (Project Leader: Research Professor So Young Choi, KAIST) of the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.11.09 View 2680 -
 A KAIST Research Team Produces Eco-Friendly Nylon with Engineered Bacterium
With worsening climate change and environmental issues, in recent years, there has been increased interest in the eco-friendly production of polymers like nylon.
On August 10, Dr. Taehee Han from a KAIST research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering revealed the successful development of a microbial strain that produces valerolactam, a monomer of nylon-5.
Valerolactam is an important monomer that constitutes nylon-5 and nylon-6,5. Nylon is the oldest synthetic polymer, and nylon-5 is one of its derivatives composed of monomers with five carbons, while nylon-5,6 is composed of two types of monomers with either five or six carbons. They not only have excellent processability, but are also light and tough, which allows them to be applied in a wide range of industrial sectors including clothing, badminton rackets, fishing nets, tents, and gear parts. Monomers are materials that can be built into polymers, and synthetic processes are what connects them into a polymer.
The chemical production of valerolactam, however, is based on petrochemistry, where extreme reaction conditions are required and toxic waste is produced. To solve these problems, efforts are being made to develop environmentally friendly and highly efficient microbial cell factories for lactam production. Systems metabolic engineering, a key strategy for effective microbial strain development, is a research field pioneered by Professor Sang Yup Lee.
Professor Lee’s team used metabolic engineering, a technique for manipulating microbial metabolic pathways, to construct a synthetic metabolic pathway for valerolactam production in Corynebacteriam glutamicum, a bacterium commonly used for amino acid production. With this, they successfully developed a microbial strain that utilizes biomass-derived glucose as a carbon source to produce high-value valerolactam.
In 2017, the team suggested a novel method that metabolically manipulates Escherichia coli to produce valerolactam. However, there were several limitations at the time including low producibility and the generation of harmful byproducts.
< Figure 1. Schematic graphical representation of the development of microorganisms that produce valerolactam, a nylon-5 monomer >
In this research, the team improved valerolactam producibility and incorporated an additional systems metabolic strategy to the developed microbial strain while eliminating the harmful byproducts. By removing the gene involved in the production of the main byproduct and through gene screening, the team successfully converted 5-aminovaleric acid, a byproduct and a precursor, into valerolactam.
Furthermore, by employing a strategy where the 5-aminovaleric acid-converting gene is inserted multiple times into the genome, the team strengthened the metabolic flux for valerolactam production. As a result, they reached a world-record concentration of 76.1 g/L, which is 6.17 times greater than what was previously reported.
This study was published in Metabolic Engineering on July 12, under the title, “Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the high-level production of valerolactam, a nylon-5 monomer”.
Dr. Taehee Han, the first author of the paper, said, “The significance of this research lies in our development of an environmentally friendly technology that efficiently produces monomer lactam for nylon production using microorganisms.” She added, “Through this technology, we will be able to take a step forward in replacing the petrochemical industry with a microorganism-based biopolymer industry.”
This work was supported by the “Development of Next-Generation Biofinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project” funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.08.24 View 2351
A KAIST Research Team Produces Eco-Friendly Nylon with Engineered Bacterium
With worsening climate change and environmental issues, in recent years, there has been increased interest in the eco-friendly production of polymers like nylon.
On August 10, Dr. Taehee Han from a KAIST research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering revealed the successful development of a microbial strain that produces valerolactam, a monomer of nylon-5.
Valerolactam is an important monomer that constitutes nylon-5 and nylon-6,5. Nylon is the oldest synthetic polymer, and nylon-5 is one of its derivatives composed of monomers with five carbons, while nylon-5,6 is composed of two types of monomers with either five or six carbons. They not only have excellent processability, but are also light and tough, which allows them to be applied in a wide range of industrial sectors including clothing, badminton rackets, fishing nets, tents, and gear parts. Monomers are materials that can be built into polymers, and synthetic processes are what connects them into a polymer.
