research
< (Clockwise from back left) Professor Jung-Wuk Hong, Professor Seokwoo Jeon, Dr. Sang-Eon Lee, and PhD Candidate Donghwi Cho >
Researchers have developed a new easy-to-use smart optical film technology that allows smart window devices to autonomously switch between transparent and opaque states in response to the surrounding light conditions.
The proposed 3D hybrid nanocomposite film with a highly periodic network structure has empirically demonstrated its high speed and performance, enabling the smart window to quantify and self-regulate its high-contrast optical transmittance. As a proof of concept, a mobile-app-enabled smart window device for Internet of Things (IoT) applications has been realized using the proposed smart optical film with successful expansion to the 3-by-3-inch scale. This energy-efficient and cost-effective technology holds great promise for future use in various applications that require active optical transmission modulation.
Flexible optical transmission modulation technologies for smart applications including privacy-protection windows, zero-energy buildings, and beam projection screens have been in the spotlight in recent years. Conventional technologies that used external stimuli such as electricity, heat, or light to modulate optical transmission had only limited applications due to their slow response speeds, unnecessary color switching, and low durability, stability, and safety.
The optical transmission modulation contrast achieved by controlling the light scattering interfaces on non-periodic 2D surface structures that often have low optical density such as cracks, wrinkles, and pillars is also generally low. In addition, since the light scattering interfaces are exposed and not subject to any passivation, they can be vulnerable to external damage and may lose optical transmission modulation functions. Furthermore, in-plane scattering interfaces that randomly exist on the surface make large-area modulation with uniformity difficult.
Inspired by these limitations, a KAIST research team led by Professor Seokwoo Jeon from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Jung-Wuk Hong of the Civil and Environmental Engineering Department used proximity-field nanopatterning (PnP) technology that effectively produces highly periodic 3D hybrid nanostructures, and an atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique that allows the precise control of oxide deposition and the high-quality fabrication of semiconductor devices.
The team then successfully produced a large-scale smart optical film with a size of 3 by 3 inches in which ultrathin alumina nanoshells are inserted between the elastomers in a periodic 3D nanonetwork.
This “mechano-responsive” 3D hybrid nanocomposite film with a highly periodic network structure is the largest smart optical transmission modulation film that exists. The film has been shown to have state-of-the-art optical transmission modulation of up to 74% at visible wavelengths from 90% initial transmission to 16% in the scattering state under strain. Its durability and stability were proved by more than 10,000 tests of harsh mechanical deformation including stretching, releasing, bending, and being placed under high temperatures of up to 70°C. When this film was used, the transmittance of the smart window device was adjusted promptly and automatically within one second in response to the surrounding light conditions. Through these experiments, the underlying physics of optical scattering phenomena occurring in the heterogeneous interfaces were identified. Their findings were reported in the online edition of Advanced Science on April 26. KAIST Professor Jong-Hwa Shin’s group and Professor Young-Seok Shim at Silla University also collaborated on this project.
Donghwi Cho, a PhD candidate in materials science and engineering at KAIST and co-lead author of the study, said, “Our smart optical film technology can better control high-contrast optical transmittance by relatively simple operating principles and with low energy consumption and costs.”
“When this technology is applied by simply attaching the film to a conventional smart window glass surface without replacing the existing window system, fast switching and uniform tinting are possible while also securing durability, stability, and safety. In addition, its wide range of applications for stretchable or rollable devices such as wall-type displays for a beam projection screen will also fulfill aesthetic needs,” he added.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), and the Korean Ministries of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP), and Science and ICT (MSIT).
