Microbiology
-
 Immune Evasion Mechanism of Hepatitis C Virus Revealed
Professor Ui-Cheol Shin
Inhibiting major histocompatibility complex [MHC] class I protein expression, T cell immune response is evaded.
The research will be a great help to the development of C hepatitis vaccine.
Roughly 1-2% of the population in Korea is known to be infected with Hepatitis C. Most Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infections progress to a chronic disease and can cause liver cirrhosis or liver cancer, which may lead to death.
Unlike Hepatitis type A or B, there is no vaccine for Hepatitis C Virus and therefore avoiding exposure to the virus is the best known method of prevention. However, a team of researchers at KAIST has produced research results, which may contribute significantly to the vaccine development.
KAIST Graduate School of Medical Sciences & Engineering’ Professor Ui-Cheol Shin and his team have successfully identified why Hepatitis C Virus does not cause an immune response within the human body. The research results were published in the May edition of The Journal of Gastroenterology, a world-renowned journal in the field of gastroenterology.
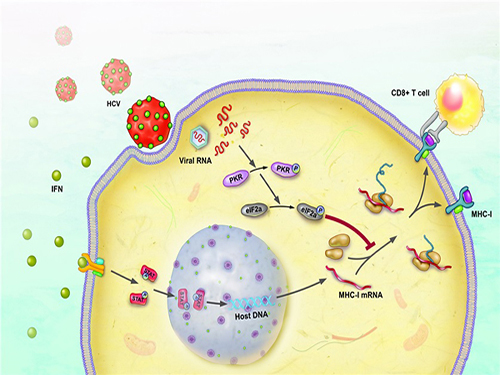
The immune response occurs to eliminate the virus that has invaded our body. During this process, a major histocompatibility complex [MHC] class I plays a key role in inducing T cell response, which is needed for the elimination of virus-infected cells.
When a cell is infected by a virus, a substance called interferon causes the increased expression of major histocompatibility complex class I. T cell recognizes the increased MHC class I and therefore finds the virus-infected cells.
However, the effect that Hepatitis C Virus has on major histocompatibility complex class I has not been clearly identified until now.
The research team has revealed, using a cell culture for infection systems, that the Hepatitis C Virus suppresses the expression of major histocompatibility complex class I. Also, the mechanism to prove that HCV activates a protein called PKR within the cell to inhibit MHC class I protein expression was identified at a molecular level.
In this study, researchers established the hypothesis that regulating PKR protein in the cell can enhance the T cell immune response, which was then proved through experiments.
Professor Ui-Cheol Shin said, “There are a lot of new drugs to treat Hepatitis C Virus, while its vaccine has not been developed yet. Revealing the HCV immune evasion mechanism will help stimulate momentum for the HCV vaccine development.”
The first author of the journal, Dr. Won-Seok Kang is a graduate from Yonsei College of Medicine. After earning his medical degree, he has continued his training as a ‘doctor-scientist’ at KAIST Graduate School of Medical Sciences & Engineering to study Hepatitis C Virus immune evasion mechanism in this research.
Hepatitis C Virus activates PKR-eIF2a pathway, which inhibits the major histocompatibility complex class I, and therefore weakens the T cell activation to the viral activity.
2014.05.19 View 10356
Immune Evasion Mechanism of Hepatitis C Virus Revealed
Professor Ui-Cheol Shin
Inhibiting major histocompatibility complex [MHC] class I protein expression, T cell immune response is evaded.
The research will be a great help to the development of C hepatitis vaccine.
Roughly 1-2% of the population in Korea is known to be infected with Hepatitis C. Most Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infections progress to a chronic disease and can cause liver cirrhosis or liver cancer, which may lead to death.
Unlike Hepatitis type A or B, there is no vaccine for Hepatitis C Virus and therefore avoiding exposure to the virus is the best known method of prevention. However, a team of researchers at KAIST has produced research results, which may contribute significantly to the vaccine development.
KAIST Graduate School of Medical Sciences & Engineering’ Professor Ui-Cheol Shin and his team have successfully identified why Hepatitis C Virus does not cause an immune response within the human body. The research results were published in the May edition of The Journal of Gastroenterology, a world-renowned journal in the field of gastroenterology.
The immune response occurs to eliminate the virus that has invaded our body. During this process, a major histocompatibility complex [MHC] class I plays a key role in inducing T cell response, which is needed for the elimination of virus-infected cells.
When a cell is infected by a virus, a substance called interferon causes the increased expression of major histocompatibility complex class I. T cell recognizes the increased MHC class I and therefore finds the virus-infected cells.
However, the effect that Hepatitis C Virus has on major histocompatibility complex class I has not been clearly identified until now.
The research team has revealed, using a cell culture for infection systems, that the Hepatitis C Virus suppresses the expression of major histocompatibility complex class I. Also, the mechanism to prove that HCV activates a protein called PKR within the cell to inhibit MHC class I protein expression was identified at a molecular level.
In this study, researchers established the hypothesis that regulating PKR protein in the cell can enhance the T cell immune response, which was then proved through experiments.
Professor Ui-Cheol Shin said, “There are a lot of new drugs to treat Hepatitis C Virus, while its vaccine has not been developed yet. Revealing the HCV immune evasion mechanism will help stimulate momentum for the HCV vaccine development.”
The first author of the journal, Dr. Won-Seok Kang is a graduate from Yonsei College of Medicine. After earning his medical degree, he has continued his training as a ‘doctor-scientist’ at KAIST Graduate School of Medical Sciences & Engineering to study Hepatitis C Virus immune evasion mechanism in this research.
Hepatitis C Virus activates PKR-eIF2a pathway, which inhibits the major histocompatibility complex class I, and therefore weakens the T cell activation to the viral activity.