The chemical production of valerolactam, however, is based on petrochemistry, where extreme reaction conditions are required and toxic waste is produced. To solve these problems, efforts are being made to develop environmentally friendly and highly efficient microbial cell factories for lactam production. Systems metabolic engineering, a key strategy for effective microbial strain development, is a research field pioneered by Professor Sang Yup Lee.
Professor Lee’s team used metabolic engineering, a technique for manipulating microbial metabolic pathways, to construct a synthetic metabolic pathway for valerolactam production in Corynebacteriam glutamicum, a bacterium commonly used for amino acid production. With this, they successfully developed a microbial strain that utilizes biomass-derived glucose as a carbon source to produce high-value valerolactam.
In 2017, the team suggested a novel method that metabolically manipulates Escherichia coli to produce valerolactam. However, there were several limitations at the time including low producibility and the generation of harmful byproducts.
< Figure 1. Schematic graphical representation of the development of microorganisms that produce valerolactam, a nylon-5 monomer >
In this research, the team improved valerolactam producibility and incorporated an additional systems metabolic strategy to the developed microbial strain while eliminating the harmful byproducts. By removing the gene involved in the production of the main byproduct and through gene screening, the team successfully converted 5-aminovaleric acid, a byproduct and a precursor, into valerolactam.
Furthermore, by employing a strategy where the 5-aminovaleric acid-converting gene is inserted multiple times into the genome, the team strengthened the metabolic flux for valerolactam production. As a result, they reached a world-record concentration of 76.1 g/L, which is 6.17 times greater than what was previously reported.
This study was published in Metabolic Engineering on July 12, under the title, “Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the high-level production of valerolactam, a nylon-5 monomer”.
Dr. Taehee Han, the first author of the paper, said, “The significance of this research lies in our development of an environmentally friendly technology that efficiently produces monomer lactam for nylon production using microorganisms.” She added, “Through this technology, we will be able to take a step forward in replacing the petrochemical industry with a microorganism-based biopolymer industry.”
This work was supported by the “Development of Next-Generation Biofinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project” funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.08.24 View 2351 -
 KAIST presents a microbial cell factory as a source of eco-friendly food and cosmetic coloring
Despite decades of global population growth, global food crisis seems to be at hand yet again because the food productivity is cut severely due to prolonged presence of abnormal weather from intensifying climate change and global food supply chain is deteriorated due to international conflicts such as wars exacerbating food shortages and nutritional inequality around the globe. At the same time, however, as awareness of the environment and sustainability rises, an increase in demand for more eco-friendly and high-quality food and beauty products is being observed not without a sense of irony. At a time like this, microorganisms are attracting attention as a key that can handle this couple of seemingly distant problems.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that Kyeong Rok Choi, a research professor of the Bioprocess Research Center and Sang Yup Lee, a Distinguished Professor of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, published a paper titled “Metabolic Engineering of Microorganisms for Food and Cosmetics Production” upon invitation by “Nature Reviews Bioengineering” to be published online published by Nature after peer review.
※ Paper title: Systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms for food and cosmetics production
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
Systems metabolic engineering is a research field founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of KAIST to more effectively develop microbial cell factories, the core factor of the next-generation bio industry to replace the existing chemical industry that relies heavily on petroleum. By applying a systemic metabolic engineering strategy, the researchers have developed a number of high-performance microbial cell factories that produce a variety of food and cosmetic compounds including natural substances like heme and zinc protoporphyrin IX compounds which can improve the flavor and color of synthetic meat, lycopene and β-carotene which are functional natural pigments that can be widely used in food and cosmetics, and methyl anthranilate, a grape-derived compound widely used to impart grape flavor in food and beverage manufacturing.
In this paper written upon invitation by Nature, the research team covered remarkable cases of microbial cell factory that can produce amino acids, proteins, fats and fatty acids, vitamins, flavors, pigments, alcohols, functional compounds and other food additives used in various foods and cosmetics and the companies that have successfully commercialized these microbial-derived materials Furthermore, the paper organized and presents systems metabolic engineering strategies that can spur the development of industrial microbial cell factories that can produce more diverse food and cosmetic compounds in an eco-friendly way with economic feasibility.
