Biochemistry
-
 Two Professors Receive the Asan Medical Award
(Professor Ho Min Kim and Chair Profesor Eunjoon Kim (from far right)
Chair Professor Eunjoon Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences and Professor Ho Min Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science & Engineering won the 11th Asan Medical Award in the areas of basic medicine and young medical scholar on March 21.
The Asan Medical Award has been recognizing the most distinguished scholars in the areas of basic and clinical medicines annually since 2007.
Chair Professor Kim won the 300 million KRW award in recognition of his research in the mechanism of synaptic brain dysfunction and its relation with neural diseases.
The young medical scholar’s award recognizes a promising scholar under the age of 40. Professor Kim won the award for identifying the key protein structure and molecular mechanism controlling immunocytes and neurons. He earned a 50 million KRW prize.
2018.03.26 View 7345
Two Professors Receive the Asan Medical Award
(Professor Ho Min Kim and Chair Profesor Eunjoon Kim (from far right)
Chair Professor Eunjoon Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences and Professor Ho Min Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science & Engineering won the 11th Asan Medical Award in the areas of basic medicine and young medical scholar on March 21.
The Asan Medical Award has been recognizing the most distinguished scholars in the areas of basic and clinical medicines annually since 2007.
Chair Professor Kim won the 300 million KRW award in recognition of his research in the mechanism of synaptic brain dysfunction and its relation with neural diseases.
The young medical scholar’s award recognizes a promising scholar under the age of 40. Professor Kim won the award for identifying the key protein structure and molecular mechanism controlling immunocytes and neurons. He earned a 50 million KRW prize.
2018.03.26 View 7345 -
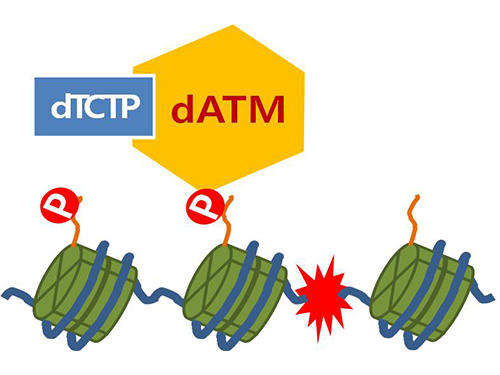 Mechanism in regulation of cancer-related key enzyme, ATM, for DNA damage and repair revealed
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi
A research team led by Professor Kwang-Wook Choi and Dr. Seong-Tae Hong from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has successfully investigated the operational mechanism of the protein Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM), an essential protein to the function of a crucial key enzyme that repairs the damaged DNA which stores biometric information. The results were published on December 19th Nature Communications online edition.
All organisms, including humans, constantly strive to protect the information within their DNA from damages posed by a number of factors, such as carbonized materials in our daily food intake, radioactive materials such as radon emitting from the cement of buildings or ultraviolet of the sunlight, which could be a trigger for cancer.
In order to keep the DNA information safe, the organisms are always carrying out complex and sophisticated DNA repair work, which involves the crucial DNA damage repair protein ATM. Consequently, a faulty ATM leads to higher risks of cancer.
Until now, academia predicted that the Translationally Controlled Tumor Protein (TCTP) will play an important role in regulating the function of ATM. However, since most of main research regarding TCTP has only been conducted in cultured cells, it was unable to identify exactly what mechanisms TCTP employs to control ATM.
The KAIST research team identified that TCTP can combine with ATM or increase the enzymatic activity of ATM. In addition, Drosophilia, one of the most widely used model organisms for molecular genetics, has been used to identify that TCTP and ATM play a very important role in repairing the DNA damaged by radiation. This information has allowed the researchers to establish TCTP’s essential function in maintaining the DNA information in cell cultures and even in higher organisms, and to provide specific and important clues to the regulation of ATM by TCTP.
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi said, “Our research is a good example that basic research using Drosophilia can make important contributions to understanding the process of diseases, such as cancer, and to developing adequate treatment.”
The research has been funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure 1. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, cells of the Drosophila's eye are abnormally deformed by radiation. Scale bars = 200mm
Figure 2. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, the chromosomes of Drosophilia are easily broken by radiation. Scale bars = 10 mm.
Figure 3. When gene expressions of TCTP and ATM are reduced, large defects occur in the normal development of the eye. (Left: normal Drosophilia's eye, right: development-deficient eye)
Figure 4. ATM marks the position of the broken DNA, with TCTP helping to facilitate this reaction. DNA (blue line) within the cell nucleus is coiled around the histone protein (green cylinder). When DNA is broken, ATM protein attaches a phosphate group (P). Multiple DNA repair protein recognizes the phosphate as a signal that requires repair and gathers at the site.
2014.01.07 View 11676
Mechanism in regulation of cancer-related key enzyme, ATM, for DNA damage and repair revealed
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi
A research team led by Professor Kwang-Wook Choi and Dr. Seong-Tae Hong from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has successfully investigated the operational mechanism of the protein Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM), an essential protein to the function of a crucial key enzyme that repairs the damaged DNA which stores biometric information. The results were published on December 19th Nature Communications online edition.
