research
With COVID-19 raging around the globe, researchers are doubling down on methods for developing diverse antimicrobial technologies that could be effective in killing a virus, but harmless to humans and the environment.
A recent study by a KAIST research team will be one of the responses to such efforts. Professor Seung Seob Lee and Dr. Ji-hun Jeong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a harmless air sterilization prototype featuring electrosprayed water from a polymer micro-nozzle array. This study is one of the projects being supported by the KAIST New Deal R&D Initiative in response to COVID-19. Their study was reported in Polymer.
The electrosprayed microdroplets encapsulate reactive oxygen species such as hydroxyl radicals, superoxides that are known to have an antimicrobial function. The encapsulation prolongs the life of reactive oxygen species, which enable the droplets to perform their antimicrobial function effectively. Prior research has already proven the antimicrobial and encapsulation effects of electrosprayed droplets.
Despite its potential for antimicrobial applications, electrosprayed water generally operates under an electrical discharge condition, which can generate ozone. The inhalation of ozone is known to cause damage to the respiratory system of humans. Another technical barrier for electrospraying is the low flow rate problem. Since electrospraying exhibits the dependence of droplet size on the flow rate, there is a limit for the amount of water microdroplets a single nozzle can produce.
With this in mind, the research team developed a dielectric polymer micro-nozzle array to perform the multiplexed electrospraying of water without electrical discharge. The polymer micro-nozzle array was fabricated using the MEMS (Micro Electro-Mechanical System) process. According to the research team, the nozzle can carry five to 19 micro-nozzles depending on the required application.
The high aspect ratio of the micro-nozzle and an in-plane extractor were proposed to concentrate the electric field at the tip of the micro-nozzle, which prevents the electrical discharge caused by the high surface tension of water. A micro-pillar array with a hydrophobic coating around the micro-nozzle was also proposed to prevent the wetting of the micro-nozzle array.
The polymer micro-nozzle array performed in steady cone jet mode without electrical discharge as confirmed by high-speed imaging and nanosecond pulsed imaging. The water microdroplets were measured to be in the range of six to 10 μm and displayed an antimicrobial effect on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
Professor Lee said, “We believe that this research can be applied to air conditioning products in areas that require antimicrobial and humidifying functions.”
< Figure 1. Polymer micro-nozzle array >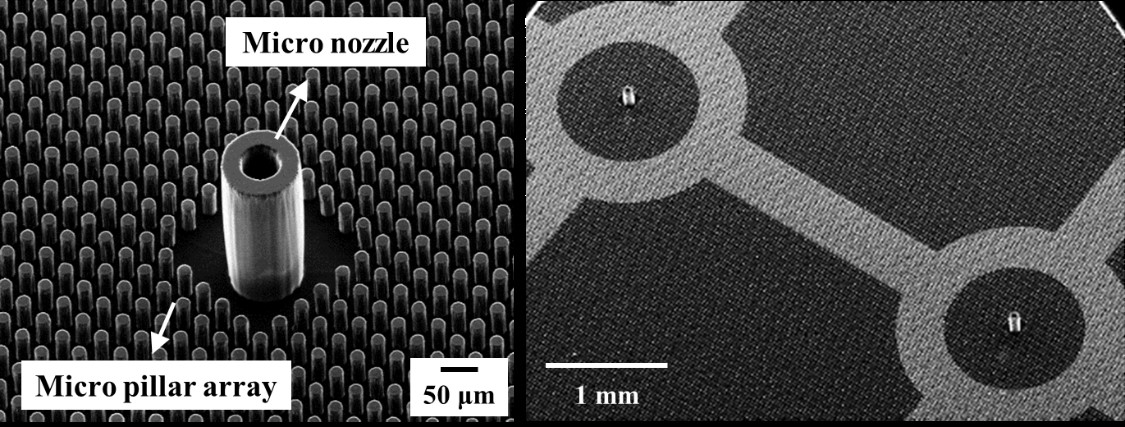
< Figure 2. The multiplexed electrospray of water and antimicrobial effect >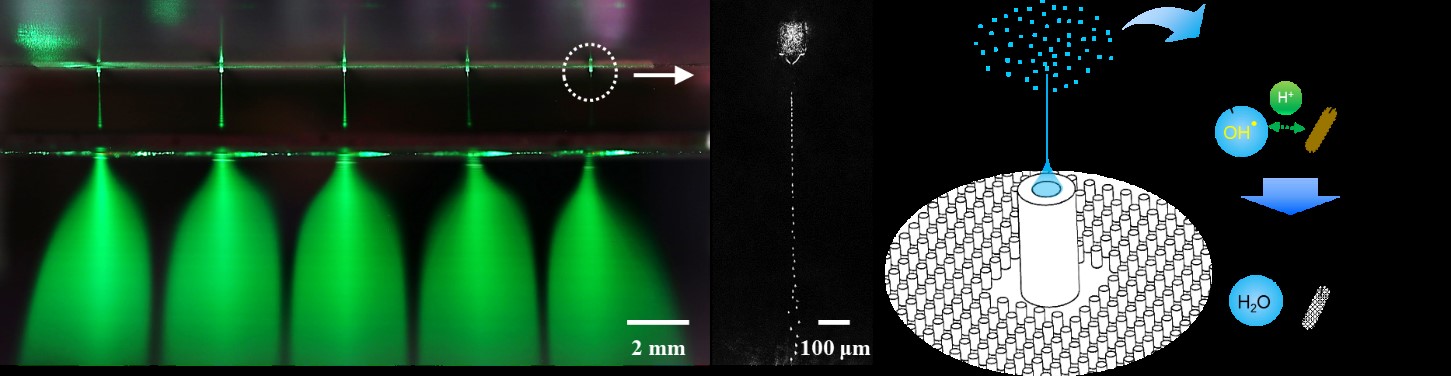
Publication:
Jeong, J. H., et al. (2020) Polymer micro-atomizer for water electrospray in the cone jet mode. Polymer. Vol. No. 194, 122405. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2020.122405