< Figure 1. Examples of production of food and cosmetic compounds using microbial cell factories >
For example, by producing proteins or amino acids with high nutritional value through non-edible biomass used as animal feed or fertilizer through the microbial fermentation process, it will contribute to the increase in production and stable supply of food around the world. Furthermore, by contributing to developing more viable alternative meat, further reducing dependence on animal protein, it can also contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and environmental pollution generated through livestock breeding or fish farming.
In addition, vanillin or methyl anthranilate, which give off vanilla or grape flavor, are widely added to various foods, but natural products isolated and refined from plants are low in production and high in production cost, so in most cases, petrochemicals substances derived from vanillin and methylanthranilic acid are added to food. These materials can also be produced through an eco-friendly and human-friendly method by borrowing the power of microorganisms.
Ethical and resource problems that arise in producing compounds like Calmin (cochineal pigment), a coloring added to various cosmetics and foods such as red lipstick and strawberry-flavored milk, which must be extracted from cochineal insects that live only in certain cacti. and Hyaluronic acid, which is widely consumed as a health supplement, but is only present in omega-3 fatty acids extracted from shark or fish livers, can also be resolved when they can be produced in an eco-friendly way using microorganisms.
KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “In addition to traditional fermented foods such as kimchi and yogurt, foods produced with the help of microorganisms like cocoa butter, a base ingredient for chocolate that can only be obtained from fermented cacao beans, and monosodium glutamate, a seasoning produced through microbial fermentation are already familiar to us”. “In the future, we will be able to acquire a wider variety of foods and cosmetics even more easily produced in an eco-friendly and sustainable way in our daily lives through microbial cell factories.” he added.
< Figure 2. Systems metabolic engineering strategy to improve metabolic flow in microbial cell factories >
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is engineers’ mission to make the world a better place utilizing science and technology.” and added, “Continuous advancement and active use of systems metabolic engineering will contribute greatly to easing and resolving the problems arising from both the food crisis and the climate change."
This research was carried out as a part of the “Development of Protein Production Technology from Inorganic Substances through Control of Microbial Metabolism System Project” (Project Leader: Kyeong Rok Choi, KAIST Research Professor) of the the Center for Agricultural Microorganism and Enzyme (Director Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration and the “Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project” (Project Leader: Sang Yup Lee, KAIST Distinguished Professor) of the Petroleum-Substitute Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.07.28 View 3406
KAIST presents a microbial cell factory as a source of eco-friendly food and cosmetic coloring
Despite decades of global population growth, global food crisis seems to be at hand yet again because the food productivity is cut severely due to prolonged presence of abnormal weather from intensifying climate change and global food supply chain is deteriorated due to international conflicts such as wars exacerbating food shortages and nutritional inequality around the globe. At the same time, however, as awareness of the environment and sustainability rises, an increase in demand for more eco-friendly and high-quality food and beauty products is being observed not without a sense of irony. At a time like this, microorganisms are attracting attention as a key that can handle this couple of seemingly distant problems.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that Kyeong Rok Choi, a research professor of the Bioprocess Research Center and Sang Yup Lee, a Distinguished Professor of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, published a paper titled “Metabolic Engineering of Microorganisms for Food and Cosmetics Production” upon invitation by “Nature Reviews Bioengineering” to be published online published by Nature after peer review.
※ Paper title: Systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms for food and cosmetics production
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
Systems metabolic engineering is a research field founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of KAIST to more effectively develop microbial cell factories, the core factor of the next-generation bio industry to replace the existing chemical industry that relies heavily on petroleum. By applying a systemic metabolic engineering strategy, the researchers have developed a number of high-performance microbial cell factories that produce a variety of food and cosmetic compounds including natural substances like heme and zinc protoporphyrin IX compounds which can improve the flavor and color of synthetic meat, lycopene and β-carotene which are functional natural pigments that can be widely used in food and cosmetics, and methyl anthranilate, a grape-derived compound widely used to impart grape flavor in food and beverage manufacturing.