All organisms, including humans, constantly strive to protect the information within their DNA from damages posed by a number of factors, such as carbonized materials in our daily food intake, radioactive materials such as radon emitting from the cement of buildings or ultraviolet of the sunlight, which could be a trigger for cancer.
In order to keep the DNA information safe, the organisms are always carrying out complex and sophisticated DNA repair work, which involves the crucial DNA damage repair protein ATM. Consequently, a faulty ATM leads to higher risks of cancer.
Until now, academia predicted that the Translationally Controlled Tumor Protein (TCTP) will play an important role in regulating the function of ATM. However, since most of main research regarding TCTP has only been conducted in cultured cells, it was unable to identify exactly what mechanisms TCTP employs to control ATM.
The KAIST research team identified that TCTP can combine with ATM or increase the enzymatic activity of ATM. In addition, Drosophilia, one of the most widely used model organisms for molecular genetics, has been used to identify that TCTP and ATM play a very important role in repairing the DNA damaged by radiation. This information has allowed the researchers to establish TCTP’s essential function in maintaining the DNA information in cell cultures and even in higher organisms, and to provide specific and important clues to the regulation of ATM by TCTP.
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi said, “Our research is a good example that basic research using Drosophilia can make important contributions to understanding the process of diseases, such as cancer, and to developing adequate treatment.”
The research has been funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure 1. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, cells of the Drosophila's eye are abnormally deformed by radiation. Scale bars = 200mm
Figure 2. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, the chromosomes of Drosophilia are easily broken by radiation. Scale bars = 10 mm.
Figure 3. When gene expressions of TCTP and ATM are reduced, large defects occur in the normal development of the eye. (Left: normal Drosophilia's eye, right: development-deficient eye)
Figure 4. ATM marks the position of the broken DNA, with TCTP helping to facilitate this reaction. DNA (blue line) within the cell nucleus is coiled around the histone protein (green cylinder). When DNA is broken, ATM protein attaches a phosphate group (P). Multiple DNA repair protein recognizes the phosphate as a signal that requires repair and gathers at the site.
2014.01.07 View 11676 -
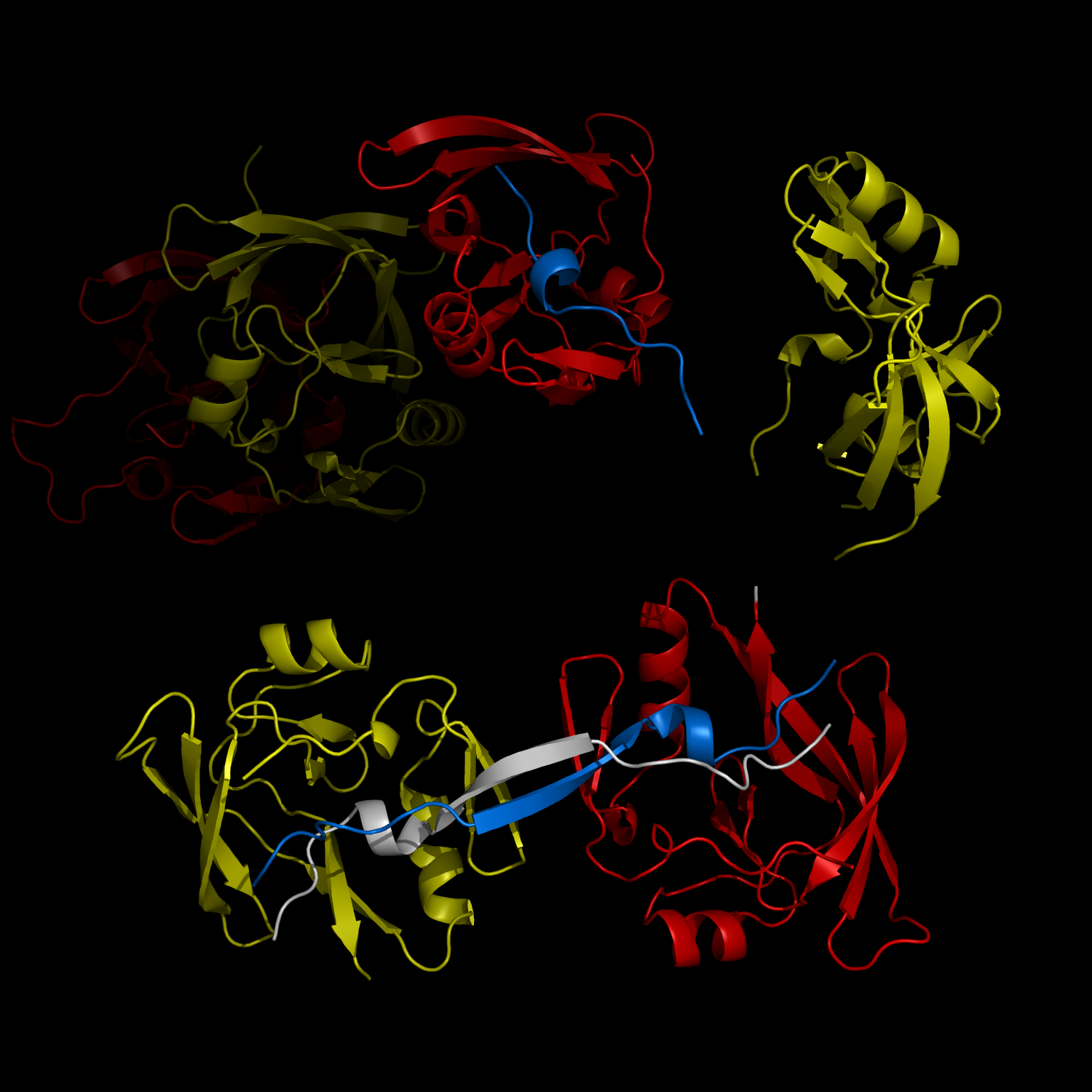 New Structural Insight into Neurodegenerative Disease
A research team from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) released their results on the structure and molecular details of the neurodegenerative disease-associated protein Ataxin-1. Mutations in Ataxin-1 cause the neurological disease, Spinocerebella Ataxia Type 1 (SCA1), which is characterized by a loss of muscular coordination and balance (ataxia), as is seen in Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Huntington’s diseases.