< Figure 1. Design concept of and fabrication procedures for the 3D scatterer >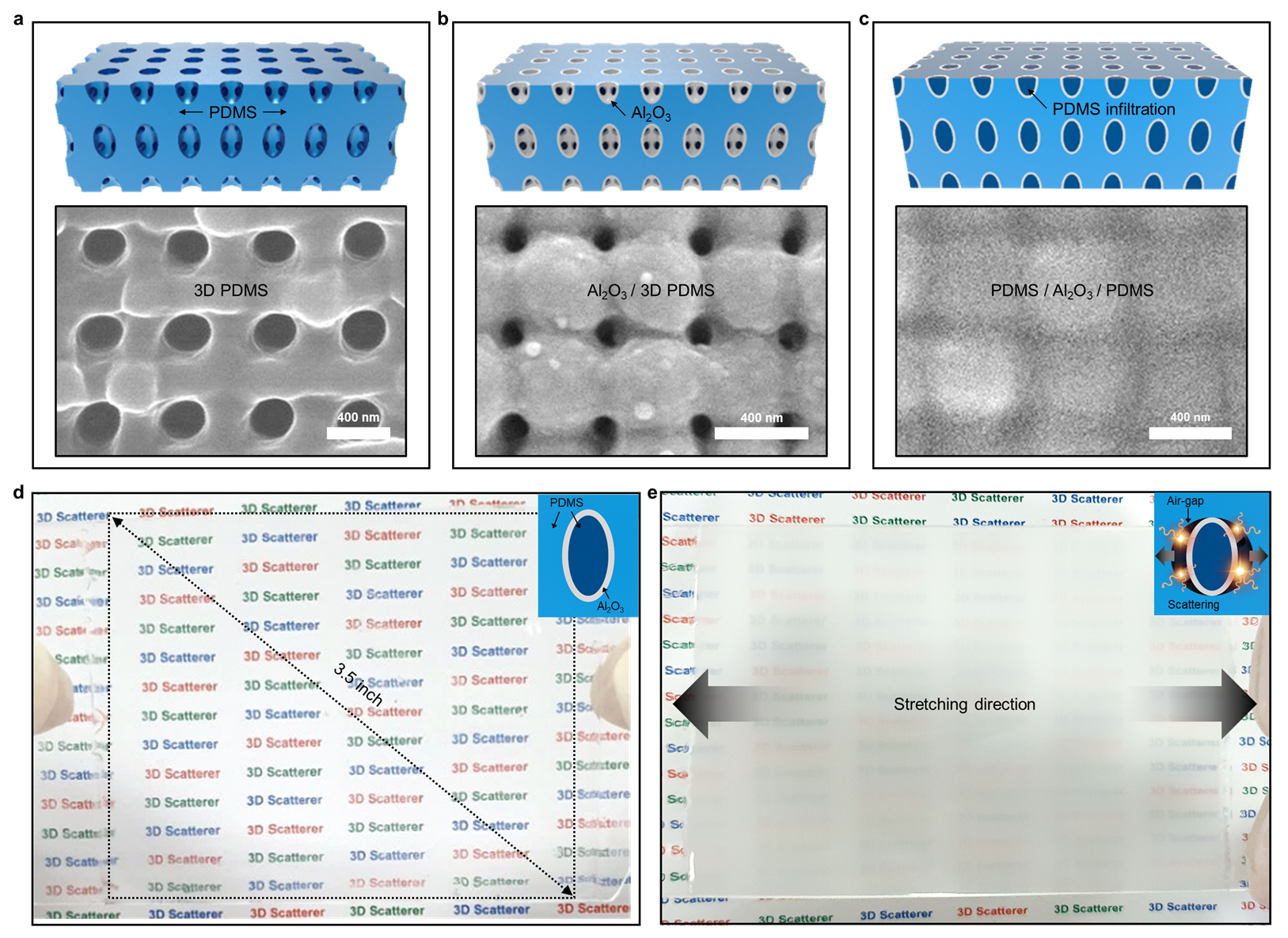
< Figure 2. Mechanical and optical simulations of the 3D scatterer >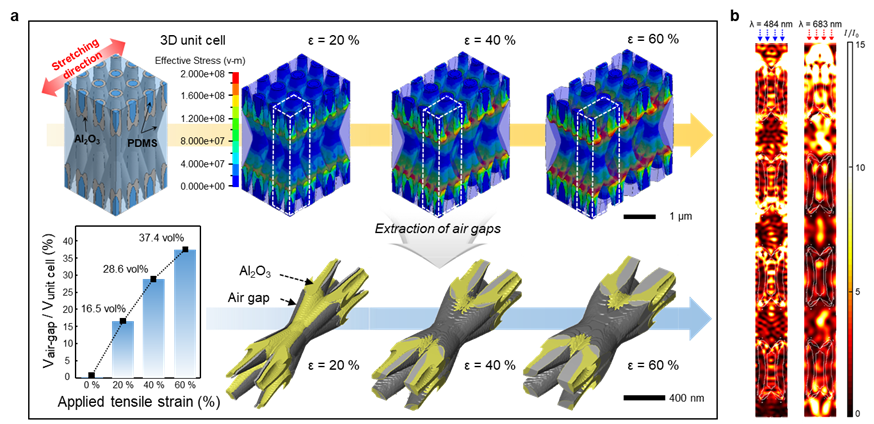
< Figure 3. Demonstrations of the internet of things (IoT) applications: a self-regulating mechano-responsive smart window (MSW) device and a beam projection screen >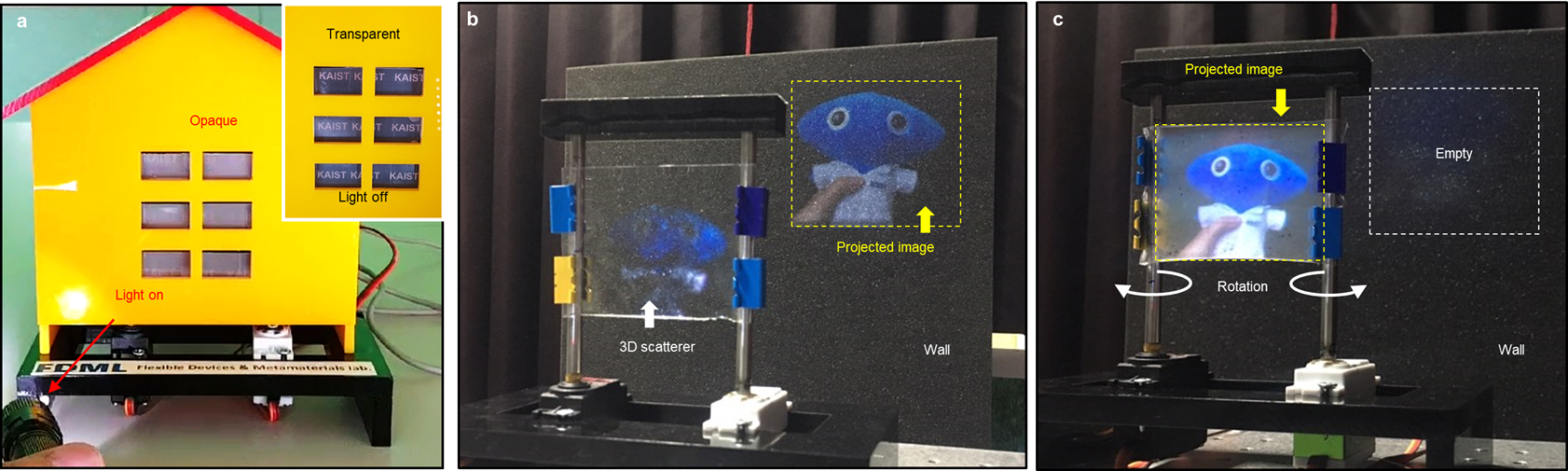
Publication:
Cho, D, et al. (2020) ‘High-Contrast Optical Modulation from Strain-Indicated Nanogaps at 3D Heterogeneous Interfaces’ Advanced Science, 1903708. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201903708
Profile: Seokwoo Jeon, PhD
Professor
jeon39@kaist.ac.kr
https://fdml.kaist.ac.kr/
Flexible Device and Metamaterials Lab (FDML)
Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Jung-Wuk Hong, PhD
Associate Professor
j.hong@kaist.ac.kr
http://aaml.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Applied Mechanics Laboratory (AAML)
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
KAIST
Profile: Donghwi Cho
PhD Candidate
roy0202@kaist.ac.kr
FDML, MSE, KAIST
Profile: Young-Seok Shim, PhD
Assistant Professor
ysshim@silla.ac.kr
Division of Materials Science and Engineering Silla University
https://www.silla.ac.kr
Busan 46958, Korea
(END)
-
research Energy Storage Using Oxygen to Boost Battery Performance
Researchers have presented a novel electrode material for advanced energy storage device that is directly charged with oxygen from the air. Professor Jeung Ku Kang’s team synthesized and preserved the sub-nanometric particles of atomic cluster sizes at high mass loadings within metal-organic frameworks (MOF) by controlling the behavior of reactants at the molecular level. This new strategy ensures high performance for lithium-oxygen batteries, acclaimed as a next-generation energy storage
2020-06-15 -
research Researchers Describe a Mechanism Inducing Self-Killing of Cancer Cells