In this paper written upon invitation by Nature, the research team covered remarkable cases of microbial cell factory that can produce amino acids, proteins, fats and fatty acids, vitamins, flavors, pigments, alcohols, functional compounds and other food additives used in various foods and cosmetics and the companies that have successfully commercialized these microbial-derived materials Furthermore, the paper organized and presents systems metabolic engineering strategies that can spur the development of industrial microbial cell factories that can produce more diverse food and cosmetic compounds in an eco-friendly way with economic feasibility.
< Figure 1. Examples of production of food and cosmetic compounds using microbial cell factories >
For example, by producing proteins or amino acids with high nutritional value through non-edible biomass used as animal feed or fertilizer through the microbial fermentation process, it will contribute to the increase in production and stable supply of food around the world. Furthermore, by contributing to developing more viable alternative meat, further reducing dependence on animal protein, it can also contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and environmental pollution generated through livestock breeding or fish farming.
In addition, vanillin or methyl anthranilate, which give off vanilla or grape flavor, are widely added to various foods, but natural products isolated and refined from plants are low in production and high in production cost, so in most cases, petrochemicals substances derived from vanillin and methylanthranilic acid are added to food. These materials can also be produced through an eco-friendly and human-friendly method by borrowing the power of microorganisms.
Ethical and resource problems that arise in producing compounds like Calmin (cochineal pigment), a coloring added to various cosmetics and foods such as red lipstick and strawberry-flavored milk, which must be extracted from cochineal insects that live only in certain cacti. and Hyaluronic acid, which is widely consumed as a health supplement, but is only present in omega-3 fatty acids extracted from shark or fish livers, can also be resolved when they can be produced in an eco-friendly way using microorganisms.
KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “In addition to traditional fermented foods such as kimchi and yogurt, foods produced with the help of microorganisms like cocoa butter, a base ingredient for chocolate that can only be obtained from fermented cacao beans, and monosodium glutamate, a seasoning produced through microbial fermentation are already familiar to us”. “In the future, we will be able to acquire a wider variety of foods and cosmetics even more easily produced in an eco-friendly and sustainable way in our daily lives through microbial cell factories.” he added.
< Figure 2. Systems metabolic engineering strategy to improve metabolic flow in microbial cell factories >
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is engineers’ mission to make the world a better place utilizing science and technology.” and added, “Continuous advancement and active use of systems metabolic engineering will contribute greatly to easing and resolving the problems arising from both the food crisis and the climate change."
This research was carried out as a part of the “Development of Protein Production Technology from Inorganic Substances through Control of Microbial Metabolism System Project” (Project Leader: Kyeong Rok Choi, KAIST Research Professor) of the the Center for Agricultural Microorganism and Enzyme (Director Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration and the “Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project” (Project Leader: Sang Yup Lee, KAIST Distinguished Professor) of the Petroleum-Substitute Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.07.28 View 3406 -
 Synthetic sRNAs to knockdown genes in medical and industrial bacteria
Bacteria are intimately involved in our daily lives. These microorganisms have been used in human history for food such as cheese, yogurt, and wine, In more recent years, through metabolic engineering, microorganisms been used extensively as microbial cell factories to manufacture plastics, feed for livestock, dietary supplements, and drugs. However, in addition to these bacteria that are beneficial to human lives, pathogens such as Pneumonia, Salmonella, and Staphylococcus that cause various infectious diseases are also ubiquitously present. It is important to be able to metabolically control these beneficial industrial bacteria for high value-added chemicals production and to manipulate harmful pathogens to suppress its pathogenic traits.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Biochemical Engineering has developed a new sRNA tool that can effectively inhibit target genes in various bacteria, including both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. The research results were published online on April 24 in Nature Communications.
※ Thesis title: Targeted and high-throughput gene knockdown in diverse bacteria using synthetic sRNAs
※ Author information : Jae Sung Cho (co-1st), Dongsoo Yang (co-1st), Cindy Pricilia Surya Prabowo (co-author), Mohammad Rifqi Ghiffary (co-author), Taehee Han (co-author), Kyeong Rok Choi (co-author), Cheon Woo Moon (co-author), Hengrui Zhou (co-author), Jae Yong Ryu (co-author), Hyun Uk Kim (co-author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author).
sRNA is an effective tool for synthesizing and regulating target genes in E. coli, but it has been difficult to apply to industrially useful Gram-positive bacteria such as Bacillus subtilis and Corynebacterium in addition to Gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli.