2014.05.19 View 10356 -
 Mechanism in regulation of cancer-related key enzyme, ATM, for DNA damage and repair revealed
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi
A research team led by Professor Kwang-Wook Choi and Dr. Seong-Tae Hong from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has successfully investigated the operational mechanism of the protein Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM), an essential protein to the function of a crucial key enzyme that repairs the damaged DNA which stores biometric information. The results were published on December 19th Nature Communications online edition.
All organisms, including humans, constantly strive to protect the information within their DNA from damages posed by a number of factors, such as carbonized materials in our daily food intake, radioactive materials such as radon emitting from the cement of buildings or ultraviolet of the sunlight, which could be a trigger for cancer.
In order to keep the DNA information safe, the organisms are always carrying out complex and sophisticated DNA repair work, which involves the crucial DNA damage repair protein ATM. Consequently, a faulty ATM leads to higher risks of cancer.
Until now, academia predicted that the Translationally Controlled Tumor Protein (TCTP) will play an important role in regulating the function of ATM. However, since most of main research regarding TCTP has only been conducted in cultured cells, it was unable to identify exactly what mechanisms TCTP employs to control ATM.
The KAIST research team identified that TCTP can combine with ATM or increase the enzymatic activity of ATM. In addition, Drosophilia, one of the most widely used model organisms for molecular genetics, has been used to identify that TCTP and ATM play a very important role in repairing the DNA damaged by radiation. This information has allowed the researchers to establish TCTP’s essential function in maintaining the DNA information in cell cultures and even in higher organisms, and to provide specific and important clues to the regulation of ATM by TCTP.
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi said, “Our research is a good example that basic research using Drosophilia can make important contributions to understanding the process of diseases, such as cancer, and to developing adequate treatment.”
The research has been funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure 1. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, cells of the Drosophila's eye are abnormally deformed by radiation. Scale bars = 200mm
Figure 2. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, the chromosomes of Drosophilia are easily broken by radiation. Scale bars = 10 mm.
Figure 3. When gene expressions of TCTP and ATM are reduced, large defects occur in the normal development of the eye. (Left: normal Drosophilia's eye, right: development-deficient eye)
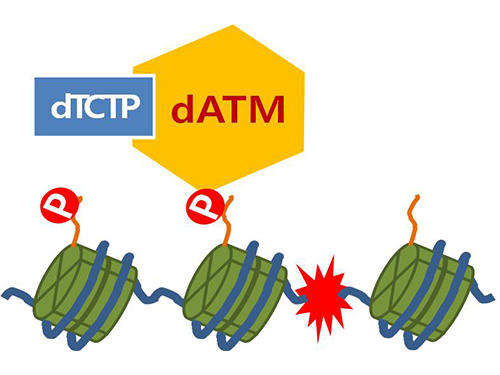
Figure 4. ATM marks the position of the broken DNA, with TCTP helping to facilitate this reaction. DNA (blue line) within the cell nucleus is coiled around the histone protein (green cylinder). When DNA is broken, ATM protein attaches a phosphate group (P). Multiple DNA repair protein recognizes the phosphate as a signal that requires repair and gathers at the site.
2014.01.07 View 11677
Mechanism in regulation of cancer-related key enzyme, ATM, for DNA damage and repair revealed
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi
A research team led by Professor Kwang-Wook Choi and Dr. Seong-Tae Hong from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has successfully investigated the operational mechanism of the protein Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM), an essential protein to the function of a crucial key enzyme that repairs the damaged DNA which stores biometric information. The results were published on December 19th Nature Communications online edition.
All organisms, including humans, constantly strive to protect the information within their DNA from damages posed by a number of factors, such as carbonized materials in our daily food intake, radioactive materials such as radon emitting from the cement of buildings or ultraviolet of the sunlight, which could be a trigger for cancer.
In order to keep the DNA information safe, the organisms are always carrying out complex and sophisticated DNA repair work, which involves the crucial DNA damage repair protein ATM. Consequently, a faulty ATM leads to higher risks of cancer.
Until now, academia predicted that the Translationally Controlled Tumor Protein (TCTP) will play an important role in regulating the function of ATM. However, since most of main research regarding TCTP has only been conducted in cultured cells, it was unable to identify exactly what mechanisms TCTP employs to control ATM.
The KAIST research team identified that TCTP can combine with ATM or increase the enzymatic activity of ATM. In addition, Drosophilia, one of the most widely used model organisms for molecular genetics, has been used to identify that TCTP and ATM play a very important role in repairing the DNA damaged by radiation. This information has allowed the researchers to establish TCTP’s essential function in maintaining the DNA information in cell cultures and even in higher organisms, and to provide specific and important clues to the regulation of ATM by TCTP.
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi said, “Our research is a good example that basic research using Drosophilia can make important contributions to understanding the process of diseases, such as cancer, and to developing adequate treatment.”
The research has been funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure 1. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, cells of the Drosophila's eye are abnormally deformed by radiation. Scale bars = 200mm
Figure 2. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, the chromosomes of Drosophilia are easily broken by radiation. Scale bars = 10 mm.
Figure 3. When gene expressions of TCTP and ATM are reduced, large defects occur in the normal development of the eye. (Left: normal Drosophilia's eye, right: development-deficient eye)
Figure 4. ATM marks the position of the broken DNA, with TCTP helping to facilitate this reaction. DNA (blue line) within the cell nucleus is coiled around the histone protein (green cylinder). When DNA is broken, ATM protein attaches a phosphate group (P). Multiple DNA repair protein recognizes the phosphate as a signal that requires repair and gathers at the site.
2014.01.07 View 11677