(Professor Kim (left) and lead author Lee) Researchers have described a new mechanism which induces the self-killing of cancer cells by perturbing ion homeostasis. A research team from the Department of Biochemical Engineering has developed helical polypeptide potassium ionophores that lead to the onset of programmed cell death. The ionophores increase the active oxygen concentration to stress endoplasmic reticulum to the point of cellular death. The electrochemical gradient between
2019-08-28 -
research High-Performance Sodium Ion Batteries Using Copper Sulfide
(Prof.Yuk and his two PhD candidates Parks) Researchers presented a new strategy for extending sodium ion batteries’ cyclability using copper sulfide as the electrode material. This strategy has led to high-performance conversion reactions and is expected to advance the commercialization of sodium ion batteries as they emerge as an alternative to lithium ion batteries. Professor Jong Min Yuk’s team confirmed the stable sodium storage mechanism using copper sulfide, a supe
2019-07-15 -
event NPKI Launch Workshop Held
Molecular Physics Department Expected to Have ‘NPKI’ Launch Workshop - Numerous physicists tracking the god-particle ‘Higgs’ attending- The NPKI: New Physics at Korea Institute which was launched a six day workshop in Shinla Hotel, Seoul with 50 physicists from in and out of the country. The event started with Professor Gi Woon Choi’s welcoming speech. A heated debate with the theme ‘Top physics and electroweak symmetry breaking in the LHC era’ took
2012-04-04 -
people Imaging technology expert from Hollywood becomes KAIST professor
Imaging technology expert from Hollywood becomes KAIST professor A U.S. imaging technology expert from Hollywood was appointed as KAIST professor. KAIST (President Nam-Pyo Suh) announced on September 18 that world-famous imaging technology expert Joonyong Noh, who deals with special effects at Hollywood, was appointed as assistant professor of Graduate School of Culture Technology. Professor Noh obtained Ph.D in Computer Science from the University of Southern California and has been working
2006-09-21