To address this issue, a research team led by Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a new sRNA platform that can effectively suppress target genes in various bacteria, including both Gram-negative and positive bacteria. The research team surveyed thousands of microbial-derived sRNA systems in the microbial database, and eventually designated the sRNA system derived from 'Bacillus subtilis' that showed the highest gene knockdown efficiency, and designated it as “Broad-Host-Range sRNA”, or BHR-sRNA.
A similar well-known system is the CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) system, which is a modified CRISPR system that knocks down gene expression by suppressing the gene transcription process. However, the Cas9 protein in the CRISPRi system has a very high molecular weight, and there have been reports growth inhibition in bacteria. The BHR-sRNA system developed in this study did not affect bacterial growth while showing similar gene knockdown efficiencies to CRISPRi.
< Figure 1. a) Schematic illustration demonstrating the mechanism of syntetic sRNA b) Phylogenetic tree of the 16 Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial species tested for gene knockdown by the BHR-sRNA system. >
To validate the versatility of the BHR-sRNA system, 16 different gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria were selected and tested, where the BHR-sRNA system worked successfully in 15 of them. In addition, it was demonstrated that the gene knockdown capability was more effective than that of the existing E. coli-based sRNA system in 10 bacteria. The BHR-sRNA system proved to be a universal tool capable of effectively inhibiting gene expression in various bacteria.
In order to address the problem of antibiotic-resistant pathogens that have recently become more serious, the BHR-sRNA was demonstrated to suppress the pathogenicity by suppressing the gene producing the virulence factor. By using BHR-sRNA, biofilm formation, one of the factors resulting in antibiotic resistance, was inhibited by 73% in Staphylococcus epidermidis a pathogen that can cause hospital-acquired infections. Antibiotic resistance was also weakened by 58% in the pneumonia causing bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae. In addition, BHR-sRNA was applied to industrial bacteria to develop microbial cell factories to produce high value-added chemicals with better production performance. Notably, superior industrial strains were constructed with the aid of BHR-sRNA to produce the following chemicals: valerolactam, a raw material for polyamide polymers, methyl-anthranilate, a grape-flavor food additive, and indigoidine, a blue-toned natural dye.
The BHR-sRNA developed through this study will help expedite the commercialization of bioprocesses to produce high value-added compounds and materials such as artificial meat, jet fuel, health supplements, pharmaceuticals, and plastics. It is also anticipated that to help eradicating antibiotic-resistant pathogens in preparation for another upcoming pandemic. “In the past, we could only develop new tools for gene knockdown for each bacterium, but now we have developed a tool that works for a variety of bacteria” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project from NRF supported by the Korean MSIT.
2023.05.10 View 3346
Synthetic sRNAs to knockdown genes in medical and industrial bacteria
Bacteria are intimately involved in our daily lives. These microorganisms have been used in human history for food such as cheese, yogurt, and wine, In more recent years, through metabolic engineering, microorganisms been used extensively as microbial cell factories to manufacture plastics, feed for livestock, dietary supplements, and drugs. However, in addition to these bacteria that are beneficial to human lives, pathogens such as Pneumonia, Salmonella, and Staphylococcus that cause various infectious diseases are also ubiquitously present. It is important to be able to metabolically control these beneficial industrial bacteria for high value-added chemicals production and to manipulate harmful pathogens to suppress its pathogenic traits.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Biochemical Engineering has developed a new sRNA tool that can effectively inhibit target genes in various bacteria, including both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. The research results were published online on April 24 in Nature Communications.
※ Thesis title: Targeted and high-throughput gene knockdown in diverse bacteria using synthetic sRNAs
※ Author information : Jae Sung Cho (co-1st), Dongsoo Yang (co-1st), Cindy Pricilia Surya Prabowo (co-author), Mohammad Rifqi Ghiffary (co-author), Taehee Han (co-author), Kyeong Rok Choi (co-author), Cheon Woo Moon (co-author), Hengrui Zhou (co-author), Jae Yong Ryu (co-author), Hyun Uk Kim (co-author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author).
sRNA is an effective tool for synthesizing and regulating target genes in E. coli, but it has been difficult to apply to industrially useful Gram-positive bacteria such as Bacillus subtilis and Corynebacterium in addition to Gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli.