Profile: Seung Seob Lee, Ph.D.
sslee97@kaist.ac.kr
http://mmst.kaist.ac.kr/
Professor
Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Ji-hun Jeong, Ph.D.
jiuni6022@kaist.ac.kr
Postdoctoral researcher
Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
-
research A KAIST Research Team Develops High-Performance Stretchable Solar Cells
With the market for wearable electric devices growing rapidly, stretchable solar cells that can function under strain have received considerable attention as an energy source. To build such solar cells, it is necessary that their photoactive layer, which converts light into electricity, shows high electrical performance while possessing mechanical elasticity. However, satisfying both of these two requirements is challenging, making stretchable solar cells difficult to develop. On December 26,
2024-01-04 -
research KAIST develops biocompatible adhesive applicable to hair transplants
Aside from being used as a new medical adhesive, the new material can be applied to developing a new method of hair transplants, which cannot be repeated multiple times using current method of implanting the wholly intact follicles into the skin. Medical adhesives are materials that can be applied to various uses such as wound healing, hemostasis, vascular anastomosis, and tissue engineering, and is expected to contribute greatly to the development of minimally invasive surgery and organ tran
2022-10-07 -
research New Polymer Mesophase Structure Discovered
Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymer sequence Polymers, large molecules made up of repeating smaller molecules called monomers, are found in nearly everything we use in our day-to-day lives. Polymers can be natural or created synthetically. Natural polymers, also called biopolymers, include DNA, proteins, and materials like silk, gelatin, and collagen. Synthetic polymers make up many different kinds of materials, including plastic, that are used in constructing everyt
2022-06-17 -
research Flexible Sensor-Integrated RFA Needle Leads to Smarter Medical Treatment
Clinical trial of flexible sensor-integrated radiofrequency ablation (RFA) needle tip monitors physical changes and steam pop Researchers have designed a thin polymeric sensor platform on a radiofrequency ablation needle to monitor temperature and pressure in real time. The sensors integrated onto 1.5 mm diameter needle tip have proven their efficacy during clinical tests and expect to provide a new opportunity for safer and more effective medical practices. The research was reported in Advance
2021-10-20 -
research Repurposed Drugs Present New Strategy for Treating COVID-19
Virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assays identifies best therapeutic medication candidates A joint research group from KAIST and Institut Pasteur Korea has identified repurposed drugs for COVID-19 treatment through virtual screening and cell-based assays. The research team suggested the strategy for virtual screening with greatly reduced false positives by incorporating pre-docking filtering based on shape similarity and post-docking filtering based on interaction similarity. Th
2021-07-08