SCA1-causing mutations in the ATAXIN1 gene alter the length of a glutamine stretch in the Ataxin-1 protein. The research team provides the first structural insight into the complex formation of ATAXIN-1 with its binding partner, Capicua (CIC). The team, led by Professor Ji-Joon Song from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST, solved the structure of Ataxin-1 and CIC complex in atomic level revealing molecular details of the interaction between Ataxin-1 and CIC.
Professor Song explained his recent research work,
“We are able to see the intricate process of complex formation and reconfiguration of the two proteins when they interact with each other. Our work, we expect, will provide a new therapeutic target to modulate SCA1 neurodegenerative disease.”
Understanding structural and molecular details of proteins at the atomic level will help researchers to track the molecular pathogenesis of the disease and, ultimately, design targeted therapies or treatments for patients, rather than just relieving the symptoms of diseases.
Professor Song’s research paper, entitled “Structural Basis of Protein Complex Formation and Reconfiguration by Polyglutamine Disease Protein ATAXIN-1 and Capicua,” will be published in the March 15th issue of Genes & Development (www.genesdev.org).
Complex Formation and Reconfiguration of ATAXIN-1 and Capicua
The complex formation between a polyglutamine disease protein, ATXIN-1 and the transcriptional repressor Capicua (CIC) plays a critical role in SCA 1 pathogenesis. The image shows that the homodimerization of ATXIN-1 (yellow and red) is disrupted upon binding of CIC (blue). Furthermore, the binding of CIC to the ATXIN-1 induces a new form of ATXIN-1 dimerization mediated by CICs (ATXIN-1 AXH domains are shown in yellow and red, and CIC peptides shown in blue and white).
2013.04.02 View 8433
New Structural Insight into Neurodegenerative Disease
A research team from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) released their results on the structure and molecular details of the neurodegenerative disease-associated protein Ataxin-1. Mutations in Ataxin-1 cause the neurological disease, Spinocerebella Ataxia Type 1 (SCA1), which is characterized by a loss of muscular coordination and balance (ataxia), as is seen in Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Huntington’s diseases.
SCA1-causing mutations in the ATAXIN1 gene alter the length of a glutamine stretch in the Ataxin-1 protein. The research team provides the first structural insight into the complex formation of ATAXIN-1 with its binding partner, Capicua (CIC). The team, led by Professor Ji-Joon Song from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST, solved the structure of Ataxin-1 and CIC complex in atomic level revealing molecular details of the interaction between Ataxin-1 and CIC.
Professor Song explained his recent research work,
“We are able to see the intricate process of complex formation and reconfiguration of the two proteins when they interact with each other. Our work, we expect, will provide a new therapeutic target to modulate SCA1 neurodegenerative disease.”
Understanding structural and molecular details of proteins at the atomic level will help researchers to track the molecular pathogenesis of the disease and, ultimately, design targeted therapies or treatments for patients, rather than just relieving the symptoms of diseases.
Professor Song’s research paper, entitled “Structural Basis of Protein Complex Formation and Reconfiguration by Polyglutamine Disease Protein ATAXIN-1 and Capicua,” will be published in the March 15th issue of Genes & Development (www.genesdev.org).
Complex Formation and Reconfiguration of ATAXIN-1 and Capicua
The complex formation between a polyglutamine disease protein, ATXIN-1 and the transcriptional repressor Capicua (CIC) plays a critical role in SCA 1 pathogenesis. The image shows that the homodimerization of ATXIN-1 (yellow and red) is disrupted upon binding of CIC (blue). Furthermore, the binding of CIC to the ATXIN-1 induces a new form of ATXIN-1 dimerization mediated by CICs (ATXIN-1 AXH domains are shown in yellow and red, and CIC peptides shown in blue and white).
2013.04.02 View 8433