To address this issue, a research team led by Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a new sRNA platform that can effectively suppress target genes in various bacteria, including both Gram-negative and positive bacteria. The research team surveyed thousands of microbial-derived sRNA systems in the microbial database, and eventually designated the sRNA system derived from 'Bacillus subtilis' that showed the highest gene knockdown efficiency, and designated it as “Broad-Host-Range sRNA”, or BHR-sRNA.
A similar well-known system is the CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) system, which is a modified CRISPR system that knocks down gene expression by suppressing the gene transcription process. However, the Cas9 protein in the CRISPRi system has a very high molecular weight, and there have been reports growth inhibition in bacteria. The BHR-sRNA system developed in this study did not affect bacterial growth while showing similar gene knockdown efficiencies to CRISPRi.
< Figure 1. a) Schematic illustration demonstrating the mechanism of syntetic sRNA b) Phylogenetic tree of the 16 Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial species tested for gene knockdown by the BHR-sRNA system. >
To validate the versatility of the BHR-sRNA system, 16 different gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria were selected and tested, where the BHR-sRNA system worked successfully in 15 of them. In addition, it was demonstrated that the gene knockdown capability was more effective than that of the existing E. coli-based sRNA system in 10 bacteria. The BHR-sRNA system proved to be a universal tool capable of effectively inhibiting gene expression in various bacteria.
In order to address the problem of antibiotic-resistant pathogens that have recently become more serious, the BHR-sRNA was demonstrated to suppress the pathogenicity by suppressing the gene producing the virulence factor. By using BHR-sRNA, biofilm formation, one of the factors resulting in antibiotic resistance, was inhibited by 73% in Staphylococcus epidermidis a pathogen that can cause hospital-acquired infections. Antibiotic resistance was also weakened by 58% in the pneumonia causing bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae. In addition, BHR-sRNA was applied to industrial bacteria to develop microbial cell factories to produce high value-added chemicals with better production performance. Notably, superior industrial strains were constructed with the aid of BHR-sRNA to produce the following chemicals: valerolactam, a raw material for polyamide polymers, methyl-anthranilate, a grape-flavor food additive, and indigoidine, a blue-toned natural dye.
The BHR-sRNA developed through this study will help expedite the commercialization of bioprocesses to produce high value-added compounds and materials such as artificial meat, jet fuel, health supplements, pharmaceuticals, and plastics. It is also anticipated that to help eradicating antibiotic-resistant pathogens in preparation for another upcoming pandemic. “In the past, we could only develop new tools for gene knockdown for each bacterium, but now we have developed a tool that works for a variety of bacteria” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project from NRF supported by the Korean MSIT.
2023.05.10 View 3346 -
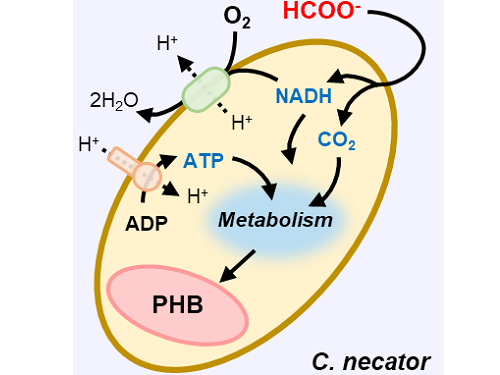 A biohybrid system to extract 20 times more bioplastic from CO2 developed by KAIST researchers
As the issues surrounding global climate change intensify, more attention and determined efforts are required to re-grasp the issue as a state of “crisis” and respond to it properly. Among the various methods of recycling CO2, the electrochemical CO2 conversion technology is a technology that can convert CO2 into useful chemical substances using electrical energy. Since it is easy to operate facilities and can use the electricity from renewable sources like the solar cells or the wind power, it has received a lot of attention as an eco-friendly technology can contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and achieve carbon neutrality.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 30th that the joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering succeeded in developing a technology that produces bioplastics from CO2 with high efficiency by developing a hybrid system that interlinked the electrochemical CO2 conversion and microbial bio conversion methods together. The results of the research, which showed the world's highest productivity by more than 20 times compared to similar systems, were published online on March 27th in the "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS)".
※ Paper title: Biohybrid CO2 electrolysis for the direct synthesis of polyesters from CO2
※ Author information: Jinkyu Lim (currently at Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, co-first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Won Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Hyunjoo Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author)
For the efficient conversion of CO2, high-efficiency electrode catalysts and systems are actively being developed. As conversion products, only compounds containing one or up to three carbon atoms are produced on a limited basis. Compounds of one carbon, such as CO, formic acid, and ethylene, are produced with relatively high efficiency. Liquid compounds of several carbons, such as ethanol, acetic acid, and propanol, can also be produced by these systems, but due to the nature of the chemical reaction that requires more electrons, there are limitations involving the conversion efficiency and the product selection.
Accordingly, a joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a technology to produce bioplastics from CO2 by linking electrochemical conversion technology with bioconversion method that uses microorganisms.
This electrochemical-bio hybrid system is in the form of having an electrolyzer, in which electrochemical conversion reactions occur, connected to a fermenter, in which microorganisms are cultured. When CO2 is converted to formic acid in the electrolyzer, and it is fed into the fermenter in which the microbes like the Cupriavidus necator, in this case, consumes the carbon source to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a microbial-derived bioplastic.
According to the research results of the existing hybrid concepts, there was a disadvantage of having low productivity or stopping at a non-continuous process due to problems of low efficiency of the electrolysis and irregular results arising from the culturing conditions of the microbes.
In order to overcome these problems, the joint research team made formic acid with a gas diffusion electrode using gaseous CO2. In addition, the team developed a 'physiologically compatible catholyte' that can be used as a culture medium for microorganisms as well as an electrolyte that allows the electrolysis to occur sufficiently without inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, without having to have a additional separation and purification process, which allowed the acide to be supplied directly to microorganisms.
Through this, the electrolyte solution containing formic acid made from CO2 enters the fermentation tank, is used for microbial culture, and enters the electrolyzer to be circulated, maximizing the utilization of the electrolyte solution and remaining formic acid. In addition, a filter was installed to ensure that only the electrolyte solution with any and all microorganisms that can affect the electrosis filtered out is supplied back to the electrolyzer, and that the microorganisms exist only in the fermenter, designing the two system to work well together with utmost efficiency.
Through the developed hybrid system, the produced bioplastic, poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), of up to 83% of the cell dry weight was produced from CO2, which produced 1.38g of PHB from a 4 cm2 electrode, which is the world's first gram(g) level production and is more than 20 times more productive than previous research. In addition, the hybrid system is expected to be applied to various industrial processes in the future as it shows promises of the continuous culture system.
The corresponding authors, Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted that “The results of this research are technologies that can be applied to the production of various chemical substances as well as bioplastics, and are expected to be used as key parts needed in achieving carbon neutrality in the future.”
This research was received and performed with the supports from the CO2 Reduction Catalyst and Energy Device Technology Development Project, the Heterogeneous Atomic Catalyst Control Project, and the Next-generation Biorefinery Source Technology Development Project to lead the Biochemical Industry of the Oil-replacement Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram and photo of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system.
(A) A conceptual scheme and (B) a photograph of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system. (C) A detailed scheme of reaction inside the system. Gaseous CO2 was converted to formate in the electrolyzer, and the formate was converted to PHB by the cells in the fermenter. The catholyte was developed so that it is compatible with both CO2 electrolysis and fermentation and was continuously circulated.
2023.03.30 View 4869
A biohybrid system to extract 20 times more bioplastic from CO2 developed by KAIST researchers
As the issues surrounding global climate change intensify, more attention and determined efforts are required to re-grasp the issue as a state of “crisis” and respond to it properly. Among the various methods of recycling CO2, the electrochemical CO2 conversion technology is a technology that can convert CO2 into useful chemical substances using electrical energy. Since it is easy to operate facilities and can use the electricity from renewable sources like the solar cells or the wind power, it has received a lot of attention as an eco-friendly technology can contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and achieve carbon neutrality.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 30th that the joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering succeeded in developing a technology that produces bioplastics from CO2 with high efficiency by developing a hybrid system that interlinked the electrochemical CO2 conversion and microbial bio conversion methods together. The results of the research, which showed the world's highest productivity by more than 20 times compared to similar systems, were published online on March 27th in the "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS)".
※ Paper title: Biohybrid CO2 electrolysis for the direct synthesis of polyesters from CO2
※ Author information: Jinkyu Lim (currently at Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, co-first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Won Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Hyunjoo Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author)
For the efficient conversion of CO2, high-efficiency electrode catalysts and systems are actively being developed. As conversion products, only compounds containing one or up to three carbon atoms are produced on a limited basis. Compounds of one carbon, such as CO, formic acid, and ethylene, are produced with relatively high efficiency. Liquid compounds of several carbons, such as ethanol, acetic acid, and propanol, can also be produced by these systems, but due to the nature of the chemical reaction that requires more electrons, there are limitations involving the conversion efficiency and the product selection.
Accordingly, a joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a technology to produce bioplastics from CO2 by linking electrochemical conversion technology with bioconversion method that uses microorganisms.
This electrochemical-bio hybrid system is in the form of having an electrolyzer, in which electrochemical conversion reactions occur, connected to a fermenter, in which microorganisms are cultured. When CO2 is converted to formic acid in the electrolyzer, and it is fed into the fermenter in which the microbes like the Cupriavidus necator, in this case, consumes the carbon source to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a microbial-derived bioplastic.
According to the research results of the existing hybrid concepts, there was a disadvantage of having low productivity or stopping at a non-continuous process due to problems of low efficiency of the electrolysis and irregular results arising from the culturing conditions of the microbes.
In order to overcome these problems, the joint research team made formic acid with a gas diffusion electrode using gaseous CO2. In addition, the team developed a 'physiologically compatible catholyte' that can be used as a culture medium for microorganisms as well as an electrolyte that allows the electrolysis to occur sufficiently without inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, without having to have a additional separation and purification process, which allowed the acide to be supplied directly to microorganisms.
Through this, the electrolyte solution containing formic acid made from CO2 enters the fermentation tank, is used for microbial culture, and enters the electrolyzer to be circulated, maximizing the utilization of the electrolyte solution and remaining formic acid. In addition, a filter was installed to ensure that only the electrolyte solution with any and all microorganisms that can affect the electrosis filtered out is supplied back to the electrolyzer, and that the microorganisms exist only in the fermenter, designing the two system to work well together with utmost efficiency.
Through the developed hybrid system, the produced bioplastic, poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), of up to 83% of the cell dry weight was produced from CO2, which produced 1.38g of PHB from a 4 cm2 electrode, which is the world's first gram(g) level production and is more than 20 times more productive than previous research. In addition, the hybrid system is expected to be applied to various industrial processes in the future as it shows promises of the continuous culture system.
The corresponding authors, Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted that “The results of this research are technologies that can be applied to the production of various chemical substances as well as bioplastics, and are expected to be used as key parts needed in achieving carbon neutrality in the future.”
This research was received and performed with the supports from the CO2 Reduction Catalyst and Energy Device Technology Development Project, the Heterogeneous Atomic Catalyst Control Project, and the Next-generation Biorefinery Source Technology Development Project to lead the Biochemical Industry of the Oil-replacement Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram and photo of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system.
(A) A conceptual scheme and (B) a photograph of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system. (C) A detailed scheme of reaction inside the system. Gaseous CO2 was converted to formate in the electrolyzer, and the formate was converted to PHB by the cells in the fermenter. The catholyte was developed so that it is compatible with both CO2 electrolysis and fermentation and was continuously circulated.
2023.03.30 View 4869